Clays as Inhibitors of Polyurethane Foams’ Flammability
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Polyurethanes—Production and Market Size
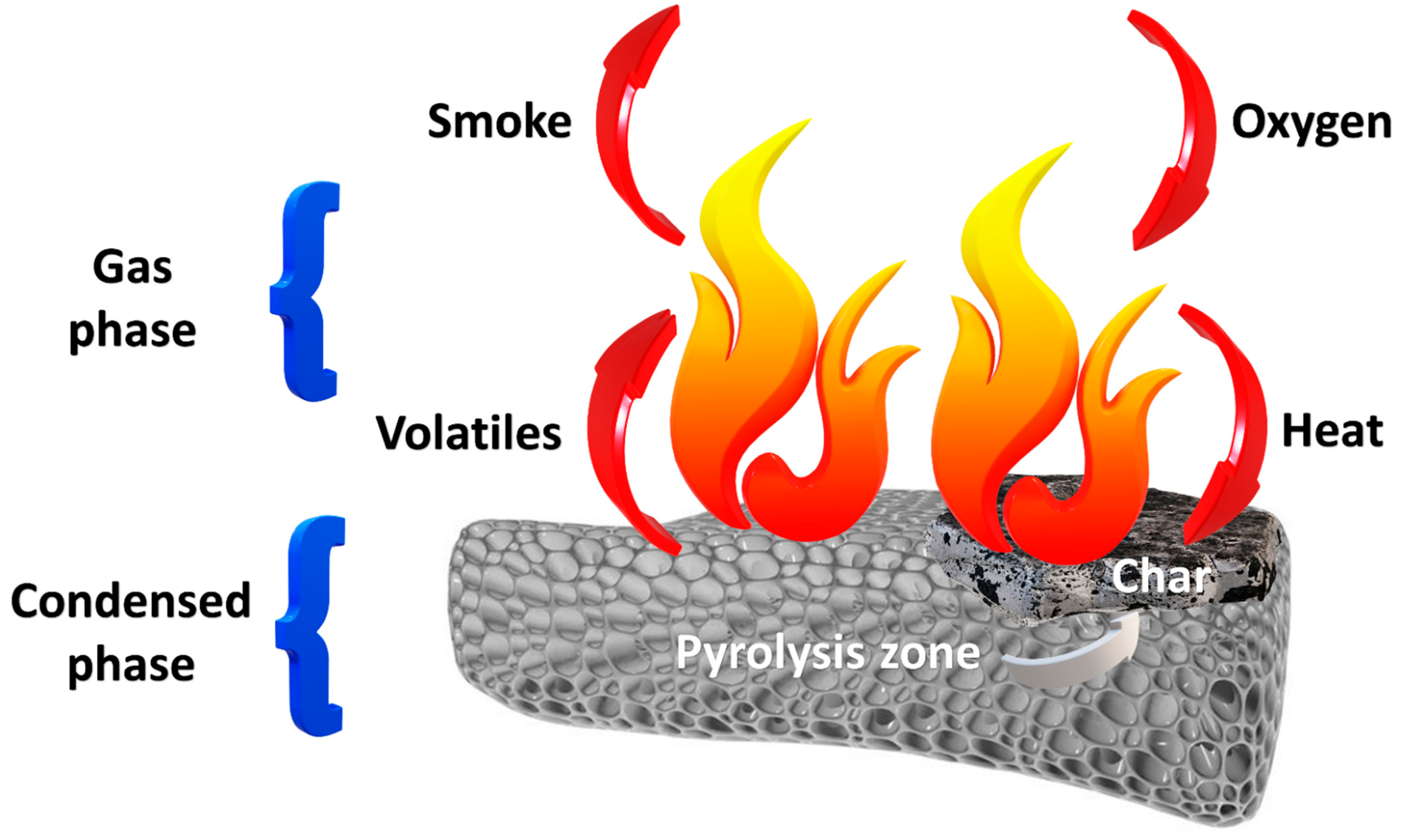
3. Polyurethanes—Flammability
3.1. General Information
3.2. Flame Retardancy of Polyurethanes
3.2.1. Mechanisms of Action of Flame Retardants
Chemical Mechanism
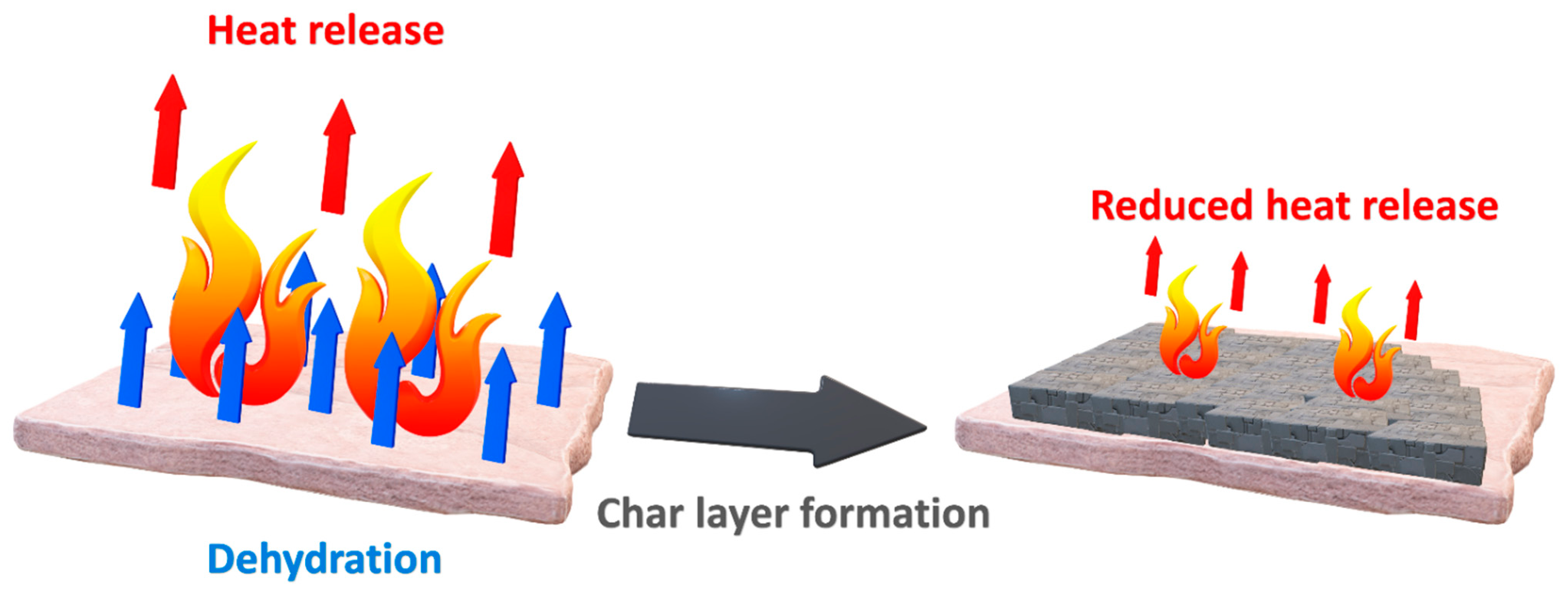
Physical Mechanism
3.3. Classification of Flame Retardants for Polyurethanes
3.3.1. Nitrogen-Based Flame Retardants
3.3.2. Phosphorus-Based Flame Retardants
3.3.3. Inorganic Flame Retardants
3.3.4. Expandable Graphite
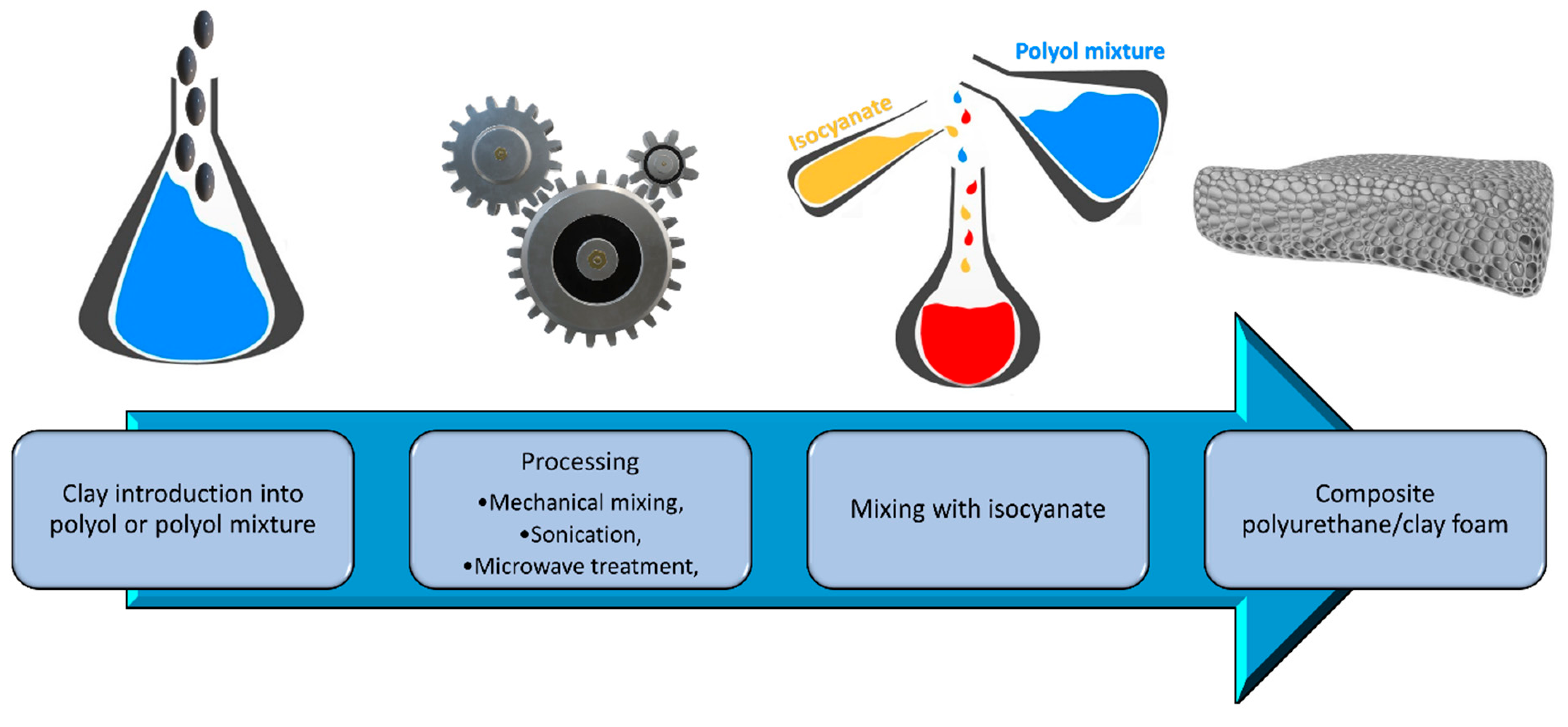
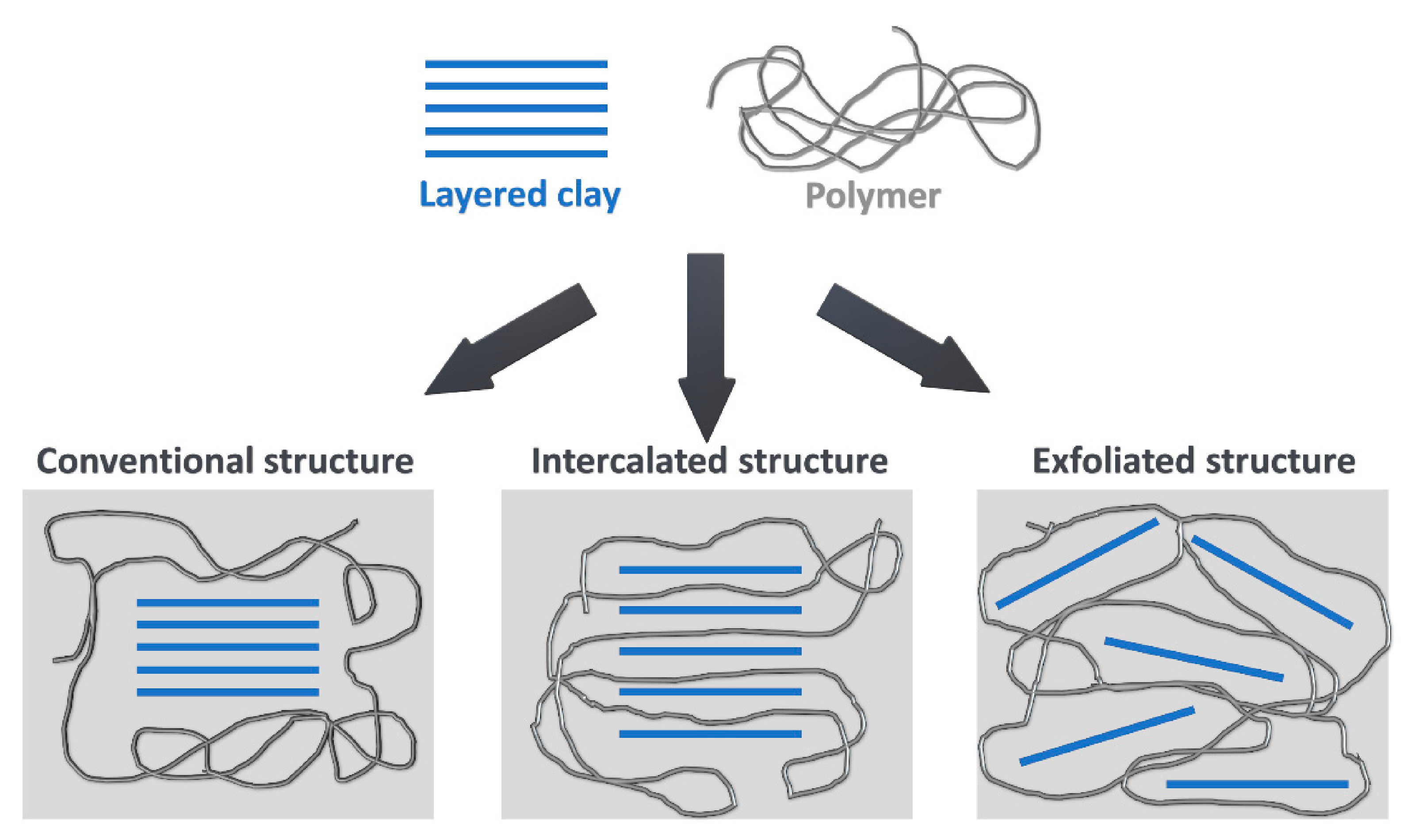
3.3.5. Clays
4. Reduction of Polyurethane Foams’ Flammability by Clays
4.1. Impact on Thermal Decomposition Onset
4.2. Impact on Limiting Oxygen Index
4.3. Impact on the Results of Combustion Tests
4.4. Impact on the Cone Calorimetry Results
5. Clay-Based Coatings for Polyurethane Foams
6. Conclusions
- a better understanding of the synergy effects between clays and flame retardants, especially novel types of halogen-free, and possibly bio-based ones;
- chemical modifications of clays, which would enhance their flame retardancy activity;
- possible applications of clays as precursors for manufacturing of flame retardants and flame-retardant polyols;
- modifications of clays, which, except for the flame retardancy, could provide other properties to foams, e.g., electrical conductivity;
- the flammability of polyurethane/clay composites based on the novel, green raw materials;
- the manufacturing of fully bio-based clay coatings without the use of additional synthetic compounds;
- simplification of the coating process;
- development of multi-purpose coatings, which could combine flame retardancy with other benefits for foams; and
- evaluation of the novel techniques for coating polyurethane foams.
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| APP | ammonium polyphosphate |
| ATH | aluminum hydroxide |
| CASE | coatings, adhesives, sealants, and elastomers |
| EHC | effective heat of combustion |
| HRR | heat-release rate |
| LbL | layer-by-layer assembly |
| LDH | layered double hydroxide |
| LOI | limiting oxygen index |
| MDH | magnesium hydroxide |
| MMT | montmorillonite |
| PA | polyamide |
| PAA | poly(acrylic acid) |
| PEI | polyethyleneimine |
| PET | poly(ethylene terephthalate) |
| pHRR | peak value of heat-release rate |
| PP | polypropylene |
| PUR | polyurethane |
| PVC | poly(vinyl chloride) |
| SPB | sodium polyborate |
| SPR | smoke production rate |
| TDI | p-toluyleneisocyanate |
| THR | total heat released |
| TSR | total smoke released |
| VMT | vermiculite |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
References
- Hejna, A.; Haponiuk, J.; Piszczyk, Ł.; Klein, M.; Formela, K. Performance properties of rigid polyurethane-polyisocyanurate/brewers’ spent grain foamed composites as function of isocyanate index. e-Polymers 2017, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asensio, M.; Costa, V.; Nohales, A.; Bianchi, O.; Gómez, C.M. Tunable Structure and Properties of Segmented Thermoplastic Polyurethanes as a Function of Flexible Segment. Polymers 2019, 11, 1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swinarew, B. Poliuretany—Nowoczesne wszechstronne materiały. Część II—Pianki poliuretanowe. Przetw. Tworzyw 2015, 5, 428–434. [Google Scholar]
- Papiński, J.; Żabski, L. Zrozumieć poliuretany. Mater. Bud. 2011, 1, 57–58. [Google Scholar]
- Piszczyk, Ł.; Hejna, A.; Formela, K.; Danowska, M.; Strankowski, M. Effect of ground tire rubber on structural, mechanical and thermal properties of flexible polyurethane foams. Iran. Polym. J. 2014, 24, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piszczyk, Ł.; Hejna, A.; Danowska, M.; Strankowski, M.; Formela, K. Polyurethane/ground tire rubber composite foams based on polyglycerol: Processing, mechanical and thermal properties. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2015, 34, 708–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmela, P.; Olszewski, A.; Zedler, Ł.; Burger, P.; Piasecki, A.; Formela, K.; Hejna, A. Ground Tire Rubber Filled Flexible Polyurethane Foam—Effect of Waste Rubber Treatment on Composite Performance. Materials 2021, 14, 3807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Formela, K.; Hejna, A.; Zedler, Ł.; Przybysz, M.; Ryl, J.; Saeb, M.R.; Piszczyk, Ł. Structural, thermal and physico-mechanical properties of polyurethane/brewers’ spent grain composite foams modified with ground tire rubber. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2017, 108, 844–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmela, P.; Olszewski, A.; Zedler, Ł.; Burger, P.; Formela, K.; Hejna, A. Structural Changes and Their Implications in Foamed Flexible Polyurethane Composites Filled with Rapeseed Oil-Treated Ground Tire Rubber. J. Compos. Sci. 2021, 5, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piszczyk, Ł.; Hejna, A.; Formela, K.; Danowska, M.; Strankowski, M. Rigid Polyurethane Foams Modified with Ground Tire Rubber—Mechanical, Morphological and Thermal Studies. Cell. Polym. 2015, 34, 45–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ograniczanie Zużycia Energii i Emisji. Available online: http://sipur.pl/rola_izolacji/oszczednosc_energii/ (accessed on 28 July 2021).
- Wang, Y.; Kuckelkorn, J.; Zhao, F.Y.; Spliethoff, H.; Lang, W. A state of art of review on interactions between energy performance and indoor environment quality in Passive House buildings. Renew Sust. Energ. Rev. 2017, 72, 1303–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pianka Poliuretanowa—Wszechstronny Materiał Izolacyjny. Available online: http://www.eko-pur.pl/pianka-poliuretanowa.htm (accessed on 28 July 2021).
- Kurańska, M.; Prociak, A. Właściwości termoizolacyjne i mechaniczne spienionych kompozytów poliuretanowych z włóknami konopnymi. Chemik 2011, 65, 1055–1058. [Google Scholar]
- Charbonnet, J.A.; Weber, R.; Blum, A. Flammability standards for furniture, building insulation and electronics: Benefit and risk. Emerg. Contamin. 2020, 6, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Code of Federal Regulations. Title 16. Chapter II. Subchapter D. Part 1640. Available online: Ecfr.federalregister.gov/current/title-16/chapter-II/subchapter-D/part-1640 (accessed on 20 August 2021).
- Fire Safety of Furniture and Furnishings in the Home. A Guide to the UK Regulations. Available online: www.fira.co.uk/images/FIRA-Flammability-Guide.pdf (accessed on 20 August 2021).
- 94/611/EC: Commission Decision of 9 September 1994 Implementing Article 20 of Directive 89/106/EEC on Construction Products. Available online: Op.europa.eu/en/publication-detail/-/publication/094eb631-2480-4454-a945-c9c3f22f19d4/language-en (accessed on 20 August 2021).
- 2000/147/EC: Commission Decision of 8 February 2000 Implementing Council Directive 89/106/EEC as Regards the Classification of the Reaction to Fire Performance of Construction Products. Available online: Eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A32000D0147 (accessed on 20 August 2021).
- Stockholm Convention. The Convention. Overview. Text of Convention. Available online: http://www.pops.int/TheConvention/Overview/TextoftheConvention/tabid/2232/Default.aspx (accessed on 20 August 2021).
- Basel Convention. The Convention. Overview. Text of Convention. Available online: http://www.basel.int/TheConvention/Overview/TextoftheConvention/tabid/1275/Default.aspx (accessed on 20 August 2021).
- Wang, N.; Chen, S.; Li, L.; Bai, Z.; Guo, J.; Qin, J.; Chen, X.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, K.; Wu, H. An Environmentally Friendly Nanohybrid Flame Retardant with Outstanding Flame-Retardant Efficiency for Polypropylene. J. Phys. Chem. C 2021, 125, 5185–5196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, L.H.; Nguyen, H.D.; Kim, J.; Hoang, D.Q. Thermal Properties and Fire Retardancy of Polypropylene/Wood Flour Composites Containing Eco-friendly Flame Retardants. Fibers Polym. 2019, 20, 2383–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, P.; Liang, M.; Ma, X.; Luo, Y.; He, M.; Gu, X.; Hussain, I.; Luo, Z. Highly Efficient, Environmentally Friendly Lignin-Based Flame Retardant Used in Epoxy Resin. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 32084–32093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chattopadhyay, D.K.; Webster, D.C. Thermal stability and flame retardancy of polyurethanes. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2009, 34, 1068–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiliaris, P.; Papaspyrides, C.D. Polymer/layered silicate (clay) nanocomposites: An overview of flame retardancy. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2010, 35, 902–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levchik, S.V.; Edward, D.W. Thermal decomposition, combustion and fire-retardancy of polyurethanes—A review of the recent literature. Polym. Int. 2004, 53, 1585–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Jain, A.K. Ignition, combustion, toxicity, and fire retardancy of polyurethane foams: A comprehensive review. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 111, 1115–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annual Production of Plastics Worldwide from 1950 to 2020. Available online: www.statista.com/statistics/282732/global-production-of-plastics-since-1950/ (accessed on 28 July 2021).
- Plastics—The Facts 2019. Available online: www.plasticseurope.org/application/files/9715/7129/9584/FINAL_web_version_Plastics_the_facts2019_14102019.pdf (accessed on 28 July 2021).
- Korol, J.; Hejna, A.; Burchart-Korol, D.; Chmielnicki, B.; Wypiór, K. Water Footprint Assessment of Selected Polymers, Polymer Blends, Composites, and Biocomposites for Industrial Application. Polymers 2019, 11, 1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plastics—The Facts 2015. Available online: www.plasticseurope.org/application/files/3715/1689/8308/2015plastics_the_facts_14122015.pdf (accessed on 28 July 2021).
- Plastics—The Facts 2016. Available online: www.plasticseurope.org/application/files/4315/1310/4805/plastic-the-fact-2016.pdf (accessed on 28 July 2021).
- Plastics—The Facts 2018. Available online: www.plasticseurope.org/application/files/6315/4510/9658/Plastics_the_facts_2018_AF_web.pdf (accessed on 28 July 2021).
- Polyurethane Chemicals and Products in Asia Pacific (APAC) 2021. Available online: http://www.ialconsultants.com/uploads/CUBE_press_release/2021-04-13/Polyurethane_APAC_Press_Release_2021.pdf (accessed on 28 July 2021).
- Shifting Production in CASE Market Highlighted at Conference. Available online: http://utech-polyurethane.com/information/shifting-production-in-case-market-highlighted-at-conferencecase/ (accessed on 28 July 2021).
- Polyurethane Chemicals and Products in Europe, Middle East & Africa (EMEA). 2018. Available online: http://www.ialconsultants.com/uploads/CUBE_press_release/2018-09-10/polyurethane_EMEA_press_release_18_KTedit.pdf (accessed on 28 July 2021).
- What Is Polyurethane? Available online: www.polyurethanes.org/en/what-is-it/ (accessed on 28 July 2021).
- Global PP Foams Market Growing at CAGR of 11%, PU Foams Market at CAGR of 6.9% from 2013 to 2018. Available online: http://www.plastemart.com/Plastic-Technical-Article.asp?LiteratureID=2070&Paper=global-Polypropylene-polyurethane-PP-PUFoams-market-2013-to-2018 (accessed on 28 July 2021).
- Polyurethane Demand Worldwide from 2012 to 2024. Available online: www.statista.com/statistics/747004/polyurethane-demand-worldwide/ (accessed on 28 July 2021).
- Polyurethane Market—Growth, Trends, Covid-19 Impact, and Forecasts (2021–2026). Available online: www.mordorintelligence.com/industry-reports/polyurethane-market/ (accessed on 28 July 2021).
- Paciorek-Sadowska, J.; Czupryński, B.; Liszkowska, J.; Kotarska, K. Ogniobezpieczne tworzywa poliuretanowe modyfikowane nowym antypirenem—Wykorzystanie nowych metod badania palności. Inż. Ap. Chem. 2012, 51, 58–60. [Google Scholar]
- Dobrzyńska, R. The toxicity of products of thermal decomposition and combustion of polyurethane foams used in manufacturing of upholstered furniture. Safety Fire Tech. 2012, 4, 53–58. [Google Scholar]
- Tabian, D.; Drochioiu, G.; Damian, S.I.; Girlescu, N.; Toma Gradinaru, O.; Toma, S.I.; Bulgaru Iliescu, D. Toxic Blood Hydrogen Cyanide Concentration as a Vital Sign of a Deceased Room Fire Victim—Case Report. Toxics 2021, 9, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Hu, X.; He, Z.; Wu, J. Experimental Study on the Combustion and Microexplosion of Freely Falling Gelled Unsymmetrical Dimethylhydrazine (UDMH) Fuel Droplets. Energies 2012, 5, 3126–3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagiotou, T.; Levendis, Y. Observations on the Combustion of Polymers (Plastics): From Single Particles to Groups of Particles. Combust. Sci. Technol. 1998, 137, 121–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, W.R.; Stenzel, M.T.; Song, X.; Schmidt, L.D. Bifurcation behavior in homogeneous-heterogeneous combustion: I. Experimental results over platinum. Combust. Flame 1991, 84, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Hamerton, I. Recent developments in the chemistry of halogen-free flame retardant polymers. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2002, 27, 1661–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Ye, J.; Zhu, L.; Jin, Z.; Matsumoto, Y. Intumescent Flame Retardant Mechanism of Lignosulfonate as a Char Forming Agent in Rigid Polyurethane Foam. Polymers 2021, 13, 1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, J. Mechanisms for flame retardancy and smoke suppression—A review. J. Fire Sci. 1996, 14, 426–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schartel, B. Phosphorus-based Flame Retardancy Mechanisms—Old Hat or a Starting Point for Future Development? Materials 2010, 3, 4710–4745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hejna, A.; Olszewski, A.; Zedler, Ł.; Kosmela, P.; Formela, K. The Impact of Ground Tire Rubber Oxidation with H2O2 and KMnO4 on the Structure and Performance of Flexible Polyurethane/Ground Tire Rubber Composite Foams. Materials 2021, 14, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurańska, M.; Beneš, H.; Sałasińska, K.; Prociak, A.; Malewska, E.; Polaczek, K. Development and Characterization of “Green Open-Cell Polyurethane Foams” with Reduced Flammability. Materials 2020, 13, 5459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Berto, F.; Zhang, D. Pyrolysis Kinetics and Flammability Evaluation of Rigid Polyurethane with Different Isocyanate Content. Molecules 2021, 26, 2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korol, J.; Hejna, A.; Burchart-Korol, D.; Wachowicz, J. Comparative Analysis of Carbon, Ecological, and Water Footprints of Polypropylene-Based Composites Filled with Cotton, Jute and Kenaf Fibers. Materials 2020, 13, 3541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idumah, C.I.; Hassan, A.; Affam, A.C. A review of recent developments in flammability of polymer nanocomposites. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2015, 31, 149–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, L.A.; Arado, M.G.; Giannuzzi, L.; Mastrantonio, G.; Guatelli, M.A. Hydrogen cyanide and carbon monoxide in blood of convicted dead in a polyurethane combustion: A proposition for the data analysis. Foren. Sci Int. 2001, 121, 140–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salasinska, K.; Borucka, M.; Leszczyńska, M.; Zatorski, W.; Celiński, M.; Gajek, A.; Ryszkowska, J. Analysis of flammability and smoke emission of rigid polyurethane foams modified with nanoparticles and halogen-free fire retardants. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2017, 130, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lefebvre, J.; Bastin, B.; Le Bras, M.; Duquesne, S.; Paleja, R.; Delobel, R. Thermal stability and fire properties of conventional flexible polyurethane foam formulations. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2005, 88, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, J.; Le Bras, M.; Bastin, B.; Paleja, R.; Delobel, R. Flexible Polyurethane Foams: Flammability. J. Fire Sci. 2003, 21, 343–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, M.; Matuschek, G.; Kettrup, A. Thermal degradation of thermoplastic polyurethane elastomers (TPU) based on MDI. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2002, 78, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, D.; Daly, J.; Liggat, J.J. Thermal volatilisation analysis of TDI-based flexible polyurethane foam. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2013, 98, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.Q.; Chow, W.K. A brief review on fire retardants for polymeric foams. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2005, 97, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, M. Carbon Monoxide Poisoning. J. Emerg. Nurs. 2008, 34, 538–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carbon Dioxide as a Fire Suppressant: Examining the Risks. Available online: www.epa.gov/snap/carbon-dioxide-fire-suppressant-examining-risks (accessed on 28 July 2021).
- National Research Council. Acute Exposure Guideline Levels for Selected Airborne Chemicals: Volume 2; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Research Council. Acute Exposure Guideline Levels for Selected Airborne Chemicals: Volume 11; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammonia. Toxicological Overview. Available online: Assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/455704/Ammonia_TO_PHE_240815.pdf (accessed on 28 July 2021).
- Benzene. Toxicological Overview. Available online: Assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/337516/hpa_benzene_toxicological_overview_v2.pdf (accessed on 28 July 2021).
- Yang, R.; Wang, B.; Han, X.; Ma, B.; Li, J. Synthesis and characterization of flame retardant rigid polyurethane foam based on a reactive flame retardant containing phosphazene and cyclophosphonate. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2017, 144, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Stoliarov, S.I.; Kraemer, R.H. Development of a Semiglobal Reaction Mechanism for the Thermal Decomposition of a Polymer Containing Reactive Flame Retardants: Application to Glass-Fiber-Reinforced Polybutylene Terephthalate Blended with Aluminum Diethyl Phosphinate and Melamine Polyphosphate. Polymers 2018, 10, 1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yanagisawa, H.; Kudo, Y.; Nakagawa, K.; Miyagawa, H.; Maruyama, F.; Fujimaki, S. Simultaneous Screening of Major Flame Retardants and Plasticizers in Polymer Materials Using Pyrolyzer/Thermal Desorption Gas Chromatography Mass Spectrometry (Py/TD–GC–MS). Molecules 2018, 23, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Covaci, A.; Harrad, S.; Abdallah, M.A.E.; Ali, N.; Law, R.J.; Herzke, D.; de Wit, C.A. Novel brominated flame retardants: A review of their analysis, environmental fate and behaviour. Environ. Int. 2011, 37, 532–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villamil Watson, D.A.; Schiraldi, D.A. Biomolecules as Flame Retardant Additives for Polymers: A Review. Polymers 2020, 12, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ubowska, A. Montmorillonite as a polyurethane foams flame retardant. Arch. Combust. 2010, 30, 459–462. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.L.; Zhang, F.H.; Jian, R.K.; Ai, Y.F.; Ma, J.L.; Hui, G.J.; Wang, D.Y. Influence of eco-friendly calcium gluconate on the intumescent flame-retardant epoxy resin: Flame retardancy, smoke suppression and mechanical properties. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2019, 176, 107200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostashari, S.M.; Nia, Y.K.; Fayyaz, F. Thermogravimetry of deposited caustic soda used as a flame-retardant for cotton fabric. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2007, 91, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visakh, P.M.; Semkin, A.O.; Rezaev, I.A.; Fateev, A.V. Review on soft polyurethane flame retardant. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 227, 116673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Zhao, Y.; Ji, G.; Wang, C.; Peng, Z. Organic Aluminum Hypophosphite/Graphitic Carbon Nitride Hybrids as Halogen-Free Flame Retardants for Polyamide 6. Polymers 2020, 12, 2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Hu, A. The Influence of Environmentally Friendly Flame Retardants on the Thermal Stability of Phase Change Polyurethane Foams. Materials 2020, 13, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xue, B.; Qin, R.; Wang, J.; Niu, M.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X. Construction of Carbon Microspheres-Based Silane Melamine Phosphate Hybrids for Flame Retardant Poly(ethylene Terephthalate). Polymers 2019, 11, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, R.; Li, W.; Mu, J.; Ding, Y.; Jiang, J. Synergistic Effects of Aluminum Diethylphosphinate and Melamine on Improving the Flame Retardancy of Phenolic Resin. Materials 2020, 13, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lotsch, B.V.; Schnick, W. New light on an old story: Formation of melam during thermal condensation of melamine. Chem. Eur. J. 2007, 13, 4956–4968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, D.; Liu, Y.; Milnes, G.J.; Hull, R.; Kandola, B.K.; Horrocks, A.R. An investigation into the mechanism of flame retardancy and smoke suppression by melamine in flexible polyurethane foam. Fire Mater. 2002, 26, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.H.; Kuan, C.F.; Kuan, H.C.; Shen, M.Y.; Yang, J.M.; Chiang, C.L. Preparation and Flame Retardance of Polyurethane Composites Containing Microencapsulated Melamine Polyphosphate. Polymers 2017, 9, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yin, S.; Ren, X.; Lian, P.; Zhu, Y.; Mei, Y. Synergistic Effects of Black Phosphorus/Boron Nitride Nanosheets on Enhancing the Flame-Retardant Properties of Waterborne Polyurethane and Its Flame-Retardant Mechanism. Polymers 2020, 12, 1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Fu, Y. Flame-Retardant Wood Composites Based on Immobilizing with Chitosan/Sodium Phytate/Nano-TiO2-ZnO Coatings via Layer-by-Layer Self-Assembly. Coatings 2020, 10, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, S.; Gong, W.; Luo, J.; Meng, X.; Xin, Z.; Wu, J.; Jiang, Z. Flame Retardancy and Mechanism of Novel Phosphorus-Silicon Flame Retardant Based on Polysilsesquioxane. Polymers 2019, 11, 1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tawiah, B.; Yu, B.; Fei, B. Advances in Flame Retardant Poly(lactic Acid). Polymers 2018, 10, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leu, T.S.; Wang, C.S. Synergistic effect of a phosphorus–nitrogen flame retardant on engineering plastics. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 92, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Cao, Y.; Qian, L.; Chen, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Xu, B.; Xin, F. Synergistic Charring Flame-Retardant Behavior of Polyimide and Melamine Polyphosphate in Glass Fiber-Reinforced Polyamide 66. Polymers 2019, 11, 1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, Z.; Peng, M.; Fang, Z. Synthesis of novel poly(aminophosphonate ester)s flame retardants and their applications in EVA copolymer. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2012, 24, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, N.; Qi, X.-L.; Nie, S.; Acuña, P.; Chen, M.-J.; Wang, D.-Y. Flame Retardant Polypropylene Composites with Low Densities. Materials 2019, 12, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, H. Flame retardant mechanism and surface modification of magnesium hydroxide flame retardant. IOP C. Ser. Earth Env. 2018, 170, 032028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Wang, Y.; Tang, D.; Wang, Q.; Li, H.; Huang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Wu, K. Flame-Retardant Mechanism of Layered Double Hydroxides in Asphalt Binder. Materials 2019, 12, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Z.; Yan, L.; Chen, L. Synergistic Flame Retardant Effects between Aluminum Hydroxide and Halogen-free Flame Retardants in High Density Polyethylene Composites. Procedia Eng. 2016, 135, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.; Wang, Y.Z. A review on flame retardant technology in China. Part I: Development of flame retardants. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2010, 21, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothon, R.N.; Hornsby, P.R. Flame retardant effects of magnesium hydroxide. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 1996, 54, 383–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.-Q.; Li, Z.; Yang, Y.-X.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Wen, X.; Li, N.; Fu, C.; Jian, R.-K.; Li, L.-J.; Wang, D.-Y. A Geometry Effect of Carbon Nanomaterials on Flame Retardancy and Mechanical Properties of Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate/Magnesium Hydroxide Composites. Polymers 2018, 10, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thangamuthu, M.; Hsieh, K.Y.; Kumar, P.V.; Chen, G.-Y. Graphene- and Graphene Oxide-Based Nanocomposite Platforms for Electrochemical Biosensing Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mazela, B.; Batista, A.; Grześkowiak, W. Expandable Graphite as a Fire Retardant for Cellulosic Materials—A Review. Forests 2020, 11, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesbains, K.; Faiz, A. The study of bonding mechanism of expandable graphite based intumescent coating. Res. J. Chem. Environ. 2011, 15, 401–405. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Luo, Y.; Guo, X.; Chen, L.; Xu, T.; Jia, D. Structure and Flame-Retardant Actions of Rigid Polyurethane Foams with Expandable Graphite. Polymers 2019, 11, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gama, N.V.; Amaral, C.; Silva, T.; Vicente, R.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Barros-Timmons, A.; Ferreira, A. Thermal Energy Storage and Mechanical Performance of Crude Glycerol Polyurethane Composite Foams Containing Phase Change Materials and Expandable Graphite. Materials 2018, 11, 1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Acuña, P.; Li, Z.; Santiago-Calvo, M.; Villafañe, F.; Rodríguez-Perez, M.Á.; Wang, D.-Y. Influence of the Characteristics of Expandable Graphite on the Morphology, Thermal Properties, Fire Behaviour and Compression Performance of a Rigid Polyurethane Foam. Polymers 2019, 11, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, H.; Liu, H.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, M.; Wan, C. Density Effect on Flame Retardancy, Thermal Degradation, and Combustibility of Rigid Polyurethane Foam Modified by Expandable Graphite or Ammonium Polyphosphate. Polymers 2019, 11, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piszczyk, Ł.; Hejna, A.; Formela, K.; Danowska, M.; Strankowski, M. Effect of halogen-free flame retardants on morphology, mechanical and thermal properties of flexible polyurethane foams synthesized from polyglycerol. Przem. Chem. 2014, 93, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Luo, Y.; Guo, X.; Chen, L.; Jia, D. The Synergistic Effect of Ionic Liquid-Modified Expandable Graphite and Intumescent Flame-Retardant on Flame-Retardant Rigid Polyurethane Foams. Materials 2020, 13, 3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, G.; Jin, W.; Chen, H.; Zhao, M.; Surampalli, R.; Ramakrishnan, A.; Zhang, T.; Tyagi, R.D. Flame-Retardant Polymer Nanocomposites and Their Heat-Release Rates. J. Hazard. Toxic Radioactiv. Waste 2015, 19, 04015006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamigaito, O.; Fukushima, Y.; Doi, H. Composite Material Composed of Clay Mineral and Organic High Polymer and Method for Producing the Same. U.S. Patent 4472538, 18 September 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury, J.A.; Rowlands, R.; Tipping, J.W. Network of Bonded Expanded Polystyrene BEADS having Chemically Delaminated Vermiculite Impregnant. U.S. Patent 4447491, 5 August 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Shain, A.L. Flame Retardant Thermoplastic MULTI-block Copolyester Elastomers. U.S. Patent 4582866, 15 April 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Gilman, J.W.; Kashiwagi, T.; Lichtenhan, J.D. Nanocomposites: A revolutionary new flame retardant approach. Sampe J. 1997, 33, 40–46. [Google Scholar]
- Gilman, J.W. Flammability and thermal stability studies of polymer layered-silicate (clay) nanocomposites. Appl. Clay Sci. 1999, 15, 31–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Hu, Y.; Zong, R.; Tang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Fan, W. Preparation and characterization of flame retardant ABS/montmorillonite nanocomposite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2004, 25, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashiwagi, T.; Harris, R.H., Jr.; Zhang, X.; Briber, R.M.; Cipriano, B.H.; Raghavan, S.R.; Awad, W.H.; Shields, J.R. Flame retardant mechanism of polyamide 6–clay nanocomposites. Polymer 2004, 45, 881–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourbigot, S.; Vanderhart, D.L.; Gilman, J.W.; Bellayer, S.; Stretz, H.; Paul, D.R. Solid state NMR characterization and flammability of styrene–acrylonitrile copolymer montmorillonite nanocomposite. Polymer 2004, 45, 7627–7638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laachachi, A.; Leroy, E.; Cochez, M.; Ferriol, M.; Lopez Cuesta, J.M. Use of oxide nanoparticles and organoclays to improve thermal stability and fire retardancy of poly(methyl methacrylate). Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2005, 89, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashiwagi, T.; Shields, J.R.; Harris, R.H., Jr.; Davis, R.D. Flame-Retardant Mechanism of Silica: Effects of Resin Molecular Weight. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 87, 1541–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorusso, C.; Vergaro, V.; Conciauro, F.; Ciccarella, G.; Congedo, P.M. Thermal and mechanical performance of rigid polyurethane foam added with commercial nanoparticles. Nanomater. Nanotechnol. 2017, 7, 184798041668411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.C.; Geng, T.; Han, J.; Liu, C.T.; Shen, C.Y.; Turng, L.S.; Yang, H.E. Effects of nanoclays on the thermal stability and flame retardancy of microcellular thermoplastic polyurethane nanocomposites. Polym. Compos. 2017, 39, E1429–E1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanra, J.; Budianto, E.; Soegijono, B. Surface modification of montmorillonite by the use of organic cations via conventional ion exchange method. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 509, 012057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slaný, M.; Jankovič, Ľ.; Madejová, J. Structural characterization of organo-montmorillonites prepared from a series of primary alkylamines salts: Mid-IR and near-IR study. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 176, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Ma, Y.; Zhu, J.; Yuan, P.; Qing, Y. Organoclays prepared from montmorillonites with different cation exchange capacity and surfactant configuration. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 48, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Xu, Z.; Wang, X. Synergistic effects of organically modified montmorillonite on the flame-retardant and smoke suppression properties of transparent intumescent fire-retardant coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2018, 122, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, X.; Wei, Q.; Yang, J.; Qiu, B.; Xu, J.; Wang, X. Synergistic effect of organophosphate functionalized montmorillonite on properties and water resistance of intumescent flame-retarded SEBS. Fire Mater. 2018, 43, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, M.; Zhong, Z.; Chen, T.; Jiang, J. Modified montmorillonite combined with intumescent flame retardants on the flame retardancy and thermal stability properties of unsaturated polyester resins. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2019, 30, 998–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Guo, J.; Tang, W.; Li, H.; Gu, X.; Sun, J.; Zhang, S. Enhancing the flame retardancy of thermoplastic polyurethane by introducing montmorillonite nanosheets modified with phosphorylated chitosan. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. 2019, 119, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Gao, J.; Li, Y.; Han, L.; Wang, X. Functionalizing nano-montmorillonites by modified with intumescent flame retardant: Preparation and application in polyurethane. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2010, 95, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarier, N.; Onder, E.; Ersoy, S. The modification of Na-montmorillonite by salts of fatty acids: An easy intercalation process. Colloid. Surface. A 2010, 371, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norshahli, M.S.; Jun, L.H.; Zubir, S.A. Mechanical Properties of Palm Oil Polyol based Polyurethane Foam Reinforced Wollastonite Clay. J. Phys-Conf. Ser. 2018, 1082, 012041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.H.M.; Rahman, H.A.; Amirnordin, S.H.; Khan, N.A. Eco-Friendly Flame-Retardant Additives for Polyurethane Foams: A Short Review. Key Eng. Mater. 2018, 791, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdolotti, L.; Di Caprio, M.R.; Lavorgna, M.; Buonocore, G.G. Polyurethane Nanocomposite Foams. Polyurethane Polym. 2017, 2017, 277–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berta, M.; Lindsay, C.; Pans, G.; Camino, G. Effect of chemical structure on combustion and thermal behaviour of polyurethane elastomer layered silicate nanocomposites. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2006, 91, 1179–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.H.; An, Y.U. Nanocomposites of polyurethane with various organoclays: Thermomechanical properties, morphology, and gas permeability. J. Polym. Sci. Pol. Phys. 2002, 40, 670–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tortora, M.; Gorrasi, G.; Vittoria, V.; Galli, G.; Ritrovati, S.; Chiellini, E. Structural characterization and transport properties of organically modified montmorillonite/polyurethane nanocomposites. Polymer 2002, 43, 6147–6157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.J.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, S.C. Synthesis of chain-extended organifier and properties of polyurethane/clay nanocomposites. Polymer 2004, 45, 6045–6057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piszczyk, Ł.; Hejna, A.; Formela, K.; Danowska, M.; Strankowski, M. Morphology, mechanical and thermal properties of flexible polyurethane foams modified with layered aluminosilicates. Polimery 2014, 59, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leszczyńska, A.; Njuguna, J.; Pielichowski, K.; Banerjee, J.R. Polymer/montmorillonite nanocomposites with improved thermal properties. Thermochim. Acta 2007, 453, 75–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agubra, V.A.; Owuor, P.S.; Hosur, M.V. Influence of Nanoclay Dispersion Methods on the Mechanical Behavior of E-Glass/Epoxy Nanocomposites. Nanomaterials 2013, 3, 550–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidarian, M.; Shishesaz, M.R.; Kassiriha, S.M.; Nematollahi, M. Characterization of structure and corrosion resistivity of polyurethane/organoclay nanocomposite coatings prepared through an ultrasonication assisted process. Prog. Org. Coat. 2010, 68, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervantes-Uc, J.M.; Espinosa, J.I.M.; Cauich-Rodríguez, J.V.; Ávila-Ortega, A.; Vázquez-Torres, H.; Marcos-Fernández, A.; San Román, J. TGA/FTIR studies of segmented aliphatic polyurethanes and their nanocomposites prepared with commercial montmorillonites. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2009, 94, 1666–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chang, C.; Luo, X.; Li, Y. Thermal, Mechanical, and Morphological Properties of Rigid Crude Glycerol-Based Polyurethane Foams Reinforced With Nanoclay and Microcrystalline Cellulose. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2018, 120, 1700413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modesti, M.; Lorenzetti, A.; Besco, S.; Hrelja, D.; Semenzato, S.; Bertani, R.; Michelin, R.A. Synergism between flame retardant and modified layered silicate on thermal stability and fire behaviour of polyurethane nanocomposite foams. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2008, 93, 2166–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenzato, S.; Lorenzetti, A.; Modesti, M.; Ugel, E.; Hrelja, D.; Besco, S.; Michelin, R.A.; Sassi, A.; Facchin, G.; Zorzi, F.; et al. A novel phosphorus polyurethane FOAM/montmorillonite nanocomposite: Preparation, characterization and thermal behaviour. Appl. Clay Sci. 2009, 44, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piszczyk, Ł.; Strankowski, M.; Danowska, M.; Haponiuk, J.T.; Gazda, M. Preparation and characterization of rigid polyurethane–polyglycerol nanocomposite foams. Eur. Polym. J. 2012, 48, 1726–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danowska, M.; Piszczyk, Ł.; Strankowski, M.; Gazda, M.; Haponiuk, J.T. Rigid polyurethane foams modified with selected layered silicate nanofillers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 130, 2272–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, M.C.; Kabir, M.E.; Jeelani, S. Enhancement in thermal and mechanical properties of polyurethane foam infused with nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. A-Struct. 2008, 479, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarier, N.; Onder, E. Organic modification of montmorillonite with low molecular weight polyethylene glycols and its use in polyurethane nanocomposite foams. Thermochim. Acta 2010, 510, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kausar, A. Exploration of novel heat and flame-resistant poly(urethane–imide)/functional layered silicate-based foams. High Perform. Polym. 2014, 27, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, S.S.; Samal, S.K.; Mohanty, S.; Nayak, S.K. Preparation, characterization, and properties of castor oil-based flexible polyurethane/Cloisite 30B nanocomposites foam. J. Compos. Mater. 2017, 52, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kausar, A. Processing and properties of poly(ester–urethane)/modified montmorillonite nanocomposite foams derived from novel diol and tolylene-2,4-diisocyanate. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2015, 30, 608–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kausar, A. Thermal, mechanical and flame retardant behavior of poly(urethane-ester) nanocomposite foams reinforced with hydroxyl modified montmorillonite. Int. J. Plast. Technol. 2015, 19, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Fernández, S.; Ugarte, L.; Peña-Rodriguez, C.; Corcuera, M.Á.; Eceiza, A. The effect of phosphorus containing polyol and layered double hydroxides on the properties of a castor oil based flexible polyurethane foam. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2016, 132, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Fernández, S.; Ugarte, L.; Peña-Rodriguez, C.; Zubitur, M.; Corcuera, M.Á.; Eceiza, A. Flexible polyurethane foam nanocomposites with modified layered double hydroxides. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 123, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piszczyk, Ł.; Danowska, M.; Mietlarek-Kropidłowska, A.; Szyszka, M.; Strankowski, M. Synthesis and thermal studies of flexible polyurethane nanocomposite foams obtained using nanoclay modified with flame retardant compound. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2014, 118, 901–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hejna, A.; Kosmela, P.; Kirpluks, M.; Cabulis, U.; Klein, M.; Haponiuk, J.; Piszczyk, Ł. Structure, Mechanical, Thermal and Fire Behavior Assessments of Environmentally Friendly Crude Glycerol-Based Rigid Polyisocyanurate Foams. J. Polym. Environ. 2017, 26, 1854–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shamini, G.; Yusoh, K. Gas Permeability Properties of Thermoplastic Polyurethane Modified Clay Nanocomposites. Int. J. Chem. Eng. Appl. 2014, 5, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.M.; Yao, C.T.; Hsieh, C.F.; Lin, L.H.; Chen, P.L.; Wu, J.C.; Yang, H.C.; Wu, C.P. Preparation, characterization and electrochemical corrosion studies on environmentally friendly waterborne polyurethane/Na+-MMT clay nanocomposite coatings. Eur. Polym. J. 2008, 44, 3046–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, R.F.; Wolfhard, H.G. Some limiting oxygen concentrations for diffusion flames in air diluted with nitrogen. Combust. Flame 1957, 1, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Zheng, G.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, L.; Feng, G. Thermal performances and fire behaviors of rosin-based rigid polyurethane foam nanocomposites. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2014, 119, 411–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Zheng, G.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, L.; Feng, G.; Zhang, M. Synergistic effect of expandable graphite, diethyl ethylphosphonate and organically-modified layered double hydroxide on flame retardancy and fire behavior of polyisocyanurate-polyurethane foam nanocomposite. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2014, 101, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Wang, G.; Zheng, X. Research on highly flame-retardant rigid PU foams by combination of nanostructured additives and phosphorus flame retardants. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2015, 111, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Zhu, X.; Chen, F.; Chen, S.; Liu, H. Flame-retardant system for rigid polyurethane foams based on diethyl bis(2-hydroxyethyl)aminomethylphosphonate and in-situ exfoliated clay. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2020, 177, 109178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zatorski, W.; Brzozowski, Z.K.; Kolbrecki, A. New developments in chemical modification of fire-safe rigid polyurethane foams. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2008, 93, 2071–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, W.J.; Sung, Y.T.; Kim, S.B.; Lee, Y.B.; Choe, K.H.; Choe, S.H.; Sung, J.Y.; Kim, W.N. Effects of ultrasound on the synthesis and properties of polyurethane foam/clay nanocomposites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 102, 3764–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyon, R.E.; Janssens, M.L. Flammability. In Encyclopedia of Polymer Science and Technology; Mark, H.F., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005; Volume 6, pp. 1–73. [Google Scholar]
- Wai, S.K.; Sahrim, A.H.; Zubir, S.A. Synergism between Flame Retardant and Phosphonium Salt Modified Layered Silicate on Properties of Rigid Polyurethane Foam Nanocomposite. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 501, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejna, A.; Kirpluks, M.; Kosmela, P.; Cabulis, U.; Haponiuk, J.; Piszczyk, Ł. The influence of crude glycerol and castor oil-based polyol on the structure and performance of rigid polyurethane-polyisocyanurate foams. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2017, 95, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahabi, H.; Rastin, H.; Movahedifar, E.; Antoun, K.; Brosse, N.; Saeb, M.R. Flame Retardancy of Bio-Based Polyurethanes: Opportunities and Challenges. Polymers 2020, 12, 1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandre, M.; Dubois, P. Polymer-layered silicate nanocomposites: Preparation, properties and uses of a new class of materials. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2000, 28, 1–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babrauskas, V.; Peacock, R.D. Heat release rate: The single most important variable in fire hazard. Fire Saf. J. 1992, 18, 255–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Tang, X.; Zheng, J. Thermal Stability and Flame Retardancy of Rigid Polyurethane Foams/Organoclay Nanocomposites. Polym.-Plast. Technol. 2008, 47, 1136–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Wang, G.; Xu, W. Roles of organically-modified montmorillonite and phosphorous flame retardant during the combustion of rigid polyurethane foam. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2014, 101, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, Q.; Yuen, R.K.K.; Song, L.; Hu, Y. A novel polymeric flame retardant and exfoliated clay nanocomposites: Preparation and properties. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 183, 542–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzetti, A.; Besco, S.; Hrelja, D.; Roso, M.; Gallo, E.; Schartel, B.; Modesti, M. Phosphinates and layered silicates in charring polymers: The flame retardancy action in pol-yurethane foams. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2013, 98, 2366–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydoğan, B.; Usta, N. Cone calorimeter evaluation on fire resistance of rigid polyurethane foams filled with nanoclay/intumescent flame retardant materials. Res. Eng. Struct. Mater. 2018, 4, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydoğan, B.; Usta, N. Fire behaviour assessment of rigid polyurethane foams containing nanoclay and intumescent flame retardant based on cone calorimeter tests. J. Chem. Technol. Metall. 2019, 54, 55–63. [Google Scholar]
- Braun, U.; Balabanovich, A.I.; Schartel, B.; Knoll, U.; Artner, J.; Ciesielski, M.; Doring, M.; Perez, R.; Sandler, J.K.W.; Altstadt, V.; et al. Influence of the oxidation state of phosphorus on the decomposition and fire behaviour of flame-retarded epoxy resin composites. Polymer 2006, 47, 8495–8508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haile, M.; Fomete, S.; Lopez, I.D.; Grunlan, J.C. Aluminum hydroxide multilayer assembly capable of extinguishing flame on polyurethane foam. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 51, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Harris, R.; Davis, R. Innovative Approach to Rapid Growth of Highly Clay-Filled Coatings on Porous Polyurethane Foam. ACS Macro Lett. 2012, 1, 820–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Cai, W.; Du, J.; Song, L.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, H. Lanthanum phenylphosphonate–based multilayered coating for reducing flammability and smoke production of flexible polyurethane foam. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2020, 31, 1330–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.; Yuan, B.; Pan, Y.; Feng, X.; Duan, L.; Zong, R.; Hu, Y. A single α-cobalt hydroxide/sodium alginate bilayer layer-by-layer assembly for conferring flame retardancy to flexible polyurethane foams. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2017, 191, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Kong, Q.; Yang, L.; Wang, D.Y. Few layered Co(OH)2 ultrathin nanosheet-based polyurethane nanocomposites with reduced fire hazard: From eco-friendly flame retardance to sustainable recycling. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 3066–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z. Flame retardant coatings prepared using layer by layer assembly: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 108–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alongi, J.; Carosio, F.; Malucelli, G. Current emerging techniques to impart flame retardancy to fabrics: An overview. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2014, 106, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Neisius, N.M.; Gaan, S. Recent developments in flame retardant polymeric coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2013, 76, 1642–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.J.; Holder, K.M.; Ruiz, S.; Hahn, W.; Song, Y.; Lvov, Y.M.; Grunlan, J.C. Environmentally Benign Halloysite Nanotube Multilayer Assembly Significantly Reduces Polyurethane Flammability. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 28, 1703289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Kundu, C.K.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z. Layer-by-layer-assembled flame-retardant coatings from polydopamine-induced in situ functionalized and reduced graphene oxide. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 13848–13862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Gao, S.; Zhao, Y.; Tao, W.; Yu, X.; Zhi, M. Review of layer-by-layer self-assembly technology for fire protection of flexible polyurethane foam. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 9605–9643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.C.; Kim, Y.S.; Shields, J.; Davis, R. Controlling polyurethane foam flammability and mechanical behaviour by tailoring the composition of clay-based multilayer nanocoatings. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 12987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.C.; Yang, Y.H.; Shields, J.R.; Davis, R.D. Layered double hydroxide-based fire resistant coatings for flexible polyurethane foam. Polymer 2015, 56, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.H.; Li, Y.C.; Shields, J.; Davis, R.D. Layer double hydroxide and sodium montmorillonite multilayer coatings for the flammability reduction of flexible polyurethane foams. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 41767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Li, Y.C.; Pitts, W.M.; Werrel, M.; Davis, R.D. Rapid Growing Clay Coatings to Reduce the Fire Threat of Furniture. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2014, 6, 2146–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.C.; Yang, Y.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Shields, J.R.; Davis, R.D. DNA-based nanocomposite biocoatings for fire-retarding polyurethane foam. Green Mater. 2014, 2, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabipour, H.; Wang, X.; Song, L.; Hu, Y. A fully bio-based coating made from alginate, chitosan and hydroxyapatite for protecting flexible polyurethane foam from fire. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 246, 116641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cain, A.A.; Plummer, M.G.B.; Murray, S.E.; Bolling, L.; Regev, O.; Grunlan, J.C. Iron-containing, high aspect ratio clay as nanoarmor that imparts substantial thermal/flame protection to polyurethane with a single electrostatically-deposited bilayer. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 17609–17617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazar, S.; Carosio, F.; Davesne, A.L.; Jimenez, M.; Bourbigot, S.; Grunlan, J.C. Extreme Heat Shielding of Clay/Chitosan Nanobrick Wall on Flexible Foam. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2018, 10, 316686–316696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holder, K.M.; Huff, M.E.; Cosio, M.N.; Grunlan, J.C. Intumescing multilayer thin film deposited on clay-based nanobrick wall to produce self-extinguishing flame retardant polyurethane. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 50, 2451–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laufer, G.; Kirkland, C.; Cain, A.A.; Grunlan, J.C. Clay–Chitosan Nanobrick Walls: Completely Renewable Gas Barrier and Flame-Retardant Nanocoatings. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2012, 4, 1643–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, T.; Song, S. Correlation of Montmorillonite Sheet Thickness and Flame Retardant Behavior of a Chitosan–Montmorillonite Nanosheet Membrane Assembled on Flexible Polyurethane Foam. Polymers 2019, 11, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, K.W.; Kim, J.W.; Kwon, T.S.; Kang, S.W.; Song, J.I.; Park, Y.T. Mechanically Sustainable Starch-Based Flame-Retardant Coatings on Polyurethane Foams. Polymers 2021, 13, 1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Milhorn, A.; Haile, M.; Mai, G.; Grunlan, J.C. Nanocoating of starch and clay that reduces the flammability of polyurethane foam. Green Mater. 2017, 5, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.; Li, Y.C.; Gervasio, M.; Luu, J.; Kim, Y.S. One-Pot, Bioinspired Coatings To Reduce the Flammability of Flexible Polyurethane Foams. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2015, 7, 6082–6092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Liu, L.; Cai, W.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, S.; Zhao, H. Effect of layer-by-layer self-assembled sepiolite-based nanocoating on flame retardant and smoke suppressant properties of flexible polyurethane foam. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 168, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Pan, H.; Shi, Y.; Yu, B.; Pan, Y.; Liew, K.M.; Song, L.; Hu, Y. Sandwichlike Coating Consisting of Alternating Montmorillonite and β-FeOOH for Reducing the Fire Hazard of Flexible Polyurethane Foam. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 3214–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Pan, Y.T.; Wan, J.T.; Wang, D.Y. An eco-friendly way to fire retardant flexible polyurethane foam: Layer-by-layer assembly of fully bio-based substances. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 46164–46169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, H.; Pan, Y.; Wang, W.; Song, L.; Hu, Y.; Liew, K.M. Synergistic Effect of Layer-by-Layer Assembled Thin Films Based on Clay and Carbon Nanotubes To Reduce the Flammability of Flexible Polyurethane Foam. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 14315–14321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palen, B.; Kolibaba, T.J.; Brehm, J.T.; Shen, R.; Quan, Y.; Wang, Q.; Grunlan, J.C. Clay-Filled Polyelectrolyte Complex Nanocoating for Flame-Retardant Polyurethane Foam. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 8016–8020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.B.; Shen, P.; Chen, M.J.; Zhao, H.B.; Schiraldi, D.A. Highly Efficient Flame Retardant Polyurethane Foam with Alginate/Clay Aerogel Coating. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2016, 8, 32557–32564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Combustion Product | Concentration, ppm | Effect on Humans after the Exposition | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon oxide, CO | 35 | Headache and dizziness within 6 to 8 h of constant exposure | [64] |
| 100 | Slight headache in 2 to 3 h | ||
| 200 | Slight headache within 2 to 3 h; loss of judgment | ||
| 400 | Frontal headache within 1 to 2 h | ||
| 800 | Dizziness, nausea, and convulsions within 45 min; insensible within 2 h | ||
| 1600 | Headache, tachycardia, dizziness, and nausea within 20 min; death in less than 2 h | ||
| 3200 | Headache, dizziness, and nausea in 5 to 10 min; death within 30 min | ||
| 6400 | Headache and dizziness in 1 to 2 min; convulsions, respiratory arrest, and death in less than 20 min | ||
| 12,800 | Unconsciousness after 2–3 breaths; death in less than 3 min | ||
| Carbon dioxide, CO2 | <40,000 | Dilatation of cerebral vessels, increased pulmonary ventilation, and increased oxygen delivery to the tissues after 30 min | [65] |
| 40,000–70,000 | Headache, hearing and visual disturbances, increased blood pressure, dyspnea, difficult breathing, depressions, and tremors | ||
| 70,000–100,000 | Unconsciousness, headache, visual and hearing dysfunction, depression, shortness of breath, and sweating after few minutes | ||
| 100,000–150,000 | Unconsciousness, severe muscle twitching, and dizziness after several minutes | ||
| >170,000 | Loss of controlled activity, unconsciousness, convulsions, coma, and death within 1 min of initial inhalation | ||
| Hydrogen cyanide, nitriles, R-CN | 20–40 | Headache, drowsiness, vertigo, weak and rapid pulse, rapid breathing, bright-red color in the face, nausea, and vomiting | [66] |
| 100 | Fatal (1 h) | ||
| 135 | Fatal (30 min) | ||
| 180 | Fatal (10 min) | ||
| 270 | Rapidly fatal | ||
| Nitrogen oxides, NxOy | 25 | Respiratory irritation, chest pain after 1 h | [67] |
| 50 | Respiratory irritation, chest pain after 15 min; pulmonary edema possible subacute after 1 h | ||
| 75 | Pulmonary edema, possible subacute, and chronic lesions in the lungs after 30 min | ||
| 100 | Pulmonary edema, possible subacute, chronic lesions in the lungs after 15 min; death after 1 h | ||
| 150 | Pulmonary edema and death after 30 min | ||
| 200 | Possible subacute and chronic lesions in the lungs after 5 min; pulmonary edema, and death after 15 min | ||
| 400 | Pulmonary edema and death after 5 min | ||
| Ammonia, NH3 | 50 | Irritation to eyes, nose, and throat after 2 h | [68] |
| 100 | Rapid eye and respiratory tract irritation | ||
| 250 | Tolerable by most persons (30–60 min exposure) | ||
| 700 | Immediately irritating to eyes and throat | ||
| >1500 | Pulmonary edema, coughing, and laryngospasm | ||
| 2500–4500 | Fatal (30 min) | ||
| 5000–10,000 | Rapidly fatal due to airway obstruction | ||
| Benzene, C6H6 | 500 | Symptoms of illness after 1 h, slight irritation of mucous membranes | [69] |
| 1500 | Serious symptoms | ||
| 3000 | Endurable | ||
| 7500 | Fatal (1 h), death associated with asphyxiation, respiratory arrest, and central nervous system depression | ||
| 20,000 | Fatal (5–10 min) |
| Foam Type | Clay | Modification of Clay | Flame Retardant | Clay Content, % | ΔTini, °C | Δresidue, % | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rigid foams | Bentonite | - | - | 6 | 32 | - | [146] |
| 9 | 7 | - | [147] | ||||
| Cloisite 30B | methyl tallow bis-2-hydroxyethyl ammonium | - | 3 | 16 | - | [147] | |
| 6 | 35 | - | [146] | ||||
| 9 | 33 | - | [147] | ||||
| aluminium phosphinate, 10% | 5 | 14 | 16.8 | [144,145] | |||
| Dellite HPS | - | aluminium phosphinate, 10% | 5 | 13 | 17.0 | ||
| [CH3OOCCH2(Ph)2PCH2CH2P(Ph)2CH2COOCH3]Br2 | 5 | 17 | 13.2 | ||||
| Halloysite | - | - | 1 | 5 | - | [143] | |
| 3 | 3 | - | |||||
| Laponite RD | - | - | 3 | 14 | - | [147] | |
| 6 | 39 | - | [146] | ||||
| MMT K10 | - | - | 1 | 16 | - | [148] | |
| Nanocor | PEG 600 | - | 2 | 25 | 1.0 | [149] | |
| PEG 1000 | 2 | 7 | 3.0 | ||||
| PEG 1500 | 2 | 20 | 2.0 | ||||
| Flexible foams | Cloisite 30B | methyl tallow bis-2-hydroxyethyl ammonium | - | 1 | 44 | 15.0 | [150] |
| 3 | 53 | 16.0 | |||||
| 5 | 76 | 26.0 | |||||
| 1 | 14 | 0.7 | [151] | ||||
| 2 | 21 | 1.2 | |||||
| 3 | 24 | 2.0 | |||||
| 1 | 6 | - | [152] | ||||
| 3 | 12 | - | |||||
| 5 | 33 | - | |||||
| 1 | 45 | 6.0 | [153] | ||||
| 3 | 49 | 8.0 | |||||
| 5 | 55 | 11.0 | |||||
| Hydro- talcite | - | - | 1.9 | −1 | 1.6 | [154,155] | |
| potassium phosphate monobasic | 1.9 | 2 | 1.2 | ||||
| Exolit OP560, 5% | 1.9 | 2 | 1.2 | ||||
| Exolit OP560, 10% | 1.9 | −7 | 2.7 | ||||
| bis(2-ethylhexyl) hydrogen phosphate | - | 1.9 | 4 | 0.3 | |||
| Exolit OP560, 5% | 1.9 | 3 | 3.1 | ||||
| Exolit OP560, 10% | 1.9 | −8 | 3.1 | ||||
| Nanofil 116 | - | Fyrol PNX, 1.5% | 1.5 | 7 | 2.0 | [156] | |
| Fyrol PNX, 3.0% | 3 | −19 | 5.0 | ||||
| Fyrol PNX | - | 3 | 0 | 1.0 | |||
| 6 | −1 | 3.0 |
| Foam Type | Clay | Modification of Clay | Flame Retardant | Clay Content, % | ΔLOI, % | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rigid foams | Cloisite 30B | methyl tallow bis-2-hydroxyethyl ammonium | - | 3 | 0.9 | [147] | |
| 9 | 1.6 | ||||||
| aluminium phosphinate, 10% | 5 | 5.9 | [144] | ||||
| Dellite HPS | - | aluminium phosphinate, 10% | 5 | 5.1 | |||
| [CH3OOCCH2(Ph)2PCH2CH2P (Ph)2CH2COOCH3]Br2 | aluminium phosphinate, 10% | 5 | 6.1 | ||||
| MMT | octadecyl bis-hydroxyethyl methyl ammonium chloride | ammonium phosphate, 8% | 5 | 6.5 | [163] | ||
| dimethyl methyl phosphonate, 8% | 5 | 7.5 | |||||
| ammonium phosphate, 8% + dimethyl methyl phosphonate, 8% | 5 | 9.5 | |||||
| Na MMT | hexadecyltrimethyl ammonium bromide | - | 2 | 0.4 | [164] | ||
| Diethyl bis(2-hydroxyethyl)aminomethylphosphonate | 10% | 2 | 4.1 | ||||
| 20% | 2 | 8.4 | |||||
| 30% | 2 | 10.7 | |||||
| Nanofil 2 | - | - | 1.2 | 1.7 | [165] | ||
| zinc stannate, 1.2% | 1.2 | 2.3 | |||||
| zinc stannate, 1.1% + expandable graphite, 2.2% | 1.1 | 3.4 | |||||
| zinc stannate, 1.1% + expandable graphite, 6.5% | 1.1 | 5.0 | |||||
| Flexible foams | Cloisite 30B | methyl tallow bis-2-hydroxyethyl ammonium | - | 1 | 2 | [152] | |
| 3 | 7 | ||||||
| 5 | 9 | ||||||
| 1 | 5 | [153] | |||||
| 3 | 7 | ||||||
| 5 | 10 | ||||||
| Clay | Modification of Clay | Flame Retardant | Clay Content, % | ΔpHRR, % | ΔTHR, % | ΔTSR, % | Δchar, % | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cloisite 30B | methyl tallow bis-2-hydroxyethyl ammonium | aluminum tris-diethylphosphinate, 10% | 3 | 40.9 | 30.3 | - | - | [176] |
| 5 | 35.5 | 27.3 | - | - | ||||
| aluminum tris-diethylphosphinate + melamine cyanurate, 10% | 3 | 40.2 | 33.3 | - | - | |||
| 5 | 44.4 | 27.3 | - | - | ||||
| aluminium phosphinate, 10% | 5 | 27.2 | 12.9 | 4.8 | 10.7 | [144] | ||
| Dellite HPS | - | aluminium phosphinate, 10% | 5 | 22.1 | 14.2 | 10.5 | 8.7 | |
| [CH3OOCCH2(Ph)2PCH2CH2P(Ph)2CH2COOCH3]Br2 | 5 | 35.9 | 18.2 | 4.3 | 5.9 | |||
| MMT | - | - | 5 | 0.0 | 3.3 | - | 18.7 | [177,178] |
| 10 | 3.0 | 11.5 | - | 26.9 | ||||
| 15 | 0.0 | 24.4 | - | 31.0 | ||||
| ammonium polyphosphate + pentaerythritol (2:1 ratio), 5% | 5 | 5.1 | 9.2 | - | 15.8 | |||
| ammonium polyphosphate + pentaerythritol (2:1 ratio), 10% | 5 | 17.9 | 29.7 | - | 23.8 | |||
| octadecyl bis-hydroxyethyl methyl ammonium chloride | ammonium phosphate, 8% + dimethyl methyl phosphonate, 8% | 5 | 42.5 | - | - | - | [163] | |
| - | 5 | 12.4 | - | 1.0 | - | [174] | ||
| ammonium polyphosphate, 8% + triphenyl phosphate, 4% | 5 | 33.7 | - | 28.0 | - | |||
| octadecyl trimethyl ammonium | - | 0.8 | 15.9 | - | - | - | [173] | |
| Na MMT | octadecyl primary ammonium | - | 0.8 | 30.2 | - | - | - | |
| decanediamine | 0.8 | 26.4 | - | - | - | |||
| hexadecyltrimethyl ammonium bromide | 2 | 19.1 | 6.2 | 5.7 | 6.3 | [164] | ||
| Diethyl bis(2-hydroxyethyl)aminomethylphosphonate, 30% | 2 | 50.5 | 43.8 | 16.5 | 20.3 |
| Hydrotalcite Modification | Content of Exolit OP560 in Polyol Mixture, % | pHRR, W/g | THR, kJ/g |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reference foam (no hydrotalcite) | 0 | 144.7 ± 6.5 | 28.2 ± 0.6 |
| - | 0 | 136.4 ± 5.5 | 26.9 ± 0.4 |
| 5 | 132.7 ± 6.5 | 26.1 ± 0.5 | |
| 10 | 114.7 ± 7.3 | 25.9 ± 0.2 | |
| potassium phosphate monobasic | 0 | 138.4 ± 6.5 | 26.5 ± 0.5 |
| 5 | 136.0 ± 5.5 | 26.2 ± 0.2 | |
| 10 | 138.8 ± 6.2 | 25.6 ± 0.5 | |
| bis(2-ethylhexyl) hydrogen phosphate | 0 | 133.2 ± 11.0 | 27.4 ± 0.8 |
| 5 | 121.4 ± 6.0 | 26.2 ± 0.5 | |
| 10 | 131.0 ± 7.4 | 25.9 ± 0.3 |
| Type of Coating | Coating Sequence | Content | Coating Mass, % | Nanoparticle Content, % | ΔpHRR, % | ΔTHR, % | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PAA | PEI | LDH | MMT | ||||||
| Bilayer | PAA/PEI + LDH | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.5 | - | 25.0 | 54 | 40 | 14 |
| PAA/PEI + LDH | 1.0 | - | 30.0 | 58 | 39 | 19 | |||
| PAA + MMT/PEI | - | 0.5 | 11.0 | 32 | 22 | 0 | |||
| PAA + MMT/PEI + LDH | 0.5 | 0.5 | 11.0 | 32 | 27 | 7 | |||
| Trilayer | PAA/PEI + LDH/MMT | 0.5 | 0.5 | 11.0 | 43 | 28 | 9 | ||
| PAA/PEI + LDH/MMT | 1.0 | 1.0 | 7.5 | 64 | 29 | 16 | |||
| Quadlayer | PAA/LDH/PEI/MMT | 0.5 | 0.5 | 13.0 | 29 | 33 | 5 | ||
| PAA/LDH/PEI/MMT | 1.0 | 1.0 | 8.4 | 56 | 31 | 21 | |||
| Coating and Number of Bilayers | ΔpHRR, % | ΔTHR, % | Δresidue, % | ΔTSR, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MMT 1 | 27.8 | 4.1 | 6.0 | −7.5 |
| MMT 2 | 53.3 | 1.5 | 4.0 | 11.0 |
| MMT 4 | 59.5 | 11.8 | 8.0 | 50.7 |
| VMT 1 | 53.9 | 8.2 | 13.0 | 30.8 |
| VMT 2 | 56.2 | 12.3 | 11.0 | 58.2 |
| Starch Content, wt% | SPB Content, wt% | MMT Content, wt% | ΔpHRR, % | Open-Flame Test Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.5 | 5.8 | - | 42 | Self-extinguished < 40 s |
| 5.8 | 2.0 | 60 | Self-extinguished < 20 s | |
| 11.5 | - | 64 | Self-extinguished < 20 s | |
| 11.5 | 2.0 | 66 | No ignition | |
| 3.0 | 5.8 | - | 53 | Self-extinguished < 20 s |
| 5.8 | 2.0 | 63 | Self-extinguished < 20 s | |
| 11.5 | - | 66 | No ignition | |
| 11.5 | 2.0 | 66 | No ignition | |
| 23.0 | - | 75 | No ignition |
| Number of Bilayers | Sepiolite Content, wt% | ΔpHRR, % | ΔTHR, % | ΔSPR, % | ΔTSR, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 0.0 | 25.4 | 4.9 | 33.3 | 9.8 |
| 6 | 39.4 | 12.9 | 41.7 | 19.5 | |
| 3 | 0.5 | 60.6 | 14.4 | 58.3 | 22.0 |
| 6 | 70.4 | 19.3 | 58.3 | 29.3 | |
| 3 | 1.0 | 76.1 | 24.2 | 58.3 | 24.4 |
| 6 | 76.1 | 23.9 | 58.3 | 26.8 |
| Alginate (A) and Clay (C) Content, wt% | Coating Thickness, mm | ΔpHRR, % | ΔTHR, % | ΔTSR, % | Δresidue, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A5C5 | 1.5 | 55.4 | −5 | 39.2 | 14.7 |
| A5C10 | 1.5 | 65.9 | 20 | 62.0 | 43.6 |
| A7.5C7.5 | 0.2 | 31.0 | 5 | 46.5 | 9.3 |
| 0.7 | 31.9 | 5 | 36.9 | 19.6 | |
| 1.5 | 60.4 | 5 | 46.3 | 33.9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hejna, A. Clays as Inhibitors of Polyurethane Foams’ Flammability. Materials 2021, 14, 4826. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14174826
Hejna A. Clays as Inhibitors of Polyurethane Foams’ Flammability. Materials. 2021; 14(17):4826. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14174826
Chicago/Turabian StyleHejna, Aleksander. 2021. "Clays as Inhibitors of Polyurethane Foams’ Flammability" Materials 14, no. 17: 4826. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14174826
APA StyleHejna, A. (2021). Clays as Inhibitors of Polyurethane Foams’ Flammability. Materials, 14(17), 4826. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14174826






