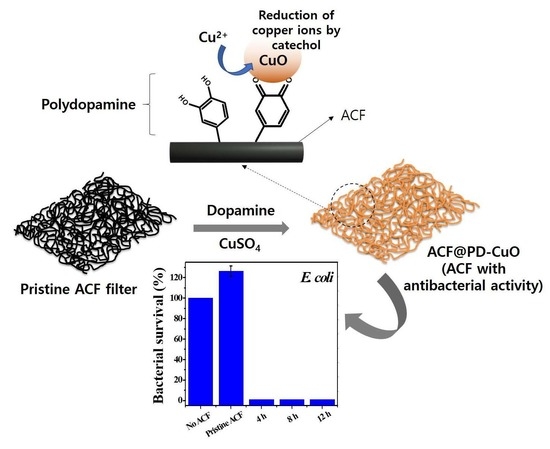
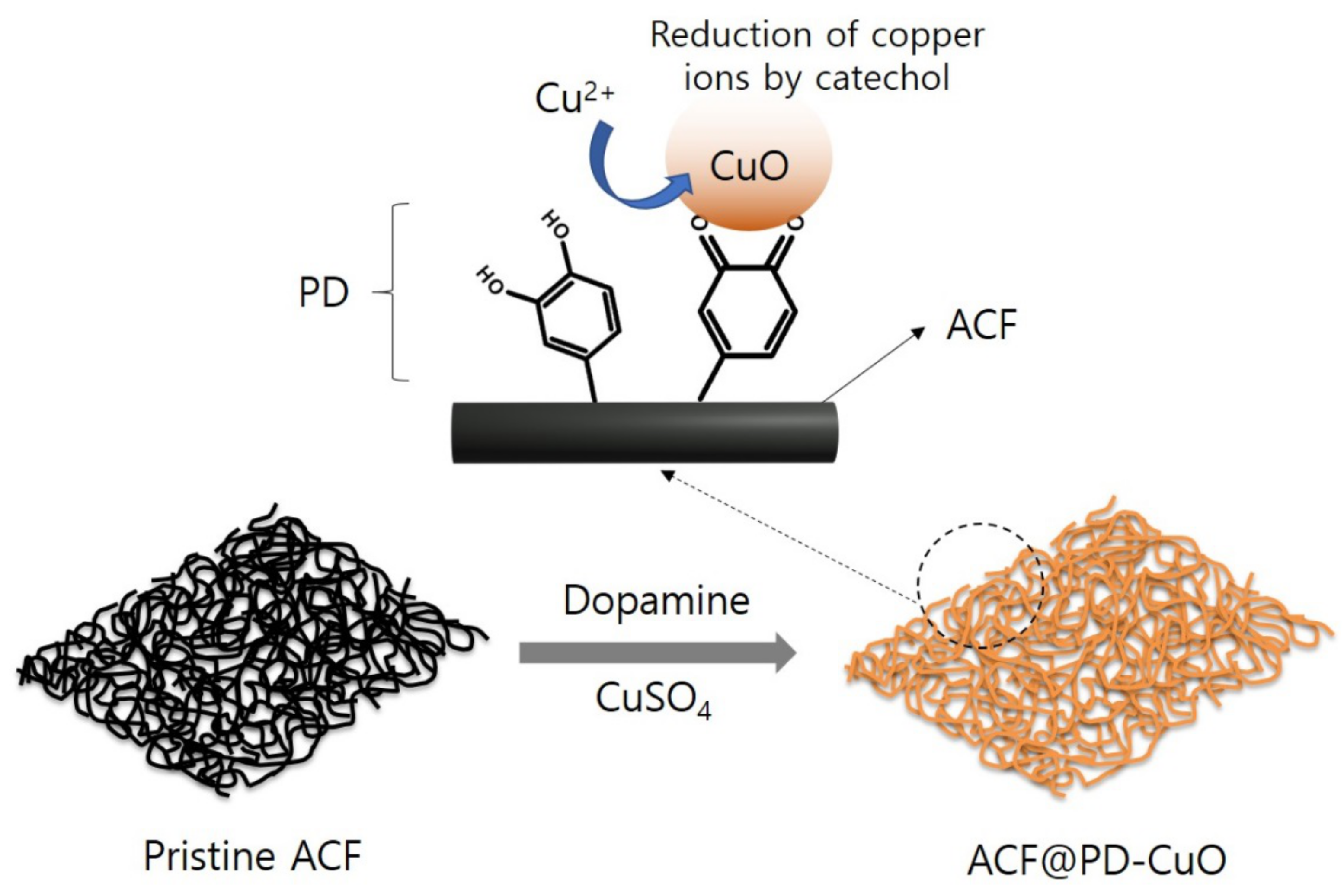
One-Pot Decoration of Cupric Oxide on Activated Carbon Fibers Mediated by Polydopamine for Bacterial Growth Inhibition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Material Characterization
2.3. Preparation of activated carbon fiber (ACF) Coated with Polydopamine and Copper(II) Oxide (ACF@PD-CuO)
2.4. Antimicrobial Test
2.5. Pressure Drop Measurement
2.6. Mechanical Property Measurement
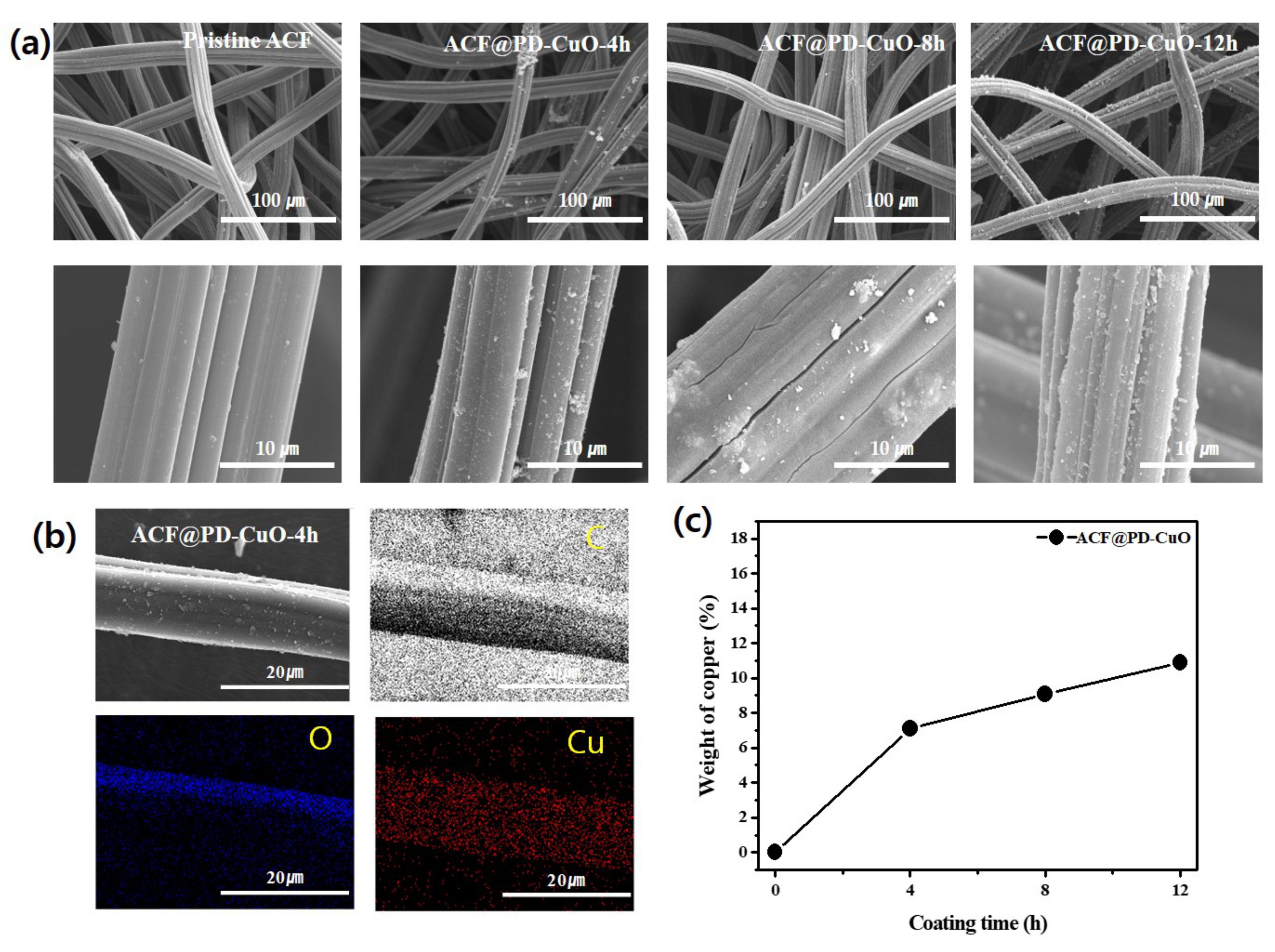
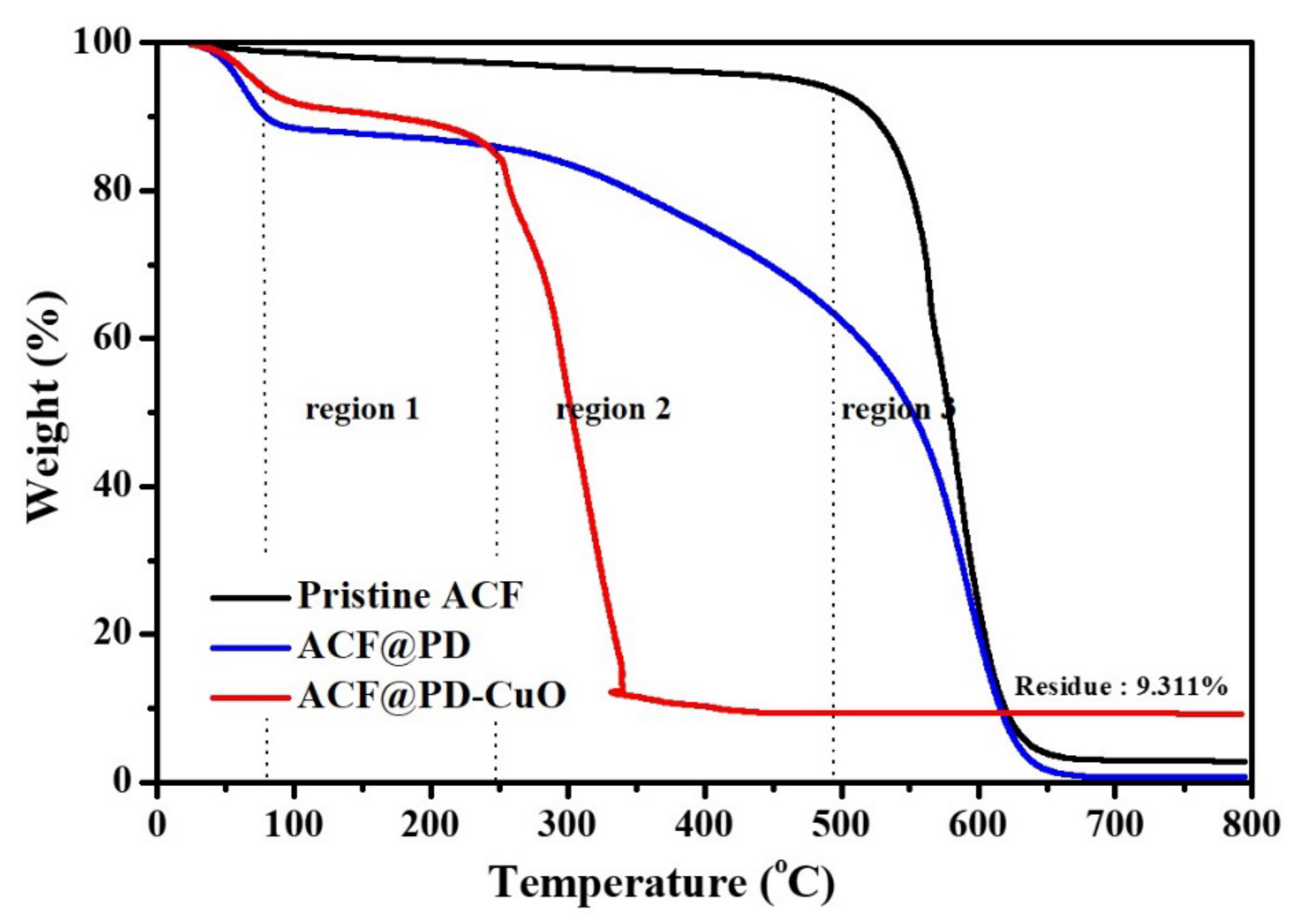
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Suzuki, M. Activated carbon fiber: Fundamentals and applications. Carbon 1994, 32, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.; Kamal, T.; Ul-Islam, M.; Khan, A.; Shah, S.J.; Zada, A. Chitosan-coated cotton cloth supported copper nanoparticles for toxic dye reduction. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 111, 832–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, Y.-C.; Chiang, P.-C.; Huang, C.-P. Effects of pore structure and temperature on VOC adsorption on activated carbon. Carbon 2001, 39, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.; Gaur, V.; Verma, N. Removal of volatile organic compound by activated carbon fiber. Carbon 2004, 42, 2949–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, P.; Amano, Y.; Machida, M. Adsorption of nitrate onto nitrogen-doped activated carbon fibers prepared by chemical vapor deposition. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 35, 2468–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douwes, J.; Thorne, P.; Pearce, N.; Heederik, D. Bioaerosol health effects and exposure assessment: Progress and prospects. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2003, 47, 187–200. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.Y.; Wan, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Han, L. Antibacterial pitch-based activated carbon fiber supporting silver. Carbon 1998, 36, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, K.Y.; Byeon, J.H.; Park, C.W.; Hwang, J. Antimicrobial effect of silver particles on bacterial contamination of activated carbon fibers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 1251–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anita, S.; Ramachandran, T.; Rajendran, R.; Koushik, C.; Mahalakshmi, M. A study of the antimicrobial property of encapsulated copper oxide nanoparticles on cotton fabric. Text. Res. J. 2011, 81, 1081–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahamed, M.; Alhadlaq, H.A.; Khan, M.; Karuppiah, P.; Al-Dhabi, N.A. Synthesis, characterization, and antimicrobial activity of copper oxide nanoparticles. J. Nanomater. 2014, 2014, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivask, A.; Juganson, K.; Bondarenko, O.; Mortimer, M.; Aruoja, V.; Kasemets, K.; Blinova, I.; Heinlaan, M.; Slaveykova, V.; Kahru, A. Mechanisms of toxic action of Ag, ZnO and CuO nanoparticles to selected ecotoxicological test organisms and mammalian cells in vitro: A comparative review. Nanotoxicology 2014, 8, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Huo, Y. The comparison of electrochemical migration mechanism between electroless silver plating and silver electroplating. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2016, 27, 931–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, I. Electrochemistry of electroless plating. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1991, 146, 33–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grujicic, D.; Pesic, B. Electrodeposition of copper: The nucleation mechanisms. Electrochim. Acta 2002, 47, 2901–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djokić, S.; Nikolić, N.; Živković, P.; Popov, K.; Djokić, N. Electrodeposition and electroless deposition of metallic powders: A comparison. ECS Trans. 2011, 33, 7–31. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Z.; Xiao, J.; Wang, Y.; Meng, M. In situ synthesis of silver nanoparticles uniformly distributed on polydopamine-coated silk fibers for antibacterial application. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 452, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponzio, F.; Barthès, J.; Bour, J.R.M.; Michel, M.; Bertani, P.; Hemmerlé, J.; d’Ischia, M.; Ball, V. Oxidant control of polydopamine surface chemistry in acids: A mechanism-based entry to superhydrophilic-superoleophobic coatings. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 4697–4705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrówczyński, R.; Markiewicz, R.; Liebscher, J. Chemistry of polydopamine analogues. Polym. Int. 2016, 65, 1288–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, H.Y.; Ryu, J.H.; Lee, H.; Nam, Y.S. Silver-Polydopamine Hybrid Coatings of Electrospun Poly (vinyl alcohol) Nanofibers. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2013, 298, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.H.; Messersmith, P.B.; Lee, H. Polydopamine surface chemistry: A decade of discovery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 7523–7540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, R.P.; Meng, X.Y.; Liu, C.M.; Qiu, J.D. PDMS microchip coated with polydopamine/gold nanoparticles hybrid for efficient electrophoresis separation of amino acids. Electrophoresis 2011, 32, 3331–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, G.; Hu, D.; Cheng, E.W.C.; Vargas-Reus, M.A.; Reip, P.; Allaker, R.P. Characterisation of copper oxide nanoparticles for antimicrobial application. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2009, 33, 587–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynge, M.E.; van der Westen, R.; Postma, A.; Städler, B. Polydopamine—A nature-inspired polymer coating for biomedical science. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 4916–4928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Ai, K.; Lu, L. Polydopamine and its derivative materials: Synthesis and promising applications in energy, environmental, and biomedical fields. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 5057–5115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trizio, A.D.; Srisuk, P.; Costa, R.R.; Fraga, A.G.; Modena, T.; Genta, I.; Dorati, R.; Pedtosa, J.; Conti, B.; Correlo, V.M.; et al. Natural based eumelanin nanoparticles functionalization and preliminary evaluation as carrier for gentamicin. React. Funct. Polym. 2017, 114, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Zhu, L.; Zhu, L.; Zhu, B.; Xu, Y.J.L. Surface characteristics of a self-polymerized dopamine coating deposited on hydrophobic polymer films. Langmuir 2011, 27, 14180–14187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreyer, D.R.; Miller, D.J.; Freeman, B.D.; Paul, D.R.; Bielawski, C.W. Elucidating the structure of poly (dopamine). Langmuir 2012, 28, 6428–6435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massardier, V.; Voron, L.; Esnouf, C.; Merlin, J. Identification of the nitrides formed during the annealing of a low-carbon low-aluminium steel. J. Mater. Sci. 2001, 36, 1363–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Cao, Y.; Feng, J. Polydopamine as an efficient and robust platform to functionalize carbon fiber for high-performance polymer composites. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 6, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Lu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, W. Preparation and characterization of dopamine-decorated hydrophilic carbon black. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 5387–5393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-H.; Lee, W.-J. Hierarchically mesoporous CuO/carbon nanofiber coaxial shell-core nanowires for lithium ion batteries. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 09754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Huang, Y.; Miao, Y.-E.; Tjiu, W.W.; Liu, T. Polydopamine-coated electrospun poly (vinyl alcohol)/poly (acrylic acid) membranes as efficient dye adsorbent with good recyclability. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 283, 730–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rim, N.G.; Kim, S.J.; Shin, Y.M.; Jun, I.; Lim, D.W.; Park, J.H.; Shin, H. Mussel-inspired surface modification of poly (L-lactide) electrospun fibers for modulation of osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2012, 91, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Zong, X.; Zhou, X.; Li, C. Cu2O/CuO photocathode with improved stability for photoelectrochemical water reduction. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 10790–10794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.-T.; Chen, J.-M.; Lin, H.-H.; Shih, H.-C. Field emission from various CuO nanostructures. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 83, 3383–3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, D.; Tougaard, S. Electronic and optical properties of Cu, CuO and Cu2O studied by electron spectroscopy. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2012, 24, 175002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viji, S.; Anbazhagi, M.; Ponpandian, N.; Mangalaraj, D.; Jeyanthi, S.; Santhanam, P.; Devi, A.S.; Viswanathan, C. Diatom-based label-free optical biosensor for biomolecules. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2014, 174, 1166–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Y.; Ma, W.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, X.; Ma, M.; Xu, Y.; Ding, Z.; Wu, X. 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilanes modified porous silicon as a voltammetric sensor for determination of silver ion. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2013, 8, 1802–1812. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; Tao, J.; Cui, Y.; Gao, J.; Li, X.; Tan, F. Preparation and characterization of hydrophilic polydopamine-coated Fe 3 O 4/oxide graphene imprinted nanocomposites for removal of bisphenol A in waters. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 35, 1836–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raul, P.K.; Senapati, S.; Sahoo, A.K.; Umlong, I.M.; Devi, R.R.; Thakur, A.J.; Veer, V. CuO nanorods: A potential and efficient adsorbent in water purification. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 40580–40587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundar, S.; Venkatachalam, G.; Kwon, S. Biosynthesis of Copper Oxide (CuO) Nanowires and Their Use for the Electrochemical Sensing of Dopamine. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azam, A.; Ahmed, A.S.; Oves, M.; Khan, M.S.; Habib, S.S.; Memic, A. Antimicrobial activity of metal oxide nanoparticles against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria: A comparative study. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 6003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papo, N.; Shai, Y. A molecular mechanism for lipopolysaccharide protection of Gram-negative bacteria from antimicrobial peptides. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 10378–10387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barzilai, A.; Zilkha-Falb, R.; Daily, D.; Stern, N.; Offen, D.; Ziv, I.; Melamed, E.; Shirvan, A. The molecular mechanism of dopamine-induced apoptosis: Identification and characterization of genes that mediate dopamine toxicity. In Advances in Research on Neurodegeneration; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; pp. 59–76. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Li, J.; Sun, S.; Li, X.; Wu, G.; Wang, Y.; Xie, F.; Huang, Y. Controlled growth of silver nanoparticles on carbon fibers for reinforcement of both tensile and interfacial strength. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 14016–14026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


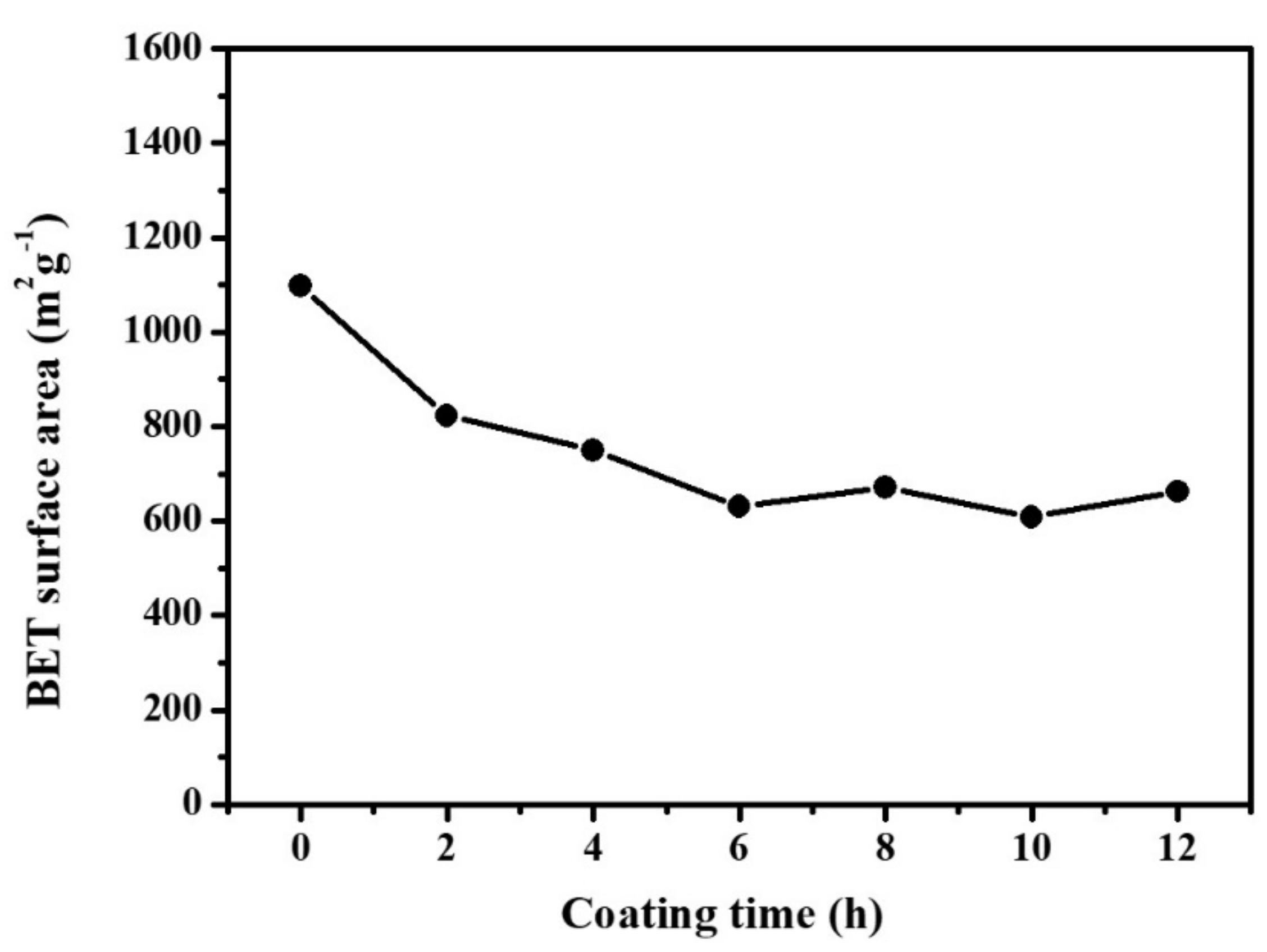


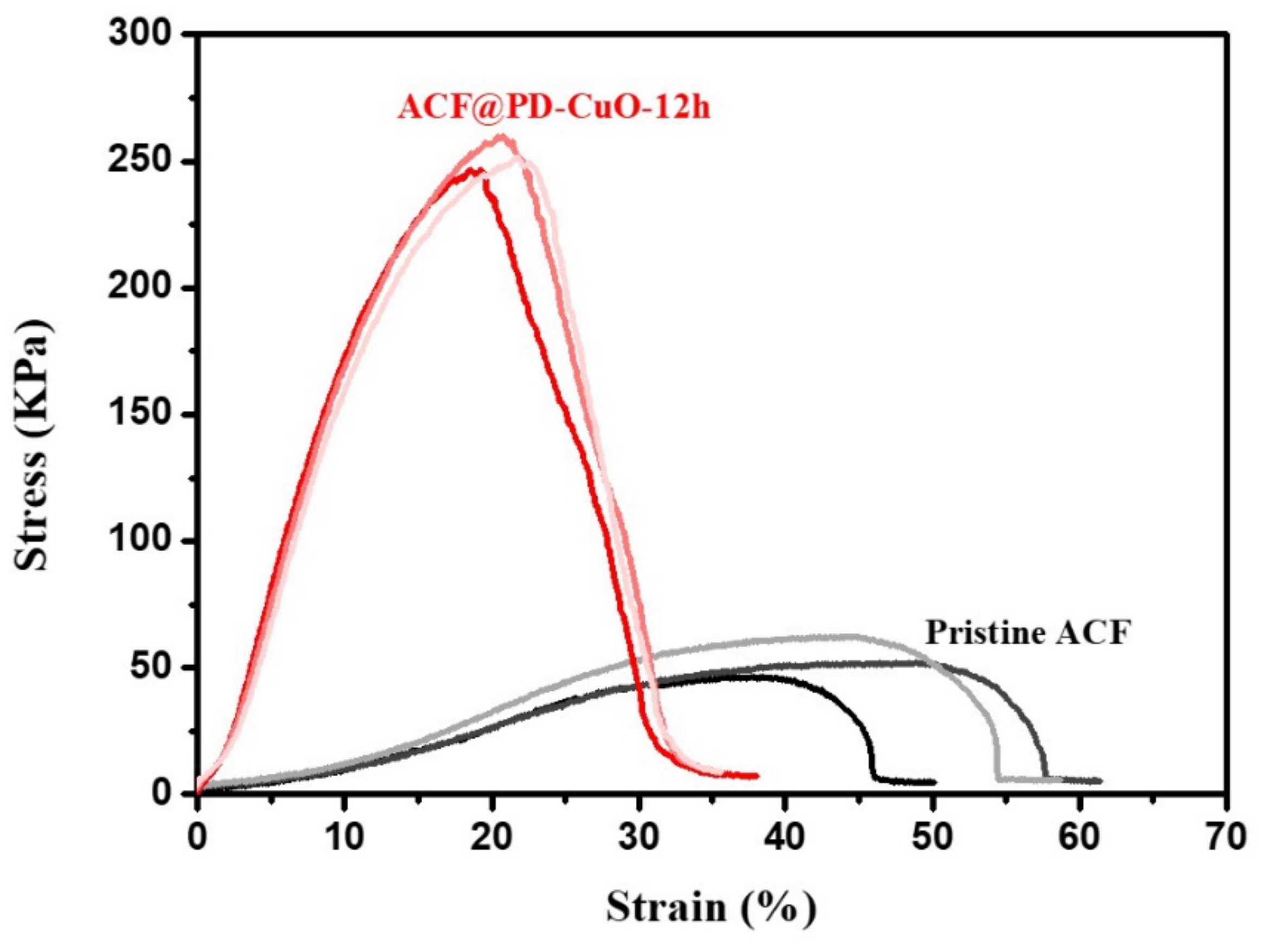
| Young’s Modulus (MPa) | Tensile Strength (kPa) | Elongation (%) | Tensile Strain(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pristine ACF | 0.21 ± 0.03 | 53.73 ± 7.97 | 43.20 ± 5.46 | 56.74 ± 5.93 |
| ACF@PD-CuO-12h | 2.09 ± 0.06 | 252.82 ± 6.61 | 20.63 ± 1.26 | 36.35 ± 1.49 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moon, H.; Lee, Y.-C.; Hur, J. One-Pot Decoration of Cupric Oxide on Activated Carbon Fibers Mediated by Polydopamine for Bacterial Growth Inhibition. Materials 2020, 13, 1158. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13051158
Moon H, Lee Y-C, Hur J. One-Pot Decoration of Cupric Oxide on Activated Carbon Fibers Mediated by Polydopamine for Bacterial Growth Inhibition. Materials. 2020; 13(5):1158. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13051158
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoon, Hangil, Young-Chul Lee, and Jaehyun Hur. 2020. "One-Pot Decoration of Cupric Oxide on Activated Carbon Fibers Mediated by Polydopamine for Bacterial Growth Inhibition" Materials 13, no. 5: 1158. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13051158
APA StyleMoon, H., Lee, Y.-C., & Hur, J. (2020). One-Pot Decoration of Cupric Oxide on Activated Carbon Fibers Mediated by Polydopamine for Bacterial Growth Inhibition. Materials, 13(5), 1158. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13051158