Study on Purge Strategy of Hydrogen Supply System with Dual Ejectors for Fuel Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Computational Fluid Dynamics Simulation of Dual Ejector Performance
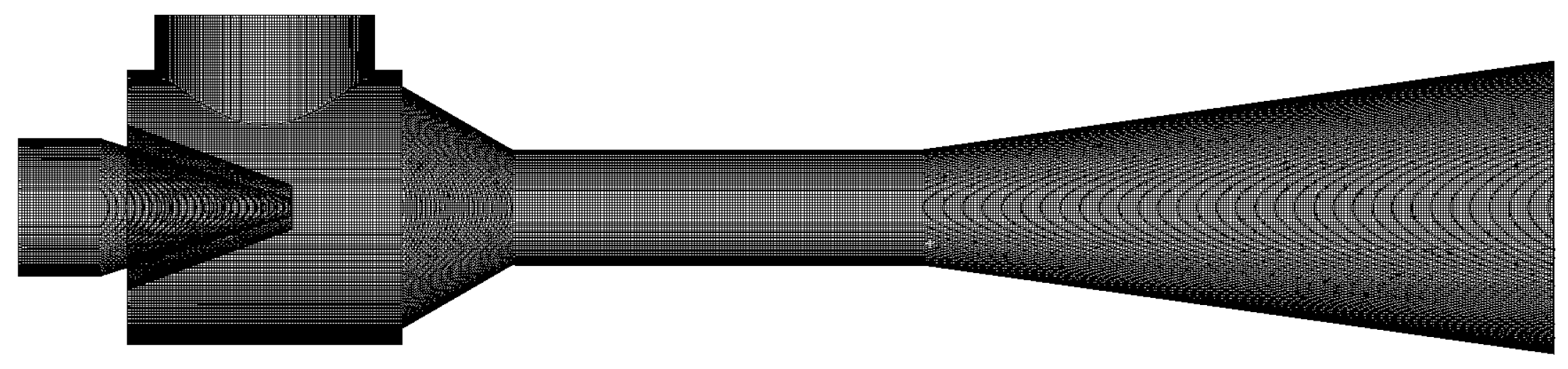
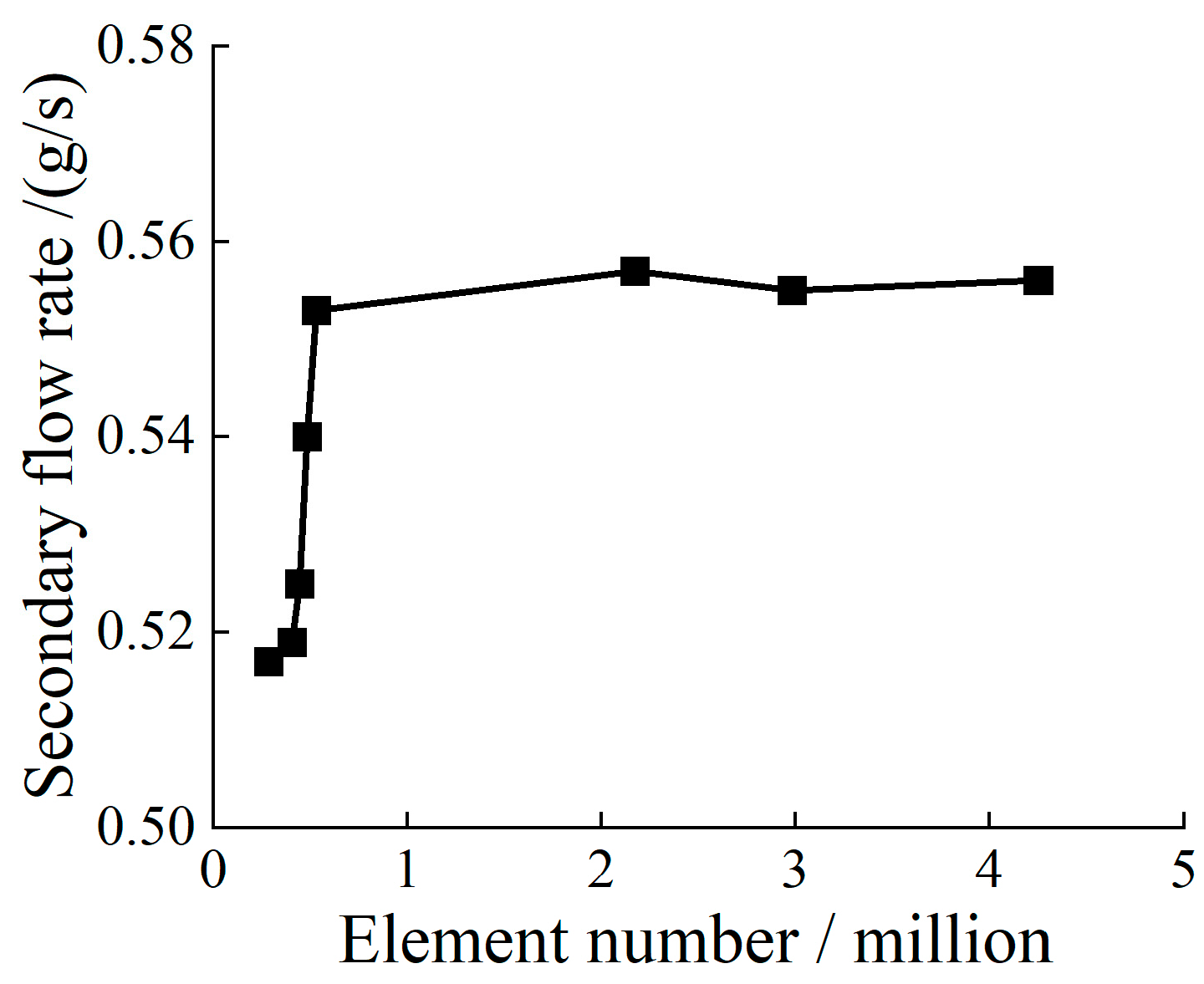
2.1. Finite Element Modeling of the Dual Ejectors
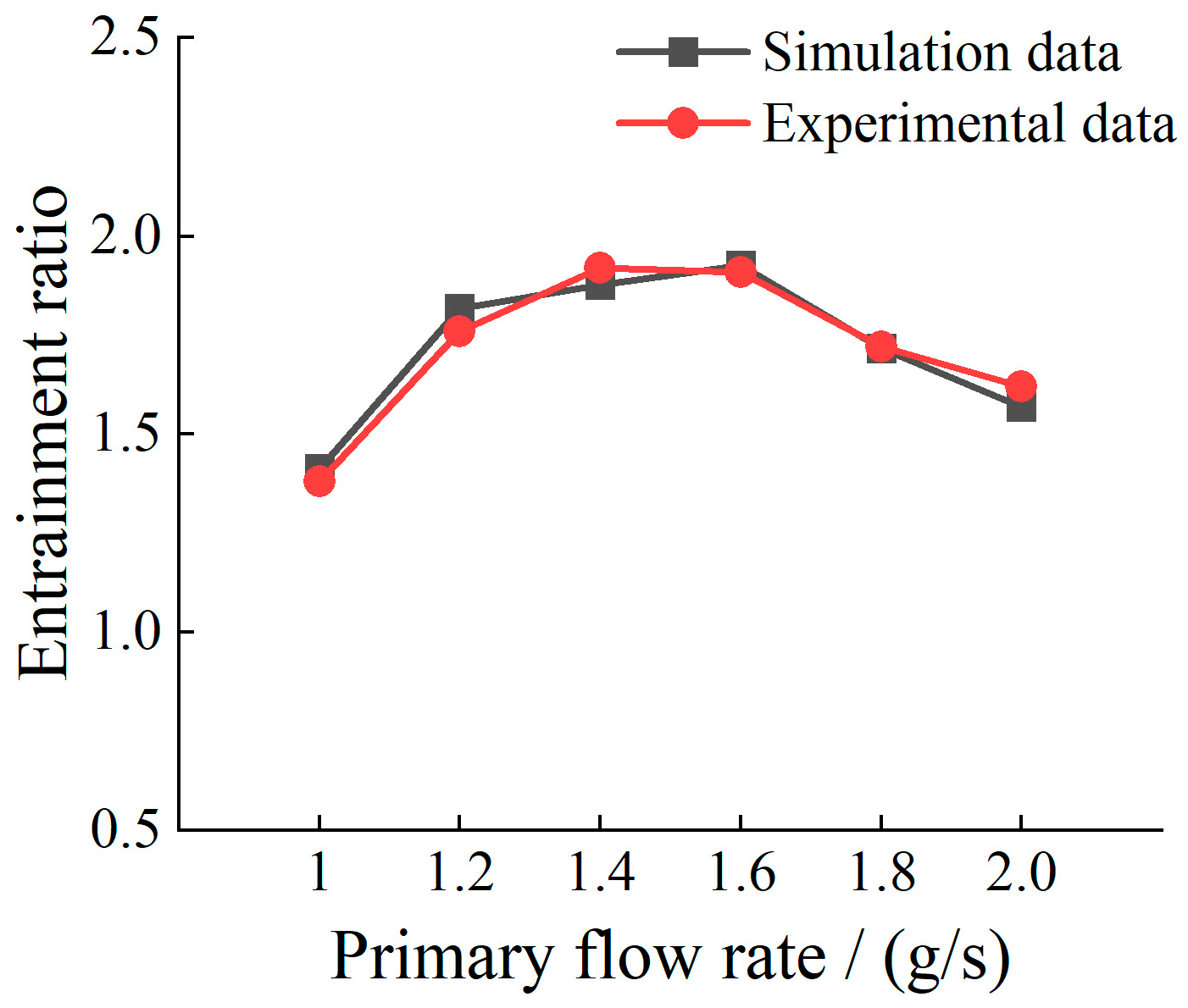
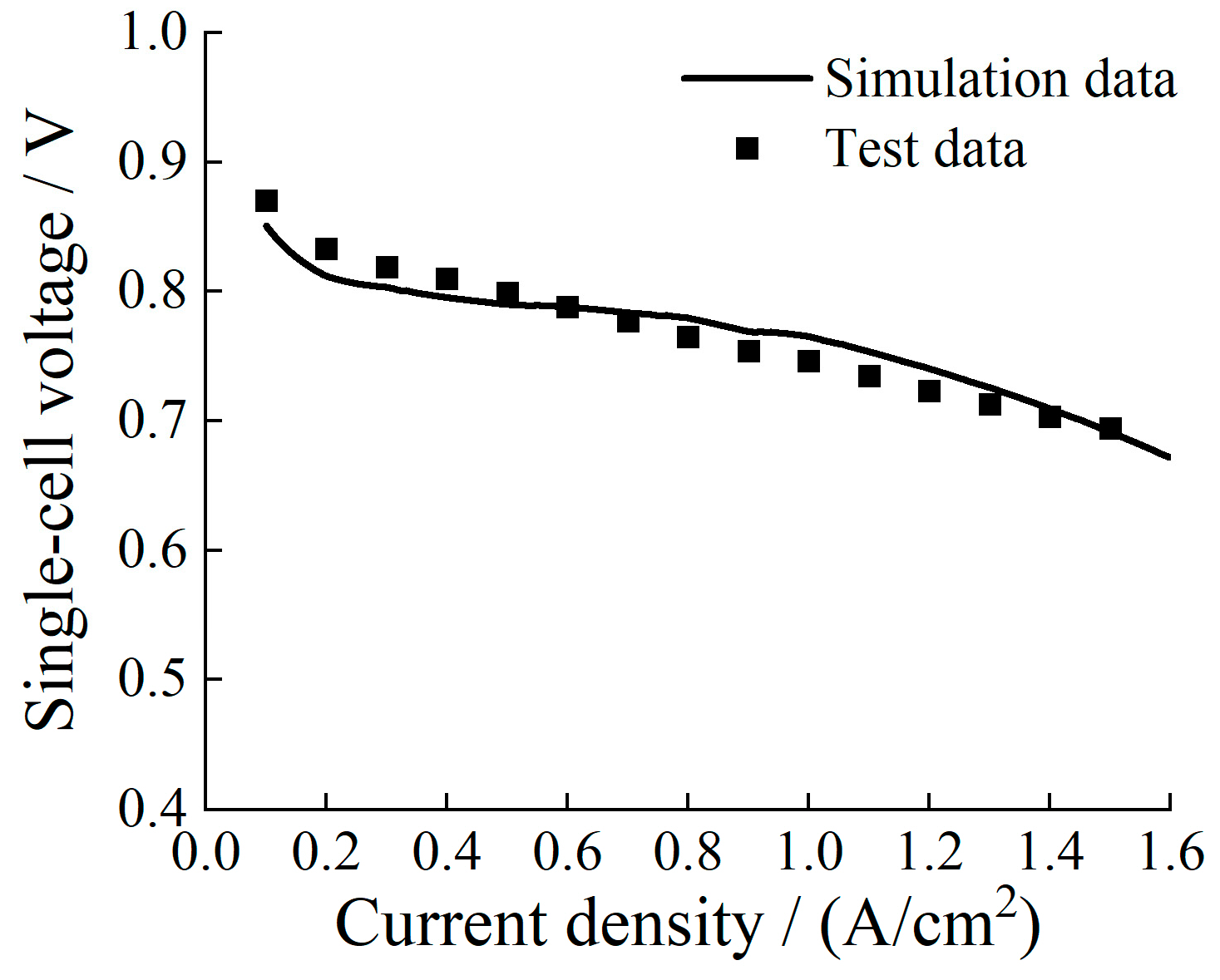
2.2. Validation with Experimental Data
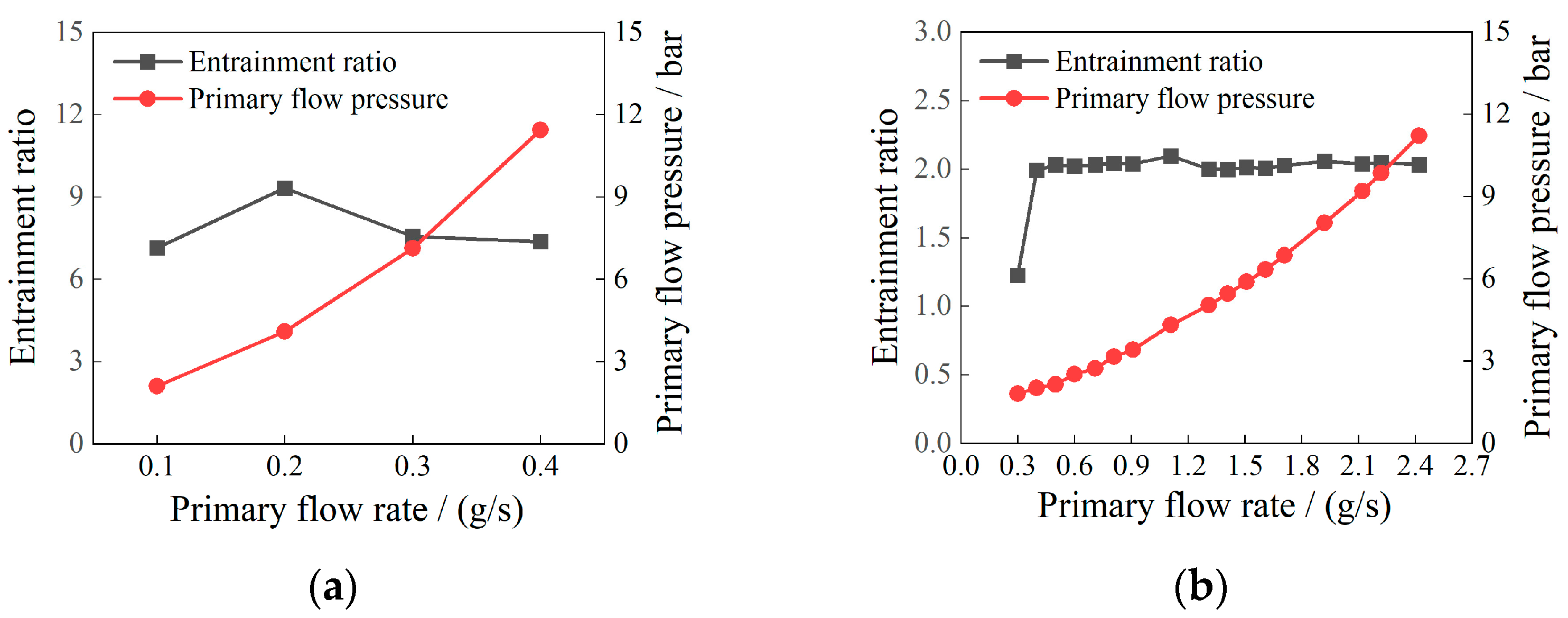
2.3. Dual Ejector Simulation Results
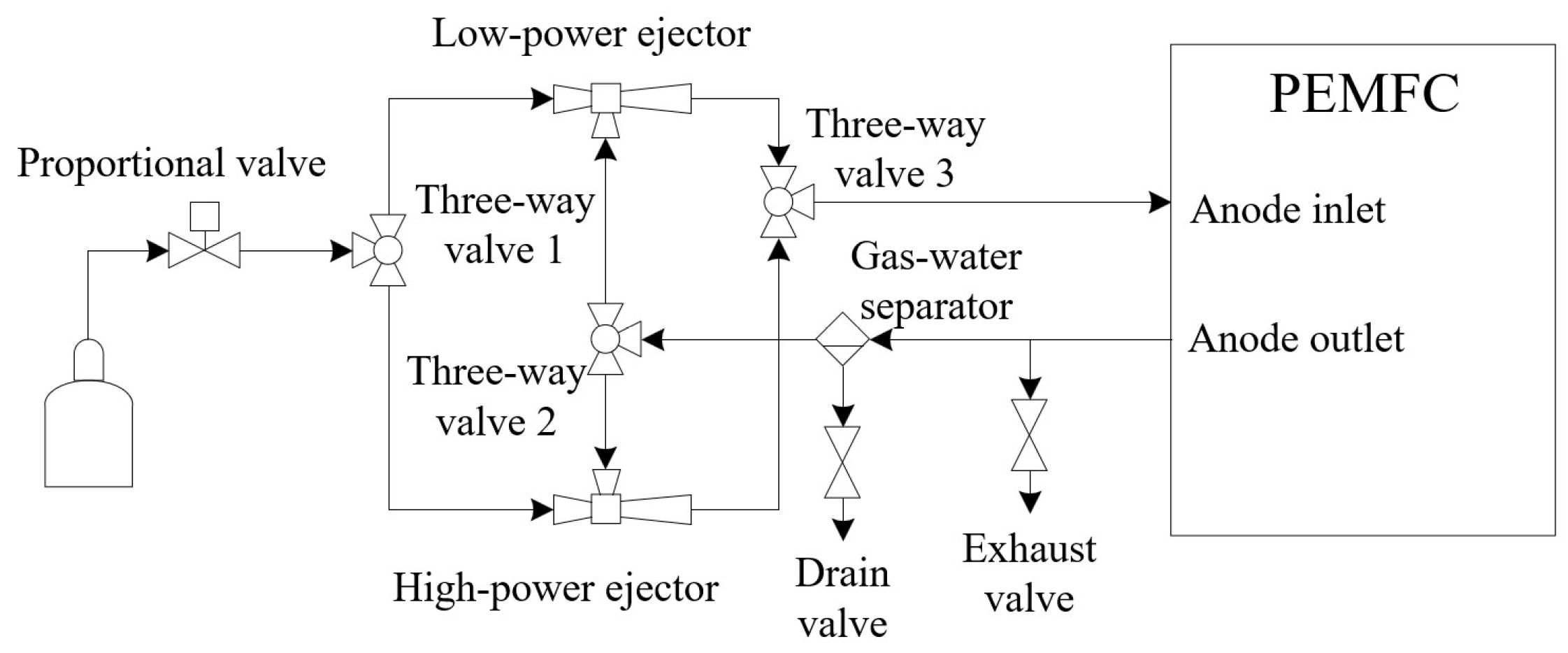
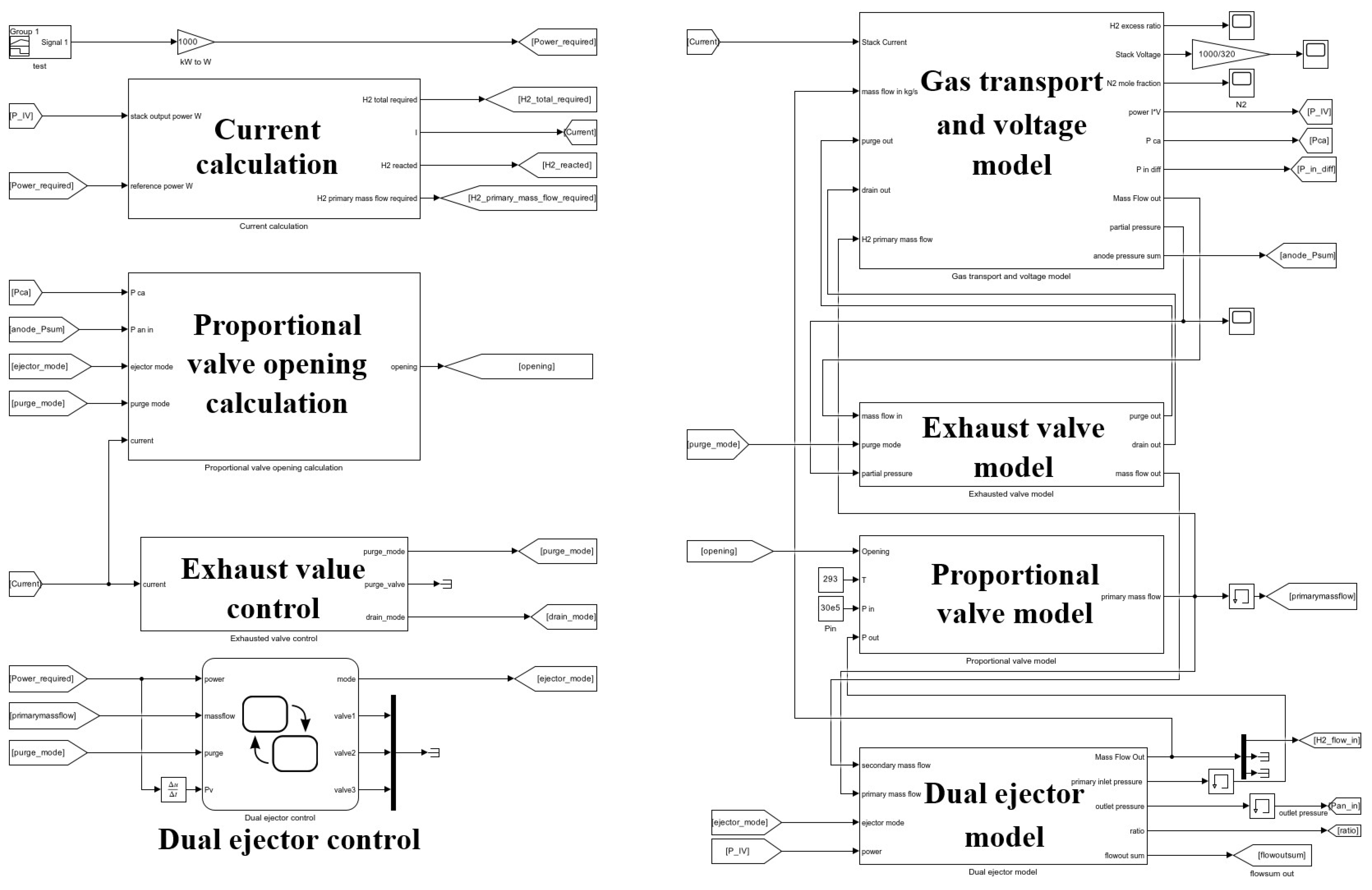
3. Modeling of the Fuel Cell Hydrogen Supply System
3.1. Gas Transport Model
3.2. Exhaust Valve Model
3.3. Proportional Valve Model
3.4. Dual Ejector Model
3.5. Stack Voltage Model
4. Simulation of Exhaust Characteristics in the Fuel Cell Hydrogen Supply System
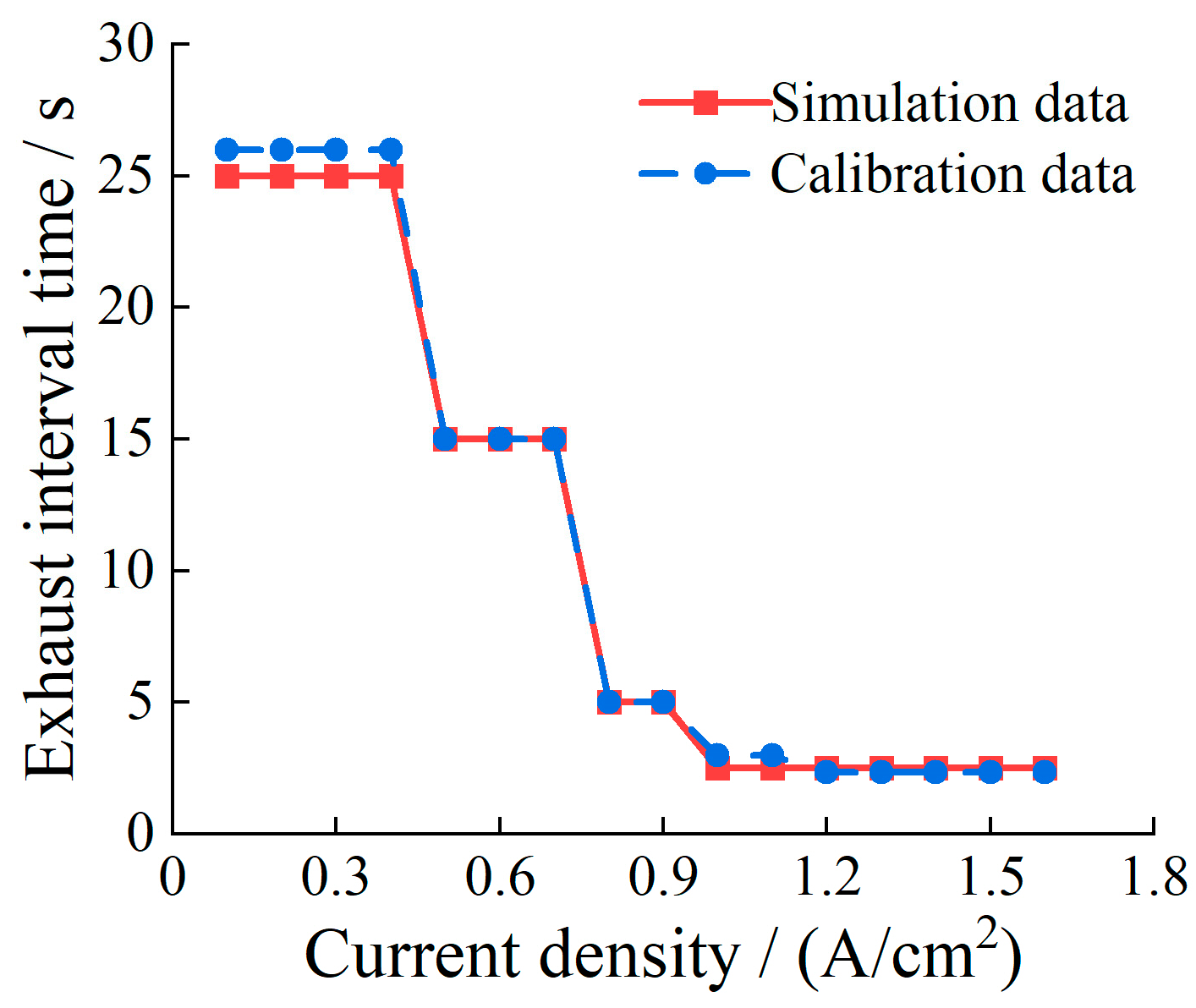
4.1. Model Validation
4.2. Simulation Scheme of Exhaust Interval Time Under Different Current Densities
5. Results and Analysis
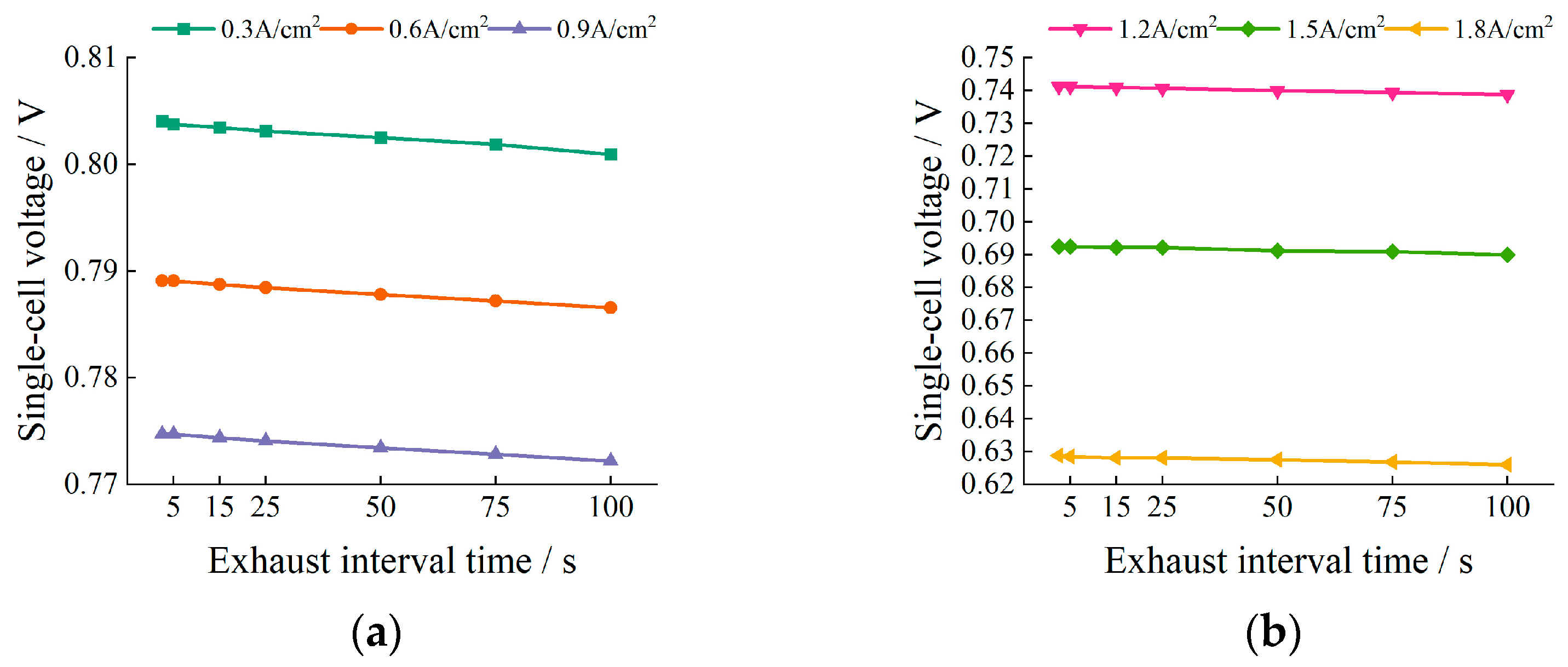
5.1. Impact of Exhaust Interval Time on Voltage
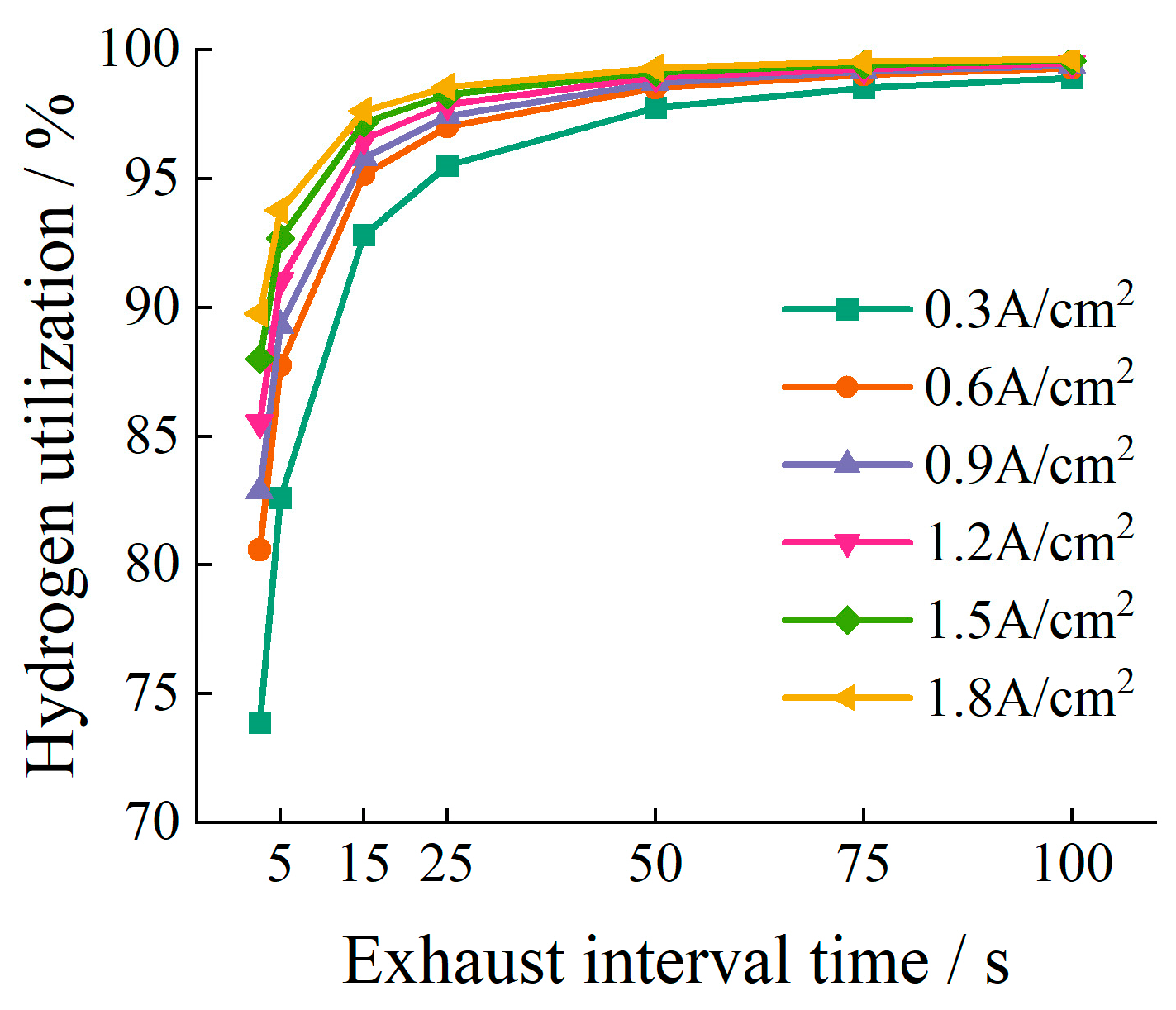
5.2. Impact of Exhaust Interval Time on Hydrogen Utilization
5.3. Impact of Exhaust Interval Time on Stack Efficiency
5.4. Impact of Exhaust Interval Time on Hydrogen Excess Coefficient
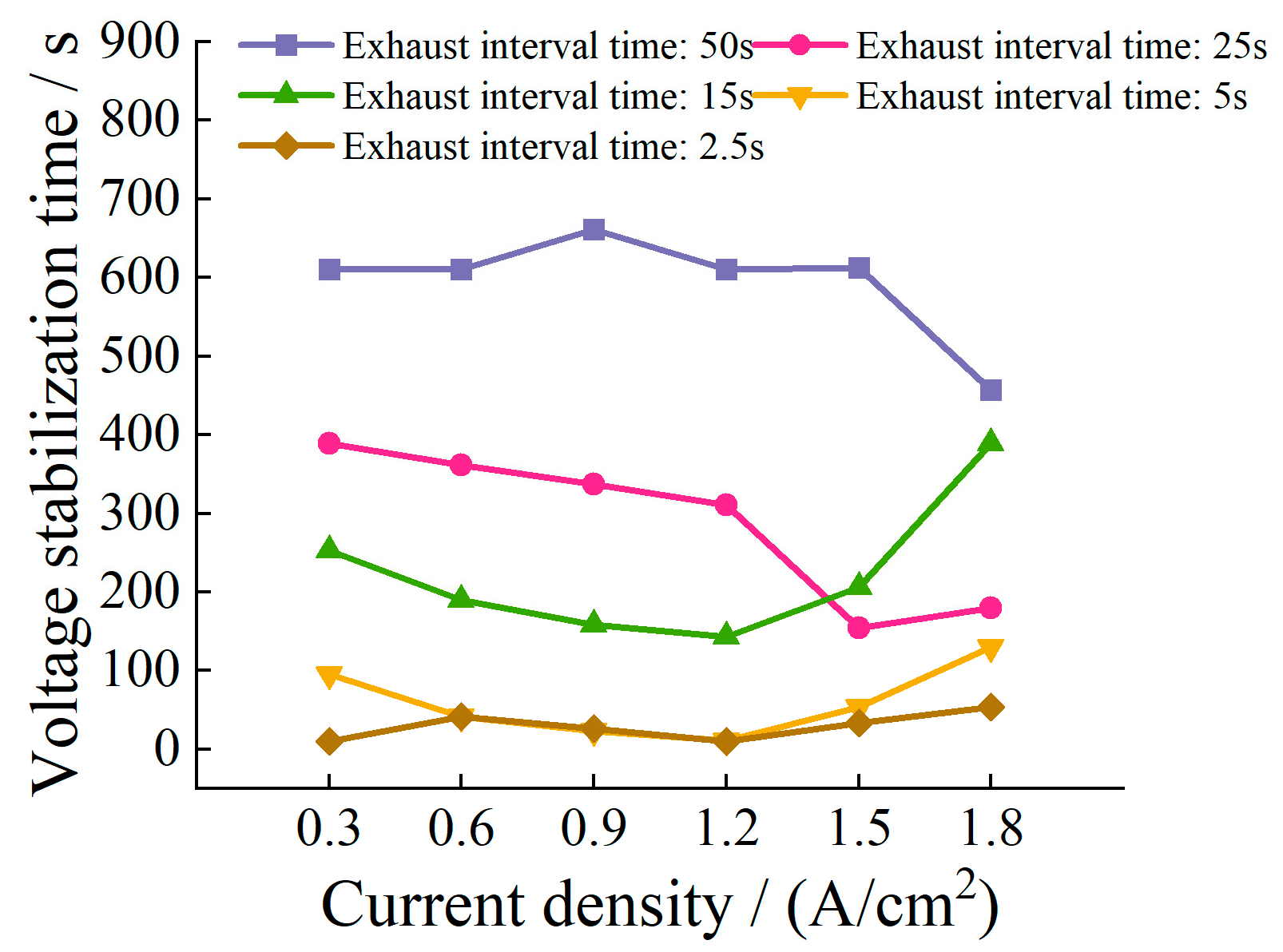
5.5. Impact of Exhaust Interval Time on Voltage Stabilization Time
5.6. Determination of Optimal Exhaust Interval Time
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tri, D.T.L.; Vu, H.N.; Nguyen, H.L.; Kim, Y.; Yu, S.S. A comparative study of single and dual ejector concepts for anodic recirculation system in high performance vehicular proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 27344–27360. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.Z.; Chen, L.Y.; Lu, L.; Li, Y.; Hao, D.; Chin, C.S.; Qiao, Y.J. The experiment and the control of hydrogen circulation of fuel cell based on of fuel ejector: A review. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 50, 1415–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.Y.; Yin, B.F.; Xu, S.; Chen, H.C.; Dong, F. Optimization of purge strategy under fuel cell startup conditions based on CFD-Simulink collaborative simulation. Ionics 2024, 30, 2969–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.W.; Deng, H.; Jiao, K. Purge strategy optimization of proton exchange membrane fuel cell with anode recirculation. Appl. Energy 2018, 225, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plooy, D.D.; Meyer, J.; Solms, S.V. Adaptive purging control of hydrogen fuel cells for high efficiency applications. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on the Domestic Use of Energy, Cape Town, South Africa, 3–5 April 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.; Yu, Y.; Wang, G.J.; Chen, X.S.; Chen, P.; Chen, J.; Zhou, S. Anode purge strategy optimization of the polymer electrode membrane fuel cell system under the dead-end anode operation. J. Power Sources 2016, 320, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberger, M.; Geiling, J.; Oechsner, R.; Frey, L. Anode recirculation and purge strategies for PEM fuel cell operation with diluted hydrogen feed gas. Appl. Energy 2018, 232, 572–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.W.; Chen, F.X.; Jiao, J.R.; Liu, S.G. Analysis and control strategy design for PEMFC purging process. Energy 2024, 290, 130233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Liu, Z.C.; Liu, F.; Liu, W. Numerical Simulation of Water Transport in a Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell Flow Channel. Energies 2018, 11, 1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Gong, L.; Cao, X.W. Structural optimization of hydrogen recirculation ejector for proton exchange membrane fuel cells considering the boundary layer separation effect. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 397, 136535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Me, D.S.; Ji, N.; Zhao, K.F.; Wu, G.P.; Pei, Y.Q. Study on optimization of hydrogen-fueled cell ejector’s structural parameters. J. Mach. Des. 2023, 40, 75–81. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, H.; Dai, H.; Wu, W.; Xie, J.P.; Shen, J.; Wei, X.Z. A fuzzy logic PI control with feedforward compensation for hydrogen pressure in vehicular fuel cell system. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 5714–5728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, L.; Chen, J.; Liu, Z.Y.; Huang, L.H.; Wu, Z.L. A Nonlinear Control Strategy for Fuel Delivery in PEM Fuel Cells Considering Nitrogen Permeation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 1565–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, J.K.; Jiang, W.Z.; Li, C.H.; Hsu, T.H. Numerical investigation into hydrogen supply stability and I-V performance of PEM fuel cell system with passive Venturi ejector. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2020, 169, 114908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyung, D.B.; Min, S.K. Characterization of nitrogen gas crossover through the membrane in proton-exchange membrane fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 732–739. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Z.Y.; Luo, L.Z.; Huang, B.; Jian, Q.F. Dynamic analysis of internal reactants and water content distribution during anode purge in a proton-exchange membrane fuel cell. Int. J. Energy Res. 2021, 45, 10609–10629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Berg, P.; Li, X. Non-isothermal transient modeling of water transport in PEM fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2007, 165, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.L.; Ahn, J.; Choe, S.Y. Analysis and control of a fuel delivery system considering a two-phase anode model of the polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell stack. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 973–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tu, Z.K.; Chan, S.H. Performance enhancement in a H2/O2 PEMFC with dual-ejector recirculation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 12698–12710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Wei, H.; Du, C.Q.; Shi, C.X.; Zhang, J.M. Control strategy for the anode gas supply system in a proton exchange membrane fuel cell system. Energy Rep. 2023, 10, 4342–4358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.B.; Dong, Y.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wen, C. Energy efficiency assessment of hydrogen recirculation ejectors for proton exchange membrane fuel cell (PEMFC) system. Appl. Energy 2023, 346, 121357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefkhani, M.B.; Ghadamian, H.; Daneshvar, K.; Alizadeh, N.; Troconis, B.C.R. Investigation of the Fuel Utilization Factor in PEM Fuel Cell Considering the Effect of Relative Humidity at the Cathode. Energies 2020, 13, 6117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, G.; Pertl, P.; Trattner, A. Experiments on maximizing hydrogen utilization and efficiency in a PEM fuel cell system. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2025, 106, 1158–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.J.; Zhang, H.L.; Liu, M.; Zhang, X.S.; Yang, D.J.; Zhang, C.M. An effective PEMFC system shutdown purge strategy for improving the purging effect of liquid water and the dehydration of stack. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 28891–28905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.Y.; Yang, Y.B.; Yao, N.Y.; Ma, T.C.; Lin, W.K. Water Status Detection Method Based on Water Balance Model for High-Power Fuel Cell Systems. Energies 2024, 17, 5410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
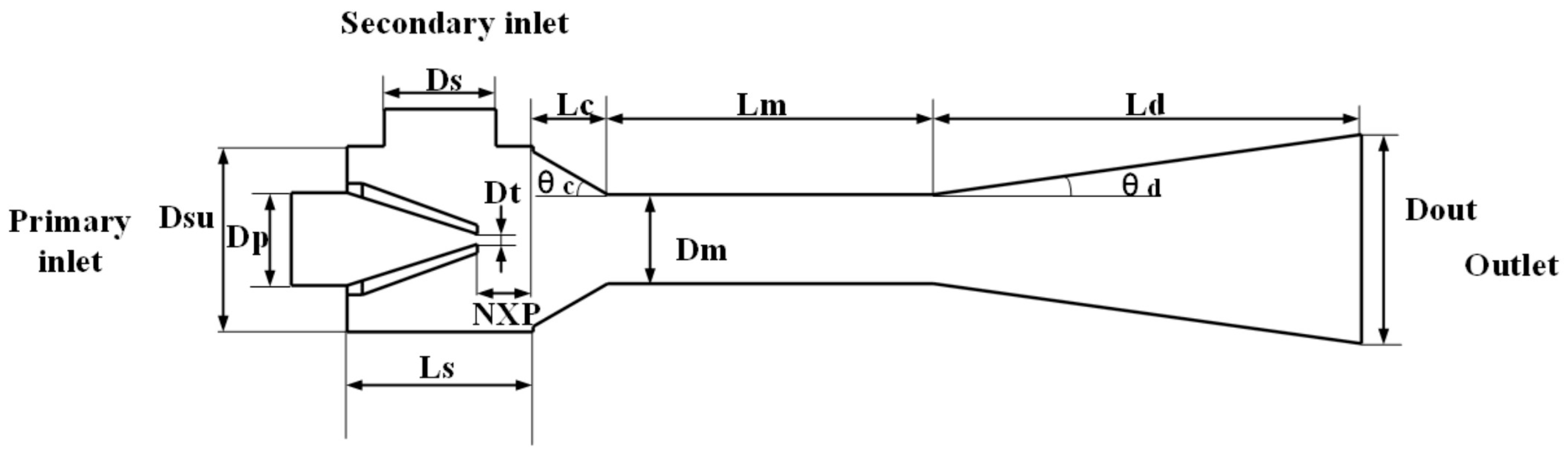



| Dt/mm | Dm/mm | Dp/mm | Dsu/mm | Ds/mm | Dout/mm | NXP/mm | Lc/mm | Ld/mm | Lm/mm | θ_c/° | θ_d/° | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low-power ejector | 1.2 | 8.4 | 10 | 20 | 12 | 22.53 | 8 | 8 | 46 | 30 | 30 | 8 |
| High-power ejector | 3 | 8.4 | 10 | 20 | 12 | 22.53 | 8 | 8 | 46 | 30 | 30 | 8 |
| Current Density/(A/cm2) | 0.3 | 0.6 | 0.9 | 1.2 | 1.5 | 1.8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exhaust interval time (s)/exhaust time (s) | 100/1 | 100/1 | 100/1 | 100/1 | 100/1 | 100/1 |
| 75/1 | 75/1 | 75/1 | 75/1 | 75/1 | 75/1 | |
| 50/1 | 50/1 | 50/1 | 50/1 | 50/1 | 50/1 | |
| 25/1 | 25/1 | 25/1 | 25/1 | 25/1 | 25/1 | |
| 15/1 | 15/1 | 15/1 | 15/1 | 15/1 | 15/1 | |
| 5/1 | 5/1 | 5/1 | 5/1 | 5/1 | 5/1 | |
| 5/2 | 5/2 | 5/2 | 5/2 | 5/2 | 5/2 |
| Current Density/(A/cm2) | 0.3 | 0.6 | 0.9 | 1.2 | 1.5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single-cell voltage/mV | 803.13 | 788.75 | 774.69 | 741.25 | 692.5 |
| Hydrogen excess coefficient | 2.033 | 1.712 | 1.693 | 1.586 | 1.471 |
| Voltage stabilization time/s | 389 | 190 | 23 | 10 | 33 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, Y.; Du, C. Study on Purge Strategy of Hydrogen Supply System with Dual Ejectors for Fuel Cells. Energies 2025, 18, 2168. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18092168
Liang Y, Du C. Study on Purge Strategy of Hydrogen Supply System with Dual Ejectors for Fuel Cells. Energies. 2025; 18(9):2168. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18092168
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Yueming, and Changqing Du. 2025. "Study on Purge Strategy of Hydrogen Supply System with Dual Ejectors for Fuel Cells" Energies 18, no. 9: 2168. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18092168
APA StyleLiang, Y., & Du, C. (2025). Study on Purge Strategy of Hydrogen Supply System with Dual Ejectors for Fuel Cells. Energies, 18(9), 2168. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18092168





