Elastic Recovery Properties of Ultralight Carbon Nanotube/Carboxymethyl Cellulose Composites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Fabrication of Ultralight Materials
2.3. Analysis Method
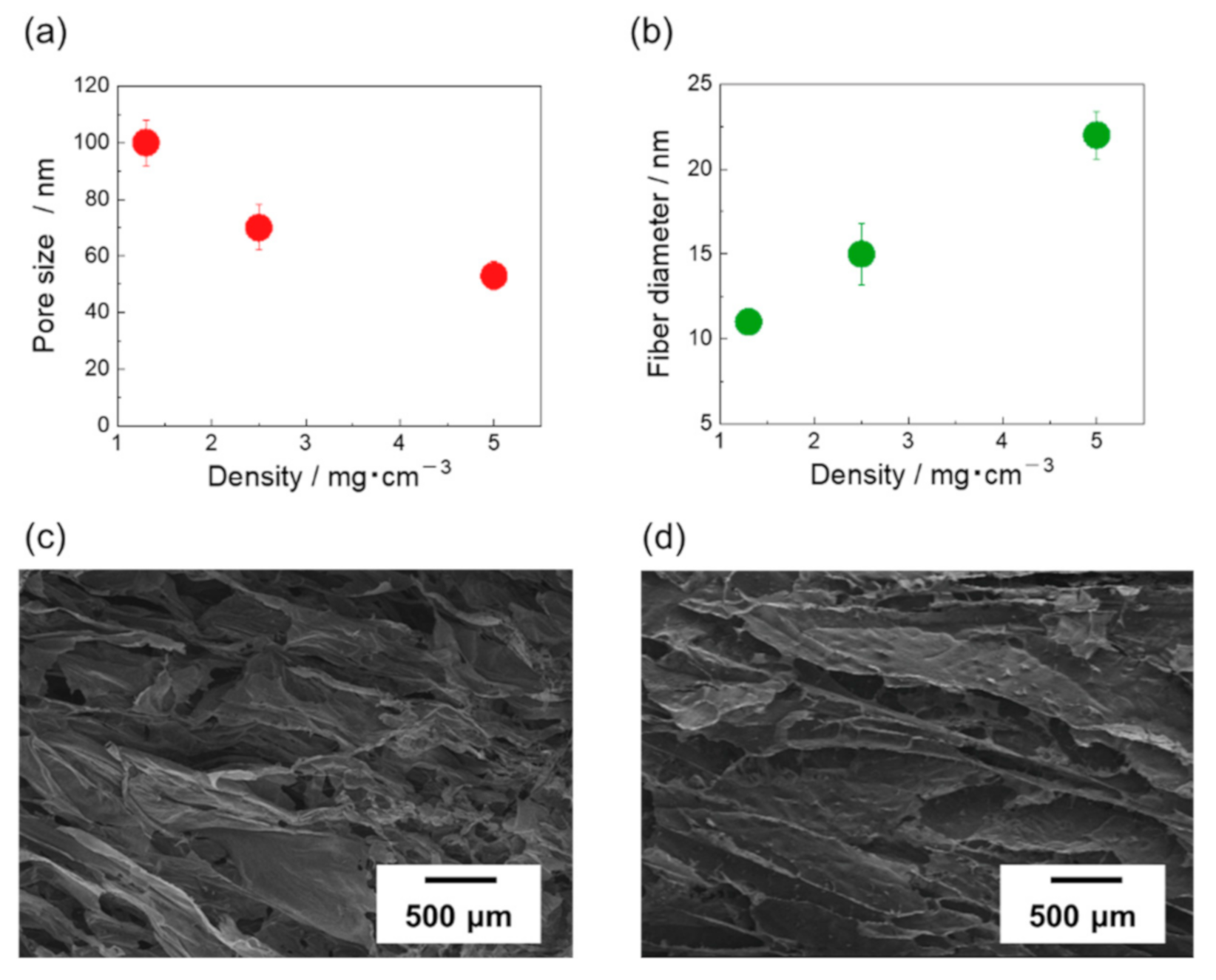
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Z.; Ren, Z.; Yan, S.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, J. Ultralight, Superelastic, and Fatigue-Resistant Graphene Aerogel Templated by Graphene Oxide Liquid Crystal Stabilized Air Bubbles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 1303–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, H.; Hu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Peng, X.; Liu, L.; Luo, Q.; Yi, J.; Liu, C.; Zhong, L. A carbon aerogel with super mechanical and sensing performances for wearable piezoresistive sensors. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 8092–8100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wu, Z.Y.; Liang, H.W.; Chen, J.F.; Yu, S.H. Ultralight Multifunctional Carbon-Based Aerogels by Combining Graphene Oxide and Bacterial Cellulose. Small 2017, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Wang, H.; Niu, M.; Fan, X.; Ma, M.; Shi, Z.; Guo, S.W. Ultralight, Recoverable, and High-Temperature-Resistant SiC Nanowire Aerogel. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 3103–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, C.; Wang, C.; Guo, R.; Lan, J.; Lin, S.; Jiang, S.; Lai, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, H. Synthesis of carboxymethyl cellulose-reduced graphene oxide aerogel for efficient removal of organic liquids and dyes. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 54, 1872–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, O.K.; Lee, J.H. Carbon nanotube-poly(vinyl alcohol) hybrid aerogels: Improvements in the surface area and structural stability by internal morphology control. Composites Part B 2018, 144, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Sung, J.; Kang, M.; Xie, X.; Lee, B.; Lee, K.; White, T.; Leal, C.; Sottos, N.; Braun, P.; et al. Correction for Shin et al., Light-triggered thermal conductivity switching in azobenzene polymers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 8629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schaedler, T.; Jacobsen, A.; Torrents, A.; Sorensen, A.; Lian, J.; Greer, J.; Valdevit, L.; Carter, W. Ultralight Metallic Microlattices. Science 2011, 334, 962–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, Y.; Han, T.; Han, J.H. Effects of shape and alignment of reinforcing graphite phases on the thermal conductivity and the coefficient of thermal expansion of graphite/copper composites. Carbon 2019, 149, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhuo, H.; Zhong, L.; Peng, X.; Sun, R.C. Advanced Compressible and Elastic 3D Monoliths beyond Hydrogels. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1904472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Wu, K.; Hu, Y.; Zhuo, H.; Chen, Z.; Jing, S.; Liu, Q.; Liu, C.; Zhong, L. A mechanically strong and sensitive CNT/rGO–CNF carbon aerogel for piezoresistive sensors. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 23550–23559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punetha, V.D.; Rana, S.; Yoo, H.J.; Chaurasia, A.; McLeskey, J.T.; Ramasamy, M.S.; Sahoo, N.G.; Cho, J.W. Functionalization of carbon nanomaterials for advanced polymer nanocomposites: A comparison study between CNT and graphene. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2017, 67, 1–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, W.; Huang, W.; Zhang, G.; Sun, R.; Wong, C.P. Fabrication of highly reinforced and compressible graphene/carbon nanotube hybrid foams via a facile self-assembly process for application as strain sensors and beyond. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 2723–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Shan, C.; Elias, A.L.; Rajukumar, L.P.; O’Brien, D.J.; Terrones, M.; Wei, B.; Suhr, J.; Lu, X.L. Hyperelasticity of three-dimensional carbon nanotube sponge controlled by the stiffness of covalent junctions. Carbon 2015, 95, 640–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, P.; Tan, X.W.; Yu, K.H.; Zheng, R.L.; Zheng, J.J.; Wei, W. Super-elastic graphene/carbon nanotube aerogel: A novel thermal interface material with highly thermal transport properties. Carbon 2016, 99, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Lin, D.; Deng, B.; Xu, X.; Nian, Q.; Jin, S.; Leedy, K.D.; Li, H.; Cheng, G.J. Flyweight, Superelastic, Electrically Conductive, and Flame-Retardant 3D Multi-Nanolayer Graphene/Ceramic Metamaterial. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1605506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Shan, Y.; Wu, L.; Mu, X.; Peng, H.; Jiang, Y. High-strength and morphology-controlled aerogel based on carboxymethyl cellulose and graphene oxide. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 197, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Hao, M.; Hu, Y.; Lin, Z.; Peng, L.; Wang, T.; Ren, X.; Wang, C.; Zhao, Z.; et al. Double-negative-index ceramic aerogels for thermal superinsulation. Science 2019, 363, 723–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shioura, N.; Matsushima, K.; Osato, T.; Ueno, T.; Isu, N.; Hashimoto, T.; Yana, T. Fabrication and Characterization of Porous Silica/Carbon Nanotube Composite Insulation. MRS Adv. 2020, 5, 1791–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapisarda, M.; Malfense, F.G.P.; Meo, M. Ultralight graphene oxide/polyvinyl alcohol aerogel for broadband and tuneable acoustic properties. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Xu, Z.; Gao, C. Multifunctional, ultra-flyweight, synergistically assembled carbon aerogels. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 2554–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagi, R.; Takemoto, R.; Ono, K.; Ueno, T. Light-induced levitation of ultralight carbon aerogels via temperature control. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadi, M.; Popov, G.A.; Lu, Z.; Eskenazi, A.G.; Bang, A.J.W.; Campbell, M.F.; Hu, H.; Bargatin, I. Controlled levitation of nanostructured thin films for sun-powered near-space flight. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabe1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Chang, H.; Wu, Y.; Xiao, P.; Yi, N.; Lu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, K.; Yan, X.Q.; et al. Macroscopic and direct light propulsion of bulk graphene material. Nat. Photon. 2015, 9, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiu, L.; Liu, J.Z.; Chang, S.L.; Wu, Y.; Li, D. Biomimetic superelastic graphene-based cellular monoliths. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bryning, M.B.; Milkie, D.E.; Islam, M.F.; Hough, L.A.; Kikkawa, J.M.; Yodh, A.G. Carbon Nanotube Aerogels. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 661–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohlmeyer, R.R.; Lor, M.; Deng, J.; Liu, H.; Chen, J. Preparation of stable carbon nanotube aerogels with high electrical conductivity and porosity. Carbon 2011, 49, 2352–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, J.; Dai, Z.; Liu, L.; Yang, Z.; Jin, M.; Zhang, Z. Synergistic effects from graphene and carbon nanotubes endow ordered hierarchical structure foams with a combination of compressibility, super-elasticity and stability and potential application as pressure sensors. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 9252–9260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chen, X.; Wang, B.; Huang, M.; Wang, B.; Jiang, Y.; Ruoff, R.S. Freeze-Casting Produces a Graphene Oxide Aerogel with a Radial and Centrosymmetric Structure. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 5816–5825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, X.; Ke, F.; Xiao, M.; Wu, K.; Kuang, Y.; Corke, H.; Jiang, F. The control of ice crystal growth and effect on porous structure of konjac glucomannan-based aerogels. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 92, 1130–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, M.C.; Carvajal, Z.Y.G.; Jobbágy, M.; Rubio, F.; Yuste, L.; Rojo, F.; Ferrer, M.L.; Monte, F. Poly(vinyl alcohol) Scaffolds with Tailored Morphologies for Drug Delivery and Controlled Release. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2007, 17, 3505–3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, L.; Yang, Q.; Xu, C.; Li, Y.; Yang, D.; Hou, F.; Yin, H.; Kang, F. Facile preparation of carbon nanotube aerogels with controlled hierarchical microstructures and versatile performance. Carbon 2015, 90, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, L.; Li, F.; Shu, M.; Zhang, C.; Weng, Y. Fabrication and Application of Carboxymethyl Cellulose-Carbon Nanotube Aerogels. Materials 2019, 12, 1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, H.; Zhao, Z.; Wan, W.; Gogotsi, Y.; Qiu, J. Ultralight and Highly Compressible Graphene Aerogels. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 2219–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matsushima, K.; Ono, K.; Yanagi, R.; Shioura, N.; Segi, T.; Ueno, T. Elastic Recovery Properties of Ultralight Carbon Nanotube/Carboxymethyl Cellulose Composites. Materials 2021, 14, 4059. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14144059
Matsushima K, Ono K, Yanagi R, Shioura N, Segi T, Ueno T. Elastic Recovery Properties of Ultralight Carbon Nanotube/Carboxymethyl Cellulose Composites. Materials. 2021; 14(14):4059. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14144059
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatsushima, Kazuki, Kenta Ono, Reo Yanagi, Naoto Shioura, Takahiro Segi, and Tomonaga Ueno. 2021. "Elastic Recovery Properties of Ultralight Carbon Nanotube/Carboxymethyl Cellulose Composites" Materials 14, no. 14: 4059. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14144059
APA StyleMatsushima, K., Ono, K., Yanagi, R., Shioura, N., Segi, T., & Ueno, T. (2021). Elastic Recovery Properties of Ultralight Carbon Nanotube/Carboxymethyl Cellulose Composites. Materials, 14(14), 4059. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14144059






