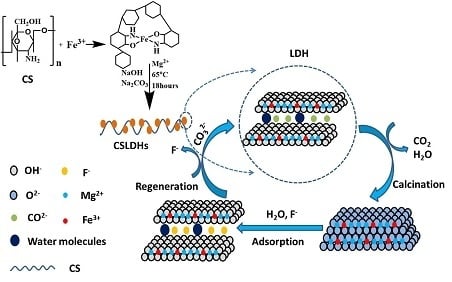
Calcined Chitosan-Supported Layered Double Hydroxides: An Efficient and Recyclable Adsorbent for the Removal of Fluoride from an Aqueous Solution
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of the Adsorbent
2.1.1. Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscope (FEI-SEM) Analysis
2.1.2. BET Analysis
2.1.3. FT-IR Analysis
2.1.4. XRD Analysis
2.2. Evaluation of Fluoride Removal Efficiency by the Prepared LDHs
2.2.1. Effect of Calcinations on F− Removal
2.2.2. CSLDO400 Dosage
2.2.3. Effect of pH
2.2.4. Effect of Co-Anions
2.3. Adsorption Theory Discussion
2.3.1. Adsorption Kinetics
2.3.2. Adsorption Isotherm
2.3.3. Adsorption Thermodynamics
2.3.4. Adsorption Mechanism
2.4. Regeneration and Reuse
2.5. Comparison of Fluoride with Other Adsorbents
3. Experimental
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis of Calcined Chitosan Support Layered Double Hydroxides (CSLDO)
3.3. Sample Characterization
3.4. Adsorption Experiments
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhatnagar, A.; Kumar, E.; Sillanpää, M. Fluoride removal from water by adsorption—A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 171, 811–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagtap, S.; Yenkie, M.K.; Labhsetwar, N.; Rayalu, S. Fluoride in drinking water and defluoridation of water. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 2454–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO, G. Guidelines for drinking-water quality. World Health Organ. 2011, 216, 303–304. [Google Scholar]
- Viswanathan, N.; Meenakshi, S. Selective fluoride adsorption by a hydrotalcite/chitosan composite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 48, 607–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batistella, L.; Venquiaruto, L.D.; Luccio, M.D.; Oliveira, J.V.; Pergher, S.B.; Mazutti, M.A.; Dallago, R. Evaluation of acid activation under the adsorption capacity of double layered hydroxides of Mg–Al–CO3 type for fluoride removal from aqueous medium. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 6871–6876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontié, M.; Dach, H.; Leparc, J.; Hafsi, M.; Lhassani, A. Novel approach combining physico-chemical characterizations and mass transfer modelling of nanofiltration and low pressure reverse osmosis membranes for brackish water desalination intensification. Desalination 2008, 221, 174–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, M.; Anand, S.; Mishra, B.K.; Giles, D.E.; Singh, P. Review of fluoride removal from drinking water. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 91, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, I.; Iwasaki, S.; Tokimoto, T.; Kawasaki, N.; Nakamura, T.; Tanada, S. Adsorption of fluoride ions onto carbonaceous materials. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 275, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çengeloğlu, Y.; Kır, E.; Ersöz, M. Removal of fluoride from aqueous solution by using red mud. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2002, 28, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorai, S.; Pant, K. Investigations on the column performance of fluoride adsorption by activated alumina in a fixed-bed. Chem. Eng. J. 2004, 98, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.; Mayadevi, S. Adsorption of fluoride ions by Zn–Al layered double hydroxides. Appl. Clay Sci. 2008, 40, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Li, Q.; Xiao, H.; Lu, H.; Zhou, Y. Synthesis of Li–Al layered double hydroxides (LDHs) for efficient fluoride removal. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 11490–11498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Peng, J.; Xiao, H. Adsorption behavior of hydrotalcite-like modified bentonite for Pb2+, Cu2+ and methyl orange removal from water. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 420, 773–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asiabi, H.; Yamini, Y.; Shamsayei, M. Highly selective and efficient removal of arsenic (V), chromium (VI) and selenium (VI) oxyanions by layered double hydroxide intercalated with zwitterionic glycine. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 339, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eshaq, G.; Rabie, A.M.; Bakr, A.A. Cr (VI) adsorption from aqueous solutions onto Mg–Zn–Al LDH and its corresponding oxide. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 20377–20387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, F.; Kawasaki, N. Adsorption of As (III) from Aqueous Solutions by Novel Fe–Mg Type Hydrotalcite. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2015, 63, 1040–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, S.; Mayadevi, S. Cellulose supported layered double hydroxides for the adsorption of fluoride from aqueous solution. Chemosphere 2008, 72, 995–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valente, J.S.; Hernandez-Cortez, J.; Cantu, M.S.; Ferrat, G.; López-Salinas, E. Calcined layered double hydroxides Mg–Me–Al (Me: Cu, Fe, Ni, Zn) as bifunctional catalysts. Catal. Today 2010, 150, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichle, W.T. Catalytic reactions by thermally activated, synthetic, anionic clay minerals. J. Catal. 1985, 94, 547–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.; He, J.; Wei, M.; Evans, D.G.; Zhou, Z. Treatment of high fluoride concentration water by MgAl-CO3 layered double hydroxides: Kinetic and equilibrium studies. Water Res. 2007, 41, 1534–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lung, Y.F.; Syu, F.F.; Lin, M.C.; Uan, Y. Converting waste magnesium scrap into anion-sorptionable nanomaterials: Synthesis and characterization of an Mg–Al–Cl hydrotalcite-like compound by hydrolysis and chemical conversion treatment in aqueous chloride solutions. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 57646–57657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.N.R. A review of chitin and chitosan applications. React. Funct. Polym. 2000, 46, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Lu, Y.; Luo, G. Ca (II) imprinted chitosan microspheres: An effective and green adsorbent for the removal of Cu (II), Cd (II) and Pb (II) from aqueous solutions. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 244, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Shen, Y.; Wen, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, W. Fast and highly efficient removal of dyes under alkaline conditions using magnetic chitosan-Fe (III) hydrogel. Water Res. 2011, 45, 5200–5210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Li, D.; Hu, C.; Wang, E.; Zou, Y.; Ding, H.; Feng, S. Preparation and photocatalytic behavior of Zn/Al/W (Mn) mixed oxides via polyoxometalates intercalated layered double hydroxides. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2002, 56, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velu, S.; Suzuki, K.; Okazaki, M.; Osaki, T.; Tomura, S.; Ohashi, F. Synthesis of new Sn-incorporated layered double hydroxides and their thermal evolution to mixed oxides. Chem. Mater. 1999, 11, 2163–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sing, K.S. Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity (Recommendations 1984). Pure Appl. Chem. 1985, 57, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, J.; Patra, B.S.; Baliarsingh, N.; Parida, K.M. Calcined Mg–Fe–CO3 LDH as an adsorbent for the removal of selenite. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 316, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, W.Q.; Chen, Y.T.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, W. Performance and mechanism of Mg-Ca-Fe hydrotalcite- like compounds for fluoride removal from aqueous solution. J. Fluor. Chem. 2017, 200, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.S.; Wu, W.H.; Li, F.H.; Yu, X.X.; Fu, J.J.; Jia, L.Y. Enhanced adsorption of bromate from aqueous solutions on orderedmesoporous Mg-Al layered double hydroxides (LDHs). J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 334, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, D.J.; Yu, X.L.; Tong, S.R.; Ge, M.F.; Zuo, J.C.; Gao, C.Y.; Song, W.G. Performance and mechanism of Mg/Fe layered double hydroxides for fluoride and arsenate removal from aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 228, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhang, L.H.; Evans, D.G.; Forano, C.; Duan, X. Structure and thermal evolution of Mg-Al layered double hydroxide containing interlayer organic glyphosate anions. Thermochim. Acta 2004, 424, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.; He, J.; Wei, M. Factors influencing the removal of fluoride from aqueous solution by calcined Mg–Al–CO3 layered double hydroxides. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 133, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Chen, S.; Fan, X.; Quan, X.; Tan, F.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, J. Adsorption of ciprofloxacin, bisphenol and 2-chlorophenol on electrospun carbon nanofibers: In comparison with powder activated carbon. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 447, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Zheng, F.; Xue, X.; Lu, Y. Investigation into adsorption mechanisms of sulfonamides onto porous adsorbents. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 362, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subbaiah, M.V.; Kim, D.S. Adsorption of methyl orange from aqueous solution by aminated pumpkin seed powder: Kinetics, isotherms, and thermodynamic studies. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 128, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalvand, A.; Nabizadeh, R.; Ganjali, M.R.; Khoobi, M.; Nazmara, S.; Mahvi, A.H. Modeling of reactive blue 19 azo dye removal from colored textile wastewater using l-arginine-functionalized Fe3O4 nanoparticles: Optimization, reusability, kinetic and equilibrium studies. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 404, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, A.; Xing, J.; Li, Z.; Li, Q. Cr-doped ZnO nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization, adsorption property, and recyclability. ACS Appl. Mater. Interface 2015, 7, 27449–27457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, K.; Saha, S.K.; Ghosh, U.C. Adsorption of fluoride from aqueous solution by a synthetic iron (III)−aluminum (III) mixed oxide. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2007, 46, 5346–5356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.; Patel, R. Evaluation of removal efficiency of fluoride from aqueous solution using quick lime. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 143, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, C.; Sugiura, N.; Li, M.; Chen, R. Fluoride removal from water by granular ceramic adsorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 348, 579–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, C.; Li, M.; Zhu, D.; Chen, R.; Sugiura, N. An excellent fluoride sorption behavior of ceramic adsorbent. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 183, 460–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]












| Materials | SBET a/m2·g−1 | Smic b/m2·g−1 | Vmic c/cm3·g−1 | Vmeso d/cm3·g−1 | Vt e/cm3·g−1 | Dp f/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSLDHs | 16.38 | 2.03 | 0.0003 | 0.0557 | 0.056 | 13.28 |
| LDO400 | 80.73 | 7.59 | 0.0056 | 0.3174 | 0.323 | 15.83 |
| CSLDO300 | 47.55 | 4.05 | 0.0012 | 0.1538 | 0.155 | 12.01 |
| CSLDO400 | 116.98 | 4.37 | 0.0014 | 0.4106 | 0.412 | 8.84 |
| CSLDO500 | 94.35 | 2.21 | 0.0005 | 0.3175 | 0.318 | 10.99 |
| qe(exp) (mg·g−1) | Pseudo-First-Order Kinetic Model | Pseudo-Second-Order Kinetic Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1 (min−1) | qe1(cal) (mg·g−1) | R2 | k2 (×10−4) (g·mg−1·min−1) | qe2(cal) (mg·g−1) | R2 | |
| 9.58 | 0.02 | 10.47 | 0.9514 | 9.99 | 12.97 | 0.9483 |
| T (K) | Langmuir Model | Freundlich Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| b (L·mg−1) | qmax (mg·g−1) | R2 | n | Kf | R2 | |
| 298 | 0.1457 | 27.56 | 0.9930 | 2.740 | 5.6423 | 0.9724 |
| 308 | 0.1689 | 31.88 | 0.9909 | 2.797 | 6.9023 | 0.9735 |
| 318 | 0.1695 | 35.77 | 0.9842 | 2.7372 | 7.5334 | 0.9756 |
| T (K) | ∆S (J·mol−1·K−1) | ∆H (kJ·mol−1) | ∆G (kJ·mol−1) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 298 | 60.52 | 5.706 | −12.33 | 0.9576 |
| 308 | - | - | −12.93 | - |
| 318 | - | - | −13.54 | - |
| Adsorbents | qmax (mg·g−1) | pH | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| CSLDO400 | 27.56 | 5~9 | Present study |
| Iron–aluminum mixed oxide | 17.73 | 5.5~5.7 | [39] |
| Quick lime | 16.67 | - | [40] |
| CSLDH-75 | 13.8 | - | [13] |
| Granular ceramic | 12.12 | 5~8 | [41] |
| Ceramic adsorbent | 2.16 | 5.8 ± 0.2 | [42] |
| Samples | NO3− (mg·L−1) | SO42− (mg·L−1) | HCO3− (mg·L−1) | PO43− (mg·L−1) | Cl− (mg·L−1) | CO32− (mg·L−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lake water | 110.97 | 62.65 | 312.78 | detection limit | 84.41 | 35.62 |
| Tap water | 5.87 | 53.71 | 225.37 | detection limit | 68.16 | 10.23 |
| Groundwater | 15.49 | 38.59 | 301.74 | detection limit | 71.36 | 27.38 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, H.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Q.; Wang, D.; Zhang, W.; Yang, X. Calcined Chitosan-Supported Layered Double Hydroxides: An Efficient and Recyclable Adsorbent for the Removal of Fluoride from an Aqueous Solution. Materials 2017, 10, 1320. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10111320
Wu H, Zhang H, Yang Q, Wang D, Zhang W, Yang X. Calcined Chitosan-Supported Layered Double Hydroxides: An Efficient and Recyclable Adsorbent for the Removal of Fluoride from an Aqueous Solution. Materials. 2017; 10(11):1320. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10111320
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Hanjun, Huali Zhang, Qingxue Yang, Dongsheng Wang, Weijun Zhang, and Xiaofang Yang. 2017. "Calcined Chitosan-Supported Layered Double Hydroxides: An Efficient and Recyclable Adsorbent for the Removal of Fluoride from an Aqueous Solution" Materials 10, no. 11: 1320. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10111320
APA StyleWu, H., Zhang, H., Yang, Q., Wang, D., Zhang, W., & Yang, X. (2017). Calcined Chitosan-Supported Layered Double Hydroxides: An Efficient and Recyclable Adsorbent for the Removal of Fluoride from an Aqueous Solution. Materials, 10(11), 1320. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10111320