Investigation of Tool Wear and Chip Morphology in Dry Trochoidal Milling of Titanium Alloy Ti–6Al–4V
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedures
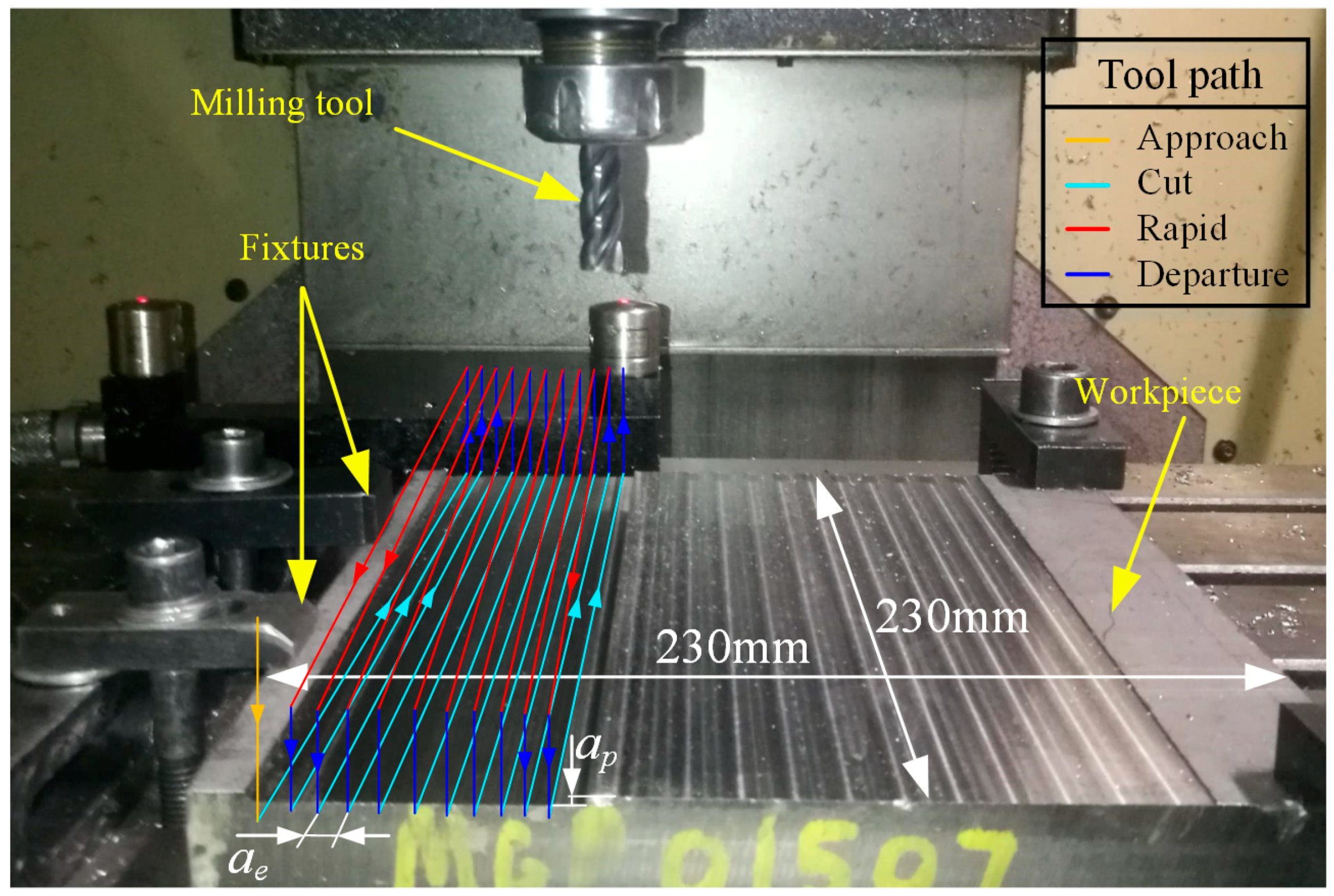
2.1. Experimental Setup
2.2. Experimental Design
- (1)
- Average flank wear VB = 0.2 mm;
- (2)
- Maximum flank wear VB_max = 0.3 mm;
- (3)
- Excessive chipping/flaking or catastrophic failure.
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Tool Wear Model Related with Radial Depth of Cut
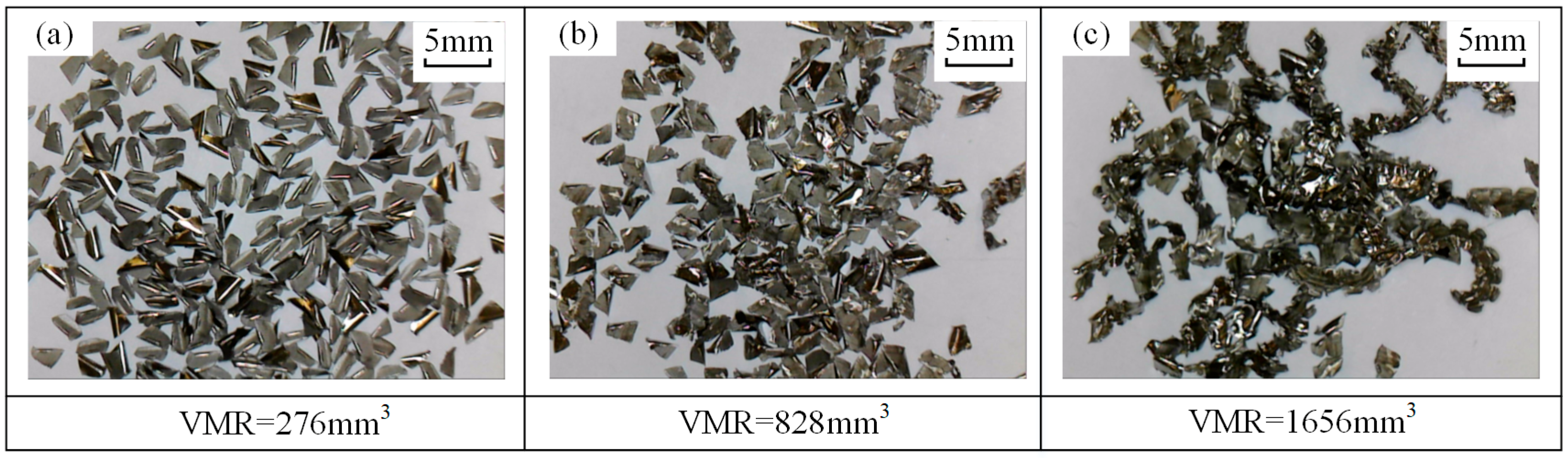
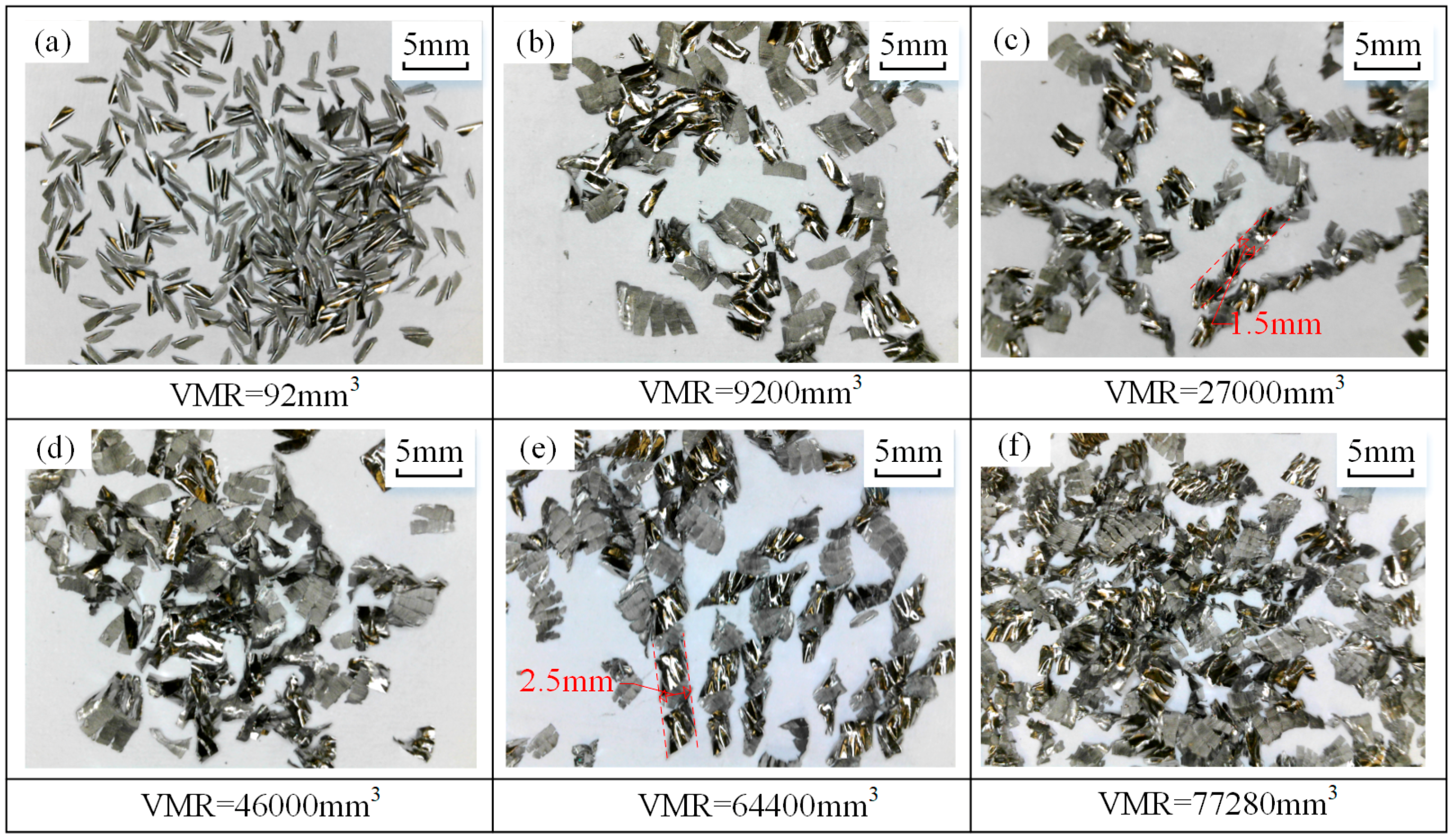
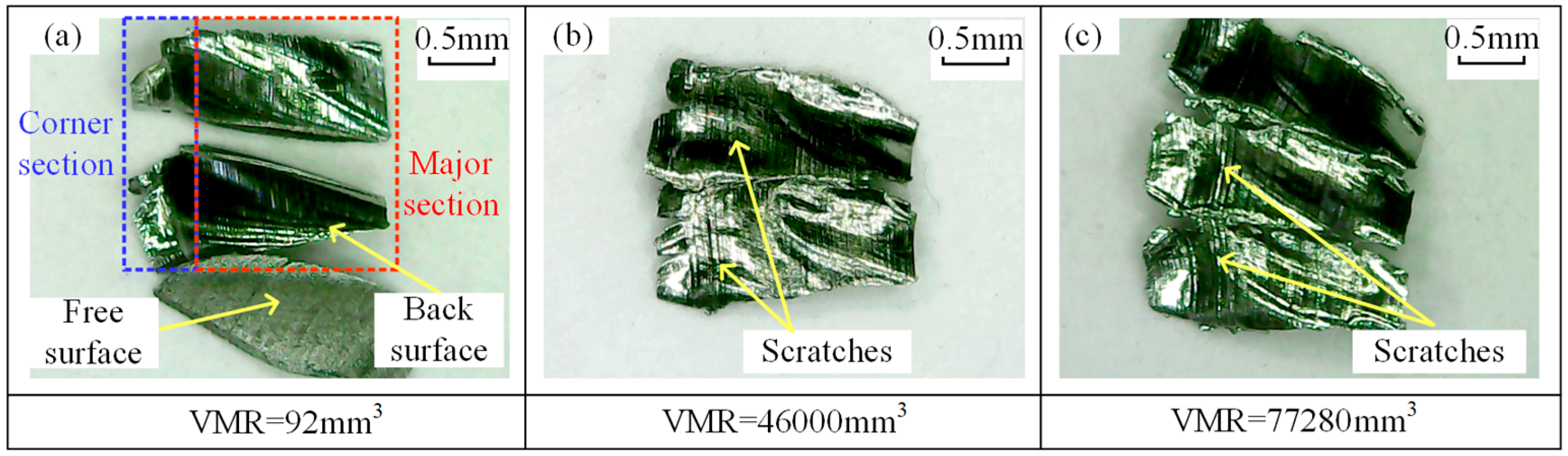
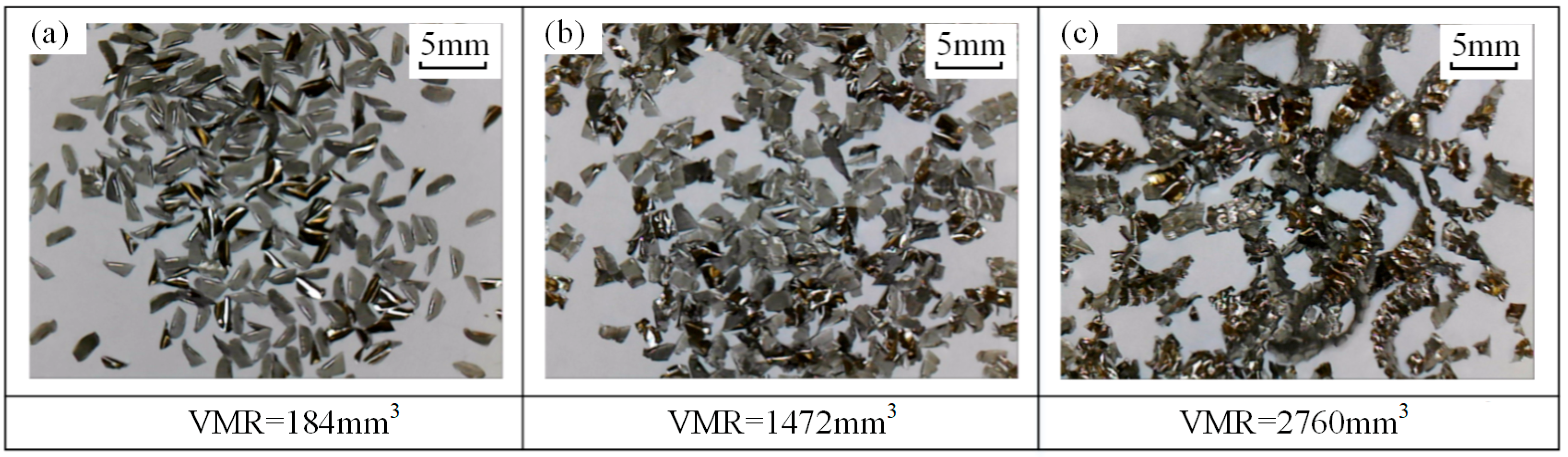
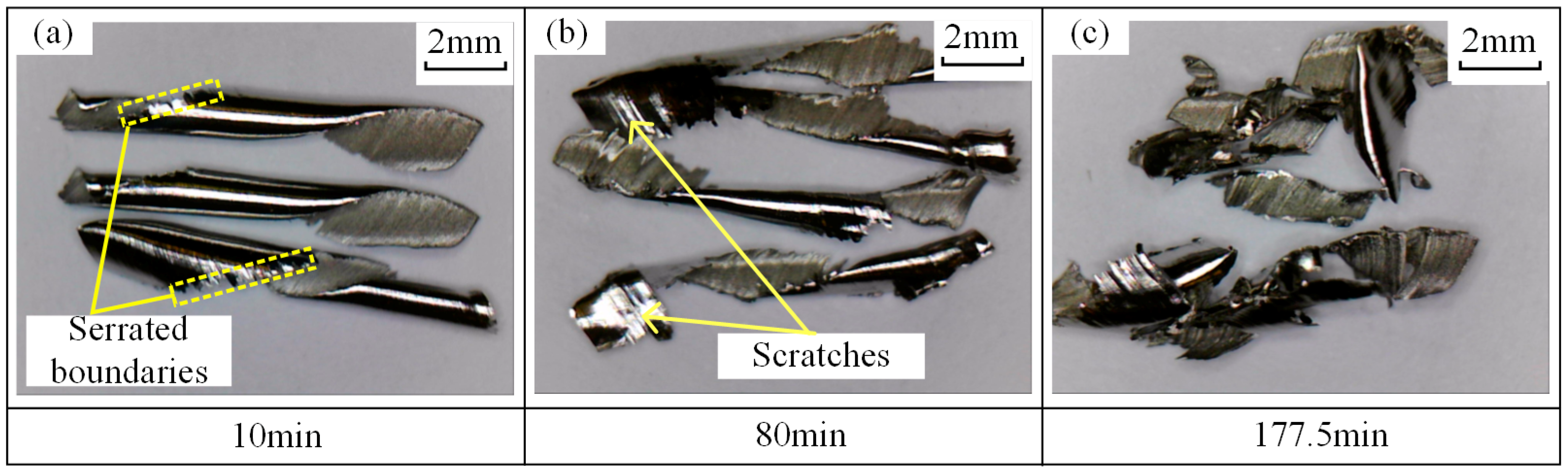
3.2. Tool Wear and Chip Morphology
3.3. Trochoidal Milling Test
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cui, C.X.; Hu, B.M.; Zhao, L.C.; Liu, S.J. Titanium alloy production technology, market prospects and industry development. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 1684–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Luo, M.; Zhang, D.H.; Wu, B. Identification of cutting force coefficients in machining process considering cutter vibration. Mech. Syst. Sig. Process. 2018, 103, 39–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Luo, M.; Zhang, D.H.; Wu, B. Iterative Learning Method for Drilling Depth Optimization in Peck Deep-Hole Drilling. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng.-Trans. ASME. 2018, 140, 121009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komanduri, R.; Von Turkovich, B.F. New observations on the mechanism of chip formation when machining titanium alloys. Wear 1981, 69, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che-Haron, C.H.; Jawaid, A. The effect of machining on surface integrity of titanium alloy Ti–6% Al–4% V. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2005, 166, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Yao, Q. Vibrations of Flat-End Cutter Entering Workpiece Process: Modeling, Simulations, and Experiments. Shock Vib. 2018, 2018, 8419013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Wan, M.; Yang, Y. Design of a tunable mass damper for mitigating vibrations in milling of cylindrical parts. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2019, 32, 748–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M’Saoubi, R.; Axinte, D.; Soo, S.L.; Nobel, C.; Attia, H.; Kappmeyer, G.; Engin, S.; Sim, W.-M. High performance cutting of advanced aerospace alloys and composite materials. CIRP Ann-Manuf. Technol. 2015, 64, 557–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Brandt, M.; Dargusch, M.S. Machining Ti–6Al–4V alloy with cryogenic compressed air cooling. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2010, 50, 933–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittalà, G.M. A study of the effect of CO2 cryogenic coolant in end milling of Ti-6Al-4V. Procedia CIRP. 2018, 77, 445–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermingham, M.J.; Palanisamy, S.; Kent, D.; Dargusch, M.S. A comparison of cryogenic and high pressure emulsion cooling technologies on tool life and chip morphology in Ti–6Al–4V cutting. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2012, 212, 752–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, O.; Rodríguez, A.; Fernández-Abia, A.I.; Barreiro, J.; López de Lacalle, L.N. Cryogenic and minimum quantity lubrication for an eco-efficiency turning of AISI 304. J. Cleaner Prod. 2016, 139, 440–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, O.; Rodríguez, A.; Barreiro, J.; Fernández-Abia, A.I.; de Lacalle, L.N.L. Nozzle design for combined use of MQL and cryogenic gas in machining. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf.-Green Technol. 2017, 4, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, O.; Martín-Alfonso, J.E.; Rodríguez, A.; Calleja, A.; Fernández-Valdivielso, A.; López de Lacalle, L.N. Sustainability analysis of lubricant oils for minimum quantity lubrication based on their tribo-rheological performance. J. Cleaner Prod. 2017, 164, 1419–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, O.; Rodríguez, A.; Ayesta, I.; García, J.B.; Fernández-Abia, A.I.; De Lacalle, L.N.L. A cryo lubri-coolant approach for finish milling of aeronautical hard-to-cut materials. Int. J. Mechatron. Manuf. Syst. 2016, 9, 370–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.Z.; Zhou, W.; Duan, H.J.; Yang, G.; Xu, H.W.; Zhao, N. Influence of cutting speed on cutting force, flank temperature, and tool wear in end milling of Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2014, 70, 1835–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffery, S.I.; Mativenga, P.T. Assessment of the machinability of Ti-6Al-4V alloy using the wear map approach. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2009, 40, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermingham, M.J.; Palanisamy, S.; Dargusch, M.S. Understanding the tool wear mechanism during thermally assisted machining Ti-6Al-4V. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2012, 62, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandekar, C.R.; Shin, Y.C.; Barnes, J. Machinability improvement of titanium alloy (Ti–6Al–4V) via LAM and hybrid machining. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2010, 50, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujana, J.; Rivero, A.; Celaya, A.; López de Lacalle, L.N. Analysis of ultrasonic-assisted drilling of Ti6Al4V. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2009, 49, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreejith, P.S.; Ngoi, B.K.A. Dry machining: Machining of the future. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2000, 101, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez, A.; Veiga, F.; Lópezde Lacalle, L.N.; Polvorosa, R.; Wretland, A. An investigation of cutting forces and tool wear in turning of Haynes 282. J. Manuf. Process. 2019, 37, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.H.; Zhao, J.; Luo, H.B.; Pei, Z.Q.; Wang, Z.M. Progressive tool failure in high-speed dry milling of Ti-6Al-4V alloy with coated carbide tools. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2012, 58, 465–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.X.; Li, Y.S.; Song, W.L. Diffusion wear in dry cutting of Ti–6Al–4V with WC/Co carbide tools. Wear 2008, 265, 1776–1783. [Google Scholar]
- Li, A.H.; Zhao, J.; Hou, G.M. Effect of cutting speed on chip formation and wear mechanisms of coated carbide tools when ultra-high-speed face milling titanium alloy Ti-6Al-4V. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2017, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otkur, M.; Lazoglu, I. Trochoidal milling. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2007, 47, 1324–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlmann, E.; Fürstmann, P.; Rosenau, B.; Gebhard, S.; Gerstenberger, R.; Müller, G. The Potential of Reducing the Energy Consumption for Machining TiAl6V4 by Using Innovative Metal Cutting Processes. In Proceedings of the Global Conference on Sustainable Manufacturing (GCSM), Berlin, Germany, 23–25 September 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, B.H.; Zheng, C.Y.; Luo, M.; He, X.D. Investigation of trochoidal milling nickel-based superalloy. Mater. Sci. Forum. 2012, 723, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, P.; Polishetty, A.; Goldberg, M.; Littlefair, G.; Nomani, J. Slot machining of Ti6Al4V with trochoidal milling technique. Mach. Eng. 2014, 14, 42. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, M.; Han, C.; Hafeez, H.M. Four-axis trochoidal toolpath planning for rough milling of aero-engine blisks. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauch, M.; Duc, E.; Hascoet, J.-Y. Improving trochoidal tool paths generation and implementation using process constraints modelling. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2009, 49, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Luo, H.; Axinte, D.; Liu, D.S.; Mei, J.W.; Liao, Z.R. A wireless instrumented milling cutter system with embedded PVDF sensors. Mech. Syst. Sig. Process. 2018, 110, 556–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.H.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, Y.H.; Chen, X.X.; Wang, D. Experimental investigation on chip morphologies in high-speed dry milling of titanium alloy Ti-6Al-4V. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2012, 62, 933–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, M.; Gómez, A.; Salguero, J.; Batista, M.; Huerta, M.M.; Marcos Bárcena, M. SOM-SEM-EDS Identification of Tool Wear Mechanisms in the Dry-Machining of Aerospace Titanium Alloys. Adv. Mater. Res. 2010, 107, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Vidal, S.R.; Mayuet, P.; Rivero, A.; Salguero, J.; del Sol, I.; Marcos, M. Analysis of the Effects of Tool Wear on Dry Helical Milling of Ti6Al4V Alloy. Procedia Eng. 2015, 132, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Element | Al | V | Fe | O | C | N | H | Ti |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wt.% | 5.5–6.8 | 3.5–4.5 | <0.5 | <0.2 | <0.1 | <0.05 | <0.015 | balance |
| Physical Properties | Density (kg/m3) | Elastic Modulus (GPa) | Yield Strength (MPa) | Thermal Conductivity (W/(m·K)) | Hardness (HRC) | Melting Point (°C) | ||
| value | 4430 | 113.8 | 880 | 6.7 | 36 | 1604–1660 | ||
| Diameter (mm) | Number of Flutes | Helix Angle (°) | Corner Radius (mm) | Coating | Rake Angle (°) | Clearance Angle (°) | Second Clearance Angle (°) | Hardness (HRC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12 | 4 | 35 | 0.5 | TiAlN (3 μm) | 4 | 8 | 20 | 65 |
| Test No. | Cutting Speed (m/min) | Radial Depth of Cut ae (mm) | Spindle Speed (rpm) | Feed Rate (mm/min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 60 | 0.2 | 1592 | 637 |
| 2 | 0.4 | |||
| 3 | 0.6 | |||
| 4 | 130 | 0.2 | 3448 | 1379 |
| 5 | 0.4 | |||
| 6 | 0.6 | |||
| 7 | 200 | 0.2 | 5305 | 2122 |
| 8 | 0.4 | |||
| 9 | 0.6 |
| Test No. | VMR (mm3) | Effective Cutting Time (s) | MRR (mm3/min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 77,280 | 18,198 | 254.8 |
| 2 | 30,360 | 3575 | 509.6 |
| 3 | 85,146 | 6683 | 764.4 |
| 4 | 45,080 | 4904 | 551.6 |
| 5 | 4692 | 255 | 1103.2 |
| 6 | 8786 | 319 | 1654.8 |
| 7 | 13,340 | 943 | 848.8 |
| 8 | 1472 | 52 | 1697.6 |
| 9 | 1518 | 36 | 2546.4 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, M.; Zhang, D. Investigation of Tool Wear and Chip Morphology in Dry Trochoidal Milling of Titanium Alloy Ti–6Al–4V. Materials 2019, 12, 1937. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12121937
Liu D, Zhang Y, Luo M, Zhang D. Investigation of Tool Wear and Chip Morphology in Dry Trochoidal Milling of Titanium Alloy Ti–6Al–4V. Materials. 2019; 12(12):1937. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12121937
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Dongsheng, Ying Zhang, Ming Luo, and Dinghua Zhang. 2019. "Investigation of Tool Wear and Chip Morphology in Dry Trochoidal Milling of Titanium Alloy Ti–6Al–4V" Materials 12, no. 12: 1937. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12121937
APA StyleLiu, D., Zhang, Y., Luo, M., & Zhang, D. (2019). Investigation of Tool Wear and Chip Morphology in Dry Trochoidal Milling of Titanium Alloy Ti–6Al–4V. Materials, 12(12), 1937. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12121937





