Synthesis of Zeolite from Carbothermal Reduction Electrolytic Manganese Residue for the Removal of Macrolide Antibiotics from Aqueous Solution
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Zeolite from CR-EMR
2.3. Adsorption Studies
3. Results and Discussion
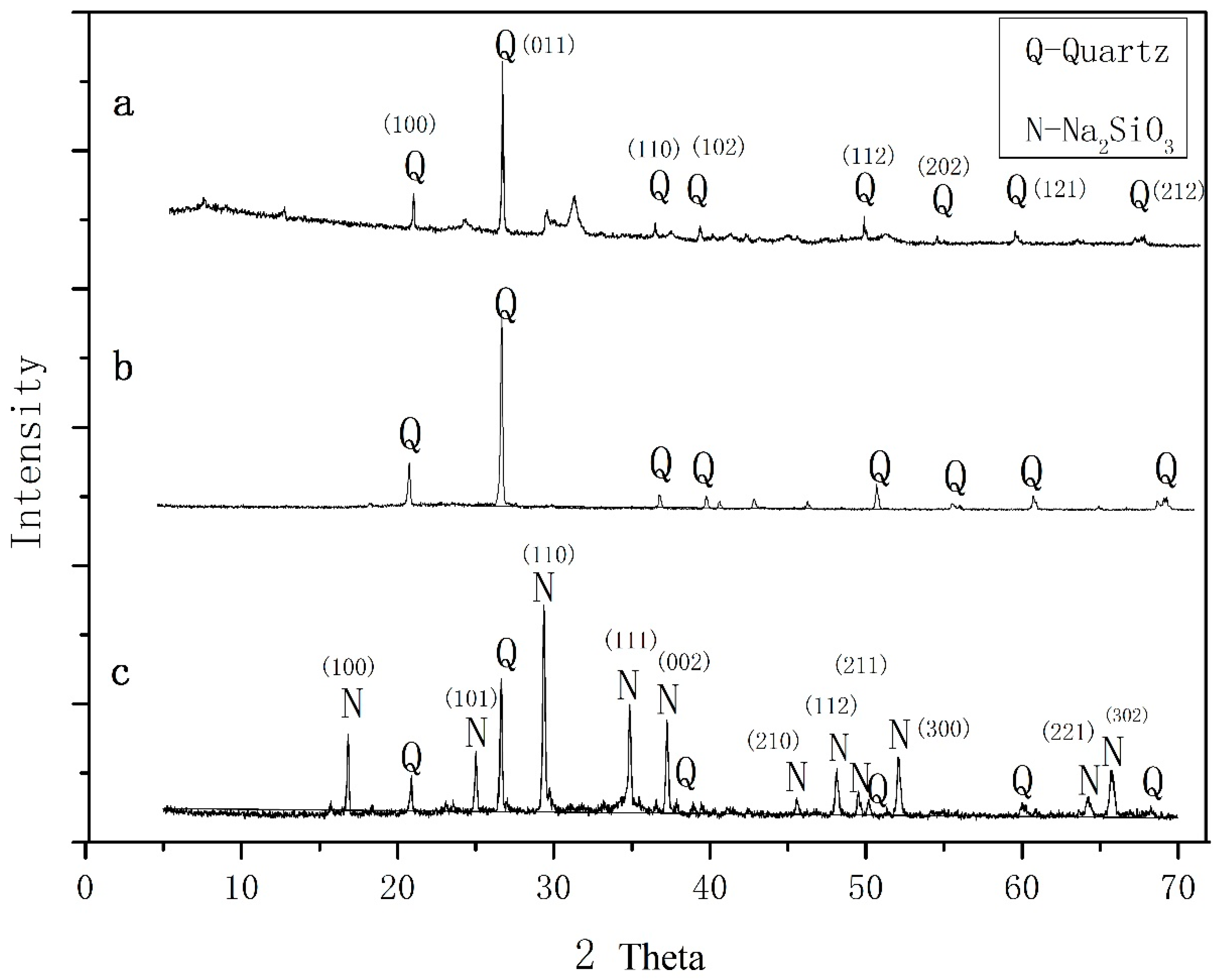
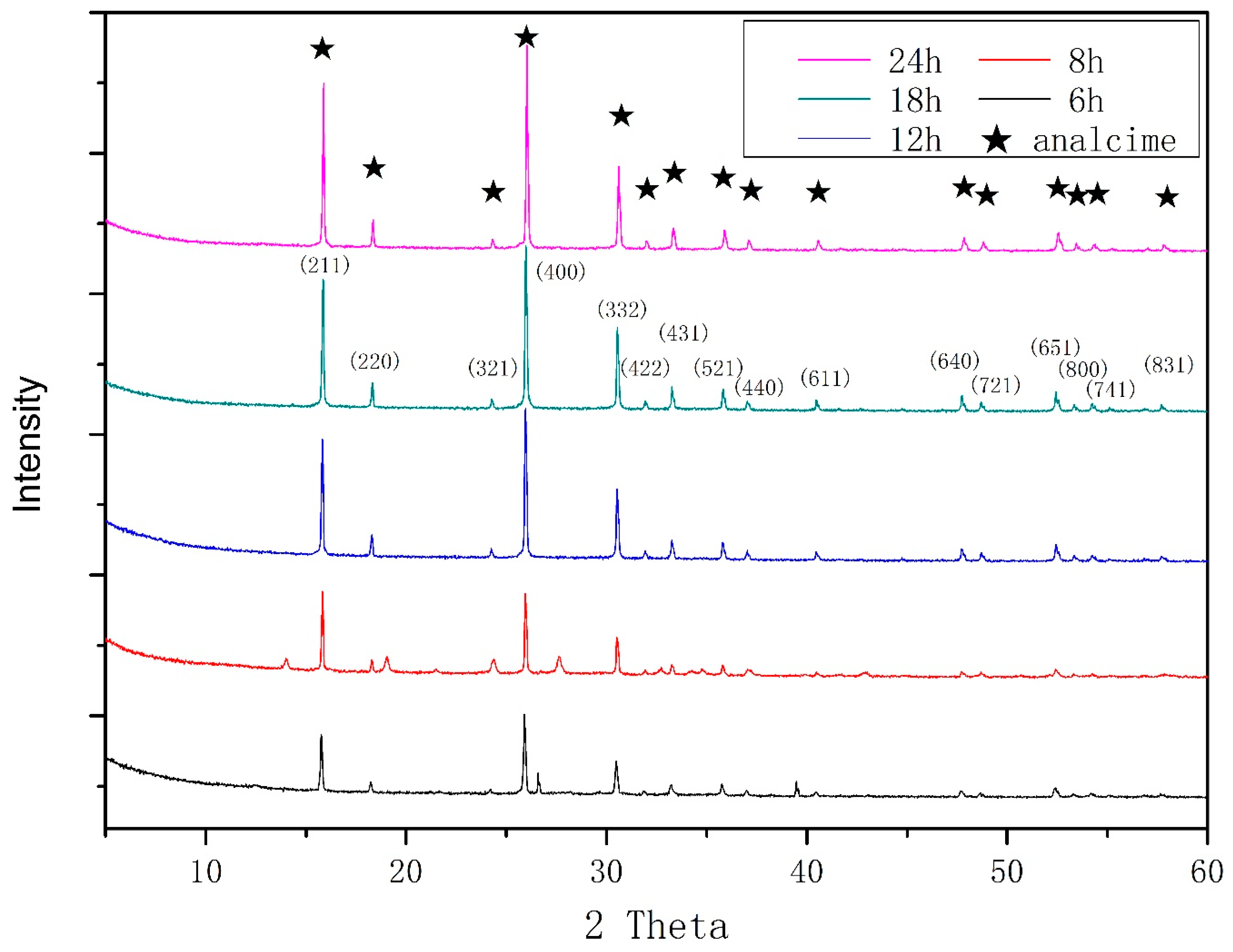
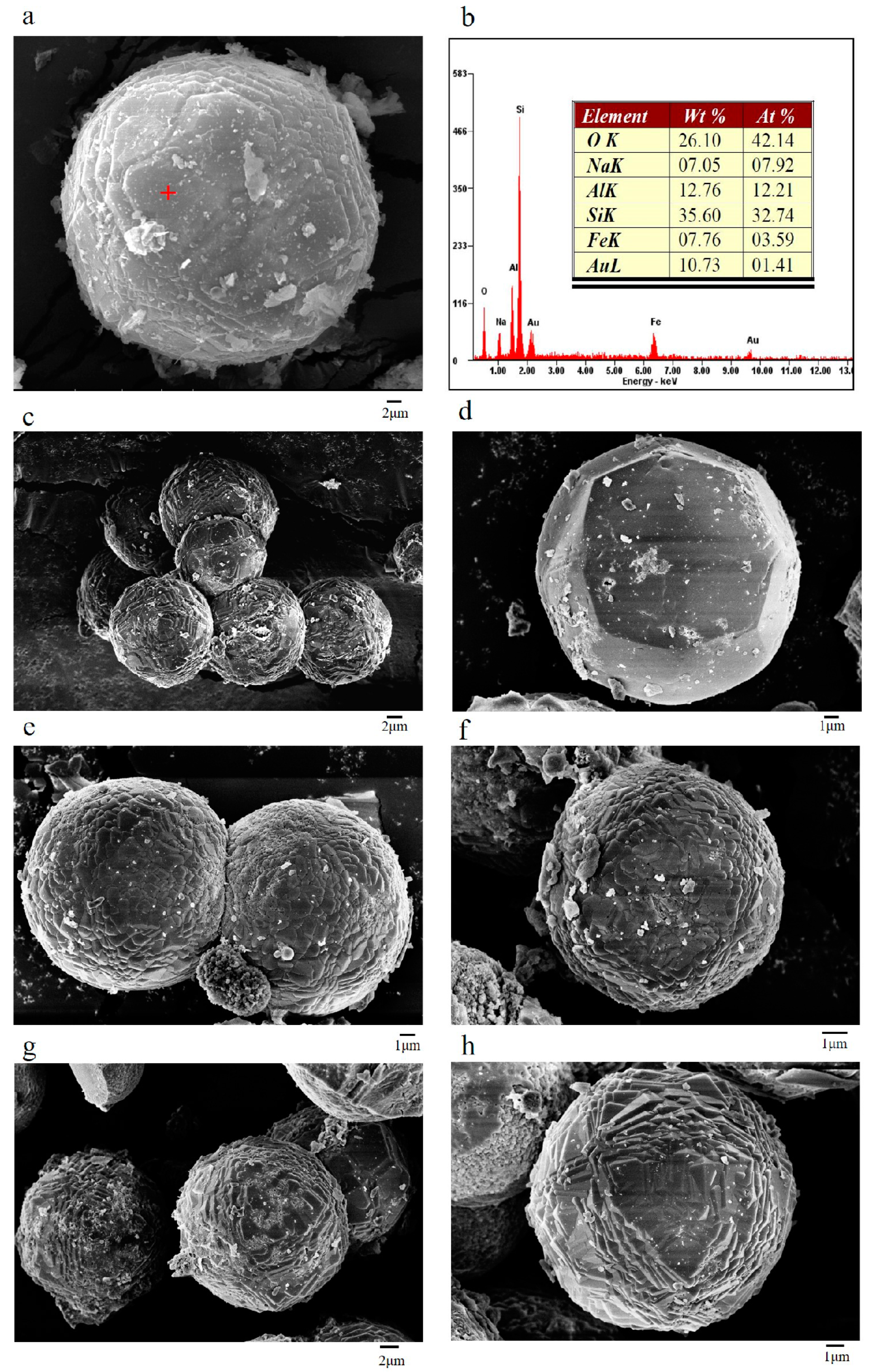
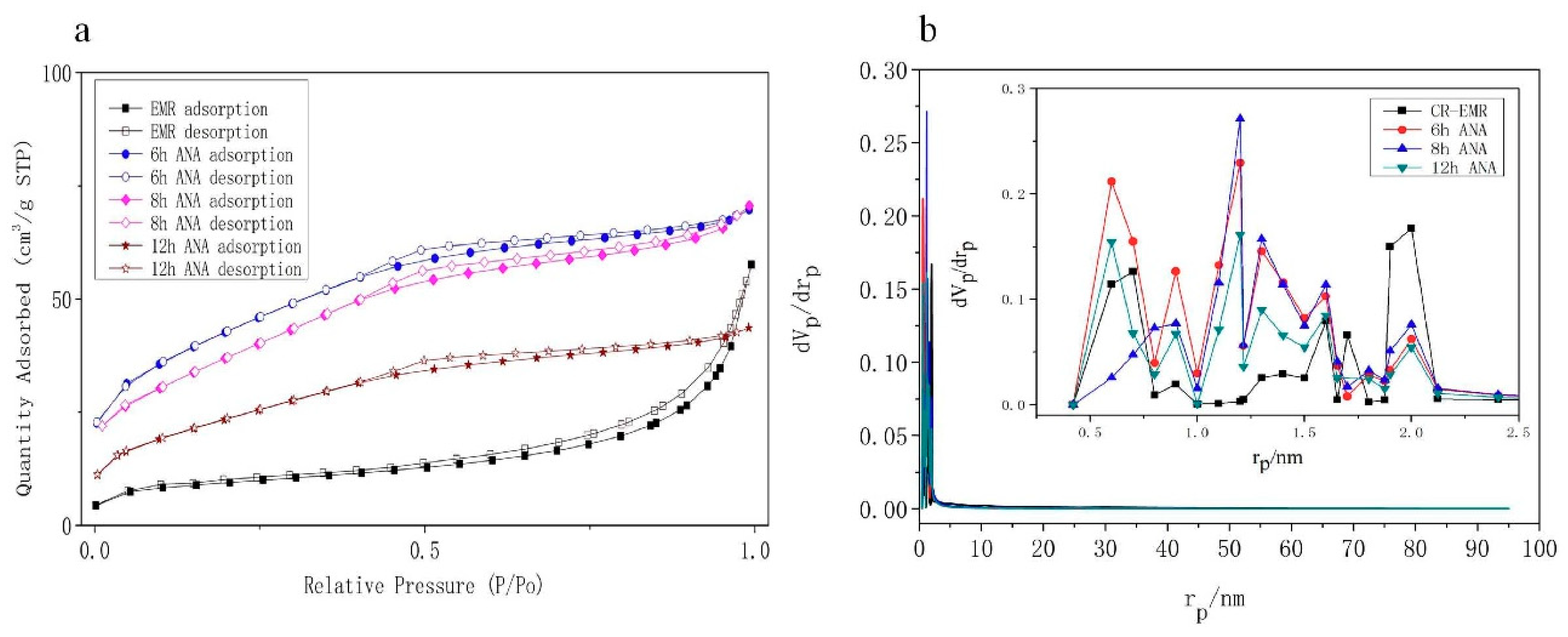
3.1. Characteristics of the Zeolite EMANA
3.2. Choice of Asorbent
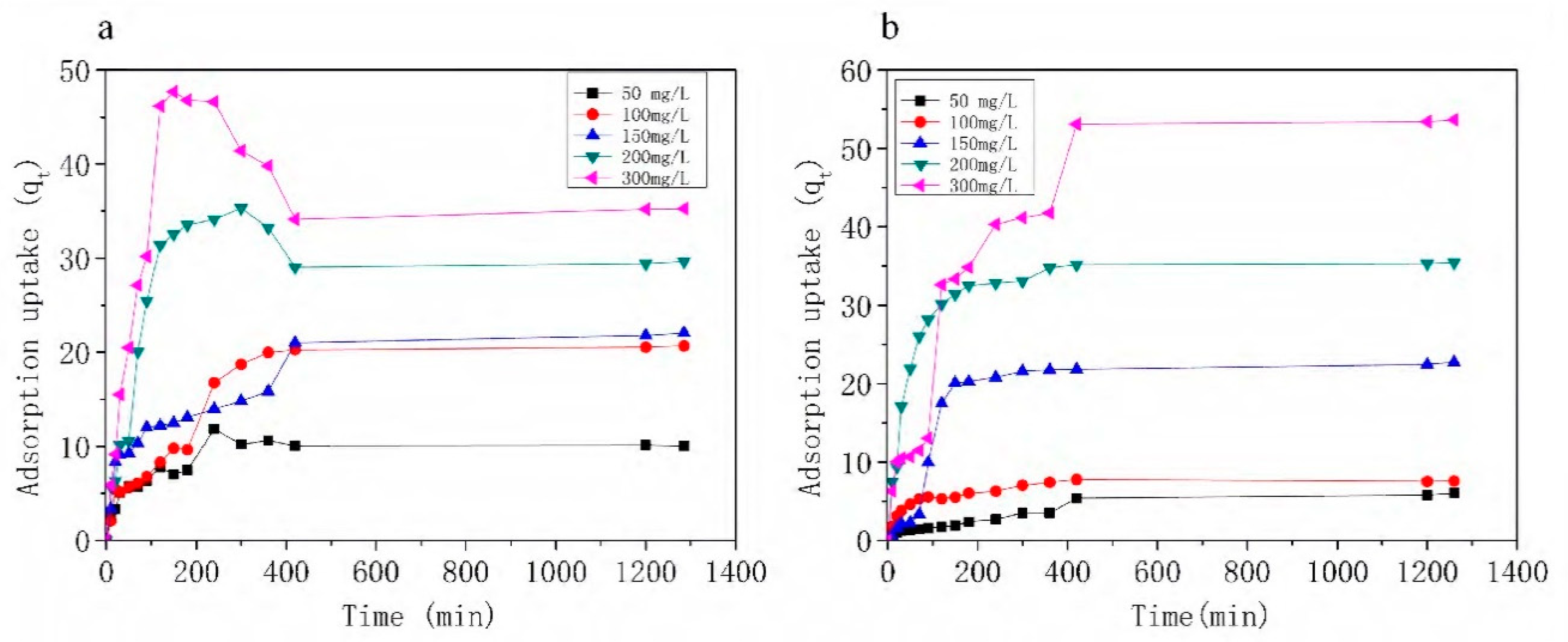
3.3. Effects of Initial Concentrations and Contact Time on Adsorption
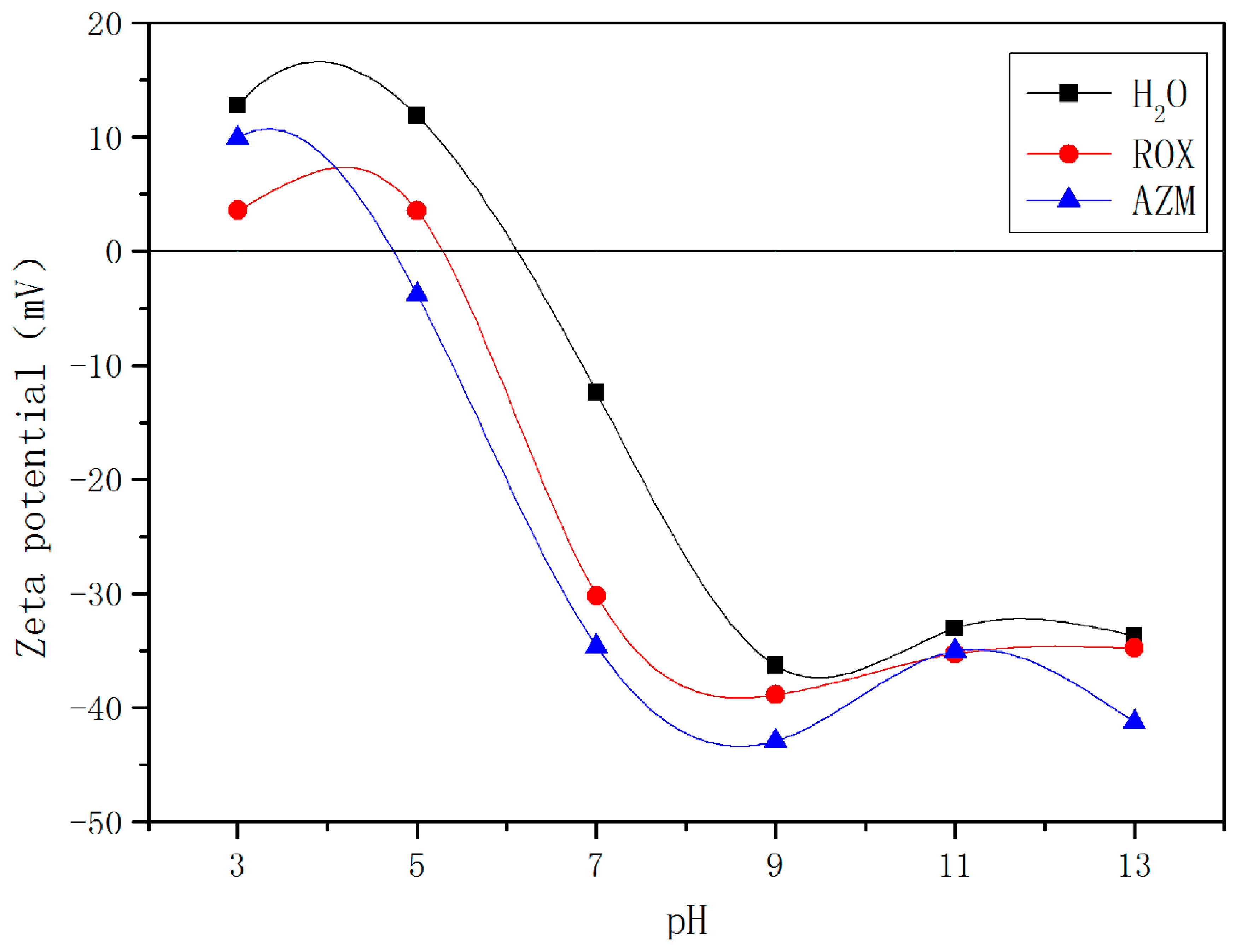
3.4. Effects of pH and Zeta Potential
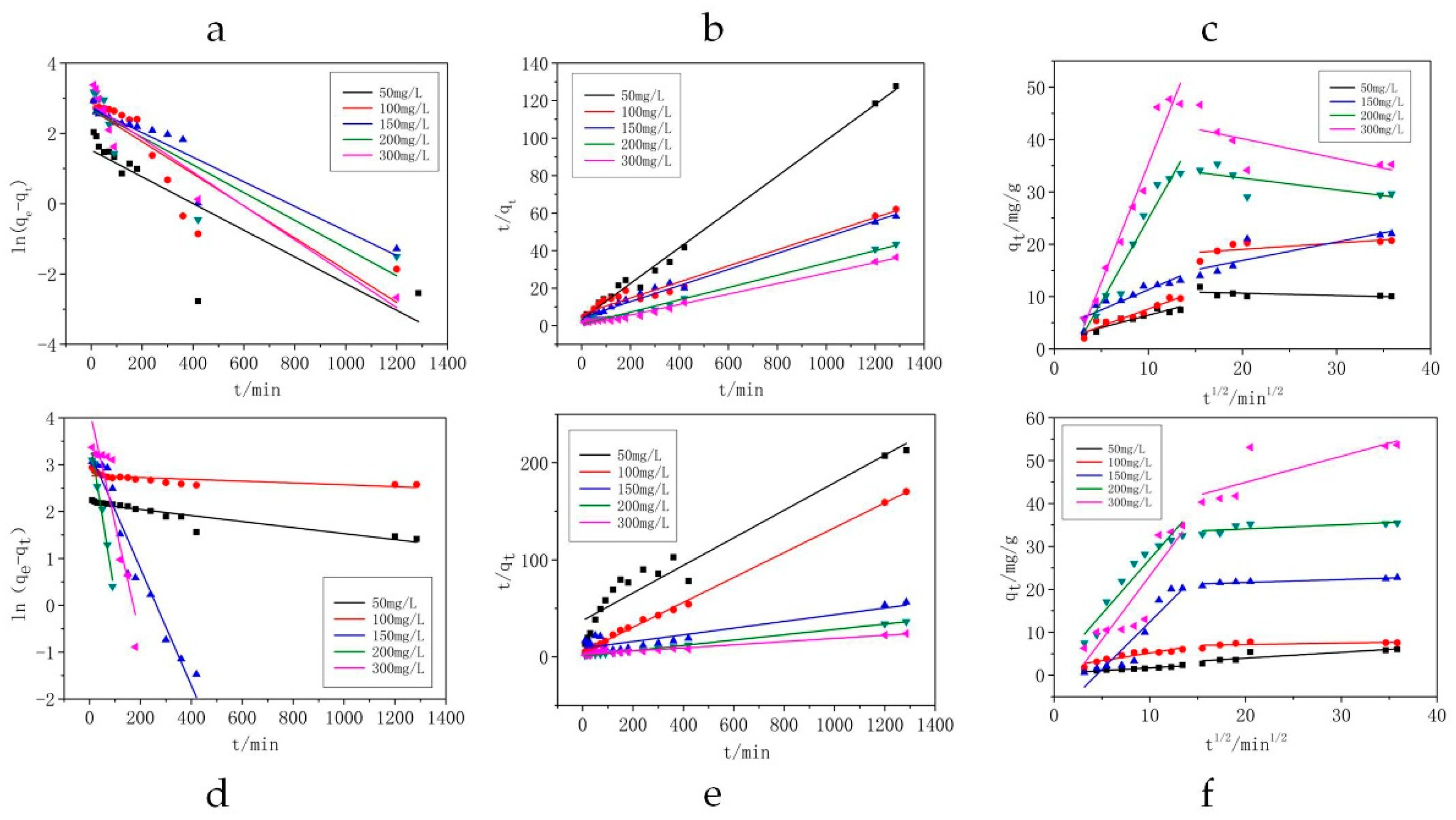
3.5. Adsorption Kinetics Analysis
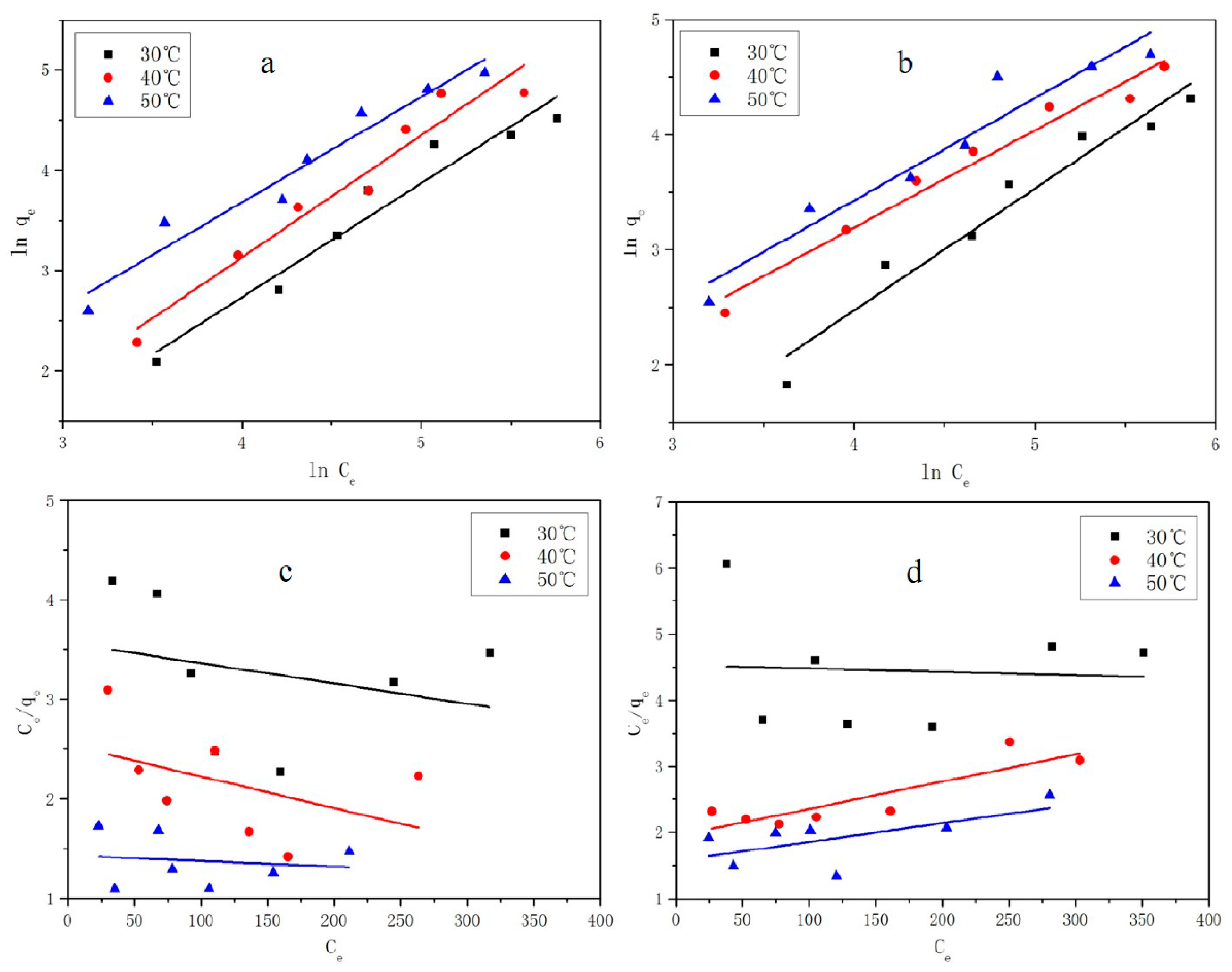
3.6. Adsorption Isotherm Analysis
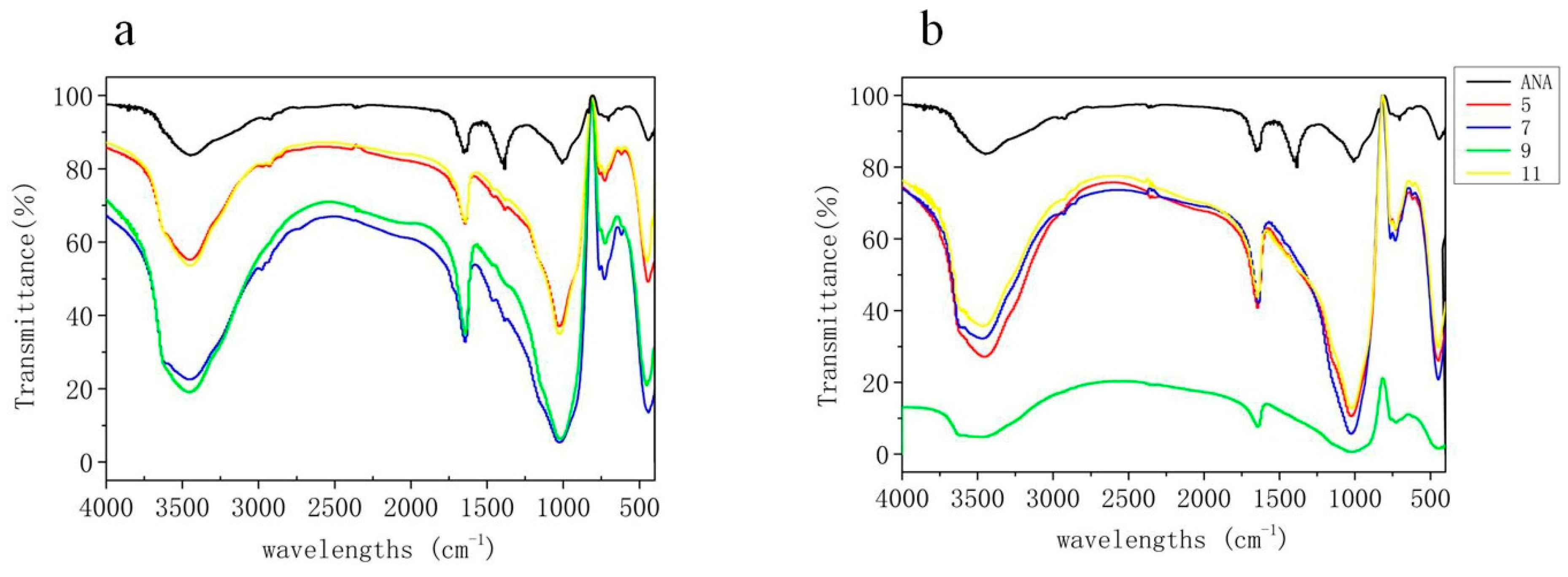
3.7. FT-IR Spectrometry Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Digernes, M.N.; Rudi, L.; Andersson, H.; Stålhane, M.; Wasbø, S.O.; Knudsen, B.R. Global optimisation of multi-plant manganese alloy production. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2018, 110, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswal, A.; Tripathy, B.C.; Sanjay, K.; Subbaiah, T.; Minakshi, M. Electrolytic manganese dioxide (EMD): A perspective on worldwide production, reserves and its role in electrochemistry. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 58255–58283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitta, N.; Wu, F.; Lee, J.T.; Yushin, G. Li-ion battery materials: Present and future. Mater. Today 2015, 18, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, J.K.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.; Choi, W.; Chang, W.; Byun, D.; Cho, B.W.; Chung, K.Y. Mechanochemical synthesis of Li2MnO3 shell/LiMO2 (M = Ni, Co, Mn) core-structured nanocomposites for lithium-ion batteries. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Cheng, C.Y. Manganese metallurgy review. Part I: Leaching of ores/secondary materials and recovery of electrolytic/chemical manganese dioxide. Hydrometallurgy 2007, 89, 137–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, J.; Wu, H.; Liu, R.; Liu, Z.; Li, B.; Chen, M.; Tao, C. Simultaneous stabilization/solidification of Mn2+ and NH4+-N from electrolytic manganese residue using MgO and different phosphate resource. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 148, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, N.; Dan, Z.; Wang, F.; Pan, C.; Zhou, C.; Jiang, L. Electrolytic manganese metal industry experience based China’s new model for cleaner production promotion. J. Clean. Prod. 2011, 19, 2082–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, B.; Chen, B.; Duan, N.; Zhou, C. Extraction of manganese from electrolytic manganese residue by bioleaching. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 1683–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, N.; Wang, F.; Zhou, C.; Zhu, C.; Yu, H. Analysis of pollution materials generated from electrolytic manganese industries in China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2010, 54, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Zhou, C.-B.; Duan, N. Recycling of electrolytic manganese solid waste in autoclaved bricks preparation in China. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2013, 16, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.; Liu, R.; Shu, J.; Li, W. Simultaneous stripping recovery of ammonia-nitrogen and precipitation of manganese from electrolytic manganese residue by air under calcium oxide assist. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2015, 50, 1282–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, J.; Liu, R.; Liu, Z.; Chen, H.; Tao, C. Leaching of manganese from electrolytic manganese residue by electro-reduction. Environ. Technol. 2016, 38, 2077–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, O.S.H.; Carvalho, C.d.F.; Silva, G.A.; Santos, C.G. Manganese ore tailing: Optimization of acid leaching conditions and recovery of soluble manganese. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 147, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Lv, X.; Tian, X.; Wang, Y.; Komarneni, S. An investigation on the use of electrolytic manganese residue as filler in sulfur concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 73, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.-K.; Qian, J.-S.; Wang, Z.; Deng, C. Production of quasi-sulfoaluminate cementitious materials with electrolytic manganese residue. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2012, 34, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Du, D.; Peng, Q.; Wu, C.; Lv, K.; Ye, H.; Chen, S.; Zhan, W. Activation of silicon in the electrolytic manganese residue by mechanical grinding-roasting. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 192, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, L.; Mackulak, T.; Grabic, R.; Golovko, O.; Koba, O.; Stanova, A.V.; Szabova, P.; Grencikova, A.; Bodik, I. Pharmaceuticals and illicit drugs—A new threat to the application of sewage sludge in agriculture. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 634, 606–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Zhang, G.; Li, X.; Zou, S.; Li, P.; Hu, Z.; Li, J. Occurrence and elimination of antibiotics at four sewage treatment plants in the Pearl River Delta (PRD), South China. Water Res. 2007, 41, 4526–4534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, M.O.; Moreira, N.F.F.; Ribeiro, A.R.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Silva, A.M.T. Occurrence and removal of organic micropollutants: An overview of the watch list of EU Decision 2015/495. Water Res. 2016, 94, 257–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben, W.; Zhu, B.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, M.; Qiang, Z. Occurrence, removal and risk of organic micropollutants in wastewater treatment plants across China: Comparison of wastewater treatment processes. Water Res. 2018, 130, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera-Utrilla, J.; Sanchez-Polo, M.; Ferro-Garcia, M.A.; Prados-Joya, G.; Ocampo-Perez, R. Pharmaceuticals as emerging contaminants and their removal from water. A review. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 1268–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McArdell, C.; Molnar, E.; Suter, M.; Giger, W. Occurrence and fate of macrolide antibiotics in wastewater treatment plants and in the Glatt Valley. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 5479–5486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Zhang, T. Biodegradation and adsorption of antibiotics in the activated sludge process. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 3468–3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.F.; Chang, C.Y.; Chen, K.H.; Tsai, W.T.; Shie, J.L.; Chen, Y.H. Adsorption of naphthalene on zeolite from aqueous solution. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 277, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, A.M.; Paprocki, A.; Ferret, L.S.; Azevedo, C.M.N.; Pires, M. Synthesis of zeolite Na-P1 under mild conditions using Brazilian coal fly ash and its application in wastewater treatment. Fuel 2015, 139, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhong, H.; Wang, S.; Xue, J.; Zhang, Z. Removal of basic dye (methylene blue) from aqueous solution using zeolite synthesized from electrolytic manganese residue. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 23, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ríos, C.A.; Williams, C.D.; Roberts, C.L. A comparative study of two methods for the synthesis of fly ash-based sodium and potassium type zeolites. Fuel 2009, 88, 1403–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Huang, W.; Chen, B.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, D.; Sun, Y.; Gong, B. Removal of tetracycline from aqueous solution by MCM-41-zeolite A loaded nano zero valent iron: Synthesis, characteristic, adsorption performance and mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 339, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ocampo-Pérez, R.; Rivera-Utrilla, J.; Gómez-Pacheco, C.; Sánchez-Polo, M.; López-Peñalver, J.J. Kinetic study of tetracycline adsorption on sludge-derived adsorbents in aqueous phase. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 213, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, W.J.; Dwyer, J.; Garforth, A.A.; Smith, W.J. The synthesis and characterisation of iron silicate molecular sieves. Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 1986, 28, 137–144. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Liu, C.; Yeung, K. Factors affecting the synthesis of hetero-atom zeolite Fe-ZSM-5 membrane. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2003, 32, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Su, J.; Li, R. Preparation and characterization of super-microporous alumina with crystalline structure. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2017, 243, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, J.; Liu, R.; Wu, H.; Liu, Z.; Sun, X.; Tao, C. Adsorption of methylene blue on modified electrolytic manganese residue: Kinetics, isotherm, thermodynamics and mechanism analysis. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2018, 82, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanday, W.A.; Hameed, B.H. Zeolite-hydroxyapatite-activated oil palm ash composite for antibiotic tetracycline adsorption. Fuel 2018, 215, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamzehloo, M.; Karimi, J.; Aghapoor, K.; Sayahi, H.; Darabi, H.R. The synergistic cooperation between MCM-41 and azithromycin: A pH responsive system for drug adsorption and release. J. Porous Mater. 2017, 25, 1275–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, G.P.S.; Isloor, A.M.; Inamuddin; Asiri, A.M.; Ismail, A.F.; Kumar, R.; Ahamed, M.I. Performance intensification of the polysulfone ultrafiltration membrane by blending with copolymer encompassing novel derivative of poly (styrene-co-maleic anhydride) for heavy metal removal from wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 353, 425–435. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, T.; Tiwari, S.K. Studies on sorption properties of zeolite derived from Indian fly ash. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 137, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Shon, H.K.; Ngo, H.H. Adsorption characteristics of antibiotics trimethoprim on powdered and granular activated carbon. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2010, 16, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahman, E.A. Synthesis of zeolite nanostructures from waste aluminum cans for efficient removal of malachite green dye from aqueous media. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 253, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilami, S.E.; Azizi, S.N. Methionine templated analcime for enhancing heavy metal adsorption. ScienceAsia 2017, 43, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojumu, T.V.; Du Plessis, P.W.; Petrik, L.F. Synthesis of zeolite A from coal fly ash using ultrasonic treatment—A replacement for fusion step. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2016, 31, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Xiao, D.; Yu, Q.; Chen, S.; Chen, S.; Miao, M. Preparation of mesoporous silica from electrolytic manganese slags by using amino-ended hyperbranched polyamide as template. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 10258–10265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, A.; Singh, A.; Kumar, S.; Khare, S.K.; Ramanan, A. Microbial mineralization of struvite: A promising process to overcome phosphate sequestering crisis. Water Res. 2014, 54, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, C.K.; Joshi, M.J. Growth and characterization of struvite-Na crystals. J. Cryst. Growth 2014, 401, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample | Chemical Composition (wt %) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | CO2 | Fe2O3 | SO3 | Al2O3 | MnO | K2O | CaO | Na2O | |
| CR-EMR | 38.75 | 15.80 | 14.94 | 10.80 | 8.12 | 6.40 | 1.74 | 1.32 | 0.10 |
| Acid washed residue | 59.97 | 27.15 | 2.51 | 3.33 | 3.68 | 1.04 | 0.9 | 0.16 | 0.05 |
| Fused mixture | 47.29 | 3.71 | 5.32 | 3.16 | 3.60 | 1.86 | 1.55 | 0.54 | 30.86 |
| EMANA (24 h) | 56.86 | 3.60 | 6.69 | 0.10 | 13.70 | 2.15 | 0.88 | 1.62 | 10.60 |
| Material | BET Surface Area m2/g | Total Pore Volume cm3/g | Mean Pore Diameter nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| CR-EMR | 29.05 | 0.08498 | 11.701 |
| 6 h synthesized zeolite ANA | 138.4 | 0.1078 | 3.1143 |
| 8 h synthesized zeolite ANA | 128.6 | 0.1089 | 3.3884 |
| 12 h synthesized zeolite ANA | 81.43 | 0.06748 | 3.3149 |
| 24 h synthesized zeolite ANA | 24.95 | 0.05687 | 9.1165 |
| Contaminant | Pseudo-First-Order Model | Pseudo-Second-Order Model | Intraparticle Diffusion Model (I) | Intraparticle Diffusion Model (II) | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C0 mg/L | qe exp mg/g | qe cal mg/g | k1 × 104 min−1 | R2 | SE | qe cal mg/g | k2 × 102 mg/min | R2 | SE | C0 mg/L | ki1 mg/(g·min1/2) | C1 mg/g | R2 | SE | ki2 mg/(g·min1/2) | C2 mg/g | R2 | SE | |
| AZM | 50 | 10.06 | 4.57 | 38.00 | 0.661 | 0.35 | 10.49 | 0.26 | 0.995 | 0.92 | 50 | 0.47528 | 1.71451 | 0.852 | 0.62 | −0.04357 | 11.52809 | 0.149 | 0.80 |
| 100 | 20.69 | 14.59 | 45.70 | 0.771 | 0.26 | 23.32 | 0.03 | 0.972 | 0.96 | 100 | 0.65600 | 1.09532 | 0.894 | 0.71 | 0.11943 | 16.64782 | 0.379 | 1.49 | |
| 150 | 22.05 | 15.18 | 35.00 | 0.878 | 0.14 | 23.31 | 0.04 | 0.986 | 0.67 | 150 | 0.77086 | 3.63343 | 0.796 | 1.21 | 0.35260 | 9.86107 | 0.654 | 2.74 | |
| 200 | 29.66 | 14.59 | 39.40 | 0.780 | 0.35 | 30.57 | 0.15 | 0.989 | 0.45 | 200 | 3.18475 | −6.89820 | 0.942 | 2.50 | −0.22403 | 37.13355 | 0.428 | 2.59 | |
| 300 | 35.26 | 16.95 | 48.20 | 0.920 | 0.24 | 35.84 | 0.80 | 0.990 | 0.37 | 300 | 4.51741 | −9.81108 | 0.958 | 2.98 | −0.37540 | 47.67356 | 0.368 | 4.78 | |
| ROX | 50 | 6.03 | 8.77 | 6.42 | 0.850 | 0.04 | 7.04 | 0.05 | 0.927 | 0.52 | 50 | 0.13121 | 0.38335 | 0.94 | 0.10 | 0.13734 | 1.21127 | 0.149 | 0.97 |
| 100 | 7.55 | 15.88 | 1.96 | 0.441 | 0.03 | 7.80 | 0.34 | 0.998 | 0.68 | 100 | 0.35932 | 1.57055 | 0.824 | 0.52 | 0.03410 | 6.44447 | 0.156 | 0.62 | |
| 150 | 22.71 | 26.41 | 1.25 | 0.950 | 0.17 | 28.99 | 0.01 | 0.816 | 0.21 | 150 | 2.21944 | −9.77361 | 0.851 | 2.90 | 0.06936 | 20.19534 | 0.803 | 0.38 | |
| 200 | 35.47 | 36.27 | 3.40 | 0.981 | 0.11 | 36.42 | 0.09 | 0.999 | 0.10 | 200 | 2.55359 | 1.49440 | 0.913 | 2.48 | 0.09797 | 32.11436 | 0.449 | 1.10 | |
| 300 | 53.64 | 63.94 | 2.42 | 0.829 | 0.38 | 61.31 | 0.01 | 0.963 | 0.42 | 300 | 2.98133 | −6.64054 | 0.777 | 4.97 | 0.60790 | 32.76858 | 0.575 | 5.49 | |
| Contaminant | Temperature (°C) | Langmuir Isotherm Model | Freundlich Isotherm Model | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qm mg/g | b L/mg | R2 | SE | kf (mg/g) (L/mg)1/n | 1/n | R2 | SE | ||
| AZM | 30 | −490.196 | −0.0005 | −0.102 | 0.53 | 0.162 | 1.138 | 0.937 | 0.58 |
| 40 | −314.465 | −0.0013 | 0.049 | 0.39 | 0.176 | 1.218 | 0.939 | 0.58 | |
| 50 | −1844.004 | −0.0004 | −0.176 | 0.20 | 0.590 | 1.052 | 0.945 | 0.45 | |
| ROX | 30 | −1921.74 | −0.0001 | −0.195 | 0.68 | 0.171 | 1.059 | 0.944 | 0.52 |
| 40 | 242.13 | 0.0021 | 0.709 | 0.18 | 0.827 | 0.846 | 0.966 | 0.30 | |
| 50 | 352.11 | 0.0018 | 0.303 | 0.22 | 0.871 | 0.891 | 0.925 | 0.47 | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Zeng, Y.; Chen, F.; Wang, T.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Hou, H.; Zhou, M. Synthesis of Zeolite from Carbothermal Reduction Electrolytic Manganese Residue for the Removal of Macrolide Antibiotics from Aqueous Solution. Materials 2018, 11, 2133. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112133
Li X, Zeng Y, Chen F, Wang T, Li Y, Chen Y, Hou H, Zhou M. Synthesis of Zeolite from Carbothermal Reduction Electrolytic Manganese Residue for the Removal of Macrolide Antibiotics from Aqueous Solution. Materials. 2018; 11(11):2133. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112133
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xuli, Yue Zeng, Fangyuan Chen, Teng Wang, Yixin Li, Yuchi Chen, Haobo Hou, and Min Zhou. 2018. "Synthesis of Zeolite from Carbothermal Reduction Electrolytic Manganese Residue for the Removal of Macrolide Antibiotics from Aqueous Solution" Materials 11, no. 11: 2133. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112133
APA StyleLi, X., Zeng, Y., Chen, F., Wang, T., Li, Y., Chen, Y., Hou, H., & Zhou, M. (2018). Synthesis of Zeolite from Carbothermal Reduction Electrolytic Manganese Residue for the Removal of Macrolide Antibiotics from Aqueous Solution. Materials, 11(11), 2133. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112133




