Preparation and Microstructural Characterization of a High-Cr White Cast Iron Reinforced with WC Particles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
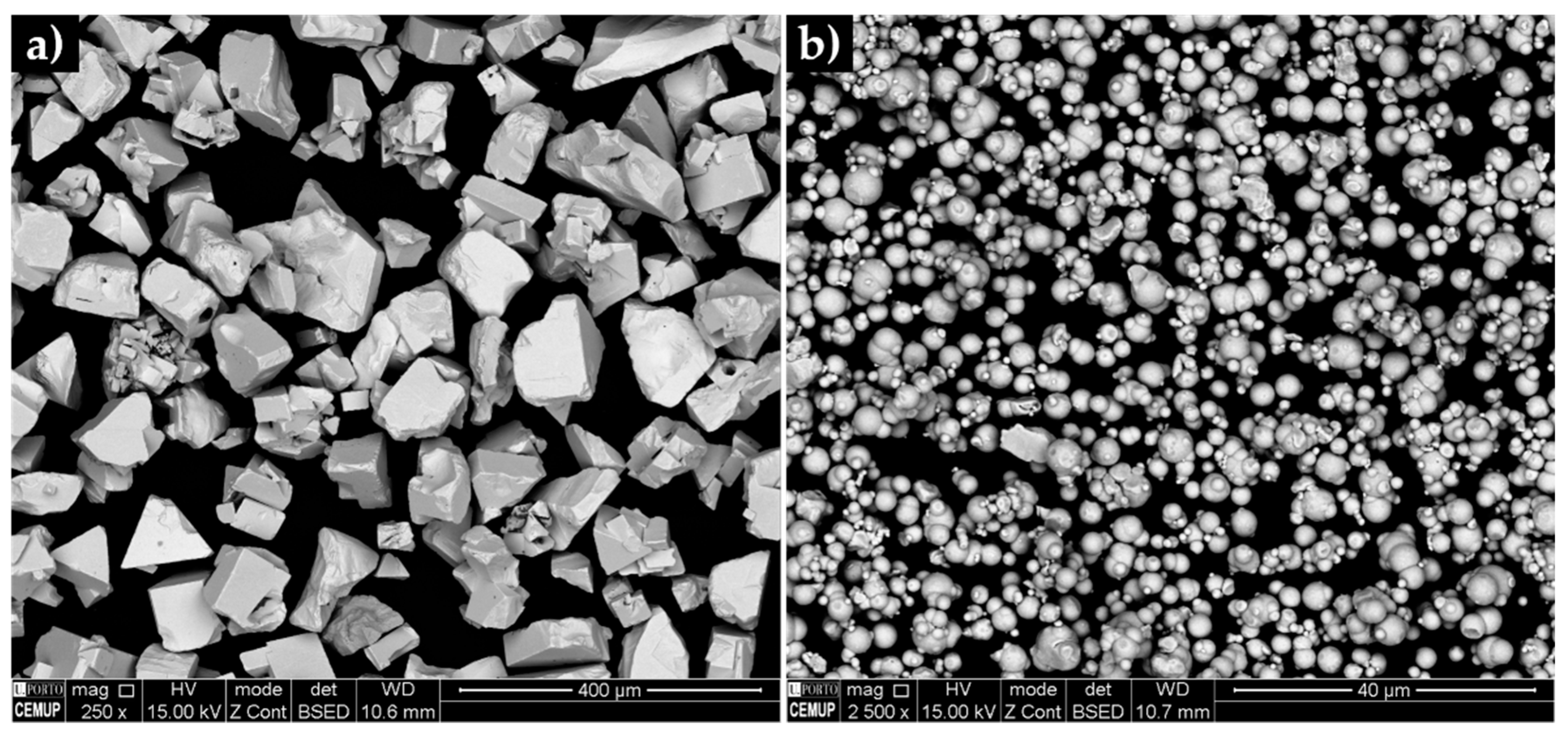
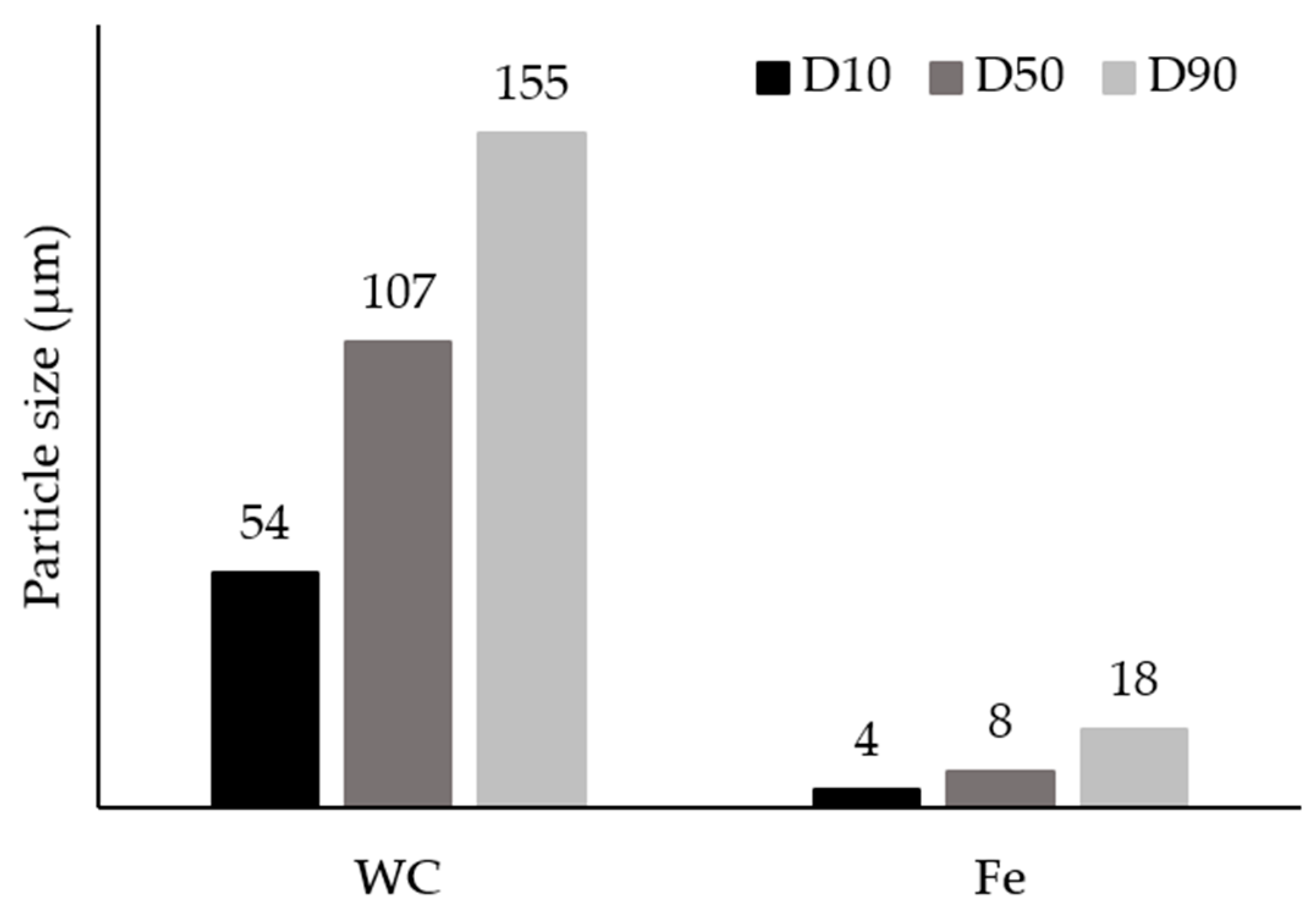
3.1. Characterization of the Initial Powders
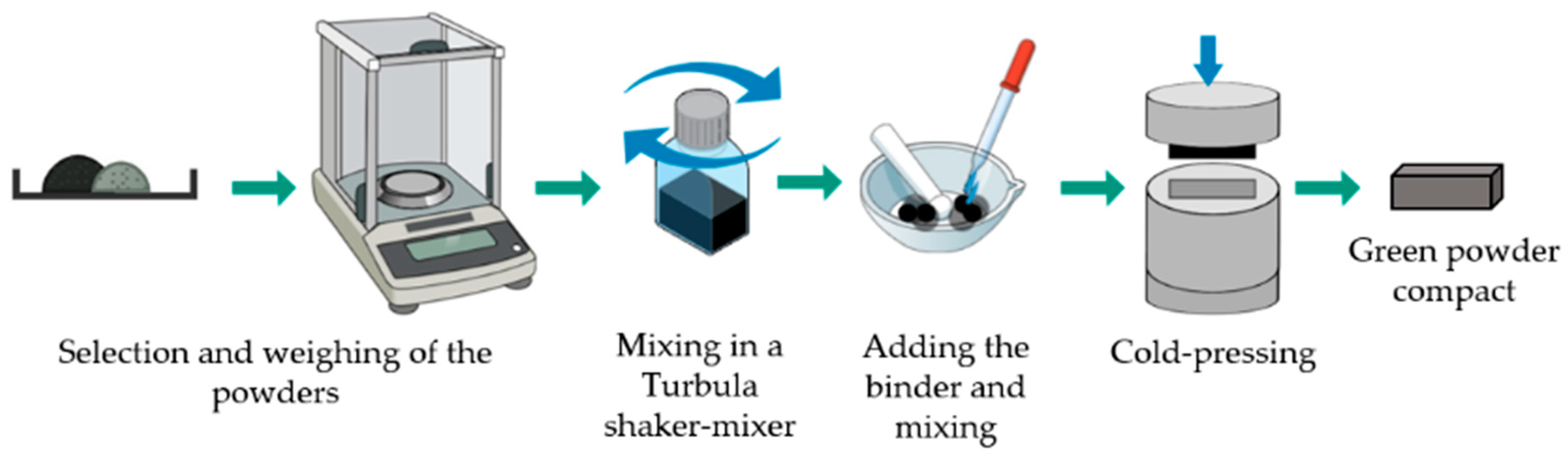
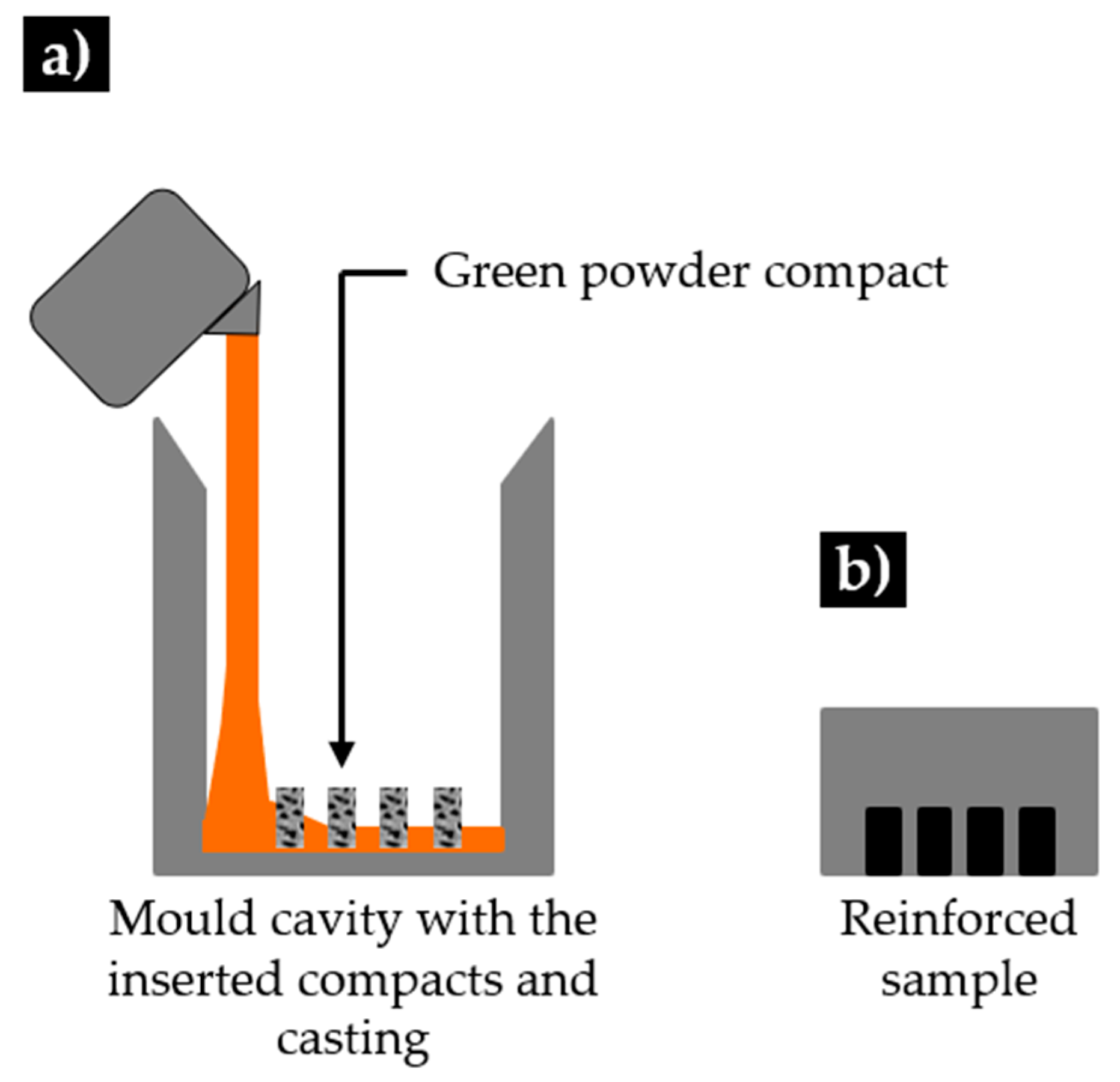
3.2. Characterization of the Green Compacts
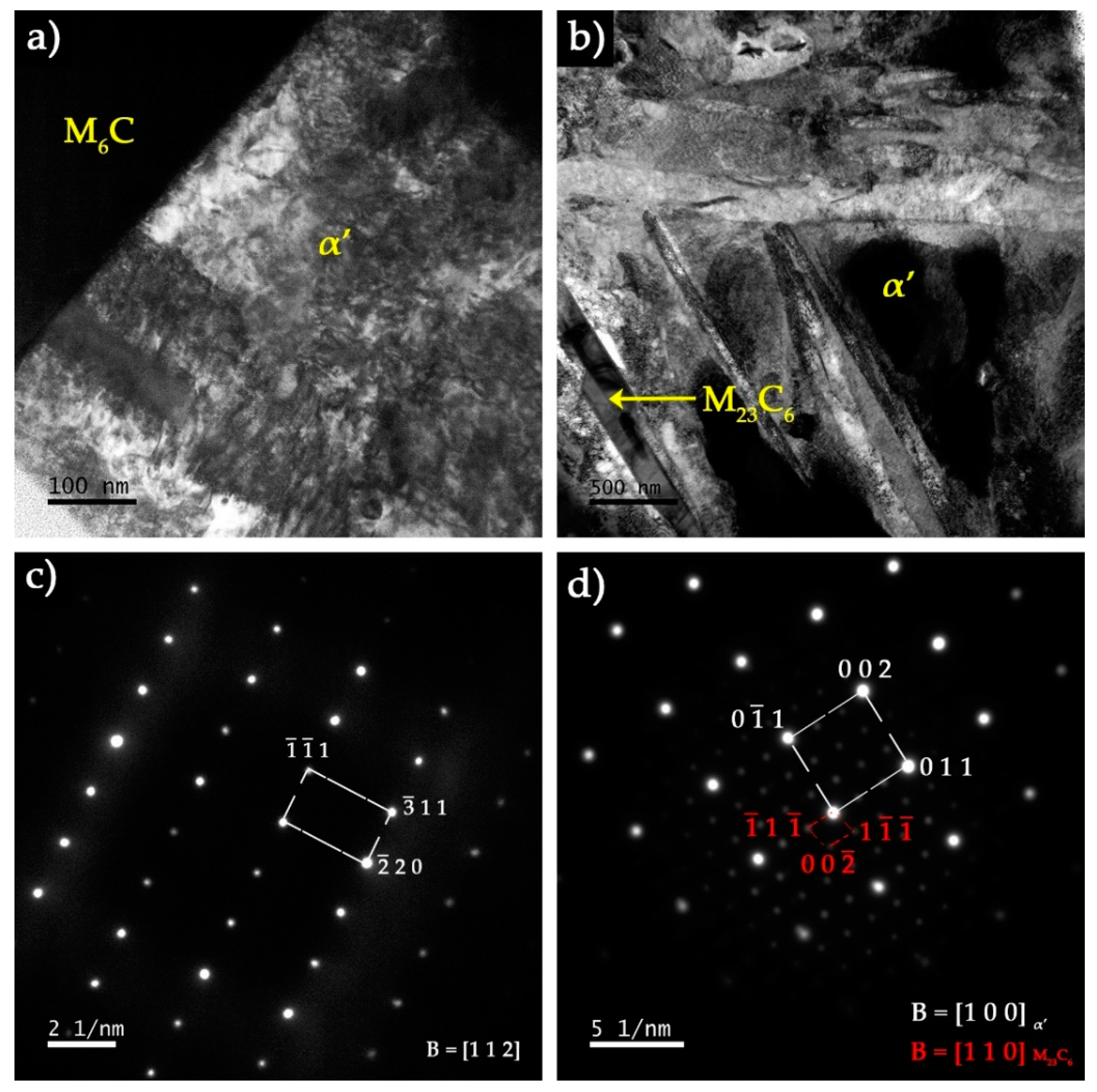
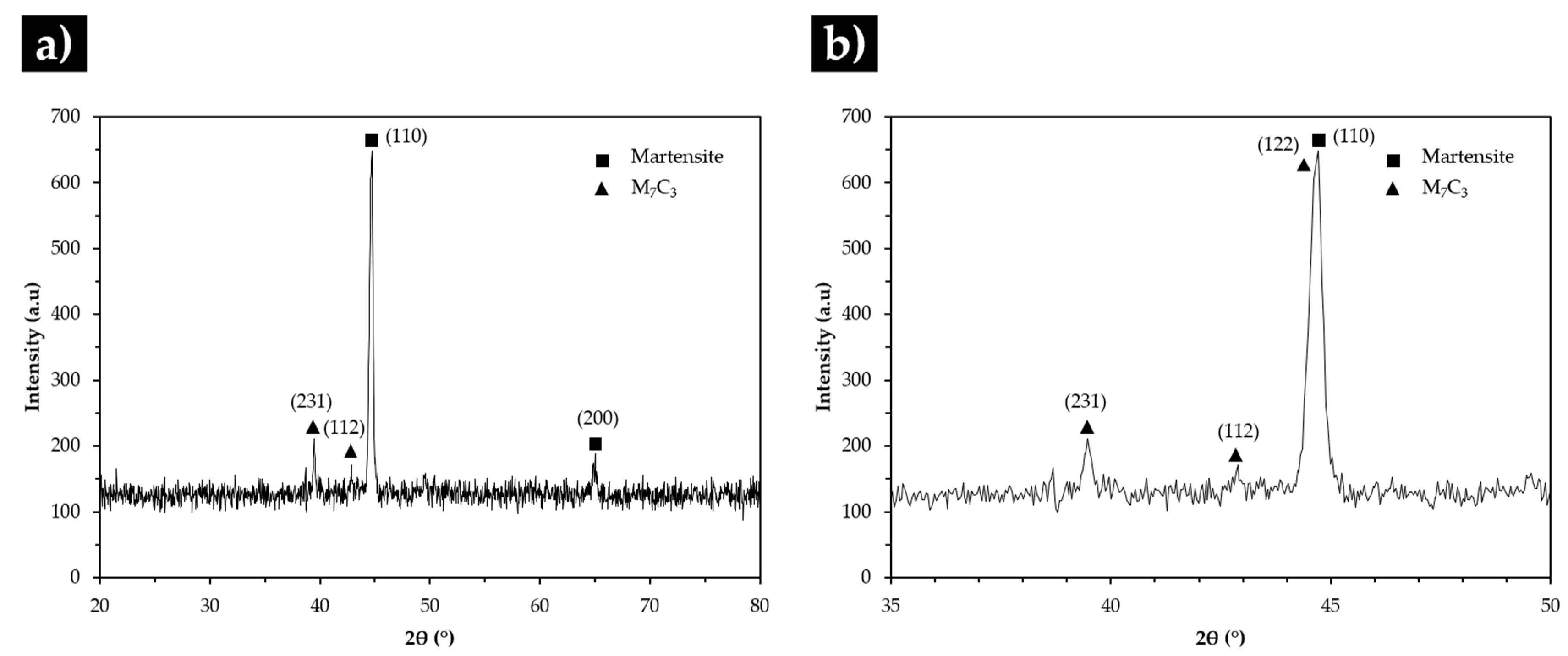
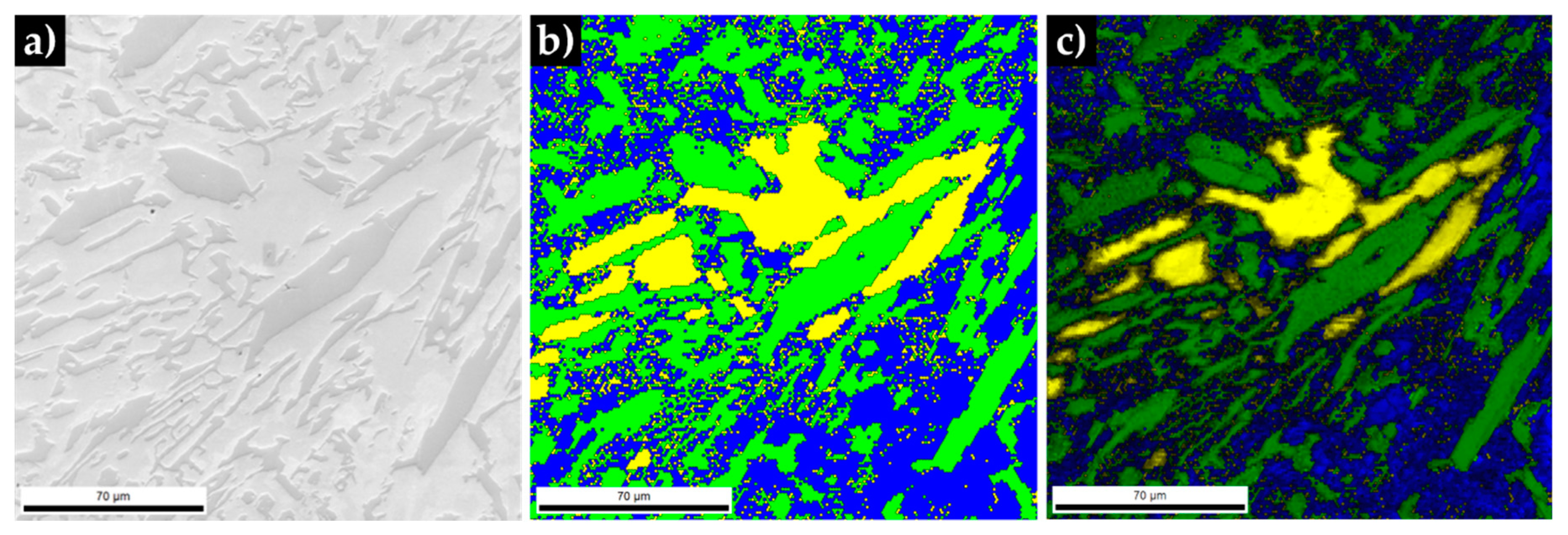
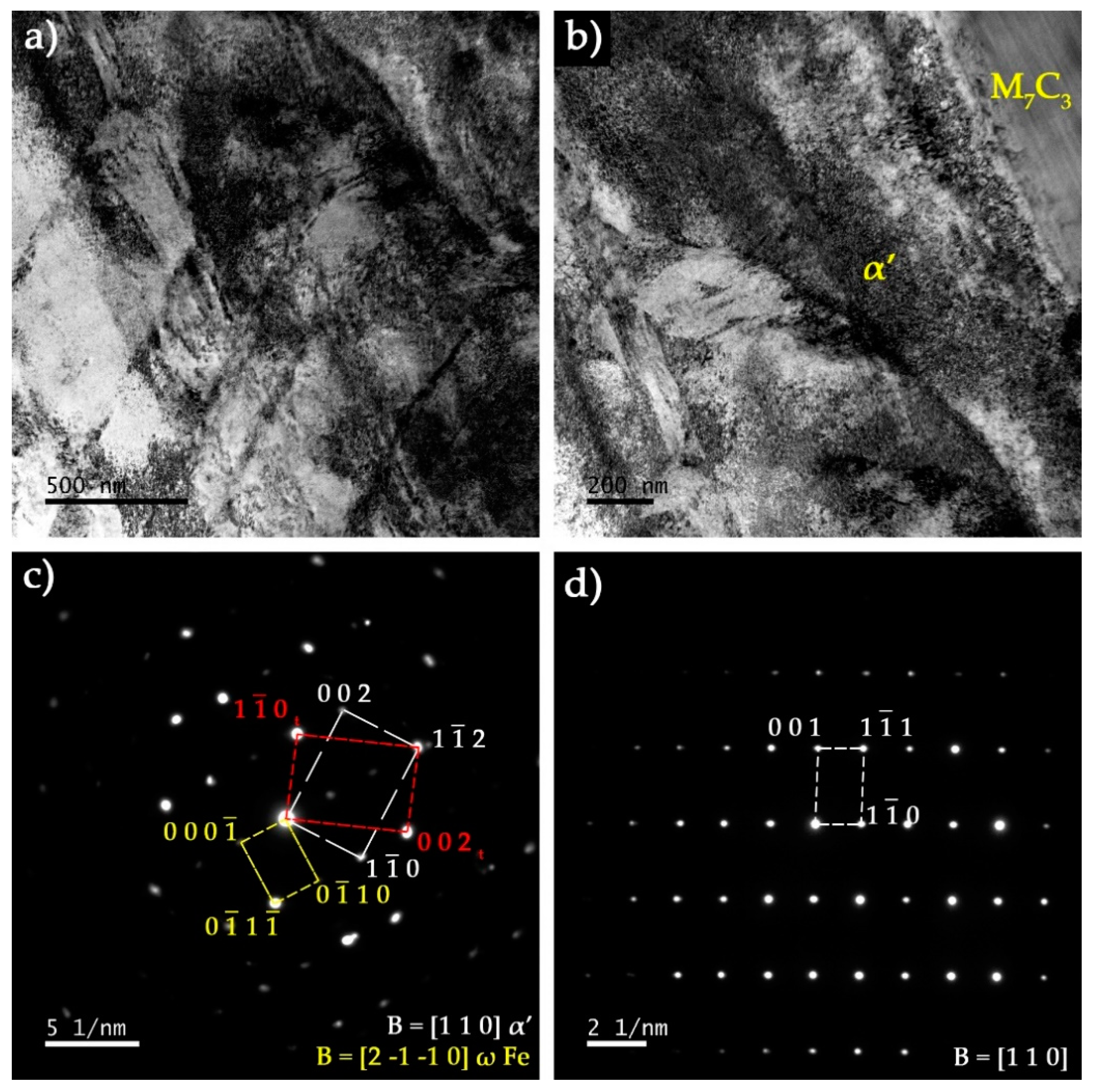
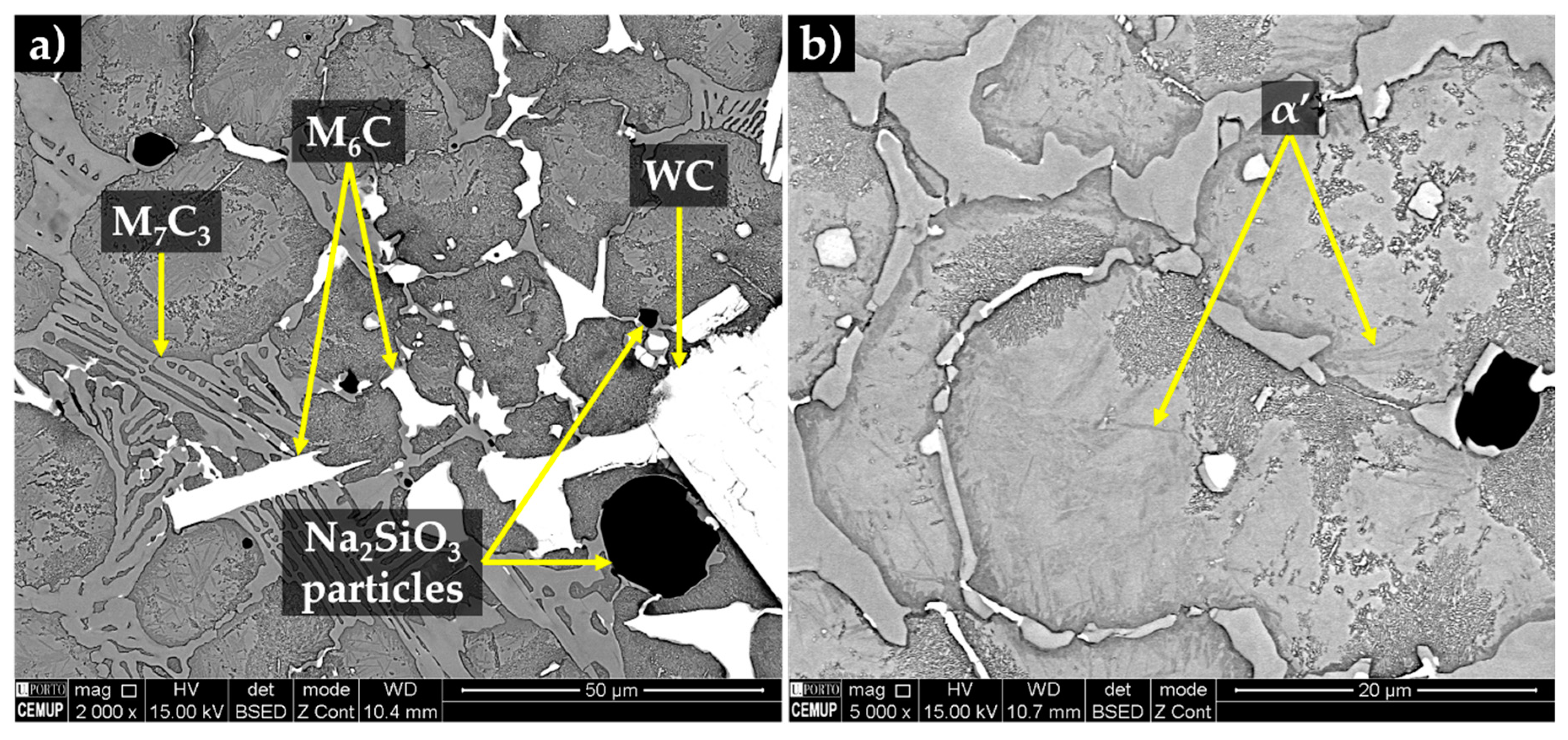
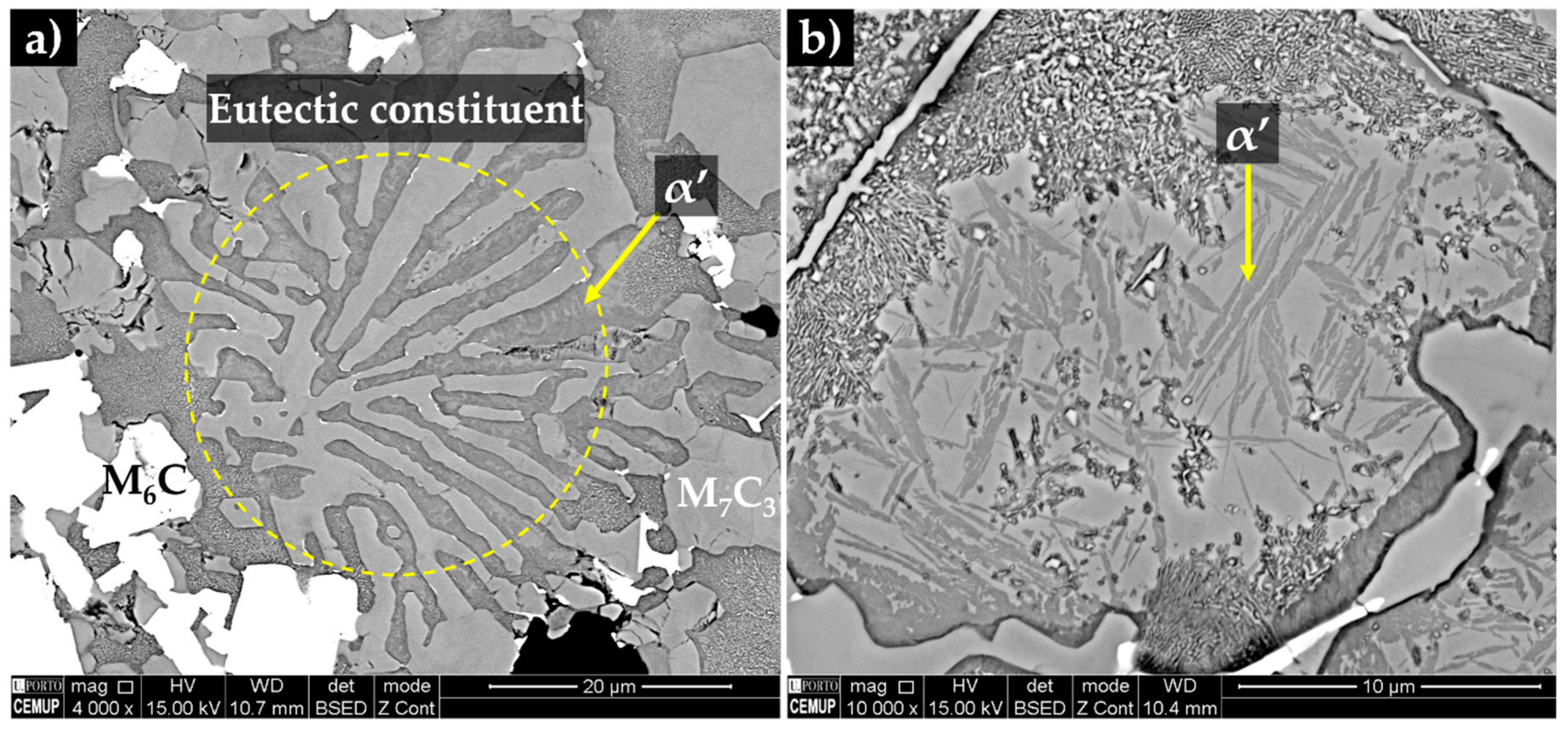
3.3. Characterization of the Base Metal
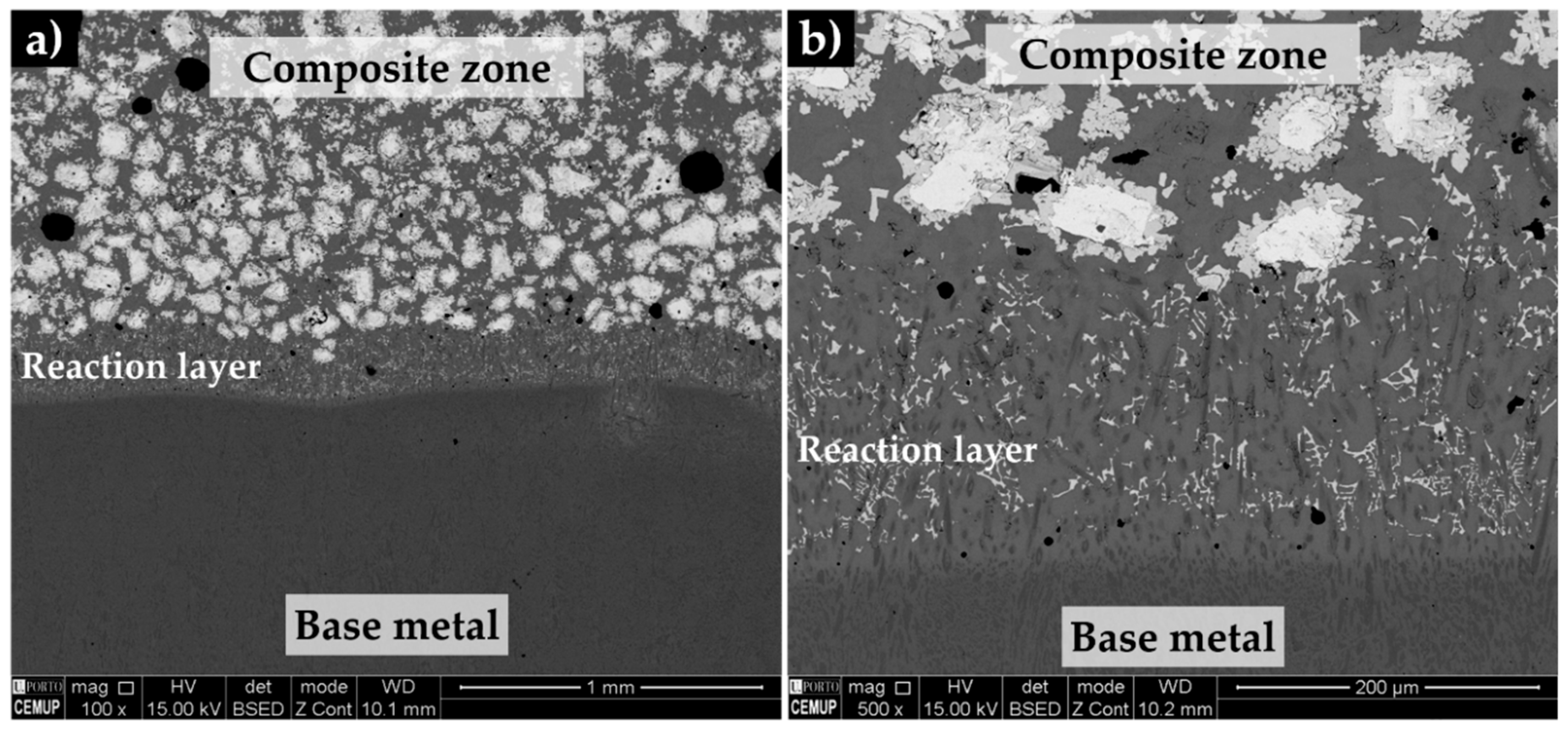
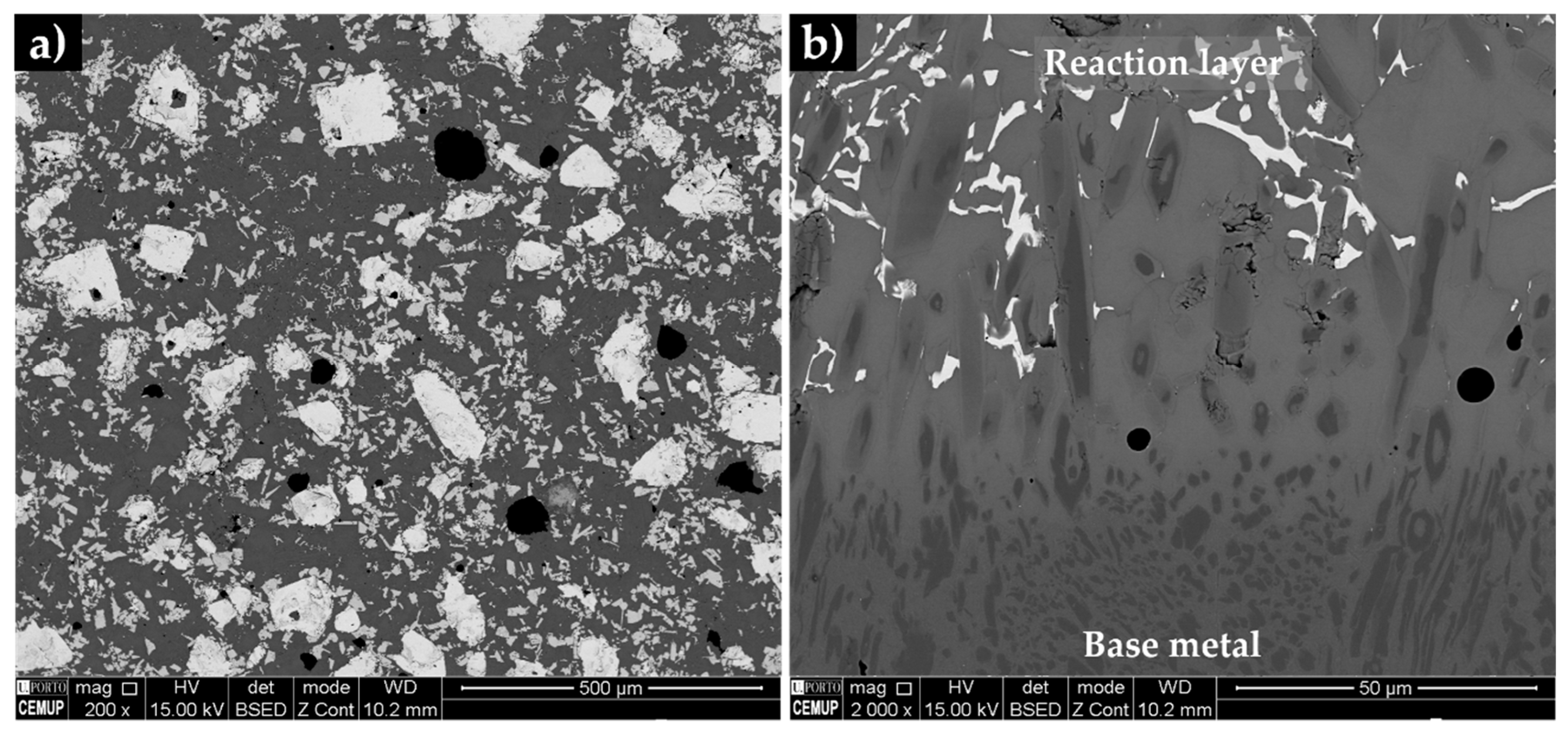
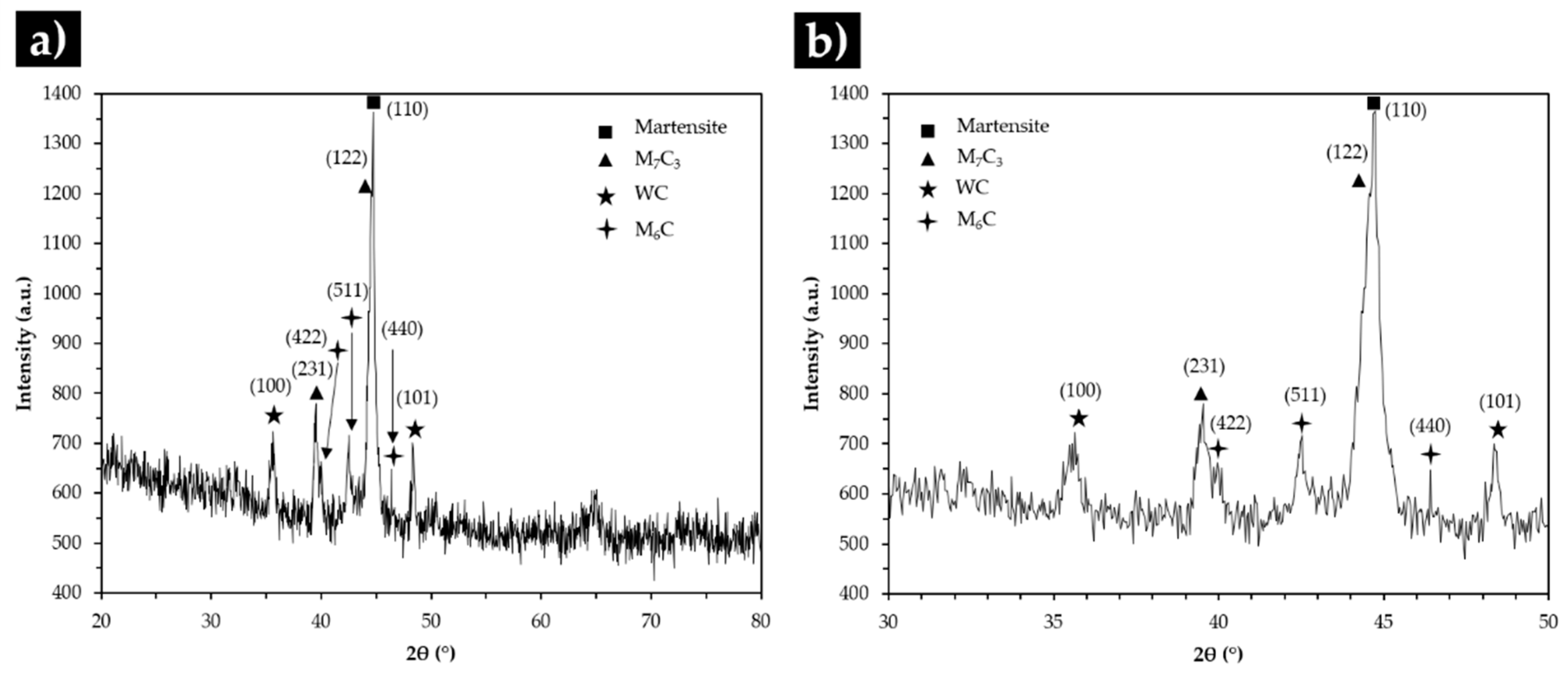
3.4. Characterization of the Reinforced Specimens
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Doğan, Ö.; Hawk, J.; Laird, G. Solidification structure and abrasion resistance of high chromium white irons. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1997, 28, 1315–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabrett, C.P.; Sare, I.R.; Ghomashchi, M.R. Microstructure-property relationships in high chromium white iron alloys. Int. Mater. Rev. 1996, 41, 59–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heino, V.; Kallio, M.; Valtonen, K.; Kuokkala, V.-T. The role of microstructure in high stress abrasion of white cast irons. Wear 2017, 388, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karantzalis, E.; Lekatou, A.; Mavros, H. Microstructure and properties of high chromium cast irons: Effect of heat treatments and alloying additions. Int. J. Cast Met. Res. 2009, 22, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.R.; Committee, A.S.M.I.H. Metallurgy and Properties of High-Alloy White Irons. In ASM Specialty Handbook: Cast Irons; Davis, J.R., Ed.; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 1996; pp. 107–122. [Google Scholar]
- Wiengmoon, A.; Pearce, J.; Chairuangsri, T. Relationship between microstructure, hardness and corrosion resistance in 20 wt.%Cr, 27 wt.%Cr and 36 wt.%Cr high chromium cast irons. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2011, 125, 739–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, S.; Carpenter, D.; Pearce, J. XRD and electron microscope study of an as-cast 26.6% chromium white iron microstructure. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2004, 85, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedolla-Jacuinde, A.; Arias, L.; Hernández, B. Kinetics of secondary carbides precipitation in a high-chromium white iron. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2003, 12, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Gao, Y.; Li, Y. Recent developments in fabrication of ceramic particle reinforced iron matrix wear resistant surface composite using infiltration casting technology. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2014, 41, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.; Bao, C.; Zhang, Z.; Bai, Y. Microstructure and Wear Behavior of High-Cr WCI Matrix Surface Composite Reinforced with Cemented Carbide Rods. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2013, 22, 2064–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kambakas, K.; Tsakiropoulos, P. Sedimentation casting of wear resistant metal matrix composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 435, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zeng, S.; Zhang, Z.; Li, W. Microstructure and hardness of WC-Co particle reinforced iron matrix surface composite. China Foundry 2013, 10, 374–379. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Zhou, R.; Chen, Z.; Shan, Q.; Tan, J. Effect of Cr addition on the microstructure and abrasive wear resistance of WC-reinforced iron matrix surface composites. J. Mater. Res. 2014, 29, 778–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leibholz, R.; Robert, M.H.; Leibholz, H.; Bayraktar, E. Development of functionally graded nodular cast iron reinforced with recycled WC particles. In Mechanics of Composite and Multi-functional Materials; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 7, pp. 241–249. [Google Scholar]
- Kambakas, K.; Tsakiropoulos, P. Solidification of high-Cr white cast iron–WC particle reinforced composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2005, 413, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, L.; Xu, Y.; Wang, X. Fabrication of WC/Fe composite coating by centrifugal casting plus in-situ synthesis techniques. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2010, 205, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zuo, L.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, Y.; Gao, K.; Liu, H.; Wang, X. In situ synthesis WC reinforced iron surface composite produced by spark plasma sintering and casting. Mater. Lett. 2018, 210, 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierson, H.O. Carbides of Group VI: Chromium, Molybdenum, and Tungsten Carbides. In Handbook of Refractory Carbides and Nitrides: Properties, Characteristics, Processing and Applications; Noyes Publications: Westwood, NJ, USA, 1996; pp. 100–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CES EduPack—Database: Level 3, 19.1.0; Granta Design Limited: Cambridge, UK, 2019.
- Zhou, R.; Jiang, Y.; Lu, D. The effect of volume fraction of WC particles on erosion resistance of WC reinforced iron matrix surface composites. Wear 2003, 255, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas, A.C.; Becerril, E.B.; Martínez, M.S.; Ruiz, J.L. Fabrication Processes for Metal Matrix Composites. In Metal Matrix Composites: Wetting and Infiltration; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 83–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manu, K.S.; Raag, L.A.; Rajan, T.; Gupta, M.; Pai, B. Liquid Metal Infiltration Processing of Metallic Composites: A Critical Review. Metall Mater Trans B 2016, 47, 2799–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, N.; Chawla, K.K. Processing. In Metal Matrix Composites, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 55–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G.J.; Guo, E.J.; Feng, Y.C.; Wang, L.P. Abrasion Behavior of WC Reinforced Cast Iron Surface Composite Fabricated by Cast-Infiltration Method. In Advanced Materials Research; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Switzerland, 2012; pp. 555–559. [Google Scholar]
- Aso, S.; Goto, S.; Komatsu, Y.; Ike, H.; Shimizu, K. Composite reinforcement of the surface of cast iron by WC powder inserts. Int. J. Cast Met. Res. 2003, 16, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leibholz, R.; Leibholz, H.; Bayraktar, E.; Robert, M.H. Investigation on Microstructure and Interfaces in Graded FE50007/WC Composites Produced by Casting. In Mechanics of Composite, Hybrid and Multifunctional Materials; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 5, pp. 321–329. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.-S.; Xing, J.-D.; Gao, Y.-M. Impact wear resistance of WC/Hadfield steel composite and its interfacial characteristics. Wear 2006, 260, 728–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.S.; Gao, Y.M.; Xing, J.D.; Wei, S.Z.; Zhang, X.L. Interfacial Characteristics and Wear Resistance of WCp/White-Cast-Iron Composites. Adv. Mater. Res. 2007, 26–28, 293–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wang, H. High speed sliding wear behavior of recycled WCP-reinforced ferrous matrix composites fabricated by centrifugal cast. Wear 2012, 276–277, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chumanov, I.; Anikeev, A.; Chumanov, V. Fabrication of functionally graded materials by introducing wolframium carbide dispersed particles during centrifugal casting and examination of FGM’s structure. Procedia Eng. 2015, 129, 816–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Niu, L.; Hojamberdiev, M.; Xu, Y. Preparation of in situ-formed WC/Fe composite on gray cast iron substrate by a centrifugal casting process. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2010, 210, 1986–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Gao, Y.; Tang, S.; Li, Y.; Ma, S.; Yi, D.; Zhang, Z. Interface Structure and Wear Behavior of Cr26 Ferrous Matrix Surface Composites Reinforced with CTCp. Tribol. Lett. 2014, 54, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gao, Y. Three-body abrasive wear behavior of CC/high-Cr WCI composite and its interfacial characteristics. Wear 2010, 268, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Q.; Li, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Zhou, R.; Sui, Y. Effect of Ni addition on microstructure of matrix in casting tungsten carbide particle reinforced composite. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2013, 29, 720–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.L.; Chen, Z.H.; Jiang, Y.H.; Zhou, R.; Shan, Q.; Song, Q.L. Influence of Addition of Tungsten-iron powder on Microstructure of WC/steel Composite Coatings. In Advanced Materials Research; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Zurich, Switzerland, 2012; pp. 394–398. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Zhou, R.; Gao, F.; Shan, Q.; Tan, J. Thermal fatigue mechanism of WC particles reinforced steel substrate surface composite at different thermal shock temperatures. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 596, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Zhou, R.; Lu, D.; Zhou, R. Dry three-body abrasive wear behavior of WC reinforced iron matrix surface composites produced by V-EPC infiltration casting process. Wear 2007, 262, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.Q.; Li, Z.L.; Jiang, Y.H.; Zhou, R.; Gao, F. Thermal Shock Cracks Initiation and Propagation of WCp/Steel Substrate Surface Composite at 500 °C. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2012, 109, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Y.; Han, L.; Jiang, Y.; Li, Z.; Shan, Q. Effects of Ni60WC25 powder content on the microstructure and wear properties of WCp reinforced surface metal matrix composites. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2018, 71, 2415–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, A.B.; Sousa, R.O.; Lacerda, P.; Ribeiro, L.M.M.; Pinto, A.M.P.; Vieira, M.F. Microstructural Characterization of TiC–White Cast-Iron Composites Fabricated by In Situ Technique. Materials 2020, 13, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standard Specification for Abrasion-Resistant Cast Irons. In A532/A532M—10; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2010. [CrossRef]
- Laird, G.; Gundlach, R.; Rohrig, K. Abrasion-Resistant Cast Iron Handbook; American Foundry Society: Des Plaines, IL, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Suwas, S.; Ray, R.K. Crystallographic Texture of Materials; Derby, B., Ed.; Springer: London, UK; Heidelberg, Germany; New York, NY, USA; Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Ping, D.; Ohmura, T.; Ohnuma, M. Electron diffraction analysis of quenched Fe–C martensite. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 2976–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, D.; Guo, S.; Imura, M.; Liu, X.; Ohmura, T.; Ohnuma, M.; Lu, X.; Abe, T.; Onodera, H. Lath formation mechanisms and twinning as lath martensite substructures in an ultra low-carbon iron alloy. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Chen, Y.; Xiao, W.; Ping, D.; Zhao, X. Twin structure of the lath martensite in low carbon steel. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2016, 26, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, D.; Ohnuma, M. ω-Fe particle size and distribution in high-nitrogen martensitic steels. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 5339–5355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| C | Si | Mn | Cr | Ni | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.07 | 0.78 | 0.65 | 26.02 | 0.20 | Balance |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moreira, A.B.; Ribeiro, L.M.M.; Lacerda, P.; Sousa, R.O.; Pinto, A.M.P.; Vieira, M.F. Preparation and Microstructural Characterization of a High-Cr White Cast Iron Reinforced with WC Particles. Materials 2020, 13, 2596. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13112596
Moreira AB, Ribeiro LMM, Lacerda P, Sousa RO, Pinto AMP, Vieira MF. Preparation and Microstructural Characterization of a High-Cr White Cast Iron Reinforced with WC Particles. Materials. 2020; 13(11):2596. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13112596
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoreira, Aida B., Laura M. M. Ribeiro, Pedro Lacerda, Ricardo O. Sousa, Ana M. P. Pinto, and Manuel F. Vieira. 2020. "Preparation and Microstructural Characterization of a High-Cr White Cast Iron Reinforced with WC Particles" Materials 13, no. 11: 2596. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13112596
APA StyleMoreira, A. B., Ribeiro, L. M. M., Lacerda, P., Sousa, R. O., Pinto, A. M. P., & Vieira, M. F. (2020). Preparation and Microstructural Characterization of a High-Cr White Cast Iron Reinforced with WC Particles. Materials, 13(11), 2596. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13112596







