Dust Loading Performance of a Novel Submicro-Fiber Composite Filter Medium for Engine
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
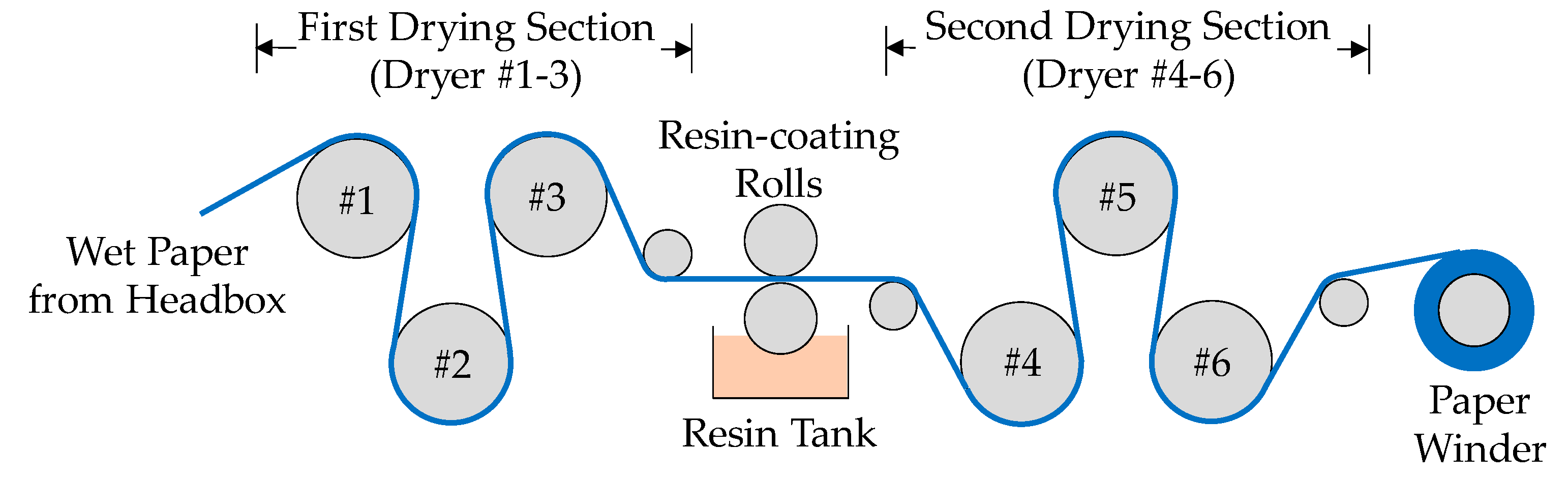
2.1. Preparation of Wet-laid Submicro-Fiber Composite Filter Medium
2.2. Loading Performance Evaluation in Laboratory—Filter Media Specifications
2.3. Loading Test Setup in Laboratory
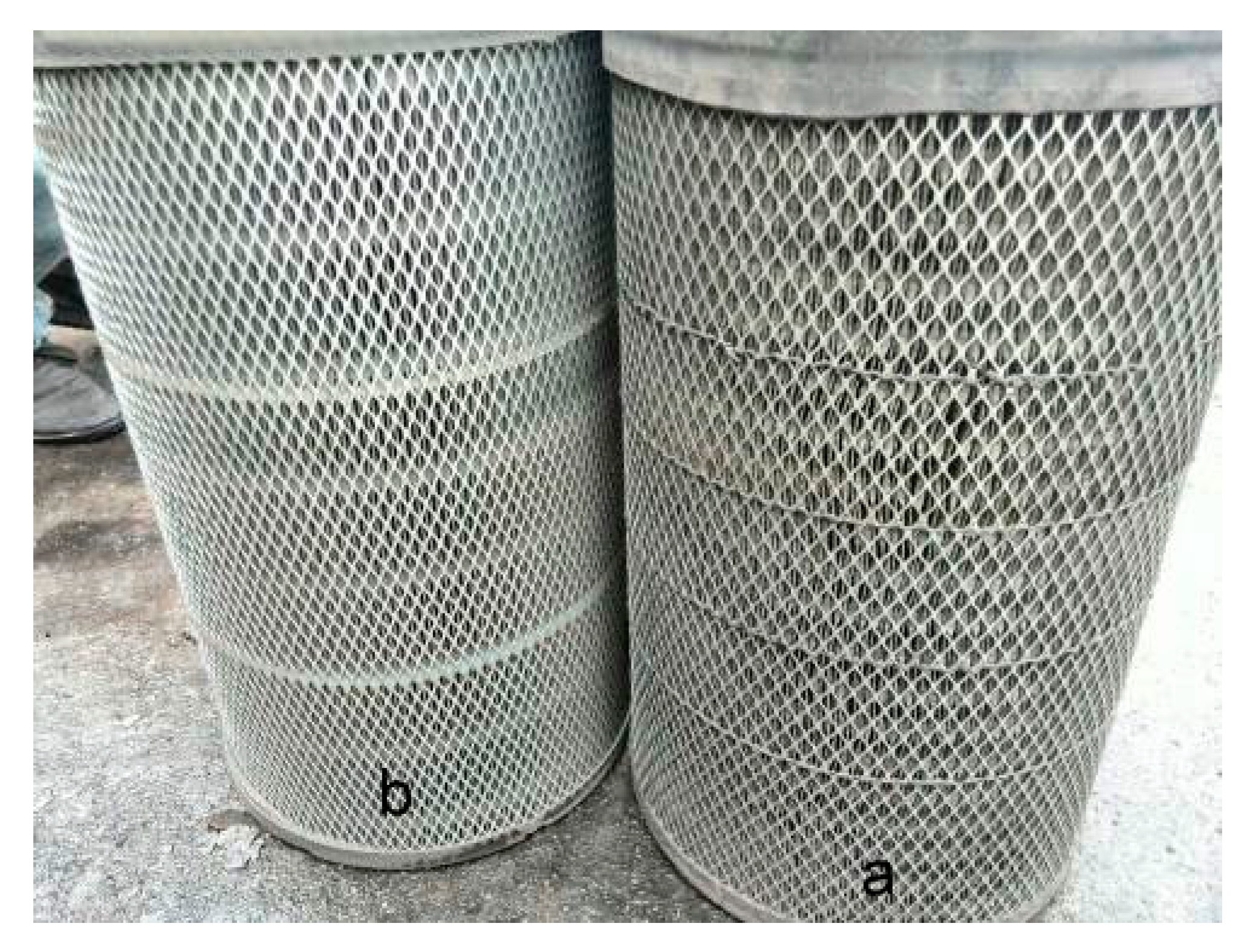
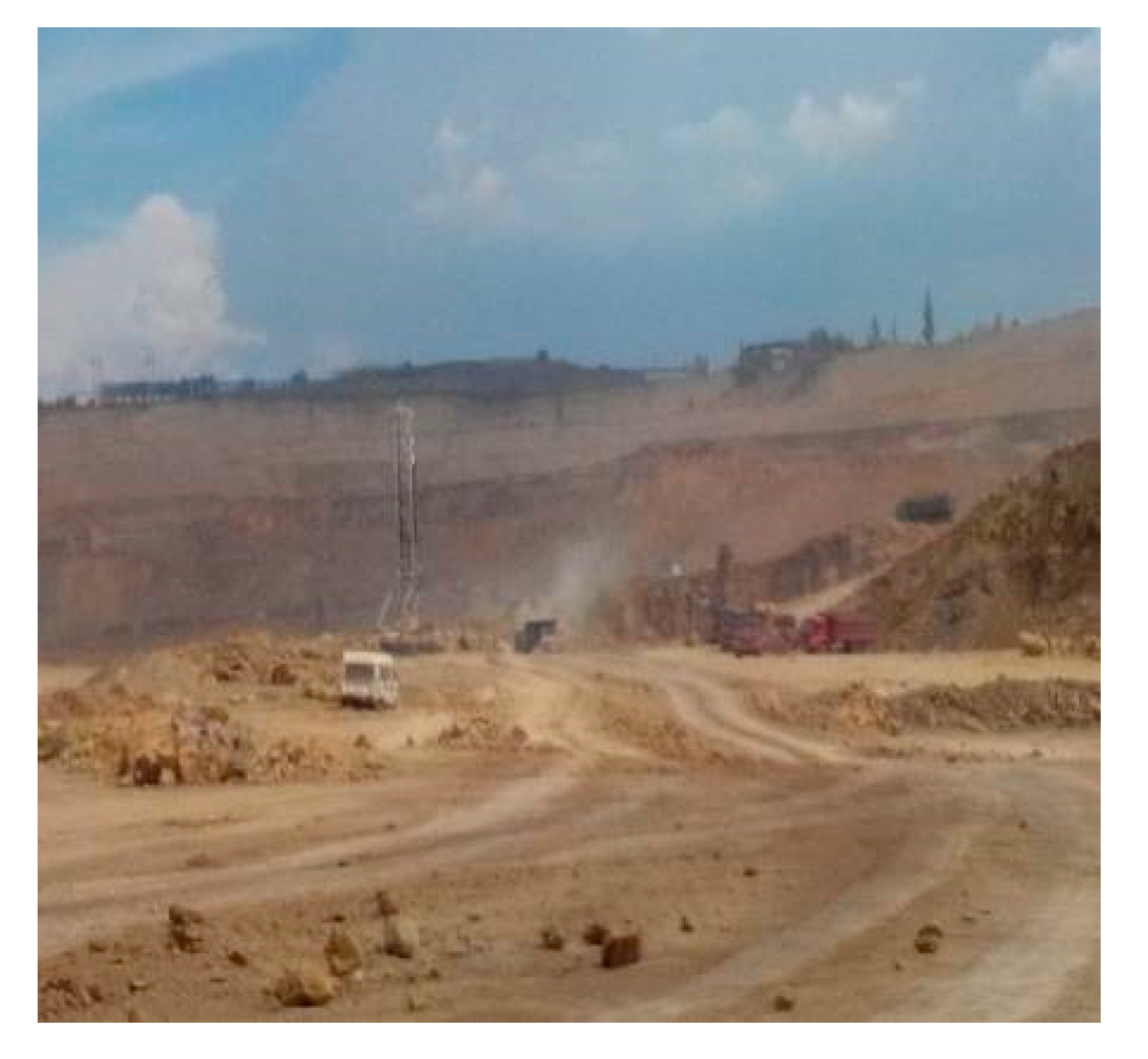
2.4. Loading Performance Evaluation in Field Test
3. Results and Discussion
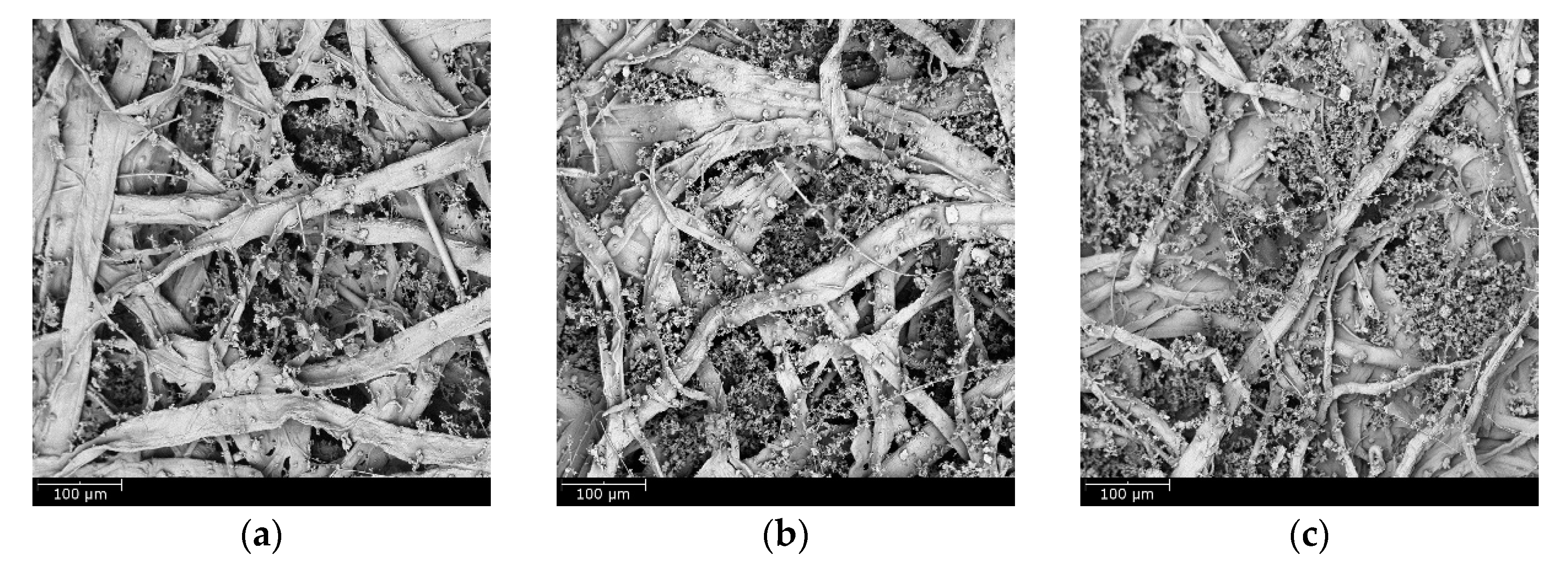
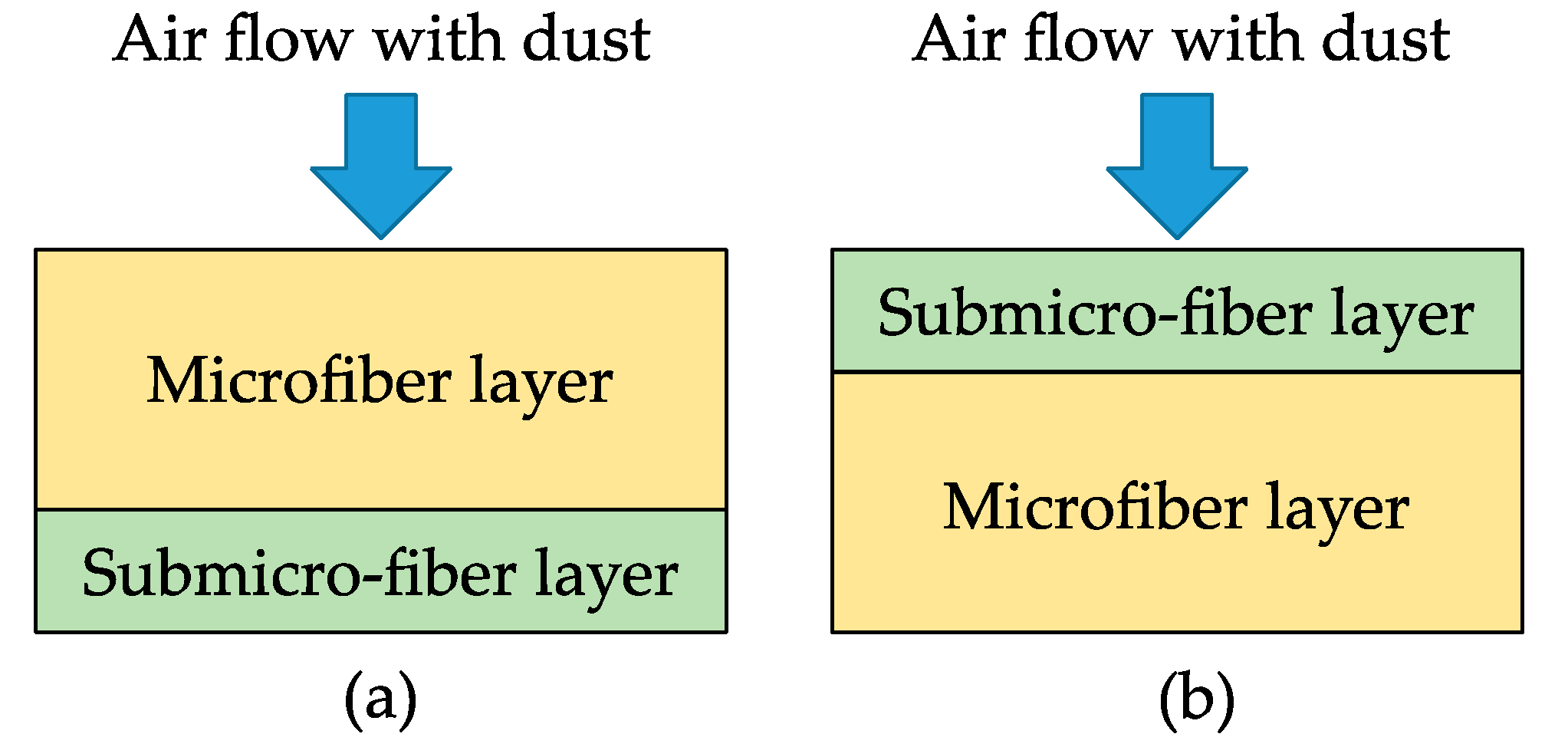
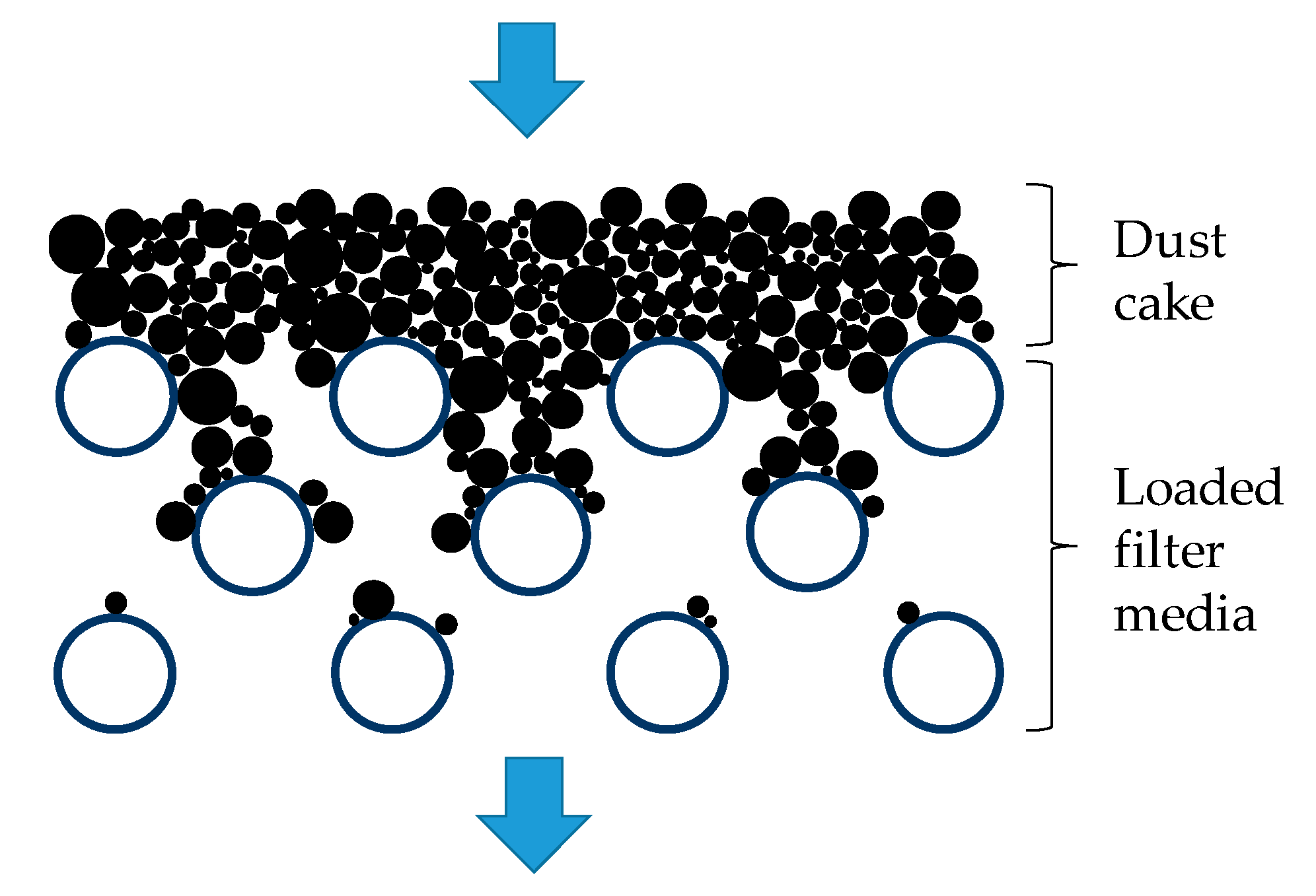
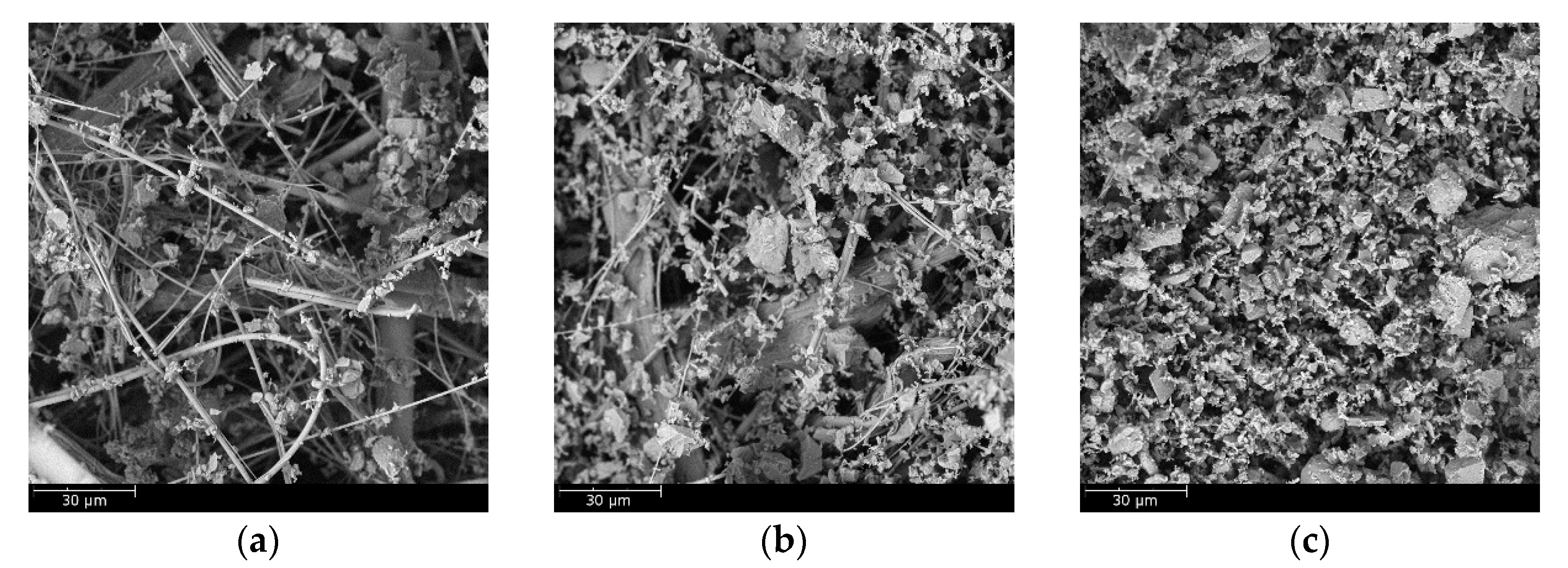
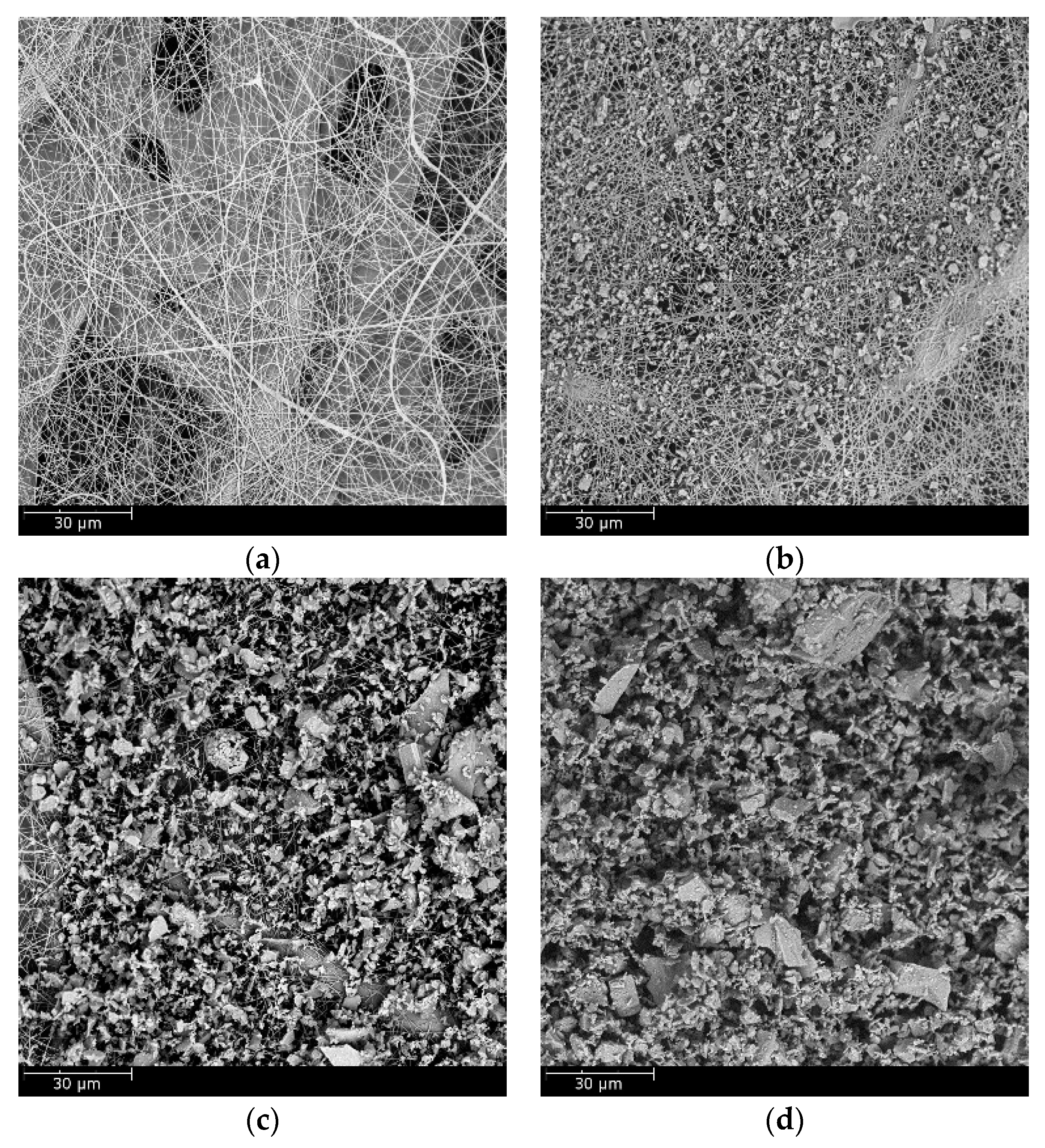
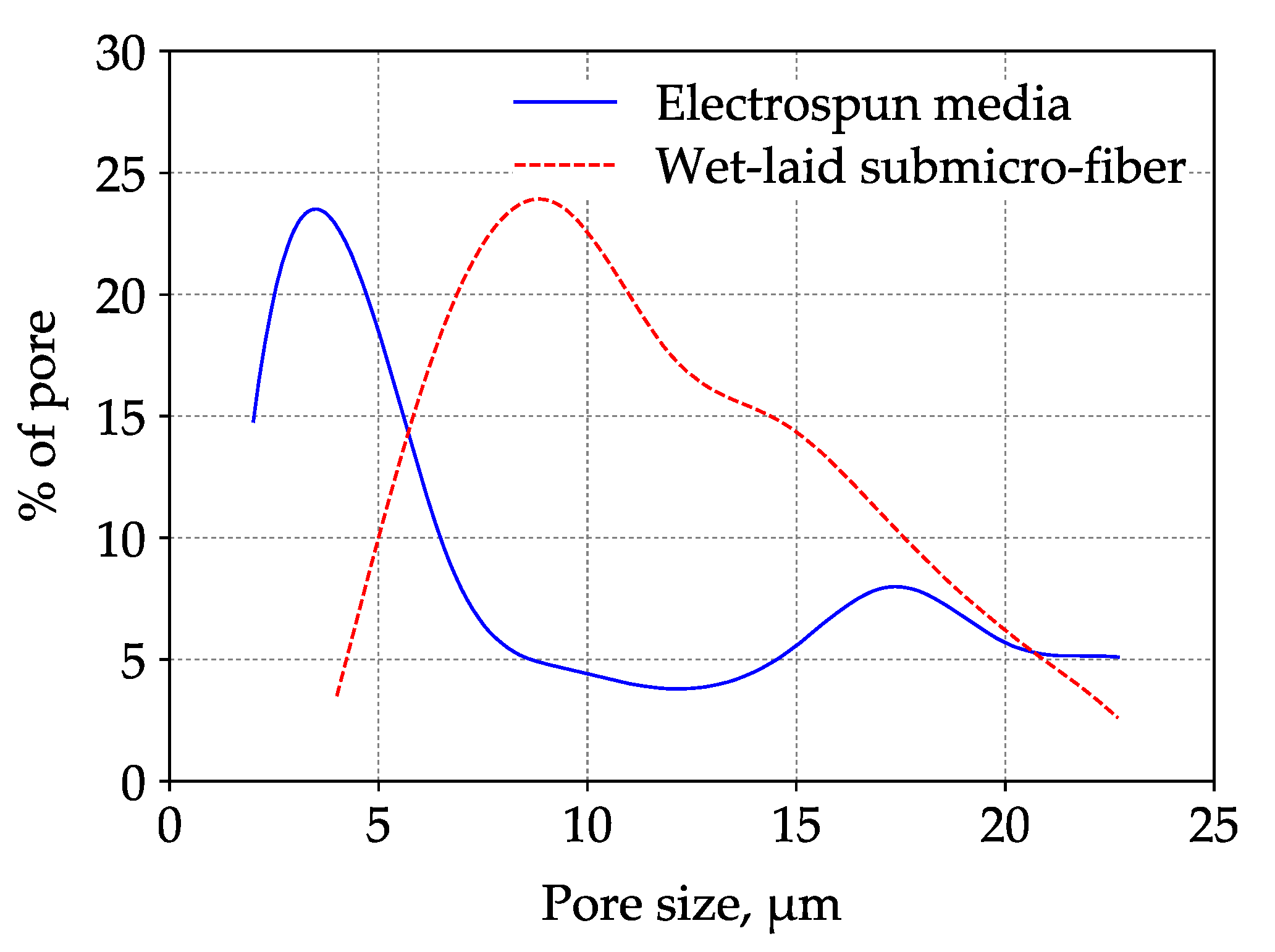
3.1. Properties and Structural Analysis of Wet-Laid Submicro-Fiber Medium
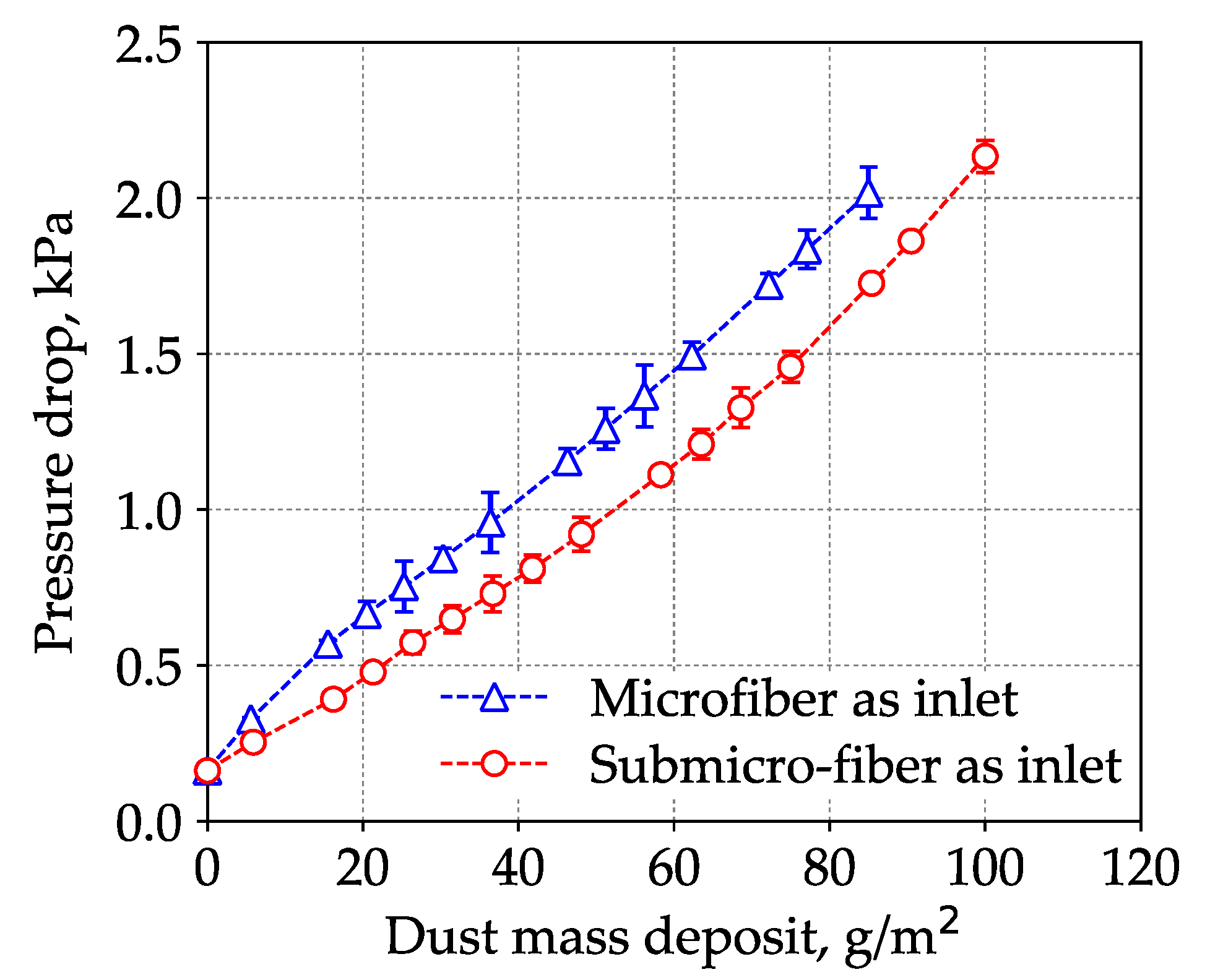
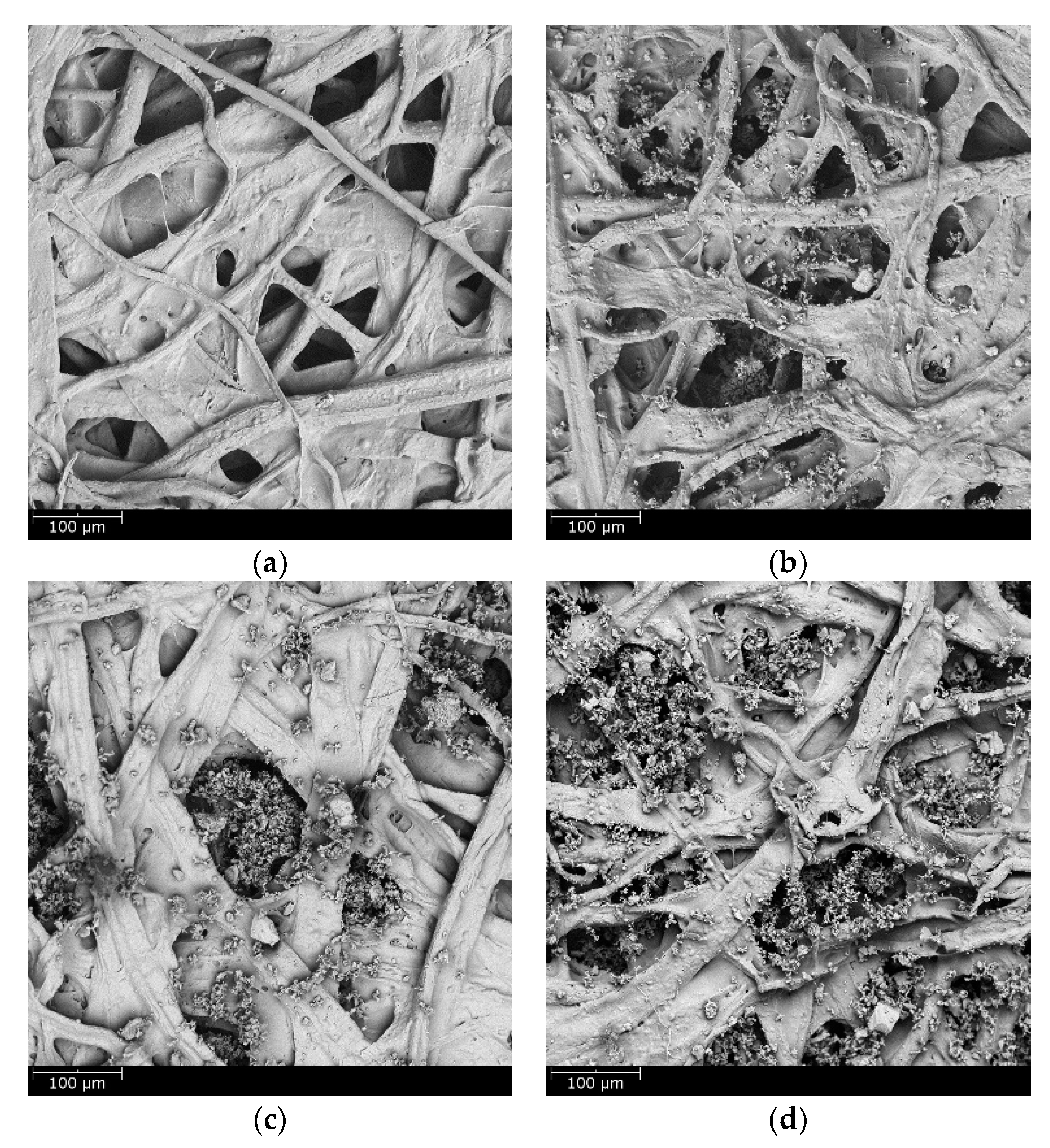
3.2. Loading Performance of Wet-laid Submicro-Fiber Medium in Laboratory
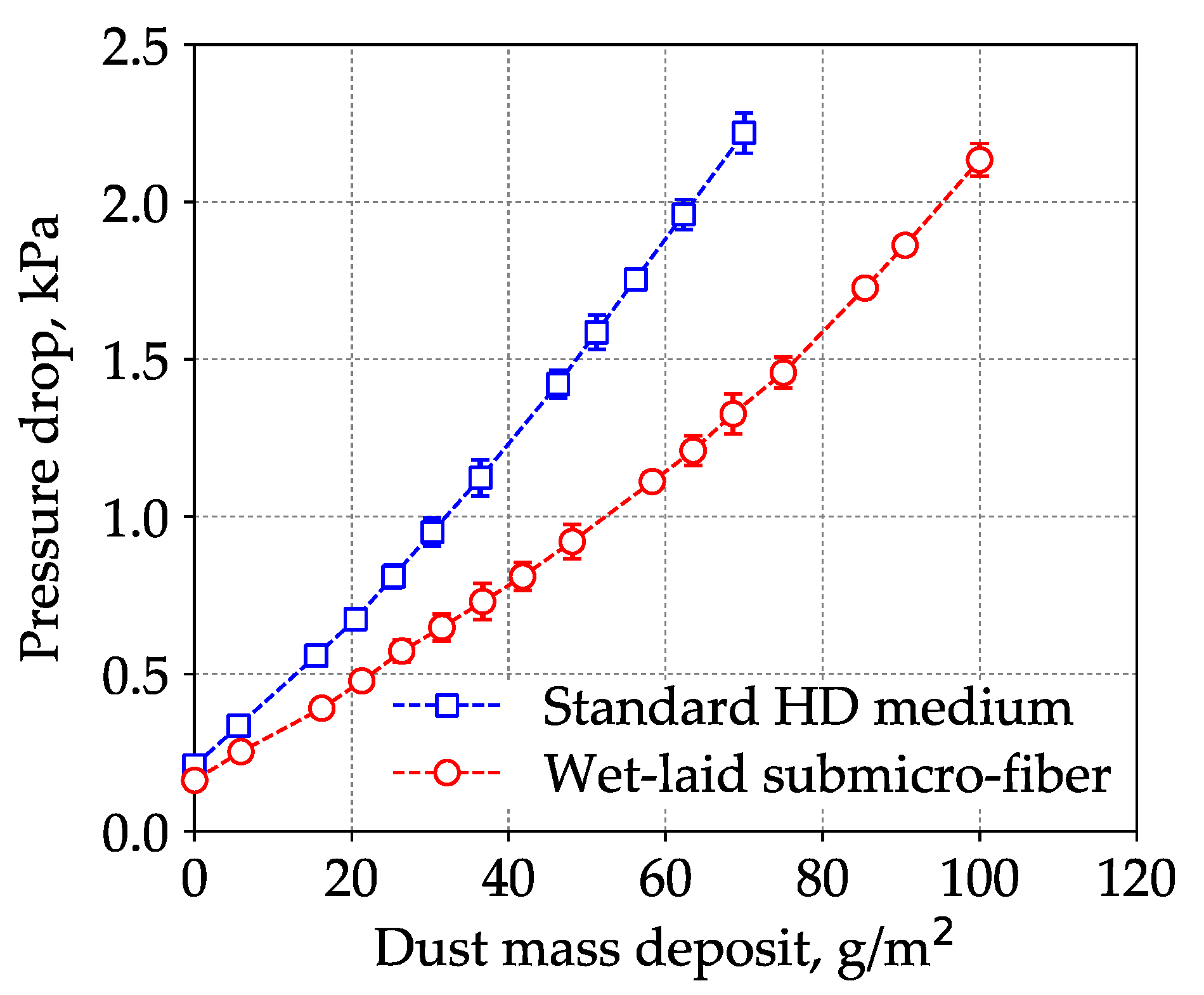
3.3. Loading Performance Comparison Between Wet-laid Submicro-Fiber Medium and Standard Heavy-duty Medium in the Laboratory and Field
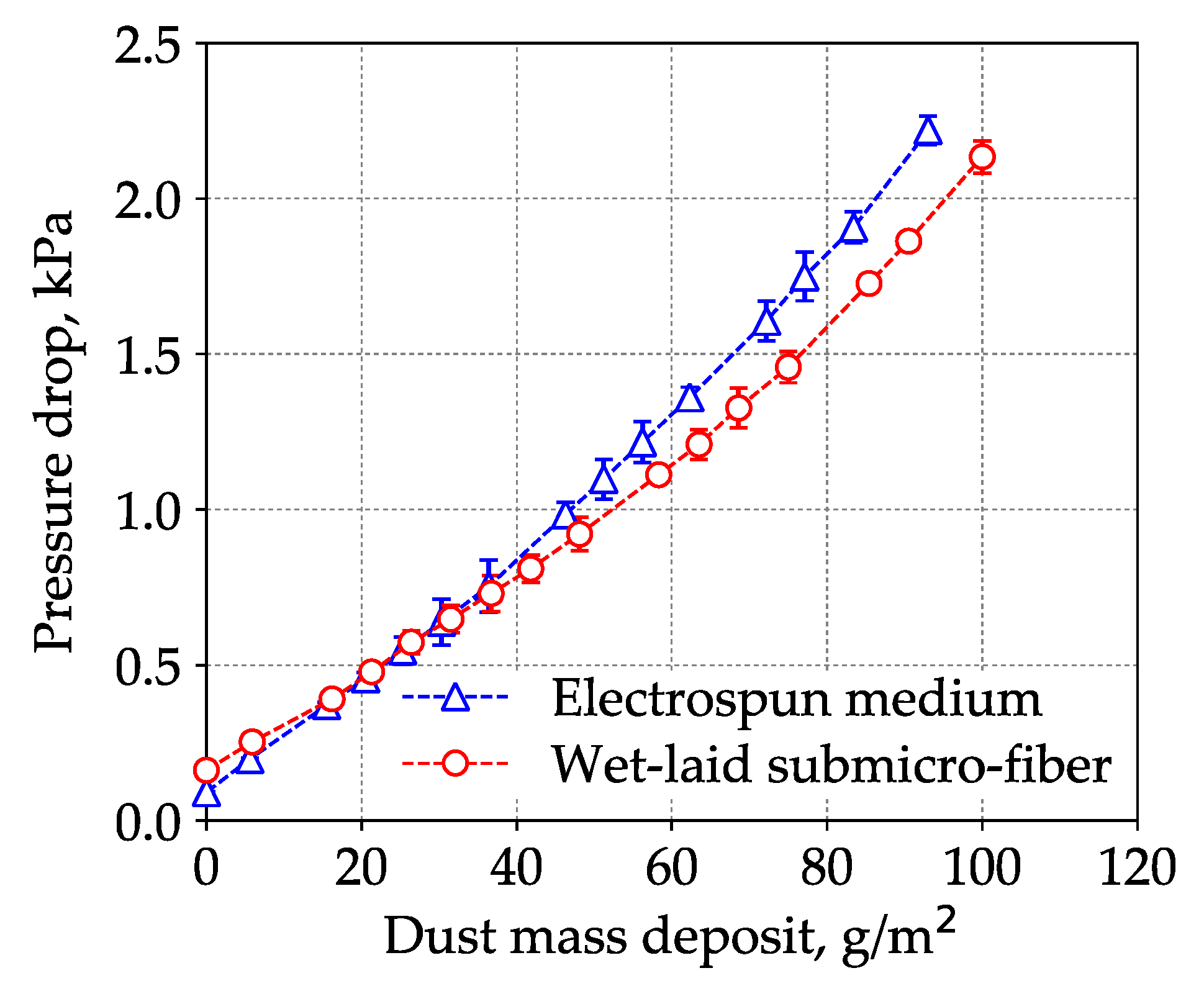
3.4. Loading Performance Comparison Between Wet-Laid Submicro-Fiber Medium and Electrospun Composite Medium in Laboratory
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chun, Y.; Kim, J.; Choi, J.C.; Boo, K.O.; Oh, S.N.; Lee, M. Characteristic number size distribution of aerosol during Asian dust period in Korea. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 2715–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csavina, J.; Field, J.; Taylor, M.P.; Gao, S.; Landázuri, A.; Betterton, E.A.; Eduardo, S.A.A. Review on the importance of metals and metalloids in atmospheric dust and aerosol from mining operations. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 433, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakshminarayanan, P.A.; Nayak, N.S. Wear in the heavy duty engine. In Critical Component Wear in Heavy Duty Engines, 1st ed.; John Wiley & Sons (Asia) Pte Ltd.: Singapore, 2011; pp. 1–11. ISBN 9780470828823. [Google Scholar]
- Sherburn, P.E. Air cleaner design—Present and future. SAE Tech. Pap. 1969, 690007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treuhaft, M.B. The use of radioactive tracer technology to measure engine ring wear in response to dust ingestion. SAE Tech. Pap. 1993, 930019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaroszczyk, T.; Petrik, S.; Donahue, K. Recent development in heavy duty engine air filtration and the role of nanofiber filter media. J. Kones 2009, 16, 207–216. [Google Scholar]
- Schilling, A. Automobile Engine Lubrication; Scientific Publications (G.B.) Limited: Broseley, UK, 1972; ISBN 9780900645044. [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox, M.; Baldwin, R.; Garcia-Hernandez, A.; Brun, K. Guideline for Gas Turbine Inlet Air Filtration Systems; Gas Machinery Research Council: Dallas, TX, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Calculation Method for the Energy Use Related to Air Filters in General Ventilation Systems, Eurovent 4/21. Available online: https://eurovent.eu/?q=content/eurovent-421-2014-calculation-method-energy-use-related-air-filters-general-ventilation (accessed on 15 October 2018).
- Long, J.; Tang, M.; Liang, Y.; Hu, J. Preparation of fibrillated cellulose nanofiber from lyocell fiber and its application in air filtration. Materials 2018, 11, 1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podgórski, A.; Bałazy, A.; Gradoń, L. Application of nanofibers to improve the filtration efficiency of the most penetrating aerosol particles in fibrous filters. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2006, 61, 6804–6815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Welch, J.; Park, H.; Wu, C.Y.; Sigmund, W.; Marijnissen, J.C.M. Improvement in nanofiber filtration by multiple thin layers of nanofiber mats. J. Aerosol Sci. 2010, 41, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.H.; Leung, W.F. Filtration of nano-aerosol using nanofiber filter under low peclet number and transitional flow regime. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 79, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Otani, Y. Removal of nanoparticles from gas streams by fibrous filters: A review. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Zhang, X.; Batchelor, W. Cellulose nanofibre aerogel filter with tuneable pore structure for oil/water separation and recovery. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 21435–21438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Y.; Fu, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhu, J.; Yu, J.; Sun, G.; Ding, B. Superelastic and superhydrophobic nanofiber-assembled cellular aerogels for effective separation of oil/water emulsions. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 3791–3799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esfahani, H.; Jose, R.; Ramakrishna, S. Electrospun Ceramic Nanofiber Mats Today: Synthesis, Properties, and Applications. Materials 2017, 10, 1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, W.; Fang, G.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Tang, Y. Using electrospinning-based carbon nanofiber webs for methanol crossover control in passive direct methanol fuel cells. Materials 2018, 11, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Yang, B.J.; Bae, G.N.; Jung, J.H. Herbal extract incorporated nanofiber fabricated by an electrospinning technique and its application to antimicrobial air filtration. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2015, 7, 25313–25320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.Y.; Chang, F.C. Development of electrospun lignin-based fibrous materials for filtration applications. BioResources 2016, 11, 2202–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barhate, R.S.; Ramakrishna, S. Nanofibrous filtering media: Filtration problems and solutions from tiny materials. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 296, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.; Gernot, K. Effect of filtration velocity and dust concentration on cake formation and filter operation in a pilot scale jet pulsed bag filter. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 144, 677–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, H.; Yin, X.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Anti-deformed polyacrylonitrile/polysulfone composite membrane with binary structures for effective air filtration. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 8086–8095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Yang, Y.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; El-Newehy, M.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Ultra-light 3D nanofibre-nets binary structured nylon 6–polyacrylonitrile membranes for efficient filtration of fine particulate matter. J. Mater. Chem. 2015, A3, 23946–23954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Si, Y.; Wang, N.; Sun, G.; El-Newehy, M.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; Ding, B. Multilevel structured polyacrylonitrile/silica nanofibrous membranes for high-performance air filtration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 126, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, W.W.F.; Hau, C.W.Y.; Choy, H.F. Microfiber-nanofiber composite filter for high-efficiency and low pressure drop under nano-aerosol loading. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 206, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langner, M.; Greiner, A. Wet-laid meets electrospinning: Nonwovens for filtration applications from short electrospun polymer nanofiber dispersions. Macromol. Rapid. Commun. 2016, 37, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galka, N.; Saxena, A. High efficiency air filtration: The growing impact of membranes. Filtr. Sep. 2009, 46, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Tang, M.; Yu, T.; Liang, Y.; Hu, J. Filtration performance of dual-layer filter paper with fibrillated nanofibers. BioResources 2016, 11, 9506–9519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Hu, J.; Liang, Y.; Pui, D.Y.H. Pressure drop, penetration and quality factor of filter paper containing nanofibers. Text. Res. J. 2017, 87, 498–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Liang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, J. Self-cleaning air filtering material and preparation method therefor. U.S. Patent 9,771,904, 26 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bernada, P. Experimental study and modelling of binder migration during drying of a paper coating. Dry. Technol. 1996, 14, 1897–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grammage of Paper and Paperboard (Weight per Unit Area); TAPPI T410 om-13; TAPPI Press: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2013.
- Thickness (Caliper of Paper, Paperboard, and Combined Board); TAPPI T411 om-15; TAPPI Press: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2015.
- Standard Test Method for Air Permeability of Textile Fabrics; ASTM D737-18; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2018.
- ISO. Inlet Air Cleaning Equipment for Internal Combustion Engines and Compressors—Performance Testing; ISO 5011; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014; Available online: https://www.iso.org/obp/ui/#iso:std:iso:5011:ed-3:v1:en (accessed on 15 October 2018).
- Bending Resistance (Stiffness) of Paper and Paperboard (Taber-Type Tester in Basic Configuration); TAPPI T489 om-15; TAPPI Press: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2015.
- ISO. Road Vehicles—Test Contaminants for Filter Evaluation—Part 1: Arizona Test Dust; ISO 12103-1; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016; Available online: https://www.iso.org/obp/ui/#iso:std:iso:12103:-1:ed-2:v1:en (accessed on 15 October 2018).
- Sun, Z.; Tang, M.; Song, Q.; Yu, J.; Liang, Y.; Hu, J.; Wang, J. Filtration performance of air filter paper containing kapok fibers against oil aerosols. Cellulose 2018, 4, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, W.W.F.; Hung, C.H. Investigation on pressure drop evolution of fibrous filter operating in aerodynamic slip regime under continuous loading of submicron aerosols. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2008, 63, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, W.W.F.; Hung, C.H.; Yuen, P.T. Experimental investigation on continuous filtration of sub-micron aerosol by filter composed of dual-layers including a nanofiber layer. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 1174–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Chen, S.C.; Chang, D.Q.; Xie, X.; Sun, J.; Pui, D.Y.H. Filtration efficiency and loading characteristics of PM2.5 through composite filter media consisting of commercial HVAC electret media and nanofiber layer. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 198, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, Y.; Chen, D.R.; Pui, D.Y.H. Effects of particle polydispersity and shape factor during dust cake loading on air filters. Powder Technol. 1998, 98, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, Y.; Chen, D.R.; Pui, D.Y.H. Air and water permeation resistance across dust cakes on filters—Effects of particle polydispersity and shape factor. Powder Technol. 2001, 118, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Parameters | Test Data | Test Standard | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wet-Laid Composite Medium | Standard Heavy-Duty Filter Medium | Electrospun Composite Medium | ||
| Basis weight (g/m2) | 119 | 110 | 118 | TAPPI T410 [33] |
| Thickness (mm) | 0.37 | 0.36 | 0.32 | TAPPI T411 [34] |
| Air permeability (L/(m2·s)) | 137 | 106 | 243 | ASTM D737 [35] |
| Gravimetric efficiency (@2000 Pa) (%) | 99.9 | 99.8 | 99.9 | ISO 5011 [36] |
| Pressure drop (@11.1 cm/s) (Pa) | 162 | 209 | 91 | ISO 5011 [36] |
| Stiffness (machine direction) (mN·m) | 3.0 | 3.7 | 2.6 | TAPPI T489 [37] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Long, J.; Tang, M.; Sun, Z.; Liang, Y.; Hu, J. Dust Loading Performance of a Novel Submicro-Fiber Composite Filter Medium for Engine. Materials 2018, 11, 2038. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11102038
Long J, Tang M, Sun Z, Liang Y, Hu J. Dust Loading Performance of a Novel Submicro-Fiber Composite Filter Medium for Engine. Materials. 2018; 11(10):2038. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11102038
Chicago/Turabian StyleLong, Jin, Min Tang, Zhaoxia Sun, Yun Liang, and Jian Hu. 2018. "Dust Loading Performance of a Novel Submicro-Fiber Composite Filter Medium for Engine" Materials 11, no. 10: 2038. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11102038
APA StyleLong, J., Tang, M., Sun, Z., Liang, Y., & Hu, J. (2018). Dust Loading Performance of a Novel Submicro-Fiber Composite Filter Medium for Engine. Materials, 11(10), 2038. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11102038





