Structural and Phase Transformations and Physical and Mechanical Properties of Cu-Al-Ni Shape Memory Alloys Subjected to Severe Plastic Deformation and Annealing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
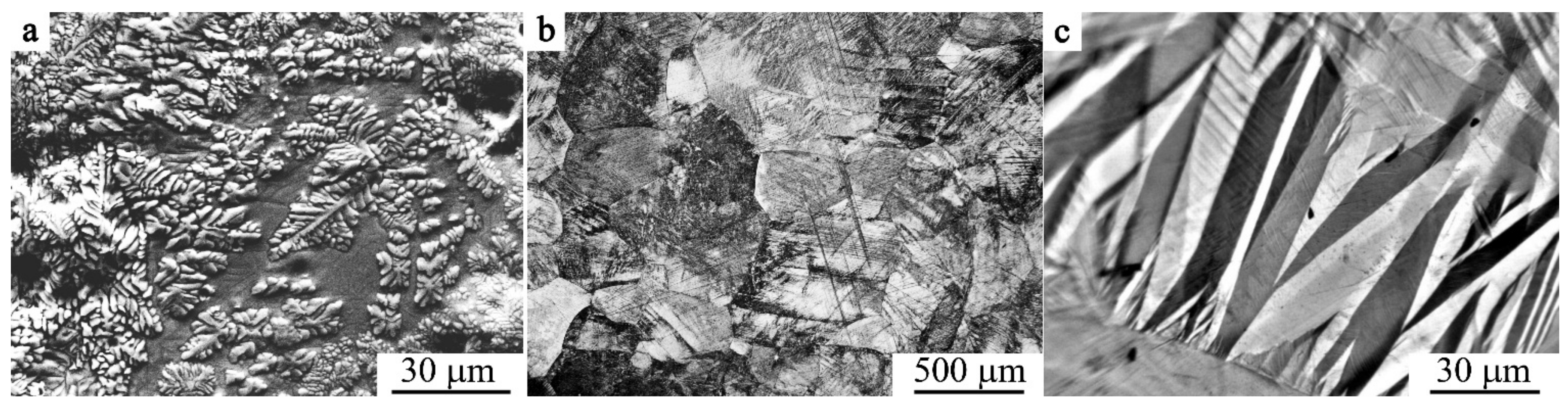
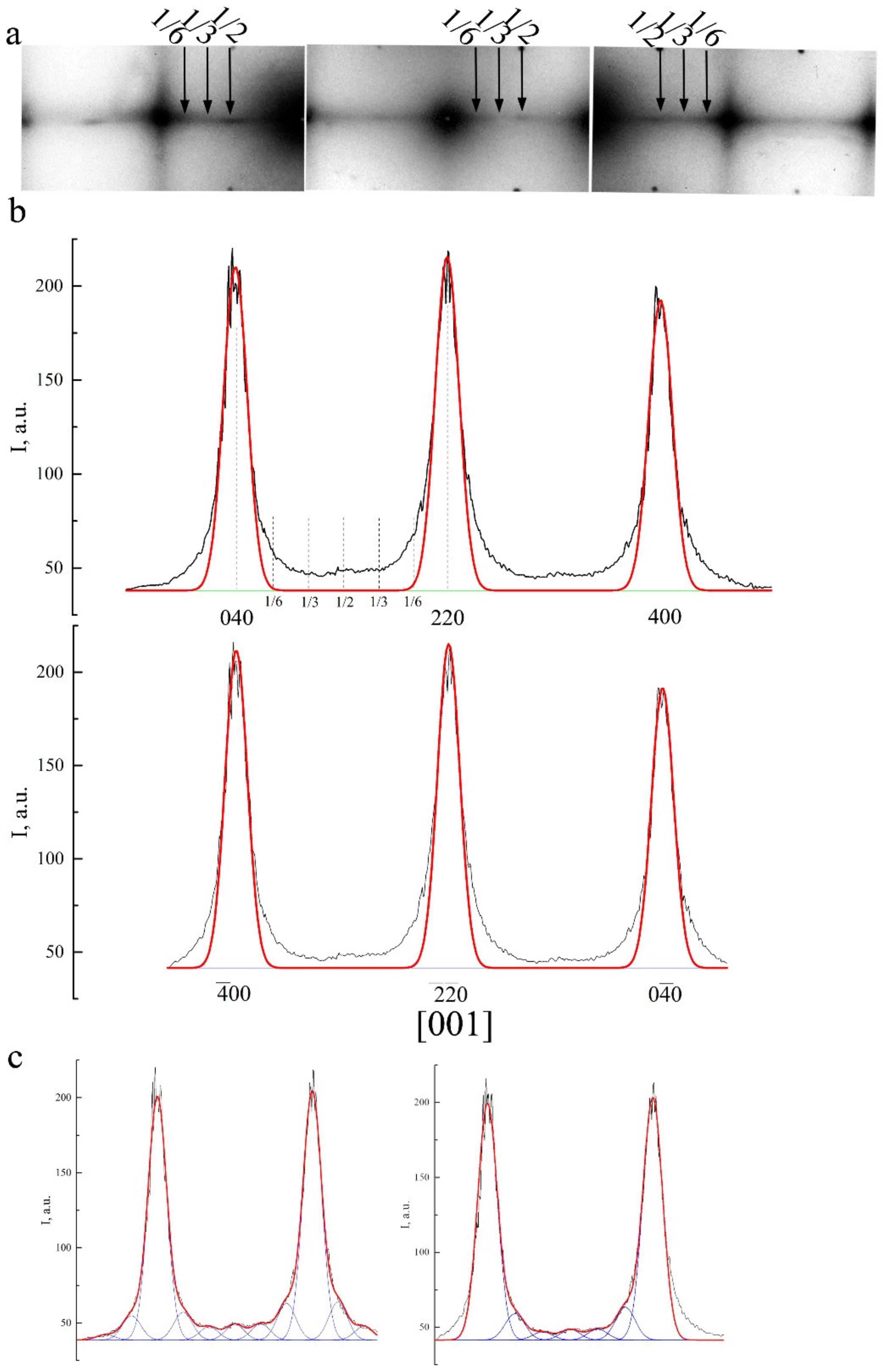
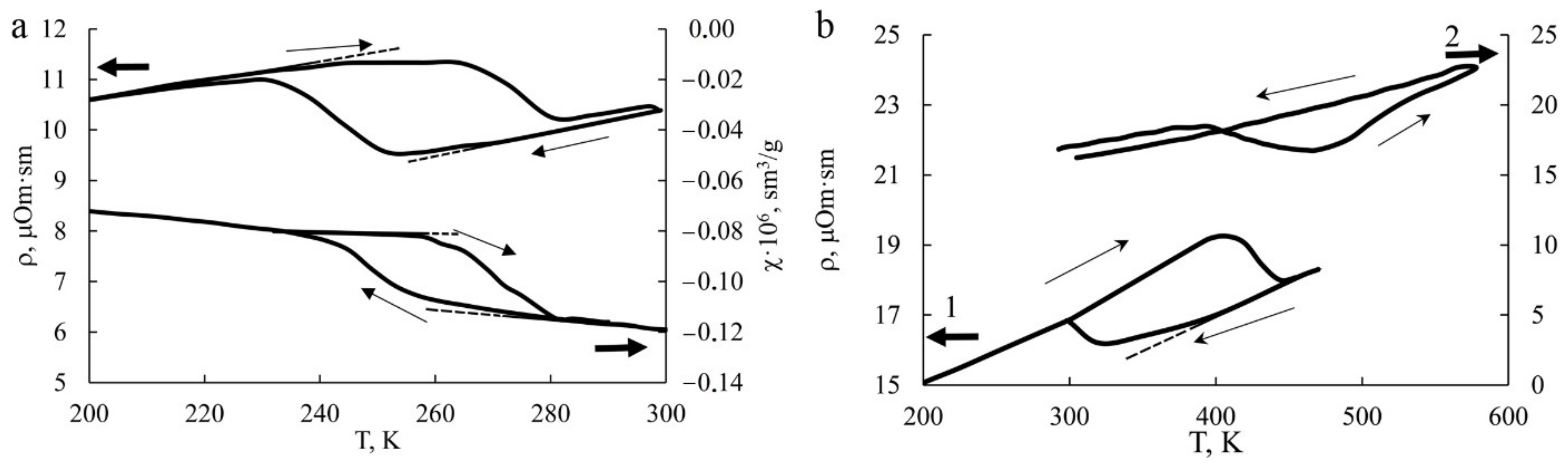
3.1. Pre-Martensitic State
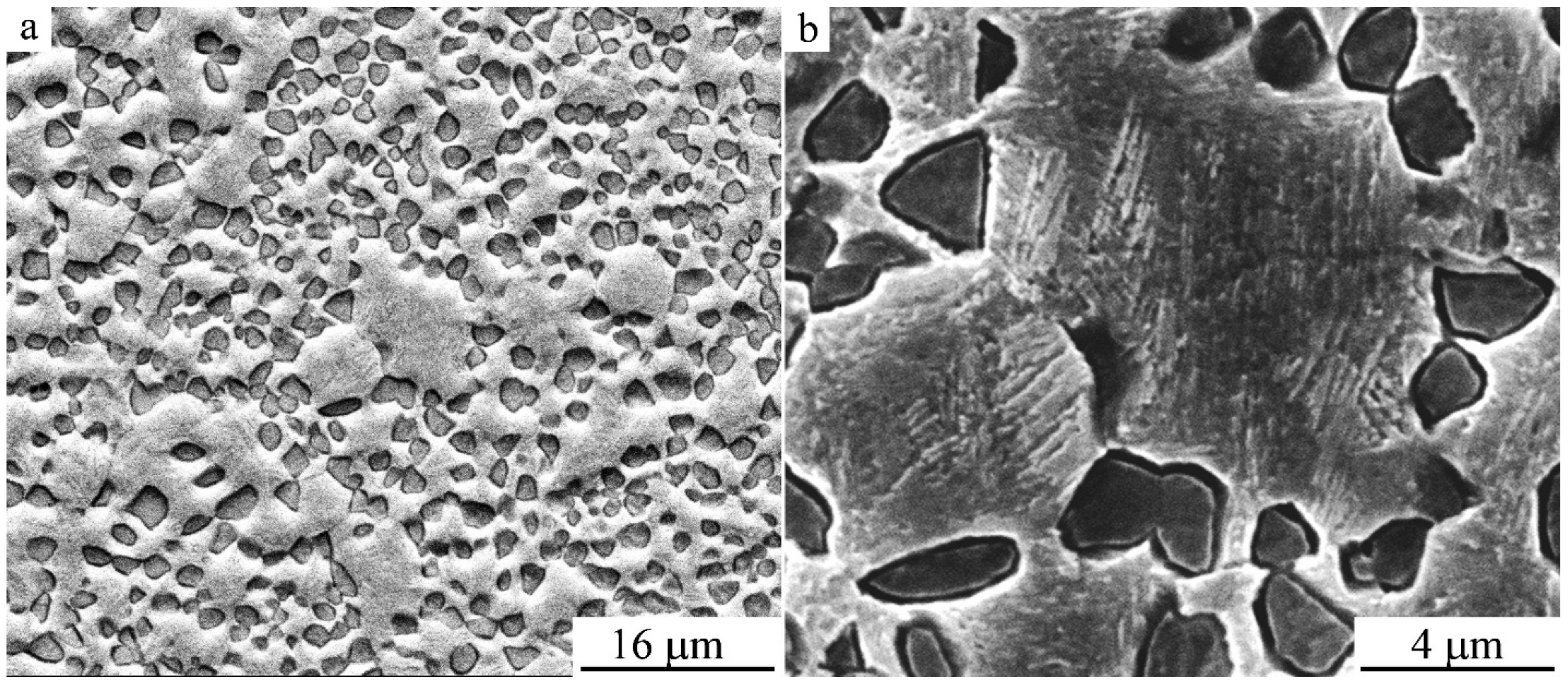
3.2. Structure, Phase Composition, and Mechnical Properties of SPD Alloys
3.3. Fractographic Study
4. Summary and Conclusions
- Non-radial diffuse streaks and complex patterns of arrangement of diffuse satellites of type 1/2, 1/3, and 1/6 were revealed and systematically investigated in detail using the diffraction mode of high resolution TEM at a high accelerating voltage 300 kV.
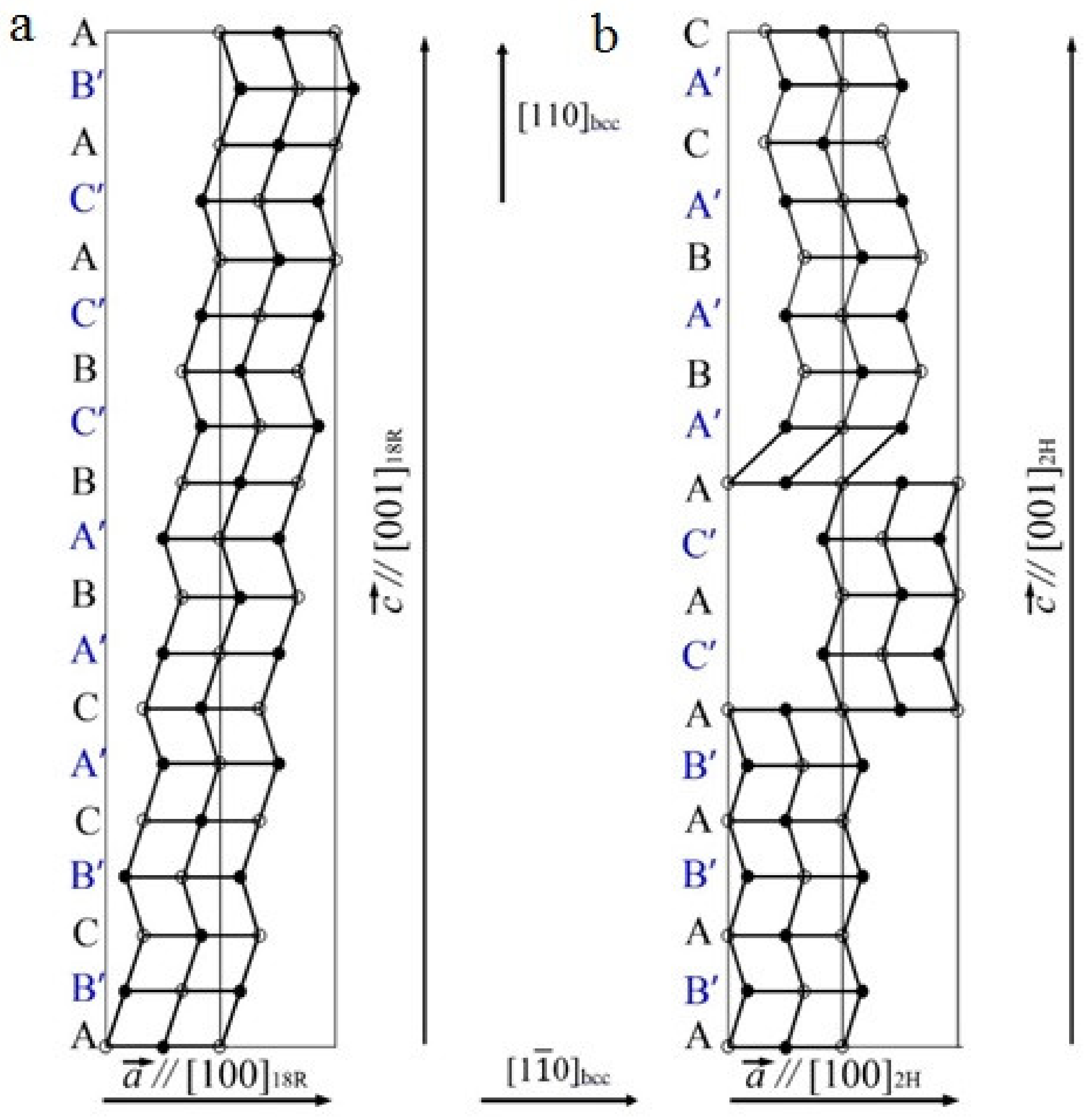
- The crystallographic mechanism of the martensite nucleation and rearrangements β1→β1′ and β1→γ1′ is proposed, based on the analysis of (i) the diffuse scattering patterns that occur in the pre-martensitic state and (ii) the internal defects of martensite substructure in these alloys.
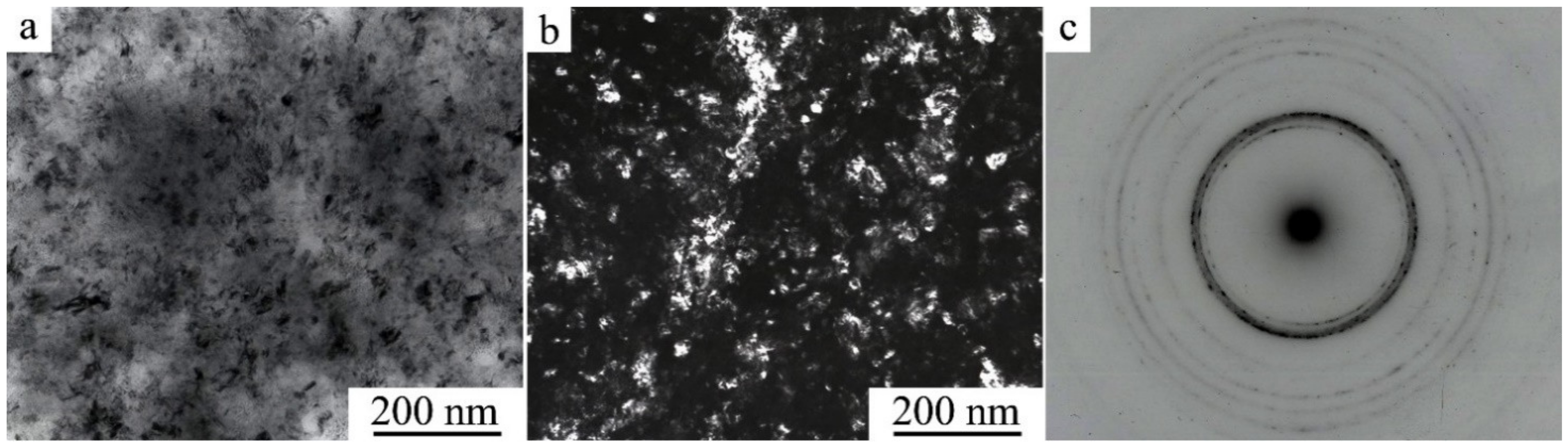
- It was revealed that SPD of metastable austenitic Cu-Al-Ni alloys via HPT of 6 GPa (with the number of revolutions from 1 to 10) leads to the creation of a deformation-induced UFG structure of martensite responsible for its high hardness and strength properties.
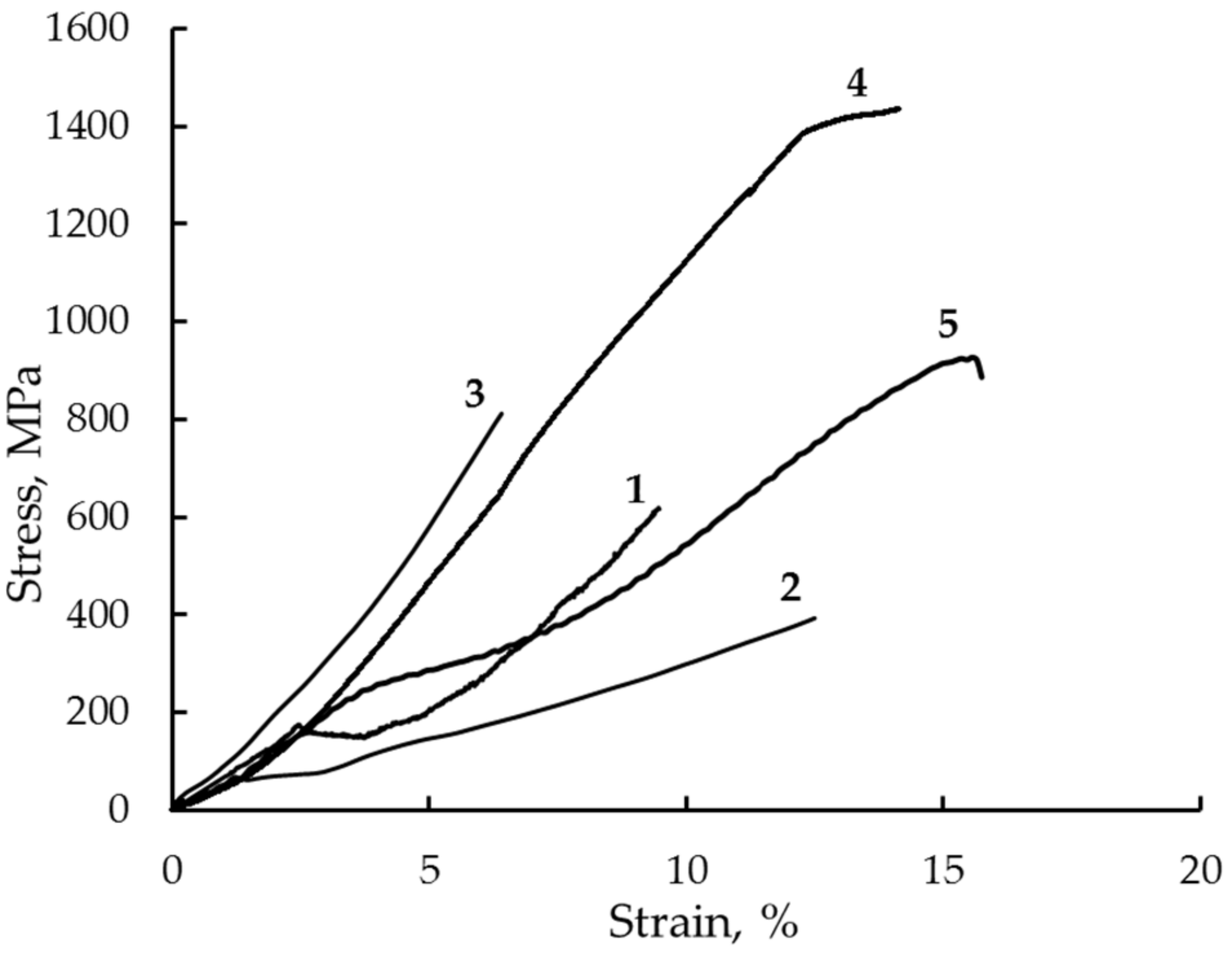
- A subsequent annealing of moderate duration provides preservation of a UFG structure and strengthening of the alloys. The highest strength(σu up to 1400 MPa) and improved ductility-related (δ = 12–13%) properties were obtained in the UFG martensitic alloy Cu–14Al–3Ni either subjected to the HPT of 10 revs and short-term annealing at 1073 K for 10 s or subjected to the increased (to 423 K) HPT temperatures.
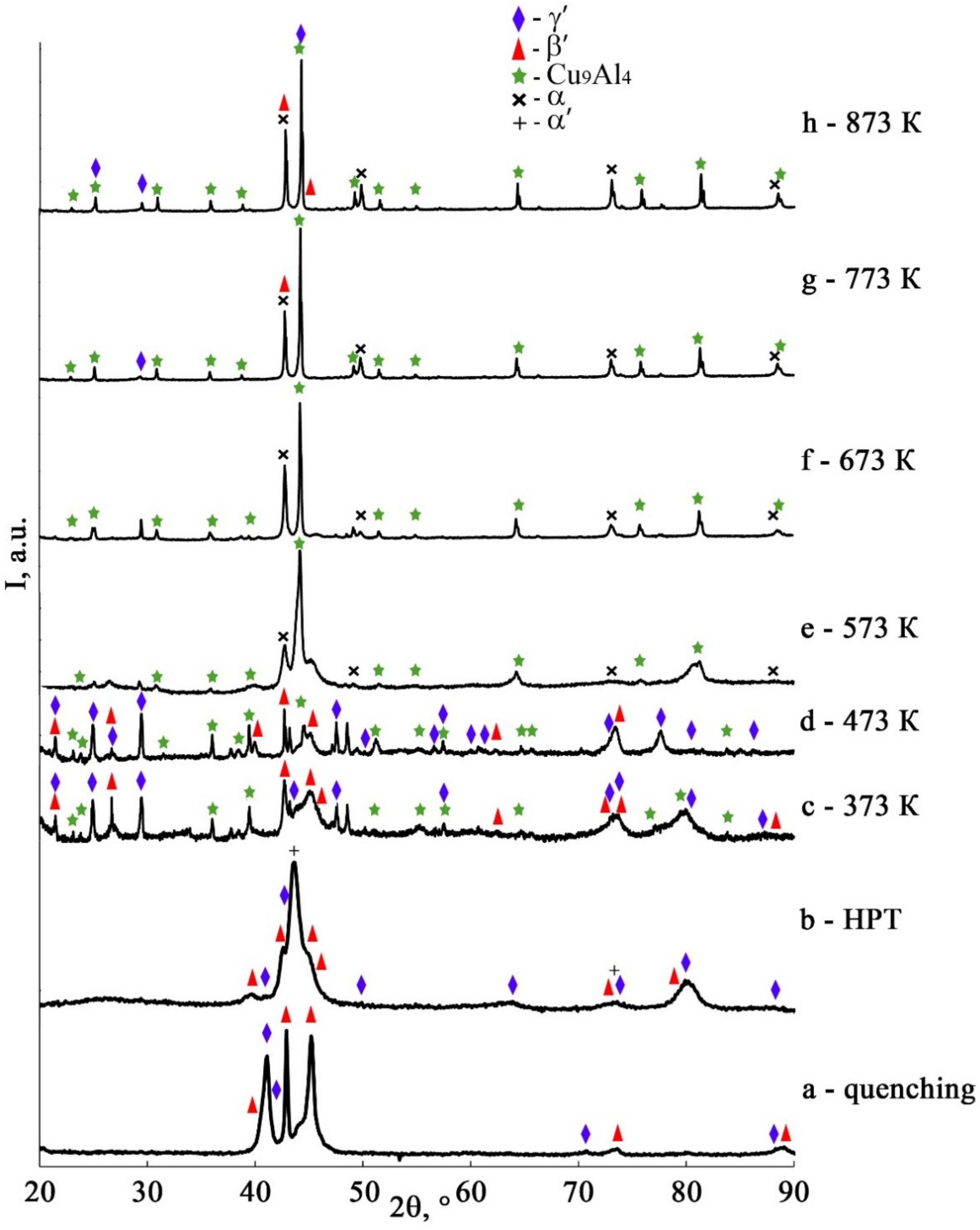
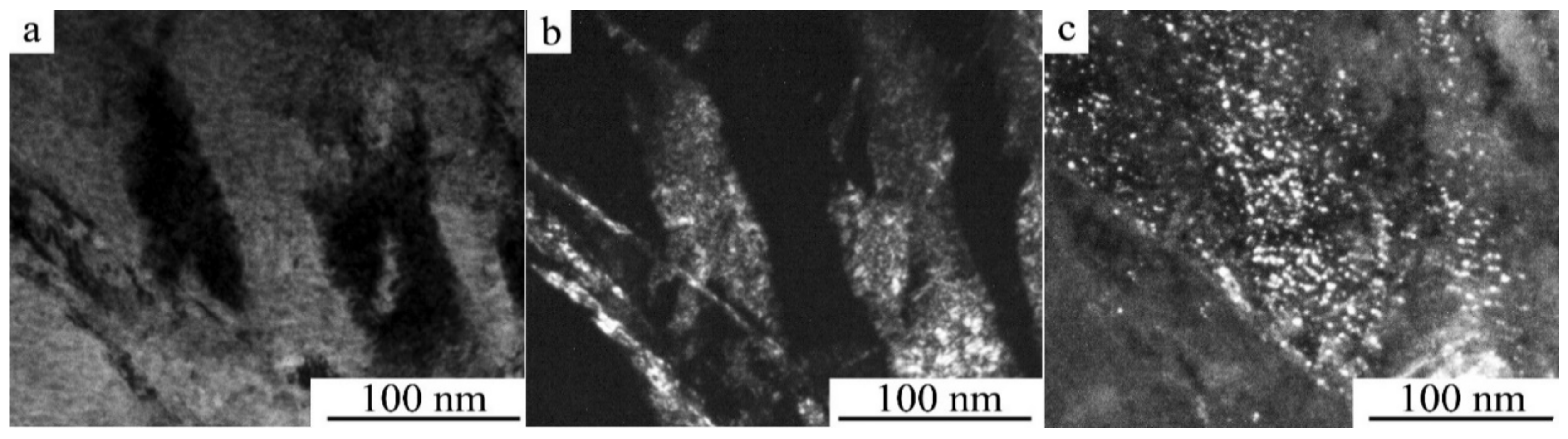
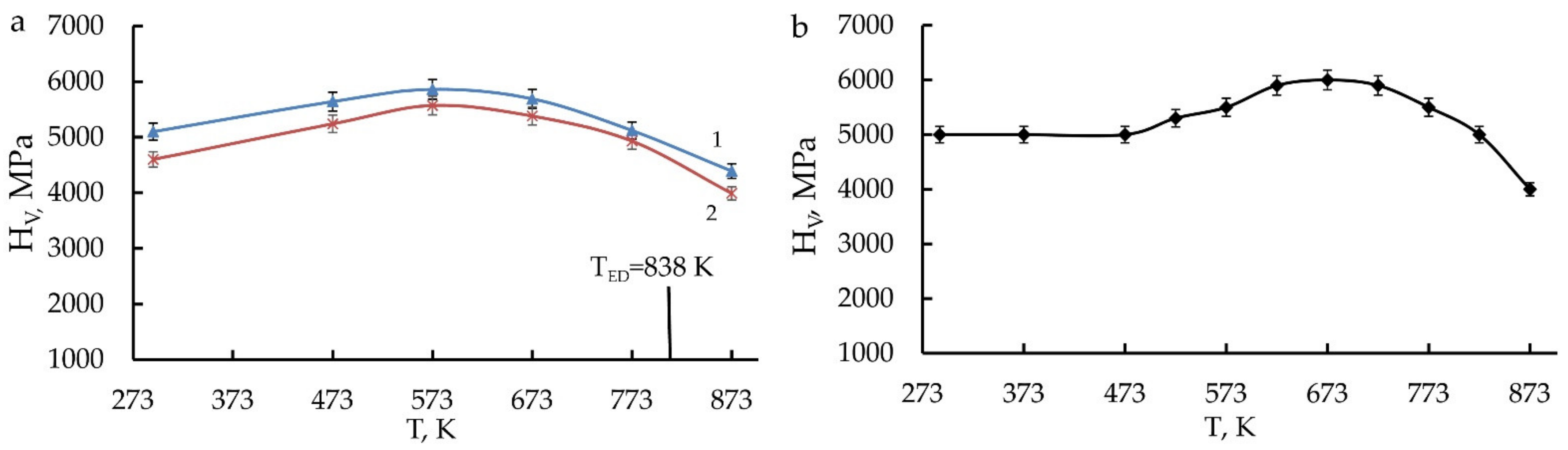
- Annealing at temperatures below Ms initiates realization of the proeutectoid decomposition of martensite in the HPT-treated alloys with precipitation of an aluminum-enriched γ2 nano phase. The grain size, phase composition, and substructure of the martensite are preserved, but its depletion of aluminum by 1–2 at.% causes the stabilization of martensite and a noticeable increase in the critical temperatures of the TMT (by 70–160 K).
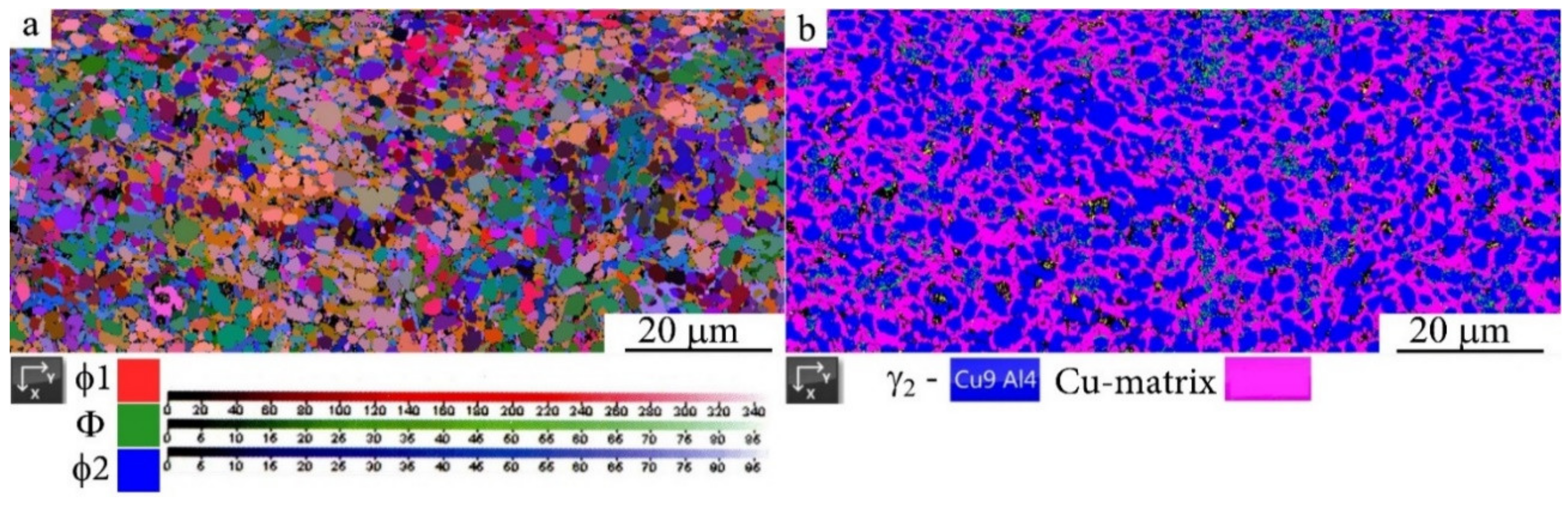
- The annealing in the austenite state in the interval 570–840 K (above the temperature Af) leads to the combined reaction of primary nanorecrystallization accompanied by a heterogeneous preferably grain-boundary eutectoid (α + γ2) decomposition of the reverted β1 austenite into the homogeneous UFG (β1 + α + γ2) nano-triplex structure. Annealing at temperatures above TED, which is close to 840 K, leads (due to a preferably heterogeneous precipitation of the γ2 nanophase) to the formation of a micro-duplex (β1 + γ2) structure. When cooled to RT, the residual β1 austenite experiences the TMT.
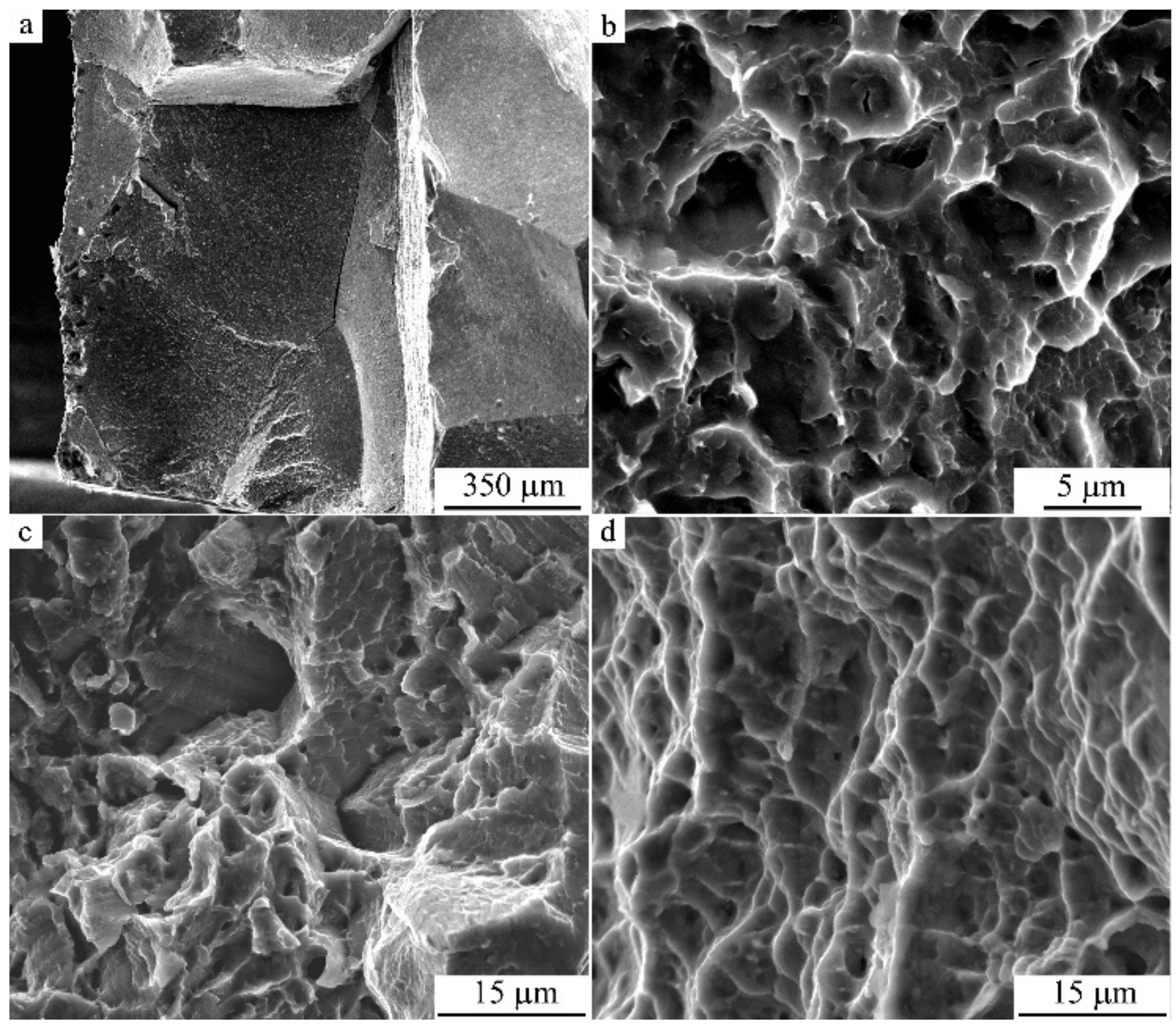
- According to the data of fractographic investigations, the alloys in a UFG state are distinguished by their ductile–brittle character of fracture with a high degree of dispersion of separate dimples along high-angle boundaries of the ensembles of nano grains unified by close-in-value, small-angle misorientations.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Perkins, J. Shape Memory Effects in Alloys; Plenum: London, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Otsuka, K.; Shimizu, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Sekiguchi, Y.; Tadaki, C.; Honma, T.; Miyazaki, S. Shape Memory Alloys; Funakubo, H., Ed.; Funakubo: Kyoto, Japan, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Duering, T.W.; Melton, K.L.; Stockel, D.; Wayman, C.M. (Eds.) Engineering Aspects of Shape Memory Alloys; Butterworth-Heineman: London, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Khachin, V.N.; Pushin, V.G.; Kondratyev, V.V. Titanium Nickelide: Structure and Properties; Nauka: Moscow, Russian, 1992. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Otsuka, K.; Wayman, C.M. Shape Memory Materials; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Pushin, V.G.; Kondratyev, V.V.; Khachin, V.N. Pretransition Phenomena and Martensitic Transformations; UrO RAN: Yekaterinburg, Russia, 1998. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Yoneyama, T.; Miyazaki, S. Shape Memory Alloys for Medical Applications; Wordhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Prokoshkin, S.D.; Pushin, V.G.; Ryklina, E.P.; Khmelevskaya, I.Y. Application of Titanium Nickelide–based Alloys in Medicine. Phys. Met. Metallogr. 2004, 97, 56–96. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, J.C.; Weselowsky, M.J. Shape Memory Alloys for Seismic Response Modification: A State-of-the-Art Review. Earthq. Spectra 2005, 21, 569–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Cai, C.S.; O’Keil, A.M. Overview of Potential and Existing Applications of Shape Memory Alloys in Bridges. J. Bridge Eng. 2011, 16, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, C.; Brown, L.C. The thermal effect due to stress-induced martensite formation in β-CuAlNi single crystals. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1980, 11, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gschneidner, K.A., Jr.; Pecharsky, V.; Tsokol, A. Recent developments in magnetocaloric materials. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2005, 68, 1479–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mischenko, A.S.; Zhang, Q.; Scott, J.F.; Whatmore, R.W.; Mathur, N.D. Giant electrocaloric effect in thin-film PbZr0.95Ti0.05O3. Science 2006, 311, 1270–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnot, E.; Romero, R.; Mañosa, L.; Vives, E.; Planes, A. Elastocaloric effect associated with the martensitic transition in shape-memory alloys. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100, 125901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planes, A.; Mañosa, L.; Acet, M. Magnetocaloric effect and its relation to shape memory properties in ferromagnetic Heusler alloys. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 2009, 21, 233201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mañosa, L.; González-Alonso, D.; Planes, A.; Bonnot, E.; Barrio, M.; Tamarit, J.-L.; Aksoy, S.; Acet, M. Giant solid-state barocaloric effect in the Ni-Mn-In magnetic shape-memory alloy. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 478–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.; Bahl, C.R.; Bjørk, R.; Engelbrecht, K.; Nielsen, K.K.; Pryds, N. Materials challenges for high performance magnetocaloric refrigeration devices. Adv. Energy Mater. 2012, 2, 1288–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechtold, C.; Chluba, C.; De Miranda, R.L.; Quandt, E. High cyclic stability of the elastocaloric effect in sputtered TiNiCu shape memory films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 101, 091903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Wu, Y.; Muehlbauer, J.; Hwang, Y.; Radermacher, R.; Fackler, S.; Wuttig, M.; Takeuchi, I. Demonstration of high efficiency elastocaloric cooling with large δT using NiTi wires. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 101, 073904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moya, X.; Stern-Taulats, E.; Crossley, S.; González-Alonso, D.; Kar-Narayan, S.; Planes, A.; Mañosa, L.; Mathur, N.D. Giant electrocaloric strength in single-crystal BaTiO3. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 1360–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mañosa, L.; Jarque-Farnos, S.; Vives, E.; Planes, A. Large temperature span and giant refrigerant capacity in elastocaloric Cu-Zn-Al shape memory alloys. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 103, 211904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J. Shape memory alloys and their applications in power generation and refrigeration. In Mesoscopic Phenomena in Multifunctional Materials; Saxena, A., Planes, A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 289–307. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, S.; Geng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Pillsbury, T.E.; Hada, Y.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Fujimoto, K.; Hwang, Y.; Radermacher, R.; Cui, J.; et al. Elastocaloric effect in CuAlZn and CuAlMn shape memory alloys under compression. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. 2016, 374, 20150309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, R. A look into Cu-based shape memory alloys: Present Scenario and future prospects. J. Mater. Res. 2014, 29, 1681–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedlak, P.; Seiner, H.; Landa, M.; Novák, V.; Šittner, P.; Manosa, L. Elastic Constants of bcc Austenite and 2H Orthorhombic Martensite in CuAlNi Shape Memory Alloy. Acta Mater. 2005, 53, 3643–3661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khachin, V.N.; Muslov, S.A.; Pushin, V.G.; Chumlyakov, Y.I. Anomalies of the Elastic Properties of Single Crystals of TiNi-TiFe. DAN Soc. Sci. Study Read. 1987, 295, 606–609. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kuznetsov, A.V.; Muslov, S.A.; Lotkov, A.I.; Pushin, V.G.; Khachin, V.N.; Grishkov, V.N. Elastic Constants Near the TiNi Martensitic Transformations. Izv. VUZov. Phys. 1987, 30, 98–99. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Muslov, S.A.; Kuznetsov, A.V.; Khachin, V.N.; Lotkov, A.I.; Grishkov, V.N.; Pushin, V.G. Anomalies of the Elastic Constants of Single Crystals Ti50Ni48Fe2 Near Martensitic Transformations. Izv. VUZov. Phys. 1987, 30, 104–105. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Khachin, V.N.; Muslov, S.A.; Pushin, V.G.; Kondratyev, V.V. Special elastic properties of B2-compounds of titanium with unstable lattice. Metallophys 1988, 10, 102–104. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Pushin, V.G.; Khachin, V.N.; Kondratyev, V.V.; Muslov, S.A.; Pavlova, S.P.; Yurchenko, L.I. Structure and Properties of B2 Compounds of Titanium. I. Pre-Martensitic Phenomena. Fiz. Met. Metallogr. 1988, 66, 350–358. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Pushin, V.G.; Kondratyev, V.V. Pretransition Phenomena and Martensitic Transformations. Fiz. Met. Metallogr. 1994, 78, 40–61. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Pushin, V.G.; Khachin, V.N.; Yurchenko, L.I.; Muslov, S.A.; Ivanova, L.Y.; Sokolova, A.Y. Microstructure and Physical Properties of Ti50Ni50-xFex Alloys with Memory Effects. II. Elastic Properties. Fiz. Met. Metallogr. 1995, 79, 70–76. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Pushin, V.G. Alloys with a Thermo-Mechanical Memory: Structure, Properties, and Application. Phys. Met. Metallogr. 2000, 90, S68–S95. [Google Scholar]
- Lobodyuk, V.A.; Koval’, Y.N.; Pushin, V.G. Crystal-Structural Features of Pretransition Phenomena and Thermoelastic Martensitic Transformations in Alloys of Nonferrous Metals. Phys. Met. Metallogr. 2011, 111, 165–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushin, V.; Kuranova, N.; Marchenkova, E.; Pushin, A. Design and Development of Ti–Ni, Ni–Mn–Ga and Cu–Al–Ni-based Alloys with High and Low Temperature Shape Memory Effects. Materials 2019, 12, 2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushin, V.G.; Stolyarov, V.V.; Valiev, R.Z.; Kourov, N.I.; Kuranova, N.N.; Prokofiev, E.A.; Yurchenko, L.I. Features of Structure and Phase Transformations in Shape Memory TiNi-Based Alloys after Severe Plastic Deformation. Ann. Chim. Sci. Matériaux 2002, 27, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiev, R.Z.; Pushin, V.G. Bulk Nanostructured Metallic Materials: Production, Structure, Properties and Functioning. Phys. Met. Metallogr. 2002, 94, S1–S4. [Google Scholar]
- Pushin, V.G.; Stolyarov, V.V.; Valiev, R.Z.; Kourov, N.I.; Kuranova, N.N.; Prokofiev, E.A.; Yurchenko, L.I. Development of Methods of Severe Plastic Deformation for the Production of High-Strength Alloys Based on Titanium Nickelide with a Shape Memory Effect. Phys. Met. Metallogr. 2002, 94, S54–S68. [Google Scholar]
- Pushin, V.G.; Valiev, R.Z. The Nanostructured TiNi Shape-Memory Alloys: New Properties and Applications. Sol. St. Phenom. 2003, 94, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushin, V.G.; Valiev, R.Z.; Yurchenko, L.I. Processing of Nanostructured TiNi-Shape Memory Alloys: Methods, Structures, Properties, Application. J. Phys. IV Fr. 2003, 112, 659–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushin, V.G. Structure, Properties, and Application of Nanostructures Shape Memory TiNi-Based Alloys. In Nanomaterials by Severe Plastic Deformation; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH &Co.: Weinheim, Germany, 2004; pp. 822–828. [Google Scholar]
- Brailovski, V.; Khmelevskaya, I.Y.; Prokoshkin, S.D.; Pushin, V.G.; Ryklina, E.P.; Valiev, R.Z. Foundation of Heat and Thermomechanical Treatments and Their on the Structure and Properties of Titanium Nickelide-Based Alloys. Phys. Met. Metallogr. 2004, 97, S3–S55. [Google Scholar]
- Pushin, V.G.; Valiev, R.Z.; Zhu, Y.T.; Gunderov, D.V.; Kourov, N.I.; Kuntsevich, T.E.; Uksusnikov, A.N.; Yurchenko, L.I. Effect of Severe Plastic Deformation on the Behavior of Ti-Ni Shape Memory Alloys. Mater. Trans. 2006, 47, 694–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushin, V.G.; Valiev, R.Z.; Zhu, Y.T.; Gunderov, D.V.; Korolev, A.V.; Kourov, N.I.; Kuntsevich, T.E.; Valiev, E.Z.; Yurchenko, L.I. Severe Plastic Deformation of Melt-Spun Shape Memory Ti2NiCu and Ni2MnGa Alloys. Mater. Trans. 2006, 47, 546–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Valiev, R.Z.; Gunderov, D.V.; Pushin, V.G. The New SPD Processing Routes to Fabricate Bulk Nanostructured Materials. Ultrafine Grained Materials IV; Zhu, Y.T., Langdon, T.G., Horita, Z., Zehetbauer, M.J., Semiatin, S.L., Lowe, T.C., Eds.; TMS (The Minerals, Metals and Materials Society): Warrendale, PA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Pushin, V.G.; Valiev, R.Z.; Zhu, Y.T.; Prockoshkin, S.; Gunderov, D.; Yurchenko, L.I. Effect of Equal Channel Angular Pressing and Repeated Rolling on Structure, Phase Transformation and Properties of TiNi Shape Memory Alloys. Mater. Sci. Forum 2006, 503, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiev, R.; Gunderov, D.; Prokofiev, E.; Pushin, V.; Zhu, Y. Nanostructuring of TiNi alloy by SPD processing for advanced properties. Mater. Trans. 2008, 49, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchiya, K.; Hada, Y.; Koyano, T.; Nakajima, K.; Ohnuma, M.; Koike, T.; Todaka, Y.; Umimota, M. Production of TiNi Amorphous/Nanocrystalline Wires with High-Strength and Elastic Modulus by Severe Cold Drawing. Scr. Mater. 2009, 60, 749–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuranova, N.N.; Gunderov, D.V.; Uksusnikov, A.N.; Luk’yanov, A.V.; Yurchenko, L.I.; Prokof’ev, E.A.; Pushin, V.G.; Valiev, R.Z. Effect of heat treatment on the structural and phase transformations and mechanical properties of TiNi alloy subjected to severe plastic deformation by Torsion. Phys. Met. Metallogr. 2009, 108, 556–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokoshkin, S.; Brailivski, V.; Korotitskiy, A.; Inaekyan, K.; Dubinsky, S.; Filonov., M.; Petrzhic, M. Formation of Nanostructures in Thermo-Mechanically-Treated Ti-Ni and Ti-Nb-(Zr, Ta) SMAs and Their Roles in Martensite Crystal Lattice Changes and Mechanical Behavior. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 2066–2075. [Google Scholar]
- Svirid, A.E.; Pushin, V.G.; Kuranova, N.N.; Luk’yanov, A.V.; Pushin, A.V.; Uksusnikov, A.N.; Ustyugov, Y.M. The structure–phase transformations and mechanical properties of the shape memory effect alloys based on the system Cu–Al–Ni. Mater. Today Proceed. 2017, 4, 4758–4762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukyanov, A.V.; Pushin, V.G.; Kuranova, N.N.; Svirid, A.E.; Uksusnikov, A.N.; Ustyugov, Y.M.; Gunderov, D.V. Effect of the Thermomechanical Treatment on Structural and Phase Transformations in Cu–14Al–3Ni Shape Memory Alloy Subjected to High-Pressure Torsion. Phys. Met. Metallogr. 2018, 119, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svirid, A.E.; Lukyanov, A.V.; Pushin, V.G.; Belosludtseva, E.S.; Kuranova, N.N.; Pushin, A.V. Effect of the Temperature of Isothermal Upsetting on the Structure and the Properties of the Shape Memory Cu–14 wt% Al–4 wt% Ni Alloy. Phys. Met. Metallogr. 2019, 120, 1159–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svirid, A.E.; Kuranova, N.N.; Lukyanov, A.V.; Makarov, V.V.; Nikolayeva, N.V.; Pushin, V.G.; Uksusnikov, A.N. Influence of thermomechanical treatment on structural-phase transformations and mechanical properties of the Cu–Al–Ni shape-memory alloys. Russ. Phys. J. 2019, 61, 1681–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svirid, A.E.; Luk’yanov, A.V.; Makarov, V.V.; Pushin, V.G.; Uksusnikov, A.N. Effect of thermomechanical treatment on the structural, phase transformations and properties of the Cu-Al-Ni shape memory alloys. Chelyabinsk Phys. Math. J. 2019, 4, 108–117. [Google Scholar]
- Svirid, A.E.; Pushin, V.G.; Kuranova, N.N.; Belosludtseva, E.S.; Pushin, A.V.; Lukyanov, A.V. The Effect of Plastification of Cu–14Al–4Ni Alloy with the Shape Memory Effect in High-Temperature Isothermal Upsetting. Tech. Phys. Lett. 2020, 46, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svirid, A.E.; Lukyanov, A.V.; Pushin, V.G.; Kuranova, N.N.; Makarov, V.V.; Pushin, A.V.; Uksusnikov, A.N. Application of Isothermal Upset for Megaplastic Deformation of Cu–Al–Ni β Alloys. Tech. Phys. 2020, 65, 1044–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagdelen, F.; Gokhan, T.; Aydogdu, A.; Aydogdu, Y.; Adiguzel, O. Effect of thermal treatments on transformation behavior in shape memory Cu-Al-Ni alloys. Mater. Lett. 2003, 57, 1079–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Roca, P.; Isola, L.; Vermaut, P.; Malarria, J. Relationship between grain size and thermal hysteresis of martensitic transformations in Cu-based shape memory alloys. Scr. Mater. 2017, 135, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, X.; Wang, F.; Qingsuo, L.; Wang, Q. Microstructure, mechanical properties and shape memory effect of Cu-Hf-Al-Ni alloys. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2018, 34, 1497–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelosin, A.; Riviere, A. Structural and mechanical spectroscopy study of the β′1 martensite decomposition in Cu–12%Al–3%Ni(wt.%) alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 1998, 268, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Pan, Z.Y.; Tang, N.; Jiang, Y.B.; Liu, N.; Fang, M.; Zheng, F. Cu-Al-Ni-Mn shape memory alloy processed by mechanical alloying and powder metallurgy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 417, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, N.; Ramamurty, U. Aging response and its effect on the functional properties of Cu-Al-Ni shape memory alloys. J. Alloy. Comp. 2008, 449, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, R.D.; Yan, H.; Chen, Y. Grain boundary engineering of Co-Ni-Al, Cu-Zn-Al, and Cu-Al-Ni shape memory alloys by intergranular precipitation of a ductile solid solution phase. Scr. Mater. 2016, 115, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qader, I.N.; Oner, E.; Kok, M.; Mohammed, S.S.; Dagdelen, F.; Kanca, M.S.; Aydogdu, Y. Mechanical and thermal behavior of Cu84-xAl13Ni3Hfx shape memory alloys. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Sci. 2021, 45, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, K.; Wayman, C.M.; Kubo, H. Diffuse Electron Scattering in β–phase alloys. Met. Trans. A. 1978, 9, 1075–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verlinden, B.; Delaey, L. Empirical relations for C′ and Ms in β–Hume-Rothery alloys. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Martensitic Transformations, Nara, Japan, 26–30 August 1986; pp. 733–768. [Google Scholar]
- Warlimont, H.; Delaey, L. Martensitic Transformations in Copper-, Silver-, and Gold-Based Alloys; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1974. [Google Scholar]



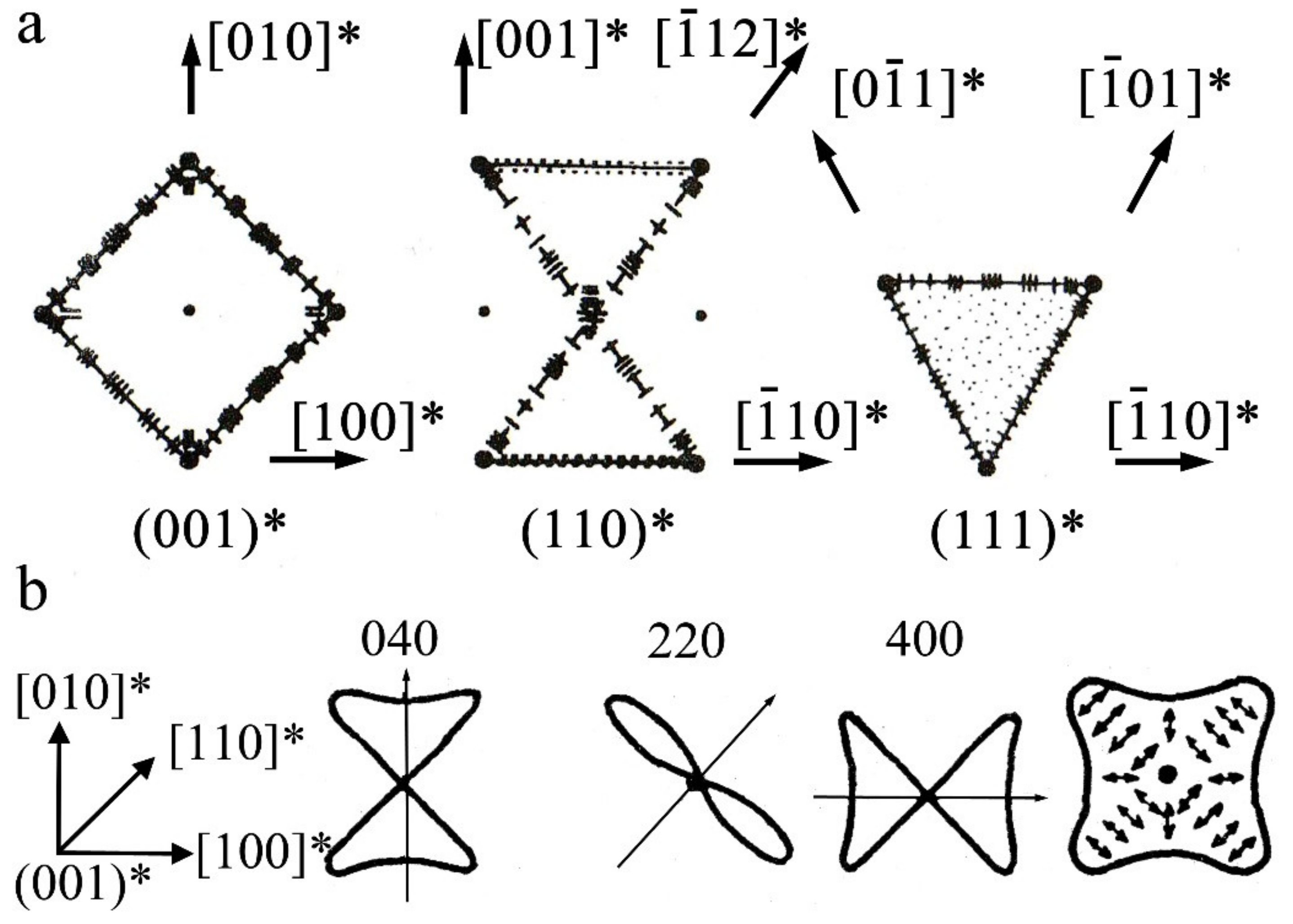




| No. | Nominal Composition | Al, wt% | Ni, wt% | Fe, wt% | Cu |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cu-14Al-3Ni | 13.95 | 3.02 | - | 83.03 |
| 2 | Cu-13.5Al-3.5Ni | 13.40 | 3.36 | 0.05 | 83.19 |
| Treatment | Ms, K; | Mf, K | As, K | Af, K | ΔT, K |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quenching from 1223 K (ρ(T)) | 250 | 230 | 265 | 280 | 33 |
| Quenching from 1223 K (χ(T)) | 255 | 240 | 265 | 280 | 25 |
| HPT of 10 revs (1) | 320 | 300 | 400 | 440 | 110 |
| HPT of 10 revs (2) | - | - | 380 | 470 | - |
| Treatment of Alloy | Average Grain Size <dG>, nm |
|---|---|
| HPT, n = 10 revs | 30 |
| HPT + 373 K, 30 min | 30 |
| HPT + 473 K, 30 min | 30 |
| HPT + 573 K, 30 min | 100 |
| HPT + 673 K, 30 min | 150 |
| HPT + 773 K, 30 min | 350 |
| HPT + 873 K, 30 min | 400 |
| HPT + 1073 K, 10 s | 3500 |
| Temperature of Annealing, K | HV, GPa | |
|---|---|---|
| Quen. 1223 K; | Quen. 1273 K; | |
| - | 4.70 | 4.22 |
| Q + HPT, n=5 | Q + HPT, n = 5 | |
| - | 5.10 | 4.60 |
| 473 | 5.65 | 5.25 |
| 573 | 5.85 | 5.55 |
| 673 | 5.70 | 5.40 |
| 773 | 5.10 | 4.90 |
| 873 | 4.40 | 4.00 |
| T, K | 290 | 373 | 473 | 523 | 573 | 623 | 673 | 723 | 773 | 823 | 873 |
| HV, GPa | 5.0 | 5.5 | 5.13 | 5.33 | 5.58 | 5.9 | 6.1 | 5.93 | 5.55 | 5.03 | 4.02 |
| Treatment | σM, MPa | σu, MPa | ɛM, % | δ, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quenching from 1223 K | 160 | 620 | 2 | 7 |
| Quenching from 1273 K | 60 | 400 | 2 | 11 |
| HPT, 10 rev, (293 K) | - | 820 | - | 4 |
| HPT, 10 rev, (423 K) | - | 1450 | 2 | 12 |
| HPT 10 rev + 573 K, 30 min | 120 | 450 | 2 | 6 |
| HPT 10 rev + 773 K, 30 min | 50 | 320 | 3 | 8 |
| HPT 10 rev + 1073 K, 10 s | 250 | 900 | 5 | 13 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Svirid, A.E.; Pushin, V.G.; Kuranova, N.N.; Makarov, V.V.; Ustyugov, Y.M. Structural and Phase Transformations and Physical and Mechanical Properties of Cu-Al-Ni Shape Memory Alloys Subjected to Severe Plastic Deformation and Annealing. Materials 2021, 14, 4394. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14164394
Svirid AE, Pushin VG, Kuranova NN, Makarov VV, Ustyugov YM. Structural and Phase Transformations and Physical and Mechanical Properties of Cu-Al-Ni Shape Memory Alloys Subjected to Severe Plastic Deformation and Annealing. Materials. 2021; 14(16):4394. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14164394
Chicago/Turabian StyleSvirid, Alexey E., Vladimir G. Pushin, Natalia N. Kuranova, Vladimir V. Makarov, and Yuri M. Ustyugov. 2021. "Structural and Phase Transformations and Physical and Mechanical Properties of Cu-Al-Ni Shape Memory Alloys Subjected to Severe Plastic Deformation and Annealing" Materials 14, no. 16: 4394. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14164394
APA StyleSvirid, A. E., Pushin, V. G., Kuranova, N. N., Makarov, V. V., & Ustyugov, Y. M. (2021). Structural and Phase Transformations and Physical and Mechanical Properties of Cu-Al-Ni Shape Memory Alloys Subjected to Severe Plastic Deformation and Annealing. Materials, 14(16), 4394. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14164394






