New Biocomposite Electrospun Fiber/Alginate Hydrogel for Probiotic Bacteria Immobilization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacteria Cultivation and Immobilization on Electrospun Material
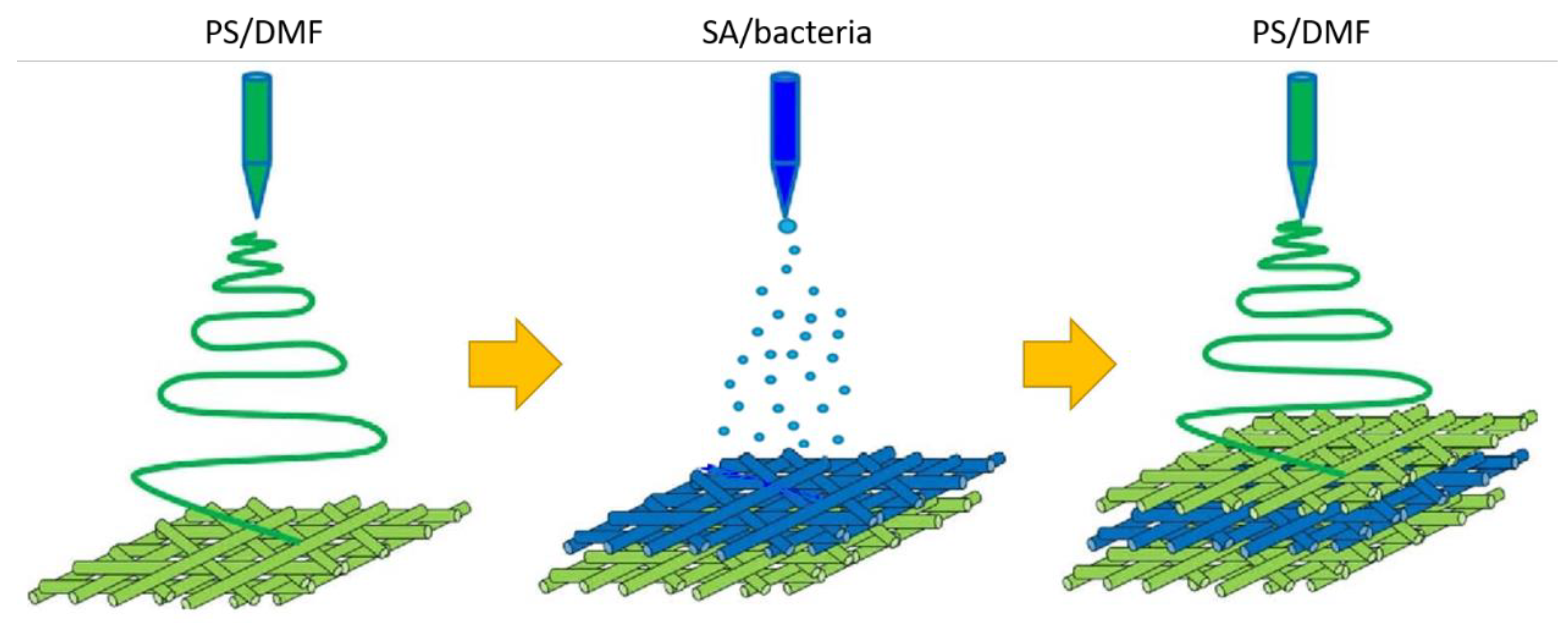
2.2. Production of Electrospun Fibers with Encapsulated Bacteria
2.3. Material Properties Analysis
2.4. Evaluation of Bacterial Metabolic Activity
3. Results and Discussion
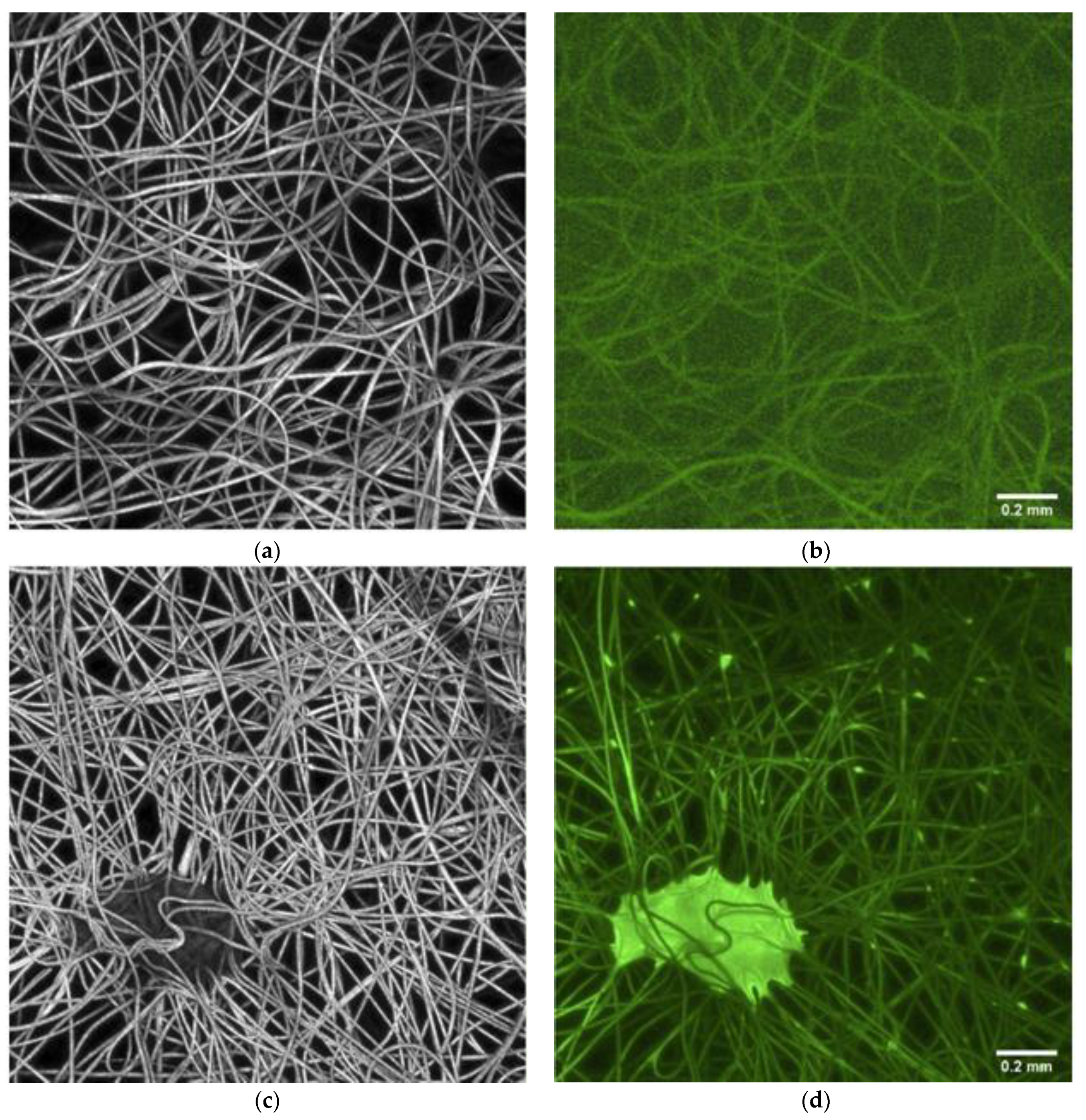
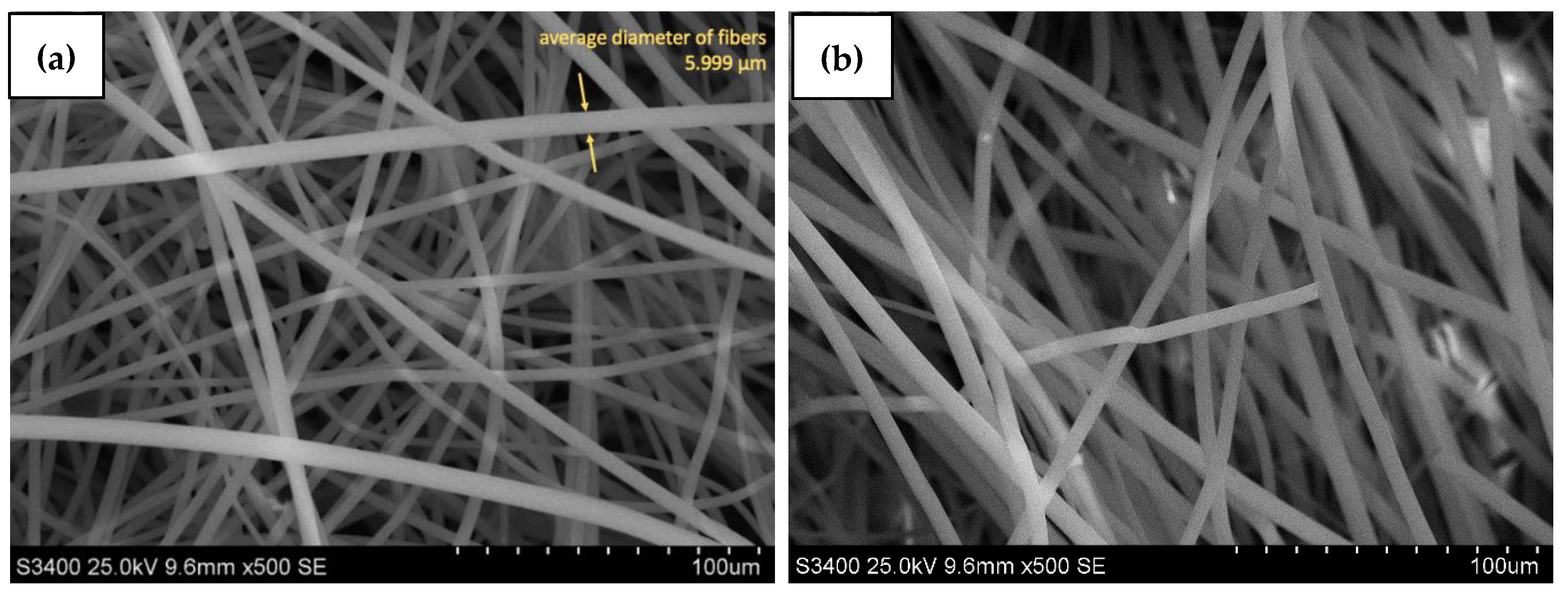
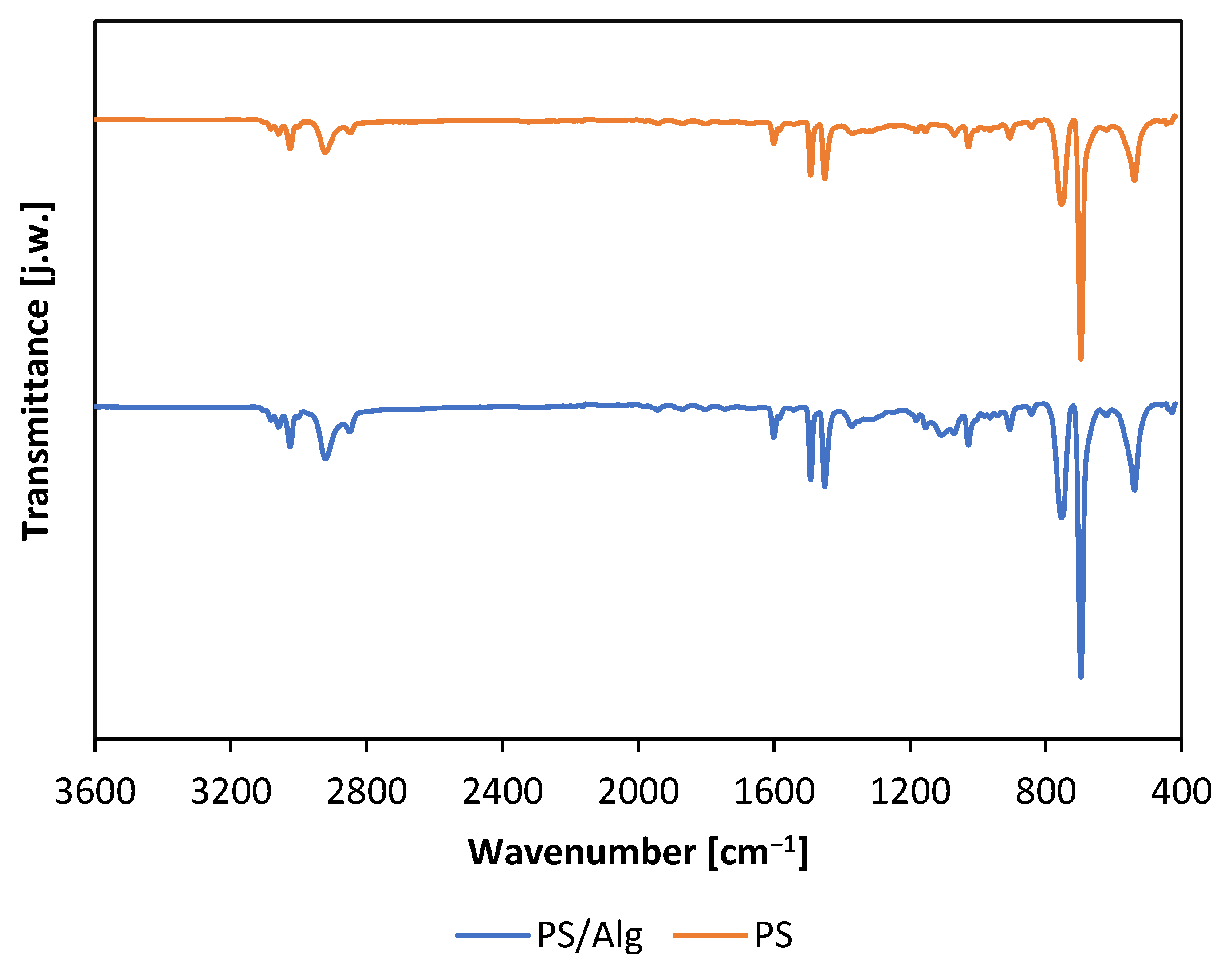
3.1. Characteristic of the Material
Microscopy
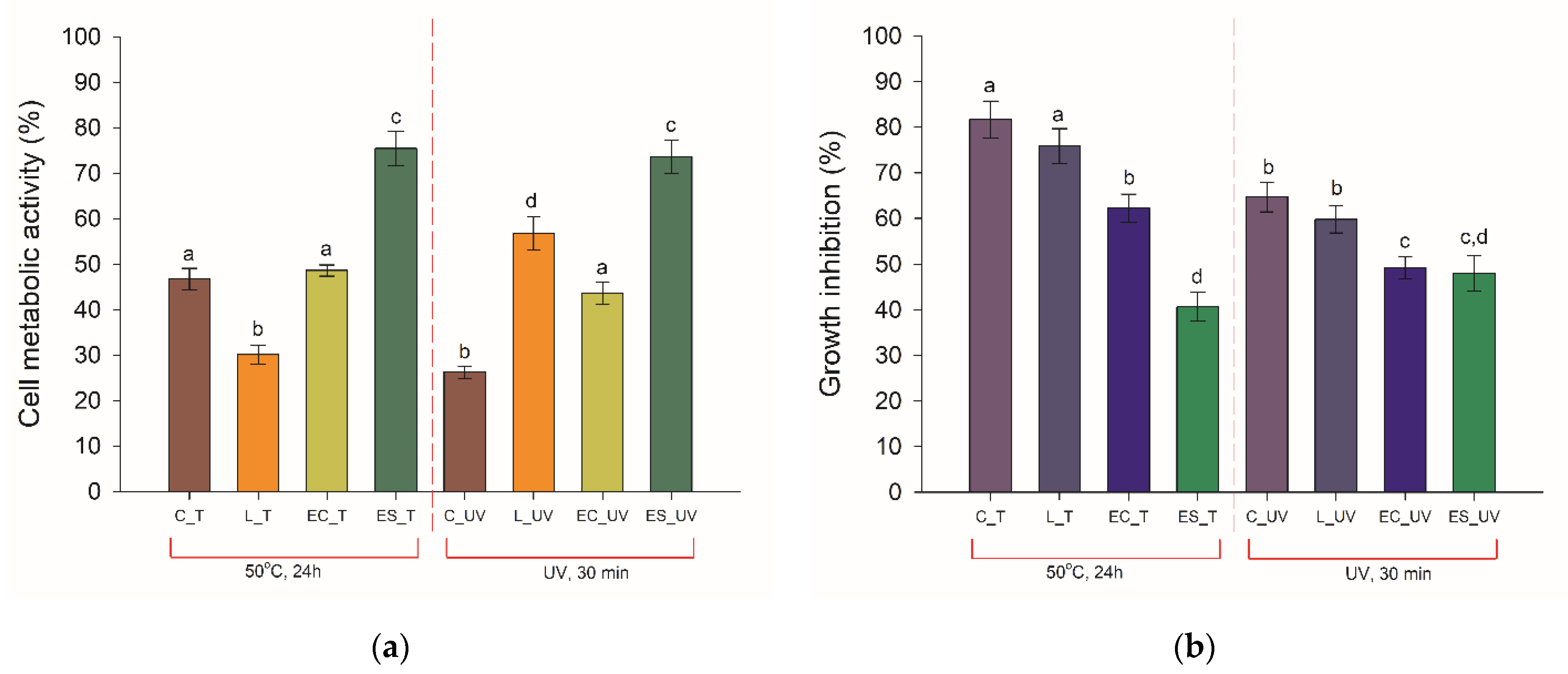
3.2. Bacterial Metabolic Activity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thomas, E. Microbial growth and physiology: A call for better craftsmanship. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Smułek, W.; Zdarta, A.; Grzywaczyk, A.; Guzik, U.; Siwińska-Ciesielczyk, K.; Ciesielczyk, F.; Strzemiecka, B.; Jesionowski, T.; Voelkel, A.; Kaczorek, E. Evaluation of the physico-chemical properties of hydrocarbons-exposed bacterial biomass. Colloid Surf. B 2020, 196, 111310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, F.U.; Andree, K.B.; Salas-Massó, N.; Fernandez-Tejedor, M.; Sanjuan, A.; Figueras, M.J.; Furones, M.D. Improved culture enrichment broth for isolation of Arcobacter-like species from the marine environment. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cultrera, R.; Torelli, R.; Sarnicola, C.; Segala, D.; Mengoli, A.; Chiaretto, G.; Perri, P.; Sanguinetti, M. Identification and molecular characterization of Subramaniula asteroides causing human fungal keratitis: A case report. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schön, T.; Werngren, J.; Machado, D.; Borroni, E.; Wijkander, M.; Lina, G.; Mouton, J.; Matuschek, E.; Kahlmeter, G.; Giske, C.; et al. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex isolates—The EUCAST broth microdilution reference method for MIC determination. Clin. Microbiol. Inf. 2020, 26, 1488–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Chen, Z.; Liu, W.; Gu, D.; Yu, Y.; Chen, X.; Wu, Y.; Xu, N.; Xie, J.; Zhao, G.; et al. A sensitive EZMTT method provides microscale, quantitative and high-throughput evaluation of drug efficacy in the treatment of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infectious diseases. J. Microbiol. Methods 2021, 181, 106136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikolajczyk, A.; Stefaniuk, E.; Bosacka, K.; Hryniewicz, W. Właściwości i zastosowanie podłoży bakteriologicznych. [Properties and uses of bacteriological media. Postępy Mikrobiol. 2016, 55, 320–329. [Google Scholar]
- Drauz, K.; Waldmann, H. Immobilization of Enzymes. In Enzyme Catalysis in Organic Synthesis, 1st ed.; Drauz, K., Gröger, H., May, O., Eds.; Wiley-VCH Verlag: Weinheim, Germany, 1995; pp. 73–87. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y. Immobilized Cell Fermentation for Production of Chemicals and Fuels. In Bioprocessing for Value-Added Products from Renewable Resources, 1st ed.; Yang, S.-T., Ed.; Elsevier Science: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 373–396. [Google Scholar]
- Willaert, R.G.; Baron, G.V. Gel entrapment and micro-encapsulation: Methods, applications and engineering principles. Rev. Chem. Eng. 1996, 12, 160–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, M.K.; Giri, S.K. Probiotic functional foods: Survival of probiotics during processing and storage. J. Funct. Food 2014, 9, 225–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, C.E.; Silva, M.F.; Guedes, A.C.; Carvalho, T.P.; Eckstein, C.; Ribeiro, N.Q.; Santos, D.A.; Melo, M.M.; Araújo, M.S.; Martins-Filho, O.A.; et al. Alginate-chitosan microcapsules improve vaccine potential of gamma-irradiated Listeria monocytogenes against listeriosis in murine model. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 176, 567–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penhasi, A.; Reuveni, A.; Baluashvili, I. Microencapsulation May Preserve the Viability of Probiotic Bacteria during a Baking Process and Digestion: A Case Study with Bifidobacterium animalis Subsp. lactis in Bread. Curr. Microbiol. 2021, 78, 576–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, M.; Tzortzis, G.; Charalampopoulos, D.; Khutoryanskiy, V. Microencapsulation of probiotics for gastrointestinal delivery. J. Control Release 2012, 162, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoname, R.M.; El-Sayed, H.S.; Ghozlan, H.A.; Sabry, S.A. Application of probiotic bacteria for the improvement of sea bream (Sparus aurata) larval production. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2020, 24, 371–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Stanishevsky, A.V.; Wetuski, J.D.; Yockell-Lelièvre, H. Crystallization and stability of electrospun ribbon- and cylinder-shaped tungsten oxide nanofibers. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Peng, S.; Lee JK, Y.; Ji, D.; Srinivasan, M.; Ramakrishna, S. Electrospun hollow nanofibers for advanced secondary batteries. Nano Energy 2017, 39, 111–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Ain, Q.T.; Huan, H.J. Branched nanofibers for biodegradable facemasks by double bubble electrospinning. Acta Chem. Malays. 2020, 4, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.X.; Zhang, R. Synthetic nanoscale fibrous matrix. J. Biomed. Mat. Res. A 1999, 46, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Samways, D.S.K.; Dong, H. Fabrication of self-assembling nanofibers with optimal cell uptake and therapeutic delivery efficacy. Bioact. Mater. 2017, 2, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zheng, M.; Lu, H.; Feng, S.; Ji, G.; Cao, J. Template synthesis of carbon nanofibers containing linear mesocage arrays. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2010, 5, 913–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Huang, Z.-M.; Zhang, Y.; Kotaki, M.; Ramakrishna, S. A review on polymer nanofibers by electrospinning and their applications in nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 2223–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, N.; Kundu, S.C. Electrospinning: A fascinating fiber fabrication technique. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 325–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, J.; Li, H.; Xu, Y.; Chen, S.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, C.; Li, H.; Wei, Z.; Sun, S.; Zhao, W.; et al. Multi-functional polyethersulfone nanofibrous membranes with ultra-high adsorption capacity and ultra-fast removal rates for dyes and bacteria. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 78, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayani, T.; Sanjeev, B.; Marimuthu, S.; Uthandi, S. Bacterial Cellulose Nano Fiber (BCNF) as carrier support for the immobilization of probiotic, Lactobacillus acidophilus 016. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 250, 116965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamvura, C.I.; Moolman, F.S.; Kalombo, L.; Hall, A.N.; Thantsha, M.S. Characterisation of the Poly-(Vinylpyrrolidone)-Poly-(Vinylacetate-Co-Crotonic Acid) (PVP:PVAc-CA) Interpolymer Complex Matrix Microparticles Encapsulating a Bifidobacterium lactis Bb12 Probiotic Strain. Probiot. Antimicrob. Proteins 2011, 3, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Liu, W.; Li, D.; Liu, C.; Feng, Z.; Jiang, B. Targeting Delivery System for Lactobacillus Plantarum Based on Functionalized Electrospun Nanofibers. Polymers 2020, 12, 1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, G.; Deng, X.; Deng, J.; Lu, X.; Kang, X.; Song, Y. Performance Evaluation of an Electrospun Nanofiber Mat as Samplers for the Trap of Trace Heavy Metals in Atmospheric Particles and Its Application. Anal. Sci. 2020, 36, 1453–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huan, S.; Liu, G.; Han, G.; Cheng, W.; Fu, Z.; Wu, Q.; Wang, Q. Effect of experimental parameters on morphological, mechanical and hydrophobic properties of electrospun polystyrene fibers. Materials 2015, 8, 2718–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorentz, H.; Rogers, R.; Jones, L. The impact of lipid on contact angle wettability. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2007, 84, 946–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardes, P.C.; Araújo, E.A.; Pires, A.C.; Júnior, J.F.Q.F.; Lelis, C.; De Andrade, N.J. Work of adhesion of dairy products on stainless steel surface. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2012, 43, 1261–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handojo, A.; Zhai, Y.; Frankel, G.; Pascall, M.A. Measurement of adhesion strengths between various milk products on glass surfaces using contact angle measurement and atomic force microscopy. J. Food Eng. 2009, 92, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, K.; Huang, R.-M.; Wu, R.-Q.; Wei, Y.-S.; Zong, M.-H.; Linhardt, R.J.; Wu, H. A novel route for double-layered encapsulation of probiotics with improved viability under adverse conditions. Food Chem. 2020, 310, 125977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, K.; Zhai, M.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Linhardt, R.J.; Zong, M.H.; Li, L.; Wu, H. Improved Viability and Thermal Stability of the Probiotics Encapsulated in a Novel Electrospun Fiber Mat. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 10890–10897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gensheimer, M.; Brandis-Heep, A.; Agarwal, S.; Thauer, R.K.; Greiner, A. Polymer/Bacteria Composite Nanofiber Nonwovens by Electrospinning of Living Bacteria Protected by Hydrogel Microparticles. Macromol. Biosci. 2019, 11, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stojanov, S.; Berlec, A. Electrospun Nanofibers as Carriers of Microorganisms, Stem Cells, Proteins, and Nucleic Acids in Therapeutic and Other Applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
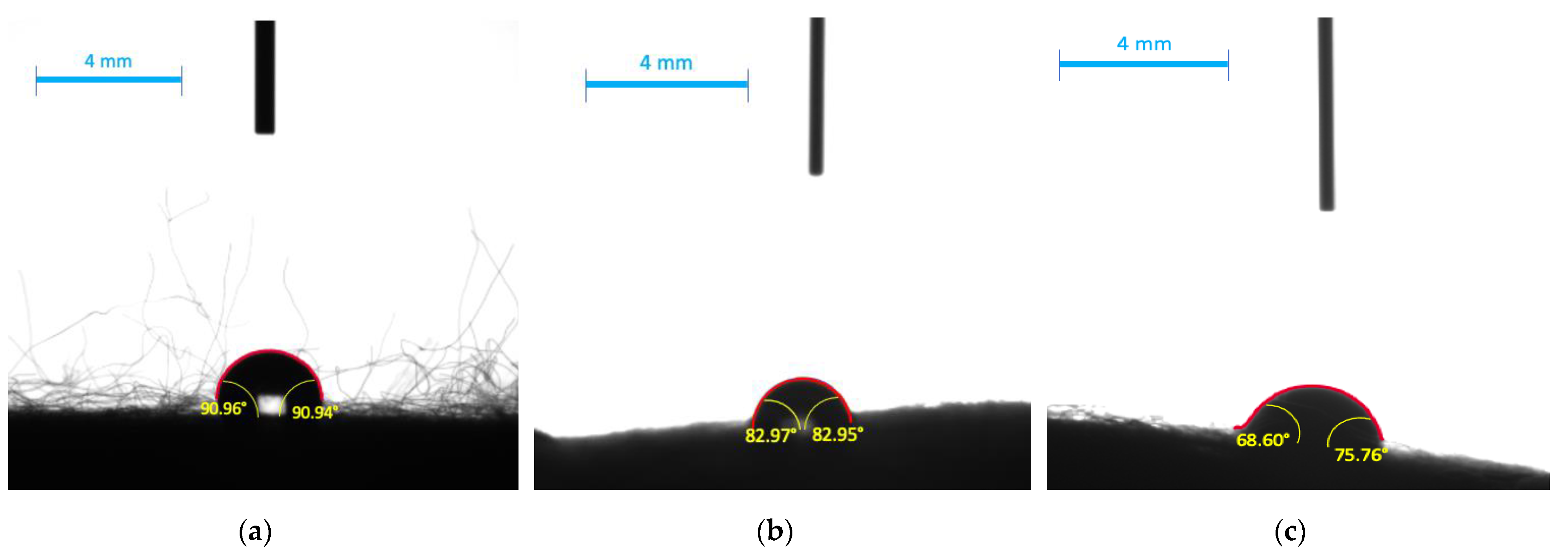
| Material | Medium | Left Angle [°] | Right Angle [°] | Average Angle [°] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PS | Water | 97.10 ± 3.6 | 97.10 ± 3.6 | 97.10 ± 3.6 |
| Broth | 97.23 ± 1.0 | 97.23 ± 1.0 | 97.23 ± 1.0 | |
| Milk (2% fat) | 77.24 ± 2.2 | 77.24 ± 2.2 | 77.24 ± 2.2 | |
| PS/Alg | Water | 91.0 ± 2.9 | 90.9 ± 3.3 | 91.0 ± 3.1 |
| Broth | 83.0 ± 3.3 | 83.0 ± 4.1 | 83.0 ± 3.7 | |
| Milk (2% fat) | 68.7 ± 0.3 | 75.8 ± 5.5 | 72.2 ± 2.9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grzywaczyk, A.; Zdarta, A.; Jankowska, K.; Biadasz, A.; Zdarta, J.; Jesionowski, T.; Kaczorek, E.; Smułek, W. New Biocomposite Electrospun Fiber/Alginate Hydrogel for Probiotic Bacteria Immobilization. Materials 2021, 14, 3861. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14143861
Grzywaczyk A, Zdarta A, Jankowska K, Biadasz A, Zdarta J, Jesionowski T, Kaczorek E, Smułek W. New Biocomposite Electrospun Fiber/Alginate Hydrogel for Probiotic Bacteria Immobilization. Materials. 2021; 14(14):3861. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14143861
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrzywaczyk, Adam, Agata Zdarta, Katarzyna Jankowska, Andrzej Biadasz, Jakub Zdarta, Teofil Jesionowski, Ewa Kaczorek, and Wojciech Smułek. 2021. "New Biocomposite Electrospun Fiber/Alginate Hydrogel for Probiotic Bacteria Immobilization" Materials 14, no. 14: 3861. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14143861
APA StyleGrzywaczyk, A., Zdarta, A., Jankowska, K., Biadasz, A., Zdarta, J., Jesionowski, T., Kaczorek, E., & Smułek, W. (2021). New Biocomposite Electrospun Fiber/Alginate Hydrogel for Probiotic Bacteria Immobilization. Materials, 14(14), 3861. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14143861











