Ultrasonic Vibration Facilitates the Micro-Formability of a Zr-Based Metallic Glass
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Setup and Procedure
2.1. Materials
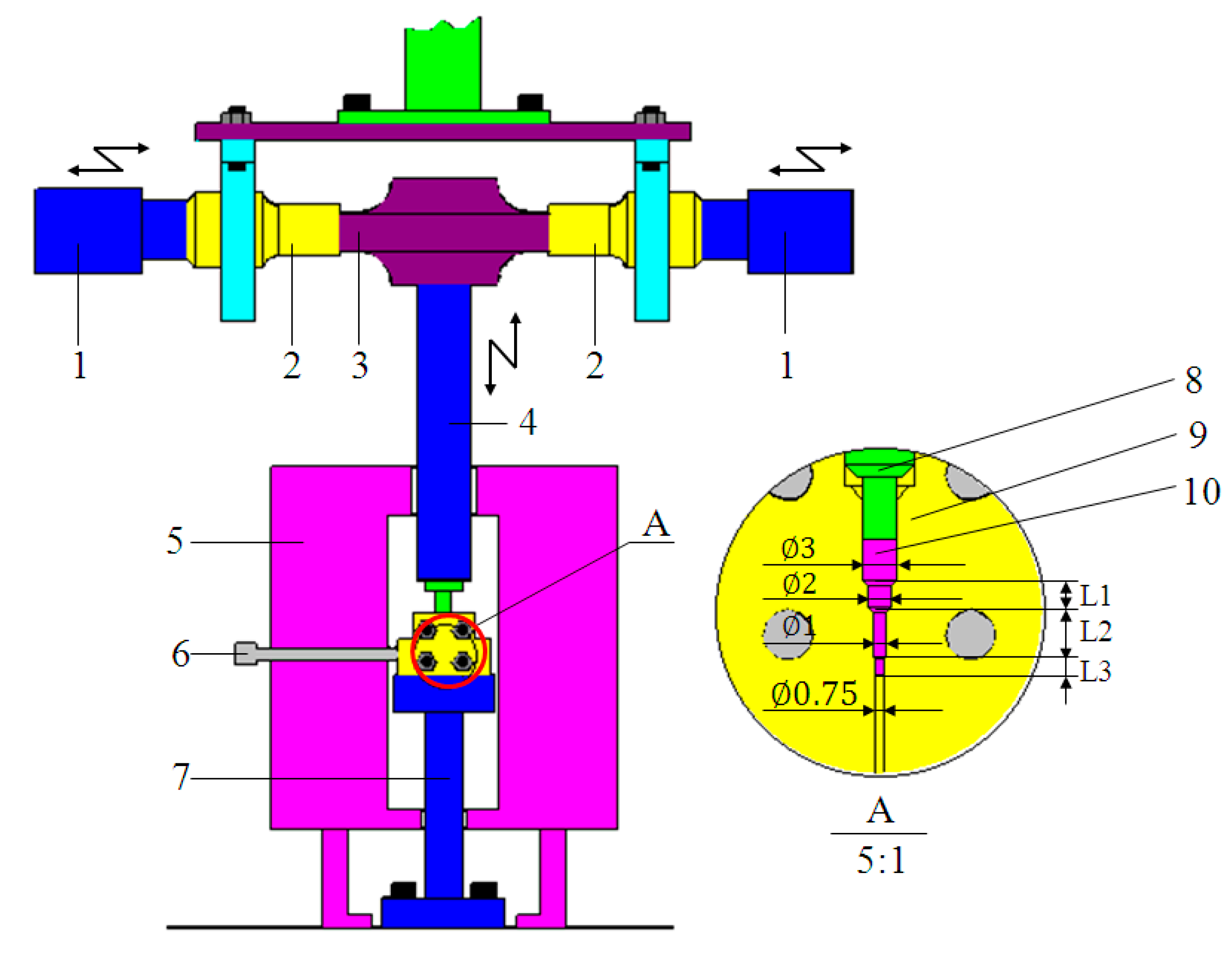
2.2. Ultrasonic Microextrusion System
3. Results
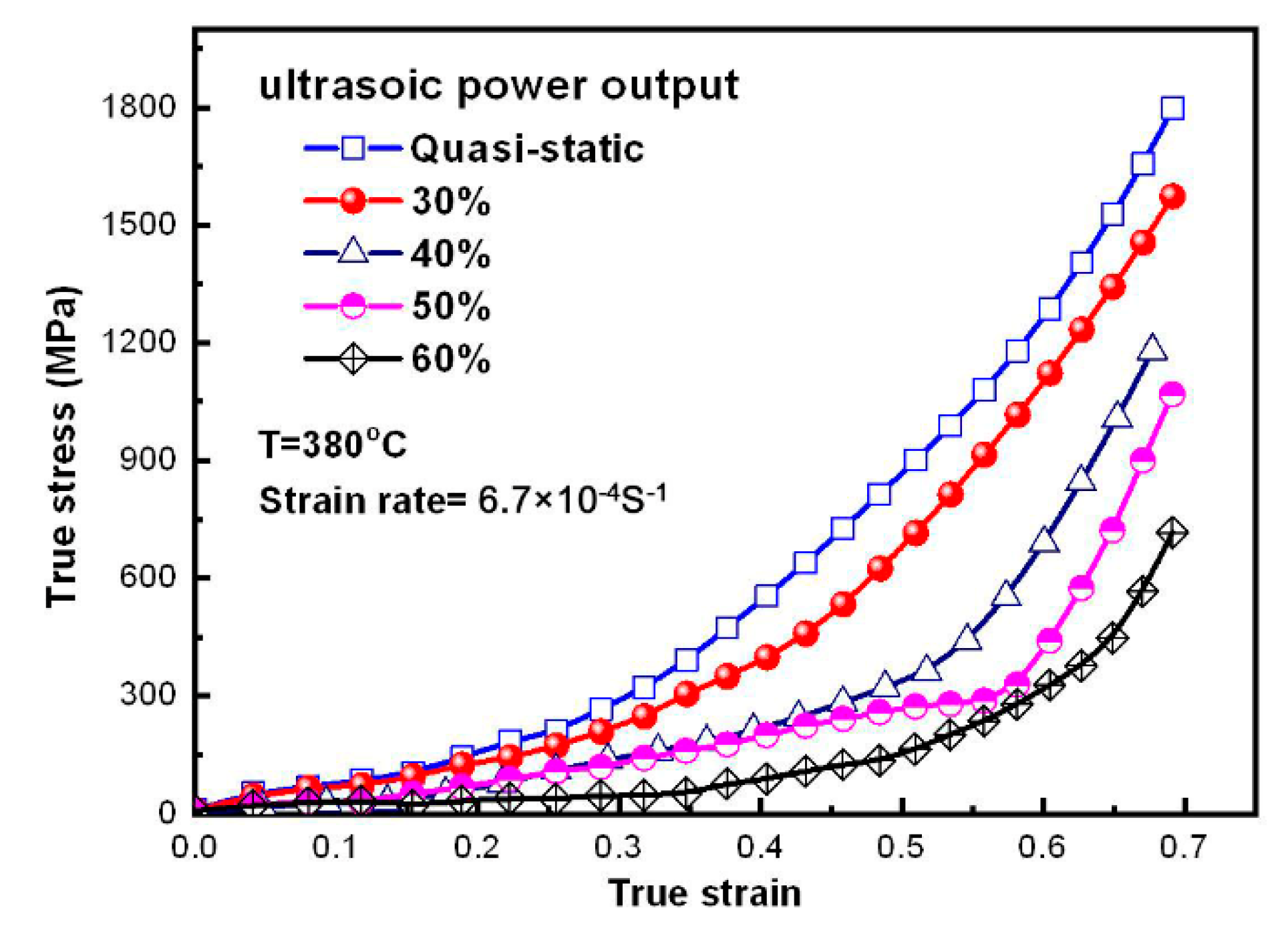
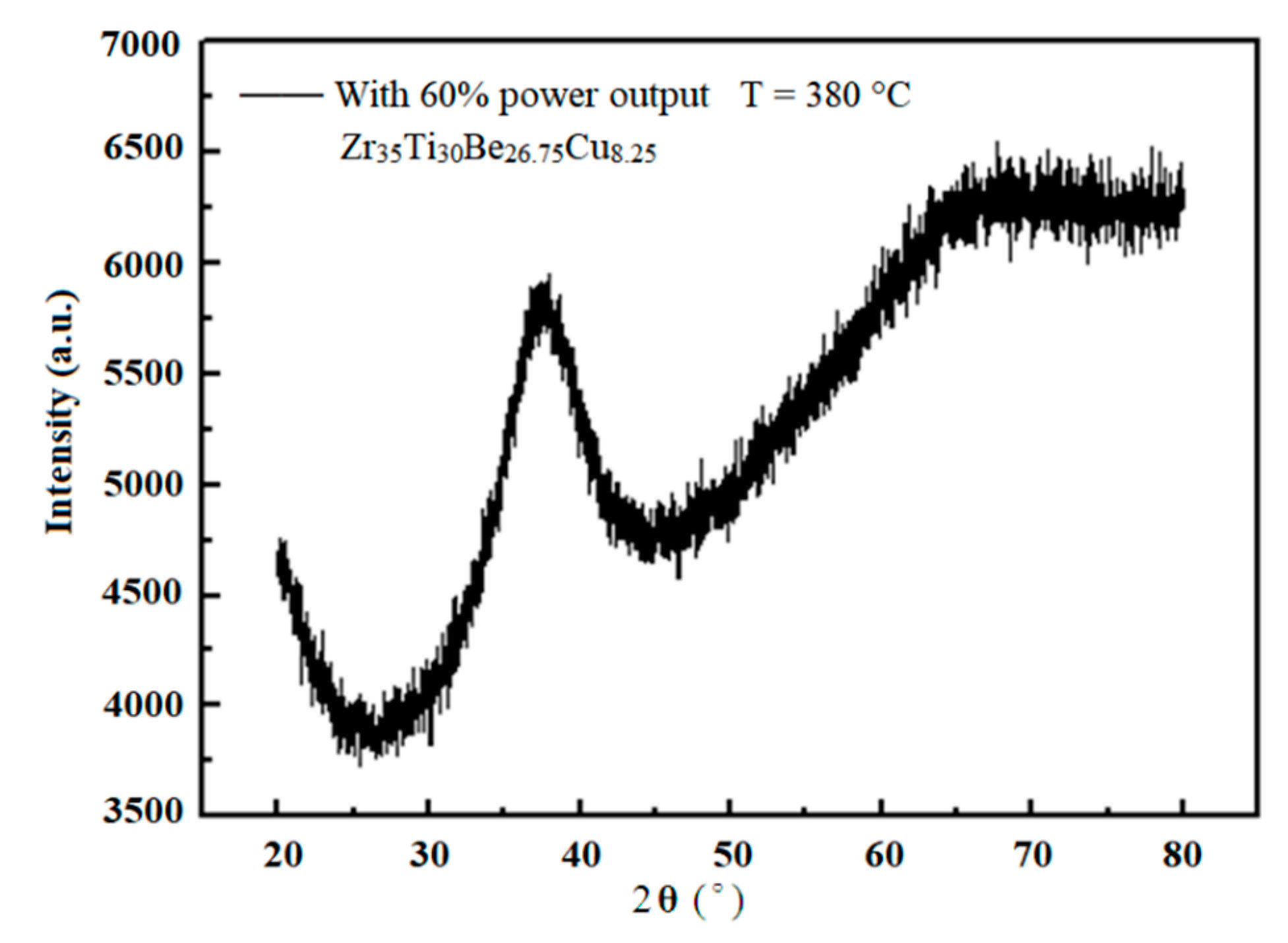
3.1. Effect of Ultrasonic Power Output
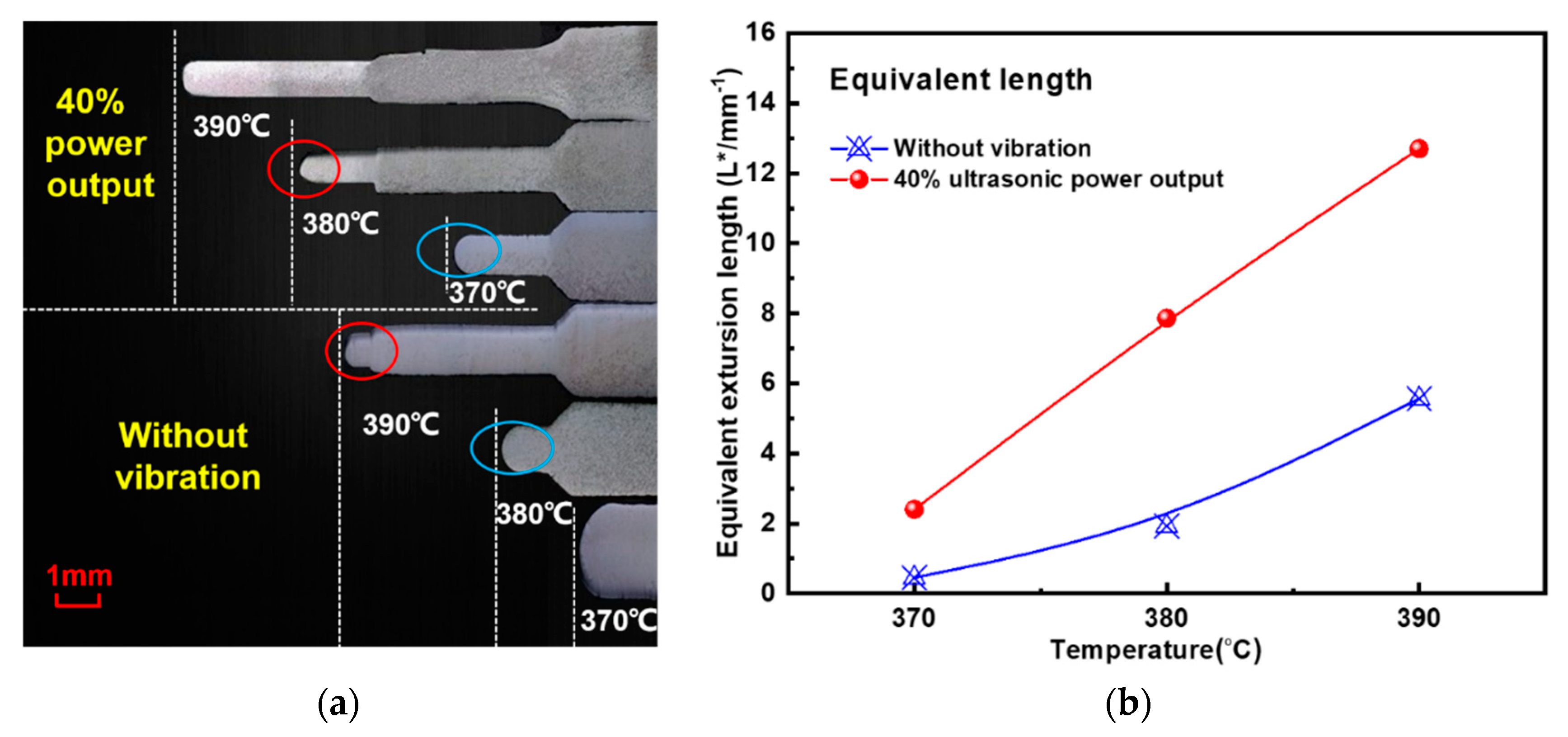
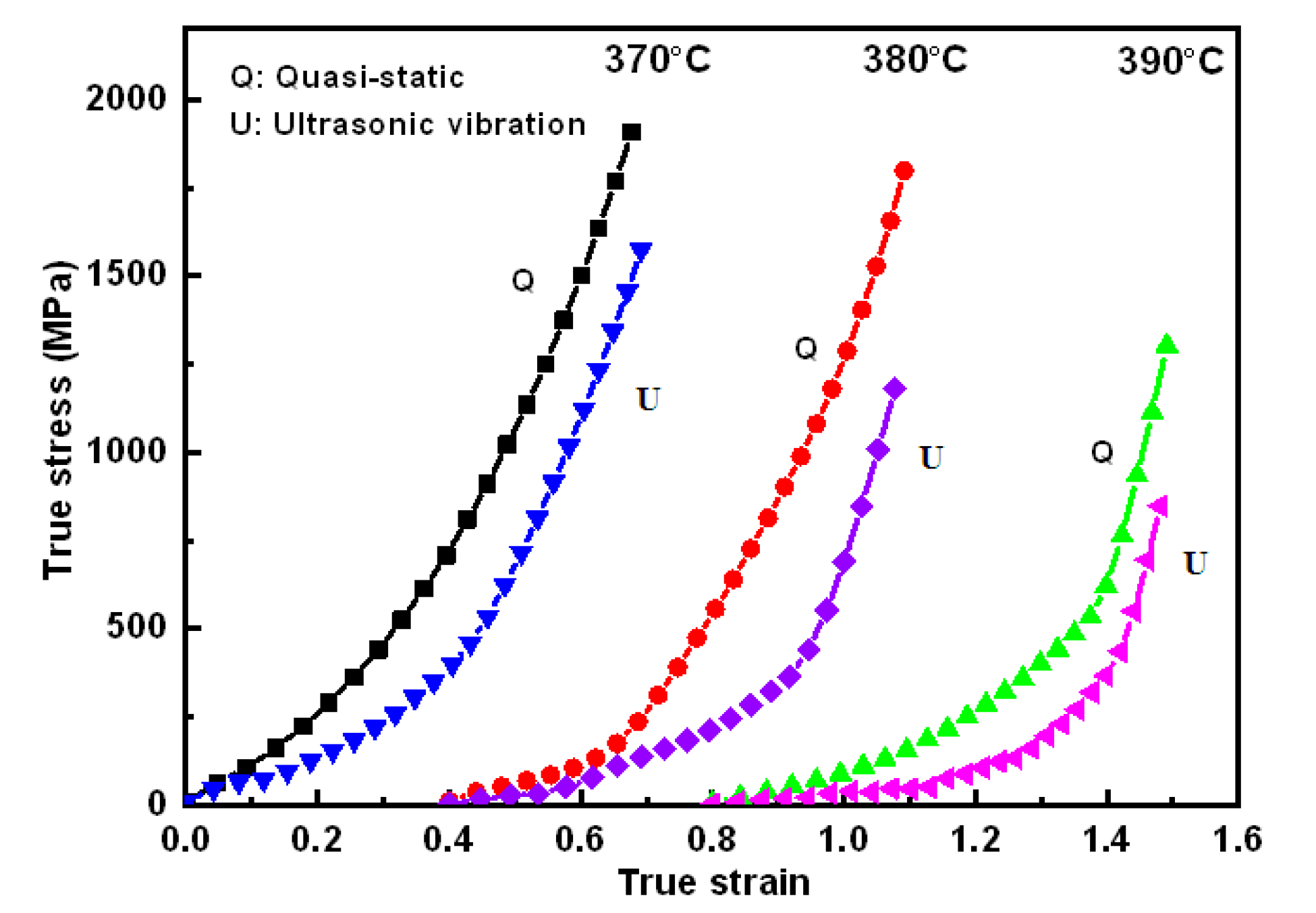
3.2. Ultrasonic Loading under Various Temperatures
3.3. Effect of Microextrusion Rate
4. Discussion
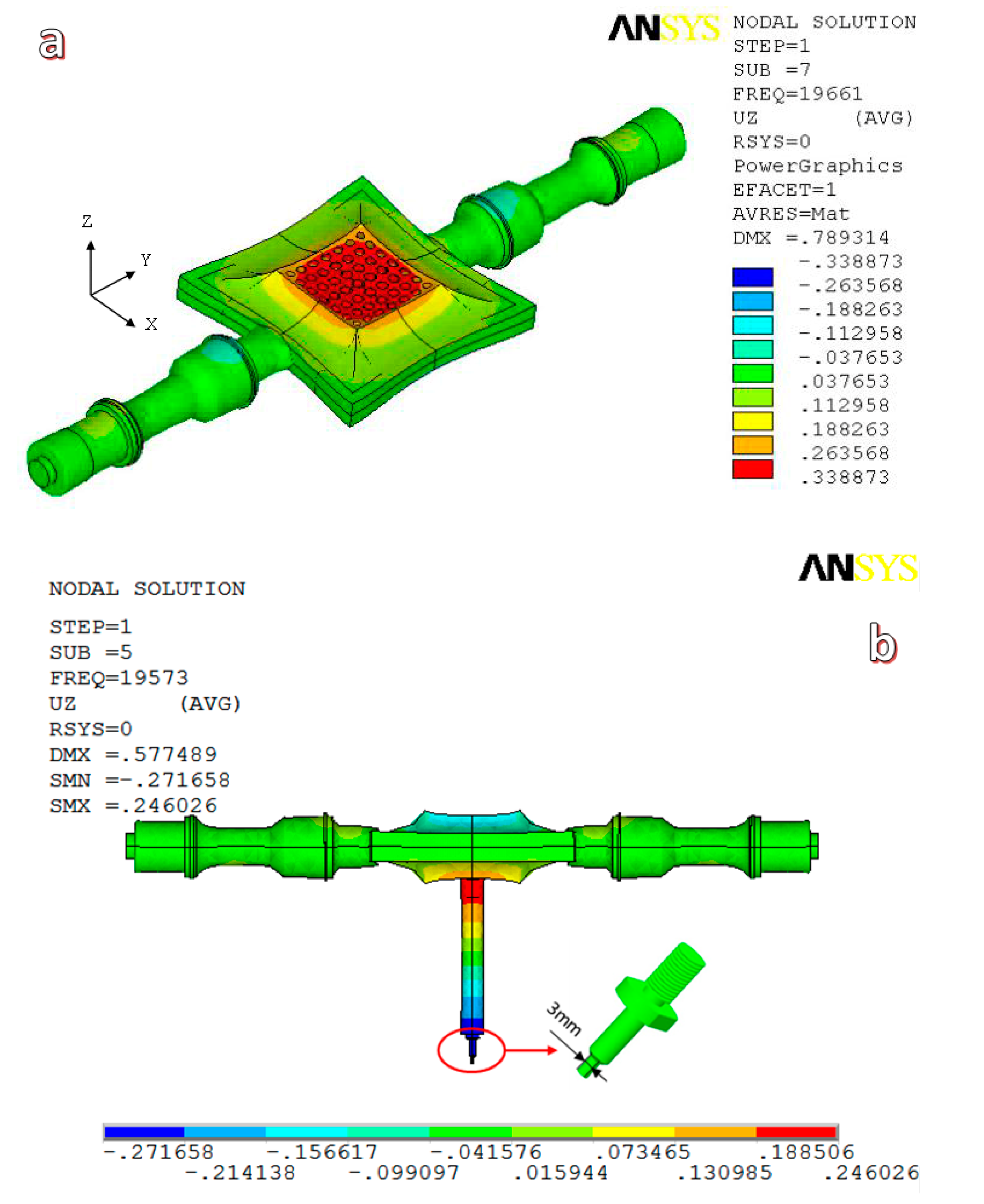
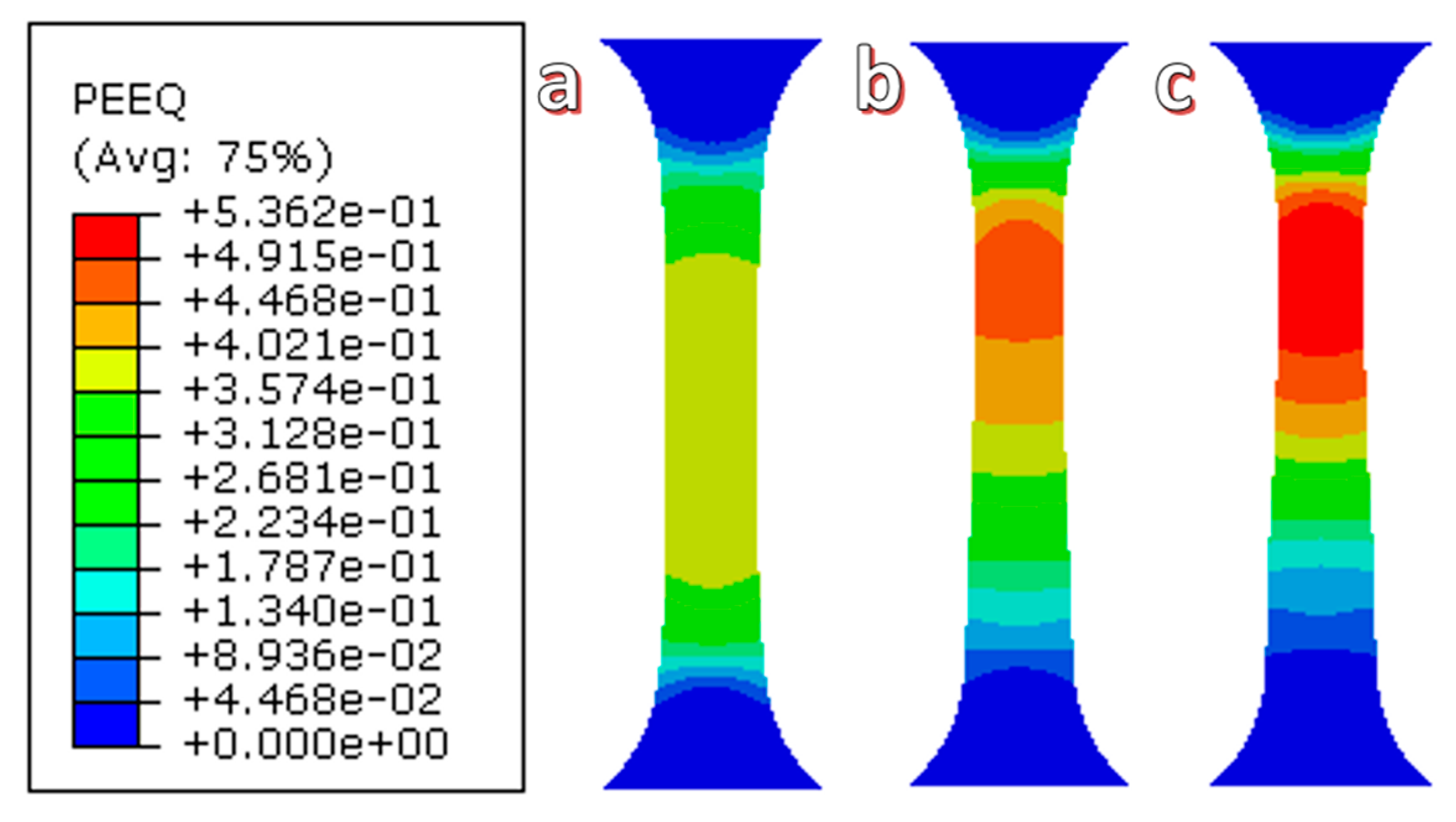
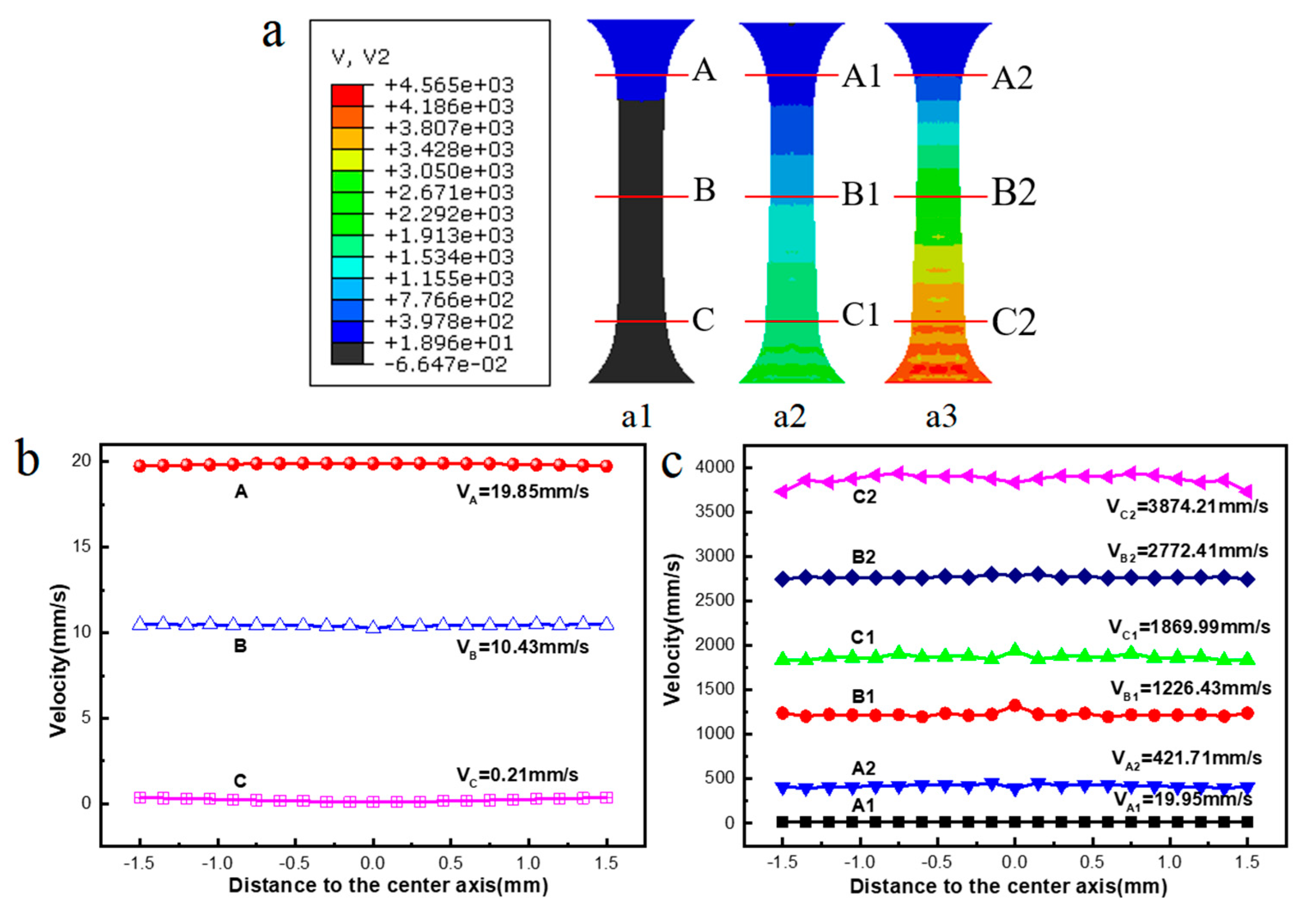
5. FEM Analysis
6. Conclusions
- Ultrasonic vibration is an effective method to improve the thermoplastic microformability of MGs by superimposing the assisted ultrasonic vibration onto the microextrusion tool.
- With increasing ultrasonic power output, the equivalent microfilling length of Zr35 can be increased by 11-fold, and the true stress can be decreased by 60.17%.
- Sufficient ultrasonic power output (>30%), which means a sufficiently large ultrasonic vibration amplitude of the microextrusion tool, is the essential condition to obtain better microformability of Zr35, which can be successfully packed into a circular slot with a 0.75 mm diameter.
- Ultrasonic vibration of the microextrusion tool can produce a similar effect as temperature increase on improving the microformability of Zr35 in the SCLR.
- Larger ultrasonic vibration amplitudes of the tool can generate more free volume in the plastic microforming process of Zr35 MGs, which can then obtain a higher flow velocity and easier material flow.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khan, M.M.; Nemati, A.; Rahman, Z.U.; Shah, U.H.; Asgar, H.; Haider, W. Recent advancements in bulk metallic glasses and their applications: A review. Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2018, 43, 233–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Chen, W.; Liu, L. Thermoplastic micro-forming of bulk metallic glasses: A review. JOM 2016, 68, 1246–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.C.; Yao, Y.; Pelletier, J.M.; Keer, L.M. Understanding of micro-alloying on plasticity in Cu46Zr47−xAl7Dyx (0 ≤ x ≤ 8) bulk metallic glasses under compression: Based on mechanical relaxations and theoretical analysis. Int. J. Plasticity 2016, 82, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Dai, W.; Zhang, M.; Gong, P.; Li, N. Thermoplastic micro-formability of TiZrHfNiCuBe high entropy metallic glass. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2018, 34, 2006–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Zhang, J.; Xing, W.; Ouyang, D.; Liu, L. 3D printing of Fe-based bulk metallic glass composites with combined high strength and fracture toughness. Mater. Des. 2018, 143, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Xu, X.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, L. Enhanced formability of a Zr-based bulk metallic glass in a supercooled liquid state by vibrational loading. Acta Mater. 2014, 65, 400–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.S.; Kim, S.; Lim, K.R.; Hong, S.H.; Kim, K.B.; Na, Y.S. Crystallization, high temperature deformation behavior and solid-to-solid formability of a Ti-based bulk metallic glass within supercooled liquid region. J. Alloy. Compd. 2016, 663, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhu, F.; Zhang, X.; Ding, J.; Yin, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Kou, S. The rheological behavior and thermoplastic deformation of Zr-based bulk metallic glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2018, 492, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.H.; Kim, J.T.; Mun, S.C.; Kim, Y.S.; Park, H.J.; Na, Y.S.; Lim, K.R.; Park, J.M.; Kim, K.B. Influence of spherical particles and interfacial stress distribution on viscous flow behavior of Ti–Cu–Ni–Zr–Sn bulk metallic glass composites. Intermetallics 2017, 91, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, M.; Li, D.; He, J.; Wu, Y.; Liu, L. A thermoplastic forming map of a Zr-based bulk metallic glass. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 1921–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, W.L.; Kaltenboeck, G.; Demetriou, M.D.; Schramm, J.P.; Liu, X.; Samwer, K.; Kim, C.P.; Hofmann, D.C. Beating crystallization in glass-forming metals by millisecond heating and processing. Science 2011, 332, 828–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaltenboeck, G.; Demetriou, M.D.; Roberts, S.; Johnson, W.L. Shaping metallic glasses by electromagnetic pulsing. Nature Commun. 2016, 7, 10576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martinez, R.; Kumar, G.; Schroers, J. Hot rolling of bulk metallic glass in its supercooled liquid region. Scr. Mater. 2008, 59, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroers, J.; Hodges, T.M.; Kumar, G.; Raman, H.; Barnes, A.J.; Pham, Q.; Waniuk, T.A. Thermoplastic blow molding of metals. Mater. Today 2011, 14, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zheng, Z.; Wu, X.; Li, J. A study on micro-forming ability of Zr55 bulk metallic glass under low frequency vibrating field. J. Plasticity Eng. 2015, 22, 118–124. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Huang, J. The influence of ultrasonic vibration-assisted micro-deep drawing process. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2014, 71, 1455–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Yang, M. Investigation on mechanism of metal foil surface finishing with vibration-assisted micro-forging. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2013, 213, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Li, K.; Peng, Z.; Jin, J.; Sun, M.; Wang, X. A new porous block sonotrode for ultrasonic assisted micro plastic forming. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 89, 2193–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalski, M.; Lechner, M.; Gruber, M.; Merklein, M. Influence of ultrasonic vibration on the shear formability of metallic materials. CIRP Annals 2018, 67, 277–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Ma, J.; Wu, X.Y.; Xu, B.; Gong, F.; Lei, J.G.; Peng, T.J.; Cheng, R. Micro injection of metallic glasses parts under ultrasonic vibration. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2017, 33, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, F.; Sun, F.; Li, K.; Gong, F.; Liang, X.; Wu, X.; Ma, J. Ultrasonic assisted micro-shear punching of amorphous alloy. Mater. Res. Lett. 2018, 6, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, G.; Wiest, A.; Lind, M.L.; Li, J.; Rhim, W.-K.; Johnson, W.L. Bulk metallic glass with benchmark thermoplastic processability. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 4272–4275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Li, K.; Wang, X. A Double Transducer Driving Ultrasonic Vibration Platform. Chinese Patent ZL 201520071898.1, 8 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Chiu, H.M.; Kumar, G.; Blawzdziewicz, J.; Schroers, J. Thermoplastic extrusion of bulk metallic glass. Scr. Mater. 2009, 61, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Kim, G.-Y.; Faidley, L.; Zou, Q.; Mei, D.; Chen, Z. Effects of superimposed high-frequency vibration on deformation of aluminum in micro/meso-scale upsetting. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2012, 212, 640–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Guo, B.; Shan, D.; Zhang, B. Acoustic softening and stress superposition in ultrasonic vibration assisted uniaxial tension of copper foil: Experiments and modeling. Mater. Des. 2016, 112, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Li, N.; Tang, N.; Wang, X.; Zhang, C.; Liu, L. The precision replication of a microchannel mould by hot-embossing a Zr-based bulk metallic glass. Intermetallics 2012, 21, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Wu, X.; Wu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Guo, D.; Lou, Y.; Ruan, S. Microstructure and mechanical properties of ultrafine-grained Al-6061 prepared using intermittent ultrasonic-assisted equal-channel angular pressing. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2017, 26, 5107–5117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Suslov, S.; Han, Q.; Hua, L.; Xu, C. Comparison between ultrasonic vibration-assisted upsetting and conventional upsetting. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2013, 44, 3232–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Li, N.; Liu, L. Intrinsic or extrinsic size-dependent deformation behavior of a Zr-based bulk metallic glass in supercooled liquid state? J. Alloy. Compd. 2014, 589, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Ultrasonic Output Power | First Section Slot Length (L1) (mm) | Second Section Slot Length (L2) (mm) | Third Section Slot Length (L3) (mm) | Whole Extrusion Length (L = L1 + L2 + L3) (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2 | 1.43 | 0 | 3.43 |
| 30% | 2 | 3.72 | 0 | 5.72 |
| 40% | 2 | 4 | 1.89 | 7.89 |
| 50% | 2 | 4 | 6.66 | 12.66 |
| 60% | 2 | 4 | 9.42 | 15.42 |
| Extrusion Length and Temperature | Without Ultrasonic Vibration | With 40% Ultrasonic Output Power | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supercooled liquid temperature (°C) | 370 | 380 | 390 | 370 | 380 | 390 |
| First section length (L1/mm) | 1.81 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 |
| Second section length (L2/mm) | 0 | 1.43 | 4.00 | 1.90 | 4.00 | 4.00 |
| Third section length (L3/mm) | 0 | 0 | 0.60 | 0 | 1.89 | 4.61 |
| Whole extrusion length (L = L1 + L2 + L3/mm) | 1.81 | 3.43 | 6.60 | 3.90 | 7.89 | 10.61 |
| Extrusion Rate and Length | Without Ultrasonic Vibration | With 40% Ultrasonic Output Power | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microextrusion rate (mm/min) | 0.12 | 0.24 | 0.36 | 0.12 | 0.24 | 0.36 |
| First section length (L1/mm) | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 |
| Second section length (L2/mm) | 3.02 | 1.93 | 0.78 | 4.00 | 4.00 | 3.93 |
| Third section length (L3/mm) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4.68 | 2.39 | 0 |
| Whole extrusion length (L = L1 + L2 + L3/mm) | 5.02 | 3.93 | 2.78 | 10.68 | 8.39 | 5.93 |
| Ultrasonic Power Output | Ultrasonic Amplitudes ξH13 (μm) | Energy Density En (kJ/m3) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 30% | 12 | 7.41 |
| 40% | 16 | 13.173 |
| 50% | 20 | 20.583 |
| 60% | 24 | 29.64 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, G.; Peng, Z.; Xu, L.; Li, N. Ultrasonic Vibration Facilitates the Micro-Formability of a Zr-Based Metallic Glass. Materials 2018, 11, 2568. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11122568
Han G, Peng Z, Xu L, Li N. Ultrasonic Vibration Facilitates the Micro-Formability of a Zr-Based Metallic Glass. Materials. 2018; 11(12):2568. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11122568
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Guangchao, Zhuo Peng, Linhong Xu, and Ning Li. 2018. "Ultrasonic Vibration Facilitates the Micro-Formability of a Zr-Based Metallic Glass" Materials 11, no. 12: 2568. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11122568
APA StyleHan, G., Peng, Z., Xu, L., & Li, N. (2018). Ultrasonic Vibration Facilitates the Micro-Formability of a Zr-Based Metallic Glass. Materials, 11(12), 2568. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11122568






