Quasi-Solid-State Electrochromic Cells with Energy Storage Properties Made with Inkjet Printing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical Materials and Characterization Techniques
2.2. Development of Electrochromic Materials and Films
2.2.1. Tungsten Trioxide Thin Layers
2.2.2. Cerium Modified-TiO2 Thin Films as Ion Storage Layers
2.2.3. Synthesis of Quasi-Solid-State Electrolyte and Completion of the EC Device
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Microstructure Properties of Both Electrodes
3.1.1. WO3 Films
3.1.2. Ce-Modified TiO2 Films
3.2. BET Surface Areas for Ce-TiO2 and Pristine TiO2 Films
3.3. Electrochemical Characterization of Electrochromic and Ion Storage Film.
3.4. Evaluation of Electrochromic Device
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Granqvist, C.G. Chromogenic materials for transmittance control of large-area windows. Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. 1990, 16, 291–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thummavichai, K.; Xia, Y.; Zhu, Y. Recent progress in chromogenic research of tungsten oxides towards energy-related applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2017, 88, 281–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granqvist, C.G.; Lansaker, P.C.; Mlyuka, N.R.; Granqvist, G.A.; Avendano, E. Progress in chromogenics: New results for electrochromic and thermochromic materials and devices. Sol. Energ. Mater. Sol. Cells 2009, 93, 2032–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granqvist, C.G. Handbook of Inorganic Electrochromic Materials, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Niklasson, G.A.; Granqvist, C.G. Electrochromics for smart windows: Thin films of tungsten oxide and nickel oxide, and devices based on these. J. Mater. Chem. 2007, 17, 127–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runnerstrom, E.L.; Llordes, A.; Lounis, S.D.; Milliron, D. Nanostructured electrochromic smart windows: Traditional materials and NIR-selective plasmonic nanocrystals. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 10555–10572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granqvist, C.G. Oxide electrochromics: An introduction to devices and materials. Sol. Energ. Mater. Sol. Cells. 2012, 99, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yu, D.B.; Zhu, Z.J.; Sun, J.Z.; Dong, S.H. Self-rechargeable-battery-driven device for simultaneous electrochromic windows, ROS biosensing, and energy storage. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 28072–28077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Fang, Y.S.; Qiao, K.; Wei, W.; Yao, Y.J.; Gao, Y.F. Printing of WO3/ITO nanocomposite electrochromic smart windows. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells. 2019, 194, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Tian, Y.; Wang, B.; Li, X.; Zhao, J.; Li, Y. Review: Recent progress in ordered macroporous electrochromic materials. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 11251–11268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Man, W.; Yu, H.; Li, Y.; Zheng, F. Fabrication of Mo-Doped WO3 nanorod arrays on FTO substrate with enhanced electrochromic properties. Materials 2018, 11, 1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokouzis, A.; Theodosiou, K.; Leftheriotis, G. Assessment of the long-term performance of partly covered photoelectrochromic devices under insolation and in storage. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells. 2018, 182, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Z.; Li, X.; He, X.; Chen, Y.; Xu, X.; Gao, X. Integrated electrochromism and energy storage applications based on tungsten trioxide monohydrate nanosheets by novel one-step low temperature synthesis. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2018, 183, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillaspie, D.T.; Tenent, R.C.; Dillon, A.C. Metal-oxide films for electrochromic applications: Present technology and future directions. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 9585–9592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Gao, C.; Du, X.; Zhu, G.; Xie, W.; Liu, P.; Tang, Z. Improved optical and electrochromic properties of NiOx films by low-temperature spin-coating method based on NiOx nanoparticles. Materials 2018, 11, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Xie, L.; Chang, T.; Bell, J.; Huang, A.; Jin, P.; Bao, S. High performance all-solid-state electrochromic device based on LixNiOy layer with gradient Li distribution. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 317, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, J.; Noguchi, K.; Yamasaki, S.; Yamazaki, S. Novel color change of electrochromic iridium oxide in a matrix aramid resin film. Electrochem. Commun. 2004, 6, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-G.; Chung, M.-H. Water-soluble poly(2-(3thienyloxy)ethanesulfonic acid)/V2O5 nanocomposites: Synthesis and electrochromic properties. J. Solid State Chem. 2004, 177, 2285–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahav, M.; van der Boom, M.E. Polypyridyl metallo-organic assemblies for electrochromic applications. Adv. Mater. 2018, 1706641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaujuge, P.M.; Reynolds, J.R. Color control in π-conjugated organic polymers for use in electrochromic devices. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 268–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banasz, R.; Wałęsa-Chorab, M. Polymeric complexes of transition metal ions as electrochromic materials: Synthesis and properties. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 389, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camino, D.; Deroo, D.; Salardenne, J.; Treuil, N. Counter electrode materials for lithium electrochromic devices. Sol. Energ. Mater. Sol. Cells 1995, 39, 349–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhosale, A.K.; Tarwal, N.L.; Shinde, P.S.; Kadam, P.M.; Patil, R.S.; Barman, S.R.; Patil, P.S. Effective utilization of spray pyrolyzed CeO2 as optically passive counter electrode for enhancing optical modulation of WO3. Solid State Ion. 2009, 180, 1324–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhosale, A.K.; Shinde, P.S.; Tarwal, N.L.; Pawar, R.C.; Kadam, P.M.; Patil, P.S. Synthesis and characterization of highly stable optically passive CeO2–ZrO2 counter electrode. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 1900–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.S.; Jan, D.-J.; Lin, J.-H.; Wang, M.-C. Electrochromic, optical and binding-energy performances of tantalum pentoxide and zirconium dioxide films deposited with RF magnetron sputtering and cathodic arc plasma. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2019, 203, 110158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wu, H.; Meng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, Z. Integrated energy storage and electrochromic function in one flexible device: An energy storage smart window. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 8384–8389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wałęsa-Chorab, M.; Skene, W.G. Investigation of an electroactive immobilized azomethine for potential electrochromic use. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2019, 200, 109977. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, J.; Hösel, M.; Dyer, A.L.; Krebs, F.C. Development and manufacture of polymer-based electrochromic devices. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 2073–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, H.; Elmaghraby, E.K.; Ali, S.A.; Abdel-Hady, K. The electrochromic behavior of nickel oxide films sprayed at different preparative conditions. Thin Solid Films 2005, 483, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenent, R.C.; Gillaspie, D.T.; Miedaner, A.; Parilla, P.A.; Curtis, C.J.; Dillon, A.C. Fast switching electrochromic Li+-doped NiO Films by ultrasonic spray deposition. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2010, 157, H318–H322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, C.; Pinheiro, C.; Henriques, I.; Laia, C.A.T. Inkjet printing of sol-gel synthesized hydrated tungsten oxide nanoparticles for flexible electrochromic devices. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 1330–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livage, J.; Ganguli, D. Sol-gel electrochromic coatings and devices: A review. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2001, 68, 365–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeck, S.-H.; Choi, K.-S.; Jaramillo, T.F.; Stucky, G.D.; McFarland, E.W. Enhancement of photocatalytic and electrochromic properties of electrochemically fabricated mesoporous WO3 thin films. Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 1269–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, G.; Cui, M.; Kumar, V.; Darmawan, P.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Lee-Sie Eh, A.; Qian, K.; Lee, P.S. Ultra-large optical modulation of electrochromic porous WO3 film and the local monitoring of redox activity. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 1373–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidmar, T.; Topič, M.; Dzik, P.; Krašovec, U.O. Inkjet printing of sol–gel derived tungsten oxide inks. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2014, 125, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosiadz, M.; Tomov, R.I.; Hopkins, S.C.; Martin, G.; Hardeman, D.; Holzapfel, B.; Glowacki, B.A. Inkjet printing of Ce0.8Gd0.2O2 thin films on Ni–5% W flexible substrates. J. Sol–Gel Sci. Technol. 2010, 54, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, G.; Darmawan, P.; Cui, M.; Chen, J.; Wang, X.; Lee-Sie Eh, A.; Magdassi, S.; Lee, P.S. Inkjet-printed all solid-state electrochromic devices based on NiO/WO3 nanoparticle complementary electrodes. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojcik, P.J.; Cruz, A.S.; Santos, L.; Pereira, L.; Martins, R.; Fortunato, E. Microstructure control of dual-phase inkjet-printed a-WO3/TiO2/WOX films for high-performance electrochromic applications. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 13268–13278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, G.; Darmawan, P.; Cheng, X.; Layani, M.; Wei Ming Tan, A.; Li, S.; Lee-Sie Eh, A.; Gao, D.; Magdassi, S.; Lee, P.S. Direct inkjet-patterning of energy efficient flexible electrochromics. Nano Energy 2018, 49, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Jeong, Y.; Koo, C.Y.; Song, K.; Moo, J. Thin film transistors with ink-jet printed amorphous oxide semiconductors. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 49, 05EB06-1–05EB06-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chao, D.; Yang, P.; Webber, L.; Li, J.; Kraus, T.; Fan, H.J. Flexible pseudocapacitive electrochromics via inkjet printing of additive-free tungsten oxide nanocrystal ink. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 5, 2000142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoski, C.G. Handbook of Electrochemistry, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Bard, A.J.; Faulkner, L.R. Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications, 2nd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Jovanovski, V.; Stathatos, E.; Orel, B.; Lianos, P. Dye-sensitized solar cells with electrolyte based on a trimethoxysilane-derivatized ionic liquid. Thin Solid Film. 2006, 511–512, 634–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephan, A.M. Review on gel polymer electrolytes for lithium batteries. Eur. Polym. J. 2006, 42, 21–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kil, E.-H.; Choi, K.-H.; Ha, H.-J.; Xu, S.; Rogers, J.A.; Kim, M.R.; Lee, Y.-G.; Kim, K.M.; Cho, K.Y.; Lee, S.-Y. Imprintable, bendable, and shape-conformable polymer electrolytes for versatile-shaped lithium-ion batteries. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 1395–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, R.-X.; Shen, S.-Y.; Chen, H.-W.; Wang, C.-C.; Shih, P.-T.; Liu, C.-T.; Vittal, R.; Lin, J.-J.; Ho, K.-C. A novel polymer gel electrolyte for highly efficient dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 8471–8478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, T.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Y. A High-performance graphene oxide-doped ion gel as gel polymer electrolyte for all-solid-state supercapacitor applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 3353–3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.J.; Chun, S.-J.; Lee, S.-S.; Kim, B.-Y.; Kim, J.H.; Chung, H.; Lee, S.-Y.; Kim, W. All-solid-state flexible supercapacitors fabricated with bacterial nanocellulose papers, carbon nanotubes, and triblock-copolymer ion gels. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 6400–6406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sygkridou, D.; Rapsomanikis, A.; Stathatos, E. Functional transparent quasi-solid state dye-sensitized solar cells made with different oligomer organic/inorganic hybrid electrolytes. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2017, 159, 600–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stathatos, E. Organic-inorganic nanocomposite materials prepared by the sol-gel route as new ionic conductors in quasi solid state electrolytes. Ionics 2005, 11, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stathatos, E.; Lianos, P.; Del Monte, F.; Levy, D.; Tsiourvas, D. Formation of TiO2 nanoparticles in reverse micelles and their deposition as thin films on glass substrates. Langmuir 1997, 13, 4295–4300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Stathatos, E.; Dionysiou, D.D. Synthesis of nanocrystalline photocatalytic TiO2 thin films and particles using sol–gel method modified with nonionic surfactants. Thin Solid Film. 2006, 510, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stengl, V.; Bakardijieva, S.; Murafa, N. Preparation and photocatalytic activity of rare earth doped TiO2 nanoparticles. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2009, 114, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapsomanikis, A.; Apostolopoulou, A.; Stathatos, E.; Lianos, P. Cerium-modified TiO2 nanocrystalline films for visible light photocatalytic activity. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2014, 280, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, G.-F.; Wang, X.-L.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, J.-H.; Xiong, Q.-Q.; Gu, C.; Tu, J.-P. Hierarchical structure Ti-doped WO3 film with improved electrochromism in visible-infrared region. RSC Adv. 2019, 3, 6896–6905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, R.-T.; Granqvist, C.G.; Niklasson, G.A. Eliminating degradation and uncovering ion-trapping dynamics in electrochromic WO3 thin films. Nature Mater. 2015, 15, 991–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, B.W.-C.; Chan, K.Y.; Knipp, D. Effect of film thickness on electrochromic performance of sol-gel deposited tungsten oxide (WO3). Opt. Mater. 2019, 94, 387–392. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Y.; Chai, Z.; Liang, Z.; Sun, P.; Xie, W.; Zhao, C.; Mai, W. Electrochromic asymmetric supercapacitor windows enable direct determination of energy status by naked eye. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 34085–34092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Counter Electrode | Charge Capacity (mC cm−2) |
|---|---|
| SnO2:F (FTO) | 4.26 |
| TiO2/FTO | 6.21 |
| Ce-modified TiO2/FTO | 26.77 |
| EC Device | Tb (%) * | Tc (%) * | ΔOD(λ) | qin (C) | A (cm2) | η (cm2/C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
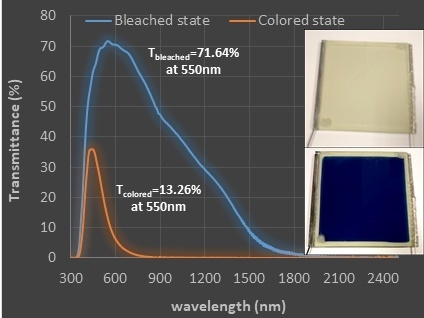
| 9 cm × 10 cm | 71.64 | 13.26 | 0.73 | 1.68 | 71.28 | 30.97 |
| EC Device | E (mWh cm−2) | P (mW cm−2) | Ca (mF cm−2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 9 cm × 10 cm | 1.95 × 10−3 | 7.82 × 10−3 | 156.2 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Theodosiou, K.; Giannopoulos, P.; Georgakopoulos, T.; Stathatos, E. Quasi-Solid-State Electrochromic Cells with Energy Storage Properties Made with Inkjet Printing. Materials 2020, 13, 3241. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13143241
Theodosiou K, Giannopoulos P, Georgakopoulos T, Stathatos E. Quasi-Solid-State Electrochromic Cells with Energy Storage Properties Made with Inkjet Printing. Materials. 2020; 13(14):3241. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13143241
Chicago/Turabian StyleTheodosiou, Krystallia, Panagiotis Giannopoulos, Tilemachos Georgakopoulos, and Elias Stathatos. 2020. "Quasi-Solid-State Electrochromic Cells with Energy Storage Properties Made with Inkjet Printing" Materials 13, no. 14: 3241. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13143241
APA StyleTheodosiou, K., Giannopoulos, P., Georgakopoulos, T., & Stathatos, E. (2020). Quasi-Solid-State Electrochromic Cells with Energy Storage Properties Made with Inkjet Printing. Materials, 13(14), 3241. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13143241