Construction of a Phytic Acid–Silica System in Wood for Highly Efficient Flame Retardancy and Smoke Suppression
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
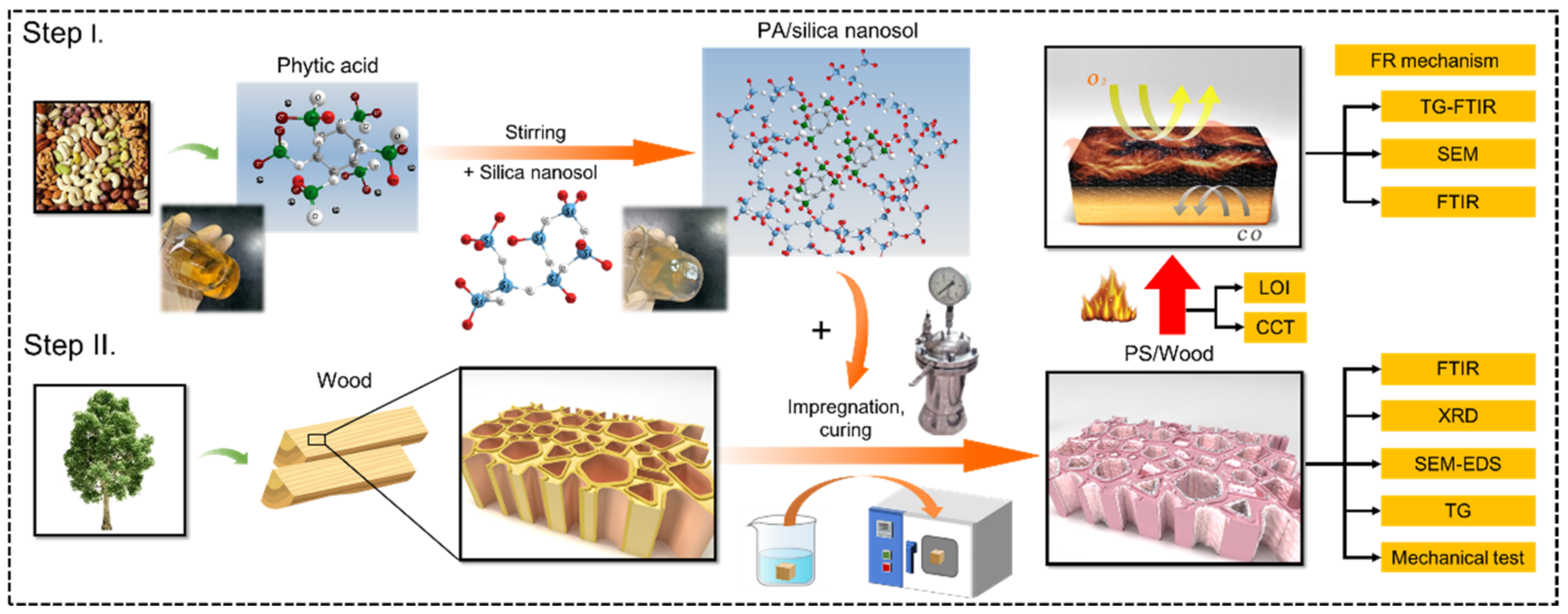
2.2. Preparation of PA/Silica Nanosol
2.3. Wood Impregnation and Curing
2.4. Physicochemical Properties of the Impregnated Solution
2.5. Physical Property Tests
2.6. Chemical Structure Analysis
2.7. Morphological Observation and Element Analysis
2.8. Thermal Degradation Analysis
2.9. Combustion Property Tests
2.10. TG-FTIR Analysis
2.11. Char Residue Analysis
2.12. Mechanical Property Tests
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemical Structure Analysis
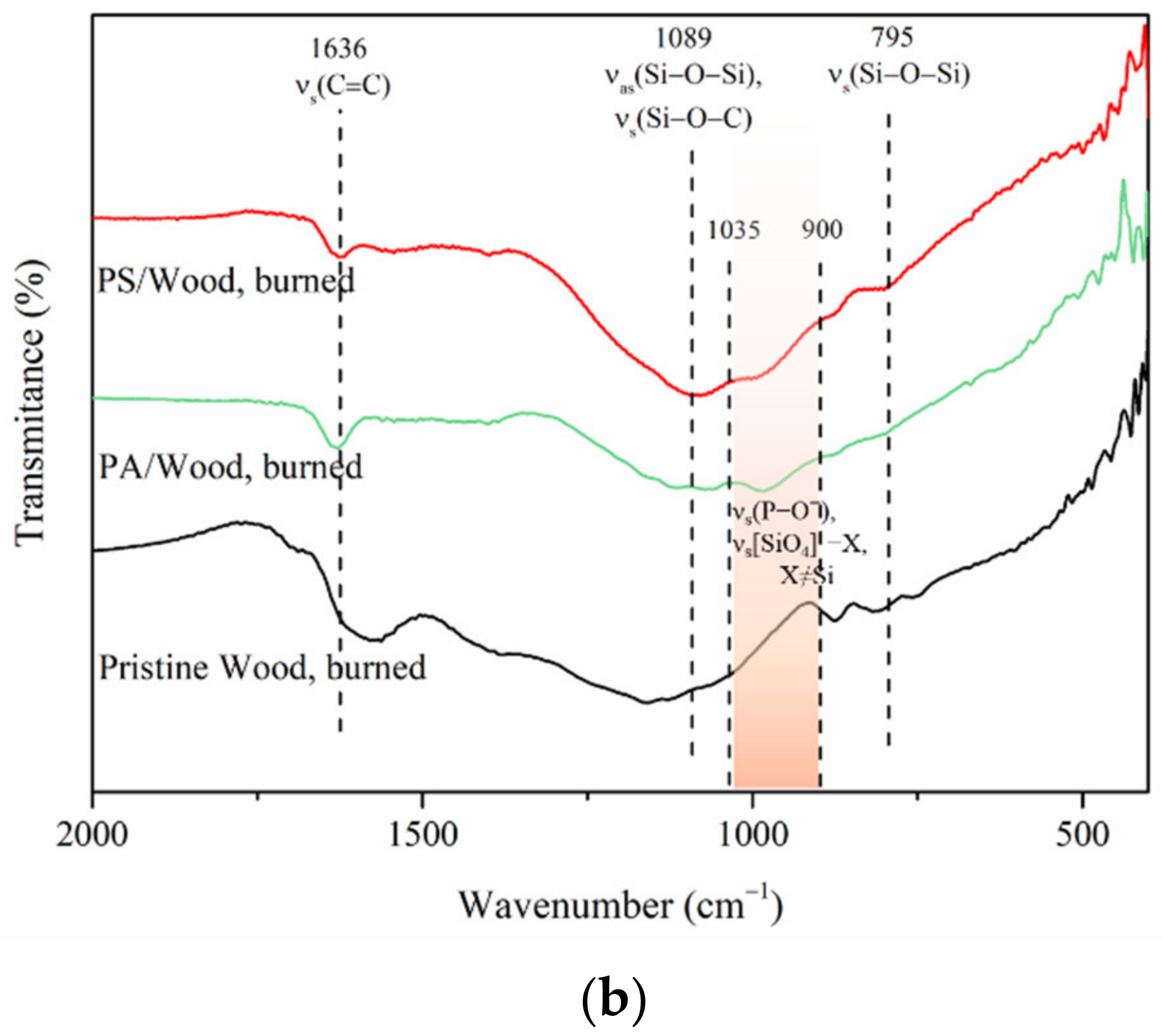
3.1.1. FTIR Analysis
3.1.2. XRD Analysis
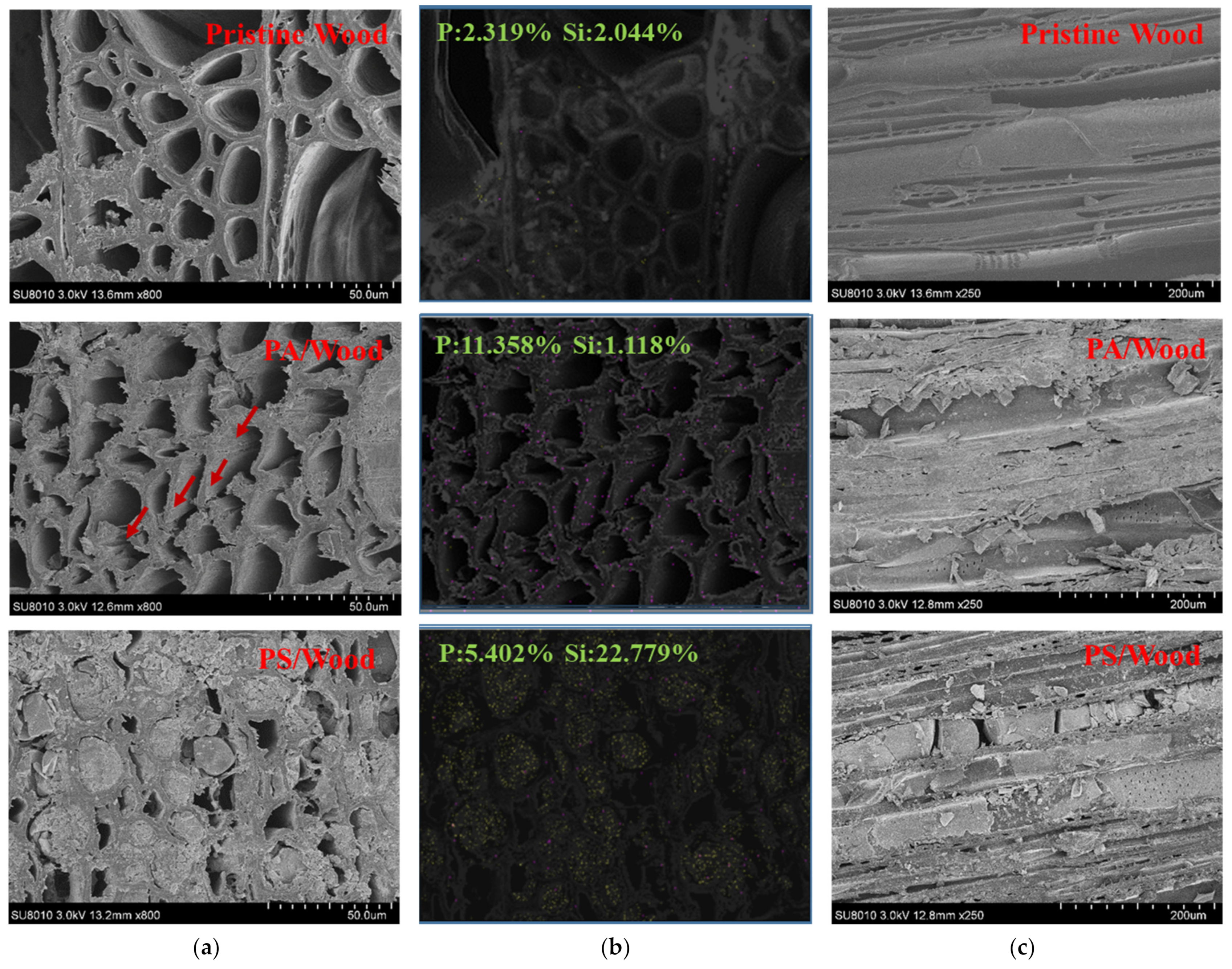
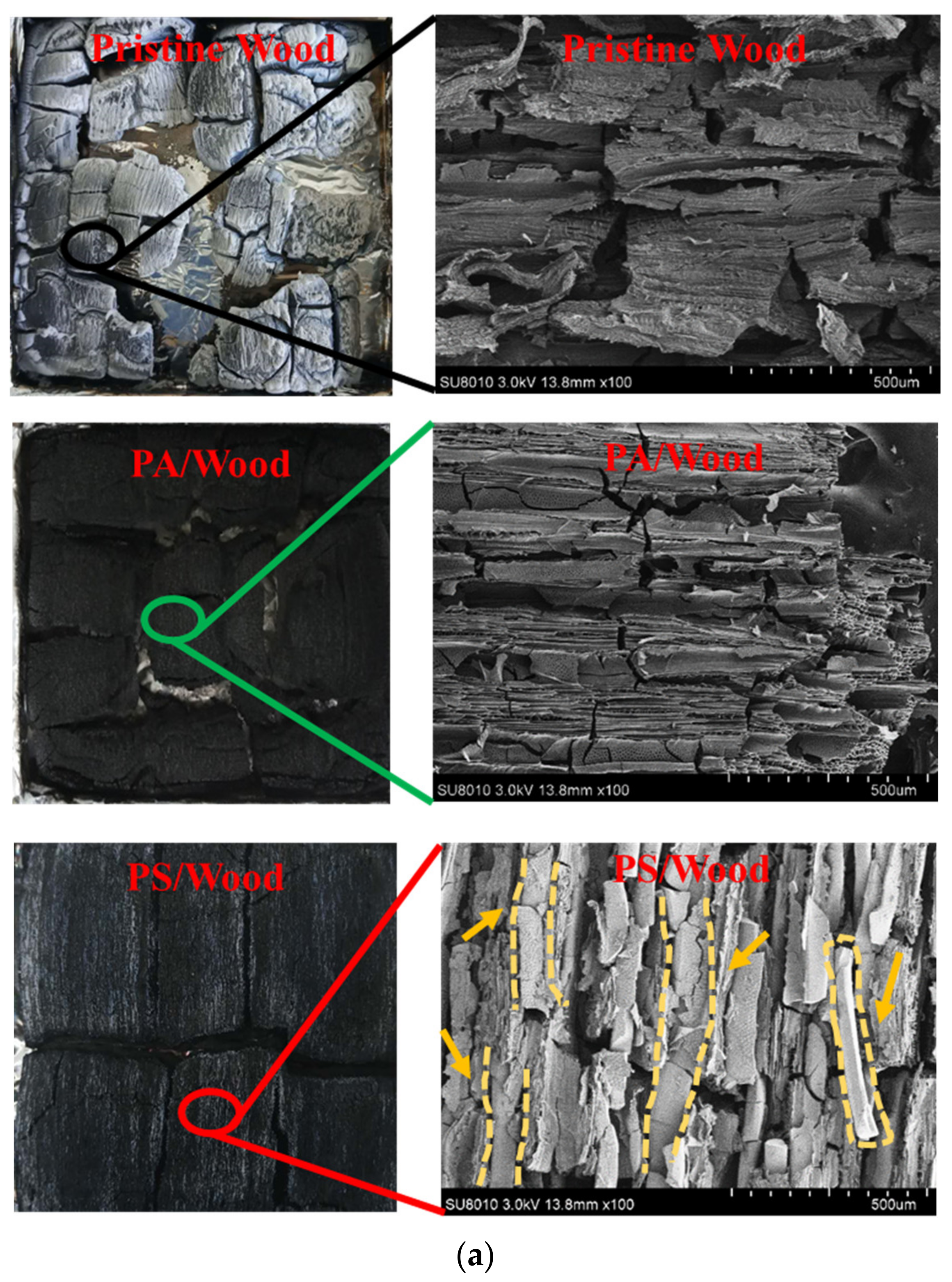
3.2. Morphology Observation and Element Analysis
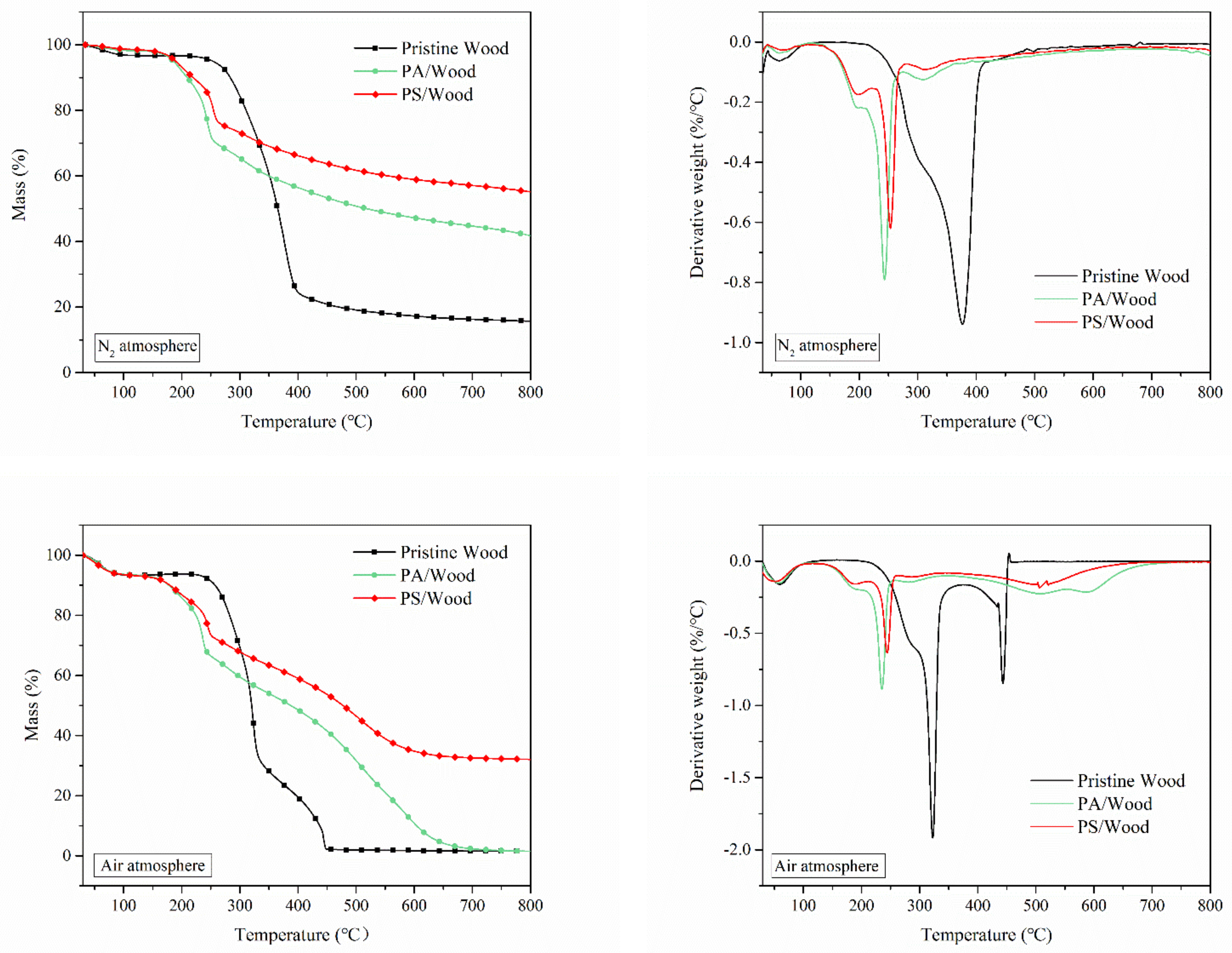
3.3. Thermal Degradation Analysis
3.4. Combustion Property
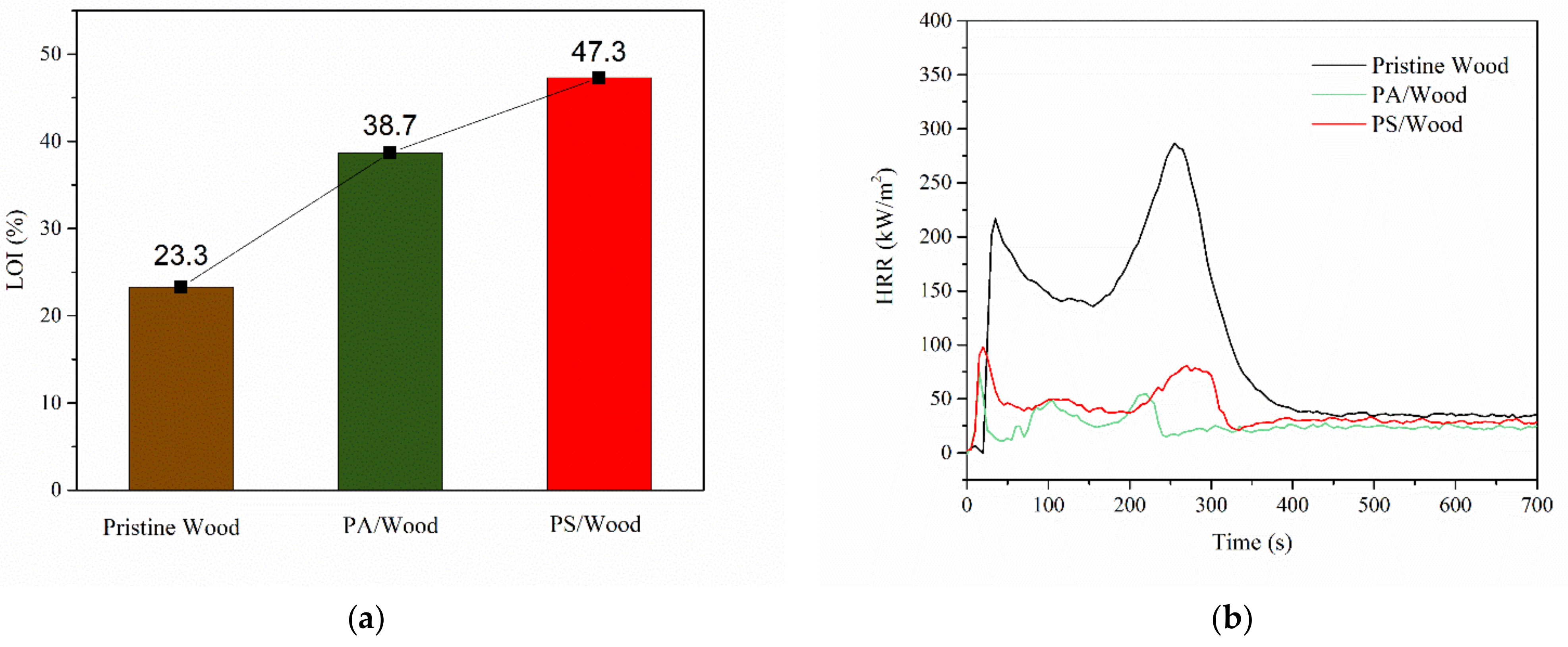
3.4.1. Flammability
3.4.2. Fire Toxicity
3.5. Flame Retardancy and Smoke-Suppression Mechanism
3.5.1. TG-FTIR Analysis
3.5.2. Char Analysis
3.5.3. Mechanism Analysis
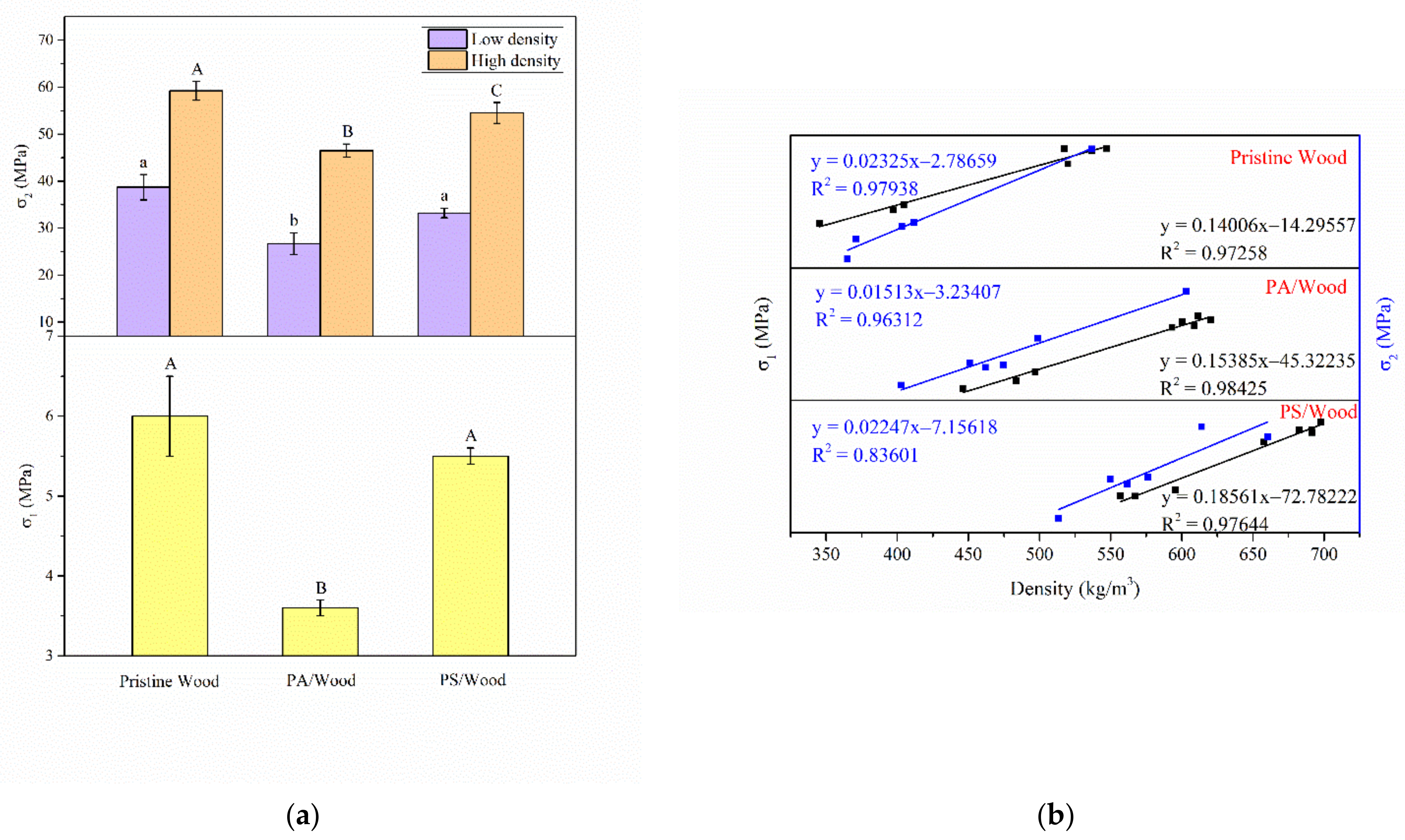
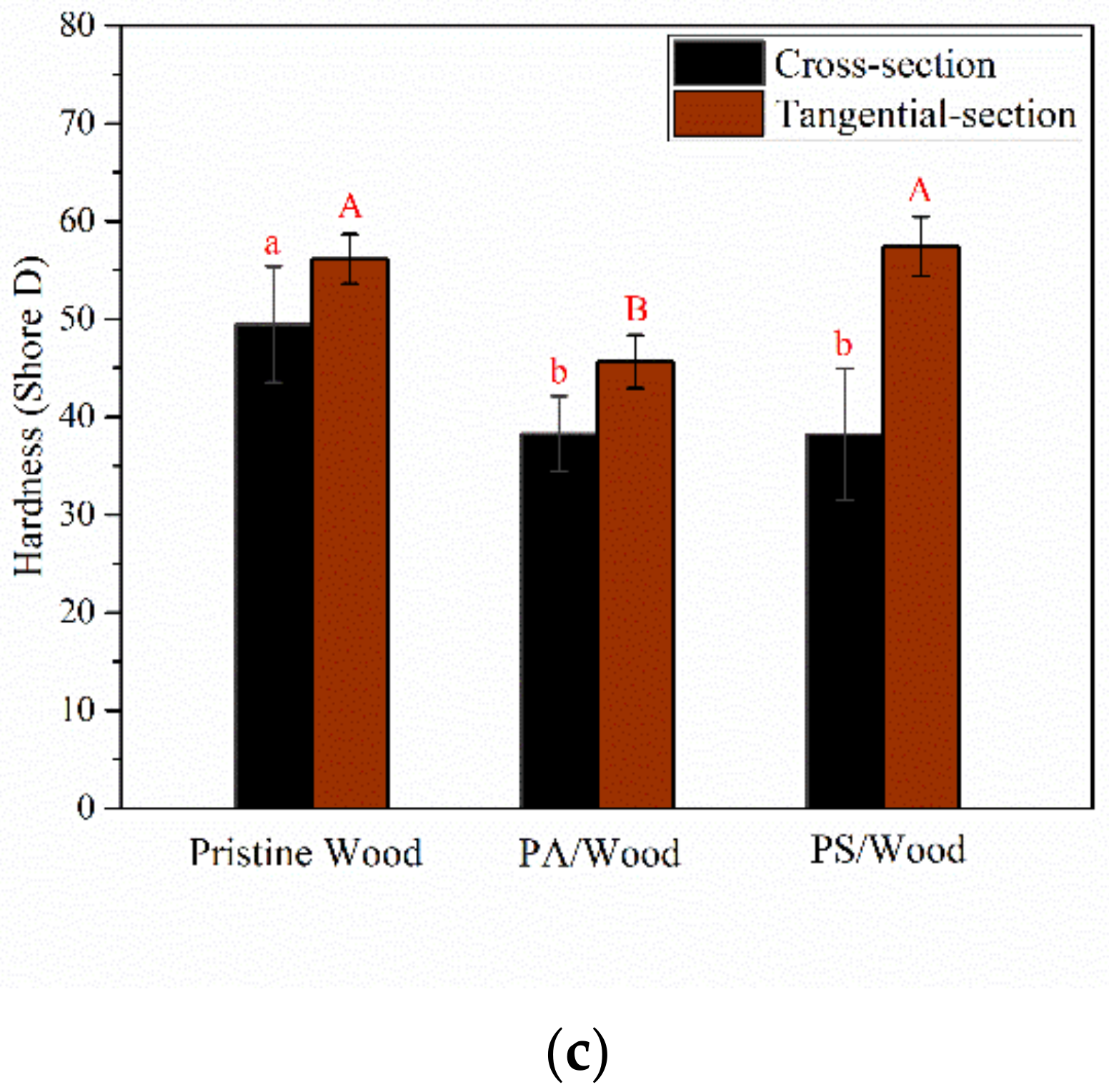
3.6. Mechanical Property
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Höglund, M.; Johansson, M.; Sychugov, I.; Berglund, L.A. Transparent wood biocomposites by fast UV-curing for reduced light-scattering through wood/thiol-ene interface design. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 46914–46922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, H.; Ma, C.; Luo, S.; Xu, M.; Wu, Z.; Li, W.; Liu, S. Luminescent transparent wood Based on lignin-derived carbon dots as a building material for dual-channel, real-time and visual detection of formaldehyde Gas. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 36628–36638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, A.; Zhu, T.; Chen, Z.; Wu, Y.; Gao, Y. Transparent wood composites fabricated by impregnation of epoxy resin and W-doped VO2 nanoparticles for application in energy-saving windows. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 34777–34783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Song, Y.; Gao, T.; Yan, S.; Hu, H.; Cao, F.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, X. Lightweight and hydrophobic three-dimensional wood-derived anisotropic magnetic porous carbon for highly efficient electromagnetic interference shielding. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 40802–40814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Sun, X.; Yang, M.; Xu, F.; Lin, Z.; Zhao, X.; Ding, Y.; Li, J.; Yin, W.; Peng, Q.; et al. Thermally stable and highly anisotropic wood-derived carbon composite monoliths for electromagnetic interference shielding. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 21371–21381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Li, R.; Chen, G.; Zhou, S.; Feng, X.; Chen, Y.; He, M.; Liu, D.; Song, T.; Qi, H. Highly stretchable, transparent and conductive wood fabricated by in situ photopolymerization with polymerizable deep eutectic solvents. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 14313–14321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Chen, C.; Wang, C.; Kuang, Y.; Li, Y.; Jiang, F.; Li, Y.; Hitz, E.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, B.; et al. Superflexible wood. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 23520–23527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Zheng, T.; Song, Z.; Shao, Y.; Li, N.; Jia, K.; Tian, Y.; Song, Q.; Liu, H.; Xue, G. Realization of low latent heat of a solar evaporator via regulating the water state in wood channels. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 18504–18511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, C.; Tan, Y.; Guo, J.; Sun, Z.; Deng, X. Harvesting electricity from water evaporation through microchannels of natural wood. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 11232–11239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Lukovic, M.; Mendoza, M.; Schleputz, C.M.; Griffa, M.; Xu, B.; Gaan, S.; Herrmann, H.; Burgert, I. Bioinspired struvite mineralization for fire-resistant wood. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 5427–5434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, F.R.; De Oliveira, A.Á.S.; Marino, R.V.; Rialto, T.C.R.; Oliveira, D.P.; Dorta, D.J. A comparison of developmental toxicity of brominated and halogen-free flame retardant on zebrafish. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Li, Z.; Ranasinghe, P.; Rockne, K.J.; Sturchio, N.C.; Giesy, J.P.; Li, A. Halogenated flame retardants in sediments from the Upper Laurentian Great Lakes: Implications to long-range transport and evidence of long-term transformation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 384, 121346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahladakis, J.N.; Velis, C.A.; Weber, R.; Iacovidou, E.; Purnell, P. An overview of chemical additives present in plastics: Migration, release, fate and environmental impact during their use, disposal and recycling. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 179–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, A.; Moinuddin, K.; Zhu, H.; Joseph, P. Passive fire protection of wood using some bio-derived fire retardants. Fire Saf. J. 2020, 120, 103074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yetilmezsoy, K.; Kocak, E.; Akbin, H.M.; Ozcimen, D. Utilization of struvite recovered from high-strength ammonium-containing simulated wastewater as slow-release fertilizer and fire-retardant barrier. Environ. Technol. 2020, 41, 153–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, W.; Li, F.; Liu, X.; Gao, Q.; Gong, S.; Li, J.; Shi, S.Q. Borate chemistry inspired by cell walls converts soy protein into high-strength, antibacterial, flame-retardant adhesive. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 1319–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oatway, L.; Vasanthan, T.; Helm, J.H. Phytic acid. Food Rev. Int. 2007, 17, 419–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yi, D.; Hao, J.; Gao, M. One-step treated wood by using natural source phytic acid and uracil for enhanced mechanical properties and flame retardancy. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2020, 32, 1176–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chen, Z.; Lu, J.; Wei, M.; Huang, Y.; Jiang, P. Combustion behavior and thermal degradation properties of wood impregnated with intumescent biomass flame retardants: Phytic acid, hydrolyzed collagen and glycerol. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 3921–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, D. Functions of phytic acid in fabricating metal-free carbocatalyst for oxidative coupling of benzylamines†. Chin. J. Chem. 2020, 38, 1292–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Chen, Z.; Ding, M.; Yang, T.; Wang, M. Reducing the fire toxicity of wood composites using hierarchically porous 4A (H4A) zeolite modified ammonium polyphosphate (APP) synthesized by a facile in-situ method. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 262, 120754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Xu, Z.; Wang, X. Synergistic flame-retardant and smoke suppression effects of zinc borate in transparent intumescent fire-retardant coatings applied on wood substrates. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2019, 136, 1563–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiayu, G.; Guochao, Y.; Lijuan, Z.; Qiuhui, Z. The synergistic smoke suppression effect of ferric oxide on flame retardant wood polyurethane composites. Wood Res. 2018, 63, 305–320. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, L.; Xu, Z.; Deng, N. Synthesis of organophosphate-functionalized graphene oxide for enhancing the flame retardancy and smoke suppression properties of transparent fire-retardant coatings. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2020, 172, 109064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Wu, Y.; Tian, C.; Qing, Y.; Yao, C. Synergistic Effect of nanosilica aerogel with phosphorus flame retardants on improving flame retardancy and leaching resistance of wood. J. Nanomater. 2014, 2014, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, J.; Cao, J.; Wang, W. Characteristics of wood-silica composites influenced by the pH value of silica sols. Holzforschung 2018, 72, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, E.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, L. Improvement of mechanical, hydrophobicity and thermal properties of Chinese fir wood by impregnation of nano silica sol. Polymers 2020, 12, 1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Xu, J.; Mai, C.; Militz, H.; Wang, Q.; Xie, Y. Combustion behavior of Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) sapwood treated with a dispersion of aluminum oxychloride-modified silica. Holzforschung 2016, 70, 1165–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hisashi, M.; Shiro, S.; Akira, Y. SiO2-P2O5-B2O3 wood-inorganic composites prepared by metal alkoxide oligomers and their Fire-resisting properties. Holzforschung 1998, 52, 410–416. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Chai, Y.; Ni, L.; Lyu, W. Flame retardant properties and thermal decomposition kinetics of wood treated with boric acid Modified silica sol. Materials 2020, 13, 4478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, D.; Guerry, P.; Knowles, J.C.; Smith, M.E.; Newport, R.J. Formation of functional phosphosilicate gels from phytic acid and tetraethyl orthosilicate. J. Sol. Gel Sci. Technol. 2008, 48, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samba-Fouala, C.; Mossoyan, J.C.; Mossoyan-Déneux, M.; Benlian, D.; Chanéac, C.; Babonneau, F. Preparation and properties of silica hybrid gels containing phytic acid. J. Mater. Chem. 2000, 10, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.-W.; Guan, J.-P.; Yang, X.-H.; Tang, R.-C.; Fan, Y. Phytic acid/silica organic-inorganic hybrid sol system: A novel and durable flame retardant approach for wool fabric. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 700–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.-W.; Tang, R.-C.; Guan, J.-P.; Zhou, S.-Q. An eco-friendly and effective flame retardant coating for cotton fabric based on phytic acid doped silica sol approach. Prog. Org. Coat. 2020, 141, 105539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbalini, M.; Bertolla, L.; Tousek, J.; Malucelli, G. Hybrid silica-phytic acid coatings: Effect on the thermal stability and flame retardancy of cotton. Polymers 2019, 11, 1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nie, S.; Jin, D.; Yang, J.-N.; Dai, G.; Luo, Y. Fabrication of environmentally-benign flame retardant cotton fabrics with hydrophobicity by a facile chemical modification. Cellulose 2019, 26, 5147–5158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.-W.; Liang, C.-X.; Guan, J.-P.; Yang, X.-H.; Tang, R.-C. Flame retardant and hydrophobic properties of novel sol-gel derived phytic acid/silica hybrid organic-inorganic coatings for silk fabric. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 427, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schartel, B.; Hull, T.R. Development of fire-retarded materials—Interpretation of cone calorimeter data. Fire Mater. 2007, 31, 327–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thygesen, A.; Oddershede, J.; Lilholt, H.; Thomsen, A.B.; Stahl, K. On the determination of crystallinity and cellulose content in plant fibres. Cellulose 2005, 12, 563–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Qiao, J.; Hong, F. Application of phosphoric acid and phytic acid-doped bacterial cellulose as novel proton-conducting membranes to PEMFC. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2012, 37, 9182–9192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F.; Yang, X.; Zhang, D. Chemical nature of phytic acid conversion coating on AZ61 magnesium alloy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 8363–8371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, T.A.; Baig, N.; Alghunaimi, F.I.; Aljuryyed, N.W. A flexible biomimetic superhydrophobic and superoleophilic 3D macroporous polymer-based robust network for the efficient separation of oil-contaminated water. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 5088–5097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sujan, M.I.; Sarkar, S.D.; Sultana, S.; Bushra, L.; Tareq, R.; Roy, C.K.; Azam, M.S. Bi-Functional silica nanoparticles for simultaneous enhancement of mechanical strength and swelling capacity of hydrogels. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 6213–6222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siuda, J.; Perdoch, W.; Mazela, B.; Zborowska, M. Catalyzed reaction of cellulose and lignin with Methyltrimethoxysilane—FT-IR, 13C NMR and 29Si NMR studies. Materials 2019, 12, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Poletto, M.; Zattera, A.J.; Santana, R.M.C. Structural differences between wood species: Evidence from chemical composition, FTIR spectroscopy, and thermogravimetric analysis. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 126, E337–E344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Rivera, J.; Terrazas, T. Lignin analysis by HPLC and FTIR. Xylem 2017, 1544, 193–211. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Yang, T.; Xu, X.; Guo, X.; Cao, J. Processing solid wood into a composite phase change material for thermal energy storage by introducing silica-stabilized polyethylene glycol. Compos. Part. A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2020, 139, 106098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bücker, M.; Jäger, C.; Pfeifer, D.; Unger, B. Evidence of Si-O-C bonds in cellulosic materials modified by sol-gel-derived silica. Wood Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 1033–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okon, K.E.; Lin, F.; Chen, Y.; Huang, B. Effect of silicone oil heat treatment on the chemical composition, cellulose crystalline structure and contact angle of Chinese parasol wood. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 164, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirna, F.C.; Rahayu, I.; Zaini, L.H.; Darmawan, W.; Prihatini, E. Improvement of fast-growing wood species characteristics by MEG and Nano SiO2 impregnation. J. Korean Wood Sci. Technol. 2020, 48, 41–49. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, G.; Du, J.; Chen, W.; Pan, M.; Chen, D. Preparation and thermostability of cellulose nanocrystals and nanofibrils from two sources of biomass: Rice straw and poplar wood. Cellulose 2019, 26, 8625–8643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, L.; Shi, S.Q. Effect of thermal treatment with water, H2SO4 and NaOH aqueous solution on color, cell wall and chemical structure of poplar wood. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Effland, M.J. Modified procedure to determine acid-insoluble lignin in wood and pulp. Tappi 1977, 60, 143–144. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zuo, Y.; Wu, Y.; Yuan, G.; Li, X. Construction of a network structure in Chinese fir wood by Na2SiF6 crosslinked Na2SiO3. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 14190–14199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Li, A.; Xie, L.; Wang, C.-C.; Wang, P.; Wang, X. Mechanism and effect of alkoxysilanes on the restoration of decayed wood used in historic buildings. J. Cult. Herit. 2020, 43, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Kuang, Y.; Zhu, S.; Burgert, I.; Keplinger, T.; Gong, A.; Li, T.; Berglund, L.; Eichhorn, S.J.; Hu, L. Structure-Property-Function relationships of natural and engineered wood. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2020, 5, 642–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roger, M.; Rowell, M.A.D. Thermal properties, combustion and fire retardancy of wood. In Handbook of Wood Chemistry and Wood Composites, 2nd ed.; Taylor & Francis Group: Oxfordshire, UK, 2013; pp. 127–149. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Wang, M.; Li, X.; Cai, L.; Shi, S.Q.; Duan, C.; Ni, Y. Microwave-Assisted catalytic Cleavage of C-C bond in lignin models by bifunctional Pt/CDC-SiC. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabir Mahr, M.; Hübert, T.; Schartel, B.; Bahr, H.; Sabel, M.; Militz, H. Fire retardancy effects in single and double layered sol-gel derived TiO2 and SiO2-wood composites. J. Sol. Gel Sci. Technol. 2012, 64, 452–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anna, A.; Stec, T.; Richard, H. Fire toxicity and its assessment. In Fire Retardancy of Polymeric Materials; Taylor & Francis Group: Oxfordshire, UK, 2009; pp. 453–477. [Google Scholar]
- Martinka, J.; Kačíková, D.; Hroncová, E.; Ladomerský, J. Experimental determination of the effect of temperature and oxygen concentration on the production of birch wood main fire emissions. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2012, 110, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kai Yang, X.L. Preparation of mineral bound particleboards with improved fire retardant and smoke suppression properties based on a mix of inorganic adhesive. Holzforschung 2019, 73, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Materazzi, S. Thermogravimetry—Infrared spectroscopy (TG-FTIR) coupled analysis. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 1997, 32, 385–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, D.K.; Gu, S.; Bridgwater, A.V. Study on the pyrolytic behaviour of xylan-based hemicellulose using TG-FTIR and Py-GC-FTIR. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2010, 87, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meng, A.; Zhou, H.; Qin, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Q. Quantitative and kinetic TG-FTIR investigation on three kinds of biomass pyrolysis. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2013, 104, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Ma, X.; Li, L.; Liu, C.; Cheng, K.; Li, Z. Pyrolysis of poplar wood sawdust by TG-FTIR and Py-GC/MS. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2013, 102, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costes, L.; Laoutid, F.; Brohez, S.; Delvosalle, C.; Dubois, P. Phytic acid-lignin combination: A simple and efficient route for enhancing thermal and flame retardant properties of polylactide. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 94, 270–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Cai, J.; Geng, Y.; Xu, B.; Zhang, Q. Cu-Modified ZSM zeolite has SYNERGISTIC flame retardance, smoke suppression, and catalytic conversion effects on pulp fiber after ammonium polyphosphate flame-retardant treatment. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 14365–14376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.X.; Zhang, J.; Lu, B.-X.; Xin, Z.X.; Kang, C.K.; Kim, J.K. Effect of flame retardants on mechanical properties, flammability and foamability of PP/wood–fiber composites. Compos. Part. B Eng. 2012, 43, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, K.K. A study of chemistry structure of soft and hardwood and wood polymers by FTIR Spectroscopy. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1999, 71, 1969–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, N.Q.; Fongarland, P.; Rataboul, F.; Dartiguelongue, C.; Charon, N.; Vallée, C.; Essayem, N. FTIR as a simple tool to quantify unconverted lignin from chars in biomass liquefaction process: Application to SC ethanol liquefaction of pine wood. Fuel Process. Technol. 2015, 134, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Sypaseuth, F.D.; Schubert, M.; Schoch, R.; Bastian, M.; Schartel, B. Routes to halogen-free flame-retardant polypropylene wood plastic composites. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2019, 30, 187–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, S.; Wu, W.; Zhang, M.; Qu, H.; Xu, J. Synergistic effect of silica sol and K2CO3 on flame-retardant and thermal properties of wood. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2016, 128, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Qiu, D. Phytic acid derived bioactive CaO-P2O5-SiO2 gel-glasses. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2011, 22, 2685–2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying-Ming, L.; Shuang-Lin, H.; De-Yi, W. Polymer-based ceramifiable composites for flame retardant applications: A review. Compos. Commun. 2020, 21, 100405. [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong, J.P.; Skaar, C.; deZeeuw, C. The effect of specific gravity on several mechanical properties of some world woods. Wood Sci. Technol. 1984, 18, 137–146. [Google Scholar]







| Sample | Impregnation | Curing | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Impregnates | Vaccum Phase | Pressurized Phase | Gelation | Drying | |||||
| Pressure (MPa) | Time (min) | Pressure (MPa) | Time (h) | Temperature (°C) | Time (d) | Temperature (°C) | Time (d) | ||
| Pristine Wood | Deionized water | −0.09 | 30 | 0.50 | 2 | 25 | 2 | 80 | 3 |
| PA/Wood | PA solution | −0.09 | 30 | 0.50 | 2 | 25 | 2 | 80 | 3 |
| PS/Wood | PA/silica sol | −0.09 | 30 | 0.50 | 2 | 25 | 2 | 80 | 3 |
| Sample | Relative Crystallinity (%) |
|---|---|
| Pristine Wood | 46.41 |
| PA/Wood | 45.05 |
| PS/Wood | 50.83 |
| Atmosphere: N2 | ||||||
| Sample | T10% (°C) | Tmax1 (°C) | |Rmax1| (%/°C) | Residue@800 °C(%) | ||
| Pristine Wood | 283 | 376 | 0.94 | 15.7 | ||
| PA/Wood | 209 | 244 | 0.79 | 41.7 | ||
| PS/Wood | 219 | 254 | 0.62 | 55.1 | ||
| Atmosphere: air | ||||||
| Sample | T10% (°C) | Tmax1 (°C) | |Rmax1| (%/°C) | Tmax2 (℃) | |Rmax2| (%/°C) | Residue@800 °C(%) |
| Pristine Wood | 257 | 323 | 1.91 | 443 | 0.85 | 1.5 |
| PA/Wood | 178 | 235 | 0.89 | 507 | 0.23 | 1.5 |
| PS/Wood | 180 | 244 | 0.63 | 522 | 0.18 | 32.1 |
| Sample | PHRR1 (kW/m2) | Time to PHRR1 (s) | PHRR2 (kW/m2) | Time to PHRR2 (s) | THR (MJ/m2) | MEHC (MJ/kg) | Mass Loss (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pristine Wood | 201.8 ± 10.6 | 38 ± 8 | 258.0 ± 67.9 | 280 ± 25 | 68.2 ± 3.3 | 14.2 ± 0.4 | 86.15 ± 0.55 |
| PA/Wood | 73.0 ± 4.5 | 15 ± 0 | 47.0 ± 5.7 | 222 ± 6 | 24.6 ± 1.1 | 5.6 ± 0.3 | 65.58 ± 1.07 |
| PS/Wood | 89.6 ± 6.4 | 20 ± 0 | 78.6 ± 13.9 | 282 ± 24 | 34.2 ± 5.8 | 8.0 ± 1.2 | 53.91 ± 0.72 |
| Sample | FR Loading (kg/m3) | Time to PCOPR (s) | COY/CO2Y | MSEA (m2/kg) | Time to PSPR1 (s) | Time to PSPR2 (s) | TSP (m2/m2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pristine Wood | - | 283 ± 19 | 0.02 ± 0.00 | 36.2 ± 12.7 | 32 ± 6 | 277 ± 21 | 1.6 ± 0.6 |
| PA/Wood | 76.8 ± 0.7 | 263 ± 8 | 0.23 ± 0.02 | 77.5 ± 7.7 | 28 ± 2 | 250 ± 8 | 3.0 ± 0.3 |
| PS/Wood | 181.4 ± 5.0 | 342 ± 24 | 0.10 ± 0.02 | 7.5 ± 0.5 | 40 ± 0 | 320 ± 16 | 0.3 ± 0.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Z.; Zhang, S.; Ding, M.; Wang, M.; Xu, X. Construction of a Phytic Acid–Silica System in Wood for Highly Efficient Flame Retardancy and Smoke Suppression. Materials 2021, 14, 4164. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14154164
Chen Z, Zhang S, Ding M, Wang M, Xu X. Construction of a Phytic Acid–Silica System in Wood for Highly Efficient Flame Retardancy and Smoke Suppression. Materials. 2021; 14(15):4164. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14154164
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Zhuoran, Shaodi Zhang, Mengyi Ding, Mingzhi Wang, and Xing Xu. 2021. "Construction of a Phytic Acid–Silica System in Wood for Highly Efficient Flame Retardancy and Smoke Suppression" Materials 14, no. 15: 4164. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14154164
APA StyleChen, Z., Zhang, S., Ding, M., Wang, M., & Xu, X. (2021). Construction of a Phytic Acid–Silica System in Wood for Highly Efficient Flame Retardancy and Smoke Suppression. Materials, 14(15), 4164. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14154164






