Load-Bearing Capacity and Retention of Newly Developed Micro-Locking Implant Prosthetic System: An In Vitro Pilot Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
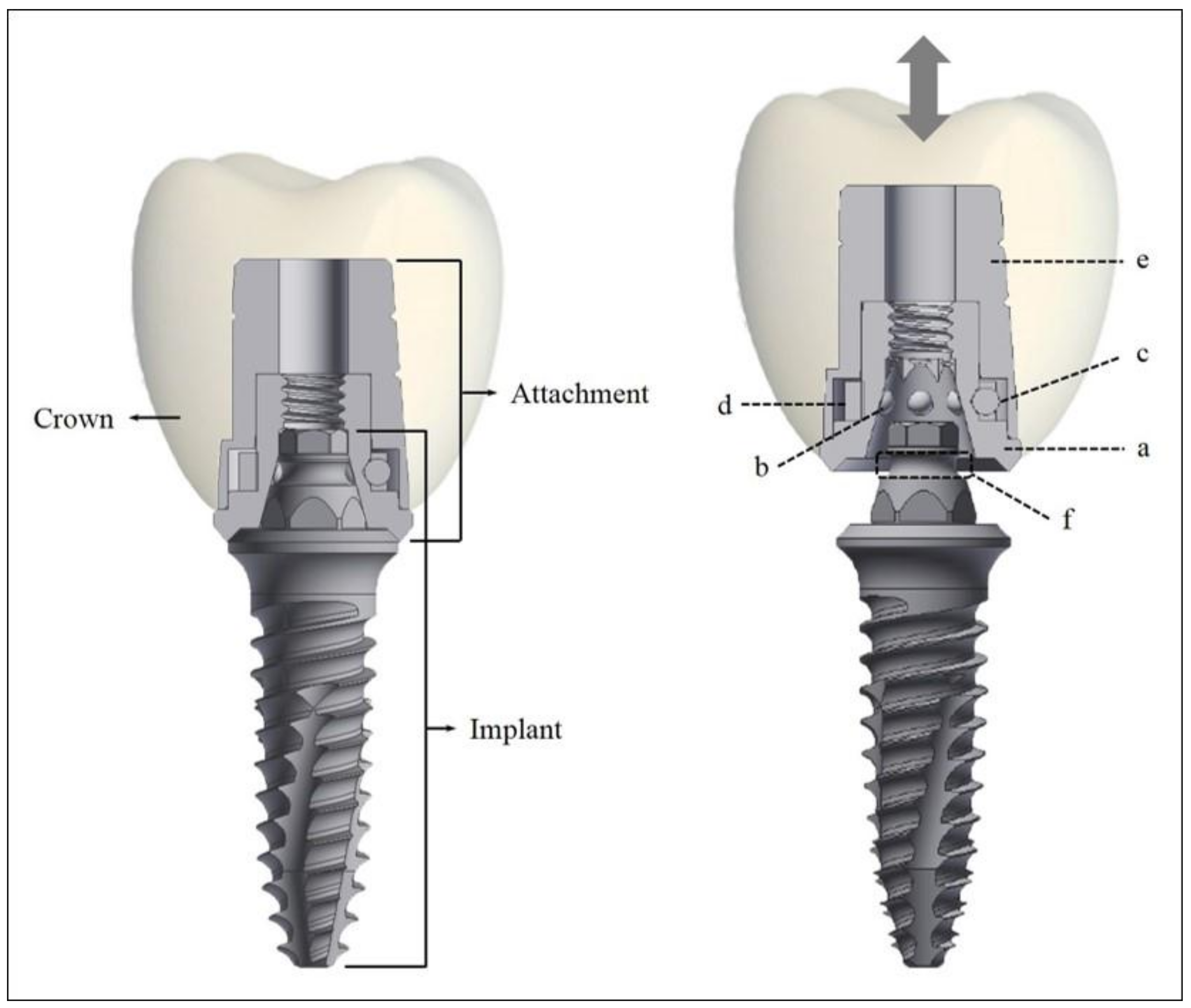
2.1. Micro-Locking Implant Prosthetic System
2.2. Load-Bearing Capacity
2.3. Effect of Structure Modifications on the Retention of the Micro-Locking Implant Prosthetic System
2.4. Effect of Compressive Cyclic Loading on the Retention of the Micro-Locking Implant Prosthetic System
3. Results
3.1. Load-Bearing Capacity
3.2. Effect of Structure Modifications on the Retention of the Micro-Locking Implant Prosthetic System
3.3. Effect of Compressive Cyclic Loading on the Retention of the Micro-Locking Implant Prosthetic System
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wittneben, J.G.; Joda, T.; Weber, H.P.; Brägger, U. Screw retained vs. cement retained implant-supported fixed dental prosthesis. Periodontology 2000 2017, 73, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adell, R.; Lekholm, U.; Rockler, B.; Brånemark, P.I. A 15-year study of osseointegrated implants in the treatment of the edentulous jaw. Int. J. Oral. Surg. 1981, 10, 387–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, T.D.; Agar, J.R. Twenty years of progress in implant prosthodontics. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2002, 88, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, R.A.; Clem, D.; Beagle, J.; Ganeles, J.; Johnson, P.; Solnit, G.; Keller, G.W. Multicenter retrospective analysis of the solid-screw ITI implant for posterior single-tooth replacements. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Implants 2002, 17, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McGlumphy, E.A.; Mendel, D.A.; Holloway, J.A. Implant screw mechanics. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 1998, 42, 71–89. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Michalakis, K.X.; Hirayama, H.; Garefis, P.D. Cement-retained versus screw-retained implant restorations: A critical review. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Implants 2003, 18, 719–728. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pietrabissa, R.; Gionso, L.; Quaglini, V.; Di Martino, E.; Simion, M. An in vitro study on compensation of mismatch of screw versus cement-retained implant supported fixed prostheses. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2000, 11, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Covey, D.A.; Kent, D.K.; St Germain, H.A., Jr.; Koka, S. Effects of abutment size and luting cement type on the uniaxial retention force of implant-supported crowns. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2000, 83, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chee, W.; Felton, D.A.; Johnson, P.F.; Sullivan, D.Y. Cemented versus screw-retained implant prostheses: Which is better? Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Implants 1999, 14, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wittneben, J.G.; Millen, C.; Brägger, U. Clinical performance of screw- versus cement-retained fixed implant-supported reconstructions—A systematic review. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Implants 2014, 29, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebel, K.S.; Gajjar, R.C. Cement-retained versus screw-retained implant restorations: Achieving optimal occlusion and esthetics in implant dentistry. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1997, 77, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Fenton, A. Screw- versus cement-retained implant prostheses: A systematic review of prosthodontic maintenance and complications. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2015, 28, 127–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, K.C.; Seo, Y.R.; Wu, B.M. Clinical application of a shape memory implant abutment system. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2017, 117, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Paek, J.H. A new retentive type of fixed implant prosthesis without cement: A case report. Implantology 2016, 20, 66–71. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, M.O.; Schiegnitz, E.; Al-Nawas, B. Systematic review on success of narrow-diameter dental implants. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Implants 2014, 29, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davarpanah, M.; Martinez, H.; Tecucianu, J.F.; Celletti, R.; Lazzara, R. Small-diameter implants: Indications and contraindications. J. Esthet. Dent. 2000, 12, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bidra, A.S.; Almas, K. Mini implants for definitive prosthodontic treatment: A systematic review. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2013, 109, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imam, A.Y.; Moshaverinia, A.; McGlumphy, E.A. Implant-abutment interface: A comparison of the ultimate force to failure among narrow-diameter implant systems. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2014, 112, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadimitriou, D.E.; Friedland, B.; Gannam, C.; Salari, S.; Gallucci, G.O. Narrow-Diameter versus Standard-Diameter Implants and Their Effect on the Need for Guided Bone Regeneration: A Virtual Three-Dimensional Study. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2015, 17, 1127–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Choi, Y.C.; Kim, H.S.; Hong, S.I. Biocompatibility and Mechanical Performance of Ni-Ti. Mater. Sci. Forum 2007, 534–6, 1617–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wayman, C.M. Shape memory and related phenomena. Prog. Mater. Sci. 1992, 36, 203–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO/DIS 14801:2007. Dentistry–Implants–Dynamic Fatigue Test for Endosseous Dental Implants; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Bordin, D.; Witek, L.; Fardin, V.P.; Bonfante, E.A.; Coelho, P.G. Fatigue Failure of Narrow Implants with Different Implant-Abutment Connection Designs. J. Prosthodont. 2016, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ongthiemsak, C.; Mekayarajjananonth, T.; Winkler, S.; Boberick, K.G. The effect of compressive cyclic loading on retention of a temporary cement used with implants. J. Oral Implantol. 2005, 31, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Lee, S.W.; Leesungbok, R.; Ahn, S.J. Influence of the connection design and titanium grades of the implant complex on resistance under static loading. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2016, 8, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dittmer, S.; Dittmer, M.P.; Kohorst, P.; Jendras, M.; Borchers, L.; Stiesch, M. Effect of implant-abutment connection design on load bearing capacity and failure mode of implants. J. Prosthodont. 2011, 20, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quek, H.C.; Tan, K.B.; Nicholls, J.I. Load fatigue performance of four implant-abutment interface designs: Effect of torque level and implant system. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Implants 2008, 23, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tagger Green, N.; Machtei, E.E.; Horwitz, J.; Peled, M. Fracture of dental implants: Literature review and report of a case. Implant Dent. 2002, 11, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinebrunner, L.; Wolfart, S.; Ludwig, K.; Kern, M. Implant-abutment interface design affects fatigue and fracture strength of implants. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2008, 19, 1276–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norton, M.R. An in vitro evaluation of the strength of a 1-piece and 2-piece conical abutment joint in implant design. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2000, 11, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Möllersten, L.; Lockowandt, P.; Lindén, L.A. Comparison of strength and failure mode of seven implant systems: An in vitro test. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1997, 78, 582–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akça, K.; Cehreli, M.C.; Iplikçioğlu, H. Evaluation of the mechanical characteristics of the implant-abutment complex of a reduced-diameter morse-taper implant. A nonlinear finite element stress analysis. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2003, 14, 444–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pessoa, R.S.; Muraru, L.; Júnior, E.M.; Vaz, L.G.; Sloten, J.V.; Duyck, J.; Jaecques, S.V. Influence of implant connection type on the biomechanical environment of immediately placed implants—CT-based nonlinear, three-dimensional finite element analysis. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2010, 12, 219–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binon, P.P. Implants and components: Entering the new millennium. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Implants 2000, 15, 76–94. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Petrie, C.S.; Williams, J.L. Comparative evaluation of implant designs: Influence of diameter, length, and taper on strains in the alveolar crest. A three-dimensional finite-element analysis. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2005, 16, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allum, S.R.; Tomlinson, R.A.; Joshi, R. The impact of loads on standard diameter, small diameter and mini implants: A comparative laboratory study. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2008, 19, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrario, V.F.; Sforza, C.; Serrao, G.; Dellavia, C.; Tartaglia, G.M. Single tooth bite forces in healthy young adults. J. Oral. Rehabil. 2004, 31, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Eijden, T.M. Three-dimensional analyses of human bite-force magnitude and moment. Arch. Oral Biol. 1991, 36, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, P.; Pujari, M.; Prithviraj, D.R.; Khare, S. Retentiveness of various luting agents used with implant-supported prosthesis: An in vitro study. J. Oral Implantol. 2014, 40, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Arenal, A.; Gonzalez-Gonzalez, I.; deLlanos-Lanchares, H.; Brizuela-Velasco, A.; Ellacuria-Echebarria, J. The selection criteria of temporary or permanent luting agents in implant-supported prostheses: In vitro study. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2016, 8, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudley, J.E.; Richards, L.C.; Abbott, J.R. Retention of cast crown copings cemented to implant abutments. Aust. Dent. J. 2008, 53, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Arenal, A.; Gonzalez-Gonzalez, I.; Pinés-Hueso, J.; deLlanos-Lanchares, H.; del Rio Highsmith, J. The Effect of Compressive Cyclic Loading on the Retention of Cast Single Crowns Cemented to Implant Abutments. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2016, 29, 80–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, A.; Serfaty, V. Cement-retained implant-supported fixed partial dentures: A 6-month to 3-year follow-up. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Implants 1996, 11, 645–649. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Trakas, T.; Michalakis, K.; Kang, K.; Hirayama, H. Attachment systems for implant retained overdentures: A literature review. Implant Dent. 2006, 15, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.W.; Bae, J.H.; Jeong, C.M.; Huh, J.B. Retention and wear behaviors of two implant overdenture stud-type attachments at different implant angulations. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2017, 117, 628–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutkunas, V.; Mizutani, H.; Takahashi, H.; Iwasaki, N. Wear simulation effects on overdenture stud attachments. Dent. Mater. J. 2011, 30, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Żmudzki, J.; Chladek, G.; Kasperski, J.; Dobrzański, L.A. One versus two implant-retained dentures: Comparing biomechanics under oblique mastication forces. J. Biomech. Eng. 2013, 135, 54503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Żmudzki, J.; Chladek, G.; Kasperski, J. Single implant-retained dentures: Loading of various attachment types under oblique occlusal forces. J. Mech. Med. Biol. 2012, 12, 1250087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Components | ASTM | Chemical Composition |
|---|---|---|
| Body/Cap | F136 (Ti grade5) | Ti: balance |
| Al: 6.07% | ||
| V: 3.97% | ||
| Fe: 0.15% | ||
| O: 0.12% | ||
| N: 0.01% | ||
| C: 0.01% | ||
| H: 0.0026% | ||
| Ball | F1873 | ZrO2 + HfO2: 85–90% |
| CeO2 + Fe2O3: 10–15% | ||
| Spring | F2063-03 | Ti: balance |
| Ni: 55.7 ± 0.3% |
| Group | Implants (LOT) | Abutment (LOT) | Implant/Abutment Material | Width/Length of the Connection (mm) | Connection Type/Index | Required Torque (N/cm) | Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EH | INNO external (16H2A) 2-piece implant, ∅3.5/14 mm | Cemented abutment (15D3A002) | Ti 4/Ti 5 | 4.1/0.75 | External butt joint/hexagon | 35 | Cowellmedi Co., Ltd., Busan, Korea |
| IO | INNO internal (16H2A) 2-piece implant, ∅3.5/14 mm | Cemented abutment (15D4A015) | Ti 4/Ti 5 | 3.5/2 | Internal conical interface/octagon | 35 | Cowellmedi Co., Ltd., Busan, Korea |
| IH | INNO submerged (16H2A) 2-piece implant, ∅3.5/14 mm | Cemented abutment (15D5B011) | Ti 4/Ti 5 | 3.35/2.9 | Internal conical interface/hexagon | 30 | Cowellmedi Co., Ltd., Busan, Korea |
| OB | SlimLine (14E14-011) 1-piece implant, ∅3.3/14 mm | Cemented dual abutment (E26D04616) | Ti 4 | 3.5/4 | Tapered external interface/cementation | - | Dentium Co., Ltd., Seoul, Korea |
| ML | INNO ML implant (17H1A) 1-piece implant, ∅3.3/14 mm | EZ cylinder (S17102615) | Ti 4/Ti 5 | 4.9/3.2 | Tapered external interface with micro-locking/hexagon | - | Cowellmedi Co., Ltd., Busan, Korea Samwon DMP Co., Yangsan, Korea |
| Specimens No. | Groups | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EH | IO | IH | OB | ML | |
| 1 | 674.52 | 604.31 | 685.40 | 425.25 | 549.09 |
| 2 | 624.40 | 677.26 | 644.01 | 515.85 | 554.82 |
| 3 | 637.27 | 775.14 | 1000.34 | 492.89 | 524.35 |
| 4 | 649.97 | 869.01 | 530.65 | 446.63 | 484.25 |
| 5 | 681.69 | 861.22 | 564.60 | 482.35 | 619.59 |
| Mean (SD) | 653.57 (21.72) a | 757.39 (103.35) b | 685.00 (167.00) c | 472.60 (32.54) ab | 546.42 (44.24) d |
| Failure Mode | Two-Piece Implant | One-Piece Implant | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EH | IO | IH | OB | ML | |
| Implant | |||||
| fracture | - | 1 | - | - | - |
| bending + crack | - | 4 | 4 | - | - |
| bending only | - | - | 1 | 5 | 5 |
| minor deformation | 5 | - | - | - | - |
| Abutment/Attachment | |||||
| dislocated | 5 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 5 |
| Abutment screw | |||||
| fracture | 5 | 1 | 5 | - | - |
| bending | - | 4 | - | - | - |
| Specimens No. | Groups | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HB3 | HB6 | NHB6 | HB3+ | |
| 1 | 17.58 | 18.29 | 24.53 | 30.28 |
| 2 | 21.20 | 20.12 | 16.66 | 25.41 |
| 3 | 14.38 | 17.38 | 17.79 | 26.13 |
| 4 | 17.04 | 19.25 | 19.91 | 28.97 |
| 5 | 16.82 | 16.50 | 16.77 | 21.32 |
| 6 | 24.53 | 19.54 | 16.68 | 23.71 |
| 7 | 18.20 | 16.72 | 15.16 | 31.02 |
| 8 | 18.79 | 24.46 | 14.95 | 24.94 |
| 9 | 22.68 | 23.61 | 13.28 | 27.38 |
| 10 | 19.94 | 20.88 | 15.49 | 24.81 |
| Mean ± SD (N) | 19.12 ± 2.87 a | 19.68 ± 2.57 a | 17.10 ± 2.99 a | 26.40 ± 2.88 b |
| Retentive Force (N) | Retention Loss (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Cycles | Mean ± SD | p | Mean ± SD |
| Initial | 29.353 ± 5.308 | - | |
| 1,000,000 | 20.930 ± 2.808 | 0.012 * | 27.705 ± 9.469 |
| 2,000,000 | 22.596 ± 3.982 | 0.161 | −7.797 ± 11.057 |
| 3,000,000 | 18.780 ± 3.250 | 0.025 * | 15.551 ± 13.746 |
| 4,000,000 | 18.924 ± 2.757 | 0.889 | −1.535 ± 8.201 |
| 5,000,000 | 17.033 ± 3.720 | 0.025 * | 10.564 ± 10.591 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, J.-W.; Choi, K.-H.; Chae, H.-J.; Chae, S.-K.; Bae, E.-B.; Lee, J.-J.; Lee, S.-H.; Jeong, C.-M.; Huh, J.-B. Load-Bearing Capacity and Retention of Newly Developed Micro-Locking Implant Prosthetic System: An In Vitro Pilot Study. Materials 2018, 11, 564. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11040564
Choi J-W, Choi K-H, Chae H-J, Chae S-K, Bae E-B, Lee J-J, Lee S-H, Jeong C-M, Huh J-B. Load-Bearing Capacity and Retention of Newly Developed Micro-Locking Implant Prosthetic System: An In Vitro Pilot Study. Materials. 2018; 11(4):564. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11040564
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Jae-Won, Kyung-Hee Choi, Hee-Jin Chae, Sung-Ki Chae, Eun-Bin Bae, Jin-Ju Lee, So-Hyoun Lee, Chang-Mo Jeong, and Jung-Bo Huh. 2018. "Load-Bearing Capacity and Retention of Newly Developed Micro-Locking Implant Prosthetic System: An In Vitro Pilot Study" Materials 11, no. 4: 564. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11040564
APA StyleChoi, J.-W., Choi, K.-H., Chae, H.-J., Chae, S.-K., Bae, E.-B., Lee, J.-J., Lee, S.-H., Jeong, C.-M., & Huh, J.-B. (2018). Load-Bearing Capacity and Retention of Newly Developed Micro-Locking Implant Prosthetic System: An In Vitro Pilot Study. Materials, 11(4), 564. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11040564





