Abstract
Most high-entropy alloys and medium-entropy alloys (MEAs) possess outstanding mechanical properties. In this study, a series of lightweight nonequiatomic Al50–Ti–Cr–Mn–V MEAs with a dual phase were produced through arc melting and drop casting. These cast alloys were composed of body-centered cubic and face-centered cubic phases. The density of all investigated MEAs was less than 5 g/cm3 in order to meet energy and transportation industry requirements. The effect of each element on the microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of these MEAs was investigated. All the MEAs demonstrated outstanding compressive strength, with no fractures observed after a compressive strain of 20%. Following the fine-tuning of the alloy composition, the Al50Ti20Cr10Mn15V5 MEA exhibited the most compressive strength (~1800 MPa) and ductility (~34%). A significant improvement in the mechanical compressive properties was achieved (strength of ~2000 MPa, strain of ~40%) after annealing (at 1000 °C for 0.5 h) and oil-quenching. With its extremely high specific compressive strength (452 MPa·g/cm3) and ductility, the lightweight Al50Ti20Cr10Mn15V5 MEA demonstrates good potential for energy or transportation applications in the future.
1. Introduction
Since the Iron Age, metallic materials have played a major role in the development of human civilization [1]. In 1996, high-entropy alloys (HEAs) were proposed [2], characterized by the multiple main elements in their design. HEAs are composed of multiprinciple elements which possess unique properties such as high entropy, lattice distortion, sluggish diffusion, and cocktail effects [3,4]. Due to these characteristics, HEAs have better mechanical properties than traditional alloys. However, despite the advantageous properties of HEAs, their density typically exceeds 10 g/cm3 [5,6], which severely limits their application in the transportation and energy industries.
In recent years, a nonequiatiomic alloy design has been proposed [7] that not only retains the characteristics of the existing HEAs but also increases the flexibility of the HEA design [8]. In this regard, design is no longer limited to high entropy but has developed toward medium entropy. With one main element accounting for approximately 50–70% of an alloy and the addition of other elements, the resultant structure can maintain a solid solution structure [9,10]. These developments have further expanded the range of alloy designs [11,12].
Some lightweight equiatiomic high-entropy alloys (LWHEAs) composed of light metals such as Al and Ti have been studied [13]. However, the intermetallic compounds composed of Al and Ti always adversely affect the mechanical properties of the LWHEAs [14,15,16]. Therefore, a simple-phase microstructure is essential to obtain the desired mechanical properties required for promising future applications.
In this study, nonequiatomic lightweight Al50–Ti–Cr–Mn–V MEAs were designed to achieve low density with well-balanced strength–ductility synergy. A high content of Al was selected to form lightweight MEAs (density defined as <5 g/cm3), and the influence of the contents of Ti, Cr, Mn, and V on the MEAs microstructure and mechanical properties was evaluated. Subsequently, the characteristics of the elements obtained through the experiments were further adjusted to an optimal ratio of Ti, Cr, Mn, and V in the MEAs to achieve advantageous mechanical properties.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Al (purity 99.99%), Ti (purity 99.99%), Cr (purity 99.99%), Mn (purity 99.9%), and V (purity 99.9%) were the raw materials used to form the lightweight nonequiatiomic Al50–Ti–Cr–Mn–V MEAs. The ingots were prepared through arc melting under an Argon gas atmosphere. All ingots were remelted four times to ensure homogeneity. The samples were fabricated through drop casting with dimensions of 35 mm × 30 mm × 5 mm.
2.2. Microstructure Characterization
The density of the MEAs was measured using Archimedes’ principle. X-ray diffraction (XRD; D2 Bruker, Billerica, MA, USA) was used to identify the crystal structure of the MEAs with Cu Kα radiation. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM; F50 Inspect, FEI, Hillsboro, OR, USA) with energy dispersive spectroscopy was employed to characterize the microstructure of the MEAs.
2.3. Mechanical Testing
A Vickers hardness testing machine (HV-100 Mitutoyo, Kawasaki, Japan) was used to measure the hardness of the MEA samples with a loading of 5 kg for 10 s and five readings were measured at random areas in the specimen. A universal testing machine (HT9102 Hung Ta, Taichung, Taiwan) was used to conduct compression testing under quasistatic loading with a strain rate 1 × 10−4/s at room temperature. The dimension of the compression testing samples was fabricated as a cylinders of Ø 3 mm × 6 mm and three readings were measured.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Density of the Al50–Ti–Cr–Mn–V MEAs
By maintaining the atomic ratio of Al at 50%, Al50–Ti–Cr–Mn–V MEAs can achieve low density (<5 g/cm3), with a density distribution from 4 to 5 g/cm3. By using Archimedes’ principle, all measured results were close to the theoretical results by mixing rules; the theoretical and measured densities are presented in Figure 1.
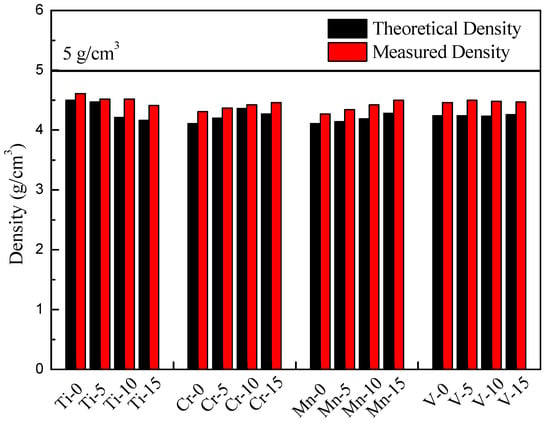
Figure 1.
Density of the Al50–Ti–Cr–Mn–V alloys.
3.2. Optimization of the Mechanical Properties of the Al50–Ti–Cr–Mn–V MEAs
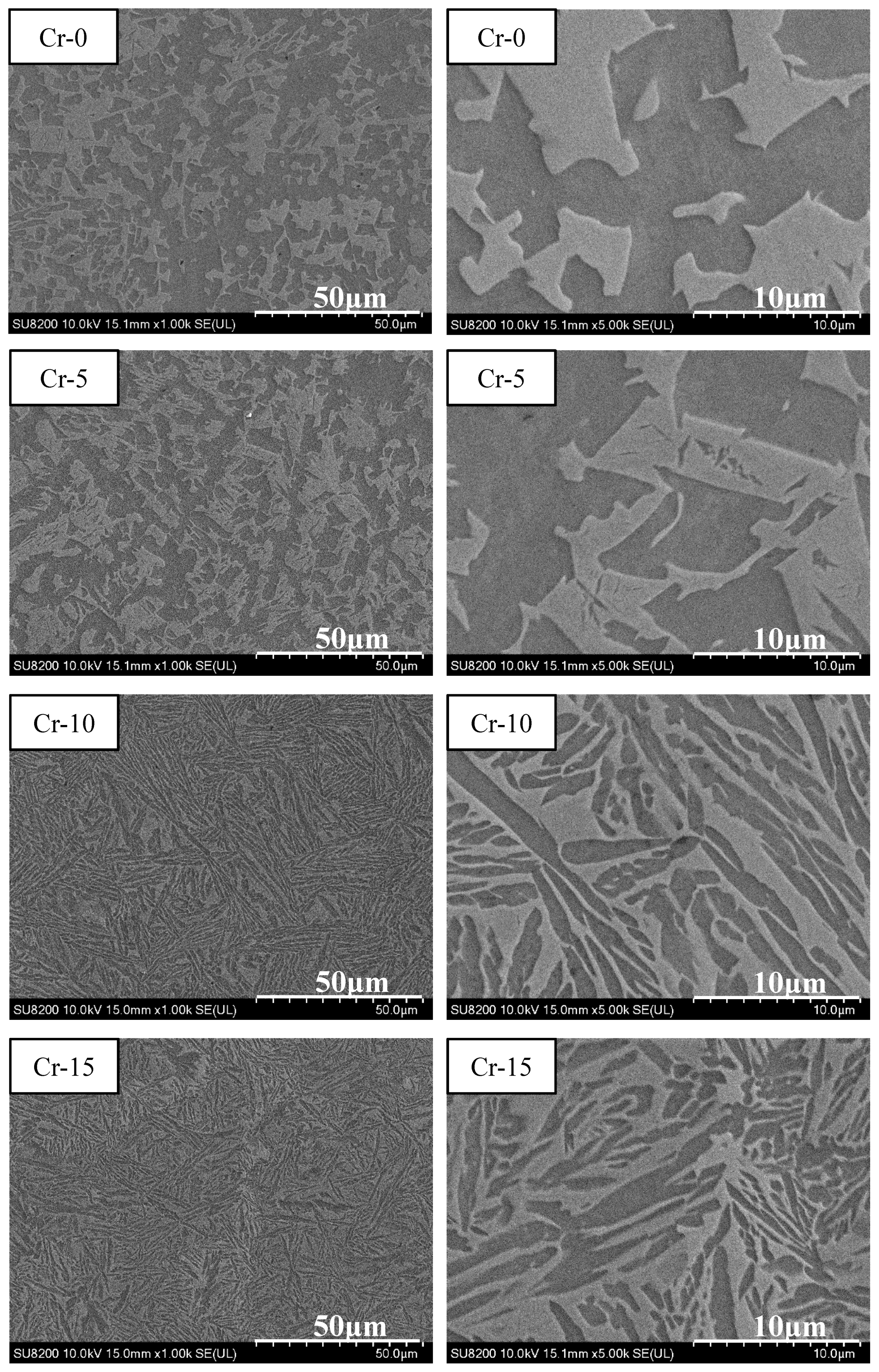
Based on the mechanical compression results and phase morphology analysis from the XRD patterns and SEM images, the effects of adding the elements Ti, Cr, Mn, and V to the Al50(CrMnV)50-xTix, Al50(TiMnV)50-xCrx, Al50(TiCrV)50-xMnx, and Al50(TiCrMn)50-xVx (x = 0, 5, 10, 15) quinary MEAs were investigated. An increase in the Ti ratio induced phase transformation from the body-centered cubic (BCC)-1 and BCC-2 phase to the BCC and face-centered cubic (FCC) phase, as depicted in Figure 2 and Figure 3. The formation of the FCC phase is ascribed to the larger atomic radii of Ti than Cr, Mn and V. As the Ti content increased, Al and Ti with large atomic radii were mainly distributed to the FCC phase, and BCC-2 phase will be gradually to disappear, as presented in Figure 4. The beginning of the FCC phase led to a decrease in the hardness and strength of these MEAs, as presented in Table 1. In Figure 5 and Table 1, the high elastic modulus of Cr (~280 GPa) resulted in high hardness, high compressive yield strength, and poor ductility. Mn addition strongly affected the morphological evolution in the BCC phase. The change of Mn content will affect the morphology of the BCC phase in MEA, resulting in a change in strength, as detailed in Figure 6 and Table 1. Finally, the addition of V increased the fraction of the BCC phase of the MEAs; their compressive yield strength is presented in Figure 7 and Table 1.
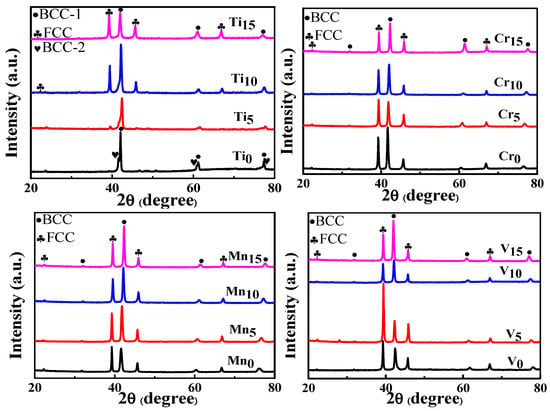
Figure 2.
XRD patterns of the Al50–Ti–Cr–Mn–V alloys.
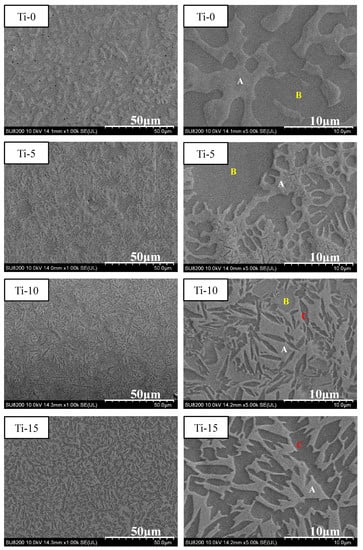
Figure 3.
SEM images of the Al50(CrMnV)50-xTix (x = 0, 5, 10, 15) alloys (A: BCC-1; B: BCC-2; C: FCC).
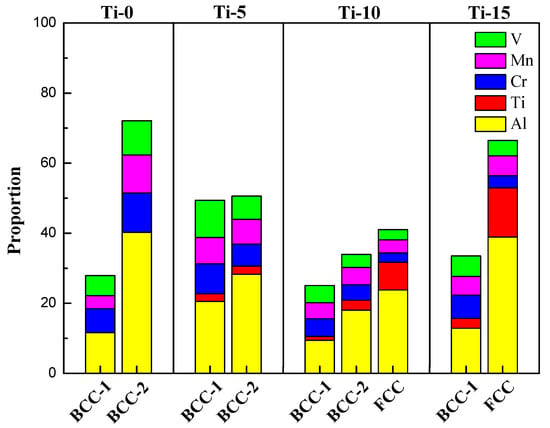
Figure 4.
The proportion of Al, Ti, Cr, Mn and V in the dual-phase of Al50–Ti–Cr–Mn–V alloys.

Table 1.
Mechanical compressive properties of the Al50–Ti–Cr–Mn–V alloys.
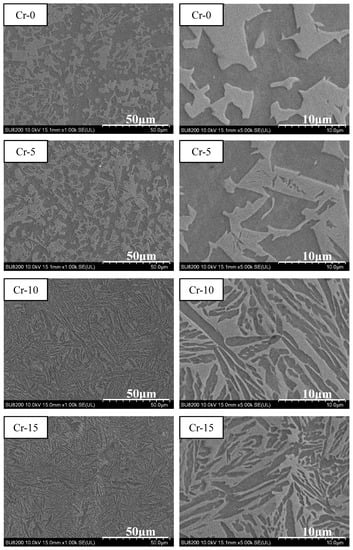
Figure 5.
SEM images of the Al50(TiMnV)50-xCrx (x = 0, 5, 10, 15) alloys.
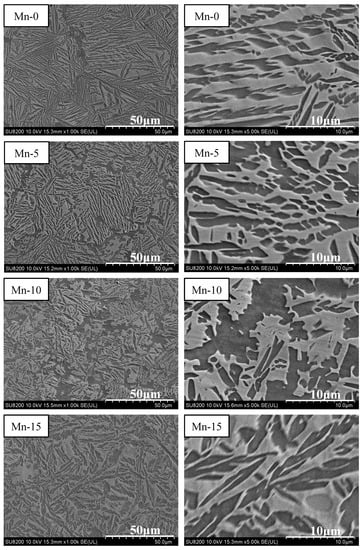
Figure 6.
SEM images of the Al50(TiCrV)50-xMnx (x = 0, 5, 10, 15) alloys.
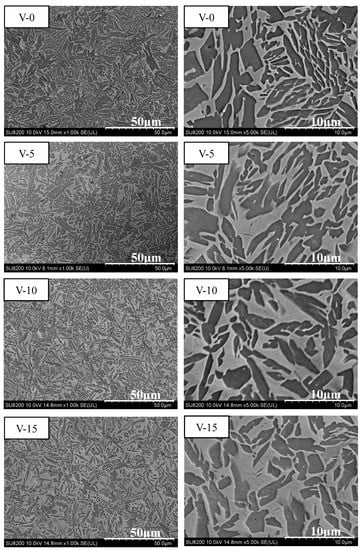
Figure 7.
SEM images of the Al50(TiCrMn)50-xVx (x = 0, 5, 10, 15) alloys.
From the previous experimental results, several factors affecting the mechanical properties of the alloy can be observed. In hardness results, the theoretical Young’s modulus has a great influence on the hardness of Al50–Ti–Cr–Mn–V alloys. With the addition of high Young’s modulus element like Cr, the theoretical Young’s modulus increases and the hardness of the MEAs will increase. On the other hand, the Ti content increase will effectively reduce the hardness of the alloys, as presented in Figure 8. In tensile testing results, not only theoretical Young’s modulus but also the theoretical atom size difference and the fraction of BCC phase will affect the yielding strength and ductility of the alloys, as presented in Table 2. It can be found that despite the increase of Mn content, there is little effect on the theoretical Young’s modulus and the strength of the alloy still changes significantly. It is believed that the reason for this is related to the variation of the phase morphology. It has been suggested that the theoretical atom size difference of the alloy will led to the variation of the phase morphology. Therefore, the manipulation of the phase morphology can affect the mechanical properties. This phenomenon can also be observed when the increase of Cr content in MEAs. Due to the difference in the atomic radius of MEAs increases obviously with the addition of Cr, the morphology of the phase is refined. Combined with the characteristics of high Young’s modulus, the strength of the MEAs are enhanced significantly. In addition, it can be noticed that the fraction of BCC phase plays an important role in mechanical properties of MEAs. It is well-known that the BCC phase is harder and more brittle than the FCC phase. With the fraction of BCC phase increase, the strength will be enhanced. This phenomenon can also explain why Al50(CrMnV)50 and Al50(CrMnV)45Ti5 alloys are too brittle to be cast successfully. Despite the theoretical Young’s modulus decrease as the V content increases, the hardness of the MEAs will increase with the V adding due to the fraction of BCC phase increase. Therefore, it is proved that the increase of the ratio of the BCC phase is more dominant than Young’s modulus in improving the mechanical properties of the MEAs.
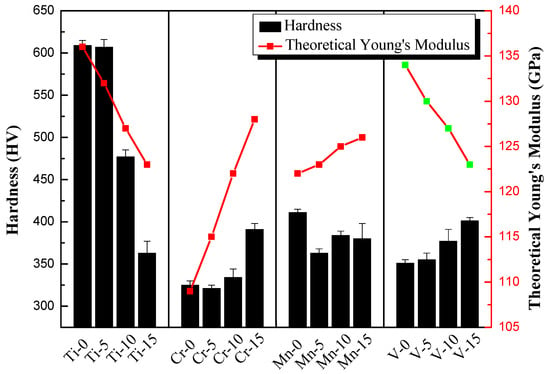
Figure 8.
The relationship between hardness and theoretical Young’s modulus of Al50–Ti–Cr–Mn–V alloys.

Table 2.
Theoretical Young’s modulus, atom size difference and the phase fraction of the Al50–Ti–Cr–Mn–V alloys.
In summary, High Ti content in Al50–Ti–Cr–Mn–V MEAs can lead to a dual phase (BCC + FCC), and the addition of V and Cr can induce high strength. Additionally, the morphology of the BCC phase can be manipulated by adding a moderate Mn ratio. Notably, the effect of the addition of V on the mechanical compressive properties of Al50(TiCrMn)50-xVx MEAs was significant; the compressive strength of MEAs increased from 1415 MPa to 1833 MPa by adding element V to Al50(TiCrMn)50 to produce Al50(TiCrMn)45V5. Therefore, fine-tuning V concentrations in Al50–Ti–Cr–Mn–V MEAs represents the key method for obtaining favorable mechanical compressive properties. Two approaches for fine-tuning V in MEAs are discussed in detail.
3.3. Al50(Ti2Cr1Mn2)50-xVx Series
Al50(Ti2Cr1Mn2)50-xVx (x = 2.5, 5, 7.5, 10) MEAs were explored. Since Al50Ti20Cr10Mn20 exhibited remarkable mechanical properties (1763 MPa, 32%) in prior studies on Al50–Ti–Cr–Mn quaternary MEAs [17], the addition of minor V with a fixing ratio of Ti2Cr1Mn2 was further investigated. The phase morphology analysis and compression results are detailed in Figure 9 and Table 3. The addition of V increased the compressive strength, and the plastic strain decreased. The content of Ti simultaneously decreased. These results are consistent with those of other studies. The addition of Mn did not markedly affect the compressive strength of the alloy. However, Cr was expected to reduce the strength when its content decreased, but the content of Cr was likely too low to exhibit an obvious effect. Al50Ti18Cr9Mn18V5 presented the most superior compressive mechanical properties in the Al50(Ti2Cr1Mn2)50-xVx series. The yield strength reached 773 MPa, the maximum compressive strength was 1610 MPa, and the compression ratio was 26%. In comparison with Al50(TiCrMn)45V5, despite the similar compression ratio of Al50Ti19Cr9.5Mn19V2.5 and Al50(TiCrMn)45V5, the compressive strength was reduced by more than 10%.
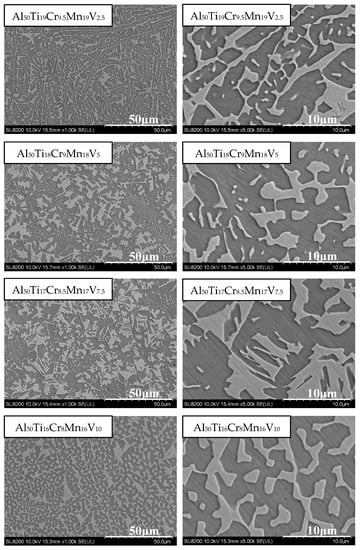
Figure 9.
SEM images of the Al50(Ti2Cr1Mn2)50-xVx (x = 2.5, 5, 7.5, 10) alloys.

Table 3.
Mechanical compressive properties of the Al50(Ti2Cr1Mn2)50-xVx (x = 2.5, 5, 7.5, 10) and Al50Ti20Cr10Mn20-xVx (x = 2.5, 5, 7.5, 10) alloys.
3.4. Al50Ti20Cr10Mn20-xVx Series
To further promote the mechanical properties of the Al50–Ti–Cr–Mn–V alloy, an alloy system of Al50Ti20Cr10Mn20-xVx (x = 2.5, 5, 7.5, 10) was designed. A high content of Ti improved the toughness, and maintaining a certain content of Cr strengthened the alloy.
In compression testing, compared with Al50(Ti2Cr1Mn2)50-xVx, the compressive strength was enhanced significantly and ductility also improved, as depicted in Figure 10. Al50Ti20Cr10Mn15V5 exhibited the excellent performance (yield strength was 713 MPa, maximum compressive strength was 1802 MPa, and ductility was 34%). In this case, BCC/FCC ratios in these Al50Ti20Cr10Mn20-xVx MEAs are similar. Therefore, significant changes in the morphology of the BCC phases dominate the strength of these investigated MEAs instead of the fraction of BCC phases. Compared with Al50(TiCrMn)45V5 (yield strength was 930 MPa, maximum compressive strength was 1833 MPa, and ductility was 26%) in other studies, and despite the slight reduction in compressive strength, the ductility of the alloy increased significantly and the toughness was enhanced (as presented in Table 3). Although Al50Ti20Cr10Mn12.5V7.5 possessed higher compressive strength than Al50Ti20Cr10Mn15V5 (as detailed in Table 3), the deviation in the compressive test results of Al50Ti20Cr10Mn12.5V7.5 was larger than in those of Al50Ti20Cr10Mn15V5. Therefore, Al50Ti20Cr10Mn15V5 is the most promising combination for Al50–Ti–Cr–Mn–V MEAs.
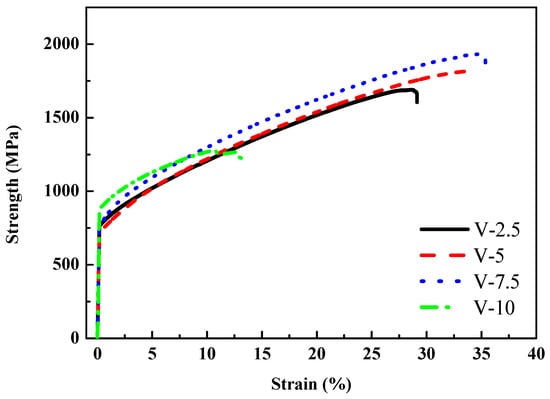
Figure 10.
Mechanical compressive stress–strain curves of the Al50Ti20Cr10Mn20-xVx (x = 2.5, 5, 7.5, 10) alloys.
The SEM analysis is illustrated in Figure 11. In Al50Ti20Cr10Mn17.5V2.5, the morphology presented as a finer dual-phase structure, differing from the morphology of Al50Ti20Cr10Mn15V5 and Al50Ti20Cr10Mn12.5V7.5, which presented in the shape of a bamboo leaf. When the V content was increased to 15%, the phase became thicker and the morphology of Al50Ti20Cr10Mn10V10 changed into an island shape.
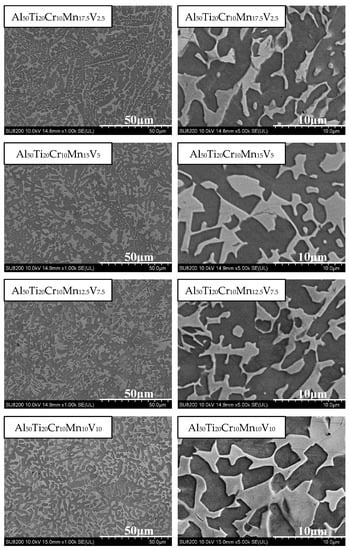
Figure 11.
SEM images of the Al50Ti20Cr10Mn20-xVx (x = 2.5, 5, 7.5, 10) alloys.
3.5. Annealing Treatment on the Al50Ti20Cr10Mn15V5 Series
As mentioned above, the mechanical properties of the MEAs are linked to the morphology of the dual phases. To improve the mechanical properties through manipulation of the morphology of the BCC and FCC phases, annealing treatments were conducted on the promising Al50Ti20Cr10Mn15V5 MEA. Annealing treatment was performed at 1000 °C for varying lengths of time, followed by air-cooling or oil-quenching processes in a high vacuum atmosphere.
Figure 12 depicts the strength–strain curves of Al50Ti20Cr10Mn15V5 annealed at 1000 °C for 0.5, 1, and 2 h, followed by air-cooling and oil-quenching. Through the annealing treatment, the plastic strain of Al50Ti20Cr10Mn15V5 increased slightly. Notably, the annealed and oil-quenched Al50Ti20Cr10Mn15V5 exhibited extraordinary compressive strength and ductility (1966 MPa and 40%). The compressive test results and phase fraction are summarized in Table 4. The oil-quenching process significantly improved the compressive strength of the MEAs through fraction evolution and the morphology of the BCC phase, as presented in Figure 13. The oil-quenching process induced higher strength in the MEAs compared with the air-cooling process. It supposed that the increase of BCC fraction which was attributed to rapid cooling rates led to increase in strength. However, with increased annealing time, the phase morphology become more rounded and the strength decreased slightly. For improving the mechanical properties through manipulation of phase morphology, the quenching approach was more effective than annealing time in this study.
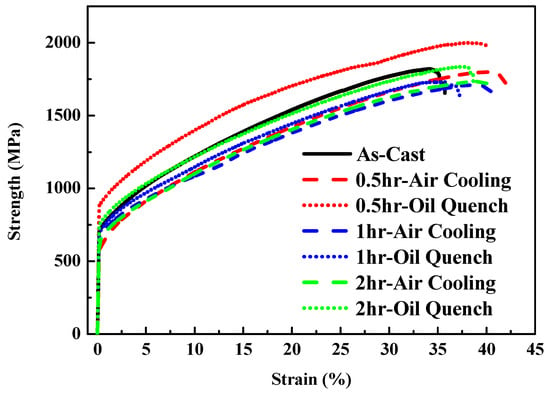
Figure 12.
Mechanical compressive stress–strain curves of the Al50Ti20Cr10Mn15V5 MEAs annealed at 1000 °C for 0.5, 1, and 2 h, followed by air-cooling and oil-quenching.

Table 4.
Mechanical compressive properties of the Al50Ti20Cr10Mn15V5 MEAs annealed at 1000 °C for 0.5, 1, and 2 h, followed by air-cooling and oil-quenching.
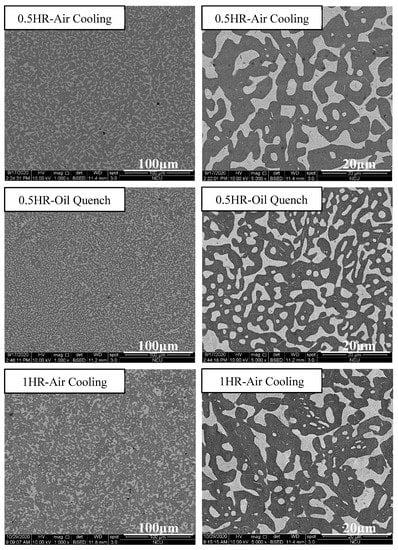
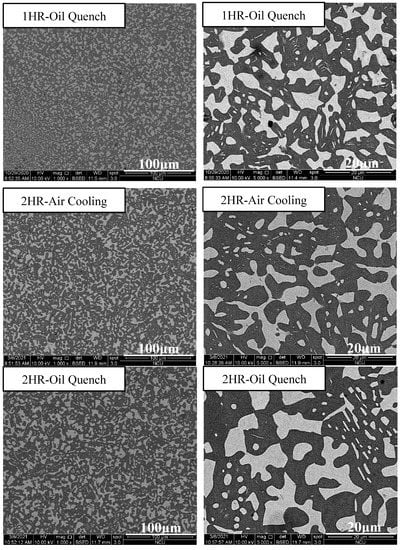
Figure 13.
SEM images of the Al50Ti20Cr10Mn15V5 MEAs annealed at 1000 °C for 0.5, 1, and 2 h, followed by air-cooling and oil-quenching.
Compared with the papers published in recent years on the study of MEAs, several of them have conducted in-depth discussions on their density and mechanical properties [10,18,19,20]. Among them, the casting Al70Cu5Mg5Si10Zn5X5 systems MEAs studied by Jon et al. [18] were the most comparable to this study due to the main element of Al. Despite the fact that the density of Al70Cr5Cu5Mg5Si10Zn5 is lower due to the relatively high proportion of light elements, the high Al content and the formation of intermetallic compounds make the performace of strength and ductility of Al70Cr5Cu5Mg5Si10Zn5 much worse than Al50Ti20Cr10Mn15V5. In particular, the specific compressive strength of Al50Ti20Cr10Mn15V5 was attended to 452 MPa·g/cm3, which is more than twice that of Al70Cr5Cu5Mg5Si10Zn5 with 199 MPa·g/cm3. On the other hand, the Al15(CuFeMn)85 MEAs proposed by Jongun et al. also represents a very comparable study [20]. Through the heat treatment, the strength and ductility of Al15(CuFeMn)85 presented exceptional performance. However, due to the large proportion of heavy elements in MEAs, the density of the material had been greatly increased, making the specific strength of the alloy only 143.87, which was less than one-third of Al50Ti20Cr10Mn15V5. In addition, Bingbing et al. proposed the MEAs about the addition of Zn and Mg in 5083 aluminum alloy which considered the strengthening mechanisms of solid solution strengthening and grain boundary strengthening. Moreover, the yield strength of the MEAs was increased from 86 MPa to 423 MPa while maintaining a certain ductility, which means that the strength of the MEAs was effectively improved through the strengthening mechanism. This characteristic will be used to explore and improve the mechanical properties of subsequent MEAs.
4. Conclusions
A novel dual-phase lightweight nonequiatiomic Al50–Ti–Cr–Mn–V quinary MEA system was developed. Based on the Al50–Ti–Cr–Mn–V quinary alloy, the ratio of each element was adjusted and the influence of each element was analyzed. According to the experiment results, conclusions about the microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of the alloy system can be summarized as follows:
- By maintaining a 50% Al atomic ratio, all designed alloys could achieve the low density (<5 g/cm3) target.
- Most of the MEAs exhibited a dual-phase (FCC + BCC) structure. Cr, Mn, and V with their small atomic radii were mainly distributed in the BCC phase, and Al and Ti with their large atomic radii were mainly distributed in the FCC phase. However, if the Ti element concentration was not sufficient in the alloy, the structure converted to dual BCC phases.
- Increasing the Ti content softened the MEAs. Different Mn concentrations affected the shape of the BCC phase, resulting in changes to the mechanical properties. An increase in Cr and V contents significantly increased the hardness and strength of the alloy.
- The fraction and morphology of the BCC phase played a key role in the resultant mechanical properties. By increasing the fraction of the BCC phase, the strength of the MEAs could be enhanced. In addition, the MEAs with a round-shaped BCC phase possessed higher ductility than those with a sharp-edged phase.
- Concerning the Al50–Ti–Cr–Mn–V MEA systems, the Al50Ti20Cr10Mn15V5 MEA exhibited the best mechanical properties after annealing (at 1000 °C for 0.5 h) and oil-quenching, with an 802 MPa yield strength, 1966 MPa compressive strength, and 40% plastic strain. The specific strength-to-density ratio could reach 452 MPa·g/cm3.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.S.C.J. and P.-S.C.; formal analysis, K.-C.H., C.-Y.C., H.-J.W., P.-S.C., Y.-T.L. and I.-Y.T.; resources, J.C.H., Y.-C.L. and Y.-T.L.; data curation, P.-S.C., P.-H.T. and Y.-T.L.; writing—original draft preparation, P.-S.C.; writing—review and editing, J.S.C.J. and Y.-C.L.; supervision, P.-H.T., J.S.C.J., K.-C.H., C.-Y.C., J.C.H. and H.-J.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan, Republic of China, grant number MOST 108-2218-E-008-009.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the support of the Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan, Republic of China, under grant number MOST 108-2218-E-008-009, and analytic support from the National Central University’s Precision Instrument Center. We also acknowledge the support of I-Shou University’s Department of Materials Science and Engineering for their experimental equipment.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- ASM International. Handbook Committee, “Properties and Selection: Irons, Steels, and High-Performance Alloys”; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 1990; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, K.H.; Yeh, J.W. A Study On Multicomponent Alloy Systems Containing Equal-Mole Elements; Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Hsinchu: National Tsing Hua University: Beijing, China, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Yeh, J.W. Recent progress in high-entropy alloys. Ann. Chim. Sci. Mat. 2006, 31, 633–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.W.; Chen, S.K.; Lin, S.J.; Gan, J.Y.; Chin, T.S.; Shun, T.T.; Tsau, C.H.; Chang, S.Y. Nanostructure High-Entropy Alloys with Multiple Principle Elements: Novel Alloy Design Concepts and Outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2004, 6, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkov, O.N.; Wilks, G.B.; Miracle, D.B.; Chuang, C.P.; Liaw, P.K. Refractory high-entropy alloys. Intermetallics 2010, 18, 1758–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilensten, L.; Couzinie, J.-P.; Perrière, L.; Bourgon, J.; Emery, N.; Guillot, I. New structure in refractory high-entropy alloys. Mater. Lett. 2014, 132, 123–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Yao, M.; Pradeep, K.; Tasan, C.; Springer, H.; Raabe, D. Phase stability of non-equiatomic CoCrFeMnNi high entropy alloys. Acta Mater. 2015, 98, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, K.; Chena, C.L.; Shen, B.L. Influence of Al content on high temperature oxidation behavior of AlxCoCrFeNiTi0.5 high entropy alloys. Vacuum 2019, 163, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.; Ondicho, I.; Park, N.; Tsuji, N. Strength–ductility balance in an ultrafine-grained non-equiatomic Fe50(CoCrMnNi)50 medium-entropy alloy with a fully recrystallized microstructure. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 780, 959–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhou, D.; Jin, X.; Zhang, L.; Du, X.; Li, B. Design of non-equiatomic medium-entropy alloys. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stepanov, N.; Shaysultanov, D.; Chernichenko, R.; Tikhonovsky, M.; Zherebtsov, S. Effect of Al on structure and mechanical properties of Fe-Mn-Cr-Ni-Al non-equiatomic high entropy alloys with high Fe content. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 770, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, M.; Pradeep, K.; Tasan, C.; Raabe, D. A novel, single phase, non-equiatomic FeMnNiCoCr highentropy alloy with ex-ceptional phase stability and tensile ductility. Scr. Mater. 2014, 72–73, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, K.; Zaddach, A.J.; Niu, C.; Irving, D.L.; Koch, C.C. A Novel Low-Density, High-Hardness, High-entropy Alloy with Close-packed Single-phase Nanocrystalline Structures. Mater. Res. Lett. 2014, 3, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, R.; Gao, J.C.; Fan, K. Study to Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Mg Containing High Entropy Alloys. Mater. Sci. Forum 2010, 650, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.H.; Wang, R.; Chen, C.; Wu, B.L.; Huang, J. Preparation of a Light-Weight MgCaAlLiCu High-Entropy Alloy. Key Eng. Mater. 2017, 727, 132–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanov, N.; Yurchenko, N.; Skibin, D.; Tikhonovsky, M.; Salishchev, G. Structure and mechanical properties of the AlCrxNbTiV (x = 0, 0.5, 1, 1.5) high entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 652, 266–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.C.; Chen, P.S.; Li, C.H.; Tsai, P.H.; Jang, J.S.C. Development of Novel Lightweight Dual-Phase Al-Ti-Cr-Mn-V Medium-Entropy Alloys with High Strength and Ductility. Entropy 2020, 22, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sanchez, J.M.; Vicario, I.; Albizuri, J.; Guraya, T.; Acuña, E.M. Design, microstructure and mechanical properties of cast medium entropy aluminium alloys. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, J.; Park, J.M.; Bae, J.W.; Do, H.S.; Lee, B.J.; Kim, H.S. A new strategy for designing immiscible medium-entropy alloys with excellent tensile properties. Acta Mater. 2020, 193, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Liaw, P.K.; Brechtl, J.; Ren, J.; Guo, X.; Zhang, Y. Effects of Cu and Zn on microstructures and mechanical behavior of the medium-entropy aluminum alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 820, 153092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).