Non-Collagenous Dentin Protein Binding Sites Control Mineral Formation during the Biomineralisation Process in Radicular Dentin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Human Radicular Dentin Specimens
2.2. Biomimetic Remineralisation Model
2.3. Determination of pH and Calcium Ion Release
2.4. Raman Analysis
2.5. Composition and Ultrastructural Examination of Precipitates and Remineralisation Model
2.6. Immunohistochemical Analyses
2.7. Zymography
3. Results
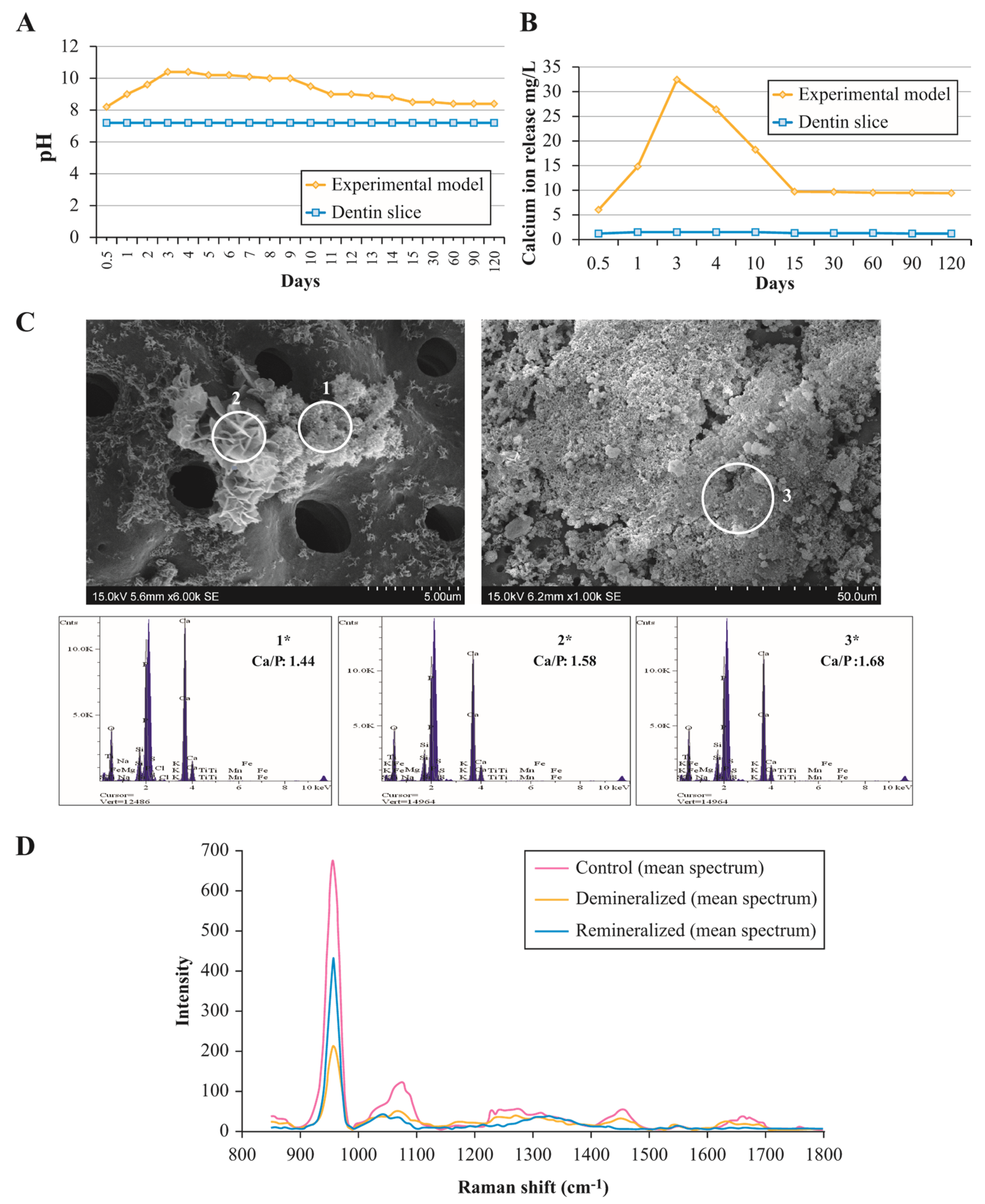
3.1. Assessment of Ion Exchange in Experimental Remineralisation Model
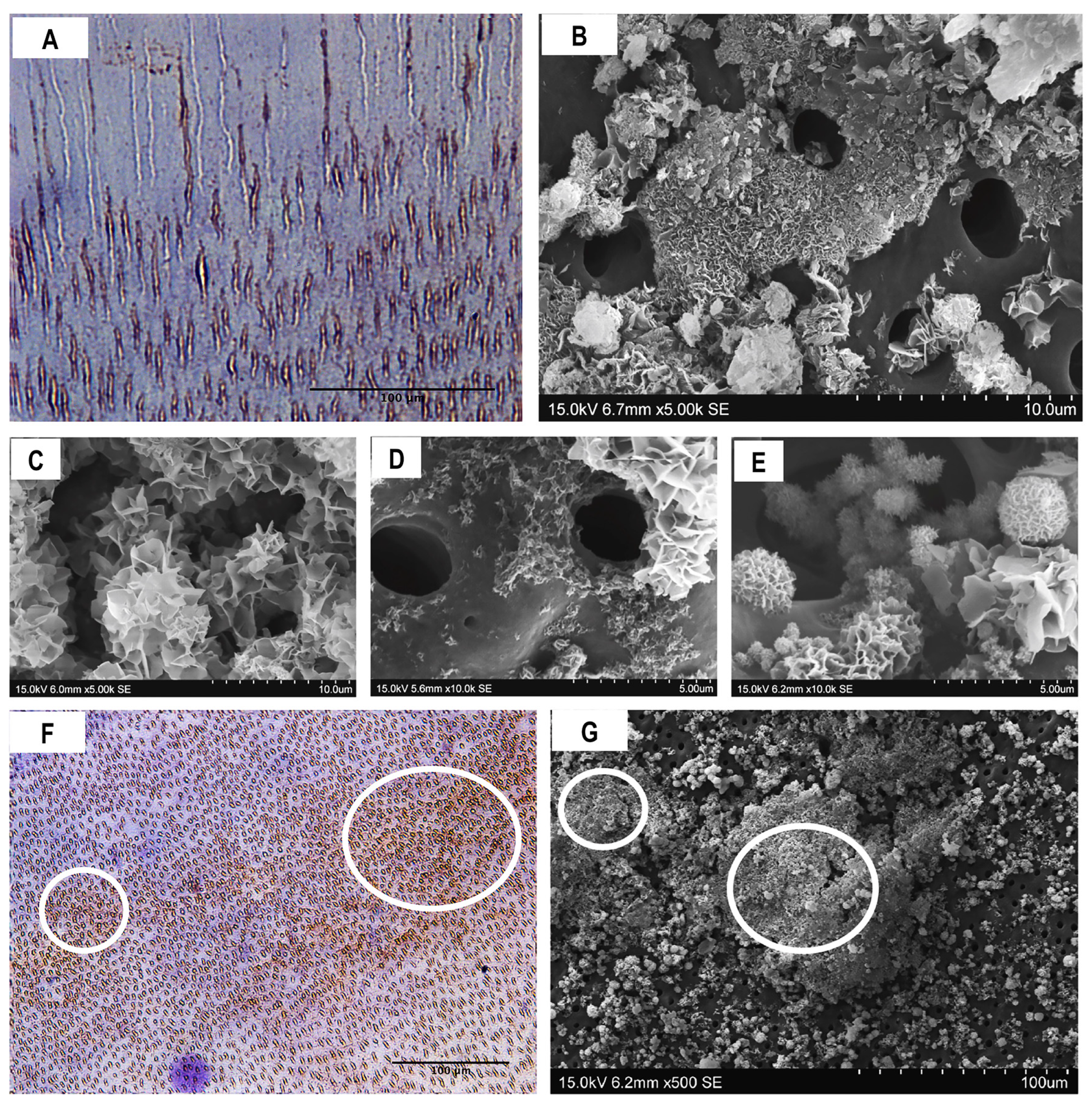
3.2. Composition and Ultrastructural Examination of Precipitates and Remineralisation Model
3.3. Functional Relationship between MMPs and NCPs
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, J.Y.; Choo, J.E.; Choi, Y.S.; Park, J.B.; Min, D.S.; Lee, S.J.; Rhyu, H.K.; Jo, I.H.; Chung, C.P.; Park, Y.J. Assembly of collagen-binding peptide with collagen as a bioactive scaffold for osteogenesis in vitro and in vivo. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 4257–4267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, J.; Ramachandran, A.; George, A. Temporal and spatial localization of the dentin matrix proteins during dentin biomineralization. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2009, 57, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gajjeraman, S.; Narayanan, K.; Hao, J.; Qin, C.; George, A. Matrix macromolecules in hard tissues control the nucleation and hierarchical assembly of hydroxyapatite. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 1193–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.T.; Mei, M.L.; Li, Q.L.; Cao, C.Y.; Chen, J.L.; Xia, R.; Zhang, Z.H.; Chu, C.H. A direct electric field-aided biomimetic mineralization system for inducing the remineralization of dentin collagen matrix. Materials 2015, 8, 7889–7899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qin, C.; D’Souza, R.; Feng, J.Q. Dentin matrix protein 1 (DMP1): New and important roles for biomineralization and phosphate homeostasis. J. Dent. Res. 2007, 86, 1134–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, T.; Niu, X.; Li, Z.; Li, P.; Feng, Q.; Fan, Y. Crosslinking induces high mineralization of apatite minerals on collagen fibers. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 113, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nudelman, F.; Pieterse, K.; George, A.; Bomans, P.H.; Friedrich, H.; Brylka, L.J.; Hilbers, P.A.; de With, G.; Sommerdijk, N.A. The role of collagen in bone apatite formation in the presence of hydroxyapatite nucleation inhibitors. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 1004–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Wang, Z.; Landis, W.J.; Cui, Q.; Sahai, N. Molecular mechanisms for intrafibrillar collagen mineralization in skeletal tissues. Biomaterials 2015, 39, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Gu, L.; Huang, Z.; Sun, Q.; Chen, H.; Ling, J.; Mai, S. Intrafibrillar mineralization of polyacrylic acid-bound collagen fibrils using a two-dimensional collagen model and Portland cement-based resins. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2017, 125, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tay, F.R.; Pashley, D.H. Guided tissue remineralisation of partially demineralised human dentine. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 1127–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Ramachandran, A.; Dahl, T.; George, S.; Schultz, D.; Cookson, D.; Veis, A.; George, A. Phosphorylation of phosphophoryn is crucial for its function as a mediator of biomineralization. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 33109–33114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, B.; Sun, Y.; Maciejewska, I.; Qin, D.; Peng, T.; McIntyre, B.; Wygant, J.; Butler, W.T.; Qin, C. Distribution of SIBLING proteins in the organic and inorganic phases of rat dentin and bone. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2008, 116, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fisher, L.W.; Torchia, D.A.; Fohr, B.; Young, M.F.; Fedarko, N.S. Flexible structures of SIBLING proteins, bone sialoprotein, and osteopontin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 280, 460–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mazzoni, A.; Pashley, D.H.; Tay, F.R.; Gobbi, P.; Orsini, G.; Ruggeri, A., Jr.; Carrilho, M.; Tjäderhane, L.; Di Lenarda, R.; Breschi, L. Immunohistochemical identification of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in human dentin: Correlative FEI-SEM/TEM analysis. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2009, 88, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaussain, C.; Eapen, A.S.; Huet, E.; Floris, C.; Ravindran, S.; Hao, J.; Menashi, S.; George, A. MMP2-cleavage of DMP1 generates a bioactive peptide promoting differentiation of dental pulp stem/progenitor cell. Eur. Cells Mater. 2016, 18, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulkala, M.; Larmas, M.; Sorsa, T.; Salo, T.; Tjäderhane, L. The localization of matrix metalloproteinase-20 (MMP-20, enamelysin) in mature human teeth. J. Dent. Res. 2002, 81, 603–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzoni, A.; Mannello, F.; Tay, F.R.; Tonti, G.A.; Papa, S.; Mazzotti, G.; Di Lenarda, R.; Pashley, D.H.; Breschi, L. Zymographic analysis and characterization of MMP-2 and -9 forms in human sound dentin. J. Dent. Res. 2007, 86, 436–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-De Las Heras, S.; Valenzuela, A.; Overall, C.M. The matrix metalloproteinase gelatinase A in human dentine. Arch. Oral Biol. 2000, 45, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Brunn, J.C.; Cook, R.G.; Orkiszewski, R.S.; Malone, J.P.; Veis, A.; Butler, W.T. Evidence for the proteolytic processing of dentin matrix protein 1. Identification and characterization of processed fragments and cleavage sites. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 34700–34708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gericke, A.; Qin, C.; Sun, Y.; Redfern, R.; Redfern, D.; Fujimoto, Y.; Taleb, H.; Butler, W.T.; Boskey, A.L. Different forms of DMP1 play distinct roles in mineralization. J. Dent. Res. 2010, 89, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Huang, B.; Wygant, J.N.; McIntyre, B.W.; McDonald, C.H.; Cook, R.G.; Butler, W.T. A chondroitin sulfate chain attached to the bone dentin matrix protein 1 NH2-terminal fragment. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 8034–8040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- MacDougall, M.; Simmons, D.; Luan, X.; Nydegger, J.; Feng, J.; Gu, T.T. Dentin phosphoprotein and dentin sialoprotein are cleavage products expressed from a single transcript coded by a gene on human chromosome 4. Dentin phosphoprotein DNA sequence determination. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 835–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baba, O.; Qin, C.; Brunn, J.C.; Wygant, J.N.; McIntyre, B.W.; Butler, W.T. Colocalization of dentin matrix protein 1 and dentin sialoprotein at late stages of rat molar development. Matrix Biol. 2004, 23, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, C.; Brunn, J.C.; Baba, O.; Wygant, J.N.; McIntyre, B.W.; Butler, W.T. Dentin sialoprotein isoforms: Detection and characterization of a high molecular weight dentin sialoprotein. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2003, 111, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Carmona, J.F.; Felippe, M.S.; Felippe, W.T. The biomineralization ability of mineral trioxide aggregate and Portland cement on dentin enhances the push-out strength. J. Endod. 2010, 36, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Carmona, J.F.; Felippe, M.S.; Felippe, W.T. A phosphate-buffered saline intracanal dressing improves the biomineralization ability of mineral trioxide aggregate apical plugs. J. Endod. 2010, 36, 1648–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Carmona, J.F.; Felippe, M.S.; Felippe, W.T. Biomineralization ability and interaction of mineral trioxide aggregate and white portland cement with dentin in a phosphate-containing fluid. J. Endod. 2009, 35, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Gajjeraman, S.; Schultz, D.; Cookson, D.; Qin, C.; Butler, W.T.; Hao, J.; George, A. Spatially and temporally controlled biomineralization is facilitated by interaction between self-assembled dentin matrix protein 1 and calcium phosphate nuclei in solution. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 16140–16148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qi, Y.P.; Li, N.; Niu, L.N.; Primus, C.M.; Ling, J.Q.; Pashley, D.H.; Tay, F.R. Remineralization of artificial dentinal caries lesions by biomimetically modified mineral trioxide aggregate. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 836–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, L.; Kim, Y.K.; Liu, Y.; Ryou, H.; Wimmer, C.E.; Dai, L.; Arola, D.D.; Looney, S.W.; Pashley, D.H.; Tay, F.R. Biomimetic analogs for collagen biomineralization. J. Dent. Res. 2011, 90, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arola, D.; Ivancik, J.; Majd, H.; Fouad, A.; Bajaj, D.; Zhang, X.; Eidelman, N. Microstructure and mechanical behavior of radicular and coronal dentin. Endod. Top. 2012, 20, 30–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.; Carrilho, M.; Tervahartiala, T.; Sorsa, T.; Breschi, L.; Mazzoni, A.; Pashley, D.; Tay, F.; Ferraz, C.; Tjäderhane, L. Determination of matrix metalloproteinases in human radicular dentin. J. Endod. 2009, 35, 686–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinfort, J.; van den Bos, T.; Beertsen, W. Differences between enamel-related and cementum-related dentin in the rat incisor with special emphasis on the phosphoproteins. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 2840–2845. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mazzoni, A.; Scaffa, P.; Carrilho, M.; Tjäderhane, L.; Di Lenarda, R.; Polimeni, A.; Tezvergil-Mutluay, A.; Tay, F.R.; Pashley, D.H.; Breschi, L. Effects of etch-and-rinse and self-etch adhesives on dentin MMP-2 and MMP-9. J. Dent. Res. 2013, 92, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bozeman, T.B.; Lemon, R.R.; Eleazer, P.D. Elemental analysis of crystal precipitate from gray and white MTA. J. Endod. 2006, 32, 425–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, N.K.; Caicedo, R.; Ritwik, P.; Moiseyeva, R.; Kawashima, I. Physicochemical basis of the biologic properties of mineral trioxide aggregate. J. Endod. 2005, 31, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yao, X. Morphological/chemical imaging of demineralized dentin layer in its natural, wet state. Dent. Mater. 2010, 26, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramakrishnaiah, R.; Rehman, G.U.; Basavarajappa, S.; Al Khuraif, A.A.; Durgesh, B.H.; Khan, A.S.; Rehman, I.U. Applications of raman spectroscopy in dentistry: Analysis of tooth structure. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2015, 50, 332–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordeiro, M.; Santos, S.; Reyes-Carmona, J. Mineral trioxide aggregate and calcium hydroxide promotes in vivo intratubular mineralization. Odovtos Int. J. Dent. Sci. 2016, 18, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, M.; Butler, W.T.; Qin, C. Dentin sialophosphoprotein in biomineralization. Connect. Tissue Res. 2010, 51, 404–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, C.; Baba, O.; Butler, W.T. Post-translational modifications of sibling proteins and their roles in osteogenesis and dentinogenesis. Crit. Rev. Oral Biol. Med. 2004, 15, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barbosa-Martins, L.F.; Sousa, J.P.; Alves, L.A.; Davies, R.P.W.; Puppin-Rontanti, R.M. Biomimetic Mineralizing Agents Recover the Micro Tensile Bond Strength of Demineralized Dentin. Materials 2018, 11, 1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Basrani, B.; Santos, J.M.; Tjäderhane, L.; Grad, H.; Gorduysus, O.; Huang, J.; Lawrence, H.P.; Friedman, S.S. Substantive antimicrobial activity in chlorhexidine-treated human root dentin. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2002, 94, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Breschi, L.; Mazzoni, A.; Nato, F.; Carrilho, M.; Visintini, E.; Tjäderhane, L.; Ruggeri, A., Jr.; Tay, F.R.; Dorigo Ede, S.; Pashley, D.H. Chlorhexidine stabilizes the adhesive interface: A 2-year in vitro study. Dent. Mater. 2010, 26, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



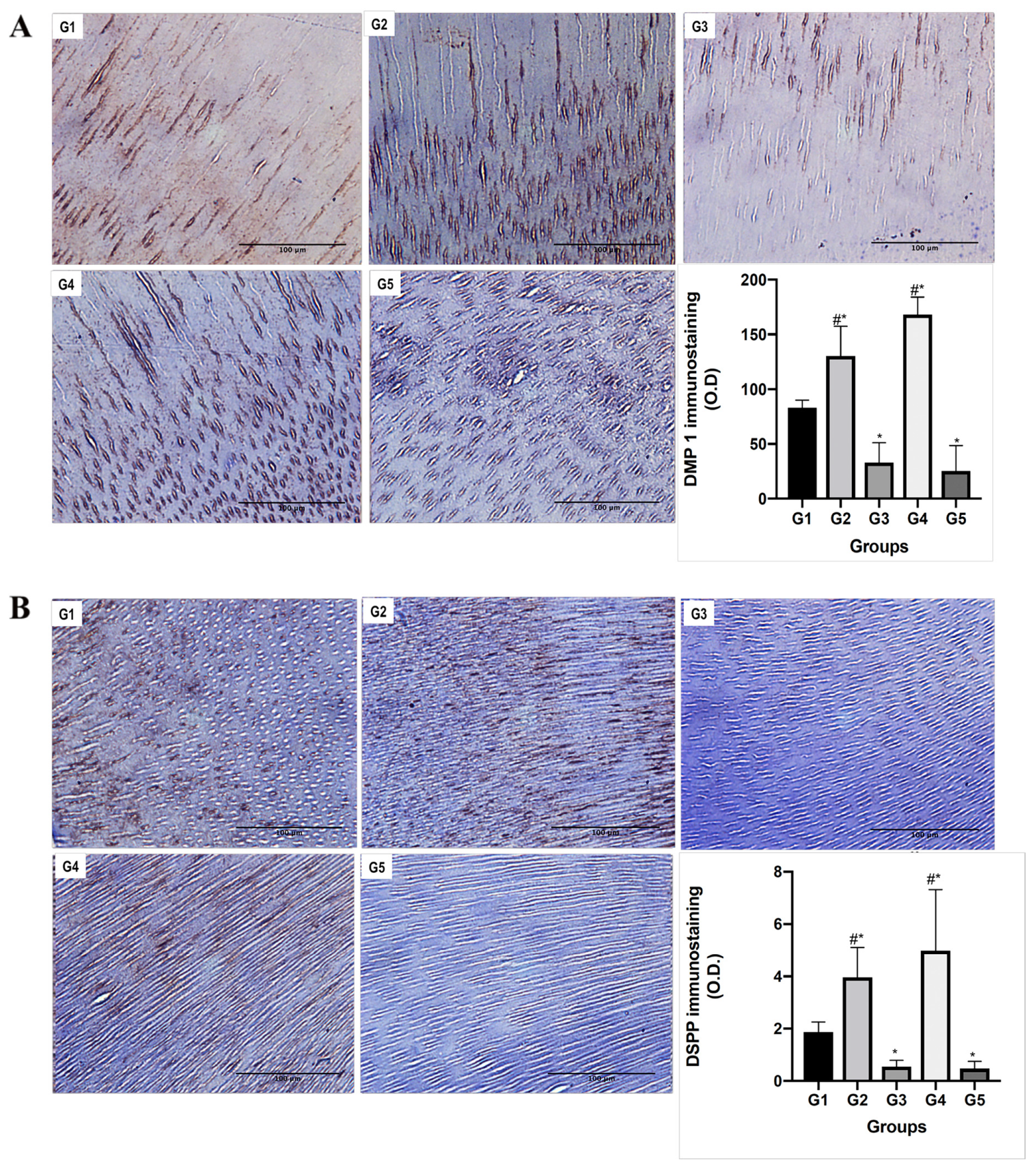
| Groups | Treatments |
|---|---|
| G1 | Control group |
| G2 | 37% H3PO4 for 30 s + distilled water |
| G3 | 37% H3PO4 for 30 s + distilled water + 5 min in 2% chlorhexidine + distilled water |
| G4 | 37% H3PO4 for 30 s + distilled water + Biomimetic remineralisation model |
| G5 | 37% H3PO4 for 30 s + distilled water + 5 min in 2% chlorhexidine + Biomimetic remineralisation model |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Retana-Lobo, C.; Guerreiro-Tanomaru, J.M.; Tanomaru-Filho, M.; Mendes de Souza, B.D.; Reyes-Carmona, J. Non-Collagenous Dentin Protein Binding Sites Control Mineral Formation during the Biomineralisation Process in Radicular Dentin. Materials 2020, 13, 1053. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13051053
Retana-Lobo C, Guerreiro-Tanomaru JM, Tanomaru-Filho M, Mendes de Souza BD, Reyes-Carmona J. Non-Collagenous Dentin Protein Binding Sites Control Mineral Formation during the Biomineralisation Process in Radicular Dentin. Materials. 2020; 13(5):1053. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13051053
Chicago/Turabian StyleRetana-Lobo, Cristina, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Mario Tanomaru-Filho, Beatriz Dulcineia Mendes de Souza, and Jessie Reyes-Carmona. 2020. "Non-Collagenous Dentin Protein Binding Sites Control Mineral Formation during the Biomineralisation Process in Radicular Dentin" Materials 13, no. 5: 1053. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13051053
APA StyleRetana-Lobo, C., Guerreiro-Tanomaru, J. M., Tanomaru-Filho, M., Mendes de Souza, B. D., & Reyes-Carmona, J. (2020). Non-Collagenous Dentin Protein Binding Sites Control Mineral Formation during the Biomineralisation Process in Radicular Dentin. Materials, 13(5), 1053. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13051053




