Oxidation Behavior of Refractory AlNbTiVZr0.25 High-Entropy Alloy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Initial Microstructure
3.2. Oxidation Behavior
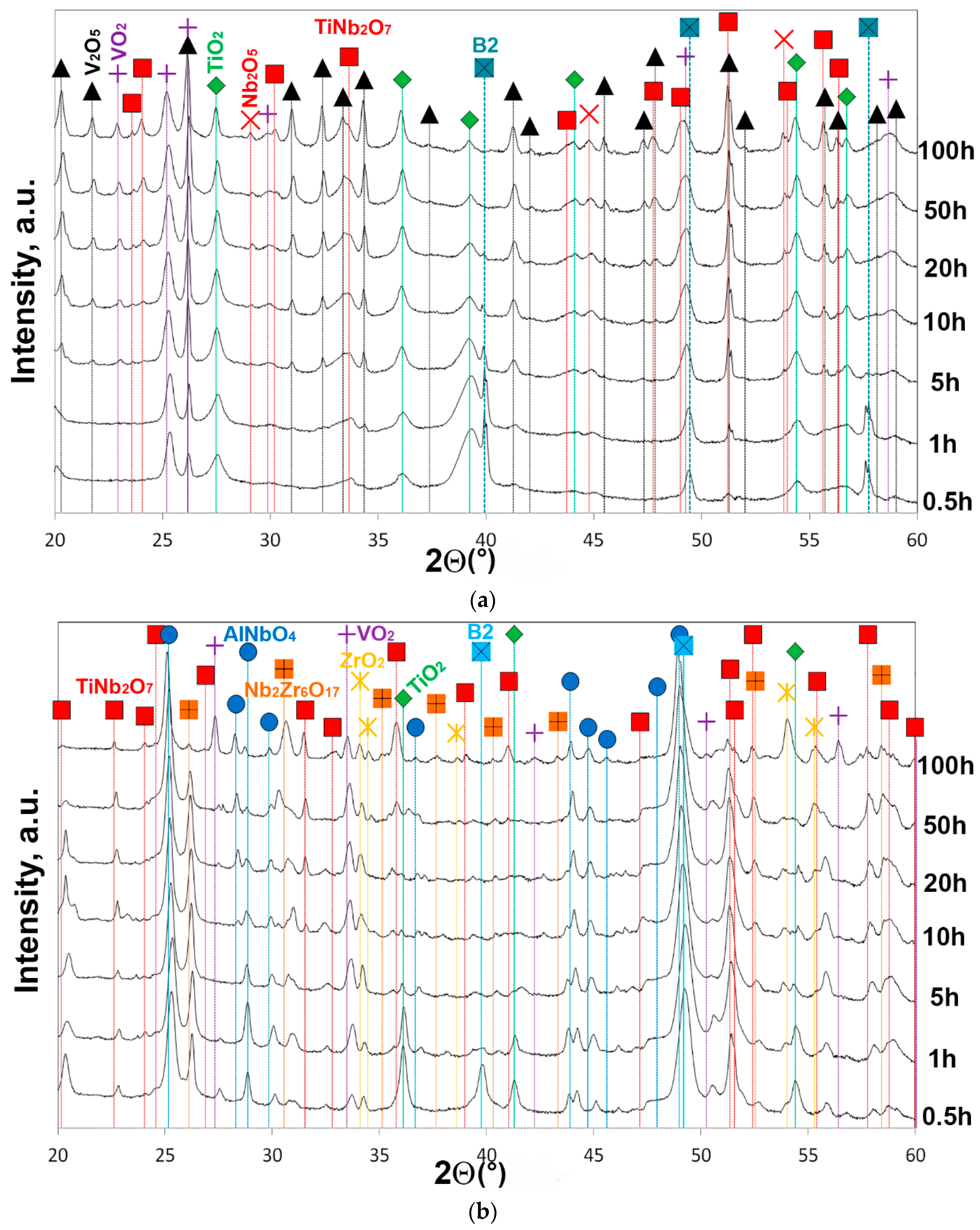
3.3. Phase Analysis and Morphology of the Surface Layer
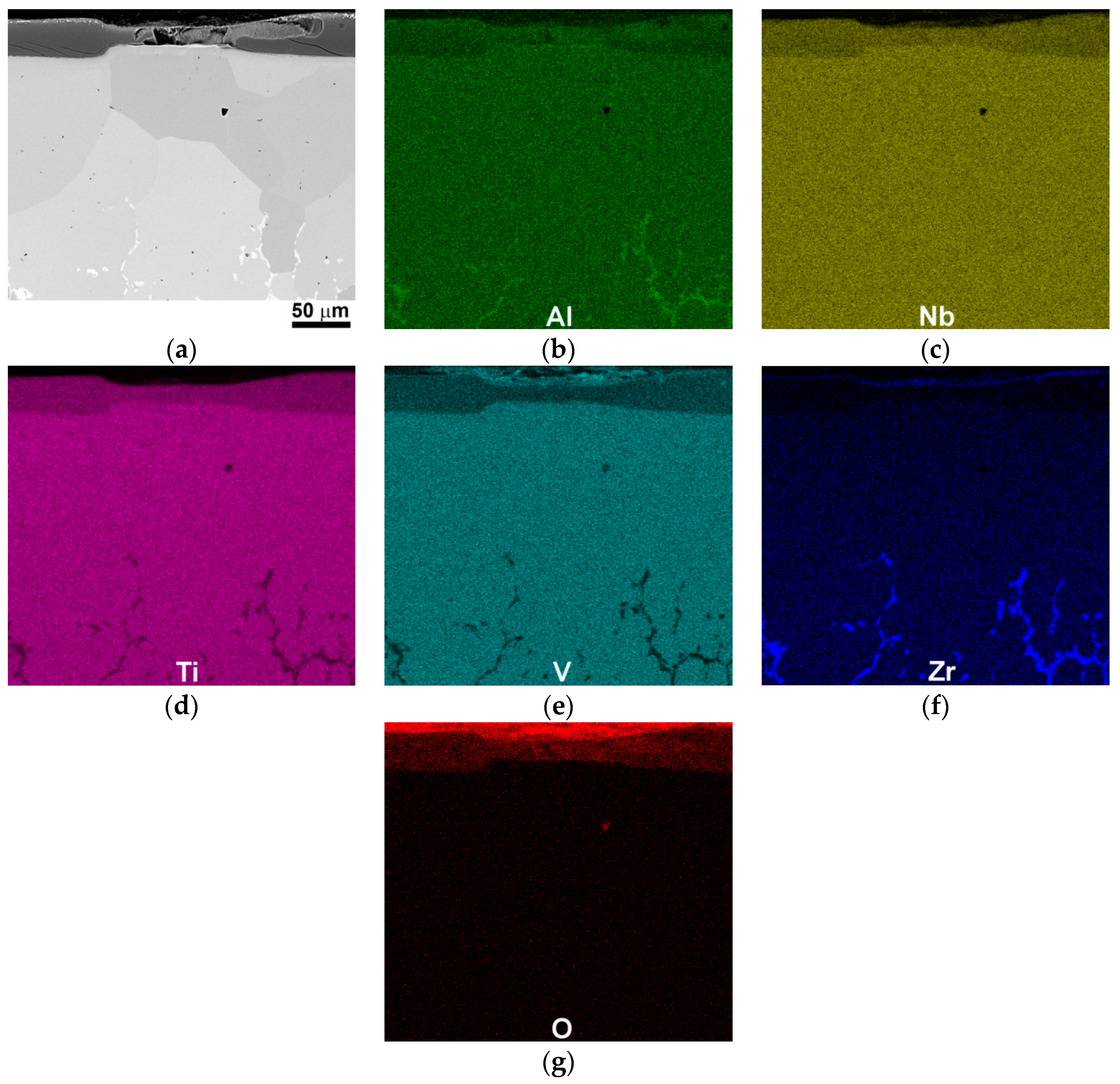
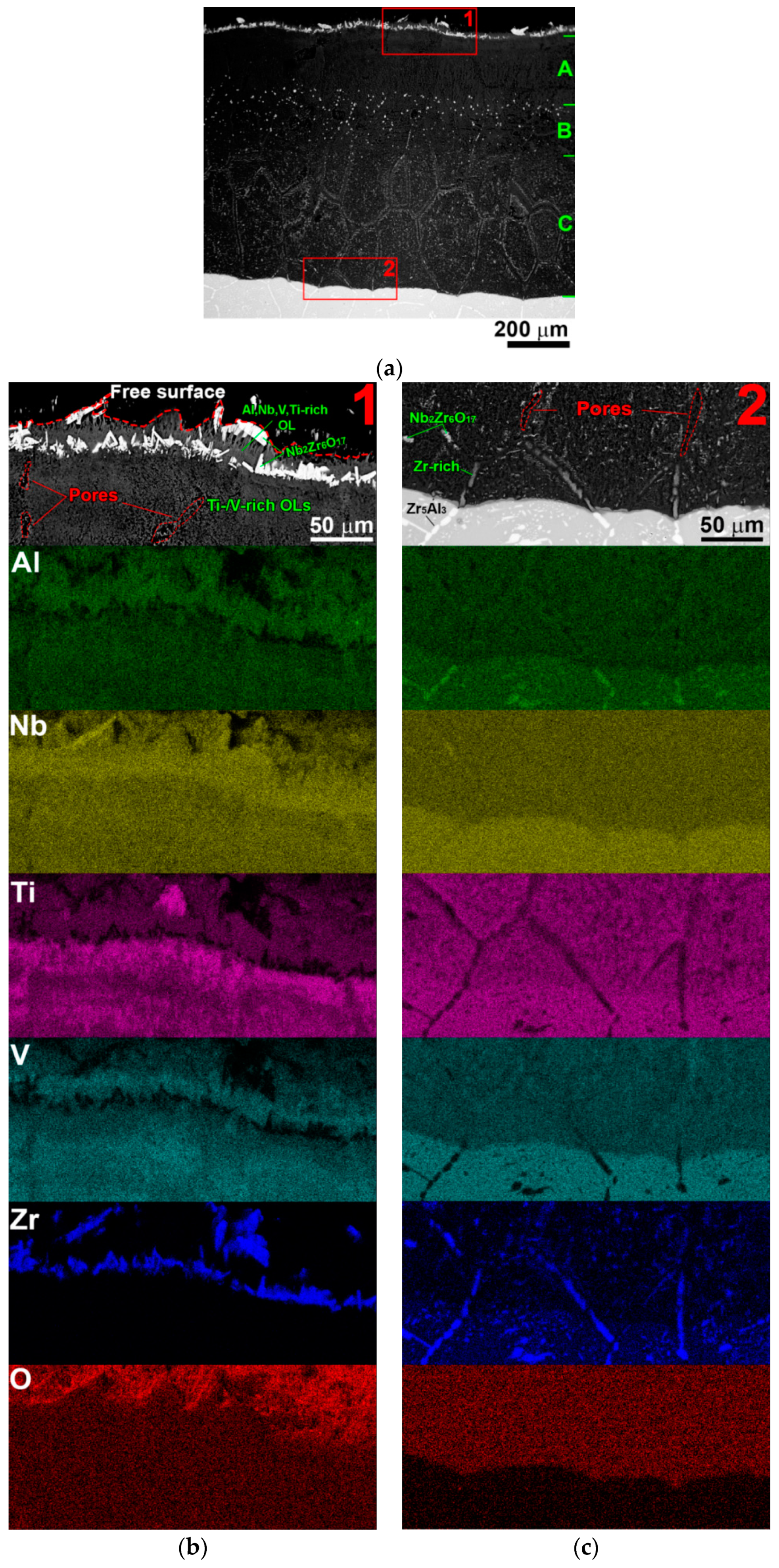
3.4. Cross-Sectional Morphologies
4. Discussion
4.1. Oxidation Kinetics and Mechanisms
4.2. Comparison with the Conventional Alloys and other RHEAs
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- At 600–700 °C, two-stage oxidation kinetics was found. Nearly parabolic oxidation (n = 0.46–0.48) at the first stage transitioned to breakaway oxidation (n = 0.75–0.72) at the second stage. The breakaway oxidation was induced by spallation of the oxide scale due to the nucleation of voluminous Nb2O5 and TiNb2O7 oxides at 600 °C, and probably connected with the partial evaporation of the V2O5 oxide at 700 °C. At the end of the test (100 h), the surface layers consisted of the V2O5, VO2, TiO2, Nb2O5, TiNb2O7 oxides at 600 °C, and the V2O5, VO2, TiO2, Nb2O5, TiNb2O7, ZrO2, AlNbO4, Nb2Zr6O17 oxides at 700 °C.
- (2)
- At 800 °C, the oxidation kinetics was nearly linear (n = 0.92). The main reason for severe oxidation were the pores, which served as places for accelerated ingress of oxygen toward the bare metal, and appeared as a result of the evaporation of V-rich oxides, and the formation of a mixture of the complex unprotective TiNb2O7, AlNbO4, Nb2Zr6O17 oxides from the very beginning of oxidation. The same oxidation mechanisms were assumed to act at 900 °C that led to the disintegration of the specimen after 50 h.
- (3)
- The oxidation resistance of the alloy can be compared with some V-based/contained alloys. The specific mass gains were estimated to be 7.2, 38.1, and 107.5, and 225.5 mg/cm2 at 600, 700, and 800 °C for 100 h, and 900 °C for 50 h, respectively.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Senkov, O.N.; Wilks, G.B.; Miracle, D.B.; Chuang, C.P.; Liaw, P.K. Refractory high-entropy alloys. Intermetallics 2010, 18, 1758–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkov, O.N.; Wilks, G.B.; Scott, J.M.; Miracle, D.B. Mechanical properties of Nb25Mo25Ta25W25 and V20Nb20Mo20Ta20W20 refractory high entropy alloys. Intermetallics 2011, 19, 698–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miracle, D.B.; Senkov, O.N. A critical review of high entropy alloys and related concepts. Acta Mater. 2017, 122, 448–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhou, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, B.; Lv, Y.; Yang, W.; Xu, D.; Liu, Y. A review on fundamental of high entropy alloys with promising high-temperature properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 760, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkov, O.N.; Miracle, D.B.; Chaput, K.J.; Couzinie, J.-P. Development and exploration of refractory high entropy alloys—A review. J. Mater. Res. 2018, 33, 3092–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkov, O.N.; Woodward, C.F. Microstructure and properties of a refractory NbCrMo0.5Ta0.5TiZr alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 529, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkov, O.N.; Senkova, S.V.; Miracle, D.B.; Woodward, C. Mechanical properties of low-density, refractory multi-principal element alloys of the Cr-Nb-Ti-V-Zr system. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 565, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkov, O.N.; Senkova, S.V.; Woodward, C. Effect of aluminum on the microstructure and properties of two refractory high-entropy alloys. Acta Mater. 2014, 68, 214–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, N.N.; Wang, L.; Luo, L.S.; Li, X.Z.; Su, Y.Q.; Guo, J.J.; Fu, H.Z. Microstructure and mechanical properties of refractory MoNbHfZrTi high-entropy alloy. Mater. Des. 2015, 81, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, C.C.; Tsai, M.H.; Tsai, C.W.; Lin, C.M.; Wang, W.R.; Yang, C.C.; Chen, S.K.; Lin, S.J.; Yeh, J.W. Enhanced mechanical properties of HfMoTaTiZr and HfMoNbTaTiZr refractory high-entropy alloys. Intermetallics 2015, 62, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurchenko, N.Y.; Stepanov, N.D.; Shaysultanov, D.G.; Tikhonovsky, M.A.; Salishchev, G.A. Effect of Al content on structure and mechanical properties of the AlxCrNbTiVZr (x = 0; 0.25; 0.5; 1) high-entropy alloys. Mater. Charact. 2016, 121, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.D.; Chen, N.; Zhao, S.F.; Fan, L.W.; Yang, G.N.; Shao, Y.; Yao, K.F. Effect of Ti additions on mechanical properties of NbMoTaW and VNbMoTaW refractory high entropy alloys. Intermetallics 2017, 84, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Kauffmann, A.; Gorr, B.; Schliephake, D.; Seemüller, C.; Wagner, J.N.; Christ, H.J.; Heilmaier, M. Microstructure and mechanical properties at elevated temperatures of a new Al-containing refractory high-entropy alloy Nb-Mo-Cr-Ti-Al. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 661, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Senkov, O.N.; Scott, J.M.; Senkova, S.V.; Miracle, D.B.; Woodward, C.F. Microstructure and room temperature properties of a high-entropy TaNbHfZrTi alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 6043–6048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.D.; Cai, Y.H.; Wang, T.; Si, J.J.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Y.D.; Hui, X.D. A refractory Hf25Nb25Ti25Zr25 high-entropy alloy with excellent structural stability and tensile properties. Mater. Lett. 2014, 130, 277–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, S.; Shafeie, S.; Hu, Q.; Ahlström, J.; Persson, C.; Veselý, J.; Zýka, J.; Klement, U.; Guo, S. Alloy design for intrinsically ductile refractory high-entropy alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 120, 164902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Juan, C.-C.; Tseng, K.-K.; Hsu, W.-L.; Tsai, M.-H.; Tsai, C.-W.; Lin, C.-M.; Chen, S.-K.; Lin, S.-J.; Yeh, J.-W. Solution strengthening of ductile refractory HfMoxNbTaTiZr high-entropy alloys. Mater. Lett. 2016, 175, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Si, J.; Lin, D.; Wang, T.; Wang, W.Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Hui, X. Phase stability and mechanical properties of AlHfNbTiZr high-entropy alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 724, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkov, O.N.; Semiatin, S.L. Microstructure and properties of a refractory high-entropy alloy after cold working. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 649, 1110–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkov, O.N.; Pilchak, A.L.; Semiatin, S.L. Effect of Cold Deformation and Annealing on the Microstructure and Tensile Properties of a HfNbTaTiZr Refractory High Entropy Alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2018, 49, 2876–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Ni, S.; Liu, Y.; Song, M. Effects of cold rolling and subsequent annealing on the microstructure of a HfNbTaTiZr high-entropy alloy. J. Mater. Res. 2016, 31, 3815–3823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, C.-C.; Tsai, M.-H.; Tsai, C.-W.; Hsu, W.-L.; Lin, C.-M.; Chen, S.-K.; Lin, S.-J.; Yeh, J.-W. Simultaneously increasing the strength and ductility of a refractory high-entropy alloy via grain refining. Mater. Lett. 2016, 184, 200–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkov, O.N.; Senkova, S.V.; Dimiduk, D.M.; Woodward, C.; Miracle, D.B. Oxidation behavior of a refractory NbCrMo0.5Ta0.5TiZr alloy. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 6522–6534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.M.; Wang, H.M.; Zhang, S.Q.; Tang, H.B.; Zhang, A.L. Microstructure and oxidation behavior of new refractory high entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 583, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorr, B.; Azim, M.; Christ, H.J.; Mueller, T.; Schliephake, D.; Heilmaier, M. Phase equilibria, microstructure, and high temperature oxidation resistance of novel refractory high-entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 624, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorr, B.; Mueller, F.; Christ, H.-J.; Mueller, T.; Chen, H.; Kauffmann, A.; Heilmaier, M. High temperature oxidation behavior of an equimolar refractory metal-based alloy 20Nb20Mo20Cr20Ti20Al with and without Si addition. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 688, 468–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorr, B.; Müller, F.; Azim, M.; Christ, H.-J.; Müller, T.; Chen, H.; Kauffmann, A.; Heilmaier, M. High-Temperature Oxidation Behavior of Refractory High-Entropy Alloys: Effect of Alloy Composition. Oxid. Met. 2017, 88, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Butler, T.M.; Chaput, K.J.; Dietrich, J.R.; Senkov, O.N. High temperature oxidation behaviors of equimolar NbTiZrV and NbTiZrCr refractory complex concentrated alloys (RCCAs). J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 729, 1004–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, S.; Bijaksana, M.K.; Motallebzadeh, A.; Shafeie, S.; Lozinko, A.; Gan, L.; Tsao, T.-K.; Klement, U.; Canadinc, D.; Murakami, H.; et al. Accelerated oxidation in ductile refractory high-entropy alloys. Intermetallics 2018, 97, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaraj, J.; Thirathipviwat, P.; Han, J.; Gebert, A. Microstructure, mechanical and thermal oxidation behavior of AlNbTiZr high entropy alloy. Intermetallics 2018, 100, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Titus, M.S.; Yeh, J. Oxidation Behavior between 700 and 1300 °C of Refractory TiZrNbHfTa High-Entropy Alloys Containing Aluminum. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2018, 20, 1700948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, S.; Gan, L.; Tsao, T.; Murakami, H.; Shafeie, S.; Guo, S. Aluminizing for enhanced oxidation resistance of ductile refractory high-entropy alloys. Intermetallics 2018, 103, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waseem, O.A.; Auyeskhan, U.; Lee, H.M.; Ryu, H.J. A combinatorial approach for the synthesis and analysis of AlxCryMozNbTiZr high-entropy alloys: Oxidation behavior. J. Mater. Res. 2018, 33, 3226–3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurchenko, N.Y.; Stepanov, N.D.; Zherebtsov, S.V.; Tikhonovsky, M.A.; Salishchev, G.A. Structure and mechanical properties of B2 ordered refractory AlNbTiVZrx (x = 0–1.5) high-entropy alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 704, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurchenko, N.Y.; Stepanov, N.D.; Gridneva, A.O.; Mishunin, M.V.; Salishchev, G.A.; Zherebtsov, S.V. Effect of Cr and Zr on phase stability of refractory Al-Cr-Nb-Ti-V-Zr high-entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 757, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birks, N.; Meier, G.; Pettit, F. Introduction to the High Temperature Oxidation of Metals, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006; ISBN 9781139163903. [Google Scholar]
- Bose, M.; Basu, A. 51V NMR of the layered δ-LiV2O5. J. Solid State Chem. 1989, 81, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oka, Y.; Sato, S.; Yao, T.; Yamamoto, N. Crystal Structures and Transition Mechanism of VO2(A). J. Solid State Chem. 1998, 141, 594–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-W.; Enomoto, N.; Nakagawa, Z.; Kawamura, K. Molecular Dynamic Simulation in Titanium Dioxide Polymorphs: Rutile, Brookite, and Anatase. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1996, 79, 1095–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercit, T.S. Refinement of the Structure of ζ-Nb2O5 and Its Relationship to the Rutile and Thoreaulite Structures. Mineral. Petrol. 1991, 43, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasperin, M. Affinement de la structure de TiNb2O7 et répartition des cations. J. Solid State Chem. 1984, 53, 144–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, C.J.; Hill, R.J. The polymorphs of zirconia: Phase abundance and crystal structure by Rietveld analysis of neutron and X-ray diffraction data. J. Mater. Sci. 1991, 26, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greis, O.; Ziel, R.; García, D.E.; Claussen, N.; Breidenstein, B.; Haase, A. Crystal Structure and Morphology of Disordered AINbO4 from X-Ray Powder Diffraction. Mater. Sci. Forum 1996, 228–231, 825–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galy, J.; Roth, R.S. The crystal structure of Nb2Zr6O17. J. Solid State Chem. 1973, 7, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korb, L.J.; Olson, D.L. Volume 13A: Corrosion: Fundamentals, Testing, and Protection. In ASM Handbook; ASM International Committee: Geauga, OH, USA, 1987; pp. 1–3455. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, B.G.; Kim, G.M.; Kim, C.J. Oxidation Behavior of TiAI-X (X = Cr, V, Si, Mo or Nb) Intermetallics at Elevated Temperature. Scr. Metall. Mater. 1995, 33, 1117–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shida, Y.; Anada, H. The Effect of Various Ternary Additives on the Oxidation Behavior of TiAl in High-Temperature Air. Oxid. Met. 1996, 45, 197–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.B.; Jang, Y.D. High Temperature Oxidation of Ti39.4Al10V Alloy. Mater. Sci. Forum 2004, 452, 813–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D. Effect of Cr, Nb, Mn, V, W and Si on High Temperature Oxidation of TiAl Alloys. Met. Mater. Int. 2005, 11, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveed, M.; Renteria, A.F.; Weiß, S. Role of alloying elements during thermocyclic oxidation of β/γ-TiAl alloys at high temperatures. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 691, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapp, R.A. Kinetics, Microstructures and Mechanism of Internal Oxidation-Its Effect and Prevention in High Temperature Alloy Oxidation. Corrosion 1965, 21, 382–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parida, S.C.; Gupta, N.K.; Krishnan, K.; Rao, G.A.R.; Sen, B.K. High-Temperature Oxidation of β-NbTi Alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2008, 39, 2020–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H. Effect of Nb on the high temperature oxidation of Ti-(0–50 at.%)Al. Scr. Mater. 2002, 46, 639–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralison, A.; Dettenwanger, F.; Schütze, M. Oxidation of orthorhombic Ti2AlNb alloys at 800 °C in air. Mater. Corros. 2000, 328, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyens, C. Environmental Effects on Orthorhombic Alloy Ti-22Al-25Nb in Air between 650 and 1000 °C. Oxid. Met. 2000, 54, 475–503. [Google Scholar]
- Leyens, C. Oxidation of Orthorhombic Titanium Aluminide Ti-22Al-25Nb in Air between 650 and 1000 °C. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2001, 10, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y. Oxidation behavior of a novel multi-element alloyed Ti2AlNb- based alloy in temperature range of 650–850 °C. Rare Met. 2018, 37, 838–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Hou, X.; Wang, X.; Meng, Y.; Zheng, X.; Zheng, L. Isothermal oxidation mechanism of a newly developed Nb-Ti-V-Cr-Al-W-Mo-Hf alloy at 800–1200 °C. Int J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2016, 54, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, J.G. The High-Temperature Oxidation Behavior of Vanadium-Aluminum Alloys. Oxid. Met. 1991, 36, 439–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natesan, K.; Uz, M. Oxidation performance of V-Cr-Ti alloys. Fusion Eng. Des. 2000, 52, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krüger, M. High temperature compression strength and oxidation of a V-9Si-13B alloy. Scr. Mater. 2016, 121, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, G.; Yao, K.; Bai, P.; Cheng, C.; Min, X. High Temperature Oxidation and Wear Behaviors of Ti–V–Cr Fireproof Titanium Alloy. Metals 2017, 7, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bania, P.J. Next Generation Titanium Alloys for Elevated Temperature Service. ISIJ Int. 1991, 31, 840–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haanappel, V.A.C.; Clemens, H.; Stroosnijder, M.F. The high temperature oxidation behaviour of high and low alloyed TiAl-based intermetallics. Intermetallics 2002, 10, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyens, C.; Gedanitz, H. Long-Term Oxidation of Orthorhombic Alloy Ti-22Al-25Nb in Air between 650 and 800 °C. Scr. Mater. 1999, 41, 901–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, N.; Shahid, K.A.; Khan, I.H.; Rahman, S. Oxidation of High-Temperature Alloys (Superalloys) at Elevated Temperatures in Air. II. Oxid. Met. 1995, 43, 363–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
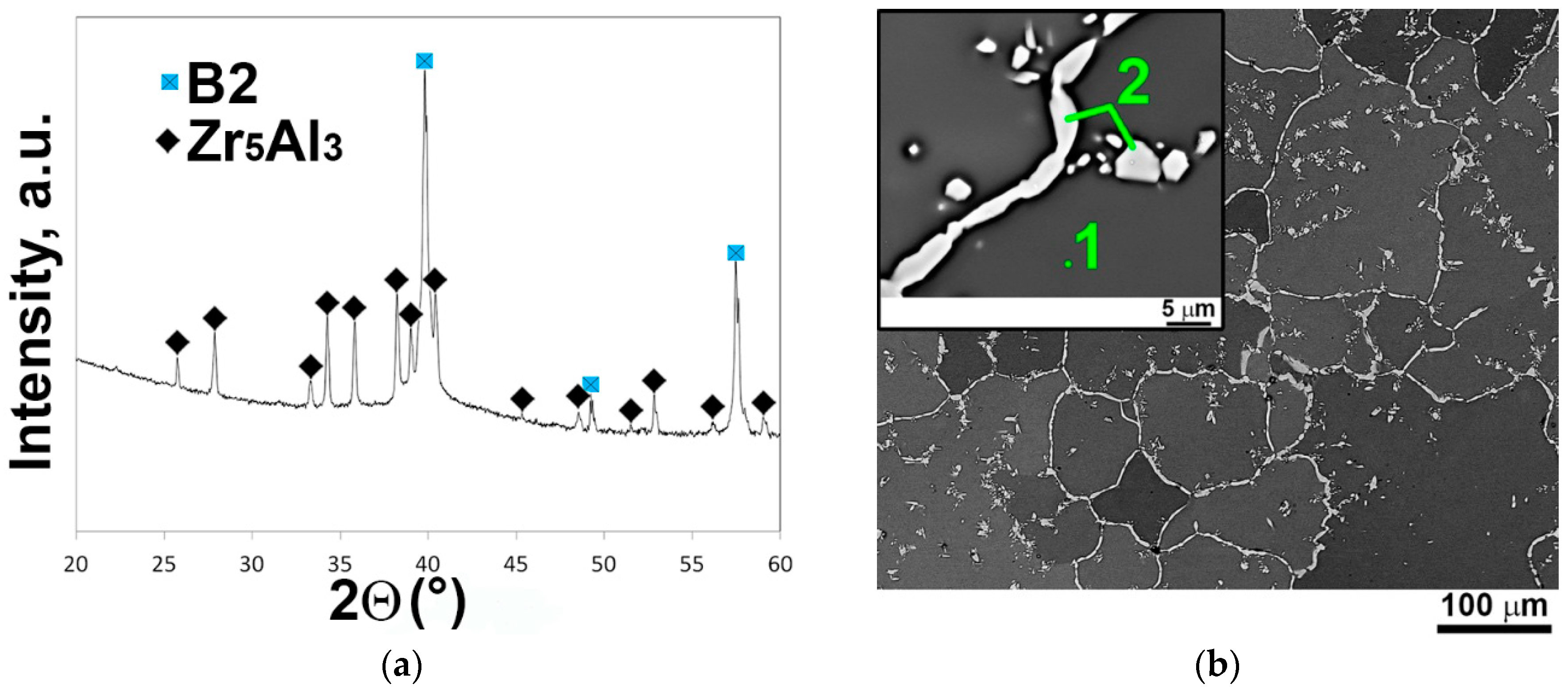



| Elements (аt.%) | Al | Nb | Ti | V | Zr | Volume Fraction (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Constituents | |||||||
| No. | Designation | ||||||
| 1 | Grains | 24.0 | 23.1 | 25.2 | 23.1 | 4.6 | 95 ± 2 |
| 2 | Light-gray particles (Zr5Al3 phase) | 38.2 | 14.0 | 11.4 | 4.4 | 32.0 | 5 ± 1 |
| Alloy composition | 25.0 | 22.4 | 24.0 | 21.9 | 6.7 | - | |
| Oxides | TiO2 | V2O5 | Nb2O5 | VO2 | ZrO2 | TiNb2O7 | AlNbO4 | Nb2Zr6O17 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lattice parameter (nm) | a = 0.4593, c = 0.2959 [39] | a = 0.3565, b = 1.1500, c = 0.4372 [37] | a = 1.2740, b = 0.4883, c = 0.5561 [40] | a = 0.8440, c = 0.7666 [38] | a = 0.5152, b = 0.5208, c = 0.5320 [42] | a = 2.0351, b = 0.3801, c = 1.1882 [41] | a = 1.2157, b = 0.3736, c = 0.6490 [43] | a = 4.0910, b = 0.4930, c = 0.5270 [44] |
| Temperature (°C) | ||||||||
| 600 | + 1 | + | + | + | − 2 | + | − | − |
| 700 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 800 | − | − | − | + | + | + | + | + |
| 900 (50 h) | − | − | − | − | − | + | + | + |
| Elements (аt.%) | Al | Nb | Ti | V | Zr | O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 h | ||||||
| 600 °C | 14.1 | 12.7 | 12.8 | 14.7 | 1.1 | 44.6 |
| 800 °C | 15.9 | 11.0 | 9.7 | 23.1 | 1.2 | 39.1 |
| 100 h | ||||||
| 600 °C | 3.6 | 4.4 | 4.6 | 27.9 | 0.6 | 58.9 |
| 800 °C | 13.7 | 12.8 | 17.1 | 12.2 | 1.0 | 43.2 |
| Temperature | 600 °C | 700 °C | 800 °C | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AlNbTiVZr0.25 | 7.2 | 38.1 | 107.5 | This study |
| AlNbTiZr | 1.3 1 | 5.6 1 | 8.8 1 | [30] |
| TiZrNbHfTa | - | 55 | - | [31] |
| Al0.3TiZrNbHfTa | - | 14 | - | [31] |
| Al0.5TiZrNbHfTa | - | 14 | - | [31] |
| Al0.75TiZrNbHfTa | - | 11 | - | [31] |
| AlTiZrNbHfTa | - | 10 | - | [31] |
| Al9.2Cr5.7Hf0.5Mo1.3Nb47.0Ti25.9V9.6W0.8 | - | - | 20 1 | [58] |
| V-30Al | - | 30 | 84 | [59] |
| V-30Al-10Cr | - | 6 | 31 | [59] |
| V-30Al-10Ti | - | 12 | 29 | [59] |
| V-5Cr-5Ti | ~4.5 | - | - | [59] |
| V-9Si-13B | ~3 | - | - | [61] |
| Ti-35.5V-14.6Cr-0.32Si-0.11C | - | - | 90 | [62] |
| Ti-6Al-4V | - | - | 40 | [62] |
| Grade 2 | - | - | 26.1 2 | [63] |
| Ti-15V-3Cr-3Sn-3Al | - | - | 174.0 2 | [63] |
| Ti-42Al-8V-(2-4)Mo | - | 6.7 3 | 92.3 3 | [50] |
| Ti-48Al-2Cr-2Nb | - | - | 0.9 | [64] |
| Ti-22Al-25Nb | - | - | 1.1 | [65] |
| Inconel 690 | - | - | 0.1 | [66] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yurchenko, N.; Panina, E.; Zherebtsov, S.; Salishchev, G.; Stepanov, N. Oxidation Behavior of Refractory AlNbTiVZr0.25 High-Entropy Alloy. Materials 2018, 11, 2526. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11122526
Yurchenko N, Panina E, Zherebtsov S, Salishchev G, Stepanov N. Oxidation Behavior of Refractory AlNbTiVZr0.25 High-Entropy Alloy. Materials. 2018; 11(12):2526. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11122526
Chicago/Turabian StyleYurchenko, Nikita, Evgeniya Panina, Sergey Zherebtsov, Gennady Salishchev, and Nikita Stepanov. 2018. "Oxidation Behavior of Refractory AlNbTiVZr0.25 High-Entropy Alloy" Materials 11, no. 12: 2526. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11122526
APA StyleYurchenko, N., Panina, E., Zherebtsov, S., Salishchev, G., & Stepanov, N. (2018). Oxidation Behavior of Refractory AlNbTiVZr0.25 High-Entropy Alloy. Materials, 11(12), 2526. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11122526







