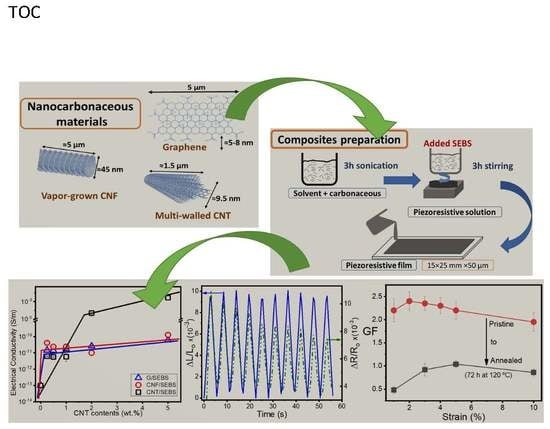
Carbonaceous Filler Type and Content Dependence of the Physical-Chemical and Electromechanical Properties of Thermoplastic Elastomer Polymer Composites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Nanocomposite Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
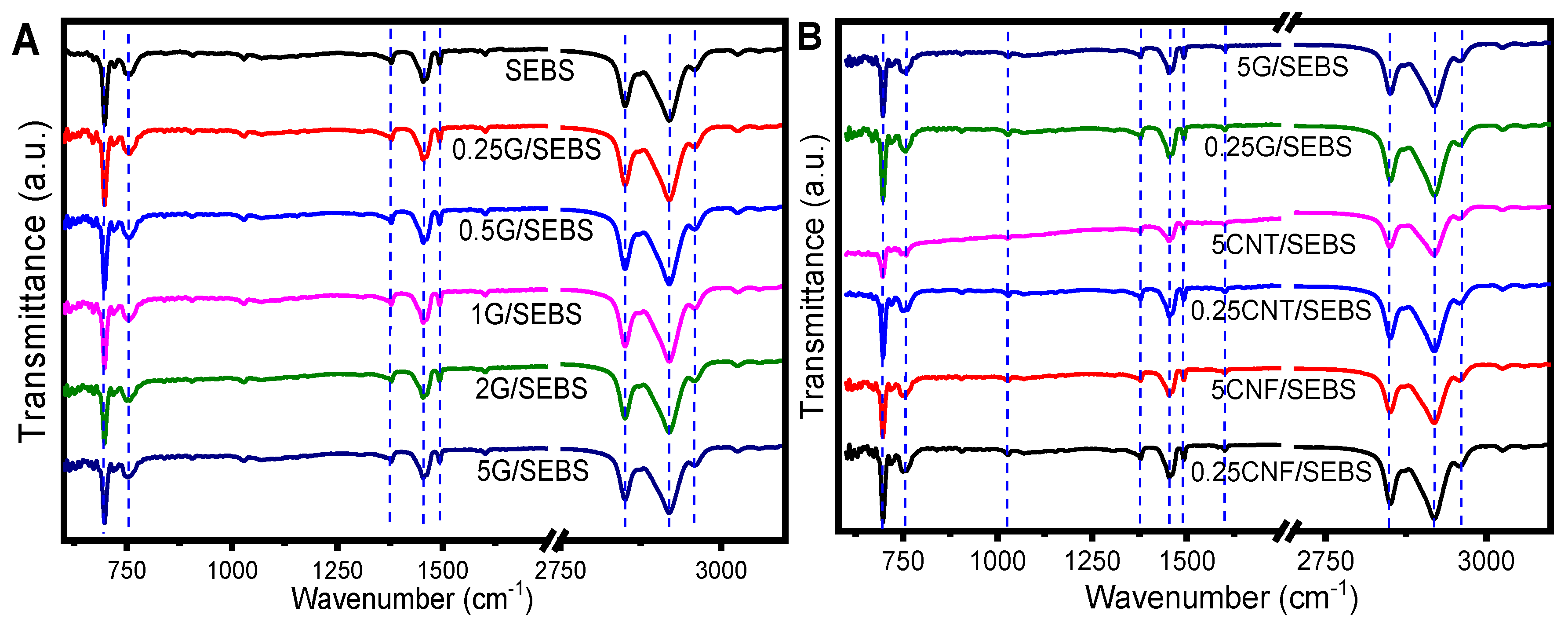
3.1. Morphological and Chemical Properties
3.2. Thermal Properties
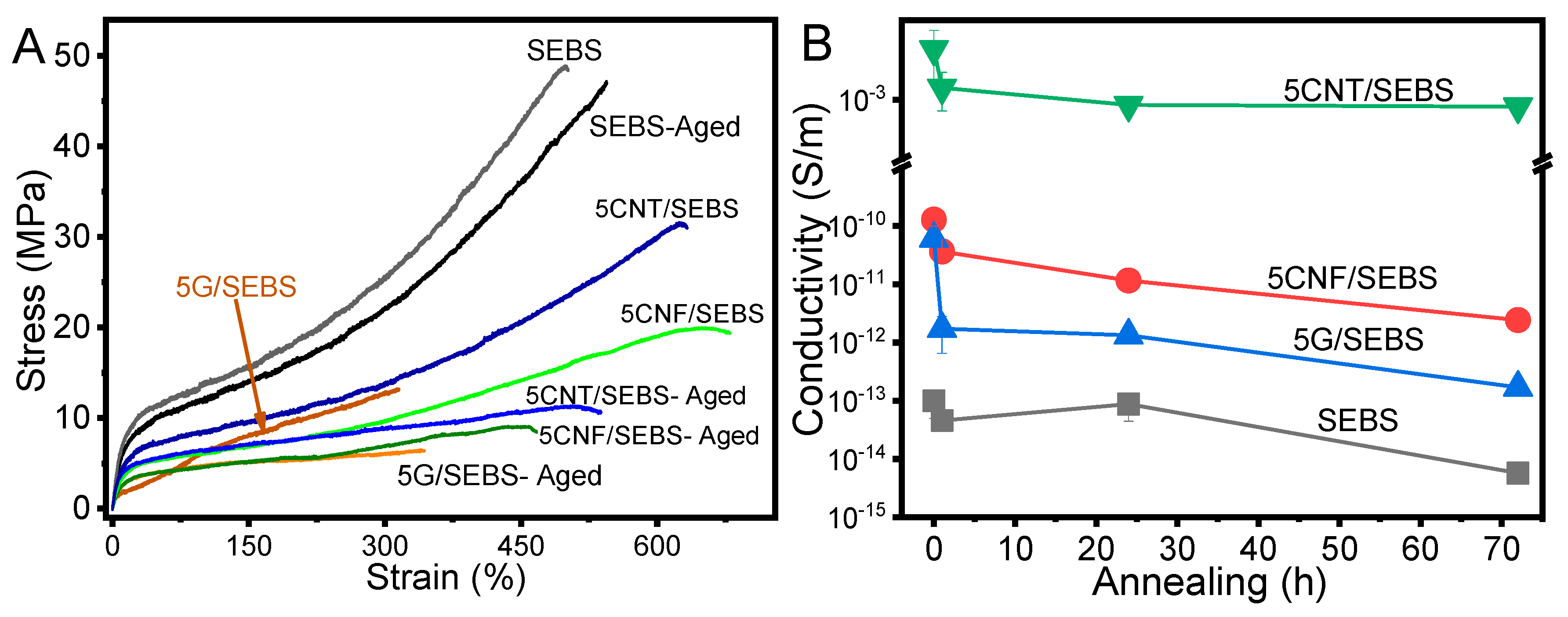
3.3. Mechanical and Electrical Properties
3.4. Thermal Annealing
3.5. Electromechanical Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martins, P.; Lopes, A.C.; Lanceros-Mendez, S. Electroactive phases of poly(vinylidene fluoride): Determination, processing and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 683–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.-X.; Pang, H.; Li, B.; Vajtai, R.; Xu, L.; Ren, P.-G.; Wang, J.-H.; Li, Z.-M. Structured Reduced Graphene Oxide/Polymer Composites for Ultra-Efficient Electromagnetic Interference Shielding. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 25, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, J.N.; Khan, U.; Blau, W.J.; Gun’ko, Y.K. Small but strong: A review of the mechanical properties of carbon nanotube–polymer composites. Carbon 2006, 44, 1624–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, G.; Rhee, K.Y.; Mišković-Stanković, V.; Hui, D. Reinforcements in multi-scale polymer composites: Processing, properties, and applications. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 138, 122–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, C.; Vilatela, J.J.; Molina-Aldareguía, J.M.; Lopes, C.S.; Llorca, J. Structural composites for multifunctional applications: Current challenges and future trends. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2017, 89, 194–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costa, P.; Nunes-Pereira, J.; Oliveira, J.; Silva, J.; Moreira, J.A.; Carabineiro, S.A.C.; Buijnsters, J.G.; Lanceros-Mendez, S. High-performance graphene-based carbon nanofiller/polymer composites for piezoresistive sensor applications. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2017, 153, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjong, S.C. Recent progress in the development and properties of novel metal matrix nanocomposites reinforced with carbon nanotubes and graphene nanosheets. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2013, 74, 281–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Shen, F.; Chua, C.K.; Zhou, K. Polymeric composites for powder-based additive manufacturing: Materials and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2019, 91, 141–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, J.; Correia, V.; Castro, H.; Martins, P.; Lanceros-Mendez, S. Polymer-based smart materials by printing technologies: Improving application and integration. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 21, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, P.; Silvia, C.; Viana, J.C.; Lanceros Mendez, S. Extruded thermoplastic elastomers styrene–butadiene–styrene/carbon nanotubes composites for strain sensor applications. Compos. Part B Eng. 2014, 57, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, P.; Silva, J.; Ansón-Casaos, A.; Martinez, M.T.; Abad, M.J.; Viana, J.; Lanceros-Mendez, S. Effect of carbon nanotube type and functionalization on the electrical, thermal, mechanical and electromechanical properties of carbon nanotube/styrene–butadiene–styrene composites for large strain sensor applications. Compos. Part B Eng. 2014, 61, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, T.; Wang, Z.; Pan, Z.-J. Flexible strain sensors fabricated using carbon-based nanomaterials: A review. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2018, 22, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, J.; Ishida, H. A review on the very high nanofiller-content nanocomposites: Their preparation methods and properties with high aspect ratio fillers. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2018, 86, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessema, A.; Zhao, D.; Moll, J.; Xu, S.; Yang, R.; Li, C.; Kumar, S.K.; Kidane, A. Effect of filler loading, geometry, dispersion and temperature on thermal conductivity of polymer nanocomposites. Polym. Test. 2017, 57, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedroni, L.G.; Araujo, J.R.; Felisberti, M.I.; Nogueira, A.F. Nanocomposites based on MWCNT and styrene–butadiene–styrene block copolymers: Effect of the preparation method on dispersion and polymer–filler interactions. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2012, 72, 1487–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, P.; Maceiras, A.; San Sebastián, M.; García-Astrain, C.; Vilas, J.L.; Lanceros-Mendez, S. On the use of surfactants for improving nanofiller dispersion and piezoresistive response in stretchable polymer composites. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 10580–10588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadasivuni, K.K.; Ponnamma, D.; Thomas, S.; Grohens, Y. Evolution from graphite to graphene elastomer composites. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 749–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, B.F.; Costa, P.; Oliveira, J.; Ribeiro, S.; Correia, V.; Botelho, G.; Lanceros-Mendez, S. Green solvent approach for printable large deformation thermoplastic elastomer based piezoresistive sensors and their suitability for biomedical applications. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2016, 54, 2092–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanabadi, N.; Nazockdast, H.; Balog, S.; Lattuada, M. Rheological characterization of nanostructured material based on Polystyrene-b-poly(ethylene-butylene)-b-polystyrene (SEBS) block copolymer: Effect of block copolymer composition and nanoparticle geometry. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2017, 149, 192–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, P.; Silva, J.; Sencadas, V.; Simoes, R.; Viana, J.C.; Lanceros-Mendez, S. Mechanical, electrical and electro-mechanical properties of thermoplastic elastomer styrene-butadiene-styrene/multiwall carbon nanotubes composites. J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 48, 1172–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, X.; Wu, Y.; Liao, G.; Johnston, P.; Topham, P.D.; Wang, L. Rinse-resistant superhydrophobic block copolymer fabrics by electrospinning, electrospraying and thermally-induced self-assembly. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 422, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.-C.; Siddiqui, N.A.; Marom, G.; Kim, J.-K. Dispersion and functionalization of carbon nanotubes for polymer-based nanocomposites: A review. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2010, 41, 1345–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calisi, N.; Salvo, P.; Melai, B.; Paoletti, C.; Pucci, A.; Di Francesco, F. Effects of thermal annealing on SEBS/MWCNTs temperature-sensitive nanocomposites for the measurement of skin temperature. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2017, 186, 456–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y. Reinforcement of styrene-butadiene-styrene tri-block copolymer by multi-walled carbon nanotubes via melt mixing. Carbon 2007, 45, 2621–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomacheski, D.; Pittol, M.; Ermel, C.E.; Simões, D.N.; Ribeiro, V.F.; Santana, R.M.C. Influence of processing conditions on the mechanical properties of SEBS/PP/oil blends. Polym. Bull. 2017, 74, 4841–4855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra, C.A.; Galán, C.; Fatou, J.G.; Parellada, M.D.; Barrio, J.A. Thermal and mechanical properties of poly (styrene-b-ethylene-co-butylene-b-styrene) triblock copolymers. Polymer 1997, 38, 4325–4335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karode, N.S.; Poudel, A.; Fitzhenry, L.; Matthews, S.; Walsh, P.R.; Coffey, A.B. Evaluation of interfacial region of microphase-separated SEBS using modulated differential scanning calorimetry and dynamic mechanical thermal analysis. Polym. Test. 2017, 62, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parodi, E.; Govaert, L.E.; Peters, G.W.M. Glass transition temperature versus structure of polyamide 6: A flash-DSC study. Thermochim. Acta 2017, 657, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Yang, J.; Zhou, X.; Wei, Q.; Li, J.; Qiu, B.; Wunderlich, K.; Wang, X. Effect of compatibilizer on morphology, rheology and properties of SEBS/clay nanocomposites. Polym. Test. 2018, 67, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helal, E.; Demarquette, N.R.; David, E.; Fréchette, M.F. Polyethylene/styrenic block copolymer blends: Morphology and dielectric properties. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Electrical Insulation and Dielectric Phenomena (CEIDP), Des Moines, IA, USA, 19–22 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, P.; Ribeiro, S.; Lanceros-Mendez, S. Mechanical vs. electrical hysteresis of carbon nanotube/styrene–butadiene–styrene composites and their influence in the electromechanical response. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2015, 109, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drobny, J.G. 5-Styrenic Block Copolymers. In Handbook of Thermoplastic Elastomers; Drobny, J.G., Ed.; William Andrew Publishing: Norwich, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Shi, D.; Li, C.; Luan, S.; Yin, J.; Li, R.K.Y. Preparation of functionalized graphene/SEBS-g-MAH nanocomposites and improvement of its electrical, mechanical properties. Mater. Lett. 2014, 133, 200–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enrique-Jimenez, P.; Quiles-Díaz, S.; Salavagione, H.J.; Wesner, D.; Schönherr, H.; González-Casablanca, J.; García-Quismondo, R.; Martínez, G.; Gómez-Fatou, M.A.; Ania, F.; et al. Control of the structure and properties of SEBS nanocomposites via chemical modification of graphene with polymer brushes. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 97, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allen, N.S.; Luengo, C.; Edge, M.; Wilkinson, A.; Parellada, M.D.; Barrio, J.A.; Quiteria, V.R.S. Photooxidation of styrene–ethylene–butadiene–styrene (SEBS) block copolymer. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2004, 162, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, N.S.; Edge, M.; Wilkinson, A.; Liauw, C.M.; Mourelatou, D.; Barrio, J.; Martínez-Zaporta, M.A. Degradation and stabilisation of styrene–ethylene–butadiene–styrene (SEBS) block copolymer. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2000, 71, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Focatiis, D.S.A.; Hull, D.; Sánchez-Valencia, A. Roles of prestrain and hysteresis on piezoresistance in conductive elastomers for strain sensor applications. Plast. Rubber Compos. 2012, 41, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]







| Filler Content | Nomenclature | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| CNF/SEBS | CNT/SEBS | Graphene/SEBS | |
| 0.25 wt.% | 0.25 CNF/SEBS | 0.25 CNT/SEBS | 0.25 G/SEBS |
| 0.5 wt.% | 0.5 CNF/SEBS | 0.5 CNT/SEBS | 0.5 G/SEBS |
| 1 wt.% | 1 CNF/SEBS | 1 CNT/SEBS | 1 G/SEBS |
| 2 wt.% | 2 CNF/SEBS | 2 CNT/SEBS | 2 G/SEBS |
| 5 wt.% | 5 CNF/SEBS | 5 CNT/SEBS | 5 G/SEBS |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dios, J.R.; García-Astrain, C.; Costa, P.; Viana, J.C.; Lanceros-Méndez, S. Carbonaceous Filler Type and Content Dependence of the Physical-Chemical and Electromechanical Properties of Thermoplastic Elastomer Polymer Composites. Materials 2019, 12, 1405. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12091405
Dios JR, García-Astrain C, Costa P, Viana JC, Lanceros-Méndez S. Carbonaceous Filler Type and Content Dependence of the Physical-Chemical and Electromechanical Properties of Thermoplastic Elastomer Polymer Composites. Materials. 2019; 12(9):1405. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12091405
Chicago/Turabian StyleDios, Jose Ramon, Clara García-Astrain, Pedro Costa, Júlio César Viana, and Senentxu Lanceros-Méndez. 2019. "Carbonaceous Filler Type and Content Dependence of the Physical-Chemical and Electromechanical Properties of Thermoplastic Elastomer Polymer Composites" Materials 12, no. 9: 1405. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12091405
APA StyleDios, J. R., García-Astrain, C., Costa, P., Viana, J. C., & Lanceros-Méndez, S. (2019). Carbonaceous Filler Type and Content Dependence of the Physical-Chemical and Electromechanical Properties of Thermoplastic Elastomer Polymer Composites. Materials, 12(9), 1405. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12091405