Wear Characteristics of Dental Ceramic CAD/CAM Materials Opposing Various Dental Composite Resins
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
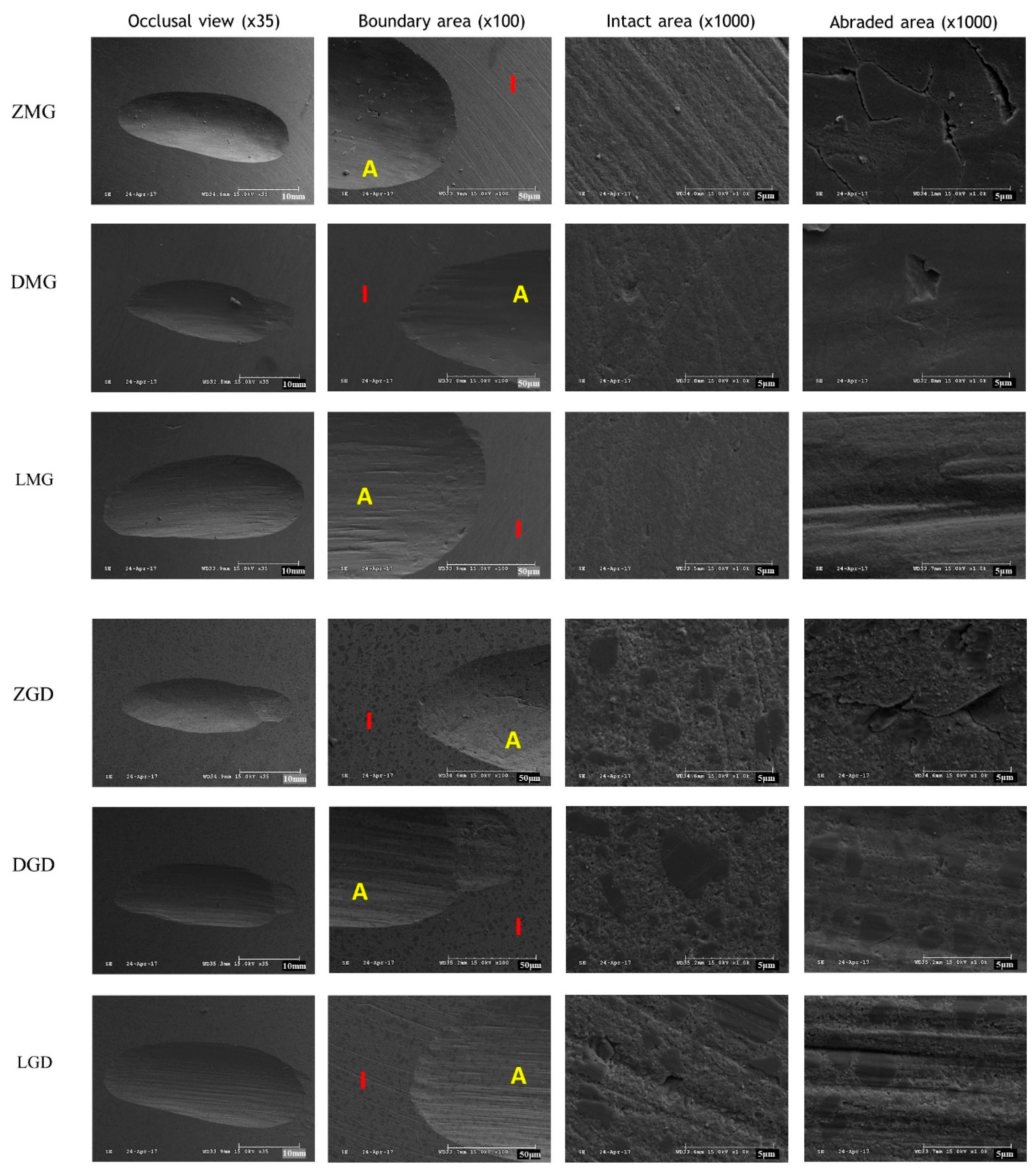
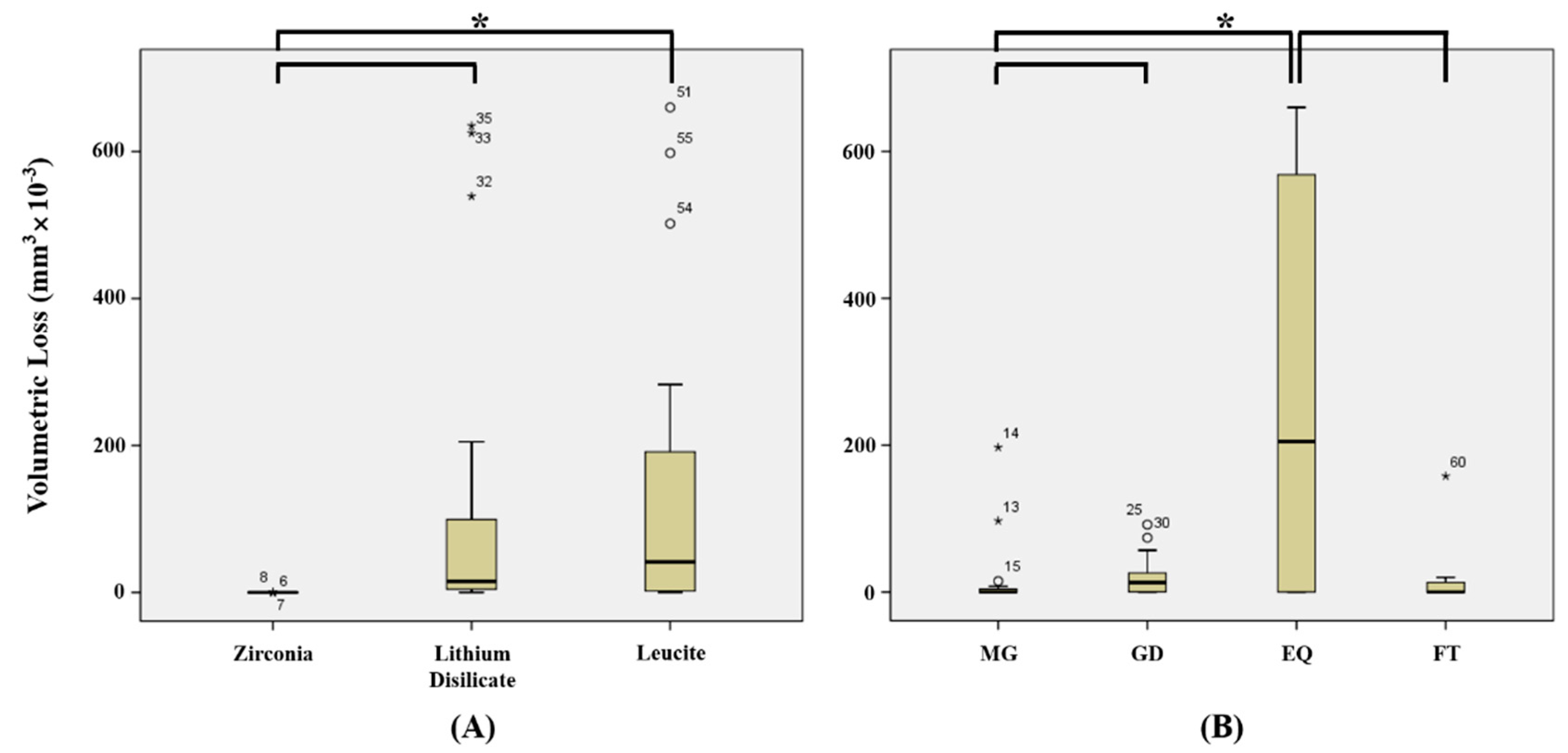
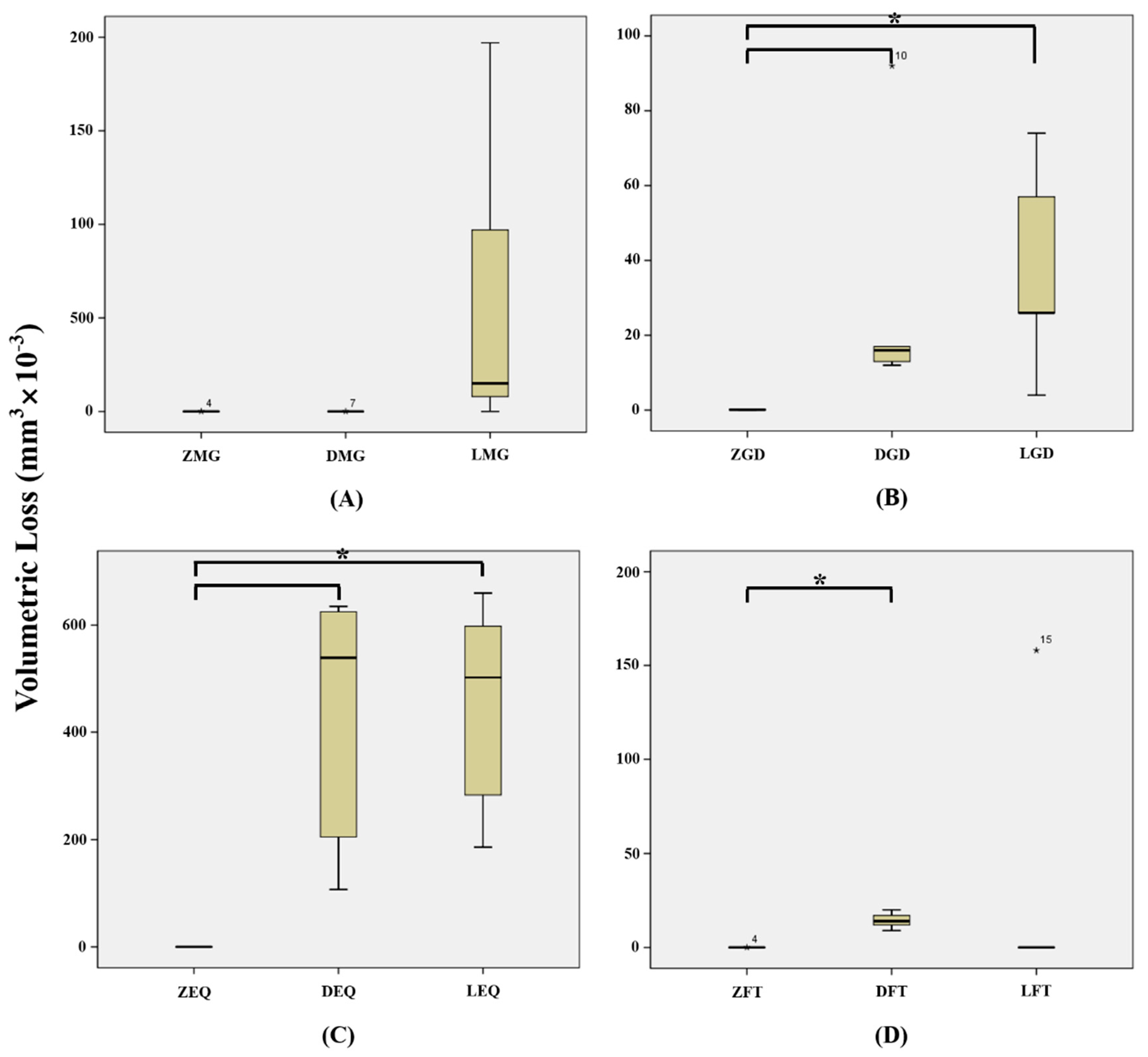
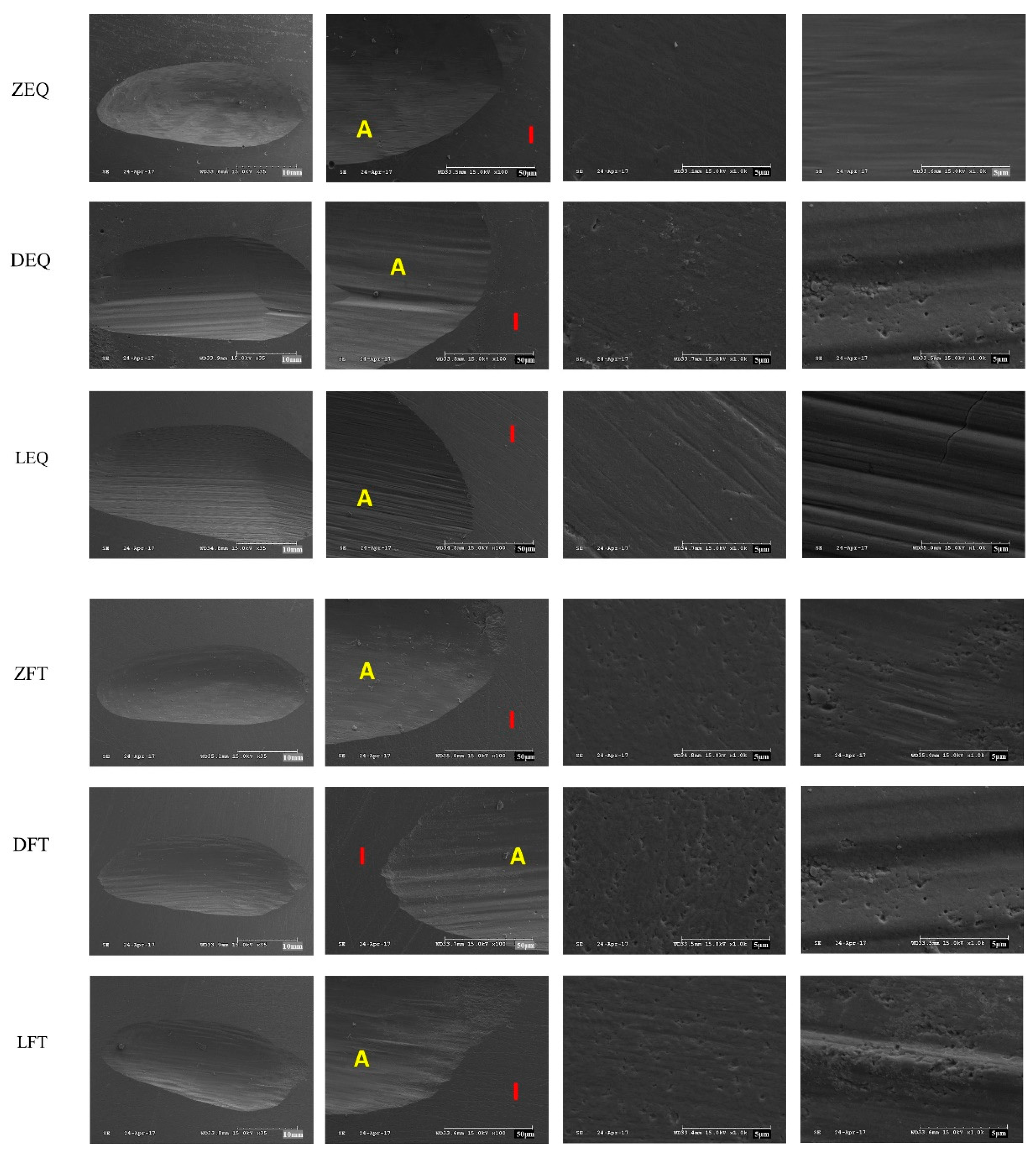
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jung, Y.S.; Lee, J.W.; Choi, Y.J.; Ahn, J.S.; Shin, S.W.; Huh, J.B. A study on the in vitro wear of the natural tooth structure by opposing zirconia or dental porcelain. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2010, 2, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Arcangelo, C.; Vanini, L.; Rondoni, G.D.; De Angels, F. Wear properties of dental ceramics and porcelains compared with human enamel. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2016, 115, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tinschert, J.; Natt, G.; Mautsch, W.; Augthun, M.; Spiekermann, H. Fracture resistance of lithium disilicate-, Alumina-, and zirconia-based three-unit fixed partial dentures: A laboratory study. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2001, 14, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sobrinho, L.C.; Cattell, M.J.; Glover, R.H.; Knowles, J.C. Investigation of the dry and wet fatigue properties of three all ceramic crown systems. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2003, 5, 57–63. [Google Scholar]
- Sorensen, J.A.; Choi, C.; Fanuscu, M.I.; Mito, W.T. IPS Empress crown system: Three-year clinical trial results. J. Calif. Dent. Assoc. 1988, 81, 672–676. [Google Scholar]
- Olsson, K.G.; Fürst, B.; Andersson, B.; Carlsson, G.E. A long-term retrospective and clinical follow-up study of In-Ceram Alumina FPDs. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2003, 16, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denry, I.; Kelly, J.R. State of the art of zirconia for dental applications. Dent. Mater. 2008, 24, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, T.; Nakamura, T.; Matsumura, H.; Ban, S.; Kobayashi, T. Current status of zirconia restoration. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2013, 57, 236–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blatz, M.B. Long-term clinical success of all ceramic posterior restorations. Quintessence Int. 2002, 33, 415–426. [Google Scholar]
- Sripetchdanond, J.; Leevailoj, C. Wear of human enamel opposing monolithic zirconia, glass ceramic, and composite resin: An in vitro study. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2014, 112, 1141–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, S.B.; Wu, D.; Holmes, B.N. An application of nanotechnology in advanced dental materials. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2003, 134, 1382–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Cai, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wei, Y.; Xu, M.; Yang, X.; Ma, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Deng, X. Improved performance of Bis-GMA/TEGDMA dental composites by net-like structures formed from SiO2 nanofiber fillers. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2016, 59, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Söderholm, K.J.; Richards, N.D. Wear resistance of composites: A solved problem? Gen. Dent. 1998, 46, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Deliperi, S.; Bardwell, D.N. Clinical evaluation of direct cuspal coverage with posterior composite resin restorations. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2006, 18, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yesil, Z.D.; Alapati, S.; Johnston, W.; Seghi, R.R. Evaluation of the wear resistance of new nanocomposite resin restorative materials. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2008, 99, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sookhakiyan, M.; Tavana, S.; Azarnia, Y.; Bagheri, R. Fracture Toughness of Nanohybrid and Hybrid Composites Stored Wet and Dry up to 60 Days. J. Dent. Biomater. 2017, 4, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shimane, T.; Endo, K.; Zheng, J.H.; Yanagi, T.; Ohno, H. Wear of opposing teeth by posterior composite resins—Evaluation of newly developed wear test methods. Dent. Mater. J. 2010, 29, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, S. Does the wear resistance of packable composite equal that of dental amalgam? J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2004, 16, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadokawa, A.; Suzuki, S.; Tanaka, T. Wear evaluation of porcelain opposing gold, composite resin, and enamel. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2006, 96, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PMonasky, G.E.; Taylor, D.F. Studies on the wear of porcelain, enamel, and gold. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1971, 25, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janyavula, S.; Lawson, N.; Cakir, D.; Beck, P.; Ramp, L.C.; Burgess, J.O. The wear of polished and glazed zirconia against enamel. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2013, 109, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, N.R.; Thompson, V.P.; Valverde, G.B.; Coelho, P.G.; Powers, J.M.; Farah, J.W.; Esquivel-Upshaw, J. Comparative reliability analyses of zirconium oxide and lithium disilicate restorations in vitro and in vivo. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2011, 142, 4S–9S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zandparsa, R.; El Huni, R.M.; Hirayama, H.; Johnson, M.I. Effect of different dental ceramic systems on the wear of human enamel: An in vitro study. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2016, 115, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preis, V.; Behr, M.; Kolbeck, C.; Handel, G.; Rosentritt, M. Wear performance of substructure ceramics and veneering porcelains. Dent. Mater. 2011, 27, 796–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seghi, R.R.; Rosenstiel, S.F.; Bauer, P. Abrasion of human enamel by different dental ceramics in vitro. J. Dent. Res. 1991, 70, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, B.S.; Ferracane, J.L.; Condon, J.R.; Adey, J.D. Effect of filler fraction and filler surface treatment on wear of microfilled composites. Dent. Mater. 2002, 18, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AMandikos, M.N.; McGivney, G.P.; Davis, E.; Bush, P.J.; Cater, J.M. A comparison of the wear resistance and hardness of indirect composite resins. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2001, 85, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manhart, J.; Kunzelmann, K.H.; Chen, H.Y.; Hickel, R. Mechanical properties and wear behavior of light-cured packable composite resins. Dent. Mater. 2000, 16, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etman, M.K.; Woolford, M.; Dunne, S. Quantitive measurement of tooth and ceramic wear: In vivo study. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2008, 21, 245–252. [Google Scholar]
- Fani, M.; Farmani, S.; Bagheri, R. Fracture toughness of resin composites under different modes and media: Review of articles. J. Dent. Biomater. 2015, 2, 73–82. [Google Scholar]
- Knobloch, L.A.; Kerby, R.E.; Seghi, R.; Berlin, J.S.; Clelland, N. Fracture toughness of packable and conventional composite materials. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2002, 88, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clelland, N.L.; Pagnotto, M.P.; Kerby, R.E.; Seghi, R.R. Relative wear of flowable and highly filled composite. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2005, 93, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagger, D.C.; Harrison, A. An in vitro investigation into the wear effects of selected restorative materials on enamel. J. Oral Rehabil. 1995, 22, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.W.; Bae, I.H.; Noh, T.H.; Ju, S.W.; Lee, T.K.; Ahn, J.S.; Jeong, T.S.; Huh, J.B. Wear of primary teeth caused by opposed all-ceramic or stainless steel crowns. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2016, 8, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibbs, C.H.; Mahan, P.E.; Lundeen, H.C.; Brehnan, K.; Walsh, E.K.; Holbrook, W.B. Occlusal forces during chewing and swallowing as measured by sound transmission. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1981, 46, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mörmann, W.H.; Stawarczyk, B.; Ender, A.; Sener, B.; Attin, T.; Mehl, A. Wear characteristics of current aesthetic dental restorative CAD/CAM materials: Two-body wear, gloss retention, roughness and Martens hardness. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2013, 20, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Arcangelo, C.; Vanini, L.; Rondoni, G.D.; Pirani, M.; Vadini, M.; Gattone, M.; De Angelis, F. Wear properties of a novel resin composite compared to human enamel and other restorative materials. Oper. Dent. 2014, 39, 612–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Him, H.C.; Kim, N.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, U.C. Successful strategy of treatment using rhBMP-2 for maxillary sinus graft. J. Korean Dent. Assoc. 2015, 53, 14–27. [Google Scholar]
- al-Hiyasat, A.S.; Saunders, W.P.; Smith, G.M. Three-body wear associated with three ceramics and enamel. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1999, 82, 476–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heintze, S.D.; Zappini, G.; Rousson, V. Wear of ten dental restorative materials in five wear simulators—Results of a round robin test. Dent. Mater. 2005, 21, 304–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazal, M.; Yang, B.; Ludwig, K.; Kern, M. Two-body wear of resin and ceramic denture teeth in comparison to human enamel. Dent. Mater. 2008, 24, 502–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambrechts, P.; Braem, M.; Vuylsteke-Wauters, M.; Vanherle, G. Quantitative in vivo wear of human enamel. J. Dent. Res. 1989, 68, 1752–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heintze, S.D.; Cavalleri, A.; Forjanic, M.; Zellweger, G.; Rousson, V. Wear of ceramic and antagonist--a systematic evaluation of influencing factors in vitro. Dent. Mater. 2008, 24, 433–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhi, L.; Bortolotto, T.; Krejci, I. Comparative in vitro wear resistance of CAD/CAM composite resin and ceramic materials. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2016, 115, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heintze, S.D.; Cavalleri, A.; Forjanic, M.; Zellweger, G.; Rousson, V. A comparison of three different methods for the quantification of the in vitro wear of dental materials. Dent. Mater. 2006, 22, 1051–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunzelmann, K.H.; Jelen, B.; Mehl, A.; Hickel, R. Wear evaluation of MZ100 compared to ceramic CAD/CAM materials. Int. J. Comput. Dent. 2001, 4, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nakashima, J.; Taira, Y.; Sawase, T. In vitro wear of four ceramic materials and human enamel on enamel antagonist. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2016, 124, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esquivel-Upshaw, J.F.; Young, H.; Jones, J.; Yang, M.; Anusavice, K.J. In vivo wear of enamel by a lithia disilicate-based core ceramic used for posterior fixed partial dentures: First-year results. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2006, 19, 391–396. [Google Scholar]
- D’Arcangelo, C.; Vanini, L.; Rondoni, G.D.; Vadini, M.; De Angelis, F. Wear Evaluation of Prosthetic Materials Opposing Themselves. Oper. Dent. 2018, 43, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLong, R.; Sasik, C.; Pintado, M.R.; Douglas, W.H. The wear of enamel when opposed by ceramic systems. Dent. Mater. 1989, 5, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, N.C.; Bansal, R.; Burgess, J.O. Wear, strength, modulus and hardness of CAD/CAM restorative materials. Dent. Mater. 2016, 32, e275–e283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumino, N.; Tsubota, K.; Takamizawa, T.; Shiratsuchi, K.; Miyazaki, M.; Latta, M.A. Comparison of the wear and flexural characteristics of flowable resin composites for posterior lesions. Acta Odontol. Scand. 2013, 71, 820–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferracane, J.L. Resin-based composite performance: Are there some things we can’t predict? Dent. Mater. 2013, 29, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mair, L.H.; Stolarski, T.A.; Vowles, R.W.; Lloyd, C.H. Wear: Mechanisms, manifestations and measurement. Report of a workshop. J. Dent. 1996, 24, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauvahutanon, S.; Takahashi, H.; Oki, M.; Arksornnukit, M.; Kanehira, M.; Finger, W.J. In vitro evaluation of the wear resistance of composite resin blocks for CAD/CAM. Dent. Mater. J. 2015, 34, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Ceramic Specimens | ||||||
| Product | Composition | Biaxial Flexural Strength (MPa) | Fracture Toughness (MPa·m1/2) | Vickers Hardness (GPa) | Manufacturer | |
| ZirtoothTM Fulluster (Monolithic Zirconia) | Zirconium dioxide, hafnium dioxide, yttrium trioxide, pigment, organic binder | 1200 | 5.5 | 13 | HASS Corp., Gangwon-do, Korea | |
| Rosetta® SM (Lithium Disilicate) | Lithium oxide, silicon dioxide, boron trioxide, phosphorus pentoxide, pigment, organic binder | 440 | 2.25 | 5.8 | HASS Corp., Gangwon-do, Korea | |
| Rosetta® BM (Leucite) | Potassium oxide, silicon dioxide, boron trioxide, titanium dioxide, aluminum oxide | 100 | 1.42 | 6 | HASS Corp., Gangwon-do, Korea | |
| Composite Resin Specimens | ||||||
| Product | Filler | Matrix | Filler Content (wt %) | Filler Size (nm) | Flexural Strength (MPa) | Manufacturer |
| MI Gracefil (Nano-Hybrid Filler Resin) | Barium silica glass | Bis-MEPP, UDMA | 82 | 300 | 170 | GC, Tokyo, Japan |
| Gradia Direct P (Micro-Hybrid Filler Resin) | Barium silica glass, silica dioxide, prepolymerized filler | UDMA | 76 | 850 | 129 | GC, Tokyo, Japan |
| Estelite Σ Quick (Micro-Hybrid Filler Resin) | Silica-zirconia supra-nano monodispersing spherical, PFSC | Bis-GMA, TEGDMA, UDMA | 78 | 200 | 110 | Tokuyama Dental, Tokyo, Japan |
| Filtek Supreme Ultra (Nano-Filler Resin) | Zirconium/silica non-agglomerated particles | Bis-GMA, UDMA, Bis-EMA, TEGDMA | 78 | 100 | 161 | 3M ESPE, MN, USA |
| Group | Start Temp (°C) | Heat Rate (°C/min) | High Temp (°C) | Hold (min) | Vacuum (°C) | Vacuum off (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lithium disilicate | 400 | 60 | 840 | 10 | 550 | 845 |
| Zirconia | 1450 | 4 | 1550 | 120 | - | - |
| Group | Mean ± SD | |
|---|---|---|
| Ceramic Volumetric Loss (mm3 × 10−3) | Composite Resin Weight Loss (mg) | |
| ZMG | 0.004 ± 0.008 | 0.26 ± 0.15 |
| ZGD | 0.134 ± 0.134 | 0.54 ± 0.29 |
| ZEQ | 0.006 ± 0.006 | 0.82 ± 0.41 |
| ZFT | 0.013 ± 0.014 | 0.72 ± 0.16 |
| DMG | 0.008 ± 0.016 | 0.42 ± 0.40 |
| DGD | 30.00 ± 34.72 | 0.26 ± 0.15 |
| DEQ | 422.2 ± 248.2 | 0.94 ± 0.40 |
| DFT | 14.40 ± 4.278 | 0.44 ± 0.22 |
| LMG | 63.40 ± 84.28 | 0.78 ± 0.58 |
| LGD | 37.40 ± 27.84 | 0.36 ± 0.26 |
| LEQ | 445.8 ± 203.8 | 1.1 ± 0.53 |
| LFT | 31.61 ± 70.66 | 0.50 ± 0.25 |
| p | <0.001 | 0.006 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gwon, B.; Bae, E.-B.; Lee, J.-J.; Cho, W.-T.; Bae, H.-Y.; Choi, J.-W.; Huh, J.-B. Wear Characteristics of Dental Ceramic CAD/CAM Materials Opposing Various Dental Composite Resins. Materials 2019, 12, 1839. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12111839
Gwon B, Bae E-B, Lee J-J, Cho W-T, Bae H-Y, Choi J-W, Huh J-B. Wear Characteristics of Dental Ceramic CAD/CAM Materials Opposing Various Dental Composite Resins. Materials. 2019; 12(11):1839. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12111839
Chicago/Turabian StyleGwon, Bora, Eun-Bin Bae, Jin-Ju Lee, Won-Tak Cho, Hyun-Young Bae, Jae-Won Choi, and Jung-Bo Huh. 2019. "Wear Characteristics of Dental Ceramic CAD/CAM Materials Opposing Various Dental Composite Resins" Materials 12, no. 11: 1839. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12111839
APA StyleGwon, B., Bae, E.-B., Lee, J.-J., Cho, W.-T., Bae, H.-Y., Choi, J.-W., & Huh, J.-B. (2019). Wear Characteristics of Dental Ceramic CAD/CAM Materials Opposing Various Dental Composite Resins. Materials, 12(11), 1839. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12111839





