Carbon Black as Conductive Additive and Structural Director of Porous Carbon Gels
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Materials
2.2. Characterization Techniques
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis of the Materials
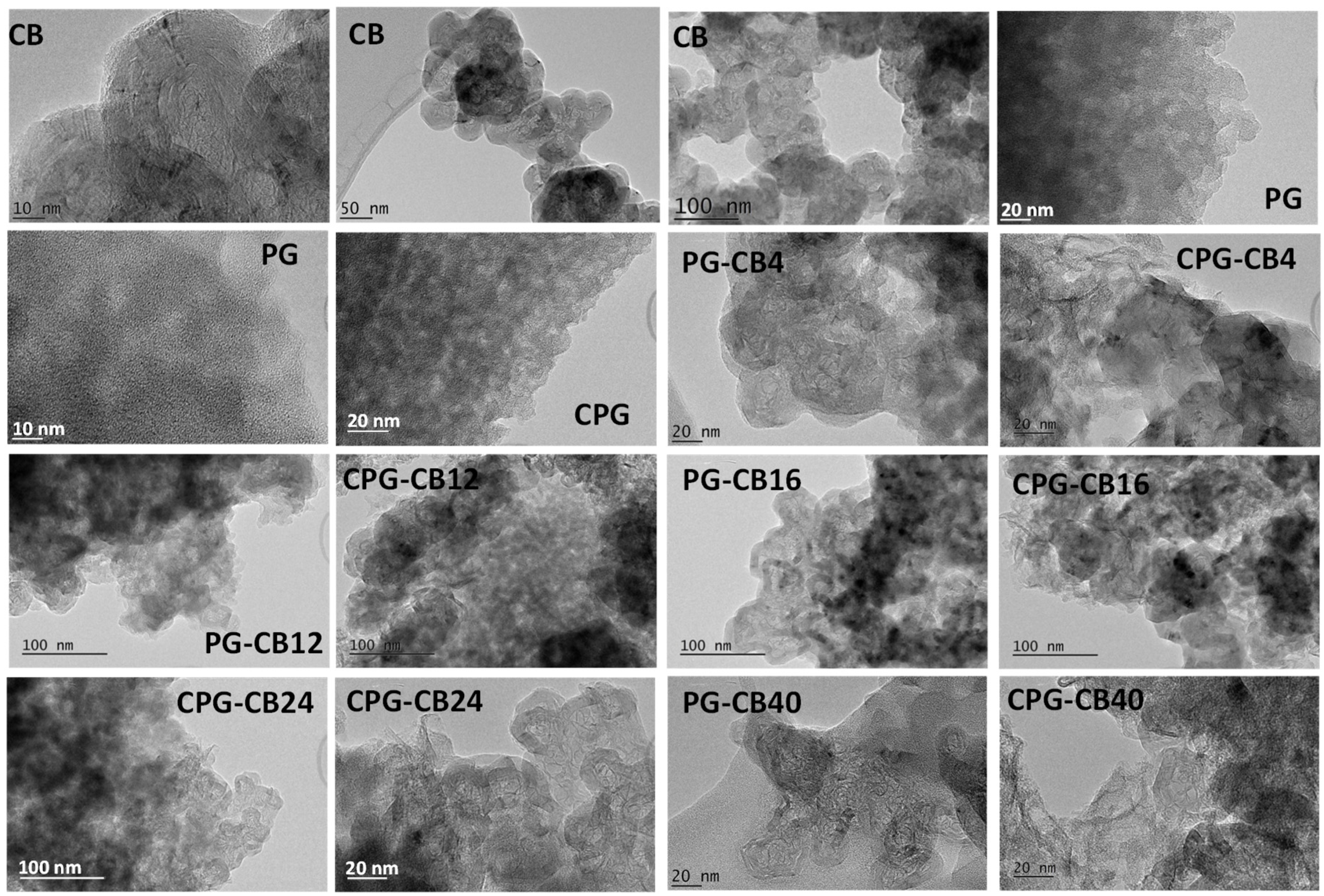
3.2. Structural Characterization
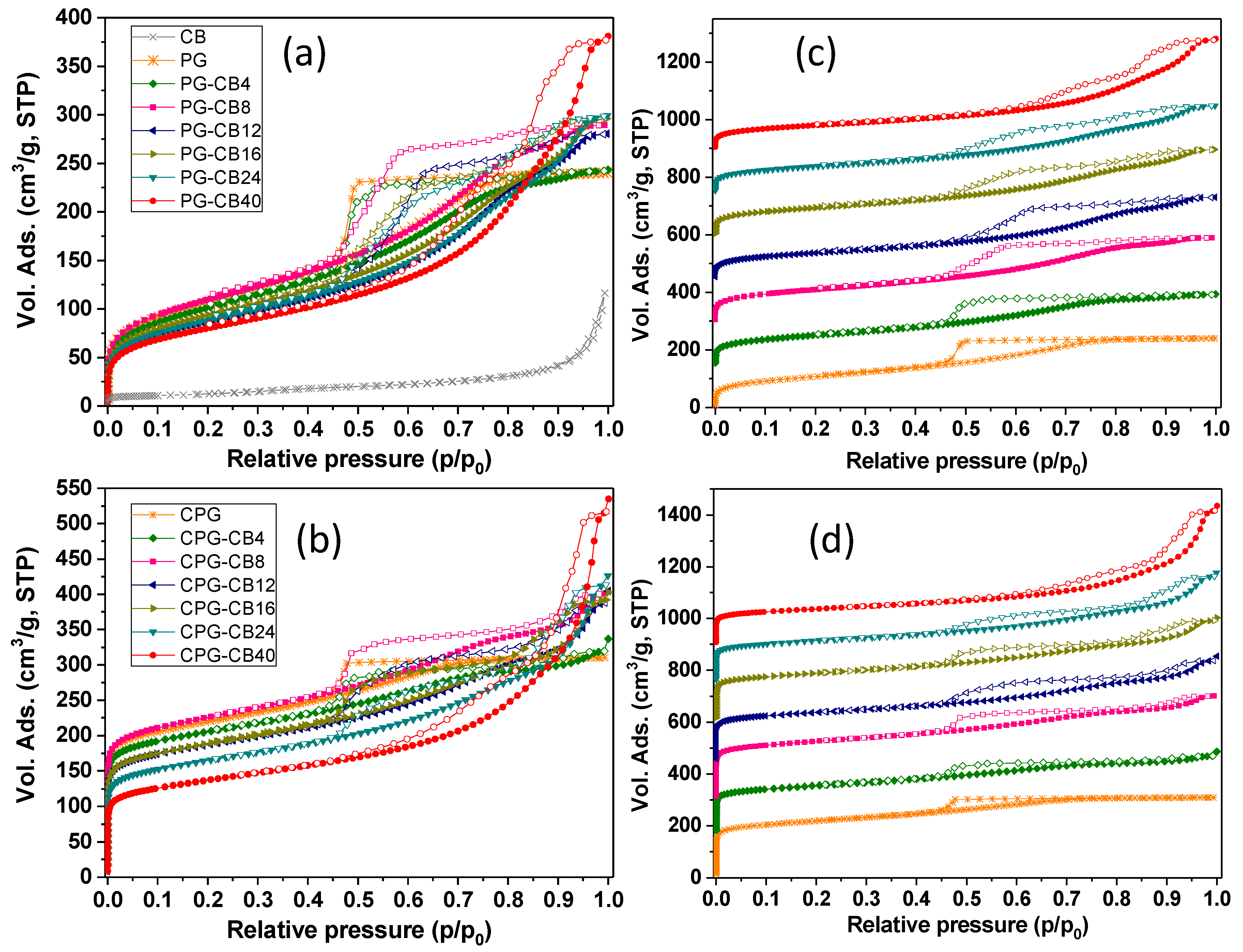
3.3. Textural Characterization
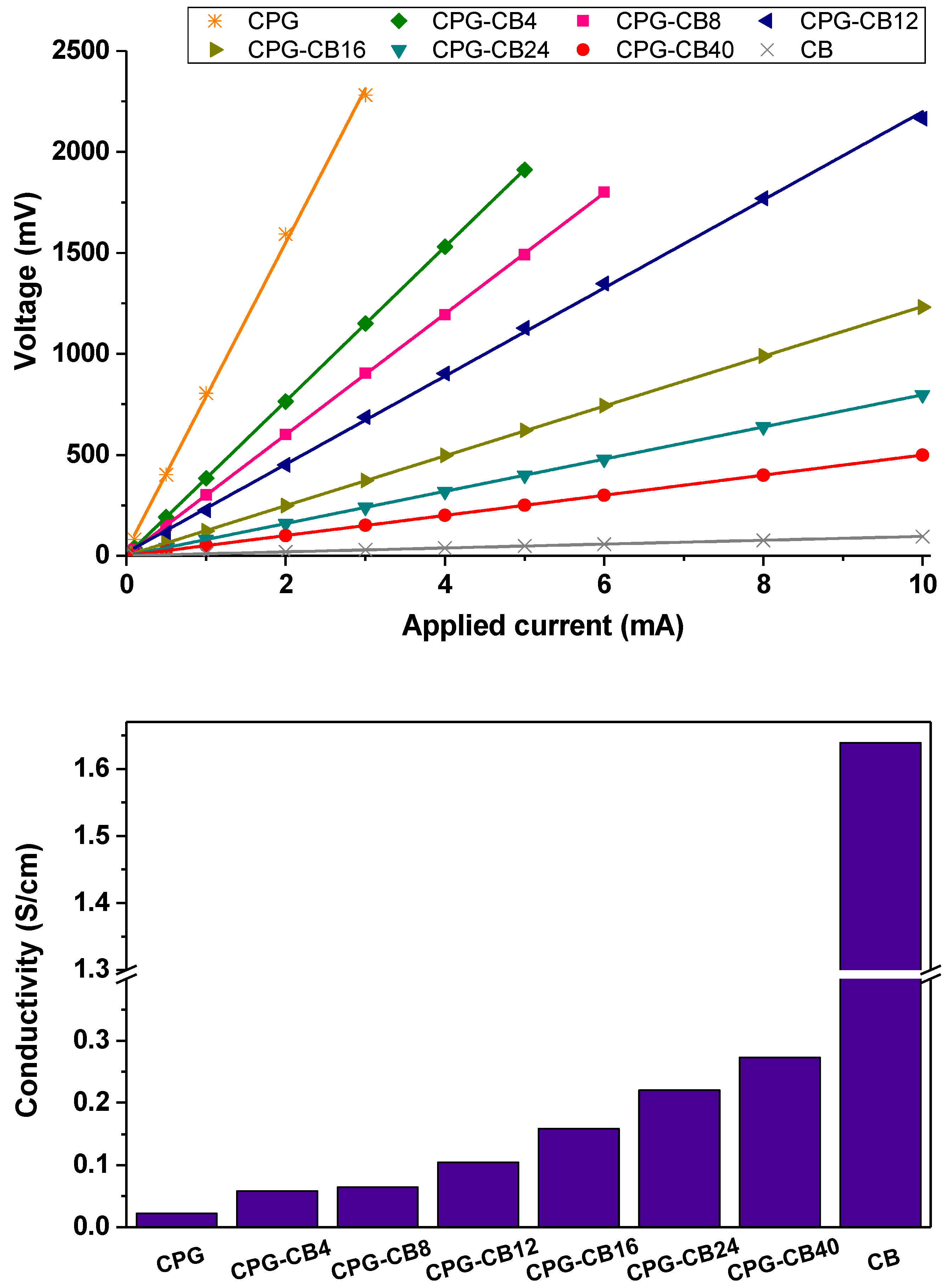
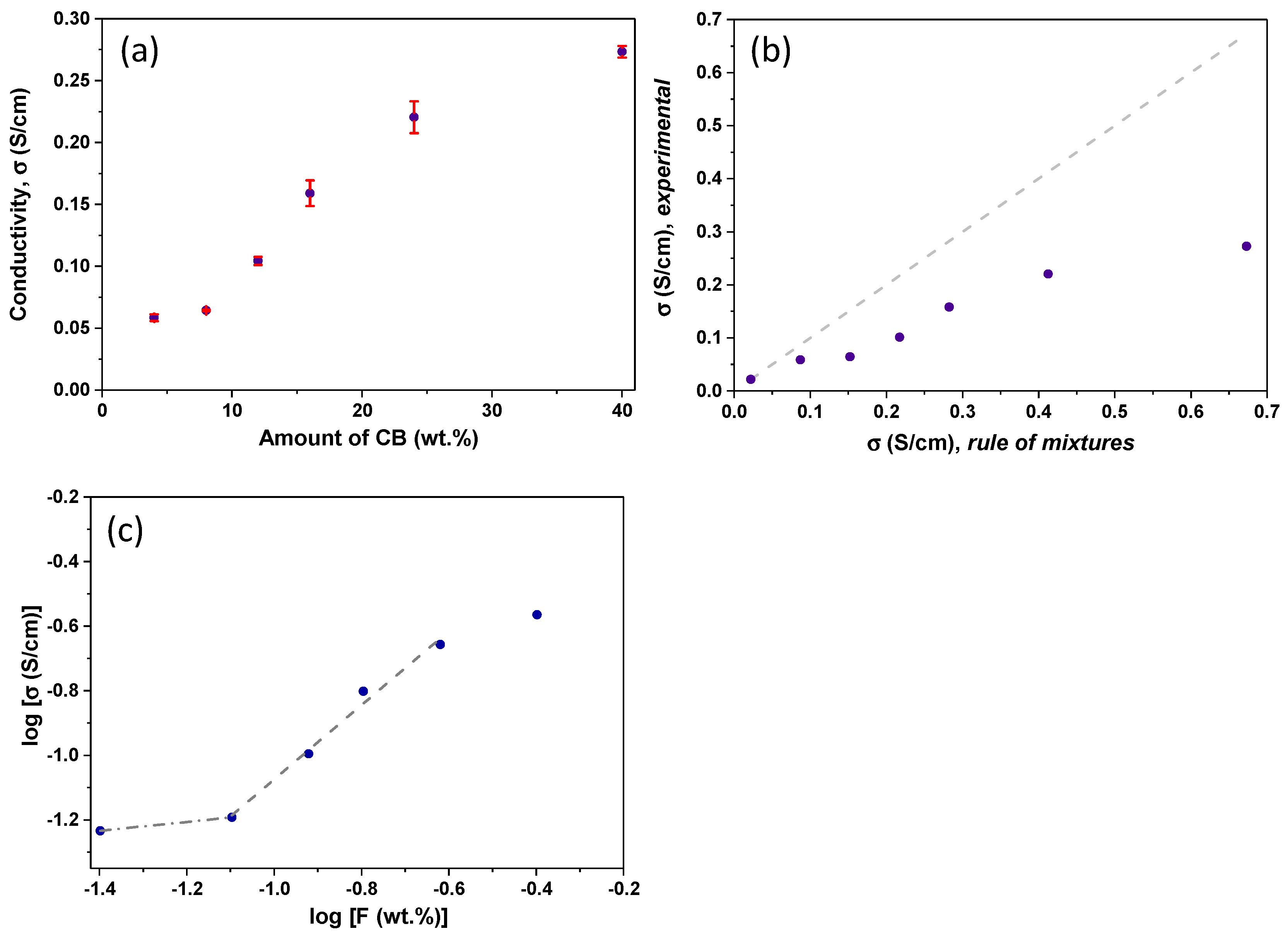
3.4. Conductivity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Beguin, F.; Frackowiak, E. Carbons for Electrochemical Energy Storage and Conversion Systems, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Iniesta, J.; Garcia-Cruz, L.; Gomis-Berenguer, A.; Ania, C.O. Carbon materials based on screen printing electrochemical platforms in biosensing applications. In Electrochemistry Series; Banks, C., Mortimer, R., Mclntosh, S., Eds.; RSC Publishing: Croydon, UK, 2016; Volume 13, pp. 133–169. [Google Scholar]
- Pandolfo, A.G.; Hollenkamp, A.F. Carbon properties and their role in supercapacitors. J. Power Sources 2006, 157, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podyacheva, O.Y.; Cherepanova, S.V.; Romanenko, A.I.; Kibis, L.S.; Svintsitskiy, D.A.; Boronin, A.I.; Stonkus, O.A.; Suboch, A.N.; Puzynin, A.V.; Ismagilov, Z.R. Nitrogen doped carbon nanotubes and nanofibers: Composition, structure, electrical conductivity and capacity properties. Carbon 2017, 122, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sun, X. Understanding and recent development of carbon coating on LiFePO4 cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 5163–5185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Kang, F.; Bai, X.; Shen, W. A novel network composite cathode of LiFePO4/multiwalled carbon nanotubes with high rate capability for lithium ion batteries. Electrochem. Commun. 2007, 9, 663–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Kim, K.; Kang, S.H.; Kwon, Y.; Kim, J.H.; Kwon, Y.K.; Ryoo, R.; Park, J.Y. Extremely high electrical conductance of microporous 3D graphene-like zeolite-templated carbon framework. Sci. Rep.-UK 2017, 7, 11602–11605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dangles, C.; Rane-Fodacarao, M.; Devarajan, T.S.; Higashiya, S.; Snyder, J.; Haldar, P. Role of conducting carbon in electrodes for electric double layer capacitors. Mater. Lett. 2011, 65, 300–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taherian, R.; Kausar, A. Electrical Conductivity in Polymer-Based Composites: Experiments, Modelling, and Applications; William Andrew Applied Science Publishers: Norwich, NY, USA; Elseeveir: Oxford, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Rey-Raap, N.; Calvo, E.G.; Bermúdez, J.M.; Cameán, I.; García, A.B.; Menéndez, J.A.; Arenillas, A. An electrical conductivity translator for carbons. Measurement 2014, 56, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pico, F.; Pecharroman, C.; Ansón, A.; Martínez, M.T.; Rojo, J.M. Understanding carbon–carbon composites as electrodes of supercapacitors: A study by AC and DC measurements. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2007, 154, A579–A586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Yu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Z.-D.; He, Y.-b.; Kim, J.-K. Percolation threshold of graphene nanosheets as conductive additives in Li4Ti5O12 anodes of Li-ion batteries. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 2100–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, T.M.; McAteer, D.; Mesquita-Coelho, J.C.; Mendoza-Sánchez, B.; Gholamvand, Z.; Moriarty, G.; McEvoy, N.; Berner, N.C.; Duesberg, G.S.; Nicolosi, V.; et al. The effect of percolation on the capacitance of supercapacitor electrodes prepared from composites of manganese dioxide nano-platelets and carbon nanotubes. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 9567–9579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymundo-Piñero, E.; Cadek, M.; Wachtler, M.; Béguin, F. Carbon nanotubes as nanotexturing agents for high power supercapacitors based on seaweed carbon. ChemSusChem 2011, 4, 943–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macías, C.; Haro, M.; Parra, J.B.; Rasines, G.; Ania, C.O. Carbon black directed synthesis of ultrahigh mesoporous carbon aerogels. Carbon 2013, 63, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasines, G.; Lavela, P.; Macías, C.; Zafra, M.C.; Tirado, J.L.; Ania, C.O. Mesoporous carbon black-aerogel composites with optimized properties for the electro-assisted removal of sodium chloride from brackish water. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2015, 741, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekala, R.W. Organic aerogels from the polycondensation of resorcinol with formaldehyde. J. Mater. Sci. 1989, 24, 3221–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Muhtaseb, S.A.; Ritter, J.A. Preparation and properties of resorcinol-formaldehyde organic and carbon gels. Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElKhatat, A.M.; Al-Muhtaseb, S.A. Advances in tailoring resorcinol-formaldehyde organic and carbon gels. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 2887–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Job, N.; Pirard, R.; Marien, J.; Pirard, J.P. Porous carbon xerogels with texture tailored by pH control during sol–gel process. Carbon 2004, 42, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouquerol, J.; Rouquerol, F.; Sing, K.S.W.; Llewellyn, P.; Maurin, G. Adsorption by Powders and Porous Solids: Principles, Methodology and Applications, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Jagiello, J.; Olivier, J.P. 2D-NLDFT adsorption models for carbon slit-shaped pores with surface energetical heterogeneity and geometrical corrugation. Carbon 2013, 55, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D4496. Standard Test Method for D-C Resistance or Conductance of Moderately Conductive Materials Edition; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1 May 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Pauw, L.J. A method of measuring specific resistivity and Hall effect of discs of arbitrary shapes. Philips Res. Rep. 1958, 13, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Macias, C.; Rasines, G.; Rodriguez, C.; Lavela, P.; Tirado, J.L.; Ania, C.O. On the use of diatomite as antishrinkage additive in the preparation of monolithic carbon aerogels. Carbon 2016, 98, 280–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macias, C.; Rasines, G.; Garcia, T.E.; Zafra, M.C.; Lavela, P.; Tirado, J.L.; Ania, C.O. Synthesis of Porous and Mechanically Compliant Carbon Aerogels Using Conductive and Structural Additives. Gels 2016, 2, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maslova, O.A.; Guimbretière, G.; Ammar, M.R.; Desgranges, L.; Jégou, C.; Canizarès, A.; Simon, P. Raman imaging and principal component analysis-based data processing on uranium oxide ceramics. Mater. Charact. 2017, 129, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomis-Berenguer, A.; García-González, R.; Mestre, A.S.; Ania, C.O. Designing micro- and mesoporous carbon networks by chemical activation of organic resin. Adsorption 2017, 23, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathy, N.A.; Rizk, M.S.; Awad, R.M.S. Pore structure and adsorption properties of carbon xerogels derived from carbonization of tannic acid-resorcinol-formaldehyde resin. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolsis 2016, 119, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S.W. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaacs Páez, E.; Haro, M.; Juárez-Pérez, E.J.; Carmona, R.J.; Parra, J.B.; Leyva Ramos, R.; Ania, C.O. Fast synthesis of micro/mesoporous xerogels: Textural and energetic assessment. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2015, 209, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasines, G.; Macías, C.; Haro, M.; Jagiello, J.; Ania, C.O. Effects of CO2 activation of carbon aerogels leading to ultrahigh micro-meso porosity. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2015, 209, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sihvola, A.; Saastamoinen, S.; Heiska, K. Mixing rules and percolation. Remote Sens. 1994, 9, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batrouni, G.G.; Hansen, A.; Larson, B. Current distribution in the three-dimensional random resistor network at the percolation threshold. Phys. Rev. E 1996, 53, 2292–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, P.; Saini, P.; Singh Malik, R.; Choudhary, V. Excellent electromagnetic interference shielding and mechanical properties of high loading carbon-nanotubes/polymer composites designed using melt recirculation equipped twin-screw extruder. Carbon 2015, 89, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, R.; Rahaman, M.; Khastgir, D. Electrical properties of polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF)/multi-walled carbon nanotube (MWCNT) semi-transparent composites: Modelling of DC conductivity. Compos. Part A-Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2015, 69, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Z.; Cai, J.; Zhang, C.; Gao, H.; Chen, Y. Electromagnetic interference shielding of graphene/epoxy composites. Carbon 2009, 47, 922–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.H.; Wu, D.J.; Weng, W.G.; He, B.; Yan, W.L. Preparation of polystyrene-graphite conducting nanocomposites via intercalation polymerization. Polym. Int. 2001, 50, 980–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongruang, W.; Spontak, R.J.; Balik, C.M. Correlated electrical conductivity and mechanical property analysis of high-density polyethylene filled with graphite and carbon fiber. Polymer 2002, 43, 2279–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezquerra, T.; Connor, M.T.; Roy, S.; Kulescza, M.; Fernandes-Nascimento, J.; Baltá-Calleja, F.J. Alternating-current electrical properties of graphite, carbon-black and carbon-fiber polymeric composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2001, 61, 903–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balberg, I. Tunneling and nonuniversal conductivity in composite materials. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1987, 59, 1305–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, D.H.; Lee, Y.K.; Park, S.S.; Lee, C.S.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, W.N. Effects of hybrid fillers on the electrical conductivity and EMI shielding efficiency of polypropylene/conductive filler composites. Macromol. Res. 2013, 21, 905–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stauffer, D.; Aharony, A. Introduction to Percolation Theory, 2nd ed.; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Vionnet-Menot, S.; Grimaldi, C.; Maeder, T.; Strässler, S.; Ryser, P. Tunneling-percolation origin of nonuniversality: Theory and experiments. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 71, 064201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample | SBET (m2/g) | VPORES a (cm3/g) | W0 b (cm3/g) | VMICRO c (cm3/g) | VMESO c (cm3/g) | Carbonization Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CB | 40 | 0.161 | 0.016 | − | 0.060 | 97 * |
| PG | 384 | 0.377 | 0.120 | 0.091 | 0.266 | − |
| PG-CB4 | 359 | 0.358 | 0.107 | 0.084 | 0.255 | − |
| PG-CB8 | 372 | 0.421 | 0.101 | 0.085 | 0.318 | − |
| PG-CB12 | 333 | 0.456 | 0.089 | 0.070 | 0.370 | − |
| PG-CB16 | 339 | 0.441 | 0.087 | 0.074 | 0.350 | − |
| PG-CB24 | 317 | 0.476 | 0.088 | 0.066 | 0.393 | − |
| PG-CB40 | 299 | 0.597 | 0.084 | 0.058 | 0.522 | − |
| CPG | 829 | 0.488 | 0.306 | 0.289 | 0.19 | 51 |
| CPG-CB4 | 780 | 0.484 | 0.284 | 0.272 | 0.210 | 52 |
| CPG-CB8 | 820 | 0.592 | 0.296 | 0.368 | 0.324 | 53 |
| CPG-CB12 | 726 | 0.636 | 0.253 | 0.229 | 0.395 | 55 |
| CPG-CB16 | 695 | 0.607 | 0.247 | 0.223 | 0.371 | 56 |
| CPG-CB24 | 601 | 0.658 | 0.217 | 0.183 | 0.468 | 60 |
| CPG-CB40 | 482 | 0.796 | 0.176 | 0.133 | 0.689 | 67 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Casanova, A.; Gomis-Berenguer, A.; Canizares, A.; Simon, P.; Calzada, D.; Ania, C.O. Carbon Black as Conductive Additive and Structural Director of Porous Carbon Gels. Materials 2020, 13, 217. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13010217
Casanova A, Gomis-Berenguer A, Canizares A, Simon P, Calzada D, Ania CO. Carbon Black as Conductive Additive and Structural Director of Porous Carbon Gels. Materials. 2020; 13(1):217. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13010217
Chicago/Turabian StyleCasanova, Ana, Alicia Gomis-Berenguer, Aurelien Canizares, Patrick Simon, Dolores Calzada, and Conchi O. Ania. 2020. "Carbon Black as Conductive Additive and Structural Director of Porous Carbon Gels" Materials 13, no. 1: 217. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13010217
APA StyleCasanova, A., Gomis-Berenguer, A., Canizares, A., Simon, P., Calzada, D., & Ania, C. O. (2020). Carbon Black as Conductive Additive and Structural Director of Porous Carbon Gels. Materials, 13(1), 217. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13010217








