“DIY” Silica Nanoparticles: Exploring the Scope of a Simplified Synthetic Procedure and Absorbance-Based Diameter Measurements
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Equipment and Software
2.3. Preparation of Silica Nanoparticles
2.4. Spectrophotometric Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Scope of Synthesis
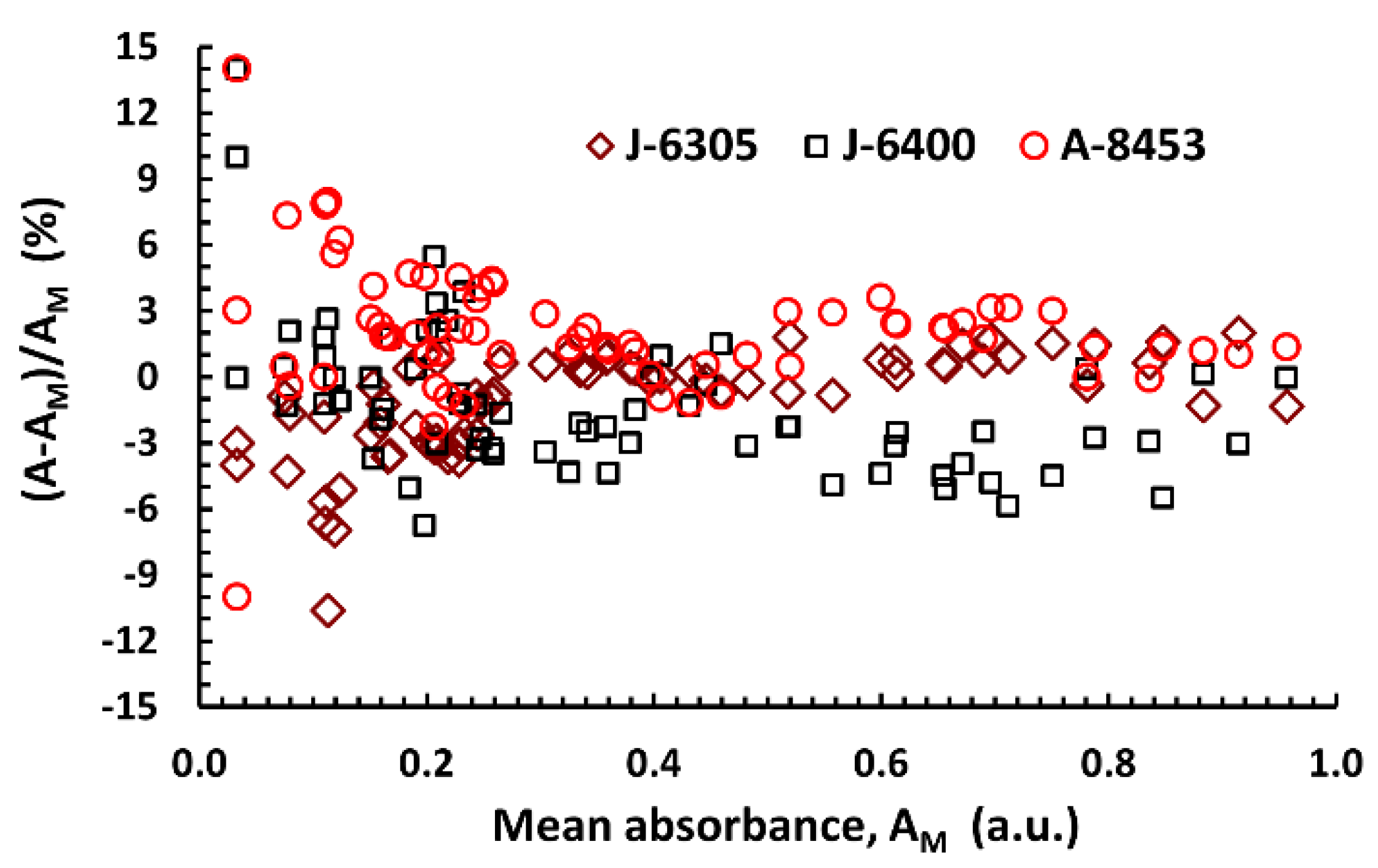
3.2. Turbidity and Reliable Spectrophotometric Measurements
3.3. Theoretical Considerations
- d-diameter of particles suspended in the medium;
- λ0-wavelength of incident light;
- ηm-refractive index of the medium at that wavelength;
- ηp-refractive index of particles at a given wavelength.
3.4. Reconciling Theoretical and Experimental Results
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nayfeh, M.H.; Mitas, L. Silicon nanoparticles. New photonic and electronic material at the transition between solid and molecule. In Nanosilicon; Kumar, V., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 1–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, P.; Nag, A.; Chakraborty, A.; Pradeep, T. Approaching materials with atomic precision using supramolecular cluster assemblies. Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 52, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shatruk, M.; Gómez-Coca, S.; Dunbar, K.R. Molecular magnetism. In Molecular Magnetic Materials: Concepts and Applications; Sieklucka, B., Pinkowicz, D., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 29–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, T.; Izumi, Y.; Hata, K.; Baron, G.V.; Bamba, T.; Desmet, G. Performance of small-domain monolithic silica columns in nano-liquid chromatography and comparison with commercial packed bed columns with 2 μm particles. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1616, 460804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, R.; Han, L.; Tu, B.; Zhao, D. One-pot synthesis of thermally stable gold@ mesoporous silica core-shell nanospheres with catalytic activity. Nano Res. 2013, 6, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, L.; Fenouillot, F.; Majesté, J.C.; Alcouffe, P.; Cassagnau, P. Immiscible polymer blends stabilized with nano-silica particles: Rheology and effective interfacial tension. Polymer 2008, 49, 4378–4385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turci, F.; Pavan, C.; Leinardi, R.; Tomatis, M.; Pastero, L.; Garry, D.; Anguissola, S.; Lison, D.; Fubini, B. Revisiting the paradigm of silica pathogenicity with synthetic quartz crystals: The role of crystallinity and surface disorder. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2015, 13, 4378–4385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biedermann, F.; Nau, W.M.; Schneider, H.-J. The hydrophobic effect revisited—Studies with supramolecular complexes imply high-energy water as a noncovalent driving force. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 11158–11171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Savateev, A.; Pronkin, S.; Papaefthimiou, V.; Wolff, C.; Willinger, M.G.; Willinger, E.; Neher, D.; Antonietti, M.; Dontsova, D. “The easier the better” preparation of efficient photocatalysts—Metastable poly (heptazine imide) salts. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1700555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stöber, W.; Fink, A.; Bohn, E. Controlled growth of monodisperse silica spheres in the micron size range. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 1968, 26, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, G.N.; Bolsoni, A.T.; Oliveira, H.P. Preparation of silica microspheres coated with V2O5 xerogel and V2O5/WO3 composite xerogel via adapted Stöber process. J. Non-Cryst. Solids. 2008, 354, 3548–3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niederberger, M. Nonaqueous sol–gel routes to metal oxide nanoparticles. Accounts Chem. Res. 2007, 40, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sumida, K.; Liang, K.; Reboul, J.; Ibarra, I.A.; Furukawa, S.; Falcaro, P. Sol–gel processing of metal–organic frameworks. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 2626–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozawa, K.; Gailhanou, H.; Raison, L.; Panizza, P.; Ushiki, H.; Sellier, E.; Delville, J.P.; Delville, M.H. Smart control of monodisperse Stöber silica particles: Effect of reactant addition rate on growth process. Langmuir 2005, 21, 1516–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, Y.J.; Zhu, L.; Teo, W.S.; Tan, Y.W.; Yang, Y.; Wang, C.; Chen, H. Revisiting the Stöber method: Inhomogeneity in silica shells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 11422–11425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, R.S.; Raimundo, I.M., Jr.; Pimentel, M.F. Revising the synthesis of Stöber silica nanoparticles: A multivariate assessment study on the effects of reaction parameters on the particle size. Colloids Surf. A 2019, 577, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogush, G.H.; Tracy, M.A.; Zukoski Iv, C.F. Preparation of monodisperse silica particles: Control of size and mass fraction. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1988, 104, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimura, N.; Ogawa, M. Growth of nanoporous silica spherical particles by the Stöber method combined with supramolecular templating approach. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2005, 78, 1154–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Yu, B.; Cong, H.L.; Tian, C.; Wang, Y.Z.; Wang, Q.B.; Liu, C.K. Synthesis of monodisperse silica microspheres by a modified Stöber method. Integr. Ferroelectr. 2014, 154, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Hulst, H.C. Light Scattering by Small Particles; Dover Publications Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Wriedt, T. Mie theory: A review. In The Mie Theory: Basics and Applications; Hergert, W., Wriedt, T., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2012; pp. 53–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudiarta, I.W.; Chylek, P. Mie-scattering formalism for spherical particles embedded in an absorbing medium. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2001, 18, 1275–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kourti, T.; MacGregor, J.F. Particle size determination using turbidimetry: Capabilities, limitations, and evaluation for on-line applications. In Particle Size Distribution II; Provder, T., Ed.; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1991; pp. 34–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guschin, V.; Becker, W.; Eisenreich, N.; Bendfeld, A. Determination of the nanoparticle size distribution in media by turbidimetric measurements. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2012, 35, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khlebtsov, B.N.; Khanadeev, V.A.; Khlebtsov, N.G. Determination of the size, concentration, and refractive index of silica nanoparticles from turbidity spectra. Langmuir 2008, 24, 8964–8970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, N.C.; Minelli, C.; Tompkins, J.; Stevens, M.M.; Shard, A.G. Emerging techniques for submicrometer particle sizing applied to Stöber silica. Langmuir 2012, 28, 10860–10872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Groenestijn, G.J.; Meulendijks, N.; Van Ee, R.; Volker, A.; Van Neer, P.; Buskens, P.; Julien, C.; Verheijen, M. Qualification of an ultrasonic instrument for real-time monitoring of size and concentration of nanoparticles during liquid phase bottom-up synthesis. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kourti, T. Turbidimetry in particle size analysis. In Encyclopedia of Analytical Chemistry: Applications, Theory and Instrumentation; Meyers, R.A., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourti, T.; MacGregor, J.F.; Hamielec, A.E. Turbidimetric techniques: Capability to provide the full particle size distribution. In Particle Size Distribution II; Provder, T., Ed.; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1991; pp. 2–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bateman, J.B.; Weneck, E.J.; Eshler, D.C. Determination of particle size and concentration from spectrophotometric transmission. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1959, 14, 308–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferri, F.; Bassini, A.; Paganini, E. Commercial spectrophotometer for particle sizing. Appl. Opt. 1997, 36, 885–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brinker, C.J. Hydrolysis and condensation of silicates: Effects on structure. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1998, 100, 31–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Green, D.L.; Jayasundara, S.; Lam, Y.F.; Harris, M.T. Chemical reaction kinetics leading to the first Stöber silica nanoparticles–NMR and SAXS investigation. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2003, 315, 166–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, D.L.; Lin, J.S.; Lam, Y.F.; Hu, M.Z.-C.; Schaefer, D.W.; Harris, M.T. Size, volume fraction, and nucleation of Stöber silica nanoparticles. J. Coll. Interf. Sci. 2003, 266, 346–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, M.; Ungerer, J.; Klinge, M.; Nirschl, H. Synthesis of nanometric silica particles via a modified Stöber synthesis route. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 538, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deirmendjian, D. Electromagnetic Scattering on Spherical Polydispersions; American Elsevier Pub. Co.: New York, NY, USA, 1969; pp. 9–88. [Google Scholar]
- Deirmendjian, D.; Clasen, R.; Viezee, W. Mie scattering with complex index of refraction. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1961, 51, 620–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.C.; Hogg, R. Estimation of particle size distributions from turbidimetric measurements. Anal. Chem. 1979, 51, 758–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refractive Index Database. Available online: https://refractiveindex.info (accessed on 1 April 2020).
- MiePlot. Available online: http://www.philiplaven.com/mieplot.htm (accessed on 22 March 2020).
- Parnell, S.R.; Washington, A.L.; Parnell, A.J.; Walsh, A.; Dalgliesh, R.M.; Li, F.; Hamilton, W.A.; Prevost, S.; Fairclough, J.P.A.; Pynn, R. Porosity of silica Stöber particles determined by spin-echo small angle neutron scattering. Soft Matter 2016, 12, 4709–4714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]





| Variable | Idealized Value 1 | Corrected Value 2 | % Change Needed |
|---|---|---|---|
| ηp | 1.470 | 1.498 | +1.90% |
| ηm | 1.370 | 1.347 | −1.68% |
| φ0 3 | 0.00556 | 0.00945 | +70.0% |
| (R) 4·A | 1.0·A | 0.6·A | −40.0% |
| d (SD%) 5 | 0% 5 | 55% 5 | − 5 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tabisz, Ł.; Stanek, J.; Łęska, B. “DIY” Silica Nanoparticles: Exploring the Scope of a Simplified Synthetic Procedure and Absorbance-Based Diameter Measurements. Materials 2020, 13, 3088. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13143088
Tabisz Ł, Stanek J, Łęska B. “DIY” Silica Nanoparticles: Exploring the Scope of a Simplified Synthetic Procedure and Absorbance-Based Diameter Measurements. Materials. 2020; 13(14):3088. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13143088
Chicago/Turabian StyleTabisz, Łukasz, Jerzy Stanek, and Bogusława Łęska. 2020. "“DIY” Silica Nanoparticles: Exploring the Scope of a Simplified Synthetic Procedure and Absorbance-Based Diameter Measurements" Materials 13, no. 14: 3088. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13143088
APA StyleTabisz, Ł., Stanek, J., & Łęska, B. (2020). “DIY” Silica Nanoparticles: Exploring the Scope of a Simplified Synthetic Procedure and Absorbance-Based Diameter Measurements. Materials, 13(14), 3088. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13143088






