Micro-Magnetic and Microstructural Characterization of Wear Progress on Case-Hardened 16MnCr5 Gear Wheels †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Wear Tests
2.2. Wear Characterization Methodologies
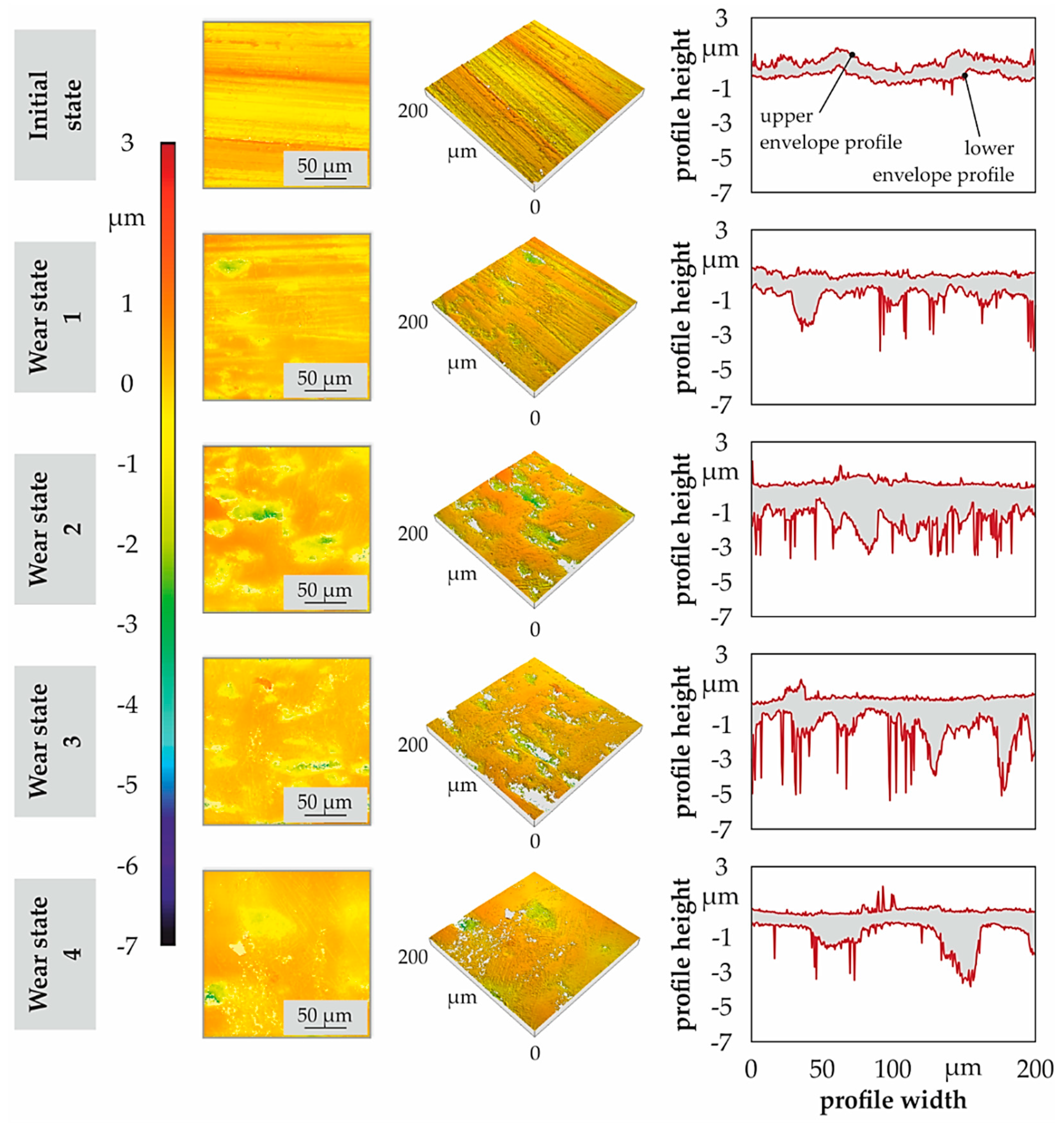
2.2.1. Characterization of Wear Progress on the Surface
2.2.2. Microstructural Characterization by Light Microscope and Scanning Electron Microscope
2.2.3. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
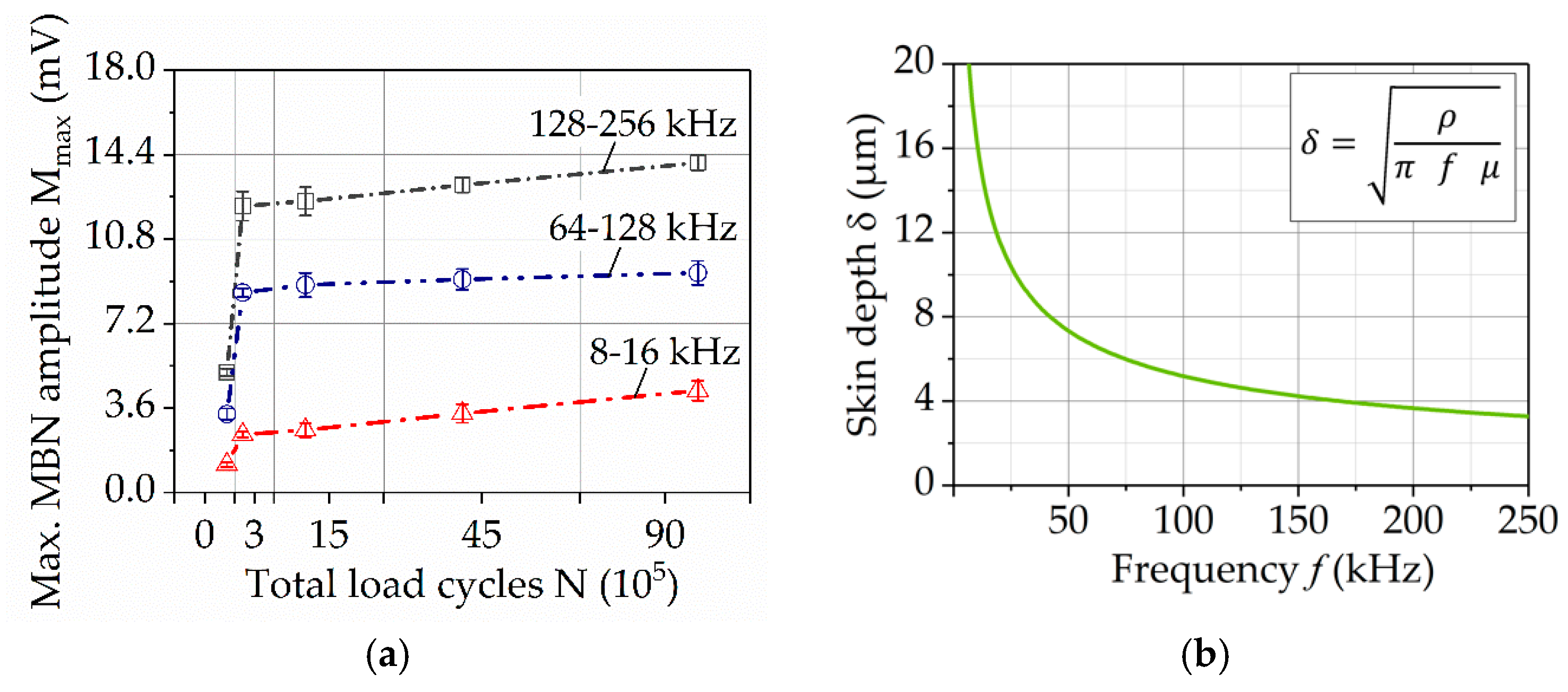
2.2.4. Micro-Magnetic Testing
3. Results
3.1. Wear Progress on the Surface of Gear Wheels Teeth
3.2. Microstructural Characterization
3.3. Electron Backscatter Diffraction
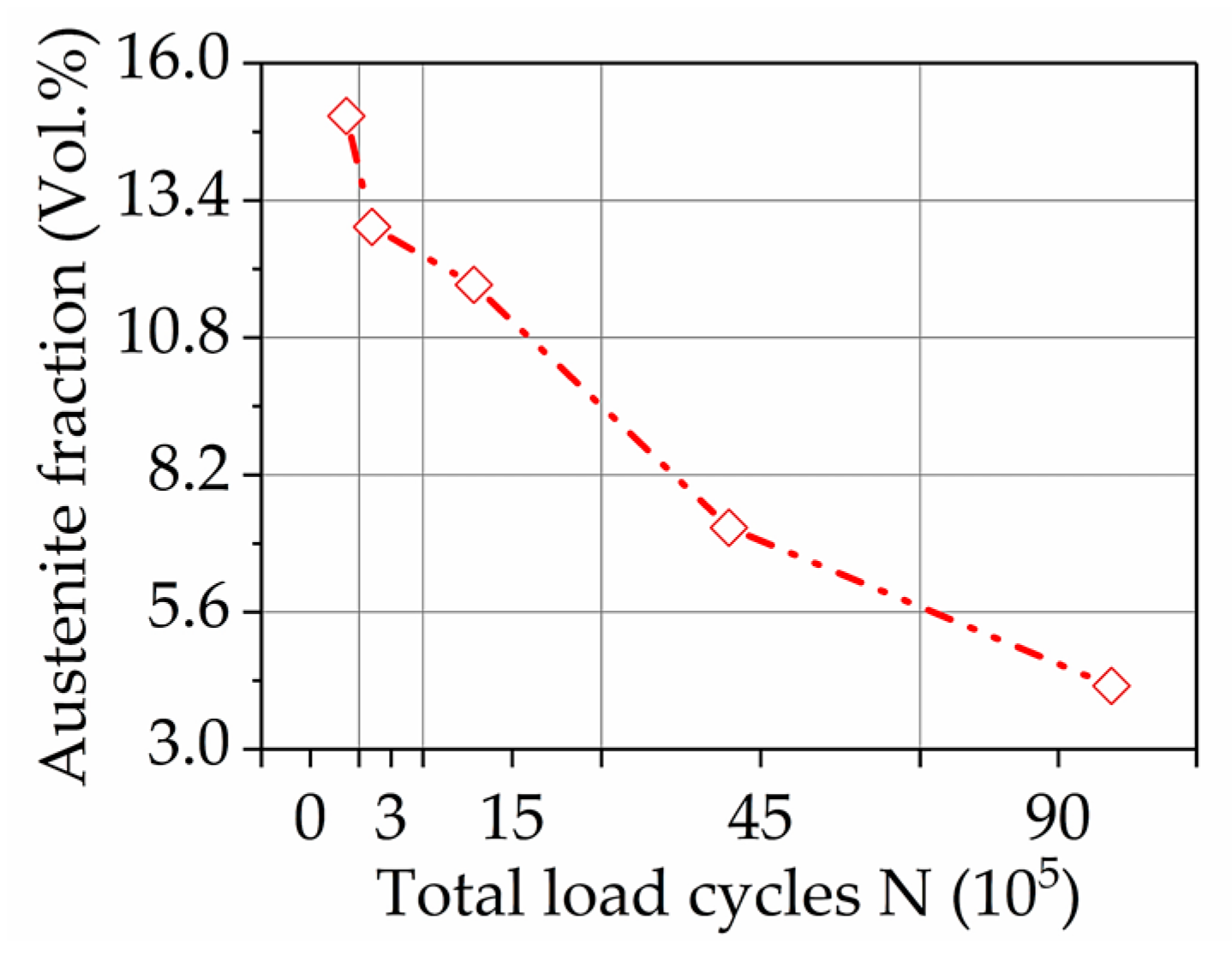
3.4. X-ray Diffraction
3.5. Micro-Magnetic Testing
4. Discussion
4.1. Surface Investigation
4.2. Microstructural Characterization
4.3. Micro-Magnetic Testing
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hergesell, M. Einfluss der Graufleckigkeit auf die Grübchentragfähigkeit Einsatzgehärteter Zahnräder; Abschlussbericht zum Projekt 459, Heft 844; FVA, Forschungsvereinigung Antriebstechnik: Frankfurt, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Balageas, D.; Fritzen, C.; Güemes, A. Structural Health Monitoring, 1st ed.; ISTE, Ltd.: London, UK, 2006; ISBN 1-905209-01-0, 978-1-905209-01-9. [Google Scholar]
- FVA 54/7. Test Procedure for the Investigation of the Micro-Pitting Capacity of Gear Lubricants; Forschungsvereinigung Antriebstechnik e.V.: Frankfurt, Germany, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- DIN ISO 14635. FZG Test Procedure; Part 1; Beuth: Berlin, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Tenkamp, J.; Haack, M.; Walther, F.; Weibring, M.; Tenberge, P. Application of micro-magnetic testing systems for non-destructive analysis of wear progress in case hardened 16MnCr5 gear wheels. Mater. Test. 2016, 58, 709–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taira, S.; Tanaka, K.; Yamasaki, T. A method of X-ray microbeam measurement of local stress and its application to fatigue crack growth problems. J. Soc. Mater. Sci. 1978, 27, 251–256. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, T.; Hirose, Y. Single incidence X-ray Stress measurement for all plane stress components using imaging plate of two-dimensional x-ray detector. J. Soc. Mater. Sci. Jpn. 1995, 44, 1138–1143. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, T.; Kamura, N.; Maruyama, Y.; Sasaki, T. Evaluation of rolling contact fatigue using X-ray diffraction ring. Mater. Perform. Charact. 2016, 5, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohri, A.; Takaku, Y.; Nakashiro, M. Comparison of X-ray residual stress measurement values by cos α method and sin2 ψ method. Mater. Res. Proc. 2017, 2, 103–108. [Google Scholar]
- Hilzinger, R.; Rodewald, W. Magnetic Materials: Fundamentals, Products, Properties, Applications; Vacuumschmelze GmbH & Co. KG: Hanau, Germany, 2013; ISBN 978-3-89578-352-4. [Google Scholar]
- Chikazumi, S. Physics of Magnetism, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- McCurrie, R.A. Ferromagnetic Materials: Structure and Properties; Academic Press Limited: London, UK, 1994; ISBN 0-12-482495-1. [Google Scholar]
- Fraunhofer Institut Zerstörungsfreie Prüfverfahren (IZFP). Testing System 3MA User Manual; Version 1.81; IZFP: Saarbrücken, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Fraunhofer Institut Zerstörungsfreie Prüfverfahren (IZFP). Mikromagnetisches Materialprüfsystem FracDim Benutzerhandbuch; Version 1.3; IZFP: Saarbrücken, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Jiles, D.C. Dynamics of domain magnetization and the barkhausen effect. Czechoslov. J. Phys. 2000, 50, 893–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blazek, D.; Neslusan, M.; Micica, M.; Pistora, J. Extraction of Barkhausen noise from the measured raw signal in high-frequency regimes. Measurement 2016, 94, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashista, M.; Moorthy, V. Influence of applied magnetic field strength and frequency response of pick-up coil on the magnetic Barkhausen noise profile. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2013, 345, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, A.; Evans, H.; Snidle, R. Understanding micropitting in gears. J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2016, 230, 1276–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Errichello, R.L. Morphology of micropitting. J. Gear Technol. 2011, 7, 74–81. [Google Scholar]
- Lohmann, C. Zusammenhang von Ermüdung, Rissbildung, Verschleiß und Graufleckentragfähigkeit an Stirnrädern. Ph.D. Thesis, Ruhr-Universität Bochum, Bochum, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ziegltrum, A.E.; Lohner, T.; Michaelis, K.; Brodyanski, A.; Merz, R.; Kopnarski, M.; Höhn, B.-R.; Stahl, K. Einfluss triboinduzierter schichten auf schäden und reibungsverhalten von zahnrädern unter besonderer berücksichtigung des einlaufvorgangs—Experimentelle und analytische untersuchungen. Tribol. Schmier. 2018, 65, 12–26. [Google Scholar]
- Vander Voort, G.F. Applied Metallography; Van Nostrand Reinhold Company Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1986; pp. 261–277. ISBN 0-442-28836-0. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, D.; Wang, F.-X.; Cai, Q.-G.; Zheng, M.-X.; Cheng, Y.-Q. Effect of retained austenite on rolling element fatigue and its mechanism. Wear 1985, 105, 223–234. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.-J.; Kweon, A.-G. The effects of retained austenite on dry sliding wear behavior of carburized steels. Wear 1996, 193, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colaco, R.; Vilar, R. On the influence of retained austenite in the abrasive wear behavior of a laser surface melted tool steel. Wear 2005, 258, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anglada-Rivera, J.; Padovese, L.R.; Capó-Sánchez, J. Magnetic Barkhausen noise and hysteresis loop in commercial carbon steel: Influence of applied tensile stress and grain size. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2001, 231, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal’a, J.; Bydzovsky, J. Barkhausen noise as a function of grain size in non-oriented FeSi steel. Measurement 2013, 46, 866–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanita, C.G.; Atherton, D.L.; Clapham, L. Plastic versus elastic deformation effects on magnetic Barkhausen noise in steel. Acta Mater. 2000, 48, 3545–3551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, D.M.; Stevens, K.J.; Kaiser, A.B. Magnetic Barkhausen noise analysis of stress in steel. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2004, 4, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Gear Set | Flank | Wear State | Loading | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pinion Torque (Nm) | Hertzian Contact Stress at Pitch Point (MPa) | Load Cycles (1 × 105) | Total Load Cycles (1 × 105) | |||
| 1 | A | 1 | 70 | 795 | 1.5 | 3 |
| 265 | 1547 | 1.5 | ||||
| B | 2 | 70 | 795 | 1.5 | 15 | |
| 265 | 1547 | 1.5 | ||||
| 265 | 1547 | 12 | ||||
| 2 | A | 3 | 70 | 795 | 1.5 | 45 |
| 265 | 1547 | 1.5 | ||||
| 265 | 1547 | 12 | ||||
| 265 | 1547 | 30 | ||||
| B | 4 | 70 | 795 | 1.5 | 90 | |
| 265 | 1547 | 1.5 | ||||
| 265 | 1547 | 12 | ||||
| 265 | 1547 | 30 | ||||
| 265 | 1547 | 45 | ||||
| Wear Condition | Stress, σ (MPa) | Retained Austenite (Vol. %) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | −447 ± 30 | 16.0 ± 0.2 |
| 1 | −496 ± 9 | 8.5 ± 0.2 |
| 2 | −435 ± 5 | 8.8 ± 0.5 |
| 3 | −490 ± 9 | 7.2 ± 0.3 |
| 4 | −517 ± 4 | 7.1 ± 0.3 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Knyazeva, M.; Rozo Vasquez, J.; Gondecki, L.; Weibring, M.; Pöhl, F.; Kipp, M.; Tenberge, P.; Theisen, W.; Walther, F.; Biermann, D. Micro-Magnetic and Microstructural Characterization of Wear Progress on Case-Hardened 16MnCr5 Gear Wheels. Materials 2018, 11, 2290. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112290
Knyazeva M, Rozo Vasquez J, Gondecki L, Weibring M, Pöhl F, Kipp M, Tenberge P, Theisen W, Walther F, Biermann D. Micro-Magnetic and Microstructural Characterization of Wear Progress on Case-Hardened 16MnCr5 Gear Wheels. Materials. 2018; 11(11):2290. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112290
Chicago/Turabian StyleKnyazeva, Marina, Julian Rozo Vasquez, Leonard Gondecki, Max Weibring, Fabian Pöhl, Monika Kipp, Peter Tenberge, Werner Theisen, Frank Walther, and Dirk Biermann. 2018. "Micro-Magnetic and Microstructural Characterization of Wear Progress on Case-Hardened 16MnCr5 Gear Wheels" Materials 11, no. 11: 2290. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112290
APA StyleKnyazeva, M., Rozo Vasquez, J., Gondecki, L., Weibring, M., Pöhl, F., Kipp, M., Tenberge, P., Theisen, W., Walther, F., & Biermann, D. (2018). Micro-Magnetic and Microstructural Characterization of Wear Progress on Case-Hardened 16MnCr5 Gear Wheels. Materials, 11(11), 2290. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112290






