Optimization of Thermoplastic Blend Matrix HDPE/PLA with Different Types and Levels of Coupling Agents
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Tensile Tests
2.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.3. Quartering
2.4. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.5. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
2.6. Attenuated Total Reflection–Fourier Transform Infrared (ATR–FTIR) Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Tensile Tests
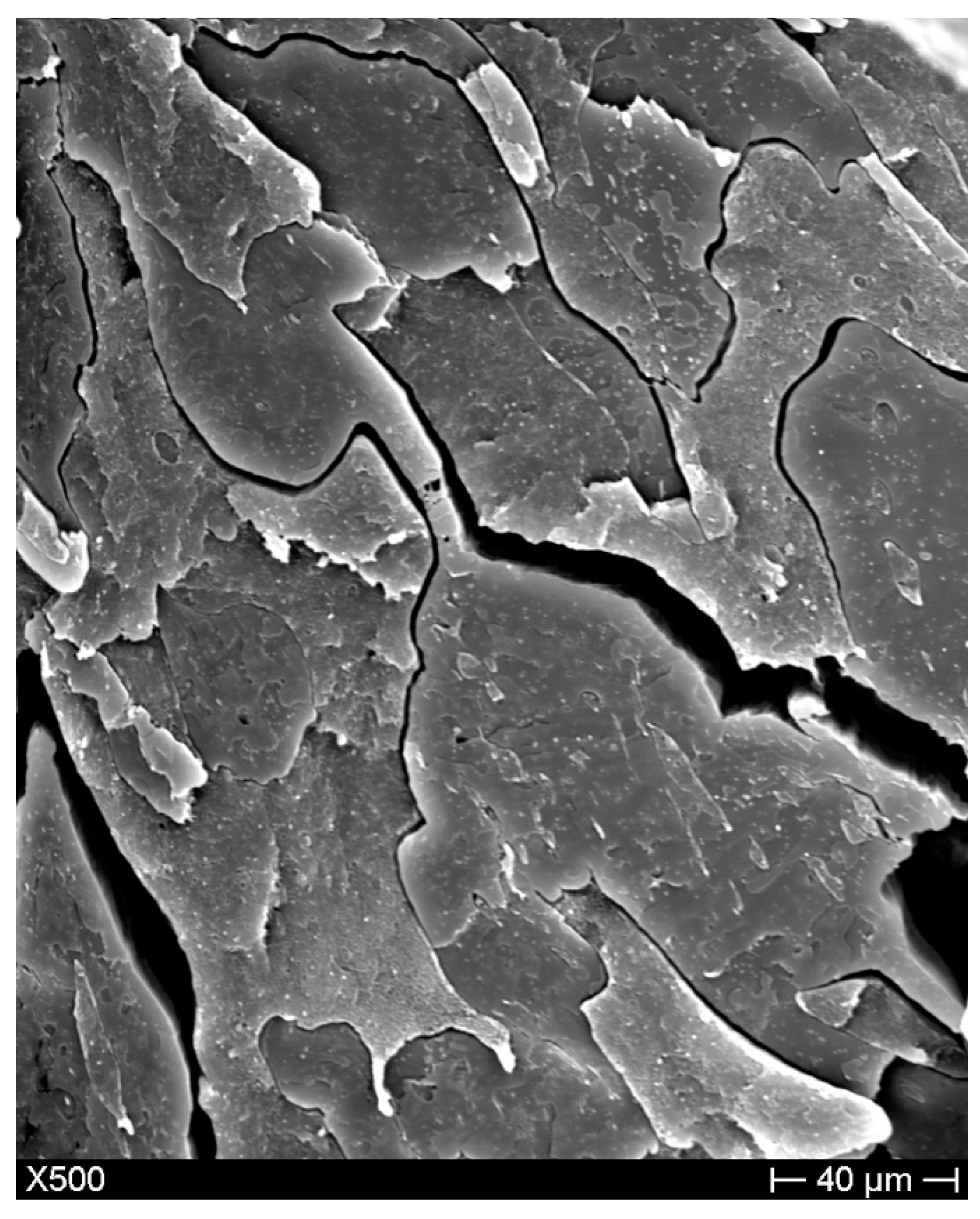
3.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
3.4. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
3.5. Attenuated Total Reflection–Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (ATR–FTIR)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Polypetchara, N.; Suppakul, P.; Atong, D.; Pechyen, C. Blend of polypropylene/poly(lactic acid) for medical packaging application: Physicochemical, thermal, mechanical, and barrier properties. Energy Proced. 2014, 56, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parameswaranpillai, J.; Thomas, S.; Grohens, Y. (Eds.) Polymer blends: State of the art, new challenges and opportunities. In Characterization of Polymer Blend, 1st ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Higgins, J.A.; Lipson, J.E.G.; White, R.P. A simple approach to polymer mixture miscibility. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2010, 368, 1009–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utracki, L.A. Compatibilization of Polymer Blends. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2008, 80, 1008–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, S. Polymeric Compatibilizers: Uses and Benefits in Polymer Blends; John Wiley & Sons: Akron, OH, USA, 1997; ISSN 00359475. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.F.; Choi, C.N.; Kim, Y.D.; Lee, K.Y.; Lee, M.S. Compatibilization of immiscible poly(L-lactide) and low density polyethylene blends. Fiber Polym. 2004, 5, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quitadamo, A.; Massardier, V.; Valente, M. Oil-based/Bio-Derived Thermoplastic Polymer Blends and Composites. In Introduction to Renewable Biomaterials: First Principles and Concepts; Lucia, L., Ayoub, A., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 239–268. [Google Scholar]
- Ebnesajjad, S. Handbook of Biopolymers and Biodegradable Plastics, 1st ed.; William Andrew, Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2013; ISBN 978-4557-2834-3. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Romain, C.; Williams, C.K. Sustainable polymers from renewable resources. Nature 2016, 540, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ermolovich, O.A.; Makarevich, A.V. Effect of Compatibilizer Additives on the Technological and Performance Characteristics of Biodegradable materials based on starch-filled polyethylene. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2006, 79, 1526–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quitadamo, A.; Massardier, V.; Valente, M. Interactions between PLA, PE and wood flour: Effects of compatibilizing agents and ionic liquid. Holzforschung 2017, 72, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luyt, A.S. Polyolefin Blends. In Polyolefin Compounds and Materials, 1st ed.; AlMa’adeed, M., Krupa, I., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; ISBN 978–3-319-25980-2. [Google Scholar]
- Baiardo, M.; Frisoni, G.; Scandola, M.; Rimelen, M.; Lips, D.; Ruffieux, K.; Wintermantel, E. Thermal and Mechanical Properties of Plasticized Poly(L-lactic acid). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 90, 1731–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekonnen, T.; Mussone, P.; Khalil, H.; Bressler, D. Progress in bio-based plastics and plasticizing modifications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 13379–13398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javadi, E.; Babaei, A.; Nouri, M. Correlation of the morphological and mechanical properties of a biodegradable blend based on polylactic acid. J. Macromol. Sci. B 2017, 56, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamad, K.; Kaseem, M.; Ayyoob, M.; Joo, J.; Deri, F. Polylactic acid blends: The future of green, light and tough. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2018, 85, 83–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiroz-Castillo, J.M.; Rodriguez-Felix, D.E.; Grijalva-Monteverde, H.; Lizarraga-Laborin, L.L.; Castillo-Ortega, M.M.; Castillo-Castro, T.; Rodriguez-Felix, F.; Herrera-Franco, P.J. Preparation and characterization of films extruded of polyethylene/Chitosan modified with poly(lactic acid). Materials 2015, 8, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madhu, G.; Bhunia, H.; Bajpai, P.K.; Nando, G.B. Physico-mechanical properties and biodegradation of oxo-degradable HDPE/PLA blends. Polym. Sci. A 2016, 58, 57–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sailaja, R.P.N.; Chanda, M. Use of Maleic Anhydride Grafted Polyethylene as Compatibilizer for HDPE Tapioca Starch Blends: Effects on Mechanical Properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2001, 80, 863–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiroz-Castillo, J.M.; Rodrigues-Felix, D.E.; Grijalva, H.; Castillo-Castro, T.; Plascencia-Jatomea, M.; Rodriguez-Felix, F.; Herrera-Franco, P. Preparation of extruded polyethylene/chitosan blends compatibilized with polyethylene-graft-maleic anhydride. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 101, 1094–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djellali, S.; Haddaoui, N.; Saoun, T.; Bergeret, A.; Grohens, Y. Structural, morphological and mechanical characteristics of polyethylene, poly(lactic acid) and poly(ethylene-co-glycidyl methacrylate) blends. Iran Polym. J. 2013, 22, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.B.; Li, K.A.; Du, A.K. Compatibilization strategies in poly(lactic acid)-based blends. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 32546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farah, S.; Anderson, D.G.; Langer, R. Physical and mechanical properties of PLA, and their functions in widespread applications-A comprehensive review. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 107, 367–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ljungberg, N.; Wesslen, B. The effects of plasticizers on the dynamic mechanical and thermal properties of poly(lactic acid). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2002, 86, 1227–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Tang, L.; Wang, L.; Zhao, J.; Li, D.; Wu, Z.; Ziao, P. Morphology and properties of bio-based poly(lactic acid)/High-density polyethylene blends and their glass fiber reinforced composites. Polym. Test. 2016, 54, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhu, G.; Bhunia, H.; Bajpai, P.K. Blends of high density polyethylene and poly(L-lactic acid): Mechanical and thermal properties. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2014, 59, 2155–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego, R.; Lopez-Quintana, S.; Basurto, F.; Nunez, K.; Villarreal, N.; Merino, J.C. Synthesis of new compatibilizers to poly(lactic acid) blends. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2014, 54, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurber, C.M.; Xu, Y.; Myers, J.C.; Lodge, T.P.; Macosko, C.W. Accelerating reactive compatibilization of PE/PLA blends by an interfacially localized catalyst. ACS Macro Lett. 2015, 4, 30–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregorova, A. Application of Differential Scanning Calorimetry to the Characterization of Biopolymers; World’s Largest Science, Technology & Medicine Open Access book publisher A Study of the Porosity of Activated Carbons Using the Scanning Electron Microscope; INTECH Open Access Publisher: Rijeka, Croatia; pp. 3–20.
- Anstey, A.; Codou, A.; Misra, M.; Mohanty, A.K. Novel Compatibilized Nylon-Based Ternary Blends with Polypropylene and Poly(lactic acid): Fractionated Crystallization Phenomena and Mechanical Performance. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 2845–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhu, G.; Mandal, D.K.; Bhunia, H.; Bajpai, P.K. Thermal degradation kinetics and lifetime of high-density polyethylene/poly(L-lactic acid) blends. J. Thermoplast. Compos. 2017, 30, 773–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salzano de Luna, M.; Filippone, G. Effects of nanoparticles on the morphology of immiscible polymer blends—Challenges and opportunities. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Samples | HDPE (%) | PLA (%) | Polybond 3029 (%) | Lotader AX8840 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HDPE70/PLA30 | 70 | 30 | ||
| HDPE50/PLA50 | 50 | 50 | ||
| HDPE30/PLA70 | 30 | 70 | ||
| HDPE50/PLA50-Poly1 | 49.5 | 49.5 | 1 | |
| HDPE50/PLA50-Poly3 | 48.5 | 48.5 | 3 | |
| HDPE50/PLA50-Poly5 | 47.5 | 47.5 | 5 | |
| HDPE50/PLA50-Lot1 | 49.5 | 49.5 | 1 | |
| HDPE50/PLA50-Lot3 | 48.5 | 48.5 | 3 | |
| HDPE50/PLA50-Lot5 | 47.5 | 47.5 | 5 |
| Samples | E (GPa) | σ (MPa) | ε (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| HDPE | 1.16 ± 0.08 | 21.59 ± 0.18 | >400 |
| PLA | 3.04 ± 0.02 | 57.34 ± 1.00 | 7.1 ± 0.3 |
| HDPE70/PLA30 | 1.51 ± 0.05 | 30.76 ± 0.73 | >400 |
| HDPE50/PLA50 | 1.88 ± 0.05 | 38.73 ± 0.18 | 99.4 ± 2.1 |
| HDPE30/PLA70 | 2.41 ± 0.05 | 49.51 ± 0.60 | 2.3 ± 0.5 |
| Samples | E (GPa) | σ (MPa) | ε (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| HDPE50/PLA50 | 1.88 ± 0.05 | 38.73 ± 0.18 | 99.4 ± 2.1 |
| HDPE50/PLA50-Poly1 | 2.24 ± 0.76 | 43.30 ± 2.76 | 86.2 ± 17.3 |
| HDPE50/PLA50-Poly3 | 2.31 ± 0.14 | 42.80 ± 2.65 | 71.9 ± 46.9 |
| HDPE50/PLA50-Poly5 | 1.92 ± 0.03 | 39.74 ± 0.41 | 34.1 ± 13.1 |
| HDPE50/PLA50-Lot1 | 2.18 ± 0.21 | 40.70 ± 3.99 | 175.3 ± 84.2 |
| HDPE50/PLA50-Lot3 | 2.14 ± 0.07 | 41.70 ± 1.93 | 193.0 ± 59.1 |
| HDPE50/PLA50-Lot5 | 1.75 ± 0.13 | 34.28 ± 1.52 | 173.2 ± 56.2 |
| ΔHccPLA | Tcc | ΔHmPE | TmPE | ΔHmPLA | TmPLA | TgPLA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (J/gPLA) | (°C) | (J/gPE) | (°C) | (J/gPLA) | (°C) | (°C) | |
| HDPE | - | - | 215 | 134 | - | - | - |
| PLA | 7 | 98 | - | - | 41 | 168 | 61 |
| HDPE50/PLA50 | 8 | 97 | 226 | 132 | 40 | 168 | 62 |
| ΔHccPLA | Tcc | ΔHmPE | TmPE | ΔHmPLA | TmPLA | TgPLA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (J/gPLA) | (°C) | (J/gPE) | (°C) | (J/gPLA) | (°C) | (°C) | |
| HDPE50/PLA50 | 8 | 97 | 236 | 132 | 40 | 168 | 62 |
| HDPE50/PLA50-Poly1 | 15 | 94 | 195 | 132 | 45 | 168 | 61 |
| HDPE50/PLA50-Poly3 | 15 | 100 | 190 | 132 | 41 | 168 | 61 |
| HDPE50/PLA50-Poly5 | 16 | 101 | 198 | 132 | 41 | 168 | 61 |
| HDPE50/PLA50-Lot1 | 20 | 103 | 192 | 132 | 40 | 168 | 61 |
| HDPE50/PLA50-Lot3 | 21 | 103 | 182 | 132 | 41 | 168 | 61 |
| HDPE50/PLA50-Lot5 | 20 | 104 | 192 | 132 | 36 | 168 | 61 |
| Tonset (°C) | TDTG (°C) | ∆m (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| HDPE | 458 | 474 | 100 |
| PLA | 319 | 351 | 100 |
| Poly | 459 | 480 | 100 |
| Lot | 434 | 464 | 100 |
| HDPE50/PLA50 | 322 | 345/471 | 100 |
| HDPE50/PLA50-Poly1 | 316 | 351/444 | 100 |
| HDPE50/PLA50-Poly3 | 322 | 358/438 | 100 |
| HDPE50/PLA50-Poly5 | 313 | 342/432 | 100 |
| HDPE50/PLA50-Lot1 | 325 | 350/470 | 100 |
| HDPE50/PLA50-Lot3 | 325 | 350/468 | 100 |
| HDPE50/PLA50-Lot5 | 334 | 351/474 | 100 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Quitadamo, A.; Massardier, V.; Santulli, C.; Valente, M. Optimization of Thermoplastic Blend Matrix HDPE/PLA with Different Types and Levels of Coupling Agents. Materials 2018, 11, 2527. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11122527
Quitadamo A, Massardier V, Santulli C, Valente M. Optimization of Thermoplastic Blend Matrix HDPE/PLA with Different Types and Levels of Coupling Agents. Materials. 2018; 11(12):2527. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11122527
Chicago/Turabian StyleQuitadamo, Alessia, Valérie Massardier, Carlo Santulli, and Marco Valente. 2018. "Optimization of Thermoplastic Blend Matrix HDPE/PLA with Different Types and Levels of Coupling Agents" Materials 11, no. 12: 2527. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11122527
APA StyleQuitadamo, A., Massardier, V., Santulli, C., & Valente, M. (2018). Optimization of Thermoplastic Blend Matrix HDPE/PLA with Different Types and Levels of Coupling Agents. Materials, 11(12), 2527. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11122527







