Circulatory Management of Polymer Waste: Recycling into Fine Fibers and Their Applications
Abstract
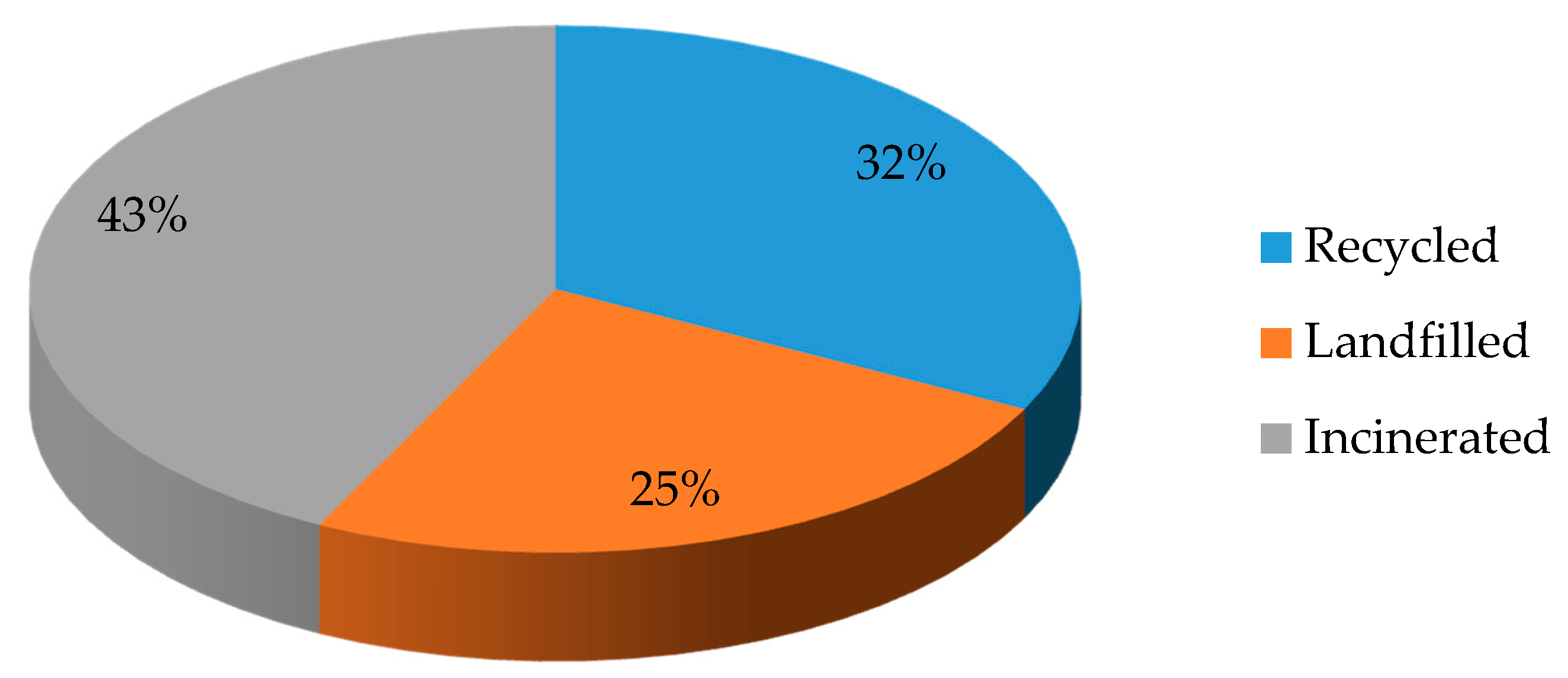
:1. Introduction
Motivation
2. Types of Polymeric Waste
3. Traditional Fiber Spinning
3.1. Direct Spinning of Recycled Plastics
3.2. Spinning of Blended Recycled and Virgin Polymers
3.3. Filler Reinforcement
4. Alternatives to Traditional Spinning Technologies
4.1. Electrospinning
4.2. Solution Blowing Spinning
4.3. Melt Spinning
4.4. Centrifugal Spinning
5. Applications of Fibers from Polymeric Waste
5.1. Filter Applications
5.2. Other Promising Applications
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hopewell, J.; Dvorak, R.; Kosior, E. Plastics recycling: Challenges and opportunities. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 27, 2115–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singhal, R.; Ishita, I.; Sow, P.K. Integrated polymer dissolution and solution blow spinning coupled with solvent recovery for expanded polystyrene recycling. J. Polym. Environ. 2019, 27, 1240–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plastics Europe. Plastics—The Facts 2019: An. Analysis of European Plastic Production, Demand and Waste Data for 2018; Association of Plastics Manufacturers: Brussels, Belgium, 2019; Available online: https://www.plasticseurope.org/en/resources/market-data (accessed on 10 July 2021).
- European Commission. Circular Economy. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/growth/industry/sustainability/circular-economy_sk (accessed on 10 July 2021).
- European Commision. Towards a Circular Economy: A Zero Waste Programme for Europe. Available online: http://www.sbagency.sk/en/the-future-belongs-to-the-circular-economy#.XzmF_egzZPY (accessed on 10 July 2021).
- Faraca, G.; Astrup, T. Plastic waste from recycling centres: Characterisation and evaluation of plastic recyclability. Waste Manag. 2019, 95, 388–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragaert, K.; Delva, L.; Geem, K.V. Mechanical and chemical recycling of solid plastic waste. Waste Manag. 2017, 69, 24–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, J.H.; Farmer, T.J.; Herrero-Davila, L.; Sherwood, J. Circular economy design considerations for research and process development in the chemical sciences. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 3914–3934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brachet, P.; Høydal, L.T.; Hinrichsen, E.L.; Melum, F. Modification of mechanical properties of recycled polypropylene from post-consumer containers. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 2456–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awoyera, P.O.; Adesina, A. Case study. Plastic wastes to construction products: Status limitations and future perspective. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2020, 12, e00330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigore, M.E. Methods of recycling, properties and applications of recycled thermoplastic polymers. Recycling 2017, 2, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shabunin, A.S.; Yudin, V.E.; Dobrovolskaya, I.P.; Zinovyev, E.V.; Zubov, V.; Ivankova, E.M.; Morganti, P. Composite wound dressing based on chitin/chitosan nanofibers: Processing and biomedical applications. Cosmetics 2019, 6, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, S.; Tuladhar, R.; Shi, F.; Shanks, R.A.; Combe, M.; Collister, T. Mechanical reprocessing of polyolefin waste: A review. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2015, 55, 2899–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zander, N.E.; Sweetser, D.; Cole, D.P.; Gillan, M. Formation of Nanofibers from Pure and Mixed Waste Streams Using Electrospinning. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 9057–9063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinchillas-Chinchillas, M.J.; Gaxiola, A.; Alvarado-Beltran, C.G.; Orozco-Carmona, V.M.; Pellegrini-Cervantes, M.J.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, M.; Castro-Beltran, A. A new application of recycled-PET/PAN composite nanofibers to cemente based materials. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 252, 119827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Zhou, H.; Wang, H. Electrospinning: An advanced nanofiber production technology. In Energy Harvesting Properties of Electrospun Nanofibers; Fang, J., Lin, T., Eds.; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2019; pp. 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunstroot, K.; Ziernicki, D.; Vanden Driessche, T. A study of black fleece garments: Can fleece fibres be recognized and how variable are they? Sci. Justice 2016, 56, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, S. If We Lose Our Snowcapped Mountains, How Will We Shered? Available online: https://www.nationalgeographic.com/science/2020/02/partner-content-evolution-of-recycled-fabrics/ (accessed on 10 July 2020).
- Statement on the Seventh Meeting of the International Health Regulations (2005) Emergency Committee Regarding the Coronavirus Deseade (COVID-19) Pandemic. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/19-04-2021-statement-on-the-seventh-meeting-of-the-international-health-regulations-(2005)-emergency-committee-regarding-the-coronavirus-disease-(covid-19)-pandemic (accessed on 20 June 2020).
- Opálková Šišková, A.; Frajová, J.; Nosko, M. Recycling of poly(ethylene terephthalate) by electrospinning to enhanced the filtration efficiency. Mat. Lett. 2020, 278, 128426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, S.S.; Oliveira, A.M.; Maia, A.; Zanin, M.H.A. Recycled PET nanofibers produced by electrospinning technique. Adv. Mater. Tech. Connect. Briefs 2020, 1, 335–338, ISBN 978-0-9975-1170-3M. [Google Scholar]
- Munir, M.M.; Nuryantini, A.Y.; skandar; Suciati, T.; Khairurrijal, K. Mass production of stacked Styrofoam nanofibers using a multinozzle and drum collector electrospinning system. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 896, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tshifularo, C.A.; Patnaik, A. Recycling of plastics into textile raw materials and products. In Sustainable Technologies for Fashion and Textiles; Nayak, N., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Textiles; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2020; pp. 311–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksen, M.K.; Christiansen, J.D.; Daugaard, A.E.; Astrup, T.F. Closing the loop for PET, PE and PP waste from households: Influence of material properties and product design for plastic recycling. Waste Manag. 2019, 96, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Izumi, T.; Yoshida, H.; Dilixiati, D.; Leeabai, N.; Suzuki, S.; Takahashi, F. The effect of recycling bin design on PET bottle collection performance. Waste Manag. 2019, 95, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryberg, M. , Laurent, A., Hauschild, M. Mapping of Global Plastics Value Chain and Plastics Losses to the Environment (with a Particular Focus on Marine Environment); United Nations Environment Programme: Nairobi, Kenya, 2018; Available online: http://wedocs.unep.org/bitstream/handle/20.500.11822/26745/mapping_plastics.pdf (accessed on 10 July 2020).
- Hanna, E.G. Recycling of waste mixed plastics blend (PE/PP). J. Eng. Sci. Technol. Rev. 2019, 12, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonakou, E.V.; Achilias, D.S. Recent advances in polycarbonate recycling: A review of degradation methods and their mechanisms. Waste Biomass Valori. 2013, 4, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, H.H.; Carlson, E.M.; Chua, J.P.; Belcher, S.M. Bisphenol A is releasing from polycarbonate drinking bottles and mimics the neurotoxic actions of estrogen in developing cerebellar neurons. Toxicol. Lett. 2008, 176, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zulfi, A.; Rezeki, Y.A.; Edikresnha, D.; Munir, M.M.; Khairurrijal, K. Synthesis of fibers and particles from polyvinyl chloride (PVC) waste using electrospinning. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 367, 012014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, W.; Walker, T.R.; Adams, M.; Zhao, J. How does the global plastic waste trade contribute to environmental benefits: Implication for reductions of greenhouse gas emissions? J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 287, 112283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piemonte, V.; Sabatini, S.; Gironi, F. Chemical recycling of PLA: A great opportunity towards the sustainable development. J. Polym. Environ. 2013, 21, 640–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Åkesson, D.; Vrignaud, T.; Tissot, C.; Skrifvars, M. Mechanical recycling of PLA filled with a high level of cellulose fibers. J. Polym. Environ. 2016, 24, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavanaie, M.A. Melt recycling of poly(lactic acid) plastic wastes to produce biodegradable fibers. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2014, 53, 742–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welker, C.M.; Balasubramanian, V.K.; Petti, C.; Rai, K.M.; DeBolt, S.; Mendu, V. Engineering Plant Biomass Lignin Content and Composition for Biofuels and Bioproducts. Energies 2015, 8, 7654–7676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, M.; Wang, F. Catalytic scissoring of lignin into aryl monomers. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1901866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Yu, B.; Xu, X.; Bourbigot, S.; Wang, H.; Song, P. Lignin-derived bio-based flame retardants toward high-performance sustainable polymeric materials. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 2129–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, C.; Westman, G. Direct Dissolution of Cellulose: Background, Means and Applications. In Cellulose, Fundamental Aspects; Van de Ven, T., Godbout, L., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2013; pp. 143–178. [Google Scholar]
- Kakoria, A.; Sinha-Ray, S. A review on biopolymer-based fibers via electrospinning and solution blowing and their applications. Fibers 2018, 6, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Burger, C.; Wan, F.; Zhang, J.; Rong, L.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B.; Cai, J.; Zhang, L. Structure study of cellulose fibers wet-spun from environmentally friendly NaOH/Urea aqueous solutions. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 1918–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, D.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, J.; Jin, H.; Chen, H. Structure and Properties of Novel Fibers Spun from Cellulose in NaOH/Thiourea Aqueous Solution. Macromol. Biosci. 2004, 4, 1105–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Burger, C.; Fang, D.; Ruan, D.; Zhang, L.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B. X-ray studies of regenerated cellulose fibers wet spun from cotton linter pulp in NaOH/Thiourea aqueous aolutions. Polymer 2006, 47, 2839–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinze, T.; Liebert, T. Unconventional methods in cellulose functionalization. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2001, 26, 1689–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, S.; Leipner, H.; Thümmler, K.; Brendler, E.; Peters, J. Inorganic molten salts as solvents for cellulose. Cellulose 2003, 10, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Striegel, A. Theory and aplications of DMAC/LiCl in the analysis of polysaccharides. Carbohydr. Polym. 1997, 34, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, P.R.; Brine, C.J.; Castle, J.E.; Zikakis, J.P. Chitin: New Facets of Research. Science 1981, 212, 749–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, C.L.; Callais, P.A. Derivatization of cellulose in lithium chloride and N-N-Dimethylacetamide solutions. Polymer 1987, 28, 2317–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swatloski, R.P.; Spear, S.K.; Holbrey, J.D.; Rogers, R.D. Dissolution of cellulose with ionic liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 4974–4975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemamalini, T.; Karunakaran, S.A.; Siva Elango, M.K.; Senthil Ram, T.; Giri Dev, V.R. Regeneration of cellulose acetate nanofibrous mat from discarded cigarette butts. Ind. J. Fibre Tex. Res. 2019, 44, 248–252. [Google Scholar]
- Dashtbani, R.; Afra, E. Producing cellulose nanofiber from cotton wastes by electrospinning method. Int. J. Nano Dimens. 2015, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jedvert, K.; Idström, A.; Köhnke, T.; Alkhagen, M. Cellulosic nonwovens produced via efficient solution blowing technique. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 48339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whetten, R.W.; MacKay, J.J.; Sederoff, R.R. Recent advances in understanding lignin biosynthesis. Annu. Rev. Plant. Physiol. Plant. Mol. Biol. 1998, 49, 585–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo-Flores, F.G.; Dobado, J.A. Lignin as Renewable Raw Material. Chem. Sus. Chem. 2010, 3, 1227–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurichesse, S.; Averous, L. Chemical modification of lignins: Towards biobased polymers. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 1266–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Yang, S.; Wang, X.L.; Yuan, T.Q.; Sun, R.C. Manufacture and application of lignin-based carbon fibers (LCFs) and lignin-based carbon nanofibers (LCNFs). Green Chem. 2017, 19, 1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barhoum, A.; Pal, K.; Rahier, H.; Uludag, H.; Kim, I.S.; Bechelany, M. Nanofibers as new-generation materials: From spinning and nano-spinning fabrication techniques to emerging applications. Appl. Mater. Today. 2019, 17, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mather, R.R.; Wardman, R.H. The Chemistry of Textile Fibres; The Royal Society of Chemistry, Thomas Graham House: Cambridge, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Pillay, V.; Dott, C.; Choonara, Y.E.; Tyagi, C.; Tomar, L.; Kumar, P.; du Toit, L.C.; Ndesendo, V.M.K. A review of the effect of processing variables on the fabrication of electrospun nanofibers for drug delivery applications. J. Nanomater. 2013, 22, 789289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shin, C.; Chase, G. Nanofibers from recycle waste expanded polystyrene using natural solvent. Polym. Bull. 2005, 55, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sow, P.K.; Ishita, I.; Singhal, R. Sustainable approach to recycle waste polystyrene to high-value submicron fibers using solution blow spinning and application towards oil-water separation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 102786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdi, M.; Mahar, F.K.; Qureshi, U.A.; Khatri, M.; Khatri, Z.; Ahmed, F.; Kim, I.S. Preparation of colored recycled polyethylene terephthalate nanofibers from waste bottles: Physicochemical studies. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2018, 37, 2820–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zander, N.E.; Gillan, M.; Sweetser, D. Recycled PET nanofibers for water filtration applications. Materials 2016, 9, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bhat, G.; Narayanan, V.; Wadsworth, L.; Dever, M. Conversion of recycled polymers fibers into melt-blown nonwovens. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. Polym. 1999, 38, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuladhar, R.; Yin, S. Production of recycled polypropylene (PP) fibers from industrial plastic waste through melt spinning process. In Use of Recycled Plastics in Eco-Efficient Concrete; Woodhead Publishing Series in Civil and Structural Engineering: Sawston, UK, 2019; pp. 70–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Lim, K.S.; Hahm, W.G.; Kim, S.H. Properties of recycled and virgin poly(ethylene terephthalate) blend fibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 128, 1250–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurudatt, K.; De, P.; Rakshit, A.K.; Bardhan, M.K. Spinning fibers from poly(ethylene terephthalate) bottle-grade waste. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 90, 3536–3545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, M.; Mojtahedi, M.R.M.; Khosroshahi, A.J. Effect of spinning speed on the structure and physical properties of filament yarns produced from used PET bottles. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 103, 3972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upasani, P.S.; Jain, A.K.; Save, N.; Agarwal, U.S.; Kelkar, A.K. Chemical recycling of PET flakes into yarn. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 123, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zander, N.E.; Gillan, M.; Sweetser, D. Composite fibers from recycled plastics using melt centrifugal spinning. Materials 2017, 10, 1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kayaisang, S.; Saikrasun, S.; Amornsakchai, T. Potential use of recycled PET in comparison with liquid crystalline polyester as a dual functional additive for enhancing heat stability and reinforcement for high density polyethylene composite fibres. J. Polym. Environ. 2013, 21, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telli, A.; Ozdil, N. Effect of recycled PET fibers on the performance properties of knitted fabrics. J. Eng. Fibr. Fabr. 2015, 10, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira Santos, R.P.; Castro, D.O.; Ruvolo-Filho, A.C.; Frolini, E. Processing and thermal properties of composite based on recycled PET, sisal fibers and renewable plasticizers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 40386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, W.S.; Asmatulu, R.; Davuluri, S.; Dandin, V.K. Improving the economic values of the recycled plastic using nanotechnology associated studie. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2014, 30, 854–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohammadkhani, F.; Montazer, M.; Latifi, M. Microwave absorption characterization and wettability of magnetic nano iron oxide/recycled PET nanofibers web. J. Text. Inst. 2019, 110, 989–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Saito, T.; Bhattacharya, P. Lignin-Derived Carbon Fibers. In Lignin in Polymer Composites; Faruk, O., Sain, M., Eds.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 207–216. [Google Scholar]
- Cayla, A.; Rault, F.; Giraud, S.; Salaün, F.; Fierro, V.; Celzard, A. PLA with intumescent system containing lignin and ammonium polyphosphate for flame retardant Textile. Polymers 2016, 8, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haider, A.; Haider, S.; Kang, I.K. A comprehensive review summarizing the effect of electrospinning parameters and potential applications of nanofibers in biomedical and biotechnology. Arab. J. Chem. 2018, 11, 1165–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubakir, M.M.; Li, H.; Barhoum, A.; Yang, W. Advances in melt electrospinning technique. In Handbook of Nanofibers; Barhoum, A., Bechelany, M., Makhlouf, A.H., Eds.; Springer Nature: Basingstoke, UK, 2018; pp. 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Haichao, L.; Li, H.; Bubakir, M.M.; Yang, W.; Barhoum, A. Engineering nanofibers as electrode and membrane materials for batteries, supercapacitors, and fuel cells. In Handbook of Nanofibers; Barhoum, A., Bechelany, M., Makhlouf, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, N.; Kundu, S.C. Electrospinning: A fascinating fiber fabrication technique. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 325–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teo, W.E.; Inai, R.; Ramakrishna, S. Technological advances in electrospinning of nanofibers. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2011, 12, 013002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Li, K.; Mohideen, M.M.; Ramakrishna, S. Melt Electrospinning: A green Method to Produce Superfine Fibers; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Esmaeili, E.; Deymeh, F.; Rounaghi, S.A. Synthesis and characterization of the Electrospun fibers prepared from waste polymeric materials. Int. J. Nano Dimens. 2017, 8, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, J.A.; Said, I.A.; Mohamed, M.A.; Yasin, S.A.; Ali, Z.A.; Ahmed, I.H. Electrospining of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) nanofibers: Optimization study using taguchi design of experiment. IOP Conf. Series Mat. Sci. Eng. 2018, 454, 012130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.O.; Youk, J.H.; Min, K.D.; Kang, Y.O.; Park, W. Electrosppinnin of cellulose acetate nanofibers using a mixed solvent of acetic acid/water: Effect of solvent composition on the fiber diameter. Mat. Lett. 2008, 62, 759–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lallave, M.; Bedia, J.; Ruiz-Rosas, R.; Rodriguez-Mirasol, J.; Cordero, T.; Otero, J.C.; Marquez, M.; Barrero, A.; Loscertales, I.G. Filled and hollow carbon nanofibers by coaxial electrospinning of alcell lignin without binder polymers. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 4292–4296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naksuwan, P.; Komárek, M.; Salačová, J.; Militký, J. The study of recycled poly(ethyeĺene terephthalate) nanofibers from PET bottle. Appl. Mech. Mat. 2016, 848, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, X.; Yang, X.; Shi, L.; Cheng, B.; Guan, K.; Kang, W. Solution blowing of submicron-scale cellulose fibers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 90, 982–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daristotle, J.L.; Behrens, A.M.; Sandler, A.D.; Kofinas, P. A review of the fundamental principles and applications of solution blow spinning. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 34951–34963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kenry; Lim, C.T. Nanofiber technology: Current status and emerging developments. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2017, 70, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutak, W.; Sarkar, S.; Lin-Gibson, S.; Farooque, T.M.; Jyotsnendu, G.; Wang, D.; Kohn, J.; Bolikal, D.; Simon, C.G., Jr. The support of bone marrow stromal cell differentiation by airbrushed nanofiber scaffolds. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 2389–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Keynton, R.S. Fabrication and characterization of biopolymer fibers for 3D oriented microvascular structures. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2019, 29, 083003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.M.; Duan, Y.S.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, B. A review on nanofiber fabrication with the effect of high-speed centrifugal force field. J. Eng. Fibers Fabr. 2019, 14, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Charuchinda, A.; Molloy, R.; Siripitayananon, J.; Molloya, N.; Sriyai, M. Factors influencing the small-scale melt spinning of poly (ε-caprolactone) monofilament fibres. Polym. Int. 2003, 52, 1175–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Qi, Y.; Pu, C.; Wang, Q.; Jia, Z.; Xiao, C. Preparation and properties of bottle-recycled polyethylene terephthalate (PET) filaments. Tex. Res. J. 2018, 89, 1207–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, M.; Mojtahedi, M.R.M.; Kotek, R. Effect of melt spinning variables on the structure changes of recycled and bottle grade filament yarn PET. J. Text. Polym. 2018, 6, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishal, H.; Tavanaie, M.A.; Mahmudi, A.G. Biodegradability modification of synthetic polyamide 6 fibers via in-situ melt blending with recycled poly(lactic) acid plastic food container flakes during the melt spinning process. Modares J. Biotechnol. 2018, 9, 69–78. [Google Scholar]
- Tavanaie, M.A.; Mahmudi, A. Green engineered polypropylene biodegradable fibers through blending with recycled poly(lactic) acid plastic waste. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2014, 53, 1506–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soekoco, A.S.; Noerat; Komalasari, M.; Kurniawan; Hananto, A. Characterization of eco-friendly polyethylene fiber from plastic bag waste. AIP Conf. Proc. 2017, 1868, 020003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weitz, R.T.; Harnau, L.; Rauschenbach, S.; Burghard, M.; Kern, K. Polymer nanofibers via nozzle-free centrifugal spinning. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 1187–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Lu, Y. Centrifugal spinning: An alternative approach to fabricate nanofibers at high speed and low cost. Polym. Rev. 2014, 54, 677–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, P.P.; Doan, H.N.; Kinashi, K.; Sakai, W.; Tsutsumi, N.; Huynh, D.R. Centrifugally spun recycled PET Processing and characterization. Polymers 2018, 10, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saleem, H.; Trabzon, L.; Kilic, A.; Zaidi, S.J. Recent advances in nanofibrous membranes: Production and applications in water treatment and desalination. Desalination 2020, 478, 114178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Reis Paganotto, G.F.; Duarte de Barros, G.; Marques, V.G.; Takimi, A.S. Production of recycled EPS fibers by centrifugal spinning. Rev. Matéria 2021, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamrani, H.; Nosrati, A. Fabrication of nanofiber filtration membranes using polyethylene terephthalate (PET): A review. J. Membr. Sci. Technol. 2018, 8, 1000183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabinejad, H.; Khajavi, R.; Rashidi, A.; Mansouri, N.; Yazdanshenas, M.E. Recycling of used bottle grade poly ethyleneterephthalate to nanofibers by melt-electrospinning method. Int. J. Enviton. Res. 2009, 3, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasin, S.A.; Zeebaree, S.Y.S.; Zeebaree, A.Y.S.; Zebari, O.I.H.; Saeed, I.A. The efficient removal of methylene blue dye using CuO/PET nanocomposite in aqueous solutions. Catalysts 2021, 11, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grumezescu, A.M.; Stoica, A.E.; Balcescu, M.S.D.; Chircov, C.; Gharbia, S.; Balta, C.; Rosu, M.; Herman, H.; Holban, A.M.; Ficai, A.; et al. Electrospun polyethylene terephthalate nanofibers loaded with silver nanoparticles: Novel approach in anti-infective therapy. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rajak, A.; Hapidin, D.A.; Iskandar, F.; Munir, M.; Khairurrijal, K. Controlled morphology of electrospun nanofibers from waste expanded polystyrene for aerosol filtration. Nanotechnology 2019, 30, 425602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Hsu, P.C.; Lee, H.W.; Ye, M.; Zheng, G.; Liu, N.; Li, W.; Cui, Y. Transparent air filter for high-efficiency PM2.5 capture. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, R.; Liu, C.; Hsu, P.C.; Zhang, C.F.; Liu, N.; Zhang, J.S.; Lee, H.R.; Lu, Y.Y.; Qiu, Y.C.; Chu, S.; et al. Nanofiber air filters with high-temperature stability for efficient PM2.5 removal from the pollution sources. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 3642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, C.; Chase, G.G.; Reneker, D.H. Recycled expanded polystyrene nanofibers applied in filter media. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2005, 262, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, C. Filtration application from recycled expanded polystyrene. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2006, 302, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzatzedeh, E.; Langroudi, M.; Sheshdeh, F.J. Synthesis of magnetic iron-oxide nanofiber composite using electrospinning: An absorbent for removal of nitrate from aqueous solution. J. Appl. Chem. Res. 2017, 11, 46–59. [Google Scholar]
- Pulido, B.A.; Habboub, O.S.; Aristizabal, S.L.; Szekely, G.; Nunes, S.P. Recycled poly (ethylene terephthalate) for high temperature solvent resistant membranes. ACS Appl. Polym. Mat. 2019, 1, 2379–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strain, I.N.; Wu, Q.; Pourrahimi, A.M.; Hedenquvist, M.S.; Olsson, R.T.; Andersson, R.L. Electrospinning of recycled PET to generate tough mesomorphic fibre membranes for smoke filtration. J. Mat. Chem. A 2015, 3, 1632–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Opálková Šišková, A.; Mosnáčková, K.; Hrůza, J.; Frajová, J.; Opálek, A.; Bučková, M.; Kozics, K.; Peer, P.; Eckstein Andicsová, A. Electrospun poly(ethylene terephthalate/silk fibroin composite for filtration application. Polymers 2021, 13, 2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonfim, D.P.F.; Cruz, F.G.S.; Bretas, R.E.S.; Guerra, V.G.; Aguiar, M.L. A sstainable recycling alternative: Electrospun PET-membranes for air nanofiltration. Polymers 2021, 13, 1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attia, A.A.M.; Abas, K.M.; Nada, A.A.A.; Shouman, M.A.H.; Opálková Šišková, A.; Mosnáček, J. Fabrication, modification, and characterization of lignin-based electrospun fibers ferived from distinctive biomass sources. Polymers 2021, 13, 2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhm, R.; Thieme, M.; Wohlfahrt, D.; Wolz, D.S.; Richter, B.; Jäger, H. Reinforcement systems for carbon concrete composites based on low-cost carbon fibers. Fibers 2018, 6, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rajak, A.; Munir, M.M.; Abdullah, M.; Khairurrijal, K. Photocatalytic activities of Electrospun TiO2/Styrofoam composite nanofiber membrane in degradation of waste water. Mater. Sci. Forum 2015, 827, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datsyuk, V.; Trotsenko, S.; Peikert, K.; Hoeflich, K.; Wedel, N.; Allar, C.; Sick, T.; Deinhart, V.; Reich, S.; Krcmar, W. Polystyrene nanofibers for nonwoven porous building insulation materials. Eng. Rep. 2019, 1, e12037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Textiles in Europe’s Circular Economy. 2019. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/textiles-in-europes-circular-economy (accessed on 4 August 2021).
- Lebreton, L.; Andrady, A. Future scenarios of global plastic waste generation and disposal. Palgrave Commun. 2019, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shanks, R. 5-Recycled synthetic polymer fibers in composites. In Woodhead Publishing Series in Composites Science and Engineering, Green Composites, 2nd ed.; Baillie, C., Jayasinghe, R., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2017; pp. 73–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveux, G.; Dandy, L.O.; Leeke, G.A. Current status of recycling of fibre reinforced polymers: Review of technologies, reuse and resulting properties. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2015, 72, 61–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muzzy, J. Composite products from post-consumer carpet. In Recycling in Textiles; Wang, Y., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2006; pp. 203–212. [Google Scholar]
- Hollaway, L.C. A review of the present and future utilisation of FRP composites in the civil infrastructure with reference to their important in-service properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 24, 2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiliński, D.; Łukowski, P.; Rokicki, G. Application of fibres from recycled PET bottles for concrete reinforcement. J. Build. Chem. 2016, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Directive 2008/98/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 19 November 2008 on Waste and Repealing Certain Directives. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/dir/2008/98/2018-07-05 (accessed on 3 August 2021).
- Ritchie, H.; Roser, M. Plastic Pollution. 2018. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/plastic-pollution (accessed on 3 August 2020).







| Type of Spinning | Advantages | Disadvantages | Literature | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Melt spinning | Dry spinning |
|
| [92] |
| Solution spinning | Dry spinning (evaporation of solvent) |
|
| [58] |
| Wet spinning (coagulation in a suitable liquid) | ||||
Electrospinning
| Solution |
|
| [79,80,81,82] |
| Melt |
| Difficulty in melting | ||
| Solution blowing electrospinning | Polymer solution and pressurized gas |
| Inferior mechanical properties of the fibers | [89,90,91] |
| Centrifugal spinning | With heated spinneret that uses polymer melts |
| Complicated control system for heating devices | [93,100,103] |
| With spinneret that uses polymer solution | [101,102] | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Šišková, A.O.; Peer, P.; Andicsová, A.E.; Jordanov, I.; Rychter, P. Circulatory Management of Polymer Waste: Recycling into Fine Fibers and Their Applications. Materials 2021, 14, 4694. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14164694
Šišková AO, Peer P, Andicsová AE, Jordanov I, Rychter P. Circulatory Management of Polymer Waste: Recycling into Fine Fibers and Their Applications. Materials. 2021; 14(16):4694. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14164694
Chicago/Turabian StyleŠišková, Alena Opálková, Petra Peer, Anita Eckstein Andicsová, Igor Jordanov, and Piotr Rychter. 2021. "Circulatory Management of Polymer Waste: Recycling into Fine Fibers and Their Applications" Materials 14, no. 16: 4694. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14164694










