Thermo-Viscoelastic Response of 3D Braided Composites Based on a Novel FsMsFE Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Multi-Scale Coupling for 3D Braided Composites
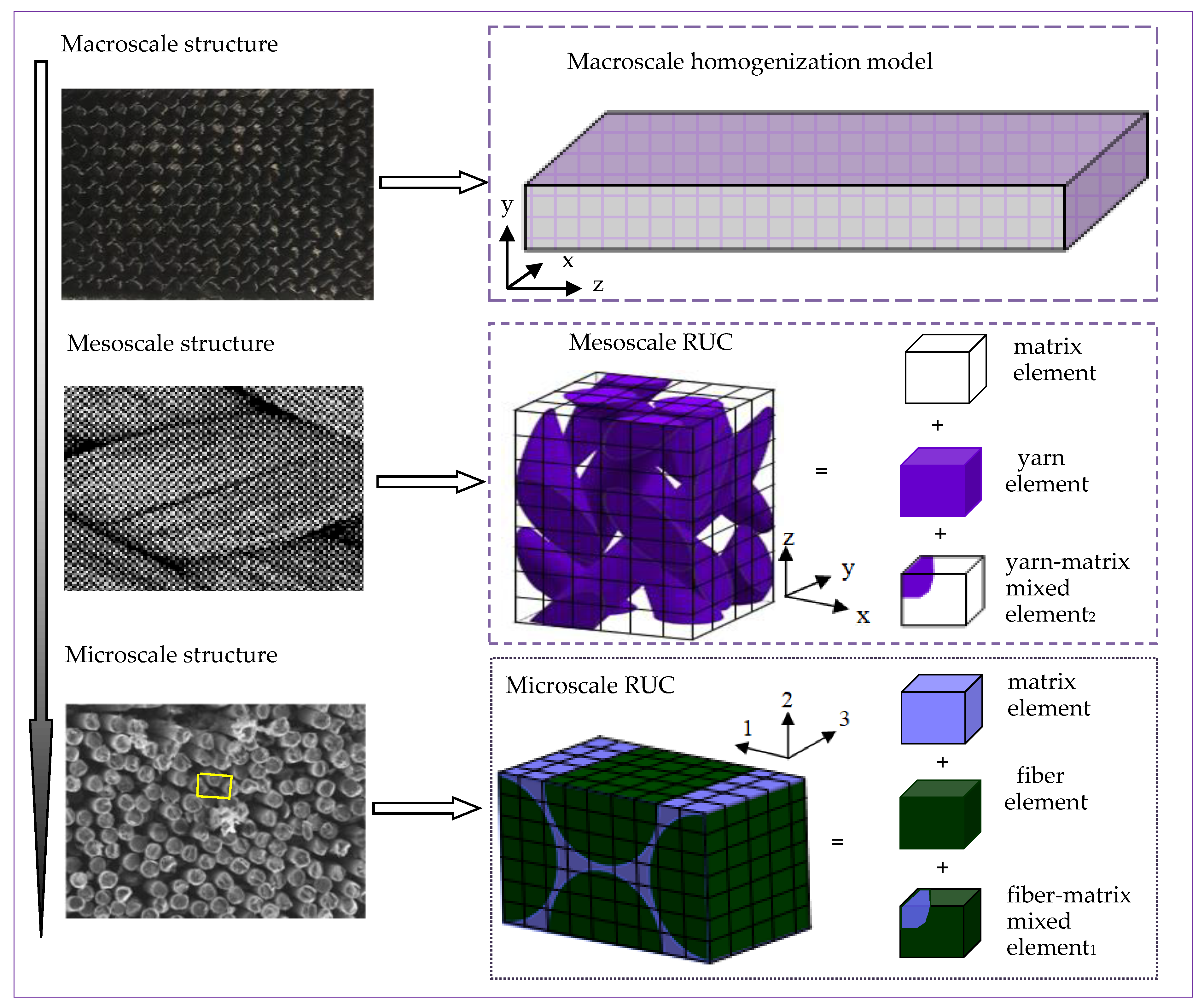
2.1. Association of Multiple Scales
2.2. Equations for the Micro-Scale, Meso-Scale and Macro-Scale
3. Analysis Procedure for 3D Braided Composites
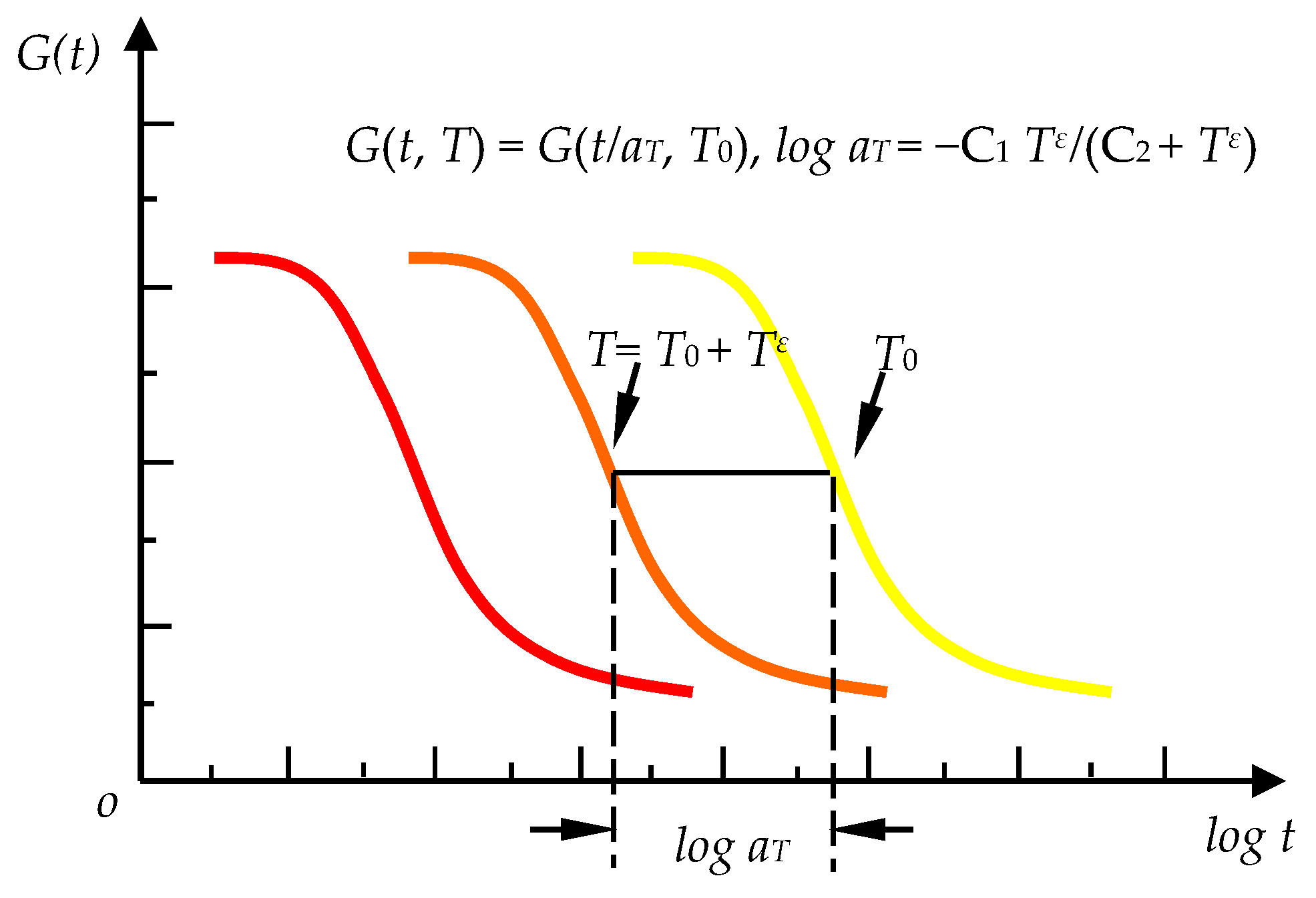
3.1. Inverse Laplace Transformation
3.2. Computation of the Effective Properties for Micro-Scale and Meso-Scale
3.3. FsMsFE Analysis Sequence
- (1)
- Establish a micro-scale RUC model. Then, Equation (35) is solved to obtain the characteristic function . Thereafter, the equivalent thermo-viscoelastic properties and of the yarns are computed by Equations (15) and (19).
- (2)
- Establish a meso-scale RUC model of 3D four-directional braided composites. The characteristic function for the meso-scale unit cell of 3D braided four-directional composites can be obtained similar to that of micro-scale RUC. Then the equivalent TTRM and equivalent TTEC of the meso-scale RUC can be calculated by means of Equations (29) and (30).
- (3)
- Establish a macroscopic model with uniform mechanical properties, which was calculated from homogenization analysis of meso-scale RUC. Based on a certain boundary condition, the homogenization displacement can be obtained.
- (4)
- Calculate the meso-scale stress field inside the basic RUC belonging to the macroscopic location by Equation (31).
- (5)
- Calculate the micro-scale stress field related to the yarn by Equation (12).
4. Results and Discussion
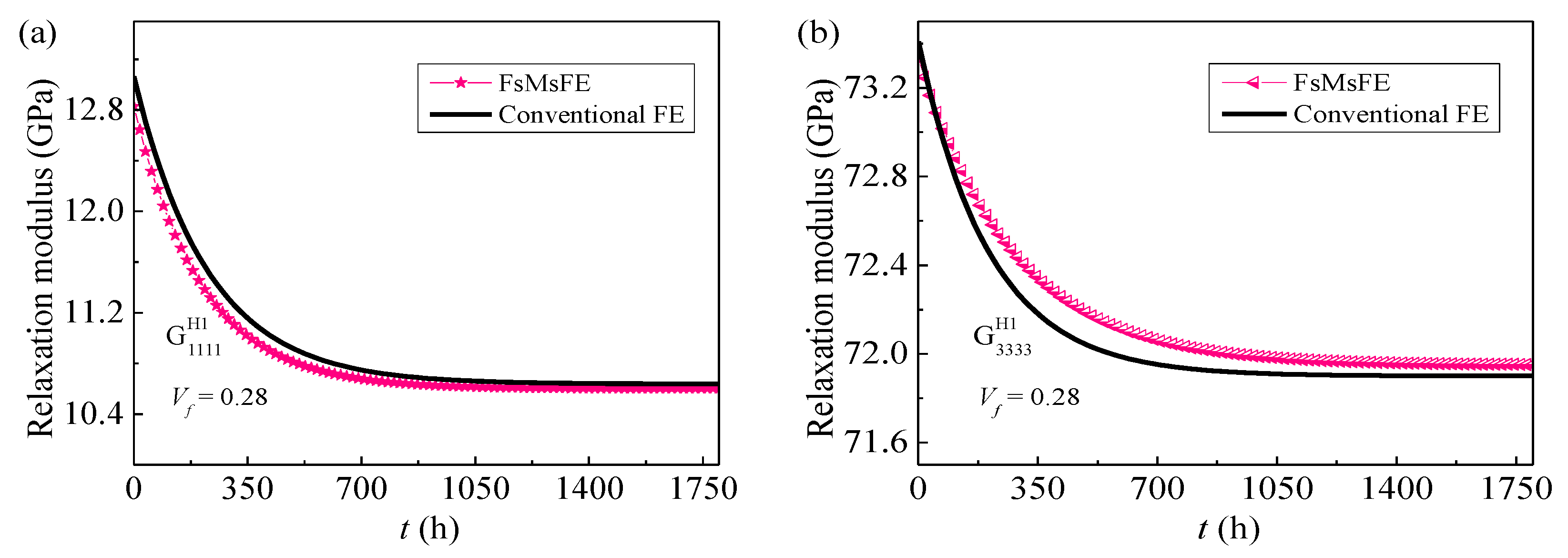
4.1. Numerical Models and Verification
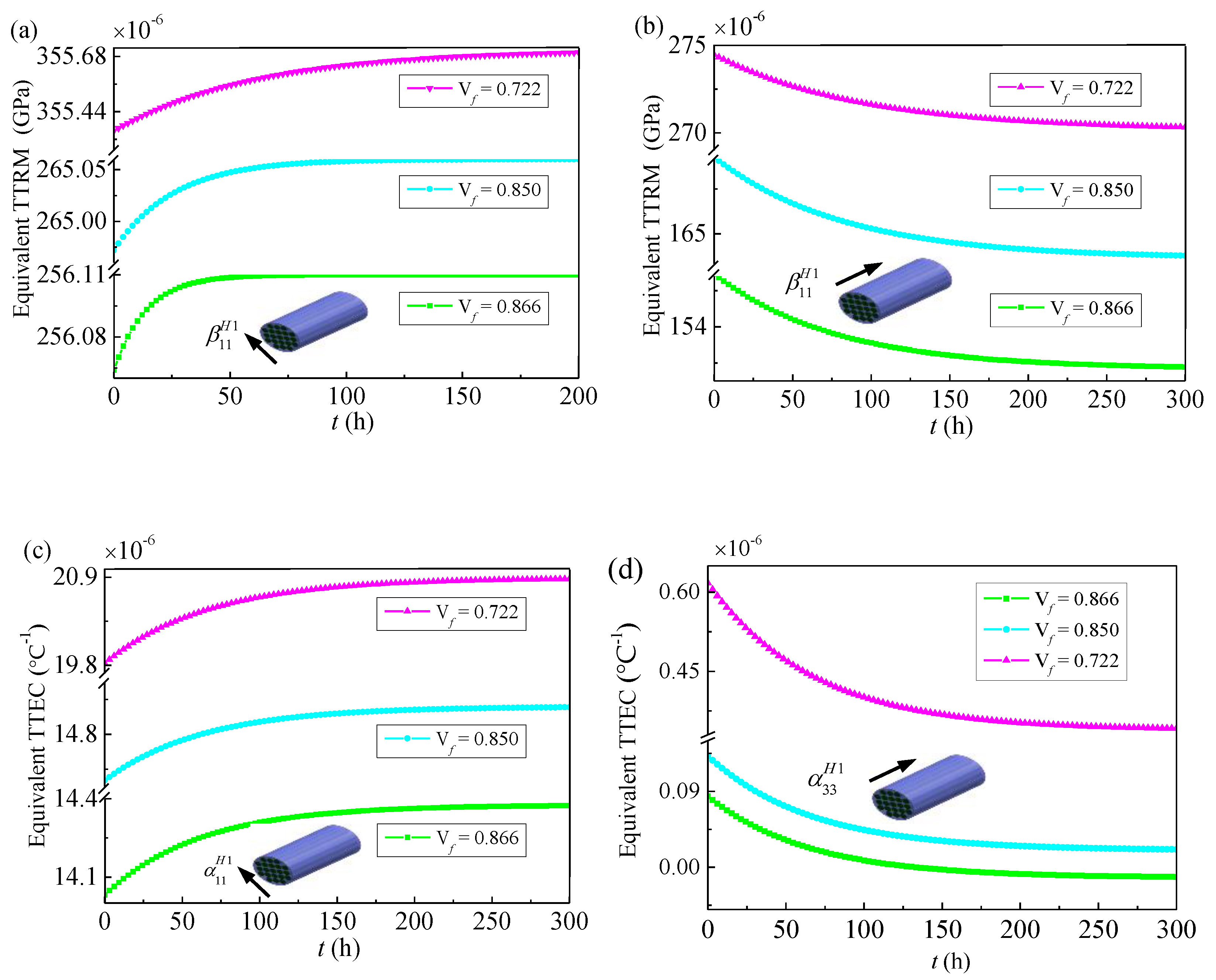
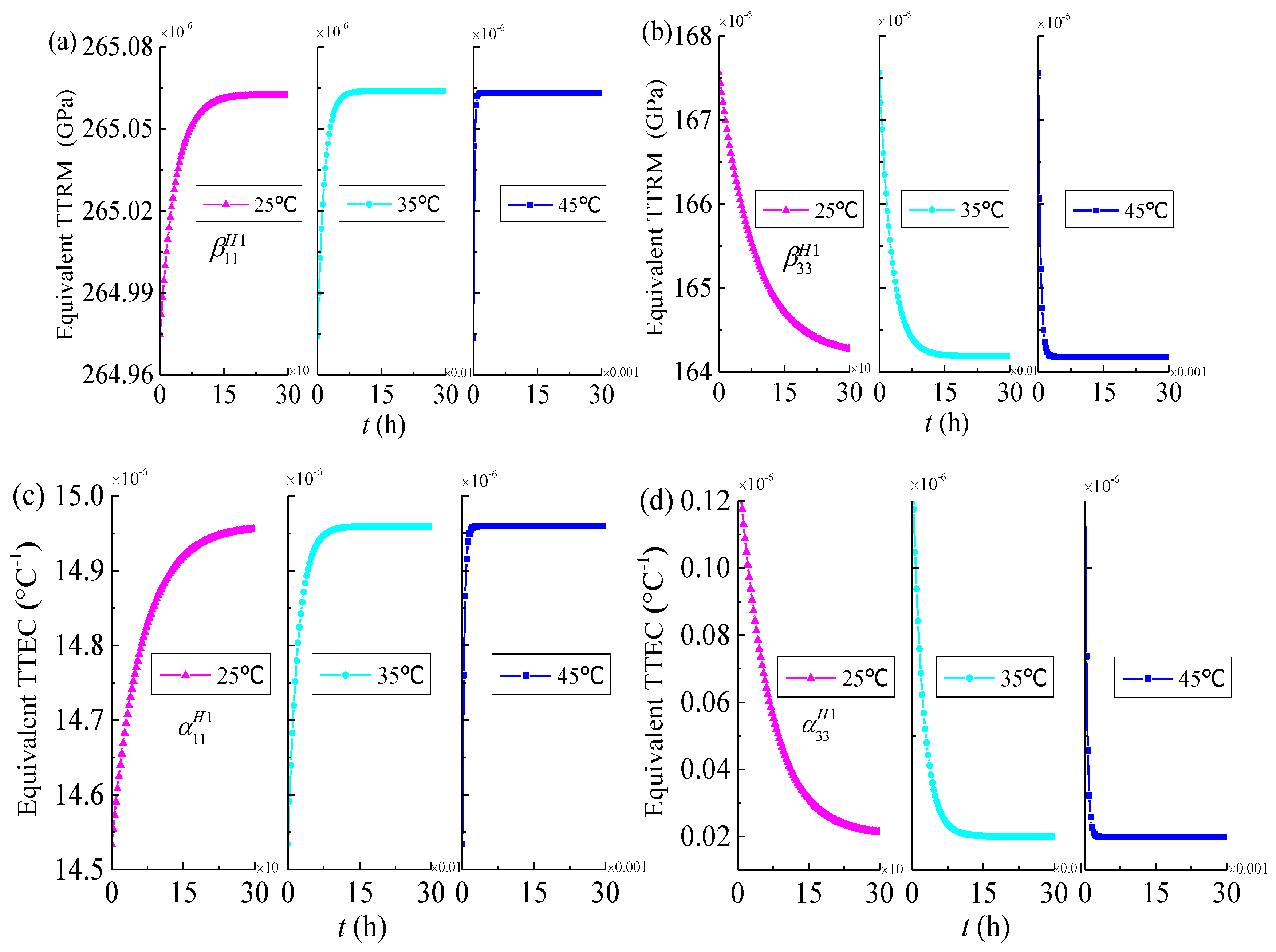
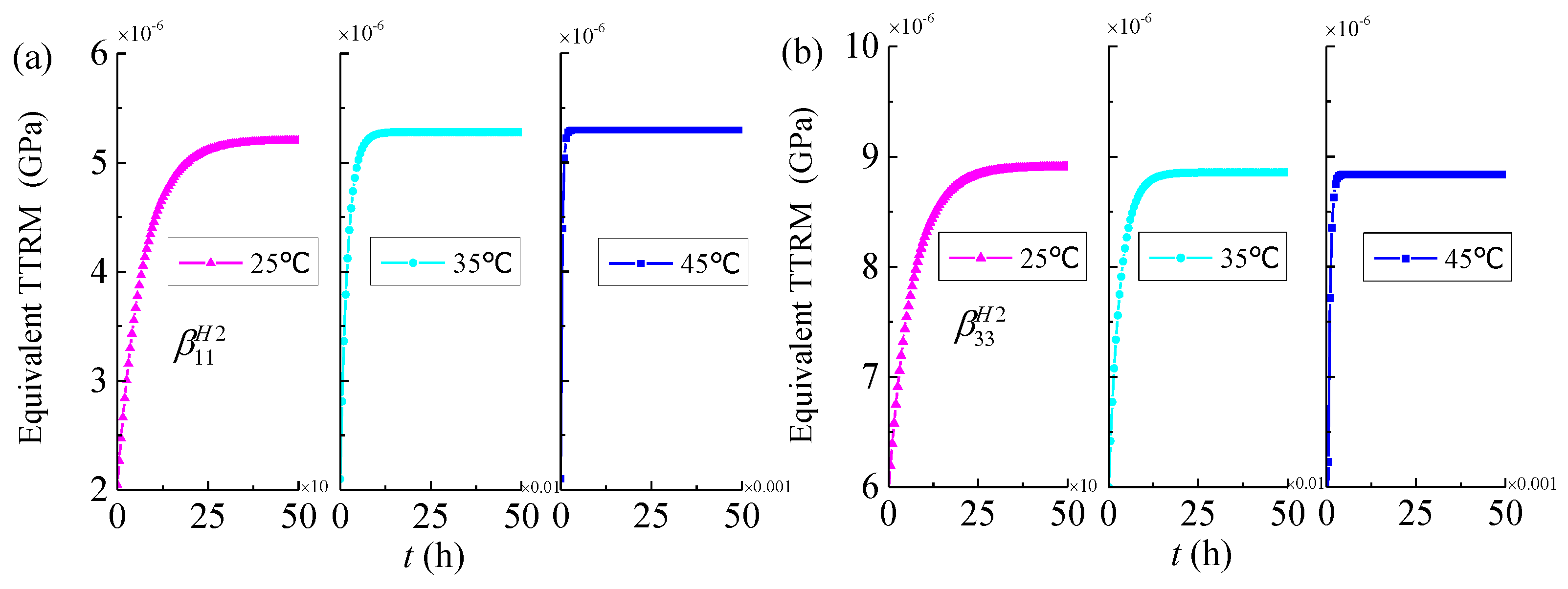
4.2. Effective Thermo-Viscoelastic Properties
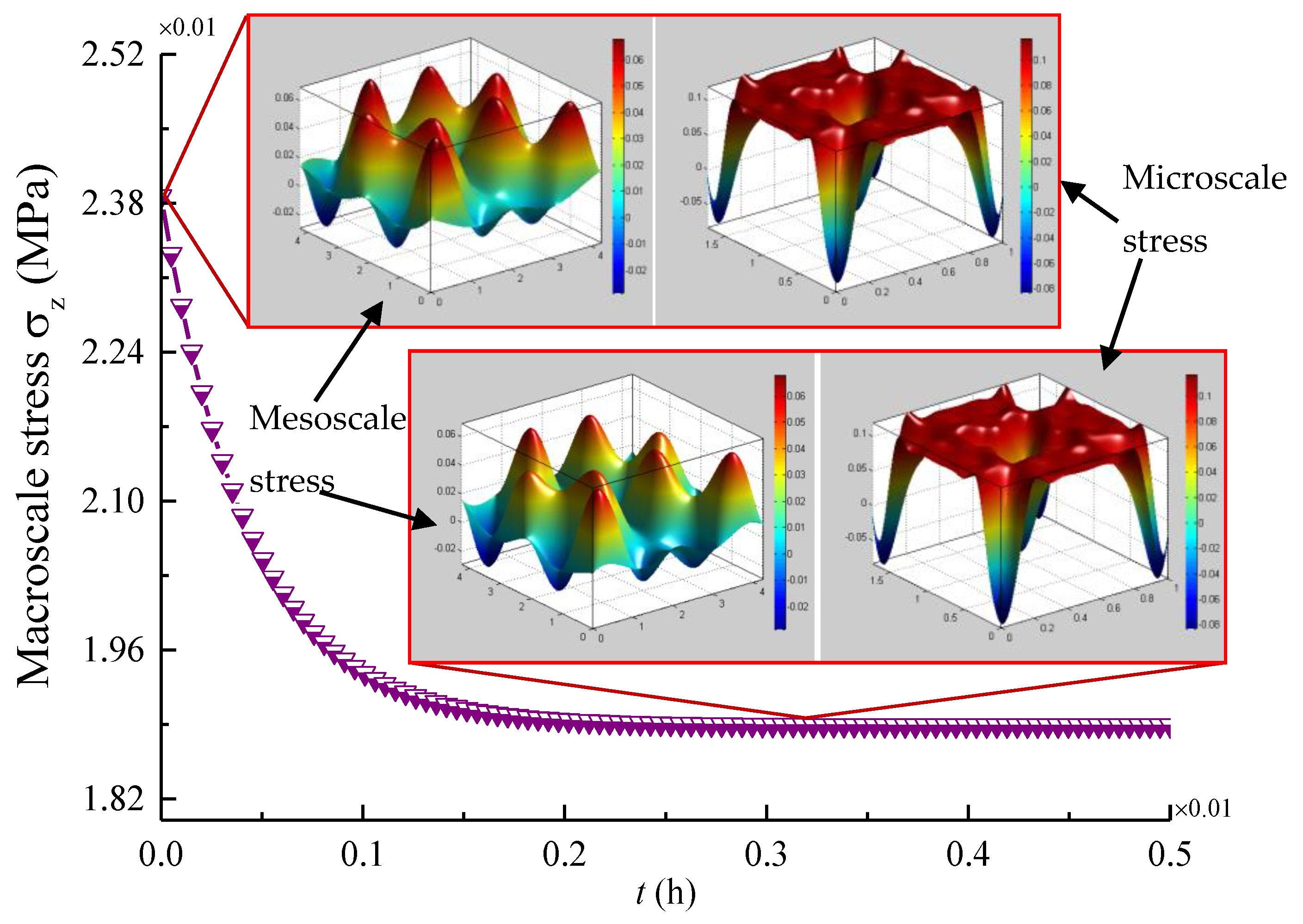
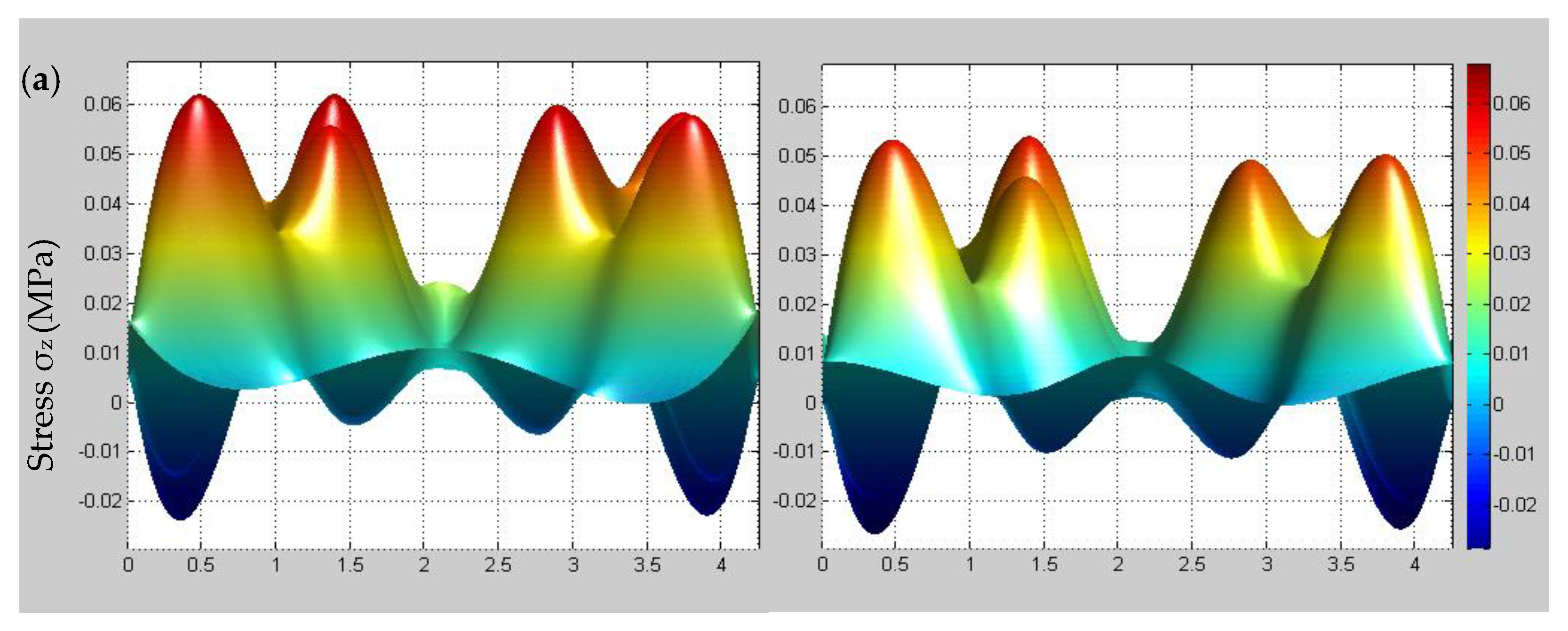
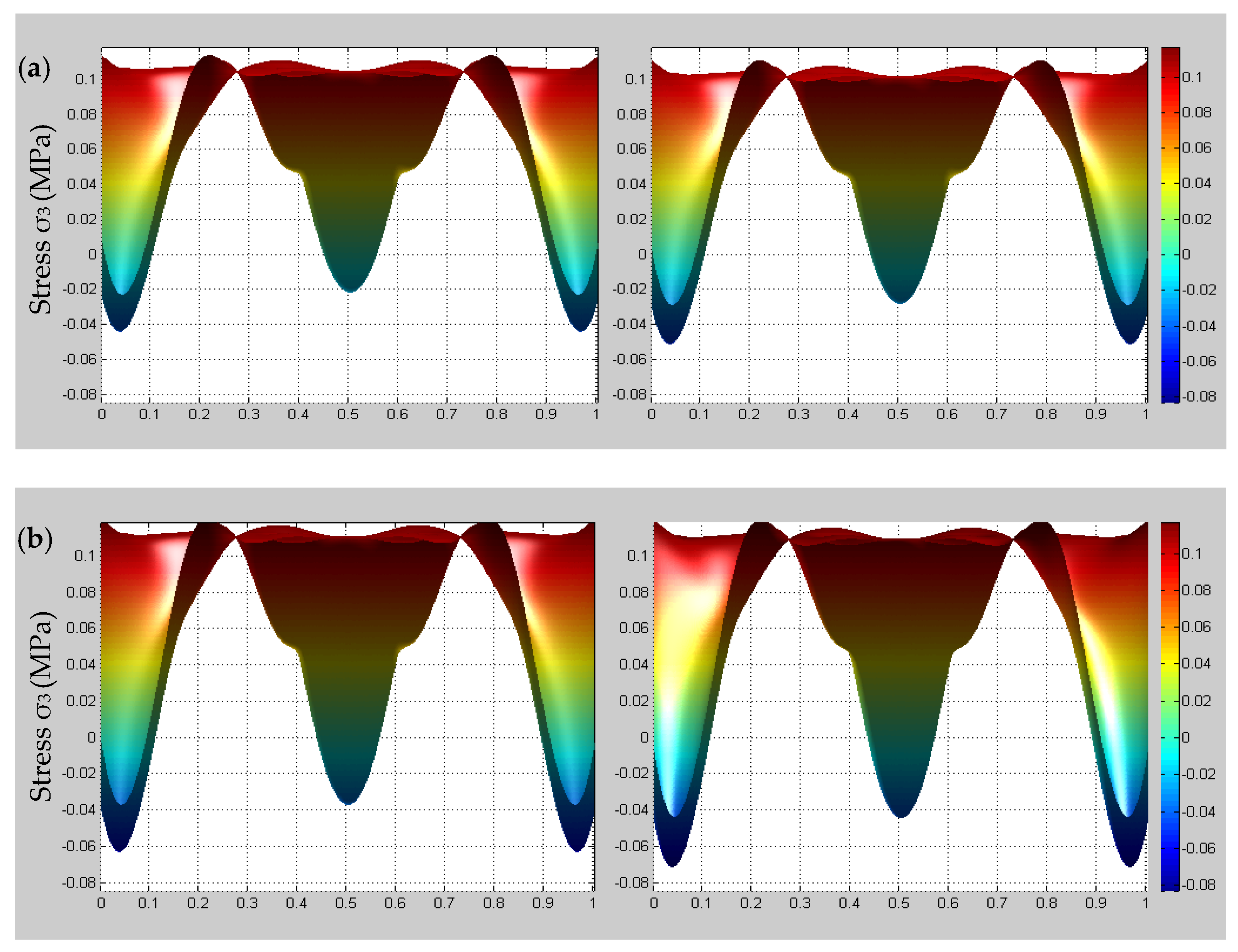
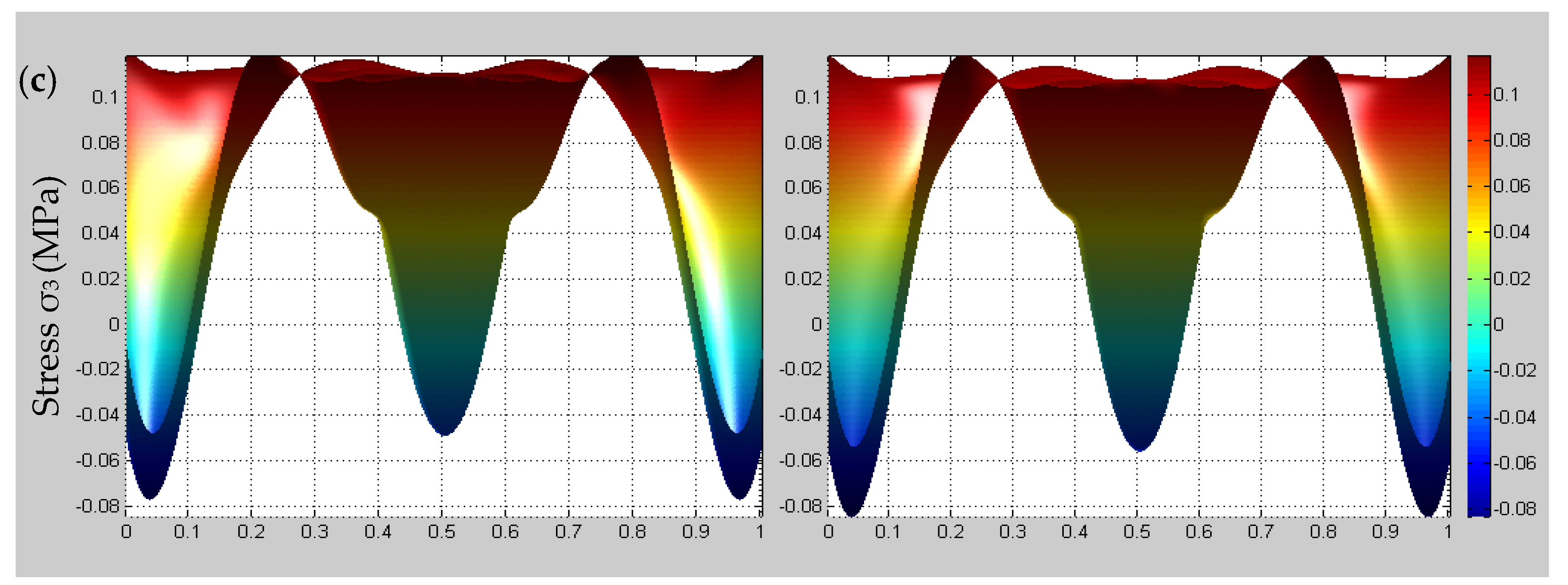
4.3. Time-Dependent Multiscale Stress Field Distributions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, J.; Zhou, G.; Zhou, C. Microstructure and mechanical properties of 3D surface-core 4-directional braided composites. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 50, 7398–7412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Ding, X.; Li, Y. Calculation and design of parameters for four-step 3D braided preform with complex rectangular cross sections. J. Ind. Text. 2008, 38, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Qian, X. Microstructure analysis and multi-unit cell model of three dimensionally four-directional braided composites. Appl. Compos. Mater. 2015, 22, 29–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Curiel-Sosa, J.L.; Duodu, E.A. Finite element analysis of the damage mechanism of 3D braided composites under high-velocity impact. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 4658–4674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Dang, H.; Xing, J. Progressive failure simulation of notched tensile specimen for triaxially-braided composites. Materials 2019, 12, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zuo, H.; Li, D.; Jiang, L. High Temperature Mechanical Response and Failure Analysis of 3D Five-Directional Braided Composites with Different Braiding Angles. Materials 2019, 12, 3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Chen, L.; Li, D.; Li, J. Analysis of creep behavior of resin-based 3-D braided composites. J. Tianjin Poly. Univ. 2004, 23, 13–15. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Li, J.; Chen, L.; Lu, Z. Studies on creep behavior of three dimensional braiding composites. J. Aeronaut. Mater. 2006, 26, 76–80. [Google Scholar]
- Priyank, U.; Upadhyay, C. A three-dimensional micromechanical model to predict the viscoelastic behavior of woven composites. Compos. Struct. 2011, 93, 2733–2739. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, X.; Sun, H. Viscoelastic properties of 3D 4-directional braided composites. Acta. Mater. Compos. Sin. 2012, 29, 167–171. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y.; Sun, H. Prediction on viscoelastic properties of three-dimensionally braided composites by multi-scale model. J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 48, 6499–6508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourid, A.; Ganesan, R.; Levesque, M. Comparison between analytical and numerical predictions for the linearly viscoelastic behavior of textile composites. Mech. Mater. 2013, 58, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Zhang, Y. Multiple scale viscoelastic analysis of 3D woven composite materials. Acta Mater. Compos. Sin. 2007, 24, 125–129. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Tang, T.; Yu, W.; Pipes, R. Multiscale modeling of viscoelastic behaviors of textile composites. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 2018, 130, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Xia, Z.; Gu, B. Nonlinear viscoelastic multi-scale repetitive unit cell model of 3D woven composites with damage evolution. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2013, 50, 3539–3554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tate, J.; Kelkar, A.; Beall, G. Viscoelastic effects on fatigue behavior of braided composites. Asme Int. Mech. Eng. Congr. Expos. 2006, 14091, 711–716. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, J.; Kong, X.; Cheng, S. A coupled multi-scale method for predicting the viscoelastic behavior of resin-based 3D braided composites. Mater. Des. 2020, 195, 109048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.; Hwang, I. Thermo-viscoelastic response of graphite/epoxy composites. J. Eng. Mater. Technol. 1988, 110, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muddasani, M.; Sawant, S.; Muliana, A. Thermo-viscoelastic responses of multilayered polymer composites: Experimental and numerical studies. Compos. Struct. 2010, 92, 2641–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yao, X.; Liu, Y. Thermo-viscoelastic analysis of the integrated T-shaped composite structures. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2010, 70, 1497–1503. [Google Scholar]
- Seifert, O.; Schumacher, S.; Hansen, A. Viscoelastic properties of a glass fabric composite at elevated temperatures: Experimental and numerical results. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2003, 34, 571–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsekorn, M.; Marcin, L.; Godon, T. Multi-scale modeling of the viscoelastic behavior of 3D woven composites. Compos. Part A 2018, 112, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, Y.; Sun, H. Thermo-viscoelastic analysis of three-dimensionally braided composites. Compos. Struct. 2013, 98, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Sun, H. Dynamic response of thermo-viscoelasticity of three-dimensionally braided composites. J. Compos. Mater. 2014, 48, 1575–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, F.; Oller, S.; Martínez, X. Numerical homogenization for composite materials analysis. Comparison with other micro mechanical formulations. Compos. Struct. 2015, 122, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karathanasopoulos, N.; Arampatzis, G.; Ganghoffer, J. Unravelling the viscoelastic, buffer-like mechanical behavior of tendons: A numerical quantitative study at the fibril-fiber scale. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. 2019, 90, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karathanasopoulos, N.; Angelikopoulos, P.; Papadimitriou, C. Bayesian identification of the tendon fascicle’s structural composition using finite element models for helical geometries. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2017, 313, 744–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, S.; Ma, N. Study on the thermal stress relaxation and constitutive equations of viscoelastic composite materials, part I: General theory. Acta Mater. Compos. Sin. 2005, 22, 152–157. [Google Scholar]
- Kalamkarov, A. Composite and Reinforced Elements of Construction; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, P.; Zhang, S.; Wu, Y. Correspondence principles and numerical methods of inverse integral transformation in viscoelastic mechanics. Adv. Mech. 1999, 29, 317–330. [Google Scholar]
- Zak, A. Structural analysis of realistic solid propellant materials. J. Spacecr. Rockets 1968, 5, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Press, W.; Flannery, B.; Teukolsky, S.; Vetterling, W. Numerical Recipes in C: The Art of Scientific Computing, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, J.; Cheng, S.; Zeng, T.; Wang, Z.; Fang, D. Extended multiscale FE approach for steady-state heat conduction analysis of 3D braided composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2017, 151, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, J.; Zeng, T.; Xu, G. A multi-scale finite element method for failure analysis of three-dimensional braided composite structures. Compos. Part B Eng. 2017, 110, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.; Liu, S. Study on the thermal stress relaxation and constitutive equations of viscoelastic composite materials, part II: Numerical simulation. Acta. Mater. Compos. Sin. 2005, 22, 158–163. [Google Scholar]





| Phase | Parameters | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Reinforced fiber | Transverse modulus Ef1 (GPa) | 13.8 |
| Longitudinal modulus Ef3 (GPa) | 220 | |
| Shear modulus Gf13 (GPa) | 9.0 | |
| Shear modulus Gf12 (GPa) | 5.52 | |
| Longitudinal poisson’s ratio γf12 | 0.25 | |
| Transverse poisson’s ratio γf31 | 0.3 | |
| Longitudinal thermal expansion coefficient α11 (10−6/K) | −0.3 | |
| Transverse thermal expansion coefficient α22 (10−6/K) | 8.0 | |
| Matrix | Elastic coefficient G1 (GPa) | 3.2 |
| Elastic coefficient G2 (GPa) | 1.8 | |
| Viscosity coefficient η2 (GPa·h) | 300 | |
| Volume modulus K (GPa) | 5.56 | |
| Thermal expansion coefficient αm (10−6/K) | 54 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhai, J.-J.; Kong, X.-X.; Wang, L.-C. Thermo-Viscoelastic Response of 3D Braided Composites Based on a Novel FsMsFE Method. Materials 2021, 14, 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14020271
Zhai J-J, Kong X-X, Wang L-C. Thermo-Viscoelastic Response of 3D Braided Composites Based on a Novel FsMsFE Method. Materials. 2021; 14(2):271. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14020271
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhai, Jun-Jun, Xiang-Xia Kong, and Lu-Chen Wang. 2021. "Thermo-Viscoelastic Response of 3D Braided Composites Based on a Novel FsMsFE Method" Materials 14, no. 2: 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14020271
APA StyleZhai, J.-J., Kong, X.-X., & Wang, L.-C. (2021). Thermo-Viscoelastic Response of 3D Braided Composites Based on a Novel FsMsFE Method. Materials, 14(2), 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14020271




