Abstract
A new application of the three-phase buck-resonant converter is presented in this paper. It is shown that the analyzed converter is suitable to operate as the rectifier stage in low power wind energy conversion systems (WECS) based on permanent magnet synchronous generators (PMSG) with variable wind speed. As main features, it presents a single controlled switch, simple implementation and control, and operates with a high power factor and low harmonic distortion over all wind speed ranges. The converter topology, its design equations and its operation are presented, as well as the simulation results of the PMSG based conversion system. From the analysis carried out in the paper it is concluded that the converter is indicated to be employed in distributed generation and hybrid systems where wind generation is associated with other sources.
1. Introduction
Power electronic converters play an essential role in wind energy conversion systems (WECS), particularly within variable speed turbine generation. Besides contributing to the system adequacy, even with variable wind speed, converters allow control of active and reactive power if necessary, as well as allowing the system to operate at maximum power point (MPP).
With wind fluctuations and the generator’s ability to operate at variable speed, power electronic converters operate with the role of maintaining constant voltage and frequency in the network, in the case of an AC-DC-AC conversion, or only maintaining constant voltage in the case of an AC-DC conversion. The converter’s role is therefore essential for proper power supply to the receiving system.
With the recent growth of distributed generation (DG), wind generation, photovoltaic arrays, fuel cells and other power sources are usually integrated [1,2,3,4], forming hybrid systems. Such systems are more robust than systems based on a single source [5]; besides they are considered to be economically better and more reliable than stand-alone systems with a single source. Such DGs along with local loads establish small power systems, the micro grids (MG) [6]. AC or DC MG architectures have been proposed concerning different applications [7,8,9,10], but architectures encompassing both AC and DC buses are also available [11,12]. DC MG can present a single DC-bus or multiple DC-buses (DC sub grids) [13]. Such single or multi-bus MG can present a DC voltage as low as 24 V [11] and as high as 3.5 kV [14], but typical values are between 48 V and 450 V.
Among the several power sources employed in MG, multipole permanent magnet synchronous generators (PMSG) are commonly used with wind turbines. The use of a PMSG in small power wind-powered systems offers important advantages in construction and operation: it presents less noise, high efficiency and has a long life span [15]. The generated voltage presents variable amplitude and frequency, according to wind conditions. Thus, it is necessary to properly investigate converter topologies carrying out the rectification for low power systems with less complexity than those developed for high power. Such topologies must combine simplicity and efficiency, for example by using a simpler control in semiconductors firing, while providing satisfactory quality of energy.
Different topologies of the interfacing converter can be used in wind energy conversion systems. Usually, the AC-DC conversion is achieved by some boost-type converter [16,17,18] which is not appropriate if a low DC-voltage is required. This paper analyses the behavior of a buck-type converter applied as a rectifier stage for such low-voltage buses.
2. Rectifier Converters for Low-Power PMSG
PMSG is a directly driven generator, not requiring a gearbox. The direct-drive WECS with PMSG is the most promising system currently, where external excitation and slip rings are not needed; thus the efficiency and reliability are high [19]. After converting the mechanical wind energy into electrical energy, the power electronic converters will operate on the electric energy produced by the generator [2]. They may act in the conversion of AC to DC voltage, feeding a DC-bus of a MG or storing energy in batteries, for example. If applied to AC MG, an inverter is necessary for grid interface.
In order to produce power over all wind speed some topologies applied to low power operating in discontinuous conduction mode (DCM) have been presented in the literature by [16,20,21] where the rectification is carried out by a bridge rectifier diode, or as in [22], where a rectifier diode plus a DC-DC boost converter is used [23] as shown in Figure 1. This is a simple, cost effective and higher-power-density solution [24]. The typical distorted generator’s current waveform is shown on Figure 2, which leads to a pulsating generator active power—Figure 3.
Some drawbacks are reported [25], mainly due to high harmonic current distortions in the generator windings, such as: increasing heating; reduction in machine efficiency; torque oscillations.
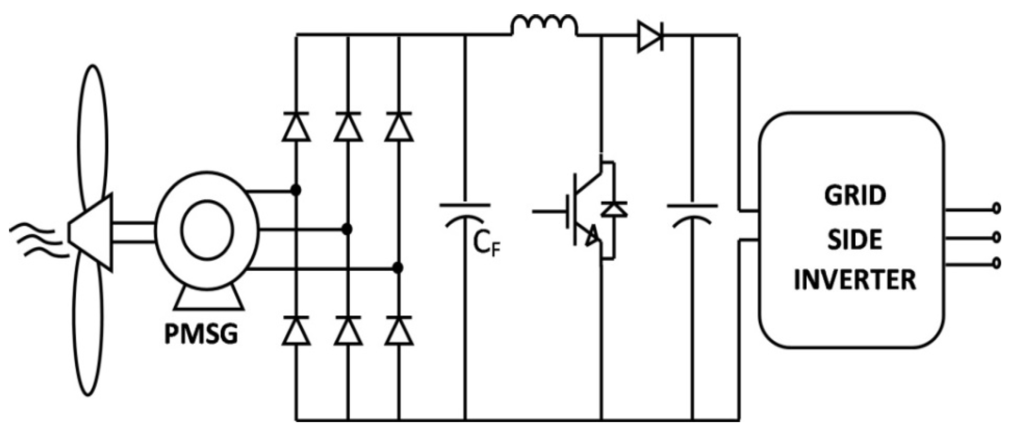
Figure 1.
Diode rectifier plus a DC-DC boost stage.
Figure 1.
Diode rectifier plus a DC-DC boost stage.
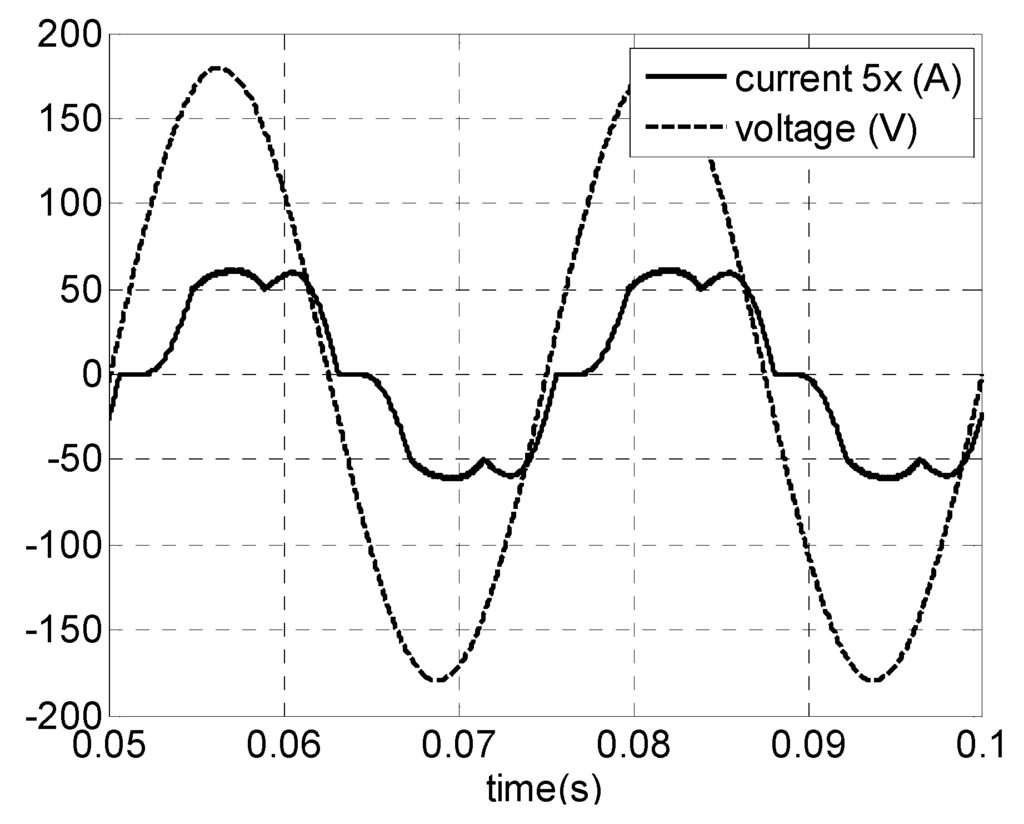
Figure 2.
Generator’s voltage and current.
Figure 2.
Generator’s voltage and current.
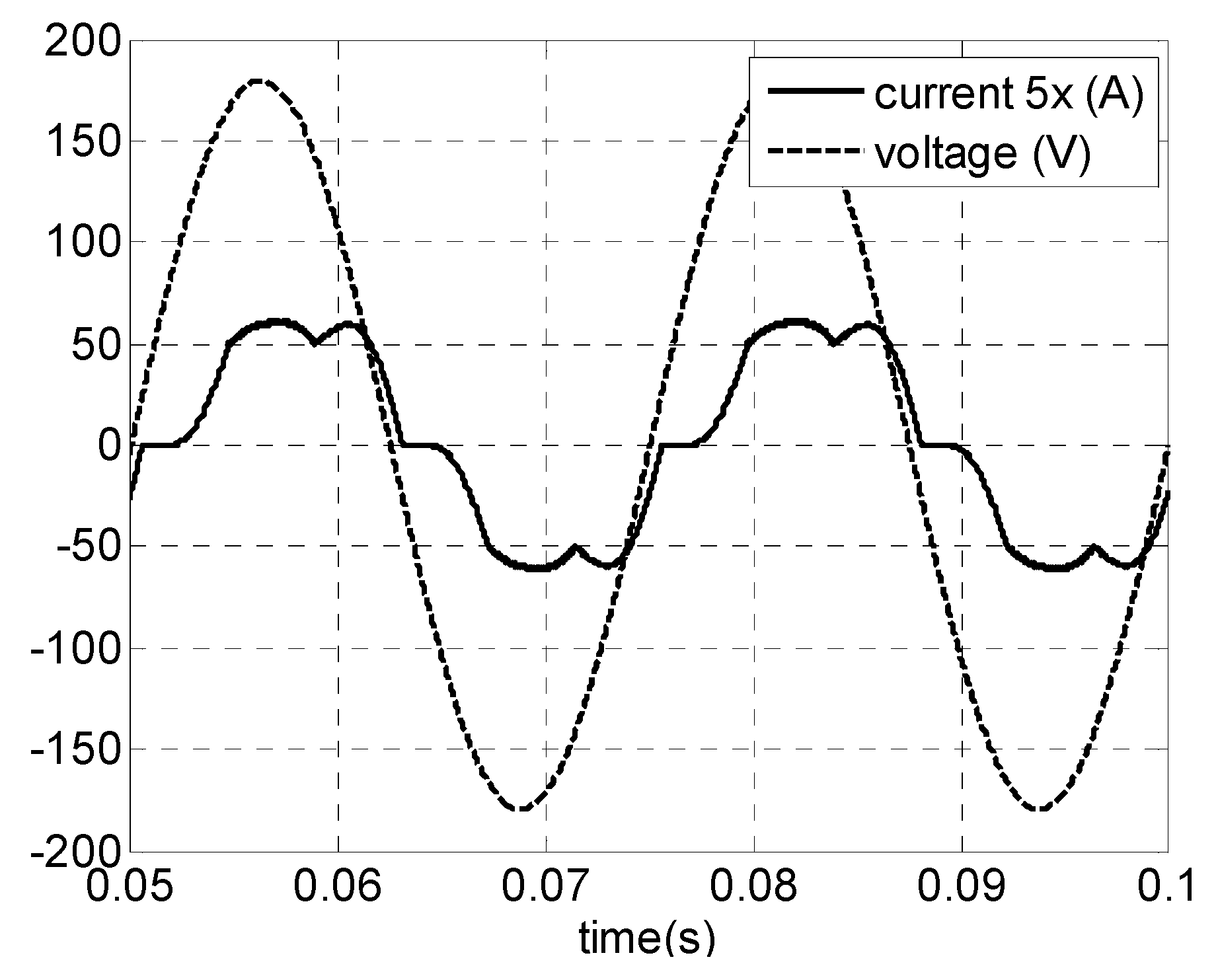
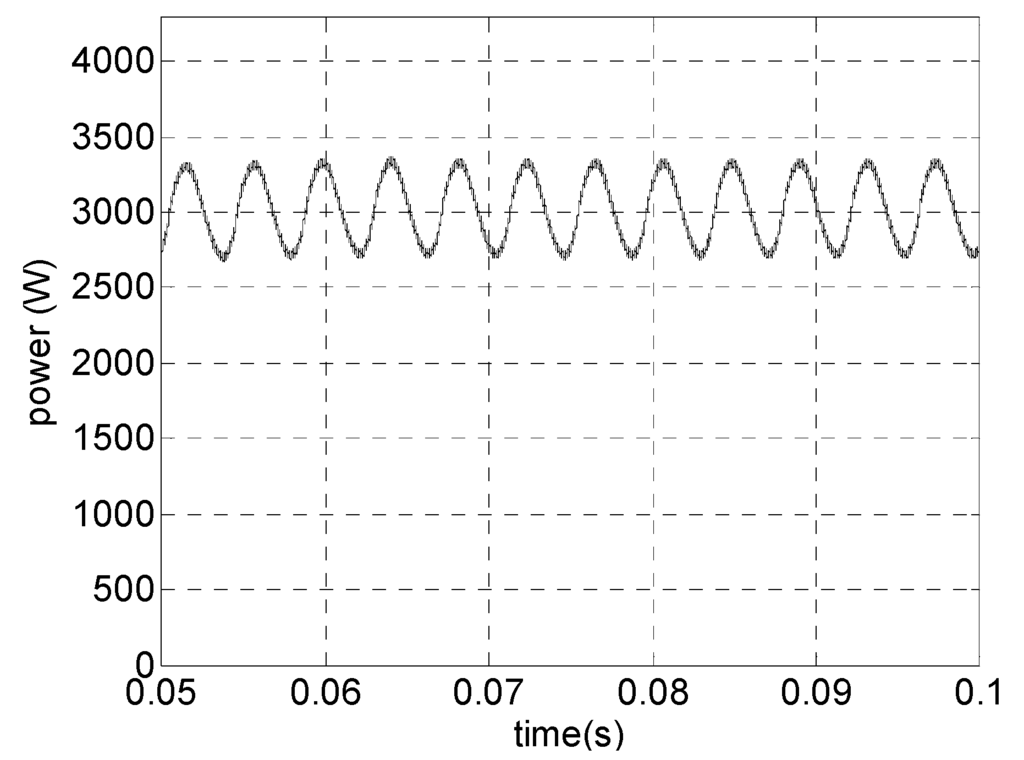
Figure 3.
Generator’s active power.
Figure 3.
Generator’s active power.
To mitigate these problems, DCM boost rectifiers have been considered. Two approaches are available: single-switch solution [17,26,27,28] as shown in Figure 4, and a semi-controlled boost rectifier [16,21,28,29,30] as it can be seen in Figure 5. These topologies produce an output voltage higher than generator voltage; therefore they are not appropriate if a lower voltage is needed.
For operation in DCM an input filter is required for smoothing the high frequency input current. At low speeds (low voltage), input current can be considered sinusoidal, but operating at rated power (high speed, higher voltages) the harmonic content may be relevant [31]. Both solutions present the same typical current behavior, showed in Figure 6.
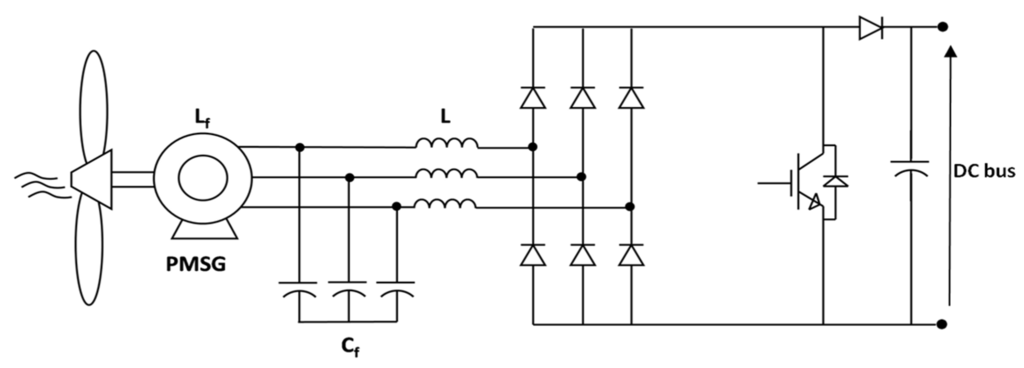
Figure 4.
Single-controlled boost rectifier.
Figure 4.
Single-controlled boost rectifier.
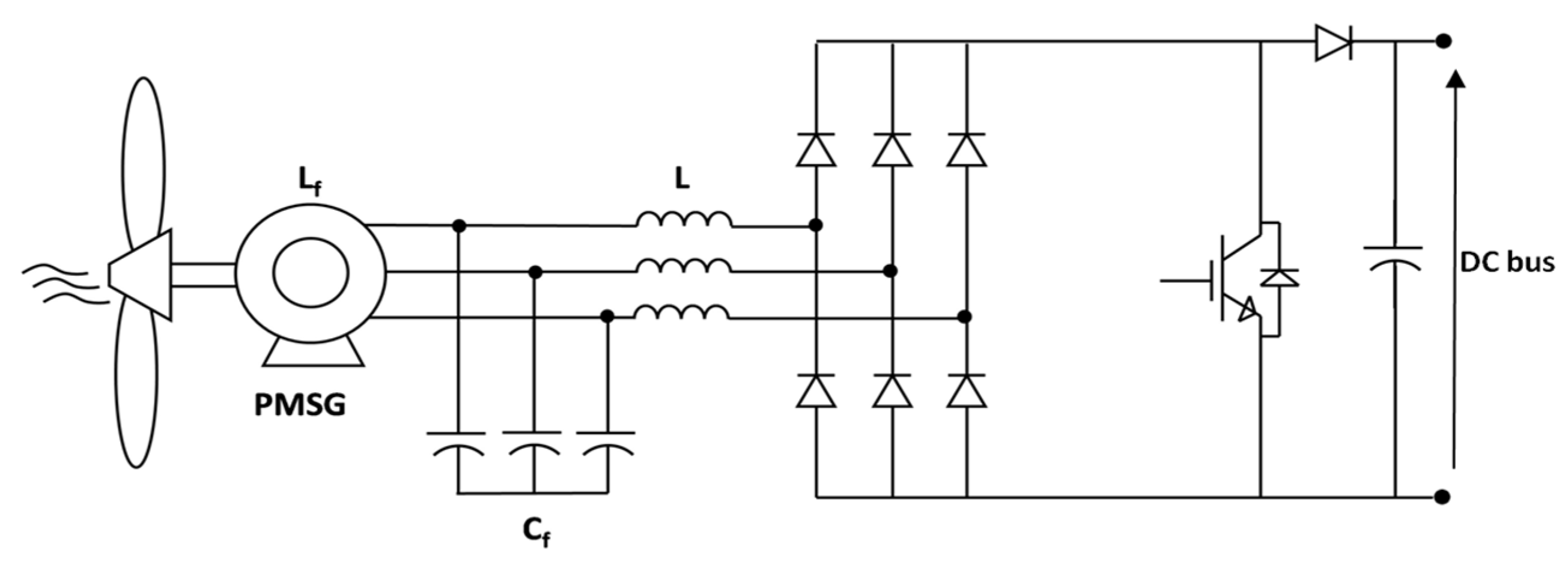
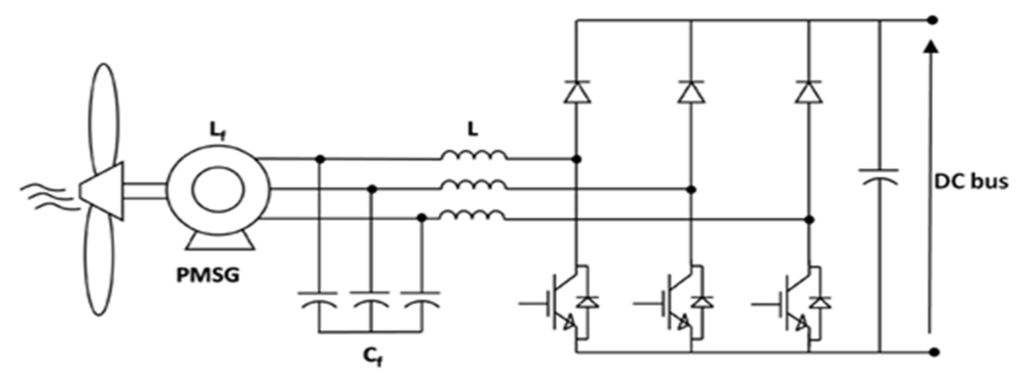
Figure 5.
Semi-controlled boost rectifier.
Figure 5.
Semi-controlled boost rectifier.
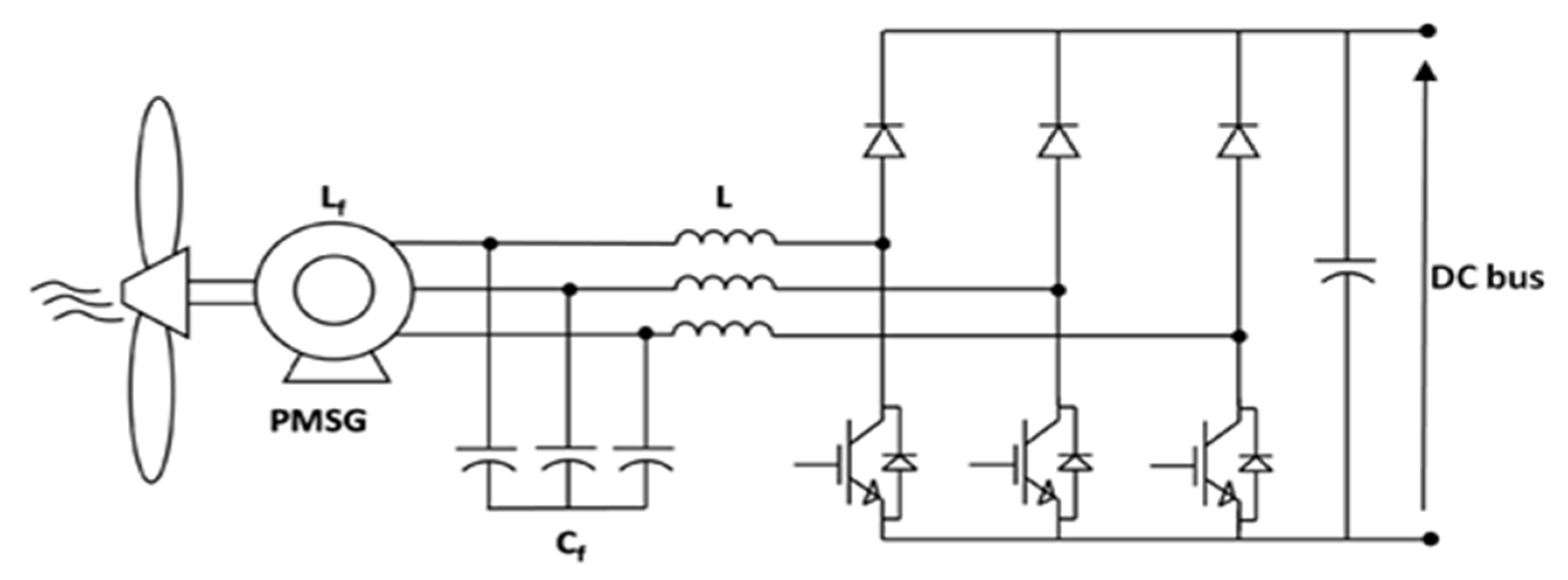
Figure 6.
Voltage and current generated in PMSG.
Figure 6.
Voltage and current generated in PMSG.
These low-order harmonics flowing in generators create a pulsating power of low frequency, which may cause resonance [32]. Figure 7 shows the active power drawn from the generator employing a three-phase boost in DCM (with one or three controlled semiconductor devices).
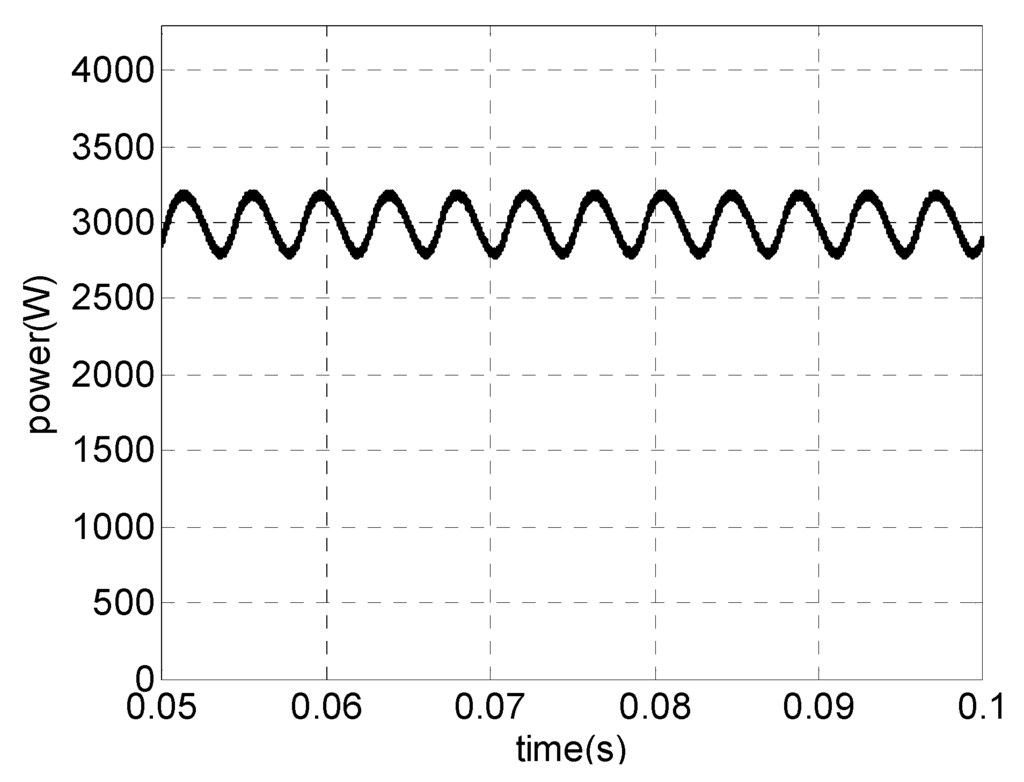
Figure 7.
Generator’s active power.
Figure 7.
Generator’s active power.
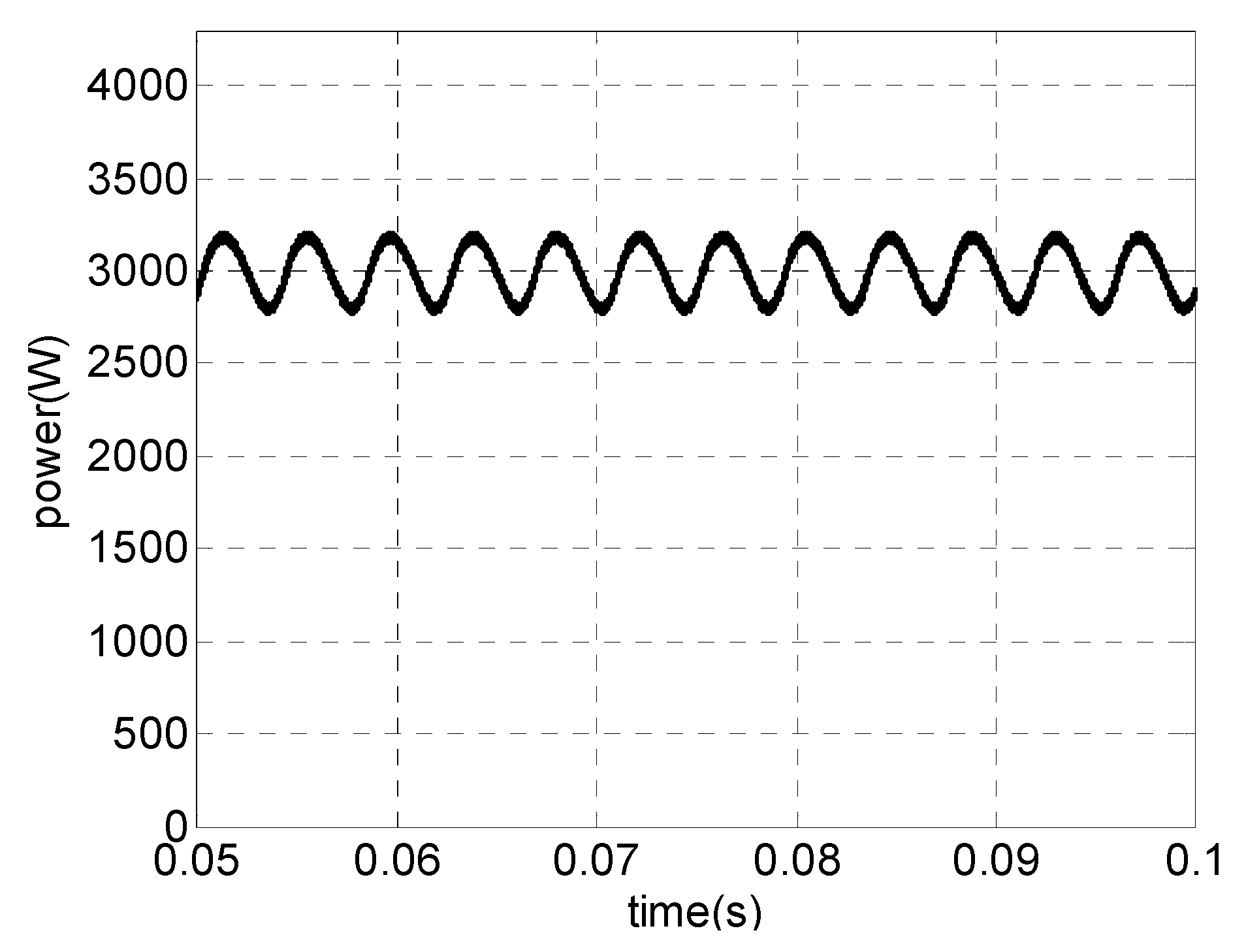
For an effective use of wind energy available, the current drawn from the generator should be an image of the generated voltage. In this context, the topologies shown before do not meet this requirement efficiently [33], since they have extremely deformed current against voltage and consequent significant harmonic content, resulting in a pulsating power of low frequency, causing torque fluctuations.
Thus, this work presents the analysis of a multi-resonant zero-current switching (ZCS) buck converter applied to wind generation, to verify its usefulness in such situations. This topology, as will be shown, provides rectification with a high power factor, low harmonic content and low switching losses—when compared with the cited conventional converters.
3. The Analyzed Converter
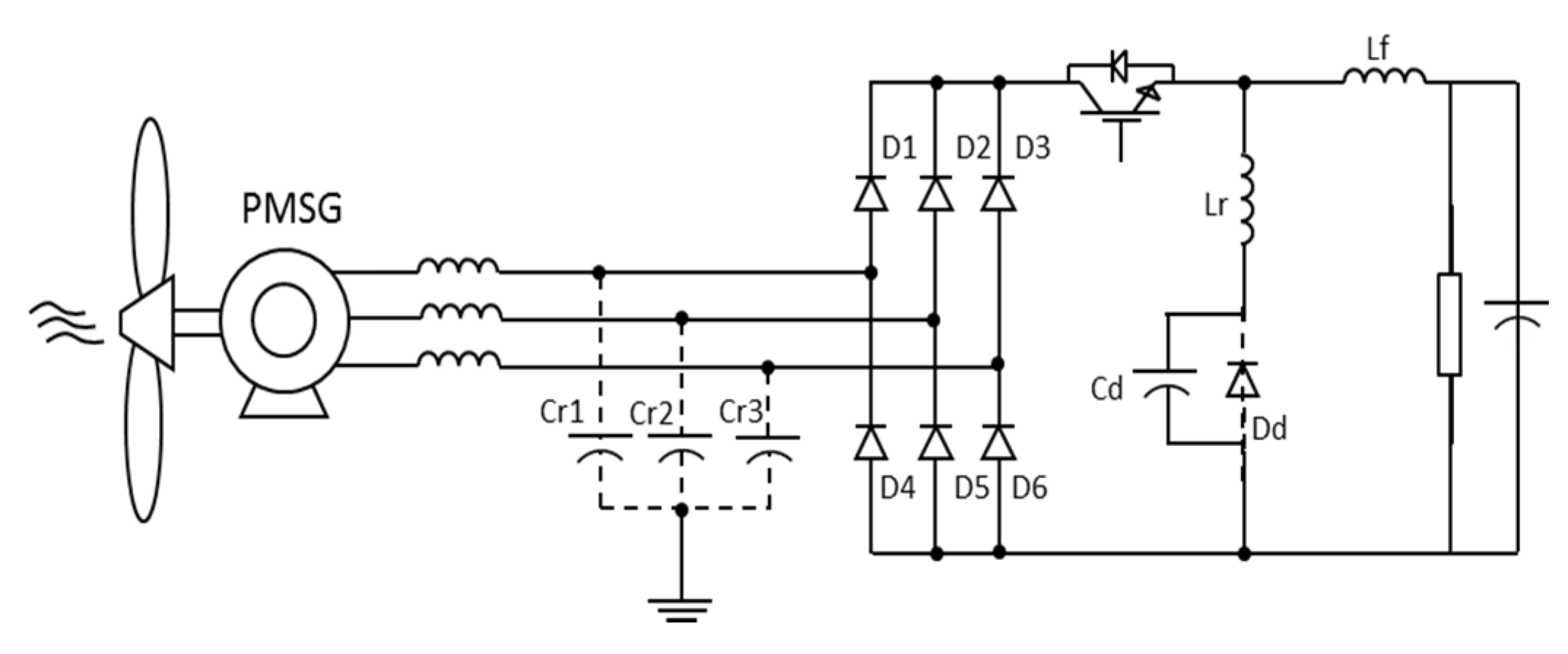
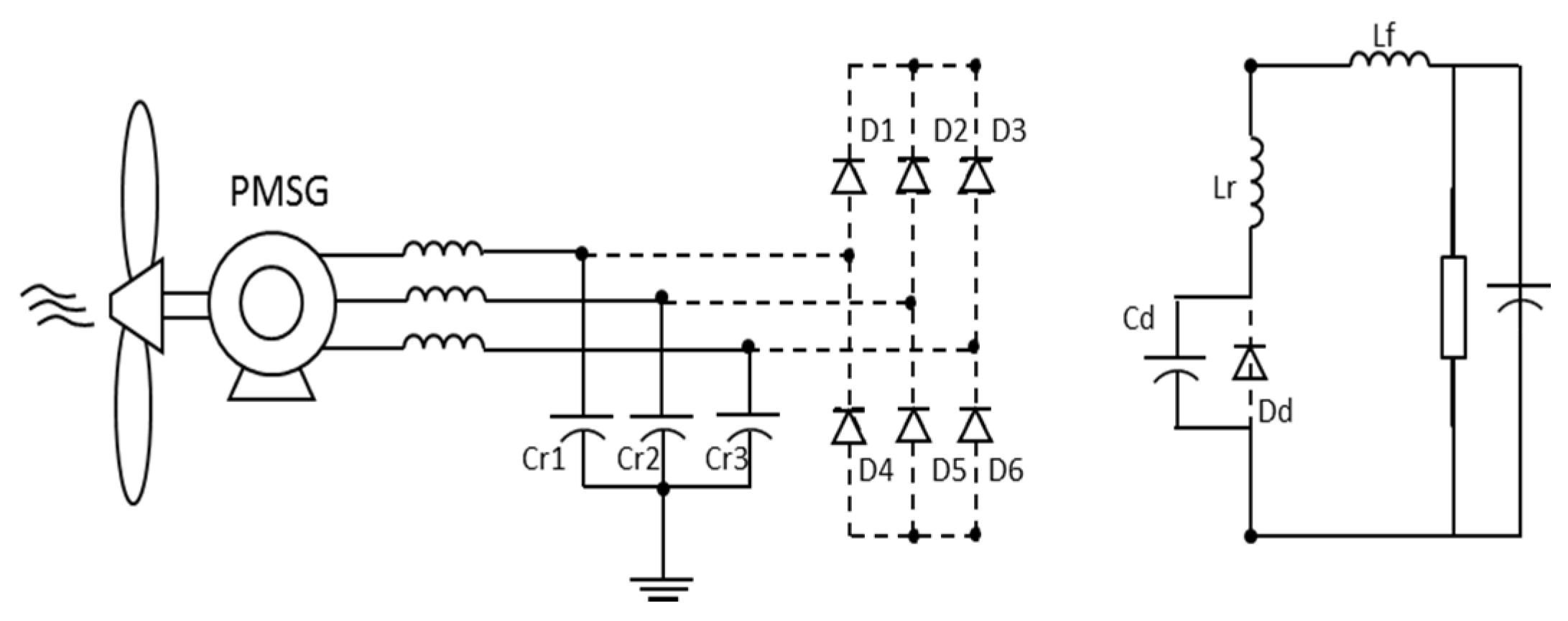
The single-switch three-phase multi-resonant ZCS topology analyzed in this paper was proposed by Jang and Erickson [34] as a high power factor rectifier fed from the mains. Its structure is shown in Figure 8.
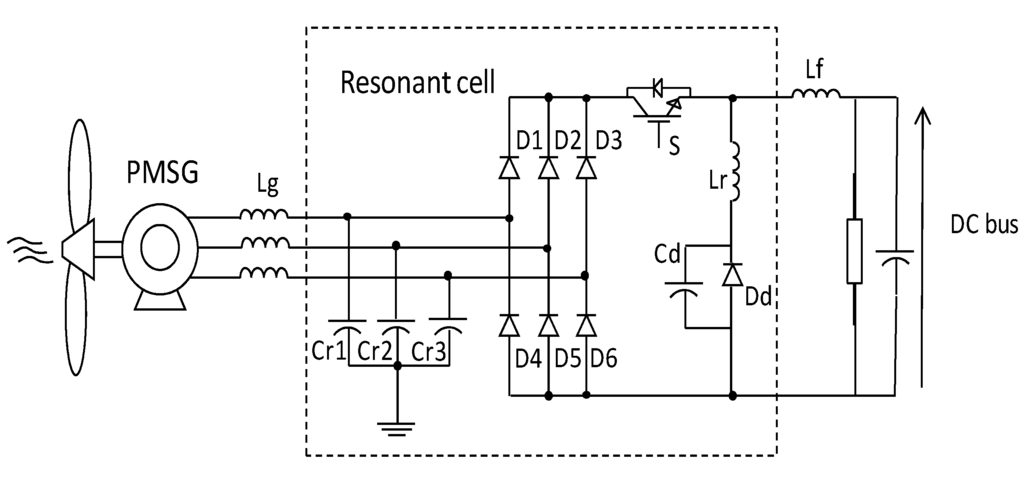
Figure 8.
Single-switch 3-phase multi-resonant ZCS topology.
Figure 8.
Single-switch 3-phase multi-resonant ZCS topology.
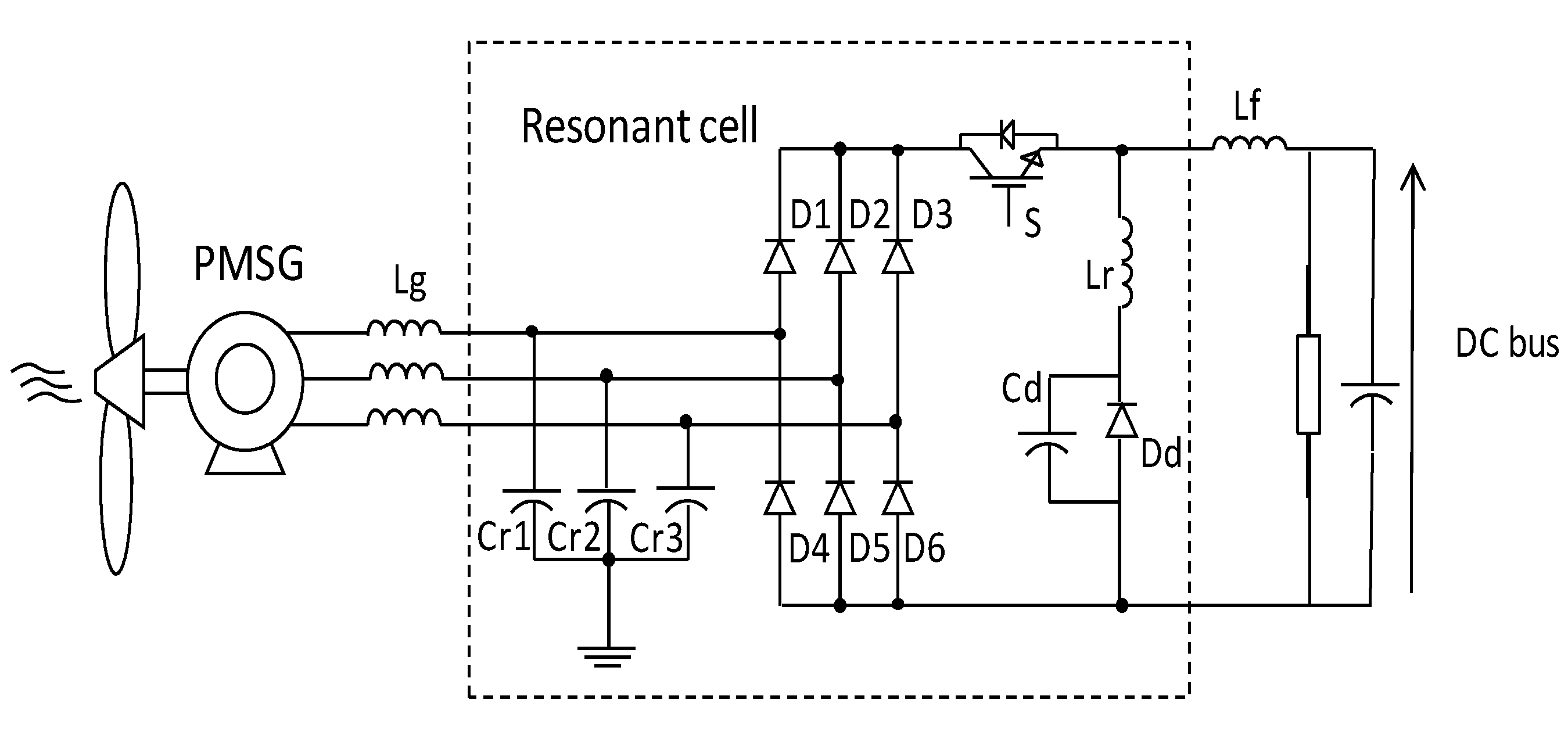
This is a topology which provides rectification with quality as when operating in multi-resonant stage the controlled semiconductor is switched at zero current (zero-current switching ZCS) and the diodes operate with zero voltage (ZVS zero-voltage switching). Furthermore, different from buck converters with one controlled device presented in [35], whose input current is pulsating, this converter input and output currents are continuous, substantially reducing harmonic content.
However, the great advantage of the structure is to operate with low output voltages (as long as it is smaller than peak value on input), which has a large scope to be implemented on hybrid systems as cited before. Furthermore, the application in a WECS has no restrictions regarding the wind speed: the operation is satisfactory for low or high wind speeds [33].
3.1. Multi-Resonant Buck-Converter Operational Steps
The analysis considers that inductors Lg and Lf are relatively large, so those switching-frequency current ripples are very small. For PMSG, the intrinsic generator inductance is naturally large enough; therefore, it can be used as input inductor of the topology.
The switching frequency, as usual, is much higher than the generator frequency, and then the waveform of the input current follows naturally the waveform of the input voltage instantaneous values, even for lower output voltage, resulting in a high power factor and lower harmonic distortion.
Voltage and current waveforms of the controlled device S1, presented as follows demonstrate the converter operation under zero current switching (ZCS).
In order to operate in multi-resonant mode, S1 “ton” time (turned on time) must be constant, regardless of load variations. The adjustment is made on the switching frequency and duty cycle, keeping however “ton” fixed.
The operation will be analyzed from 0°–30°: in this interval the current IA is positive, IB and IC are negative and IB is the smallest of them. Its operation can be divided into six stages (divided from t0 to t6) and will be explained as follows.
3.1.1. Step 1
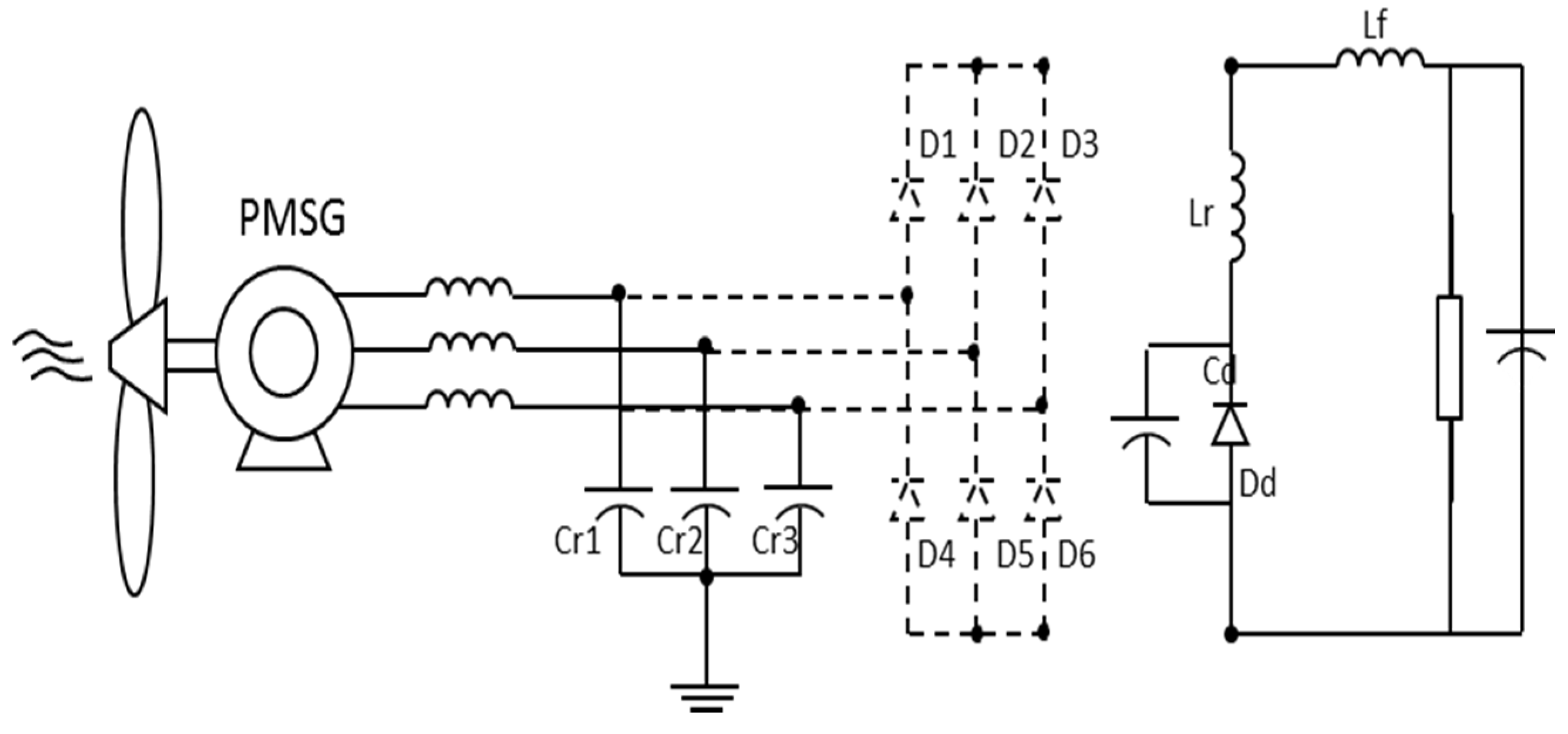
In this operation step (t0–t1), no device conducts except diode Dd. Input capacitors Cr are charged until the switch S1 is turned on. The load is supplied by the inductor Lr. Figure 9 outlines this operation.
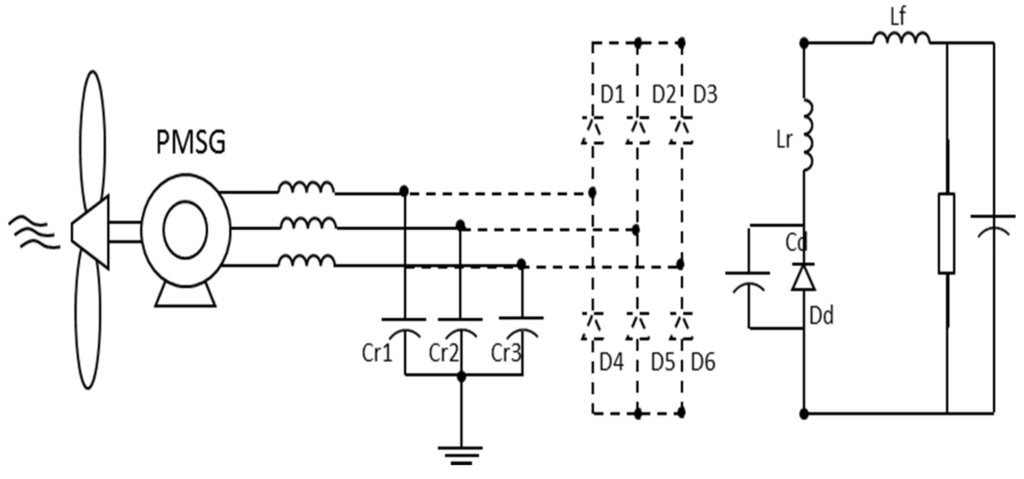
Figure 9.
First Stage: Equivalent circuit.
Figure 9.
First Stage: Equivalent circuit.
After this step, when switch S1 is turned on, it will be imposed on the bridge rectifier maximum line voltage input, and thus diodes D1 and D5 will conduct.
3.1.2. Steps 2 to 5
Step 2 (t1–t2)—shown in Figure 10—starts when diodes D1 and D5 begin to conduct. Besides them, controlled switch S1 and diode Dd remain active. Capacitors Cr1 and Cr2 are in resonance with inductor Lr while capacitor Cr3 continues charging. The current in the inductor Lr (same of diode Dd) increases to zero and diode Dd blocks, starting the next step.
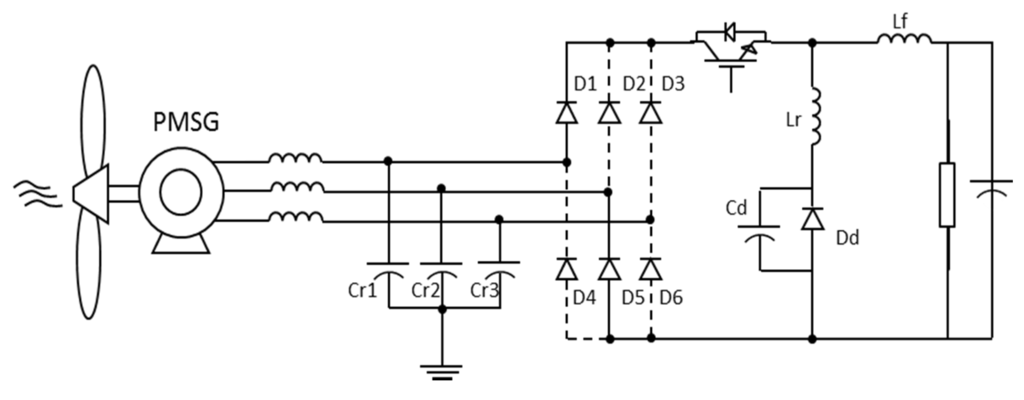
Figure 10.
Equivalent circuit: Step 2.
Figure 10.
Equivalent circuit: Step 2.
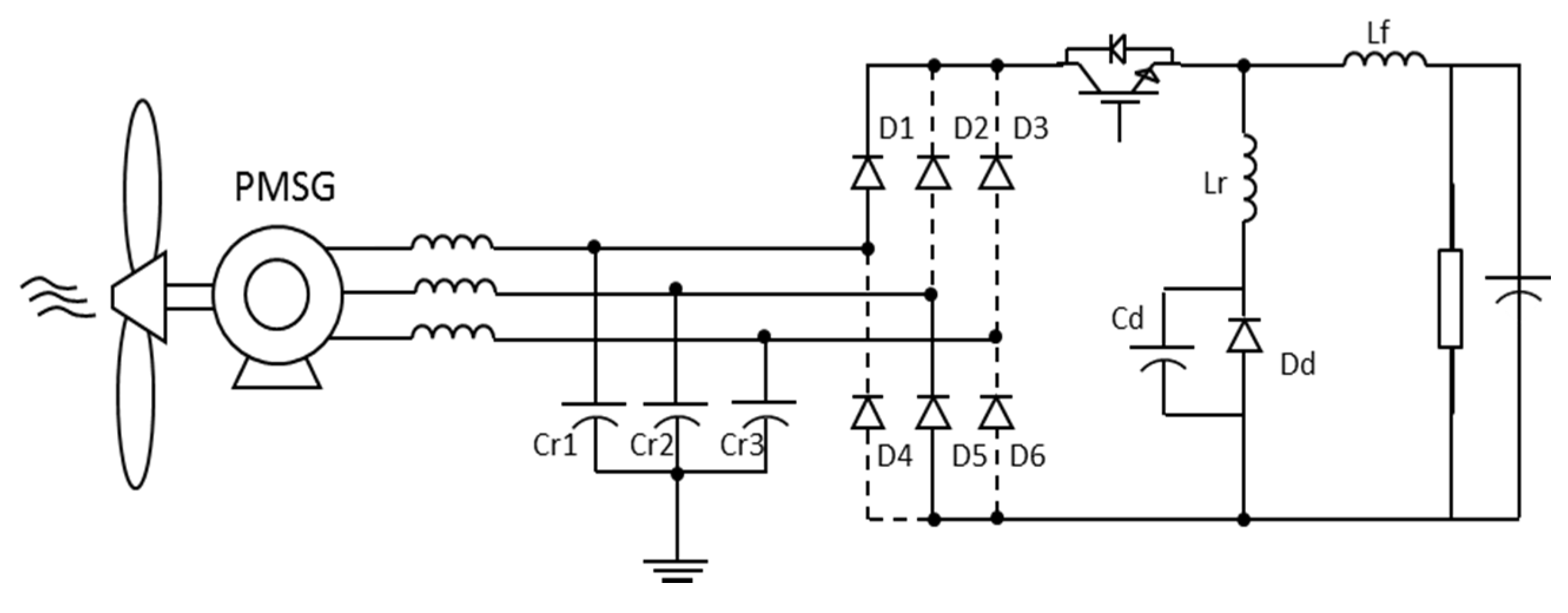
Figure 11 shows the flow chart of operation step 3 (t2–t3). The difference between this and the second step is that the diode Dd is now blocked. Capacitors Cr1 and Cr2 remain in resonance with inductor Lr and capacitor Cd, while capacitor Cr3 continues charging until its voltage equals the voltage of the capacitor Cr2. S1 is still turned on. At the end of this stage diode D6 starts conducting.
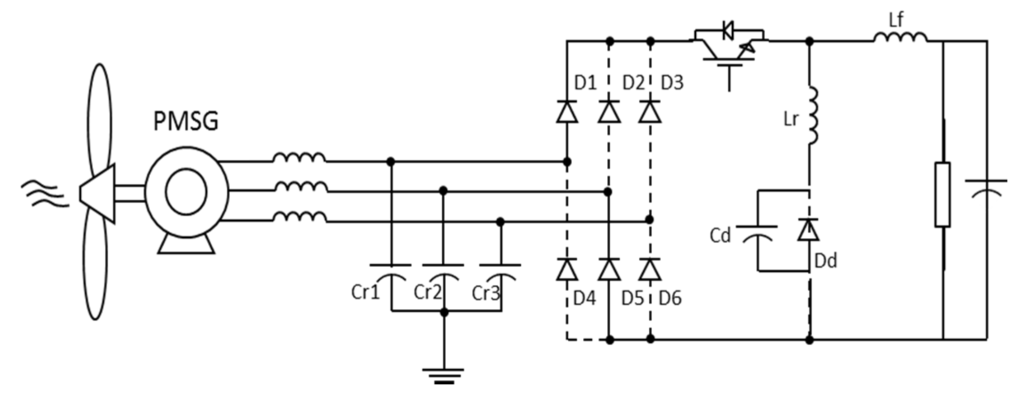
Figure 11.
Equivalent circuit: Step 3.
Figure 11.
Equivalent circuit: Step 3.
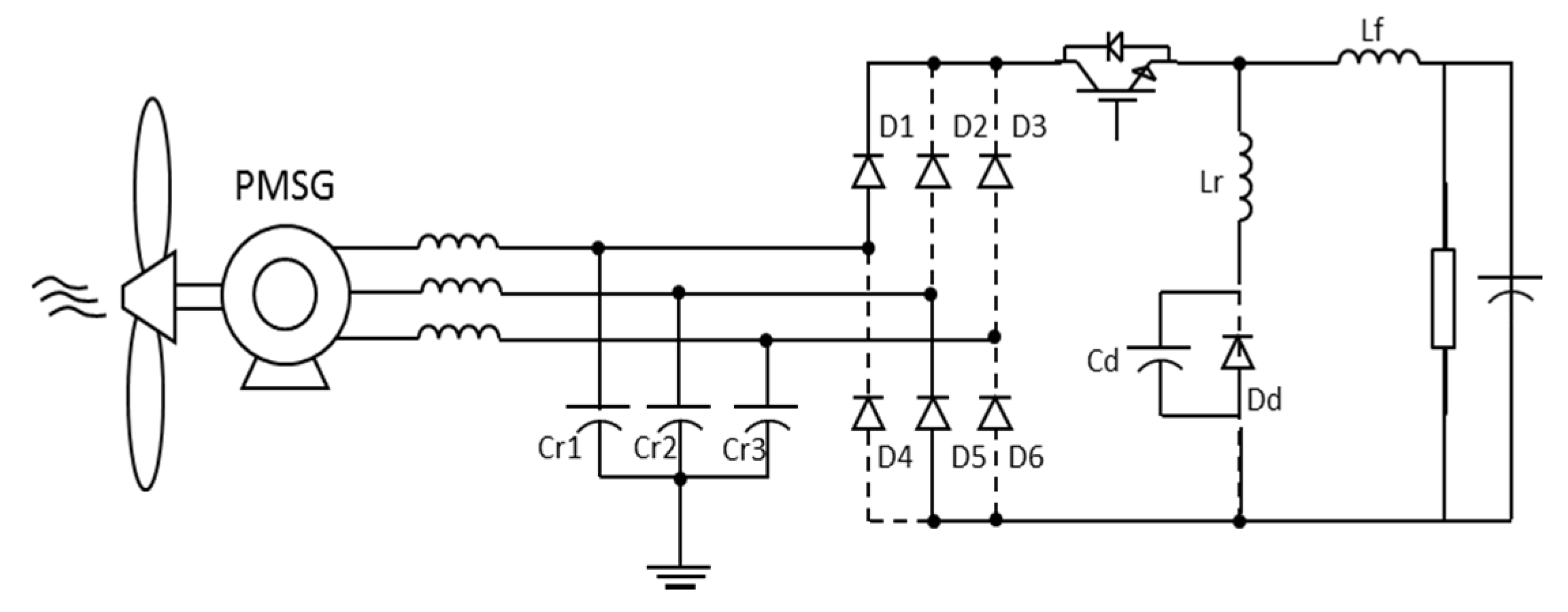
In step 4 (t3–t4), diodes D1, D5 and D6 are conducting, and so is S1. The inductor Lr is in resonance with the input capacitor and the output capacitor Cd. This step—Figure 12—lasts until the capacitors Cr1, Cr2 and Cr3 reach zero voltage.
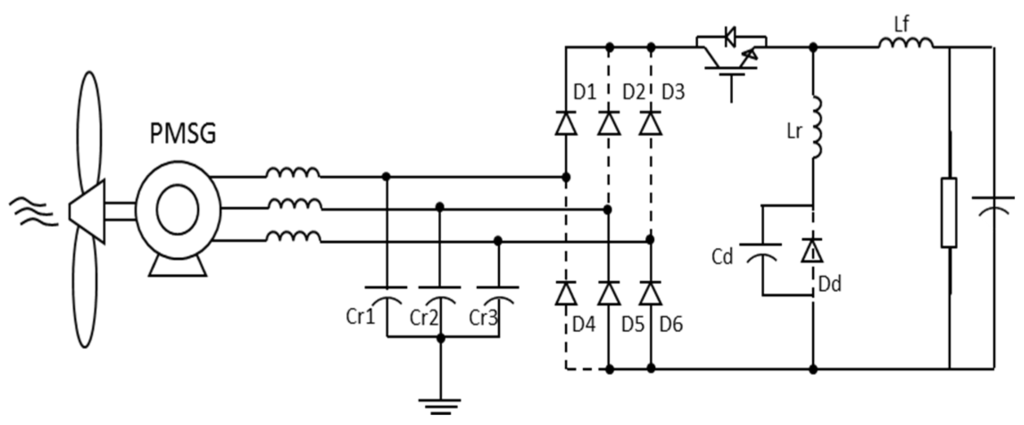
Figure 12.
Equivalent circuit: Step 4.
Figure 12.
Equivalent circuit: Step 4.
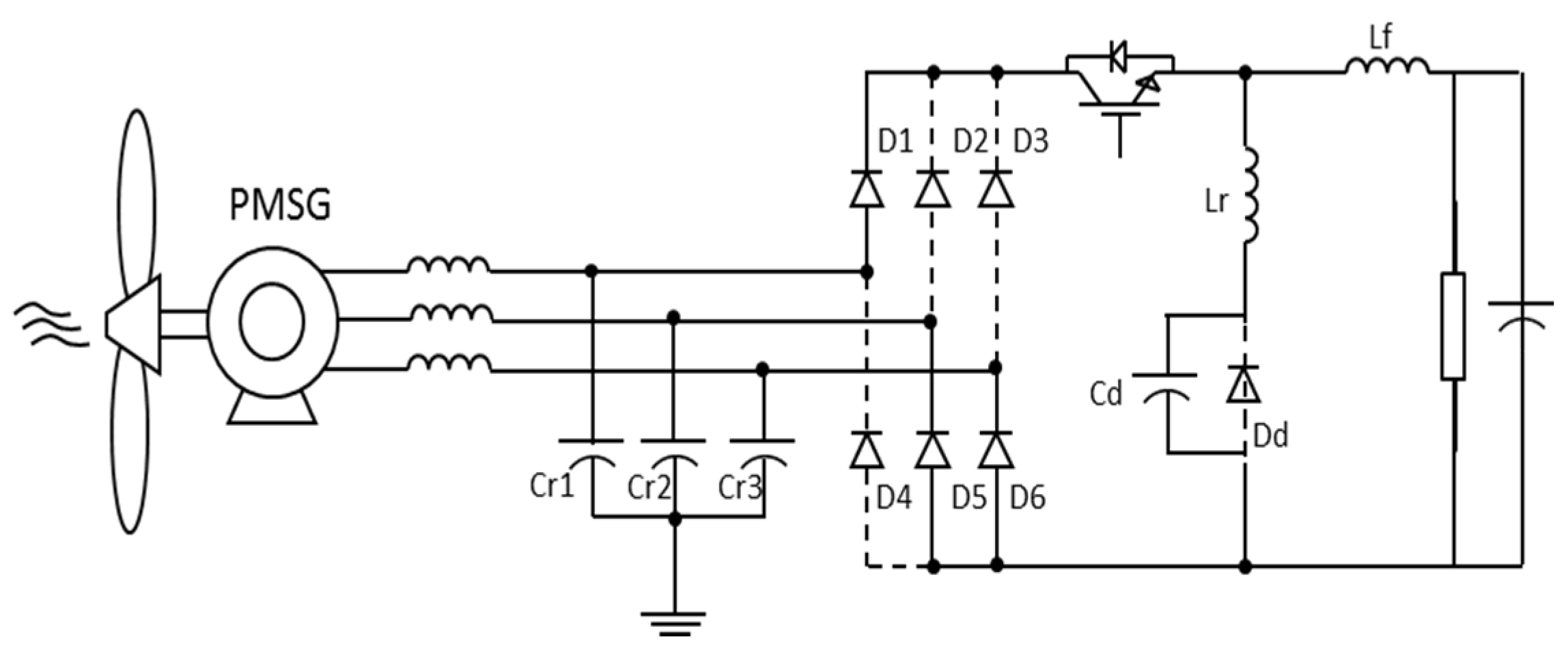
Figure 13 shows the flow chart of step 5, (t4–t5). Excepting diode Dd, all semiconductor devices are conducting. The capacitor Cd and the resonant inductor Lr operate until the inductor current is negative. When this point is reached, the rectifier bridge is reverse-biased and then the current in switch S1 is set to zero.
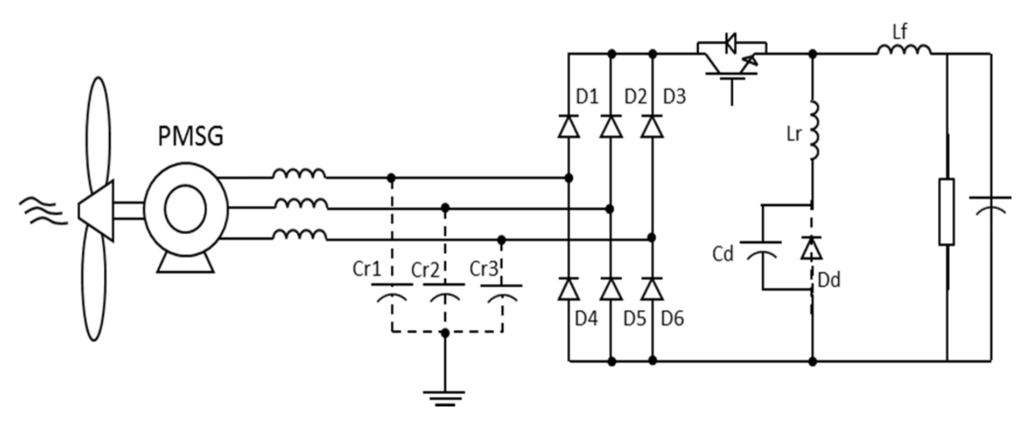
Figure 13.
Equivalent circuit: Step 5.
Figure 13.
Equivalent circuit: Step 5.
3.1.3. Step 6
In fact, this step (t5–t6)—Figure 14—is the beginning of step 1, as presented. With the zero current in switch S1—started at the end of the fifth stage—it can be switched off with no current flowing, that is, S1 is turned off with zero current (ZCS). At this stage, the load is supplied by the capacitor Cd. The voltage in this capacitor decreases to zero, at which time the diode Dd starts to conduct.
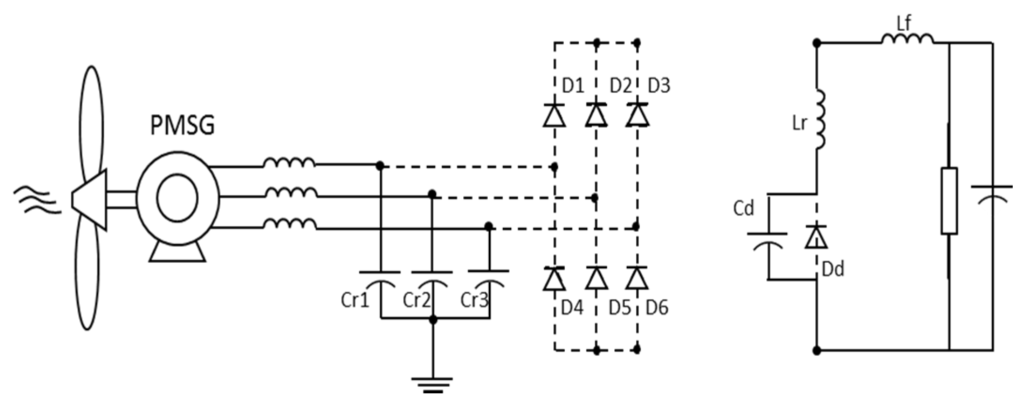
Figure 14.
Sixth stage: Equivalent circuit.
Figure 14.
Sixth stage: Equivalent circuit.
Main waveforms of the converter according to stages description are shown in Figure 15.
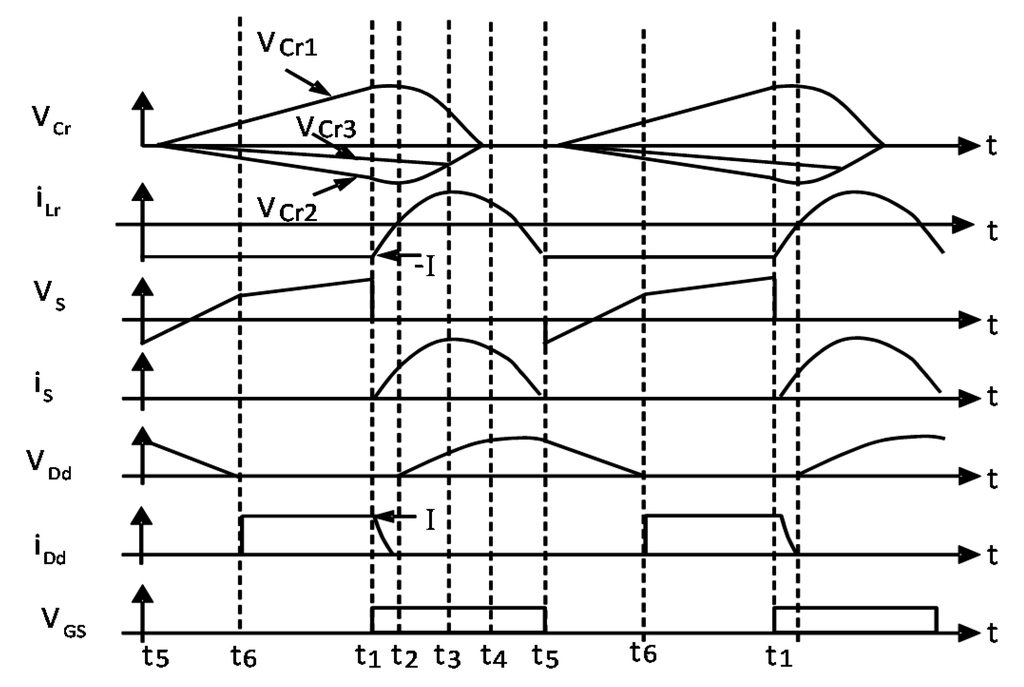
Figure 15.
Main ideal waveforms of the converter under analysis.
Figure 15.
Main ideal waveforms of the converter under analysis.
From the PMSG point of view, the converter operation can be summarized in two periods. The first one lasts (t5–t1) until the switch-off time. The three resonant capacitors Cr are disconnected from the buck converter, and input inductors (the generator ones) see a symmetric high-frequency triangular three-phase source modulated by the generator voltages. The equivalence of the capacitors’ voltage at their connection point is a short circuit, and inductors’ current evolves proportionally to the input voltage. During the on-time of the switch, this voltage assumes other values and the inductors’ currents evolve according to the resulting voltage over them. Assuring that the switch-off time is much greater than the on-time, the generator currents will present low distortion, operating with a high power factor [34].
3.2. Design Equations
The equations that define the project of the converter based on input and output voltages and power supplied have been developed by [34,36]. To facilitate the development of the equations, it has been proposed in those articles a single-phase equivalent of the three-phase converter, and from it the variables were normalized according to the converter output voltage.
So, for a chosen switching frequency fs, an input voltage Vin and an output voltage Vout, the normalized peak input voltage can be stated, given by Equation (1).
The normalized switch-off time α is the control variable for this rectifier. The switch-on period is essentially constant for the complete output range [34]. Therefore, the switch-on period is maintained as a constant value and the switch-off period is controlled. The graphic presented by [34] shows the normalized peak input current (Jg) versus normalized peak input voltage for a given chosen α. So, by selecting the value of α and with the value of Mg, Jg can be obtained.
With the values of α and fs, the resonance frequency can be calculated, given by Equation (2):
The resonant resistance, named R0, is given by Equation (3)
With the values of f0 and R0 and some mathematics calculation, the values of Lr, Cd e Cr can be calculated, based on Equations (4)–(6), presented as follows.
The half-resonant period is given by Equation (7). The minimum on-time of the switch must be greater than this value in order to assure ZCS at turn-off.
Using these equations, and the normalized input characteristics of the converter presented in [34], the converter can be designed.
3.3. Sensitive Analysis of Parameters
Capacitance and inductance of the resonant capacitor and inductor may change with operational conditions, which directly affect the resonant resistance R0 and resonant frequency f0, previously presented in Equations (4) and (5). In order to maintain the resonant characteristics, some adjustments must be made. The effect of ±10% variation on these elements is shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Effect of variation of resonant elements on resonant properties.
| Lr | Cd | R0 | f0 | ton |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| +10% | +10% | = | −10% | +10% |
| −10% | −10% | = | +10% | −10% |
| −10% | +10% | ≈−10% | = | ≅ |
| +10% | −10% | ≈+10% | = | = |
As one can see, when both capacitance and inductance vary +10% or −10%, the effect is on the period ton. Despite these variations on Lr e Cd, in order to guarantee the resonance, it is recommended using a value Ton 10% higher than the theoretical value ton; its use avoids an inadequate operation even if an increase in inductance or capacitance occurs. If Equation (8) is satisfied, there are no significant impacts on the results for a variation of ±10% in the resonant elements.
If the variations are not in the same direction, e.g., Lr varies +10% and −10%, or the opposite case, the effect occurs on R0. As ton is kept constant, to adapt the converter to the new operational point, the switching frequency fs is modified. This entire alteration is done by the MPPT technique control, with a variation as much as +10% to −10% in R0.
4. Design Example and Simulation Results
To validate the operation of the three-phase buck-resonant converter with direct application in wind generation, a simulation of a WECS was implemented in platform MATLAB/Simulink®. A simulation was developed with blocks already available on Simulink, and some others were designed.
The turbine, the generator and the converter employed the original elements of Simulink, while the MPPT control (acting to ensure operation at MPP), which outputs the drive signal of the controlled semiconductor, was implemented using mask systems encompassing a MATLAB function and Simulink components.
4.1. MPPT Control
Under varying wind speed, the MPP and corresponding turbine-generator speed of a WECS continuously changes. Consequently, autonomous tracking of the MPP is essential to any WECS to provide maximum energy at all times.
Many MPPT algorithms have been proposed, varying in complexity, accuracy, convergence speed and cost. A good analysis of MPPT methods is provided in [16,37,38,39]. The most widely applied algorithm is the “perturb and observe” (P&O) method. It mostly involves the perturbation of the duty ratio on the converter and measuring the change in power due to the perturbation.
In this work, a P&O MPPT technique was also implemented, but instead of using the duty cycle as the perturbation variable, the converter switching frequency was used, as in [40]. Thus, for an operating point in the power curve, the switching frequency is disturbed, and the influence on the controlled variable—in this case the power—is observed. If the result is an increase in the power, then the same disturbance is applied in the next instant control; otherwise, the disturbance signal is inverted in the next instant control in order to check the power increase direction.
For this buck-converter analysed, as the switch on-time is constant for all wind speeds (output power), the output of the MPPT algorithm must guarantee that the duty cycle and the switching frequency vary at a constant rate, given by “ton”, as given by Equation (9).
4.2. Converter Project
The behavior of the three-phase ZCS buck rectifier presented here was verified by simulation. The 3-Ф wind PMSG to be simulated has the following parameters (Table 2).

Table 2.
PMSG parameters.
| Prated | Lg | vwind,rated | vwind,cut-in | VLL,rms (40 Hz) | VLL,rms (10 Hz) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 kW | 12 mH | 12 m/s (40 Hz) | 3 m/s (10 Hz) | 220 V | 78 V |
To operate as a buck converter, the output voltage must be less than the peak value of minimum line-to-line voltage. Thus, the DC output voltage V = 60 V was chosen.
Using the previous equations and graphic, converter parameters were calculated and are presented in Table 3.

Table 3.
Parameters of buck-resonant converter.
| ton | fo | Lr | Cd | Cr |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12 µs | 42 kHz | 20.52 µH | 0.704 µF | 1.056 µF |
The switching frequency for the rated condition was chosen as 20 kHz. If the wind speed decreases by a ratio of 4, the maximum extractable power decreases by a ratio of 64. Therefore, for a wind speed of 3 m/s, the maximum power is about 50 W. To maintain the switch-on period constant, switching frequency in this case decreases to 8 kHz.
4.3. Simulation Results
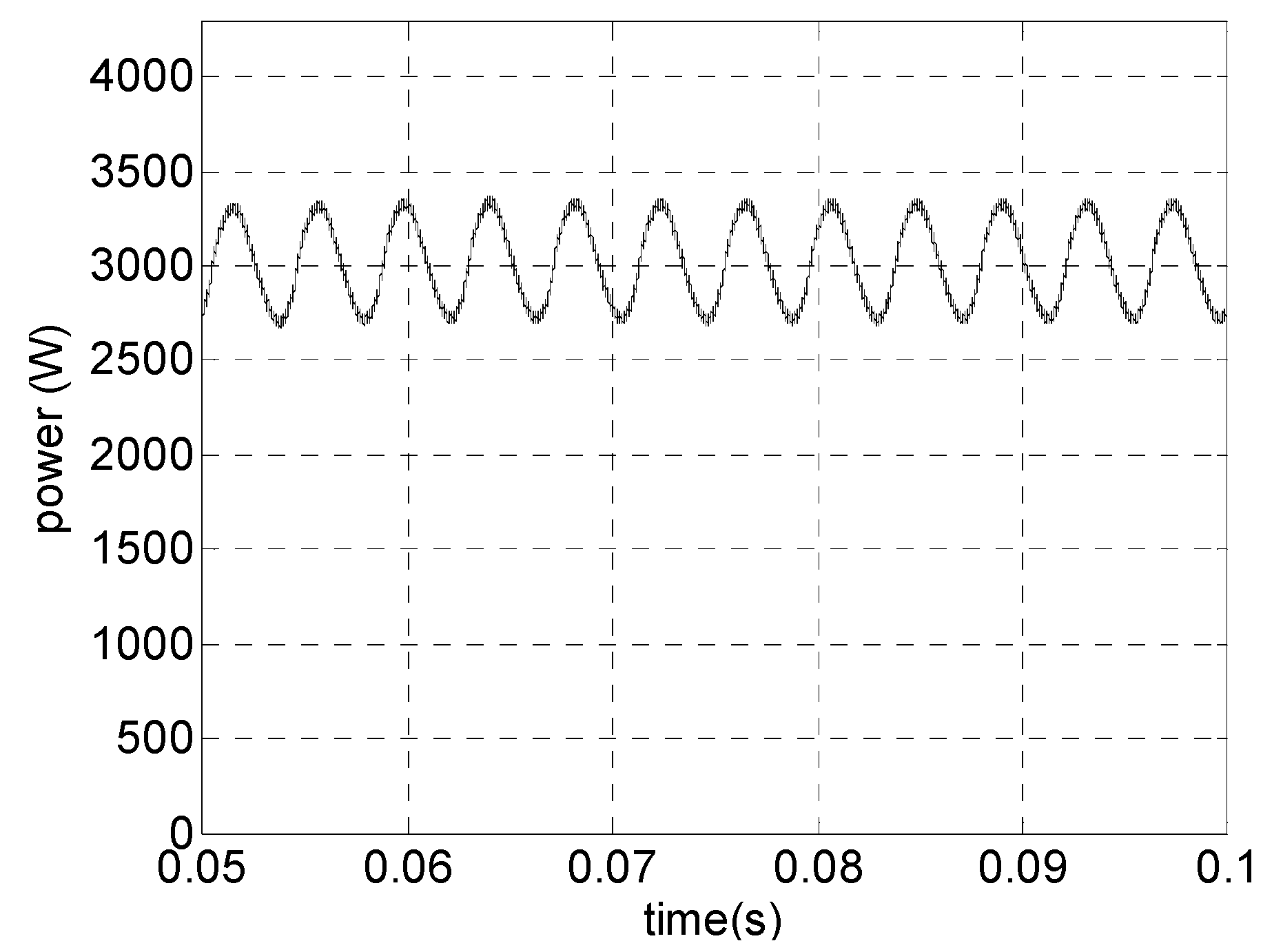
Steady-state (open-loop) simulation results are presented as follows. Figure 16 shows PMSG phase voltage and current for vwind = 12 m/s (rated power, 40 Hz). The high quality of generator current can be observed. It can be seen that the current waveform is an image of voltage waveform showing high power factor and low harmonic content. The THD is 4.6% and power factor is 0.98. As a comparison, in the topology presented by [21] for the semi-controlled three-phase boost, the power factor is 0.982 and THD is about 18%. In [28] using a boost as DC intermediate stage, the THD is 11.06%, while for the bridge rectifier diode it is approximately 27%.
Figure 17 shows PMSG electrical power for this case. Despite a little ripple due to switching frequency, the generated power is almost constant.
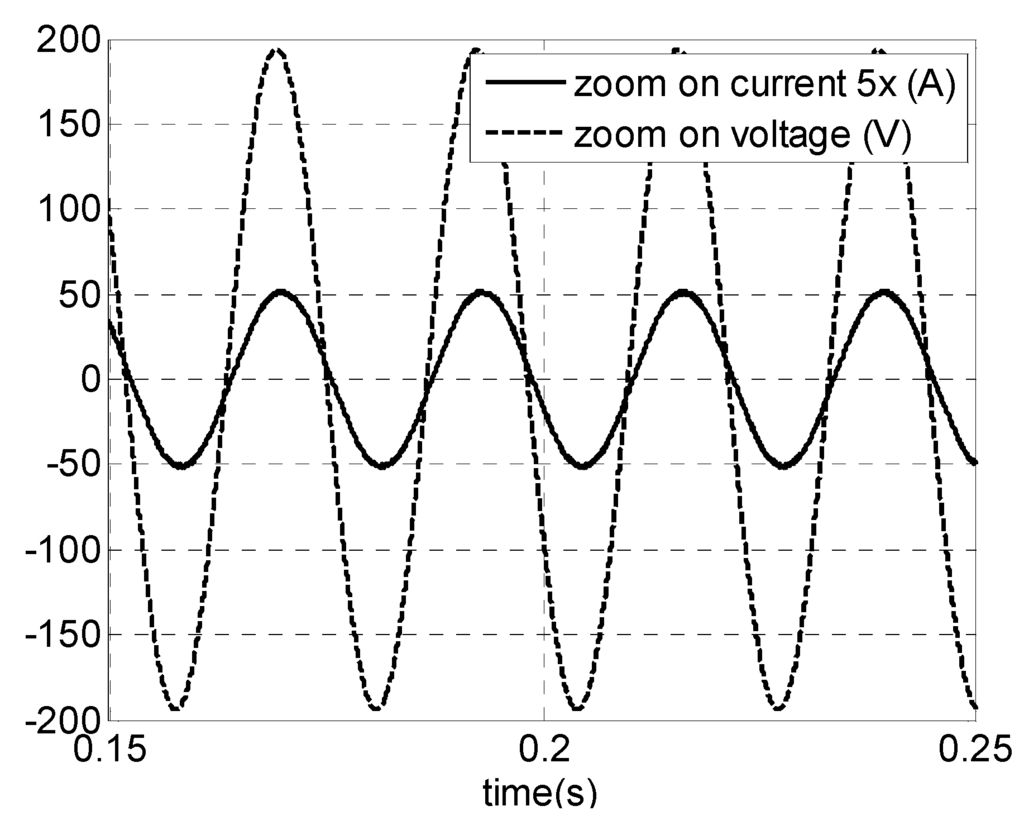
Figure 16.
Simulations results for a PMSG. For vwind = 12 m/s (rated power): phase voltage and current.
Figure 16.
Simulations results for a PMSG. For vwind = 12 m/s (rated power): phase voltage and current.
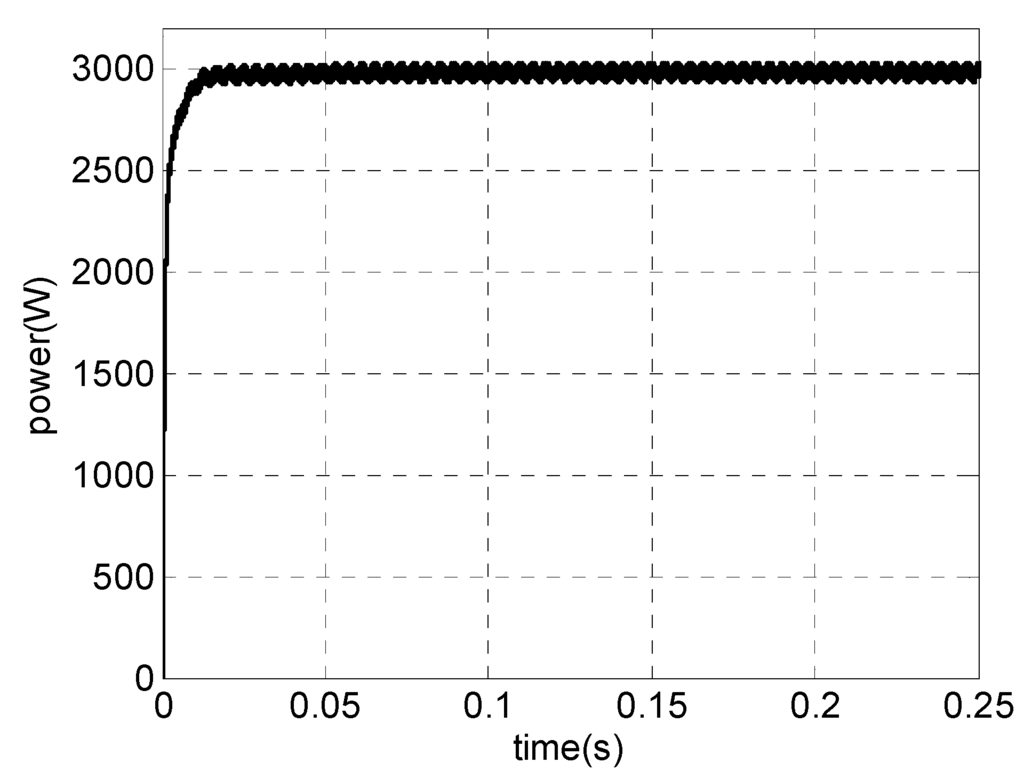
Figure 17.
Simulations results for a PMSG. For vwind = 12 m/s (rated power): electrical power.
Figure 17.
Simulations results for a PMSG. For vwind = 12 m/s (rated power): electrical power.
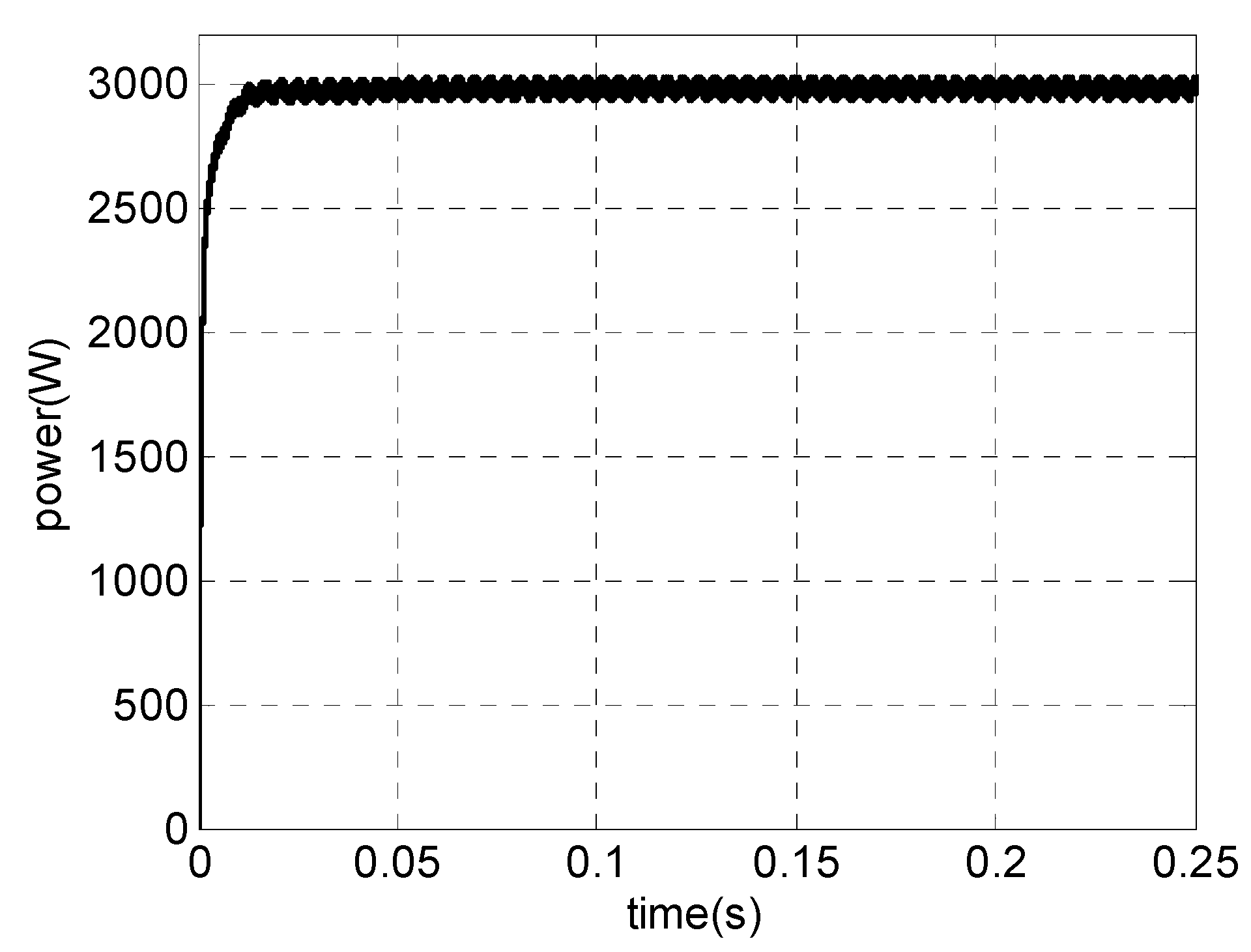
A similar analysis was carried out for the cut-in wind speed (3 m/s). Figure 18 shows the simulation result of PMSG phase voltage and current (10 Hz). It can be observed that the high quality of generator current is maintained. The PMSG current presents a THD = 4.57% and a power factor of cos (θ) = 0.98. The respective PMSG electrical power is shown in Figure 19. The initial response is only a simulation transient. For both extreme situations, the high quality of PMSG current and electrical generator power can be observed.
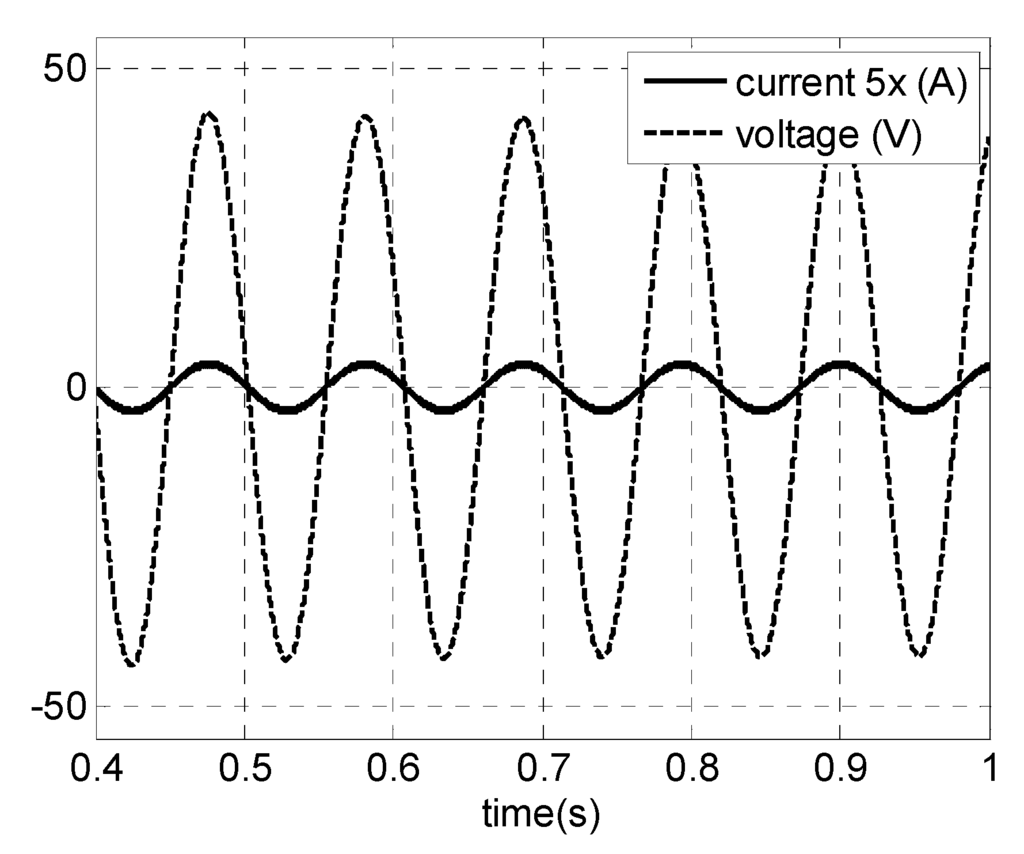
Figure 18.
Simulations results for a PMSG. For vwind = 3 m/s: phase voltage and current.
Figure 18.
Simulations results for a PMSG. For vwind = 3 m/s: phase voltage and current.
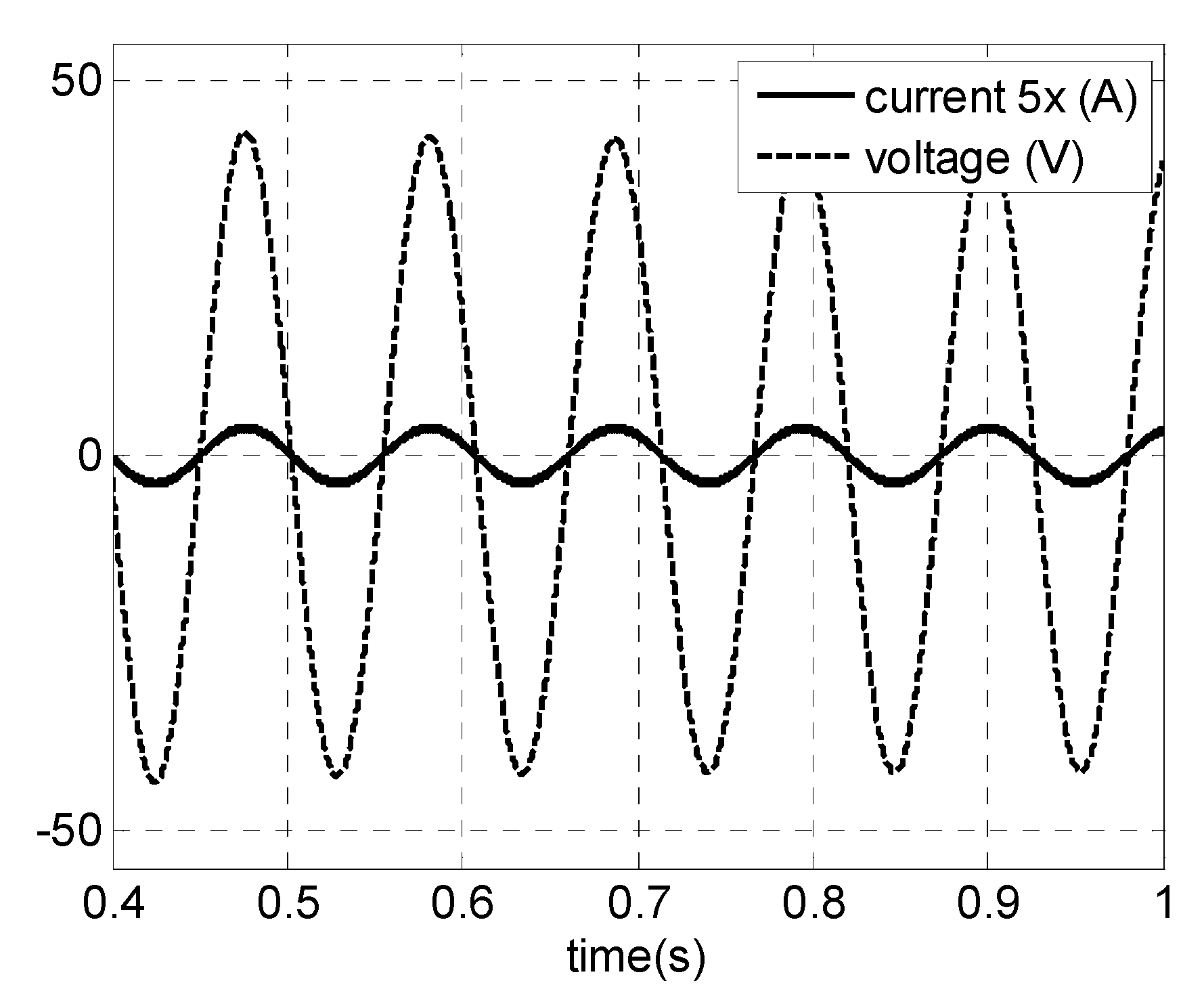
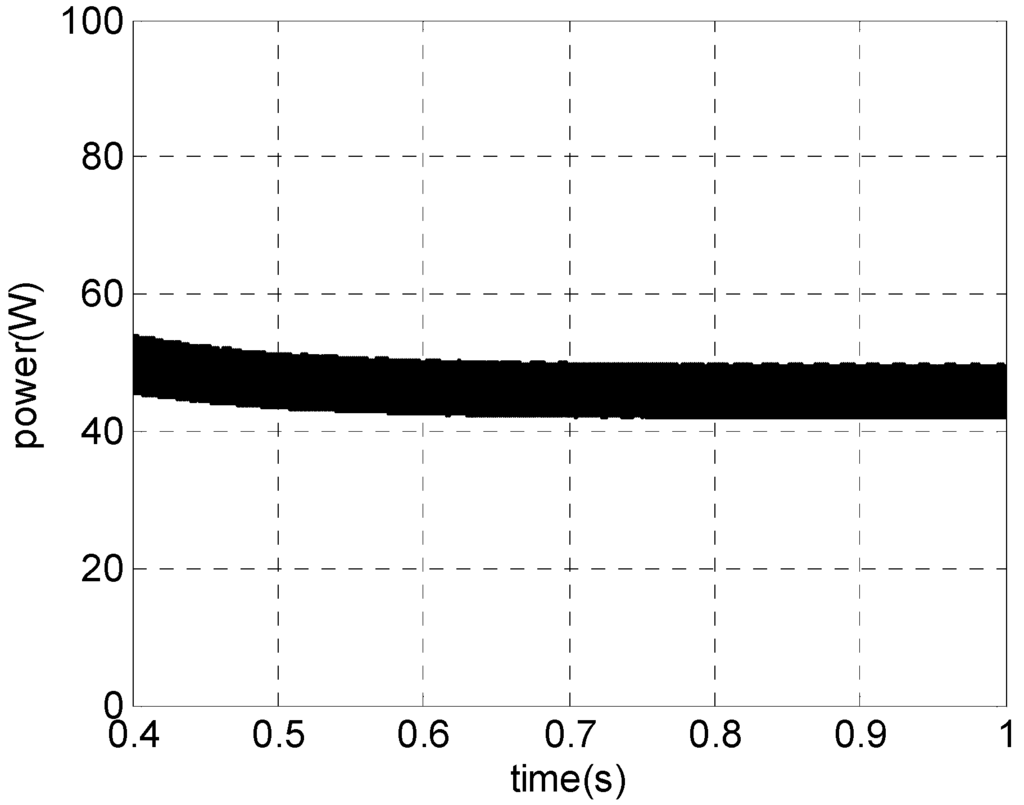
Figure 19.
Simulations results for a PMSG. For vwind = 3 m/s: electrical power.
Figure 19.
Simulations results for a PMSG. For vwind = 3 m/s: electrical power.
Voltage and current signals on the controlled semiconductor S1 can be seen on Figure 20, for both cases, vwind = 12 m/s and vwind = 3 m/s. It shows the ZCS characteristic, once S1 is turned off with no current flowing.
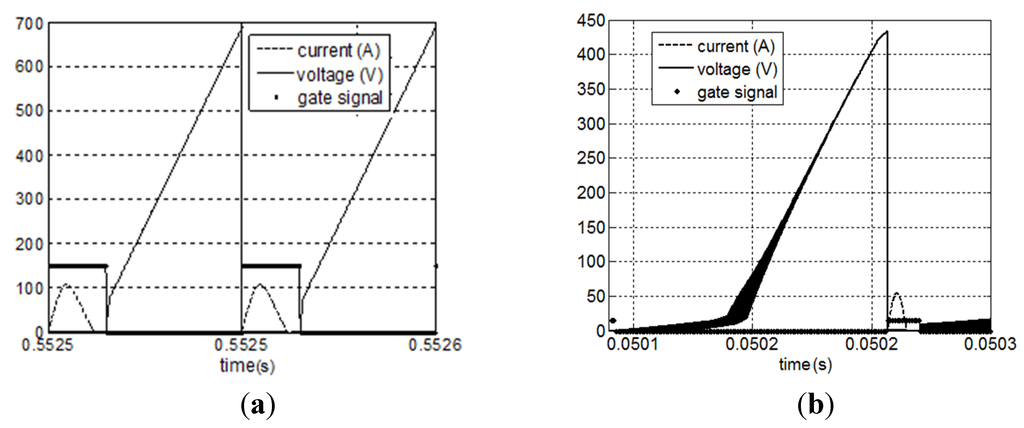
Figure 20.
Voltage and current signals on controlled semiconductor device; (a) vwind = 12 m/s; (b) vwind = 3 m/s.
Figure 20.
Voltage and current signals on controlled semiconductor device; (a) vwind = 12 m/s; (b) vwind = 3 m/s.
To complete the analysis, the WECS was simulated with a variation in wind speed. In this situation, the load is robust enough to keep the voltage fixed on 60 V. In this simulation, the MPPT algorithm presented in this paper was used; in order to compare the output power obtained with the MPPT algorithm and the MP theoretical value, Figure 21 shows for the employed turbine the power characteristics, where the output power and speed of the turbine for certain wind speeds can be seen.
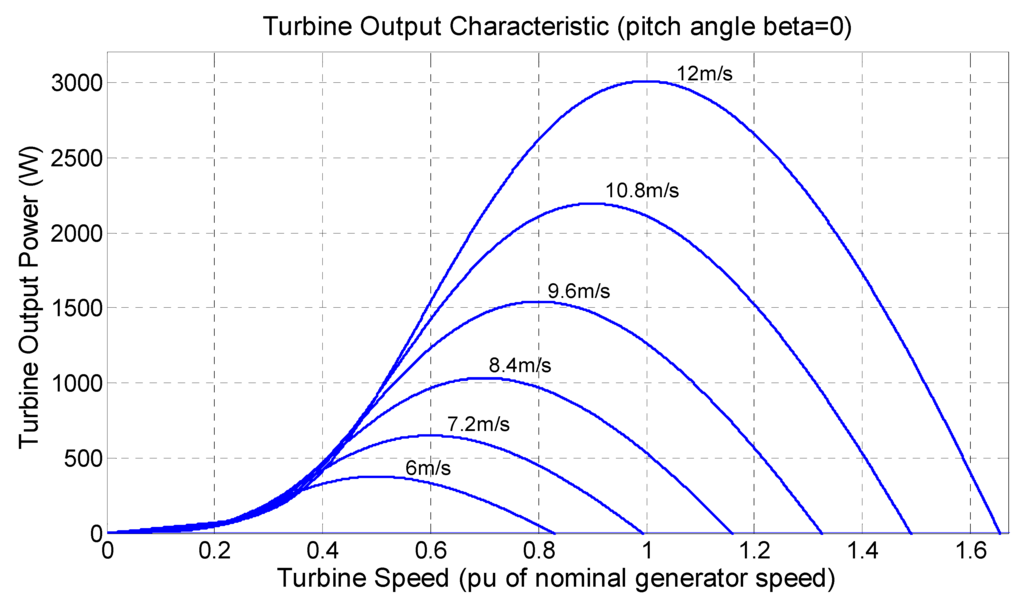
Figure 21.
Turbine power output versus turbine speed for a given wind speed.
Figure 21.
Turbine power output versus turbine speed for a given wind speed.
The nominal wind speed for generator rated power is vwind = 12 m/s. The wind speed is subjected to step changes, as it can be seen in Figure 22; ramp transitions, shown in Figure 23; and random behavior around a point, as can be seen in Figure 24. The simulated generated power and the MPP theoretical value is also shown. It can be noticed that the MPPT algorithm can track the MPP.
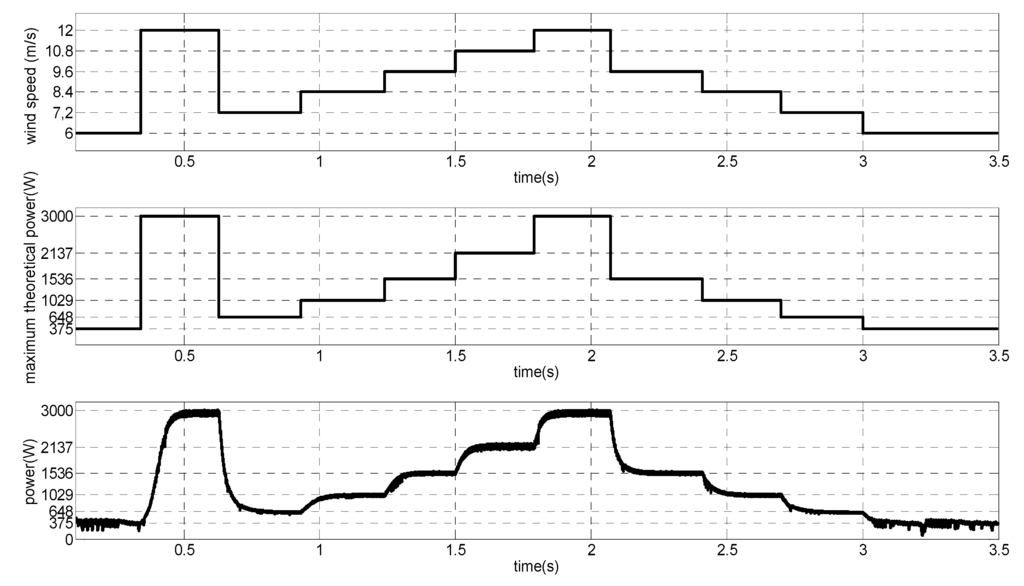
Figure 22.
Wind speed with step variation, theoretical MPP and output power.
Figure 22.
Wind speed with step variation, theoretical MPP and output power.
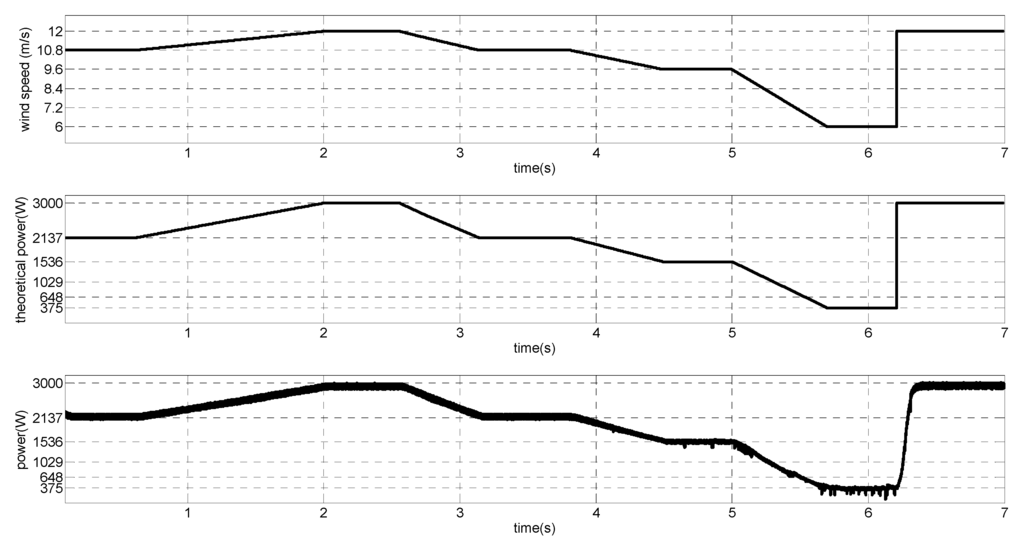
Figure 23.
Wind speed with slow variation, theoretical MPP and output power.
Figure 23.
Wind speed with slow variation, theoretical MPP and output power.
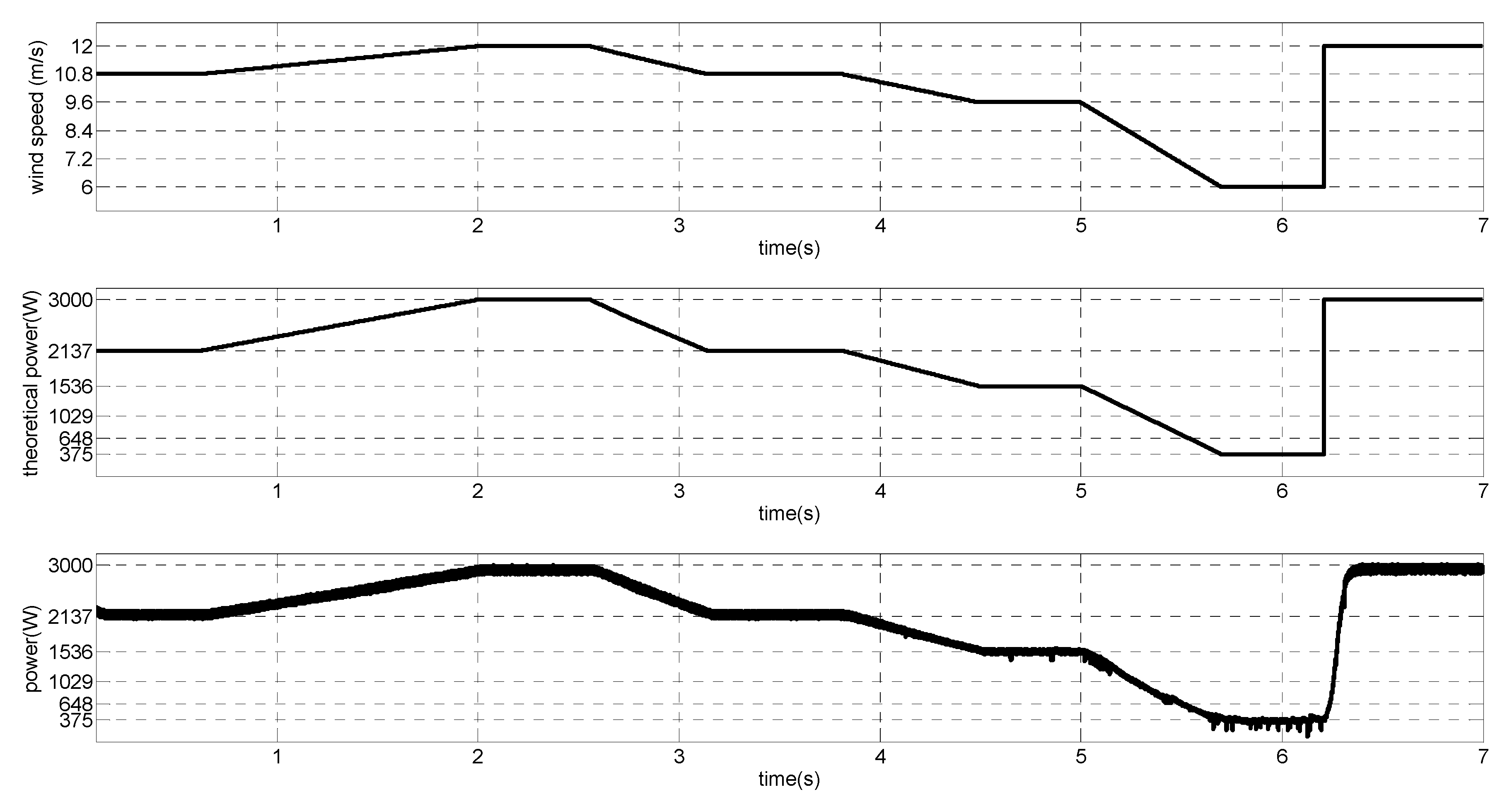
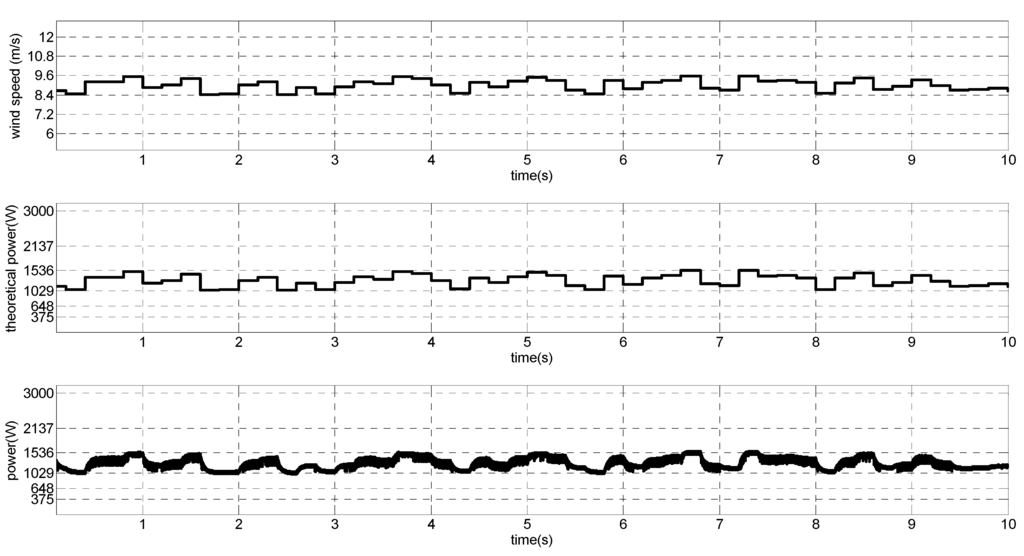
Figure 24.
Wind speed with random behavior, theoretical MPP and output power.
Figure 24.
Wind speed with random behavior, theoretical MPP and output power.
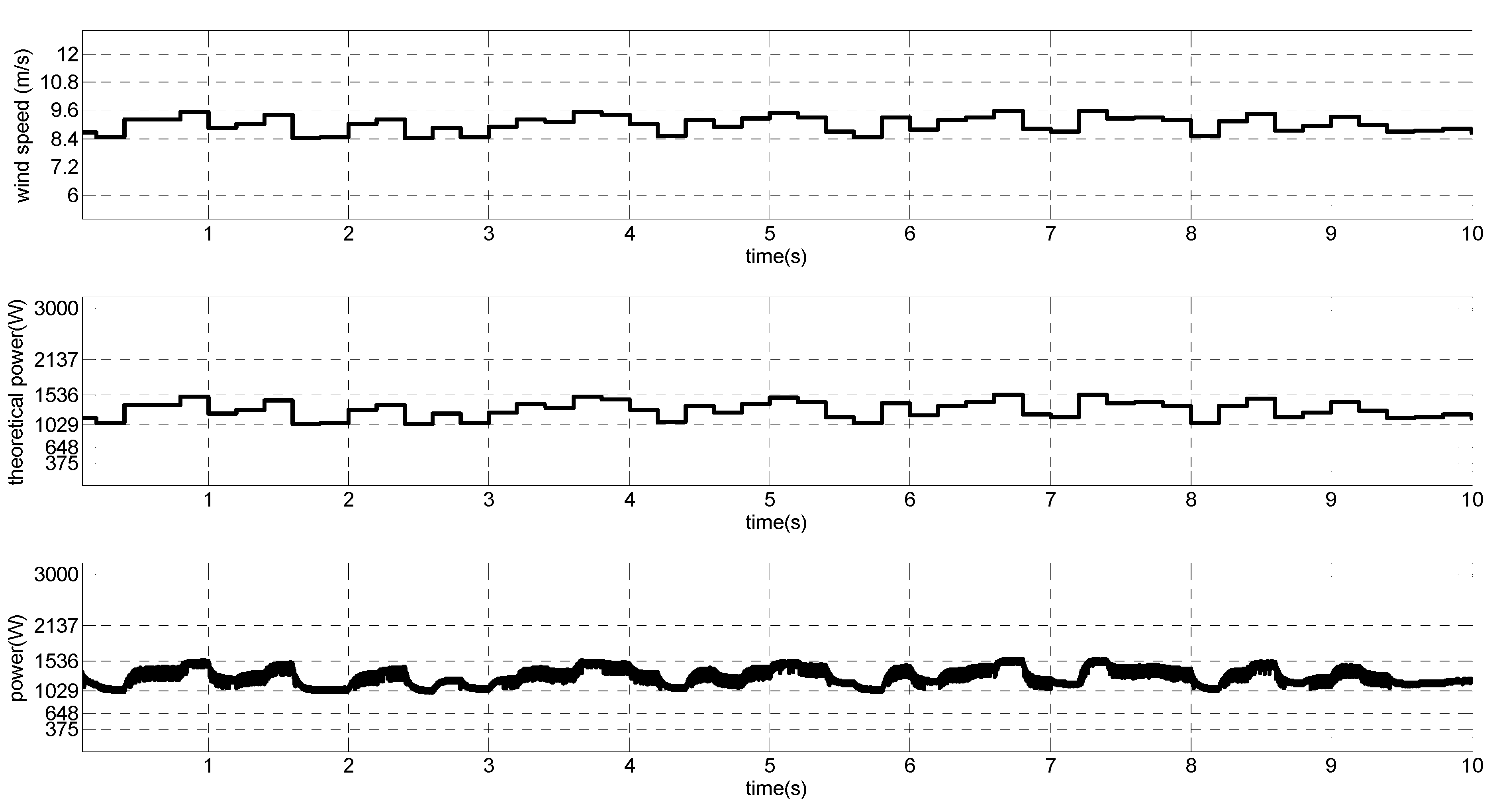
Figure 25a displays PSMG voltage and current during a wind transition from 12 m/s to 6 m/s. A zoom of the waveforms during wind transition from 12 m/s to 6 m/s is shown in Figure 25b. It can be seen that the high quality of input current is kept at all times.
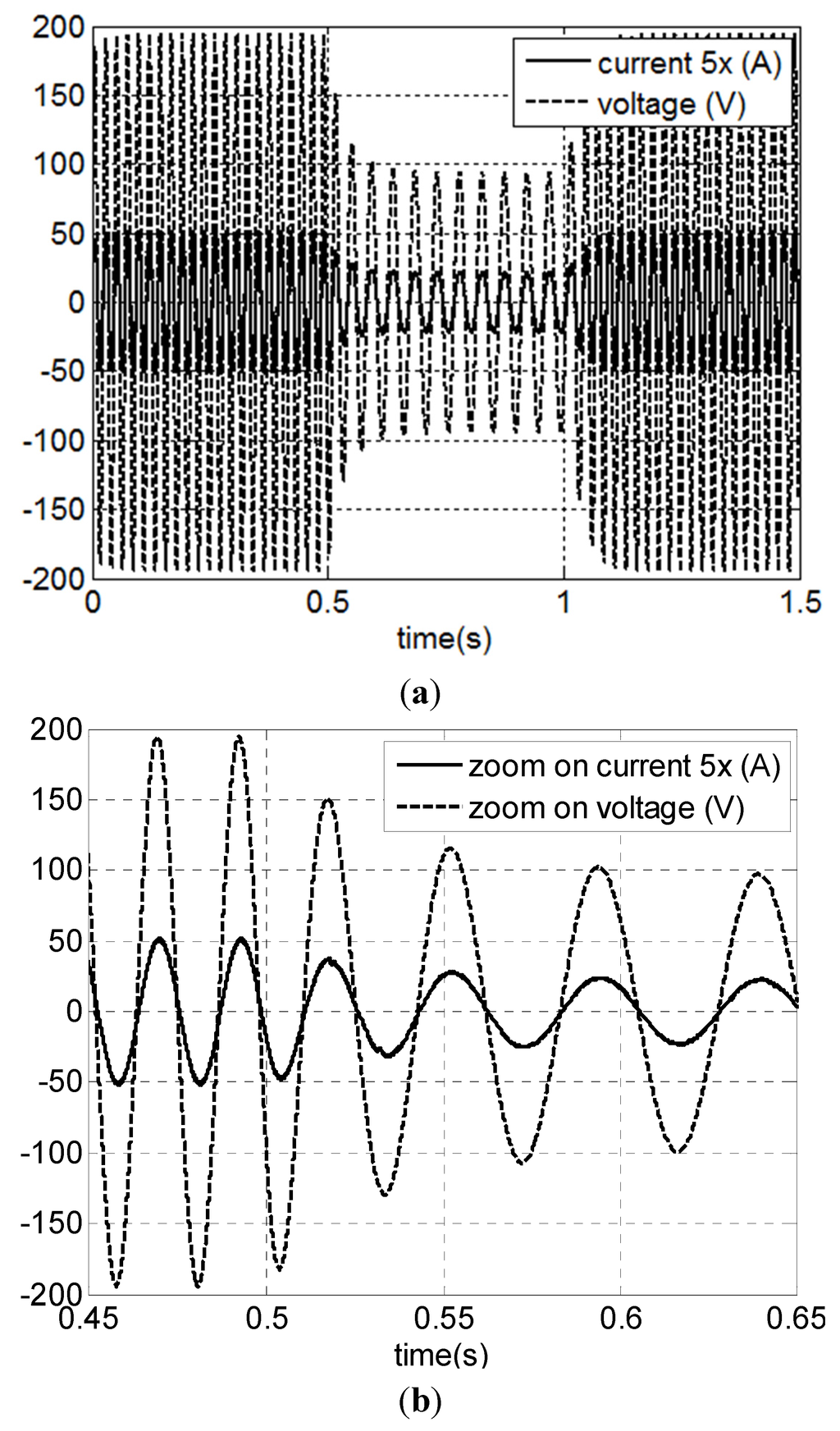
Figure 25.
Simulation with P&O MPPT technique and variable wind speed: (a) PMSG voltage and current; (b) zoom of (a).
Figure 25.
Simulation with P&O MPPT technique and variable wind speed: (a) PMSG voltage and current; (b) zoom of (a).
The figures show the good quality of the input current. It can be seen that the current waveform is sinusoidal.
5. Conclusions
A single-switch three-phase ZCS buck high-power-factor rectifier was analyzed to verify its applicability as a rectifier stage in low-power wind PMSG. The study intended to explore its use in low-voltage DC micro grids. This topology applied to low power generation allows for simplicity in its design and implementation, as the use of controlled switches is reduced: one controlled switch was presented instead of the usual application of six. The reduction in the number of controlled devices is efficient allowing for easy control and low cost.
From the simulation results, it has been proved that the selected topology presented the input current in the generator as an almost identical image to the generated voltage, obtaining low harmonic content compared with the topologies for low power described in the literature (which presents currents extremely deformed).
Regarding the power generated, there was also a significant improvement, since the low-frequency oscillations were reduced, which could also be seen in the presented simulation.
The results were satisfactory for extreme wind speed, 3 m/s and 12 m/s, with no restriction for its implementation for the whole operating speed range of the turbine-generator set. Furthermore, the analyzed converter was tested for variations in wind speed responding appropriately with the use of a MPPT control.
Thus, it was confirmed that the three-phase resonant buck converter can be widely used in applications in hybrid systems with PMSG based WECS presenting DC bus voltage with lower values than the peak input voltage for the minimum wind speed condition.
Acknowledgments
This work is being supported by FAPES/CNPq (PRONEX 48508675/2009).
Author Contributions
The authors have the same contribution to the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ahmed, N.A.; Miyatake, M. A stand-alone hybrid generation system combining solar photovoltaic and wind turbine with simple maximum power point tracking control. In Proceedings of the CES/IEEE 5th International Power Electronics and Motion Control Conference, Shanghai, China, 14–16 August 2006; pp. 1–7.
- Carrasco, J.M.; Franquelo, L.G.; Bialasiewicz, J.T.; Galvan, E.; Guisado, R.C.P.; Prats, M.A.M.; Leon, J.I.; Moreno-Alfonso, N. Power-electronic systems for the grid integration of renewable energy sources: A survey. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2006, 53, 1002–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ribeiro, L.A.S.; Saavedra, O.R.; de Matos, J.G.; Lima, S.L.; Bonan, G.; Martins, A.S. Design, control, an operation of a hybrid electrical generation system based on renewable energy sources. Rev. Eletrôn. Potênc. 2010, 15, 313–322. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, C.-T.; Shen, C.-L.; Su, J.-C. A power supply system with ZVS and current-doubler features for hybrid renewable energy conversion. Energies 2013, 6, 4859–4878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liserre, M.; Sauter, T.; Hung, J.Y. Future energy systems: Integrating renewable energy sources into the smart power grid through industrial electronics. IEEE Ind. Electron. Mag. 2010, 4, 18–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.S.; Azher Hussain, S.; Abido, M.A. Modeling and control of micro grid: An overview. J. Frankl. Inst. 2014, 351, 2822–2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Guerrero, J.M.; Chen, Z.; Blaabjerg, F. Distributed energy resources in grid interactive AC micro grids. In Proceedings of the 2nd IEEE International Symposium on Power Electronice for Distributed Generation Systems (PEDG), Hefei, China, 16–18 June 2010; pp. 806–812.
- Meegahapola, L.G.; Robinson, D.; Agalgaonkar, A.P.; Perera, S.; Ciufo, P. Micro grids of commercial buildings: Strategies to manage mode transfer from grid connected to islanded mode. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2014, 5, 1337–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justo, J.J.; Mwasilu, F.; Lee, J.; Jung, J.W. AC-micro grids versus DC-micro grids with distributed energy resources: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 24, 387–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocabert, J.; Luna, A.; Blaabjerg, F.; Rodríguez, P. Control of power converters in AC micro grids. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2012, 27, 4734–4749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, P.; Loh, P.C. A hybrid AC/DC micro grid and its coordination control. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2011, 2, 278–286. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.-H.; Choi, J.-Y.; Won, D.-J. Cooperative control between the distributed energy resources in AC/DC hybrid micro grid. In Proceedings of the Innovative Smart Grid Technologies Conference (ISGT), Washington, DC, USA, 19–22 February 2014; pp. 1–5.
- Dragicevic, T.; Vasquez, J.C.; Guerrero, J.M.; Skrlec, D. Advanced LVDC electrical power architectures and micro grids: A step towards a new generation of power distribution networks. IEEE Electr. Mag. 2014, 2, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, R. A hybrid micro grid with DC connection at back to back converters. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2014, 51, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, C.-Y.; Yeh, S.-N.; Hwang, J.-C. Design of high performance permanent-magnet synchronous wind generators. Energies 2014, 7, 7105–7124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, D.S., Jr.; Reis, M.M.; Silva, C.E.A.; Barreto, L.H.S.C.; Antunes, F.L.M.; Soares, B.L.A. Three-phase high-frequency semi controlled rectifier for PM WECS. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2010, 25, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Reis, F.S.; Tan, K.; Islam, S. Using PFC for harmonic mitigation in wind turbine energy conversion systems. In Proceedings of the 30th Annual Conference of IEEE Industrial Electronics Society (IECON 2004), Busan, Korea, 2–6 November 2004; pp. 3100–3105.
- Wang, Y.-F.; Yang, L.; Wang, C.-S.; Li, W.; Qie, W.; Tu, S.-J. High step-up 3-Phase rectifier with fly-back cells and switched capacitors for small-scaled wind generation systems. Energies 2015, 8, 2742–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Zhu, Y. The state of the art of wind energy conversion systems and technologies: A review. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 88, 332–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazmi, S.M.R.; Goto, H.; Guo, H.; Ichinokura, O. A novel algorithm for fast and efficient speed-sensorless maximum power point tracking in wind energy conversion systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 58, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, B.; Sourkounis, C. Influence of wind-energy-converter control methods on the output frequency components. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2009, 45, 2116–2122. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, D.S.; de Sousa, G.J.M.; Rangel, A.R.; Queiroz, D.L.; de Oliveira, E.F.; dos Santos, L.P.C.; Fontenele, L.F.A.; Bezerra, P.A.M. Low cost and high efficiency static converter for small wind systems. In Proceedings of the 35th Annual Conference of IEEE Industrial Electronics Society (IECON 2009), Porto, Portugal, 3–5 November 2009; pp. 601–608.
- Orlando, N.A.; Liserre, M.; Mastromauro, R.A.; Dell’Aquila, A. A survey of control issues in PMSG-based small wind-turbine systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 2013, 9, 1211–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vattuone, L.; Kouro, S.; Estay, G.; Wu, B. Open-end-winding PMSG for wind energy conversion system with dual boost NPC converter. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (ICIT), Cape Town, South Africa, 25–28 February 2013; pp. 1763–1768.
- Zhang, S.; Tseng, K.-J.; Vilathgamuwa, D.M.; Nguyen, T.D.; Wang, X.-Y. Design of a robust grid interface system for PMSG-based wind turbine generators. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 58, 316–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Ran, L.; Bumby, J.R. New constant electrical power soft-stalling control for small-scale VAWTs. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2010, 25, 1152–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carranza, O.; Figueres, E.; Garcerá, G.; González, L.G. A control circuit small wind turbines with low harmonic distortion and improved power factor. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Renewable Energies and Power Quality—ICREPQ, Valencia, Spain, 15–17 April 2009.
- Tonkoski, R.; Lopes, L.A.C.; dos Reis, F.S. A single-switch three-phase boost rectifier to reduce the generator losses in wind energy conversion systems. In Proceedings of the IEEE Electrical Power & Energy Conference, Montreal, QC, Canada, 22–23 October 2009; pp. 1–8.
- Reis, M.M.; Soares, B.; Barreto, L.H.S.C.; Freitas, E.; Silva, C.E.A.; Bascope, R.T.; Oliveira, D.S. A variable speed wind energy conversion system connected to the grid for small wind generator. In Proceedings of the 23rd Annual IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition, Austin, TX, USA, 24–28 February 2008; pp. 751–755.
- Juan, Y.-L. An integrated-controlled AC/DC interface for microscale wind power generation systems. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2011, 26, 1377–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.H.; Lin, Y.L. Current waveform distortion in power factor correction circuits employing discontinuous mode boost converter. In Proceedings of the 20th Annual IEEE Power Electronics Specialists Conference, Milwaukee, WI, USA, 26–29 June 1989; pp. 825–829.
- Faulstich, A.; Stinke, J.K.; Wittwer, F. Medium voltage converter for permanent magnet wind power generators up to 5 MW. In Proceedings of the European Conference Power Electronics Applications, Dresden, Germany, 11–14 September 2005; pp. 1–9.
- Freitas, T.R.S. Alternativas de Topologias Retificadoras para Geração Eólica com Geradores Síncronos a Ímã Permanente de Baixa Potência. Doctoral Thesis, Qualification Exam, Federal University of Espírito Santo, Espírito Santo, Brazil, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, Y.; Erickson, R.W. New Single-Switch Three-Phase High-Power-Factor Rectifiers Using Multiresonant Zero-current Switching. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 1998, 13, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, E.H.; Erickson, R.W. A single transistor three-phase resonant switch for high quality rectification. In Proceedings of the 23rd Annual IEEE Power Electronics Specialists Conference, Toledo, Spain, 29 June–3 July 1992; pp. 1341–1351.
- Jang, Y.; Jovanovic, M.M. Design considerations and performance evaluation of a 6-kW, single-switch, three-phase, high-power-factor, multi-resonant, zero-current-switching buck rectifier. In Proceedings of the 19th International IEEE Telecommunications Energy Conference, Melbourne, Australia, 22–23 October 1997; pp. 715–722.
- Kazmi, S.M.R.; Goto, H.; Guo, H.-J.; Ichinokura, O. Review and critical analysis of the research papers published till date on maximum power point tracking in wind energy conversion system. In Proceedings of the IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Atlanta, GA, USA, 12–16 September 2010; pp. 4075–4082.
- Abdullah, M.A.; Yatim, A.H.M.; Tan, C.W. A study of maximum power point tracking algorithms for wind energy system. In Proceedings of the IEEE First Conference on Clean Energy and Technology (CET), Kuala Lumpur, Malasian, 27–29 June 2011; pp. 321–326.
- Dixit, A.; Singh, P.; Mishra, N.; Singh, D. Maximum power tracking with voltage stability studies in wind energy conversion system: A review. In Proceedings of the IET Chennai 3rd International on Sustainable Energy and Intelligent Systems, Tiruchengode, India, 27–29 December 2012; pp. 1–9.
- Simeonov, G. Resonant Boost Converter for Distributed Maximum Power Point Tracking in Grid-Connected Photovoltaic Systems. Master Thesis, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada, 2010. [Google Scholar]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
