Performance Evaluation of Asphalt Rubber Mixture with Additives
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Asphalt Binder
2.2. Aggregate
2.3. Crumb Rubber
2.4. Additives
2.5. Asphalt Rubber Preparation
2.6. Specimen Preparation
2.7. Mechanical Property Testing
2.7.1. Wheel Tracking Test
2.7.2. Fatigue Test
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Mixture Design
3.2. Mechanical Property Testing
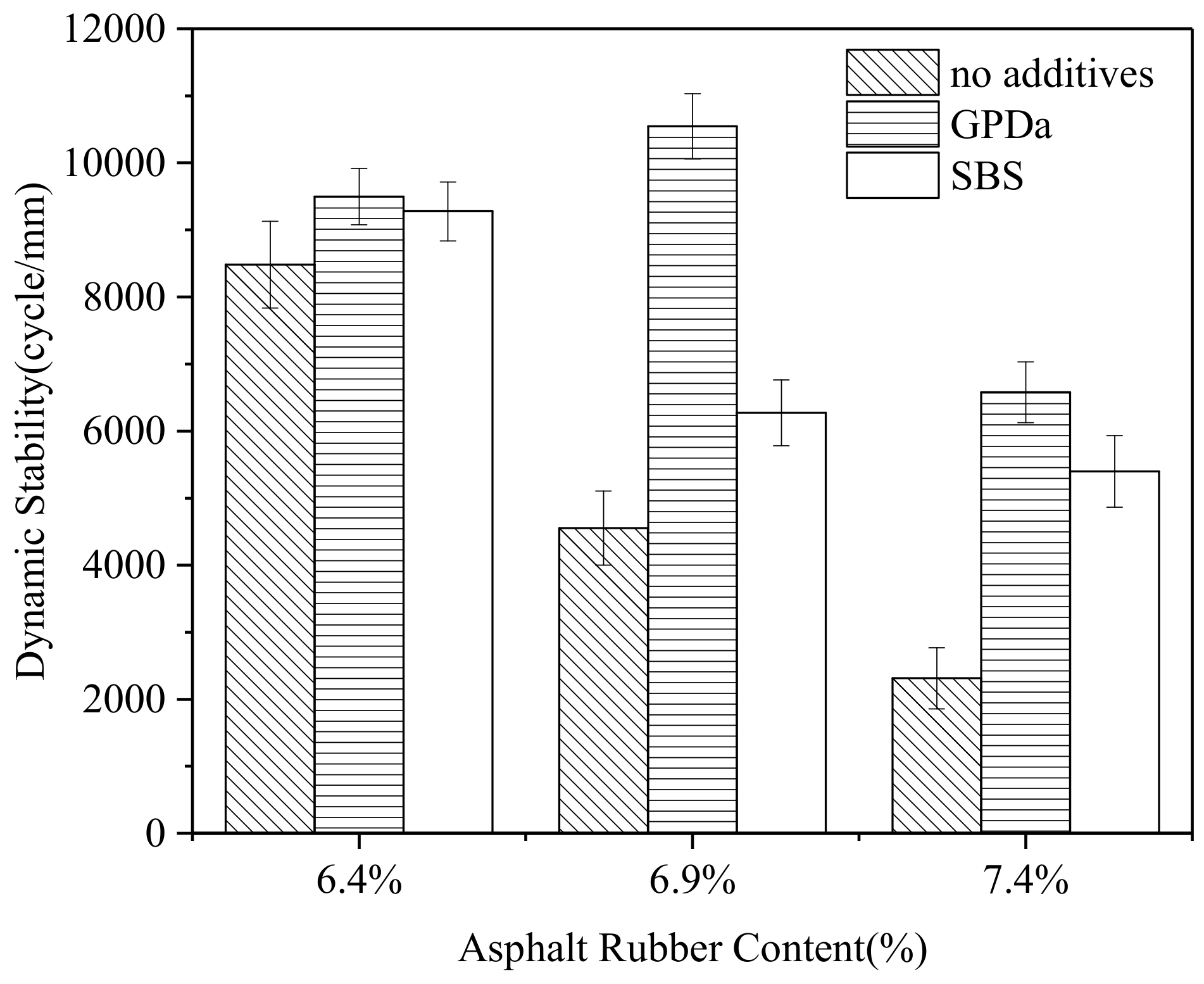
3.2.1. Wheel Tracking Test
Different ARC
Different Additives
The Significance of Additives and ARC
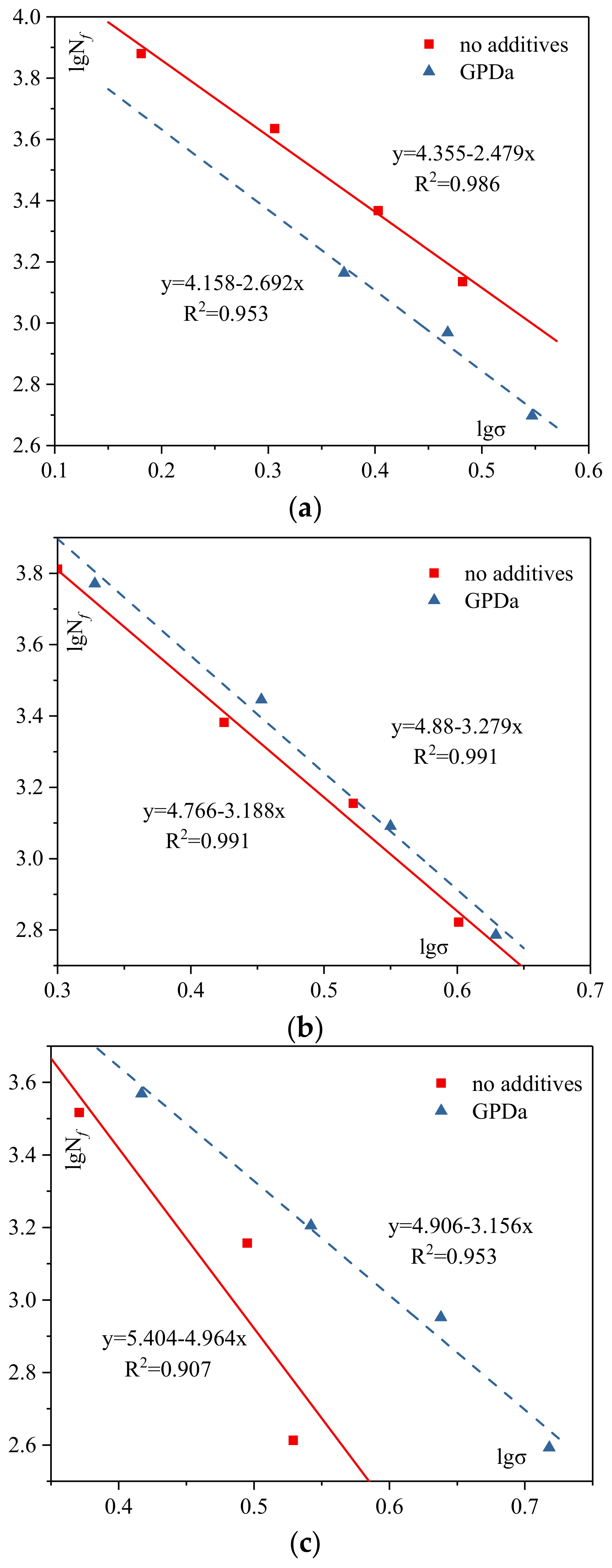
3.2.2. Fatigue Test
Different Additives
Different ARC
The Significance of Additives and ARC
4. Conclusions
- In the wheel tracking test, both SBS and GPDa could improve the high-temperature performance of the mixture. The rutting resistance of AR-SMA with GPDa at ARC 6.9% performs best.
- GPDa is an alternative additive to improve the high-temperature performance of mixtures.
- Under the condition of mixtures with appropriate ARC, AR-SMA with GPDa has higher fatigue life and sensitivity to fatigue cracking than that without additives.
- Both ARC and additives significantly affect rutting performance statistically, and ARC has a greater impact on rutting performance than additives. The variance analysis of the fatigue test shows that various additives and ARC significantly affect stress statistically, but have no significant effect on fatigue life.
- Optimal asphalt content is very important for the design and performance of mixture. Similarly, the additive may be selected at the appropriate asphalt content in order to perform well.
- Further study should be undertaken on the effect of additives on other performances of mixtures, for example, moisture susceptibility, aging, and low-temperature performance.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bouzid, C.; Sholar, G.A.; Musselman, J.A.; Page, G.C. Ten-year performance evaluation of asphalt-rubber surface mixes. Transp. Res. Rec. 1999, 1681, 10–18. [Google Scholar]
- Kaloush, K.; Witczak, M.; Way, G. Performance Evaluation of Arizona Asphalt Rubber Mixtures Using Advanced Dynamic Material Characterization Tests; Arizona State University: Tempe, AZ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W. Research on Performance and Application of Crumb Rubber Modified Asphalt Mixture. Ph.D. Thesis, Tongji University, Shanghai, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Asphalt Rubber Usage Guide; State of California Department of Transportation: Sacramento, CA, USA, 2006.
- Liu, Y.; Han, S.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, O. Design and evaluation of gap-graded asphalt rubber mixture. Mater. Des. 2012, 35, 873–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, D.; Way, G.; Zareh, A.; Kaloush, K.; Biligiri, K. Noise Characteristics and Field Performance of Five Different Wearing Courses in Arizona. In Proceedings of the Asphalt Rubber 2009 International Conference, Nanjing, China, 2–4 November 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kaloush, K.; Zborowski, A.; Biligiri, K.; Rodezno, M.; De Mello, L. Performance Evaluation of Asphalt Rubber Mixtures in Arizona–Silver Springs and Badger Springs Projects; Final Report; Arizona State University: Tempe, AZ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Way, G.B.; Kaloush, K.; Sousa, J.; Biligiri, K.P. Performance characteristics of Arizona asphalt rubber and conventional mixes using beam fatigue and simple shear tests. In Proceedings of the Asphalt Rubber 2012, Munich, Germany, 23–26 October 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, B.; Mohammad, L.; Graves, P.; Abadie, C. Louisiana experience with crumb rubber modified hot-mix asphalt pavement. Transp. Res. Rec. 2002, 1789, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santagata, E.; Baglieri, O.; Alam, M.; Lanotte, M.; Riviera, P. Evaluation of rutting resistance of rubberized gap-graded asphalt mixtures. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference of Bituminous Mixtures and Pavements, Thessaloniki, Greece, 10–12 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y. Study on Cause and Countermeasure on Rutting of Highway Asphalt Pavement in Shaanxi Province. Master’s Thesis, Chang’an University, Xi’an, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Tayfur, S.; Ozen, H.; Aksoy, A. Investigation of rutting performance of asphalt mixtures containing polymer modifiers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2007, 21, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.H. Research and application of anti-rutting in the asphalt mixtures. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 594–597, 1467–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Zhang, C.; Gao, J.; Mi, J. Experimental study on improving the road performances of asphalt mixture with granular polymer. J. Chongqing Jiaotong Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2004, 23, 63–66. [Google Scholar]
- Kaloush, K. Asphalt rubber: Performance tests and pavement design issues. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 67, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangiorgi, C.; Tataranni, P.; Simone, A.; Vignali, V.; Lantieri, C.; Dondi, G. Stone mastic asphalt (SMA) with crumb rubber according to a new dry-hybrid technology: A laboratory and trial field evaluation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 182, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, J.; Bejarano, M.; Popescu, L. Accelerated pavement testing of rutting and cracking performance of asphalt-rubber and conventional asphalt concrete overlay strategies. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2001, 2, 229–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JTJ E20-2011. In Standard Test Methods of Bitumen and Bituminous Mixtures for Highway Engineering; Ministry of Communication: Beijing, China, 2011.
- Liu, Y. Research on Technical Performance of Asphalt Rubber and Asphalt Rubber SMA. Master’s Thesis, Chang’an University, Xi’an, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- JTG F40-2004. In Technical Specification for Construction of Highway Asphalt Pavements; Ministry of Communication: Beijing, China, 2004.
- Li, N. The Research of High-Modulus Asphalt Mixes. Master’s Thesis, Chang’an University, Xi’an, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, L.; Cheng, J.; Que, G. Microstructure and performance of crumb rubber modified asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 3586–3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, K.; Lee, S.; Amirkhanian, S.; Kim, K. Interaction effects of crumb rubber modified asphalt binders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 24, 824–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Ren, W.; Jia, J.; Yang, H.; Niu, D. Modification Mechanisms of Granulated Polymer Anti-rutting Additive Toward Asphalt and Asphalt Mixture. Mater. Rev. 2017, 31, 129–134. [Google Scholar]
- Raad, L.; Saboundjian, S.; Minassian, G. Field aging effects on the fatigue of asphalt concrete and asphalt-rubber concrete. Transp. Res. Rec. 2001, 1767, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Shen, J.; Earnest, M.; Li, B. Fatigue Performance Evaluation of Rubberized Porous European Mixture by Simplified Viscoelastic Continuum Damage Model. Transp. Res. Rec. 2015, 2506, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Test Items | Unit | Value | Specification |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25 °C penetration | 0.1 mm | 81 | T0604 |
| 10 °C ductility | cm | 72 | T0605 |
| Softening point | °C | 47.5 | T0606 |
| Test Items | Unit | Value | Specification | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10–15 mm | 5–10 mm | 3–5 mm | |||
| Crushing value | % | 13.4 | - | - | T0316 |
| Los Angeles abrasion | % | 11.8 | - | - | T0317 |
| Apparent relative density | - | 2.856 | 2.857 | 2.812 | T0304 |
| Bulk relative density | - | 2.781 | 2.762 | 2.709 | |
| Water absorption | % | 0.51 | 0.63 | 0.59 | |
| Flat or elongated | % | 4.0 | 6.7 | - | T0312 |
| Test Items | Unit | Value | Specification |
|---|---|---|---|
| Apparent relative density | - | 2.797 | T0328 |
| Mud content (percent of <0.075 mm) | % | 1.1 | T0333 |
| Sand equivalent | % | 95.5 | T0334 |
| Angularity | s | 57.1 | T0344 |
| Test Items | Unit | Value | Specification |
|---|---|---|---|
| Apparent relative density | - | 2.799 | T0352 |
| Water absorption | % | 0.2 | |
| Grain sizes <0.6 mm | % | 100.0 | T0351 |
| <0.15 mm | % | 95.0 | |
| <0.075 mm | % | 90.1 | |
| Hydrophilic coefficient | - | 0.60 | T0353 |
| Aggregates with Different Sizes | Passing Percentage of Aggregates with Different Sizes/% | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16 | 13.2 | 9.5 | 4.75 | 2.36 | 1.18 | 0.6 | 0.3 | 0.15 | 0.075 | |
| 10–15 mm | 100 | 92.3 | 6.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| 5–10 mm | - | 100 | 96.1 | 1.5 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| 3–5 mm | - | - | 100 | 88.1 | 4.3 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 |
| 0–3 mm | - | - | - | 100 | 92.0 | 4.4 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 |
| Mineral filler | - | - | - | - | 100 | 100 | 100 | 99 | 97 | 89 |
| Sieve Sizes (mm) | 1.18 | 0.6 | 0.3 | 0.15 | 0.075 |
| Passing Percentage/% | 100.0 | 99.2 | 66.6 | 25.4 | 5.2 |
| Test Item | Rate (S/B) | Rate of Liquid Volume/% | Volatile ≤% | Ash Content ≥% | Tensile Strength ≥MPa | Shore Hardness A | Melt Flow Rate g/min |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | 30/70 | 0 | 0.7 | 0.2 | 8 | 70 | 0~1 |
| Test Item | Density/(g/cm3) | Melting Point/°C | Tensile Strength/MPa | Elongation at Break/% | Melt Flow Rate/(g/10 min) | Ash Content/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | 0.94 | 146 | 22.0 | 8.7 | 7.431 | 2.4 |
| Asphalt Binder | Crumb Rubber | 180 °C Viscosity (Pa·s) | 25 °C Penetration (0.1 mm) | Softening Point (°C) | 5 °C Ductility (cm) | Elastic Recovery (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ESSO A-90 | Shanxi | 3.650 | 63 | 59.4 | 17.4 | 53 |
| Sieve Sizes (mm) | 16 | 13.2 | 9.5 | 4.75 | 2.36 | 1.18 | 0.6 | 0.3 | 0.15 | 0.075 |
| Passing Percentage (%) | 100 | 97.9 | 63.5 | 27 | 23.5 | 20 | 16.4 | 12.9 | 9.7 | 6 |
| Source of Variation | Sum of Square | Degree of Freedom | Mean of Square | F | p-Value | Fcritical |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Additives | 2.1 × 107 | 2 | 1.0 × 107 | 5.57 | 0.070 | 6.94 |
| ARC | 2.9 × 107 | 2 | 1.4 × 107 | 7.86 | 0.041 | 6.94 |
| Error | 0.057 | 4 | 0.011 | - | - | - |
| Total | 18.123 | 11 | - | - | - | - |
| Source of Variation | Degree of Freedom | Mean of Square | F | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Additives | lgσ | 1 | 0.052 | 20.702 | 0.000 |
| lgNf | 1 | 0.349 | 3.436 | 0.085 | |
| ARC | lgσ | 2 | 0.036 | 7.036 | 0.008 |
| lgNf | 2 | 0.583 | 2.874 | 0.090 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, X.; Liu, Y.; Ren, W.; Huang, K. Performance Evaluation of Asphalt Rubber Mixture with Additives. Materials 2019, 12, 1200. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12081200
Cheng X, Liu Y, Ren W, Huang K. Performance Evaluation of Asphalt Rubber Mixture with Additives. Materials. 2019; 12(8):1200. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12081200
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Xianpeng, Yamin Liu, Wanyan Ren, and Ke Huang. 2019. "Performance Evaluation of Asphalt Rubber Mixture with Additives" Materials 12, no. 8: 1200. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12081200
APA StyleCheng, X., Liu, Y., Ren, W., & Huang, K. (2019). Performance Evaluation of Asphalt Rubber Mixture with Additives. Materials, 12(8), 1200. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12081200





