Effects of Electrical Stimulation on Peripheral Nerve Regeneration in a Silicone Rubber Conduit in Taxol-Treated Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Statement
2.2. Experimental Design and Surgical Protocols
2.3. Electrical Stimulation
2.4. Thermal Hyperalgesia
2.5. Motor Coordination Test
2.6. Electrophysiological Techniques
2.7. Fluorogold Retrograde Labelling
2.8. Histological Analyses and Image Assay
2.9. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
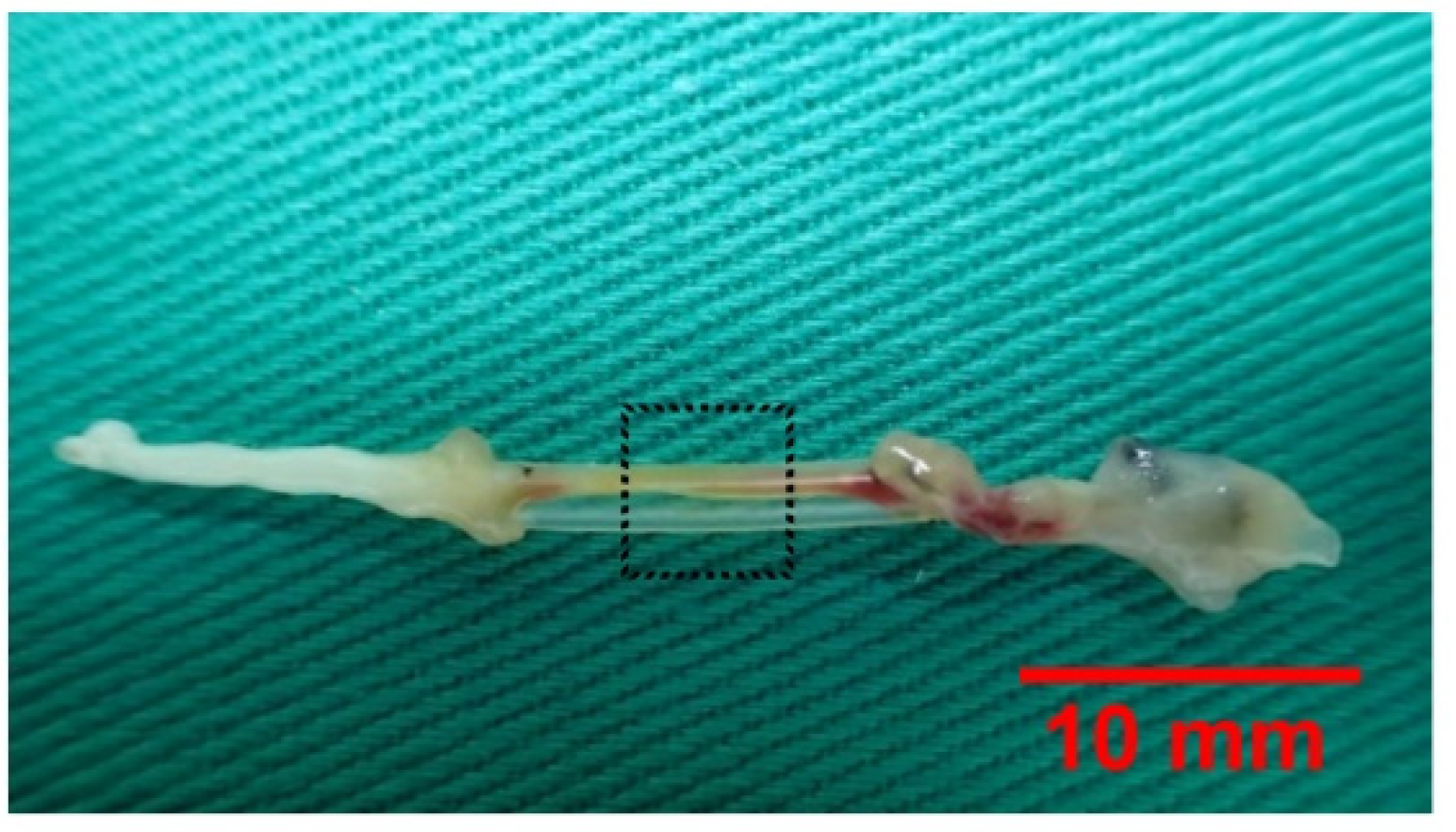
3.1. Regeneration Across Gaps
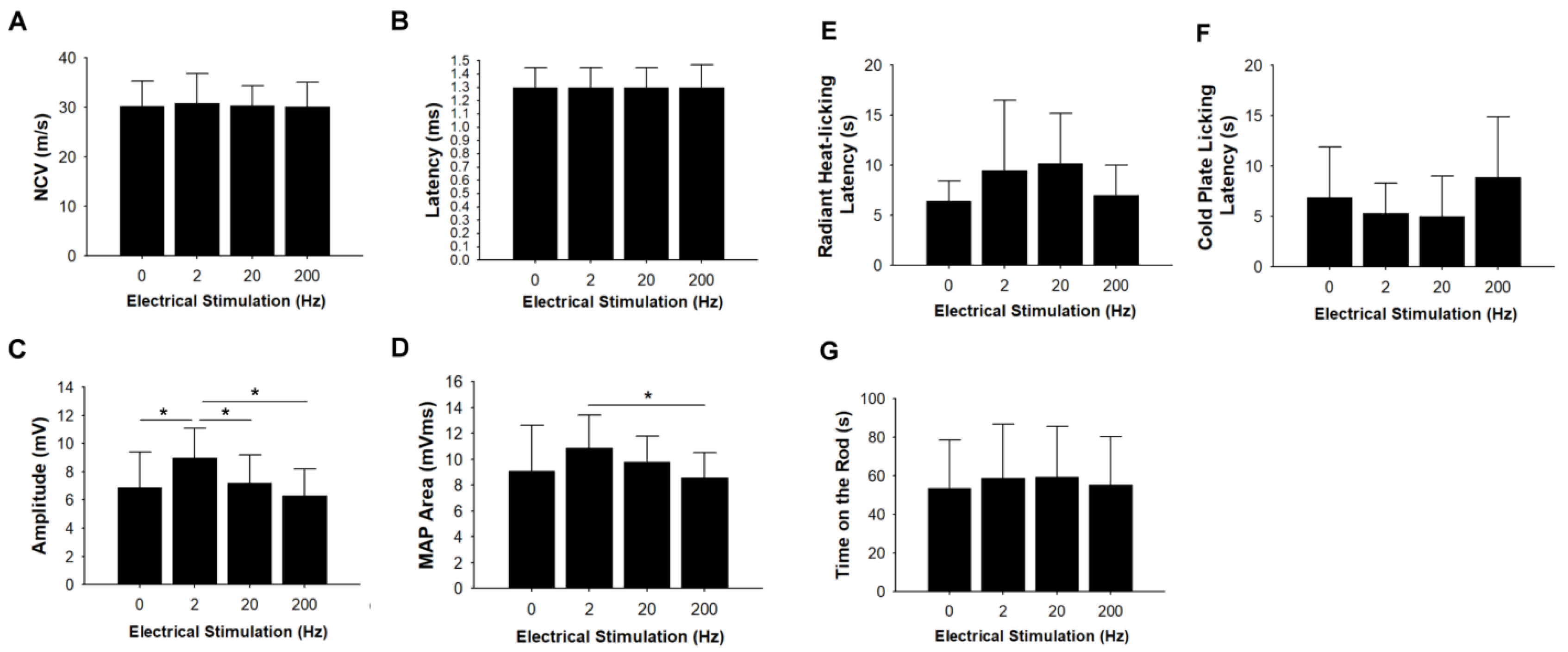
3.2. Electrophysiological Measurements
3.3. Thermal Hyperalgesia and Motor Coordination Tests
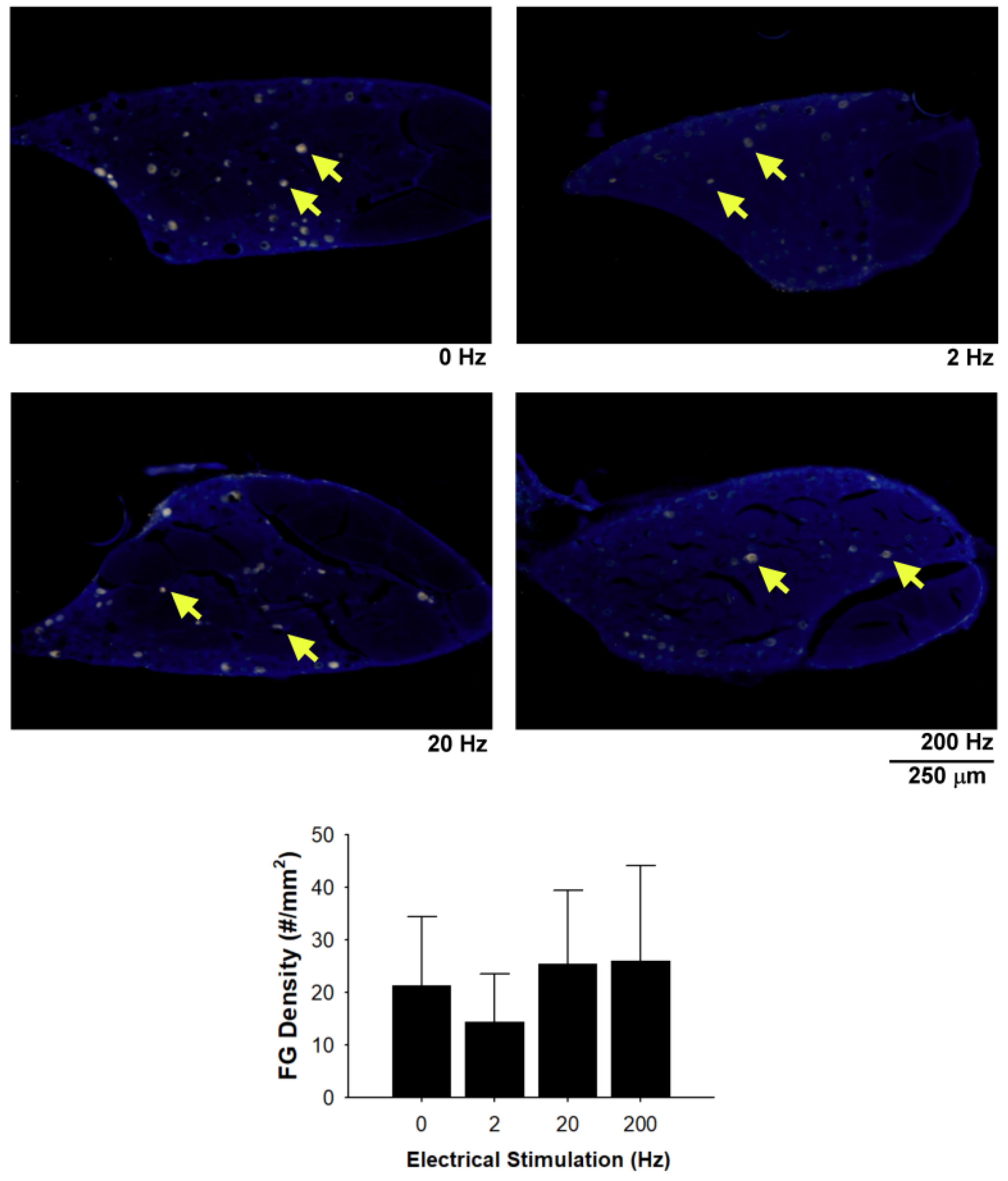
3.4. Fluorogold Retrograde Labelling
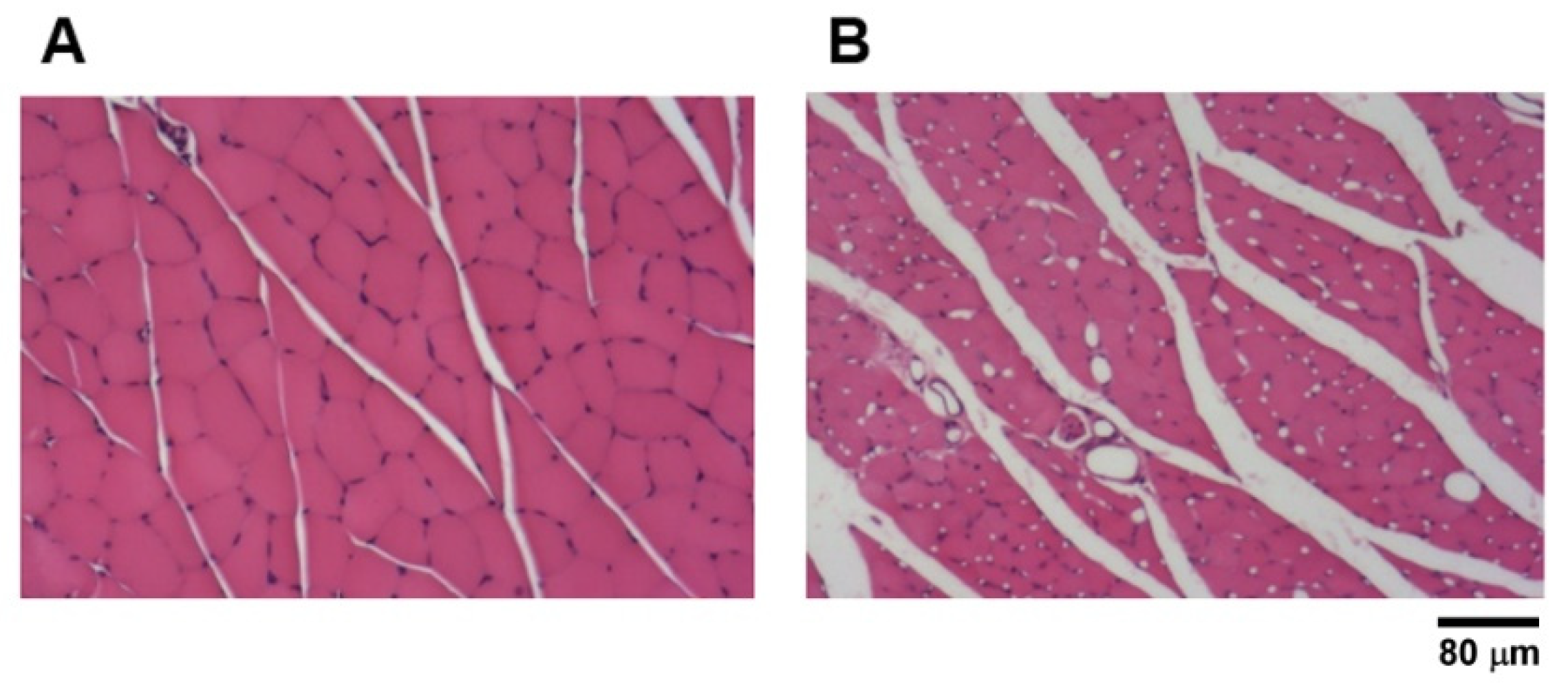
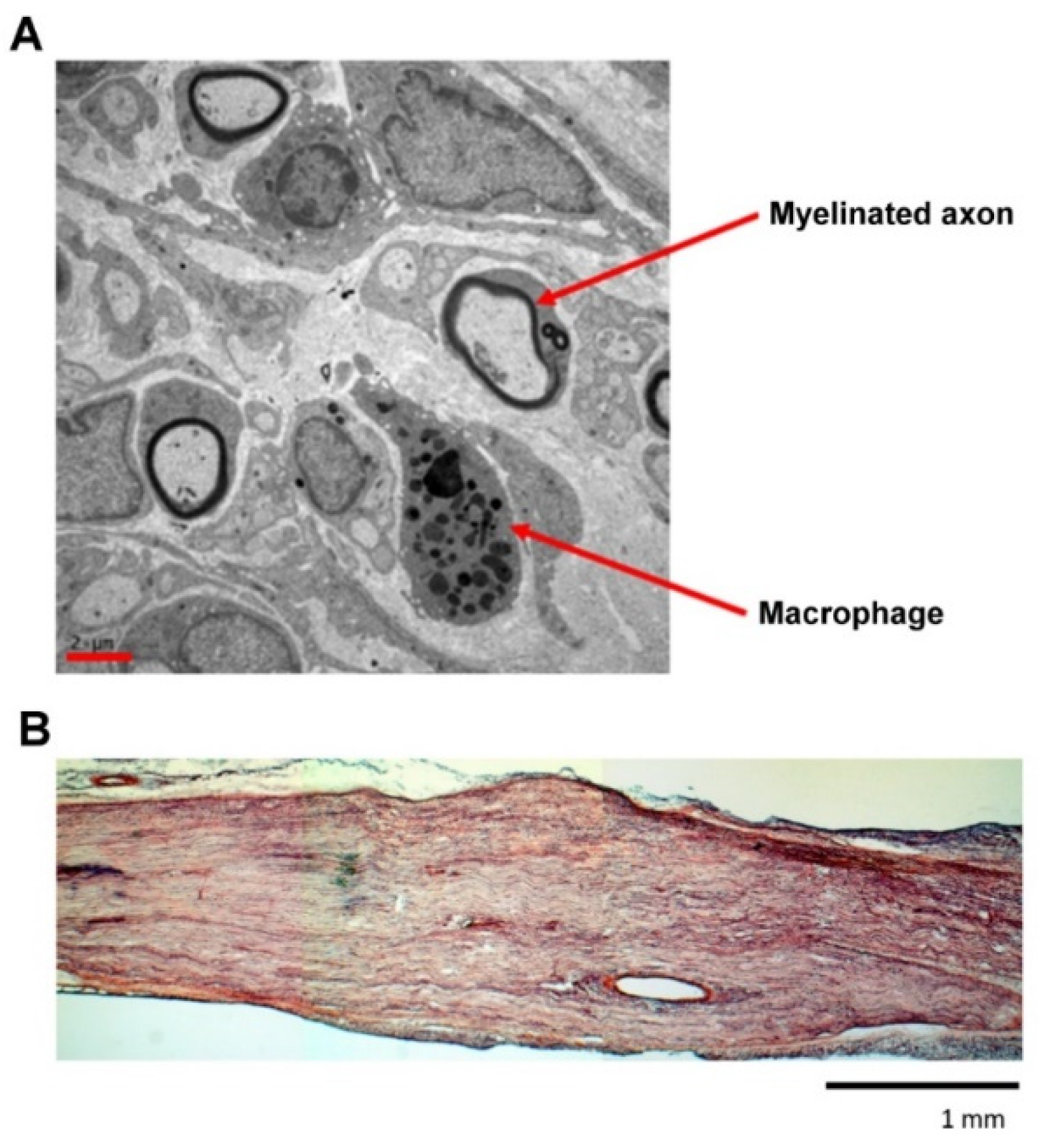
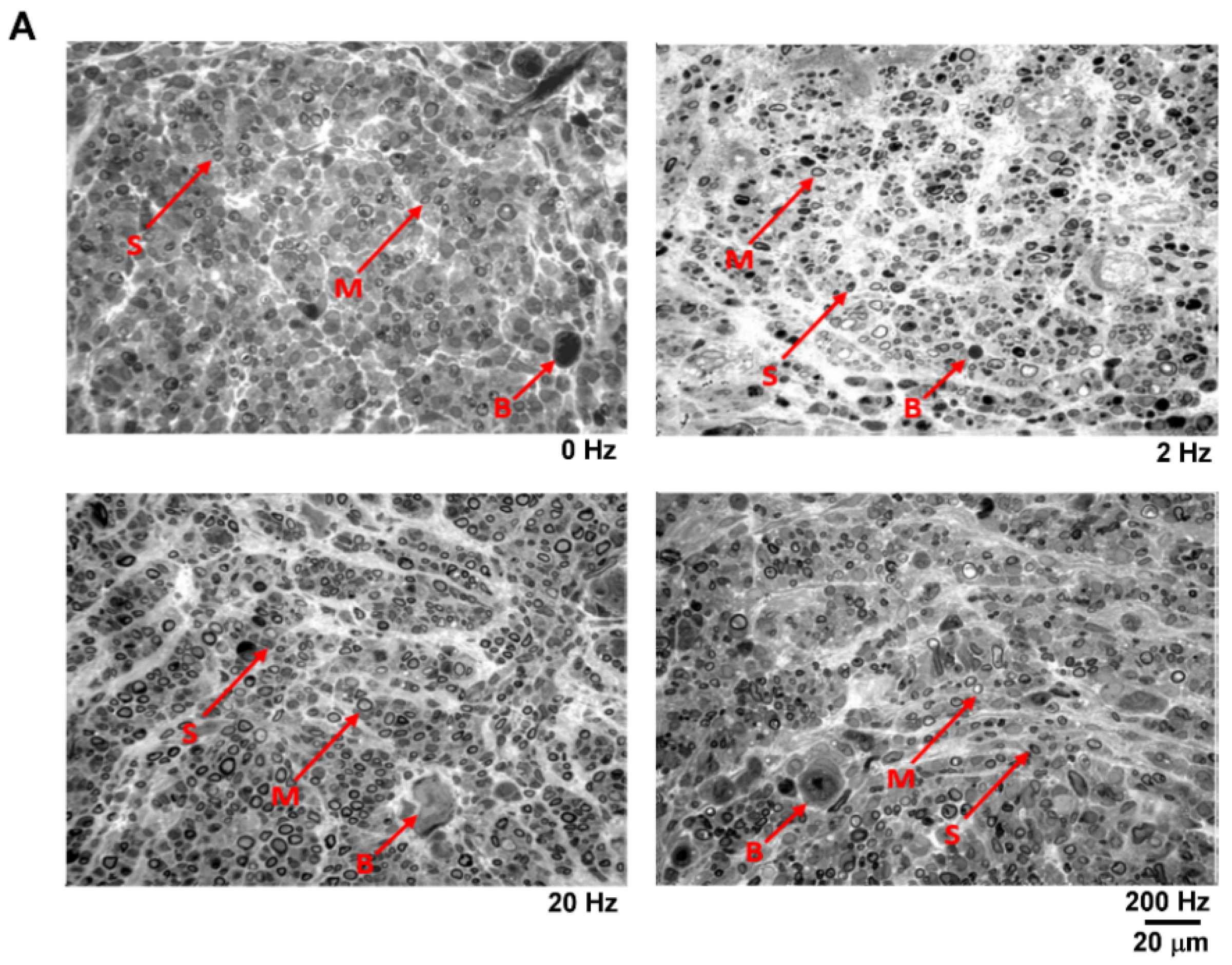
3.5. Ultrastructural Analysis and Maturation of Regenerated Nerves
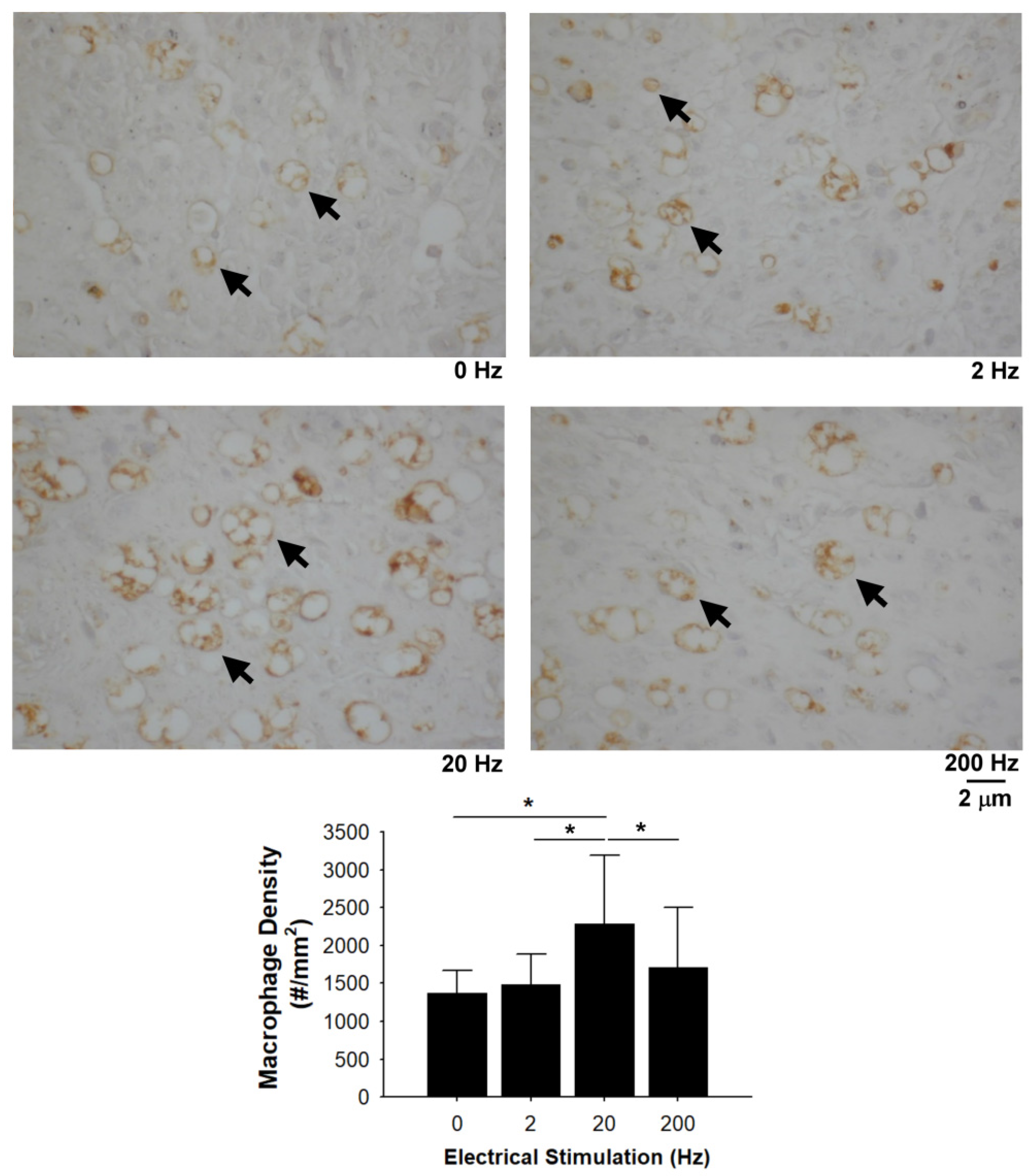
3.6. Recruited Macrophages in the Distal Nerve Ends
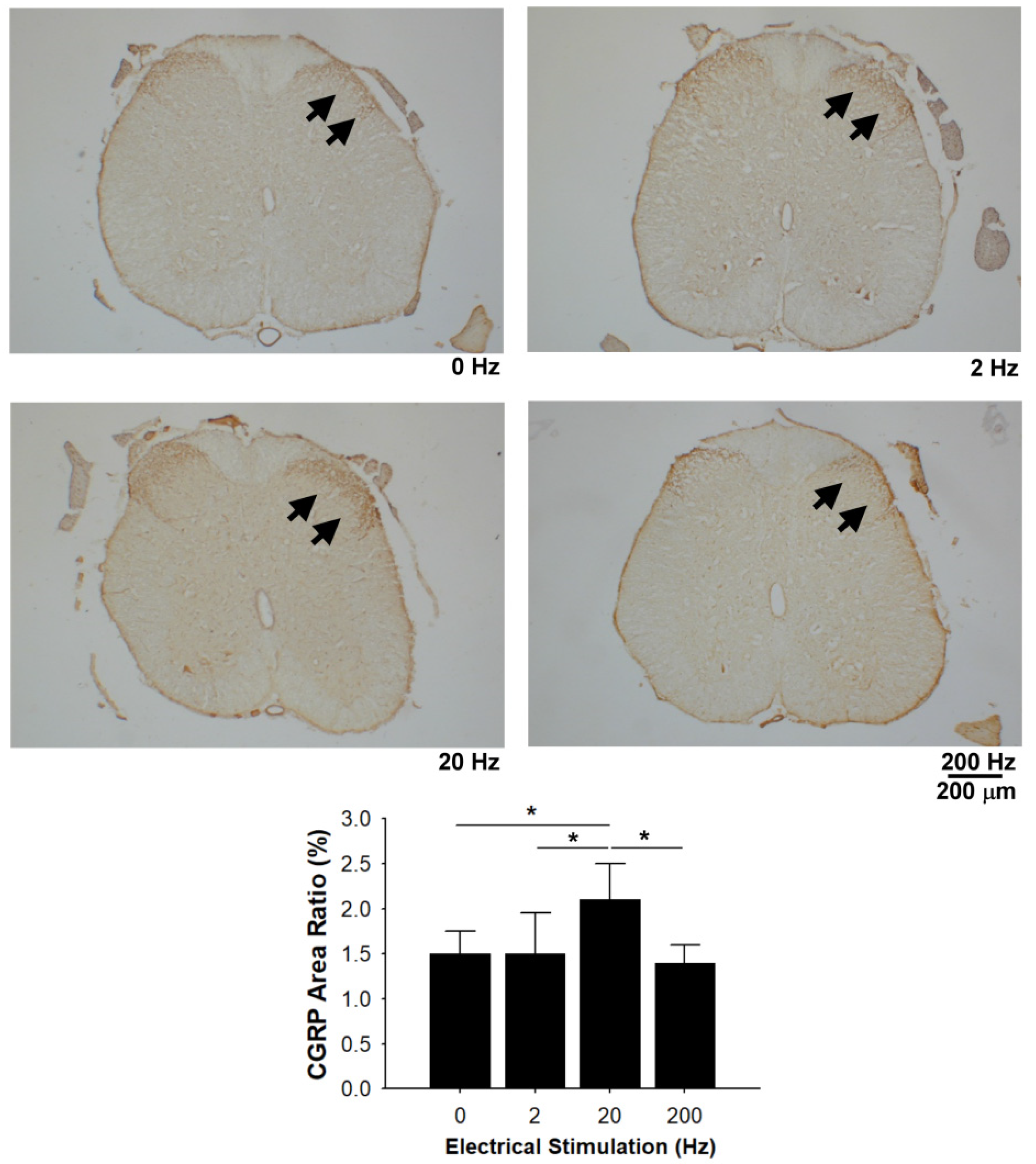
3.7. CGRP Immunoreactivity in the Dorsal Horn
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferreira, M.; Sousa, J.; Pais, A.; Vitorino, C. The Role of Magnetic Nanoparticles in Cancer Nanotheranostics. Materials 2020, 13, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Staff, N.P.; Fehrenbacher, J.C.; Caillaud, M.; Damaj, M.I.; Segal, R.A.; Rieger, S. Pathogenesis of paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy: A current review of in vitro and in vivo findings using rodent and human model systems. Exp. Neurol. 2020, 324, 113121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starobova, H.; Vetter, I. Pathophysiology of Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shichinohe, H.; Ishihara, T.; Takahashi, K.; Tanaka, Y.; Miyamoto, M.; Yamauchi, T.; Saito, H.; Takemoto, H.; Houkin, K.; Kuroda, S. Bone marrow stromal cells rescue ischemic brain by trophic effects and phenotypic change toward neural cells. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair 2015, 29, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polomano, R.C.; Mannes, A.J.; Clark, U.S.; Bennett, G.J. A painful peripheral neuropathy in the rat produced by the chemotherapeutic drug, paclitaxel. Pain 2001, 94, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengottuvel, V.; Fischer, D. Facilitating axon regeneration in the injured CNS by microtubules stabilization. Commun. Integr. Biol. 2011, 4, 391–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellal, F.; Hurtado, A.; Ruschel, J.; Flynn, K.C.; Laskowski, C.J.; Umlauf, M.; Kapitein, L.C.; Strikis, D.; Lemmon, V.; Bixby, J.; et al. Microtubule stabilization reduces scarring and causes axon regeneration after spinal cord injury. Science 2011, 331, 928–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, Y.; Cavalli, V. HDAC5 is a novel injury-regulated tubulin deacetylase controlling axon regeneration. EMBO J. 2012, 31, 3063–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baas, P.W. Beyond taxol: Microtubule-based strategies for promoting nerve regeneration after injury. Neural Regen. Res. 2014, 9, 1265–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, S.T.; Yao, C.H.; Hsu, Y.M.; Lin, J.H.; Chen, Y.H.; Chen, Y.S. Effects of Taxol on Regeneration in a Rat Sciatic Nerve Transection Model. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.S.; Yao, C.H.; Chen, T.H.; Lin, J.G.; Hsieh, C.L.; Lin, C.C.; Lao, C.J.; Tsai, C.C. Effect of acupuncture stimulation on peripheral nerve regeneration using silicone rubber chambers. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2001, 29, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.S.; Hu, C.L.; Hsieh, C.L.; Lin, J.G.; Tsai, C.C.; Chen, T.H.; Yao, C.H. Effects of percutaneous electrical stimulation on peripheral nerve regeneration using silicone rubber chambers. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2001, 57, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Rouabhia, M.; Wang, Z.; Roberge, C.; Shi, G.; Roche, P.; Li, J.; Dao, L.H. Electrically conductive biodegradable polymer composite for nerve regeneration: Electricity-stimulated neurite outgrowth and axon regeneration. Artif. Organs 2007, 31, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, M.; Tanemura, K.; Okada, S.; Iwanami, A.; Nakamura, M.; Mizuno, H.; Ozawa, M.; Ohyama-Goto, R.; Kitamura, N.; Kawano, M.; et al. Electrical stimulation modulates fate determination of differentiating embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells 2007, 25, 562–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Majed, A.A.; Tam, S.L.; Gordon, T. Electrical stimulation accelerates and enhances expression of regeneration-associated genes in regenerating rat femoral motoneurons. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2004, 24, 379–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zealear, D.L.; Rodriguez, R.J.; Kenny, T.; Billante, M.J.; Cho, Y.; Billante, C.R.; Garren, K.C. Electrical stimulation of a denervated muscle promotes selective reinnervation by native over foreign motoneurons. J. Neurophysiol. 2002, 87, 2195–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.H.; Chang, R.L.; Chang, S.L.; Tsai, C.C.; Tsai, F.J.; Chen, Y.S. Electrical stimulation improves peripheral nerve regeneration in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2012, 72, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, Y.C.; Kao, C.H.; Cheng, Y.K.; Chen, J.J.; Yao, C.H.; Chen, Y.S. Current-modulated electrical stimulation as a treatment for peripheral nerve regeneration in diabetic rats. Restor. Neurol. Neurosci. 2014, 32, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kao, C.H.; Chen, J.J.; Hsu, Y.M.; Bau, D.T.; Yao, C.H.; Chen, Y.S. High-frequency electrical stimulation can be a complementary therapy to promote nerve regeneration in diabetic rats. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, Y.C.; Kao, C.H.; Chen, C.C.; Ke, C.J.; Yao, C.H.; Chen, Y.S. Time-course effect of electrical stimulation on nerve regeneration of diabetic rats. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, R.; Berger, F.; Piallat, B.; Benabid, A.L. Alteration of hormone and neurotransmitter production in cultured cells by high and low frequency electrical stimulation. Acta Neurochir. 2007, 149, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelleher, M.O.; Al-Abri, R.K.; Lenihan, D.V.; Glasby, M.A. Use of a static magnetic field to promote recovery after peripheral nerve injury. J. Neurosurg. 2006, 105, 610–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, W.L.; Lin, C.C. The effects of different electrical stimulation protocols on nerve regeneration through silicone conduits. J. Trauma 2004, 56, 1241–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnew, W.F.; McCreery, D.B.; Yuen, T.G.; Bullara, L.A. Evolution and resolution of stimulation-induced axonal injury in peripheral nerve. Muscle Nerve 1999, 22, 1393–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.M.; Hsu, Y.M.; Ying, M.C.; Tsai, F.J.; Tsai, C.H.; Chung, J.G.; Yang, J.S.; Tang, C.H.; Cheng, L.Y.; Su, P.H.; et al. High-density lipoprotein ameliorates palmitic acid-induced lipotoxicity and oxidative dysfunction in H9c2 cardiomyoblast cells via ROS suppression. Nutr. Metab. 2019, 16, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, M.J.; Peng, S.F.; Chueh, F.S.; Tsai, C.H.; Tsai, F.J.; Huang, C.Y.; Tang, C.H.; Yang, J.S.; Hsu, Y.M.; Huang, W.W.; et al. Lupeol suppresses migration and invasion via p38/MAPK and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways in human osteosarcoma U-2 OS cells. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2019, 83, 1729–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatsushima, Y.; Egashira, N.; Kawashiri, T.; Mihara, Y.; Yano, T.; Mishima, K.; Oishi, R. Involvement of substance P in peripheral neuropathy induced by paclitaxel but not oxaliplatin. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2011, 337, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, M.C.; Ho, C.Y.; Hsu, S.F.; Lee, H.C.; Lin, J.H.; Yao, C.H.; Chen, Y.S. Effects of electrical stimulation at different frequencies on regeneration of transected peripheral nerve. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair 2008, 22, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zylka, M.J.; Sowa, N.A.; Taylor-Blake, B.; Twomey, M.A.; Herrala, A.; Voikar, V.; Vihko, P. Prostatic acid phosphatase is an ectonucleotidase and suppresses pain by generating adenosine. Neuron 2008, 60, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ta, L.E.; Low, P.A.; Windebank, A.J. Mice with cisplatin and oxaliplatin-induced painful neuropathy develop distinct early responses to thermal stimuli. Mol. Pain 2009, 5, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.H.; Tzen, J.T.; Hsieh, C.L.; Chen, Y.H.; Lin, T.J.; Chen, S.Y.; Lin, Y.W. Attenuation of TRPV1 and TRPV4 Expression and Function in Mouse Inflammatory Pain Models Using Electroacupuncture. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 2012, 636848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tredici, G.; Tredici, S.; Fabbrica, D.; Minoia, C.; Cavaletti, G. Experimental cisplatin neuronopathy in rats and the effect of retinoic acid administration. J. Neurooncol. 1998, 36, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scripture, C.D.; Figg, W.D.; Sparreboom, A. Peripheral neuropathy induced by paclitaxel: Recent insights and future perspectives. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2006, 4, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Foecking, E.M.; Fargo, K.N.; Coughlin, L.M.; Kim, J.T.; Marzo, S.J.; Jones, K.J. Single session of brief electrical stimulation immediately following crush injury enhances functional recovery of rat facial nerve. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2012, 49, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teodori, R.M.; Silva, A.M.; Silva, M.T.; Oliveira, L.S.; Polacow, M.L.; Guirro, E.C. High-voltage electrical stimulation improves nerve regeneration after sciatic crush injury. Rev. Bras. Fisioter. 2011, 15, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alrashdan, M.S.; Park, J.C.; Sung, M.A.; Yoo, S.B.; Jahng, J.W.; Lee, T.H.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, J.H. Thirty minutes of low intensity electrical stimulation promotes nerve regeneration after sciatic nerve crush injury in a rat model. Acta Neurol. Belg. 2010, 110, 168–179. [Google Scholar]
- Baptista, A.F.; Gomes, J.R.; Oliveira, J.T.; Santos, S.M.; Vannier-Santos, M.A.; Martinez, A.M. High- and low-frequency transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation delay sciatic nerve regeneration after crush lesion in the mouse. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2008, 13, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- English, A.W.; Schwartz, G.; Meador, W.; Sabatier, M.J.; Mulligan, A. Electrical stimulation promotes peripheral axon regeneration by enhanced neuronal neurotrophin signaling. Dev. Neurobiol. 2007, 67, 158–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geremia, N.M.; Gordon, T.; Brushart, T.M.; Al-Majed, A.A.; Verge, V.M. Electrical stimulation promotes sensory neuron regeneration and growth-associated gene expression. Exp. Neurol. 2007, 205, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haastert-Talini, K.; Schmitte, R.; Korte, N.; Klode, D.; Ratzka, A.; Grothe, C. Electrical stimulation accelerates axonal and functional peripheral nerve regeneration across long gaps. J. Neurotrauma 2011, 28, 661–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, C.H.; Shie, M.Y.; Lin, J.H.; Chen, Y.W.; Yao, C.H.; Chen, Y.S. Biodegradable Bisvinyl Sulfonemethyl-crosslinked Gelatin Conduit Promotes Regeneration after Peripheral Nerve Injury in Adult Rats. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fujimaki, H.; Matsumine, H.; Osaki, H.; Ueta, Y.; Kamei, W.; Shimizu, M.; Hashimoto, K.; Fujii, K.; Kazama, T.; Matsumoto, T.; et al. Dedifferentiated fat cells in polyglycolic acid-collagen nerve conduits promote rat facial nerve regeneration. Regen. Ther. 2019, 11, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.W.; Chen, C.C.; Ng, H.Y.; Lou, C.W.; Chen, Y.S.; Shie, M.Y. Additive Manufacturing of Nerve Decellularized Extracellular Matrix-Contained Polyurethane Conduits for Peripheral Nerve Regeneration. Polymers 2019, 11, 1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kehoe, S.; Zhang, X.F.; Boyd, D. FDA approved guidance conduits and wraps for peripheral nerve injury: A review of materials and efficacy. Injury 2012, 43, 553–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muheremu, A.; Ao, Q. Past, Present, and Future of Nerve Conduits in the Treatment of Peripheral Nerve Injury. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 237507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stocco, E.; Barbon, S.; Lora, L.; Grandi, F.; Sartore, L.; Tiengo, C.; Petrelli, L.; Dalzoppo, D.; Parnigotto, P.P.; Macchi, V.; et al. Partially oxidized polyvinyl alcohol conduitfor peripheral nerve regeneration. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balogun, J.A.; Biasci, S.; Han, L. The effects of acupuncture, electroneedling and transcutaneous electrical stimulation therapies on peripheral haemodynamic functioning. Disabil. Rehabil. 1998, 20, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toth, C.C.; Willis, D.; Twiss, J.L.; Walsh, S.; Martinez, J.A.; Liu, W.Q.; Midha, R.; Zochodne, D.W. Locally synthesized calcitonin gene-related Peptide has a critical role in peripheral nerve regeneration. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2009, 68, 326–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, Y.J.; Hsu, C.M.; Lin, C.H.; Lu, M.S.; Chen, L. Electrical stimulation promotes nerve growth factor-induced neurite outgrowth and signaling. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1830, 4130–4136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Knoferle, J.; Ramljak, S.; Koch, J.C.; Tonges, L.; Asif, A.R.; Michel, U.; Wouters, F.S.; Heermann, S.; Krieglstein, K.; Zerr, I.; et al. TGF-beta 1 enhances neurite outgrowth via regulation of proteasome function and EFABP. Neurobiol. Dis. 2010, 38, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liao, C.-F.; Hsu, S.-T.; Chen, C.-C.; Yao, C.-H.; Lin, J.-H.; Chen, Y.-H.; Chen, Y.-S. Effects of Electrical Stimulation on Peripheral Nerve Regeneration in a Silicone Rubber Conduit in Taxol-Treated Rats. Materials 2020, 13, 1063. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13051063
Liao C-F, Hsu S-T, Chen C-C, Yao C-H, Lin J-H, Chen Y-H, Chen Y-S. Effects of Electrical Stimulation on Peripheral Nerve Regeneration in a Silicone Rubber Conduit in Taxol-Treated Rats. Materials. 2020; 13(5):1063. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13051063
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiao, Chien-Fu, Shih-Tien Hsu, Chung-Chia Chen, Chun-Hsu Yao, Jia-Horng Lin, Yung-Hsiang Chen, and Yueh-Sheng Chen. 2020. "Effects of Electrical Stimulation on Peripheral Nerve Regeneration in a Silicone Rubber Conduit in Taxol-Treated Rats" Materials 13, no. 5: 1063. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13051063
APA StyleLiao, C. -F., Hsu, S. -T., Chen, C. -C., Yao, C. -H., Lin, J. -H., Chen, Y. -H., & Chen, Y. -S. (2020). Effects of Electrical Stimulation on Peripheral Nerve Regeneration in a Silicone Rubber Conduit in Taxol-Treated Rats. Materials, 13(5), 1063. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13051063






