Development of Janus Cellulose Acetate Fiber (CA) Membranes for Highly Efficient Oil–Water Separation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
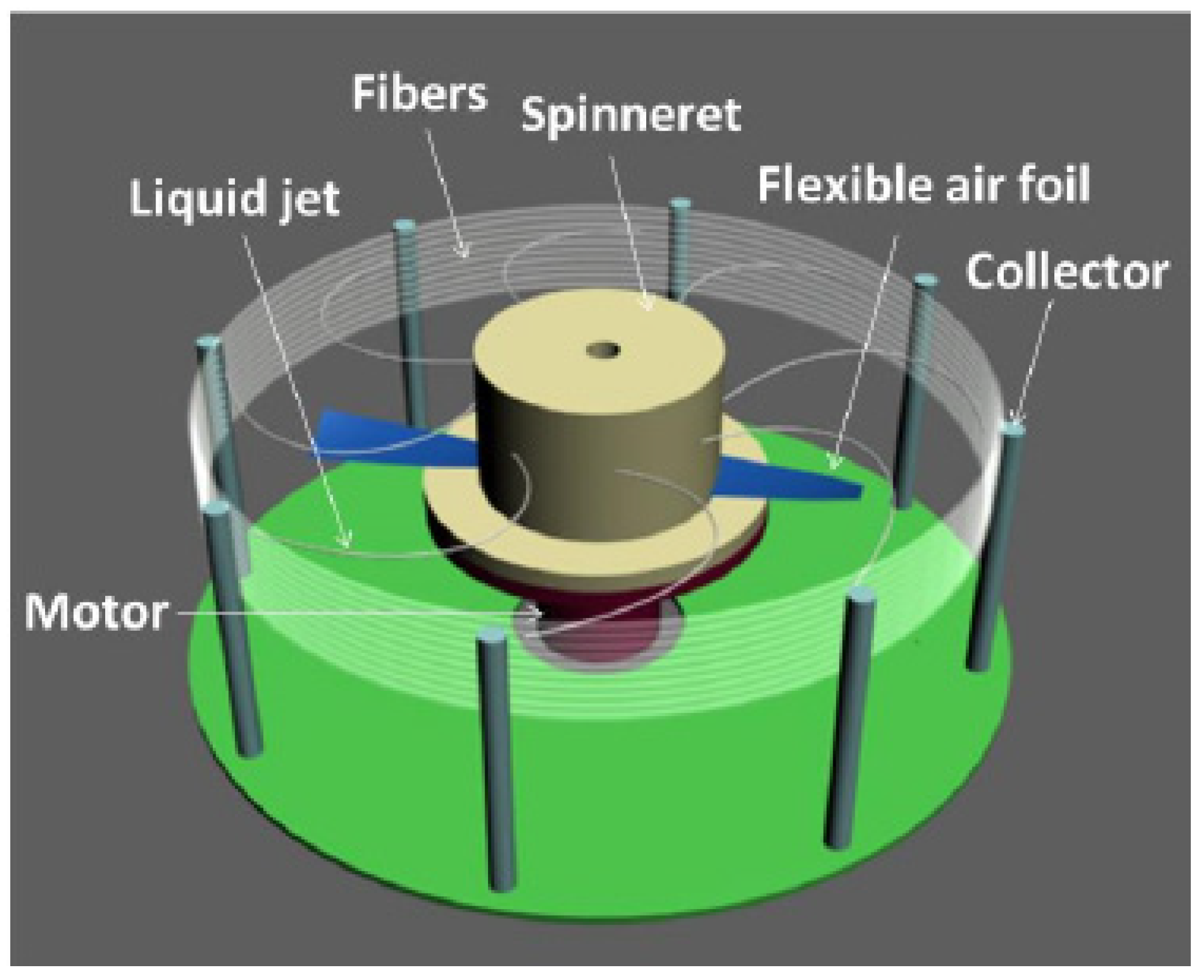
2.2. Preparation of Superhydrophobic/Hydrophilic Janus–CA Fiber Membrane
2.3. Membrane Characterizations
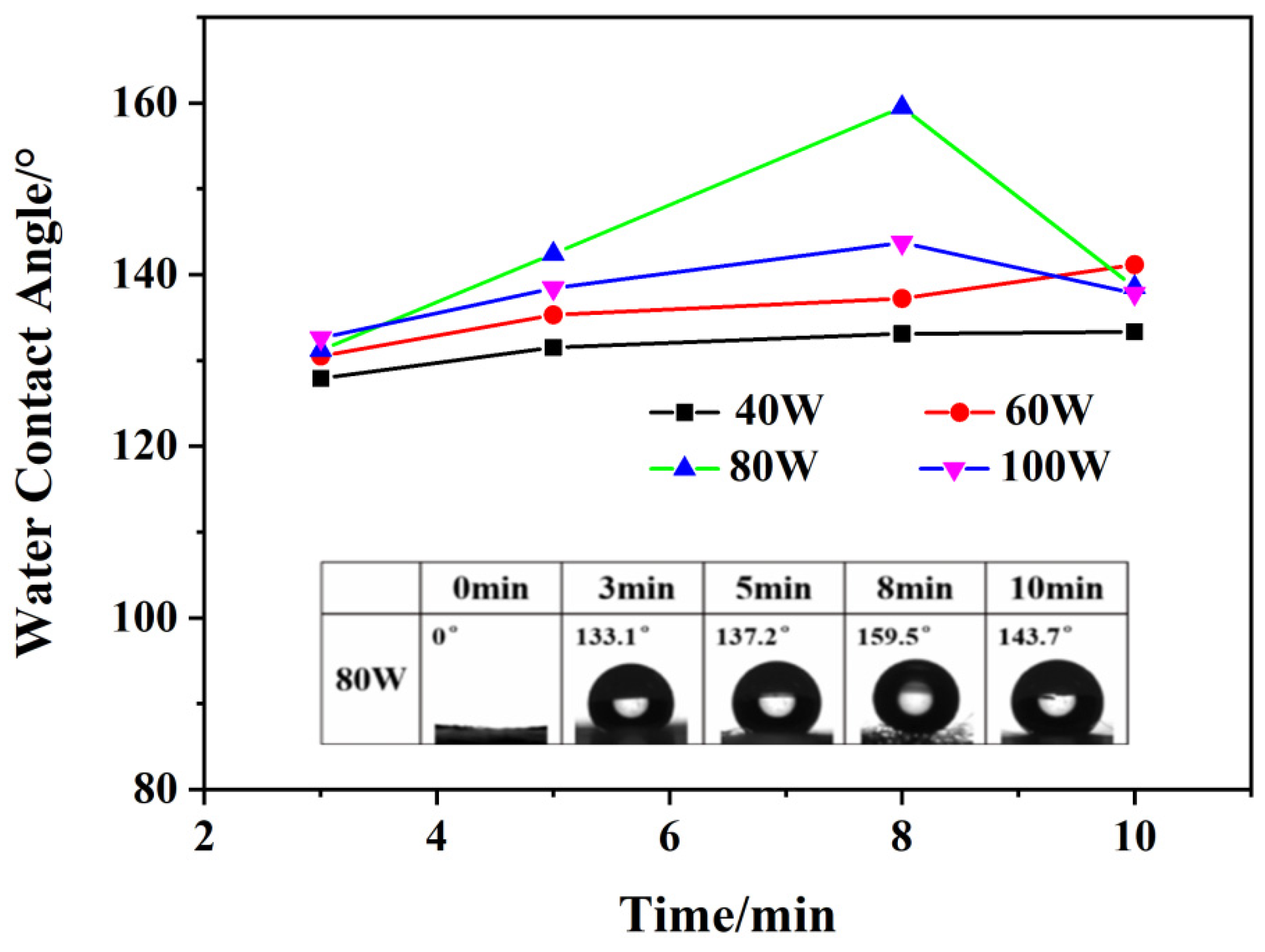
2.4. Water Contact Angle Test
2.5. Membrane Flux Test
2.6. Interception Rate Test
3. Results and Discussion
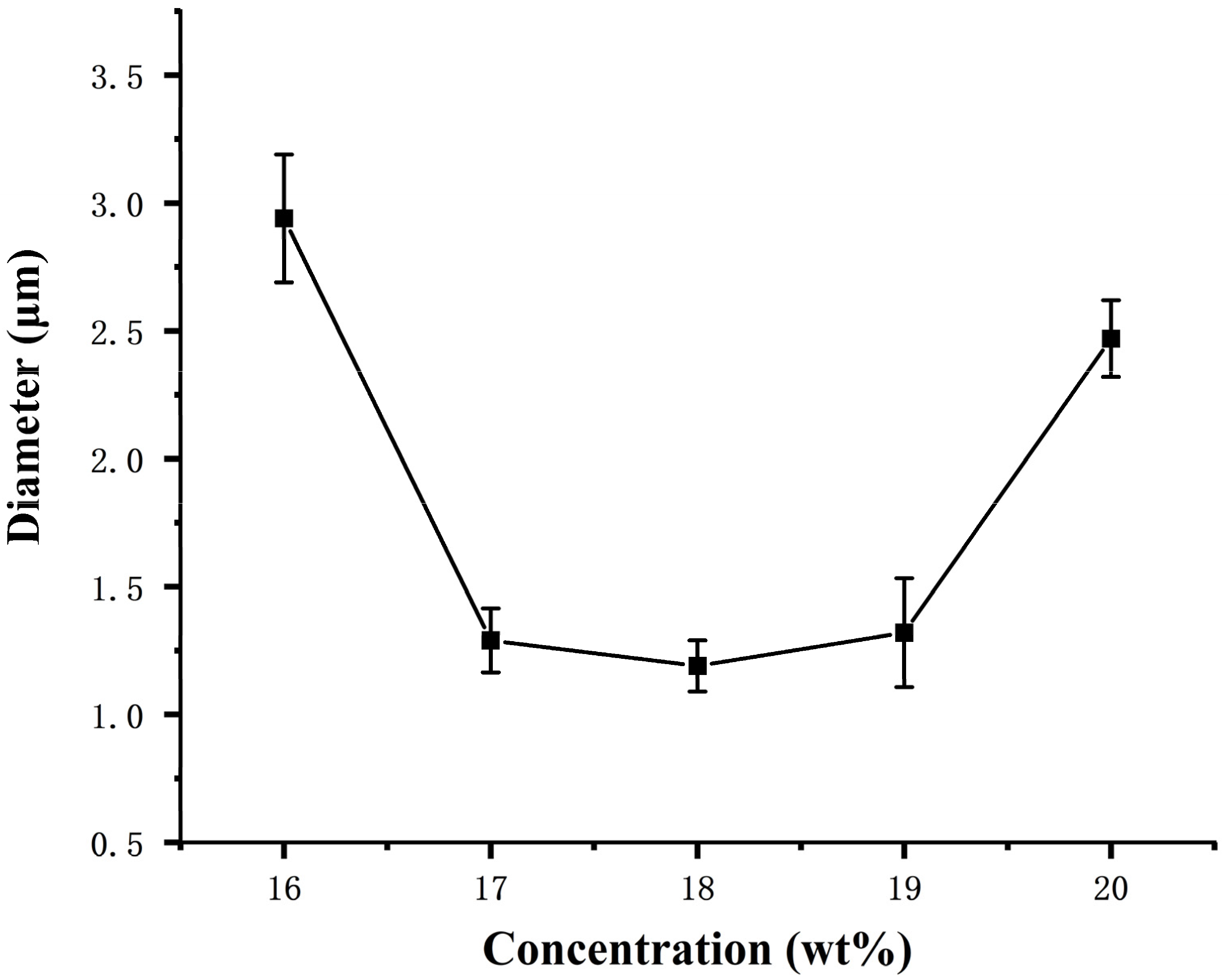
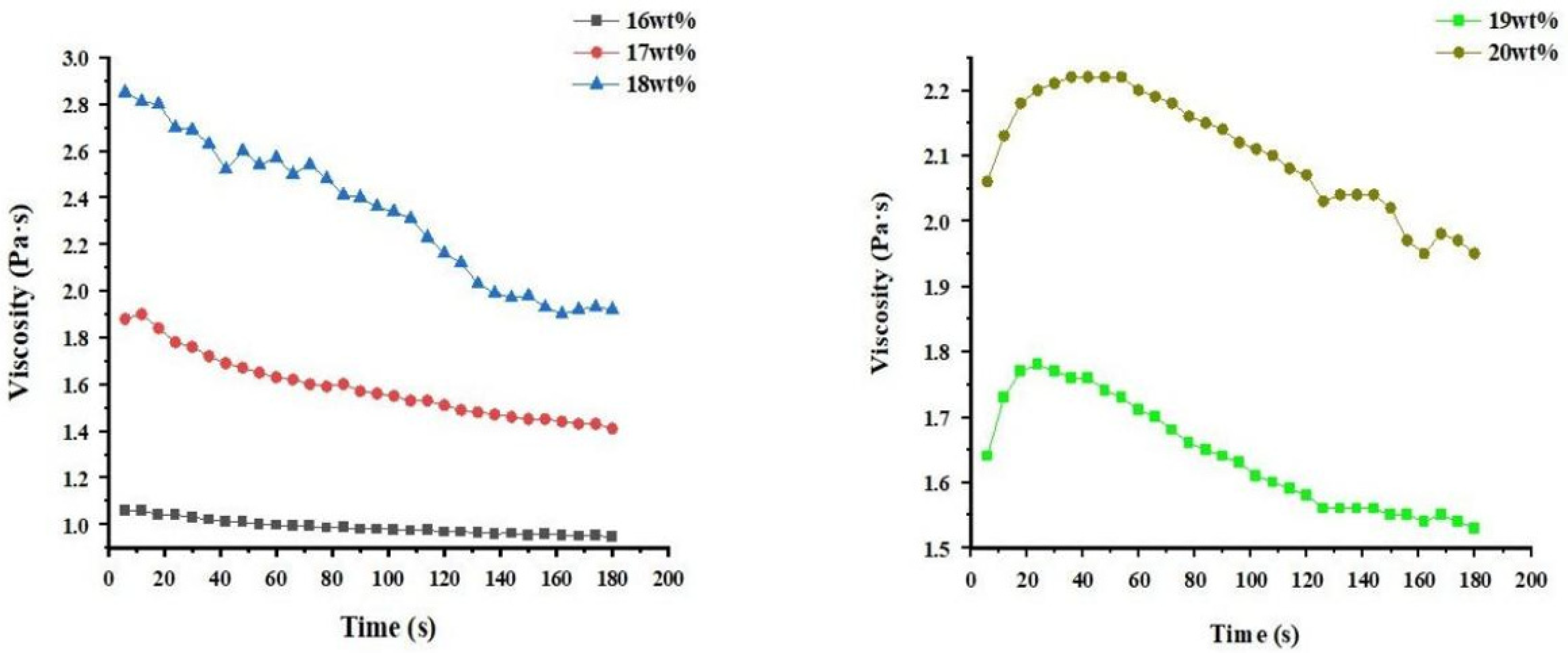
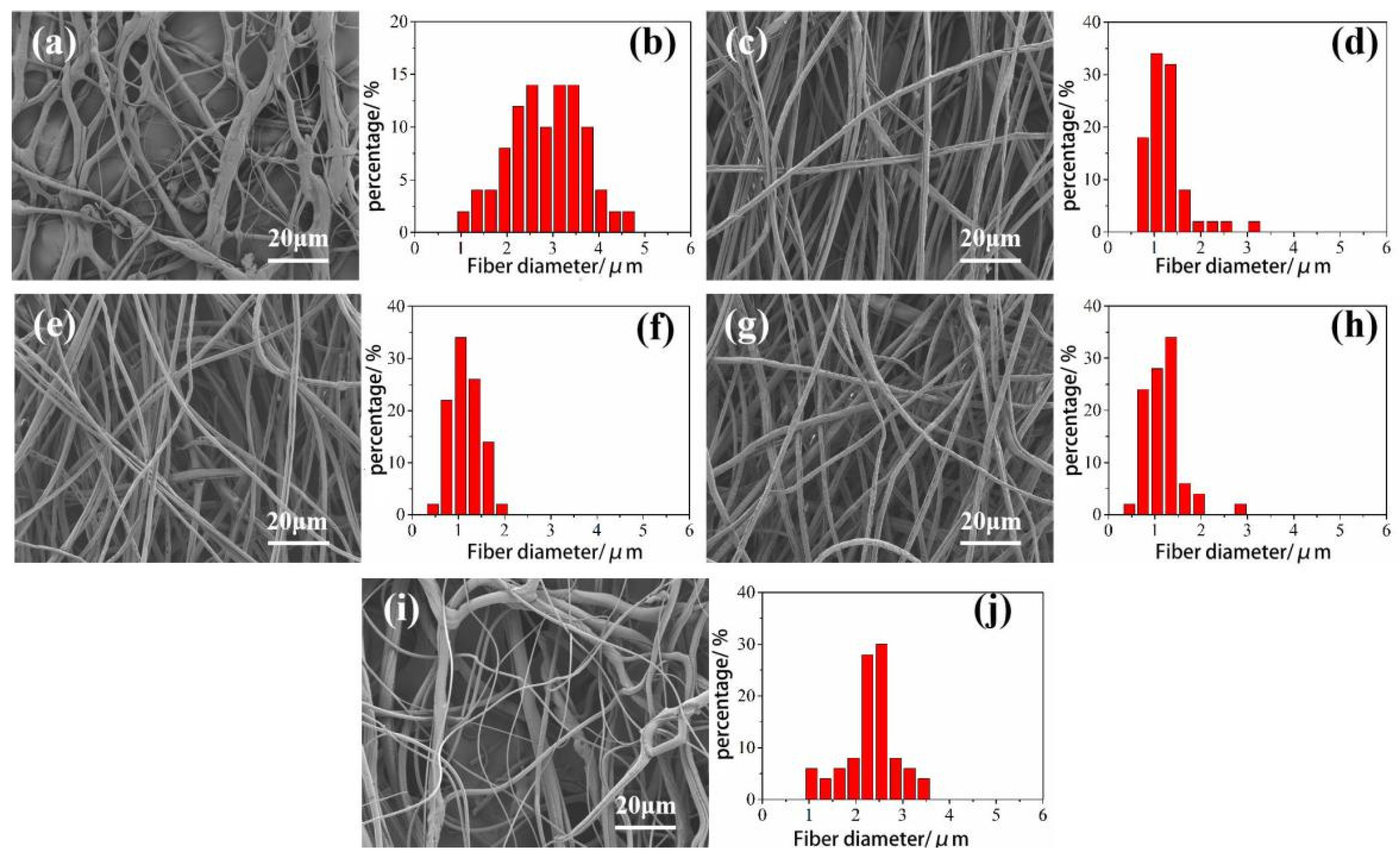
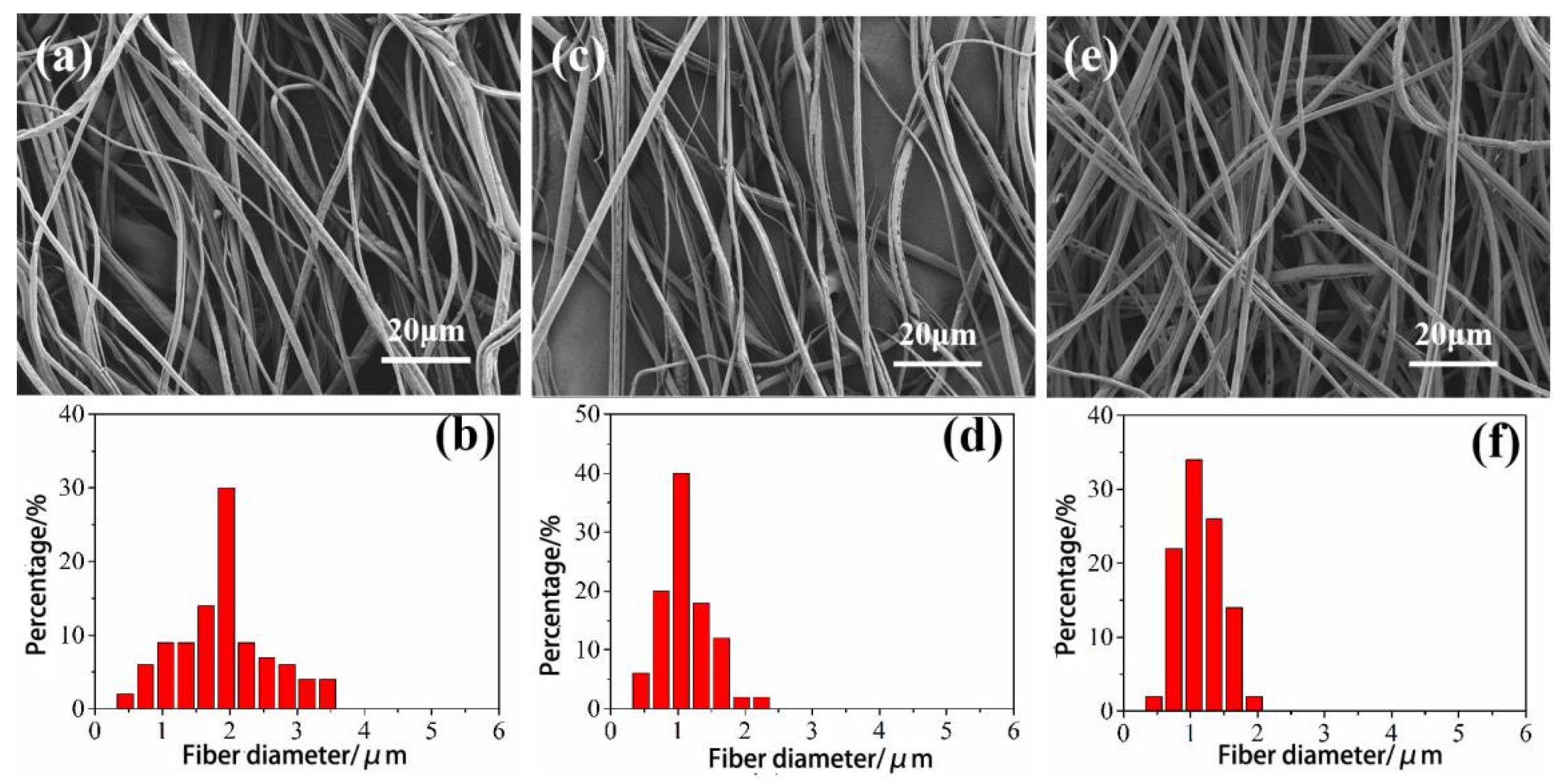
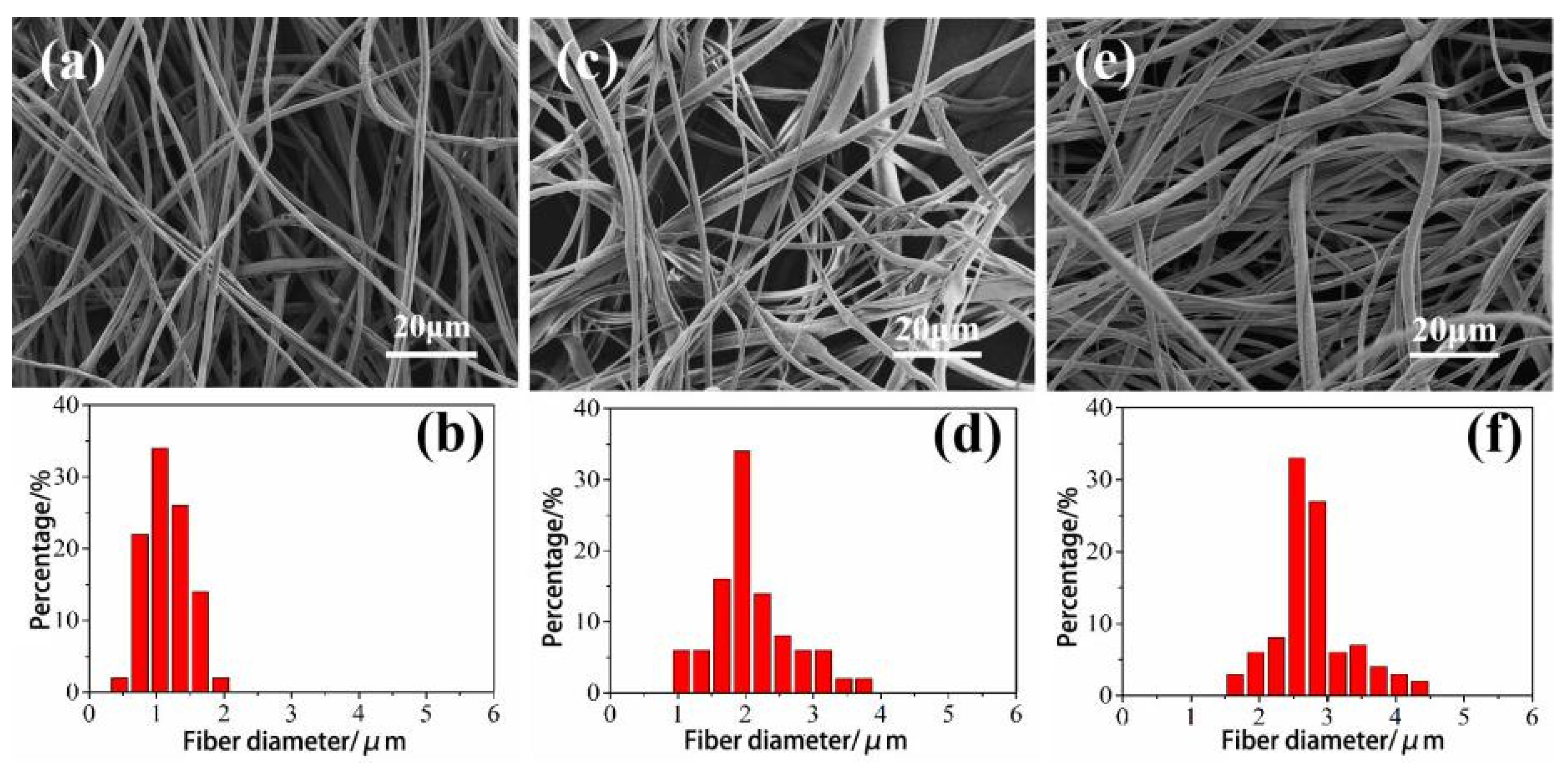
3.1. Analysis on the Influence of Spinning Parameters of Centrifugal Spinning on the Morphology of CA Fiber
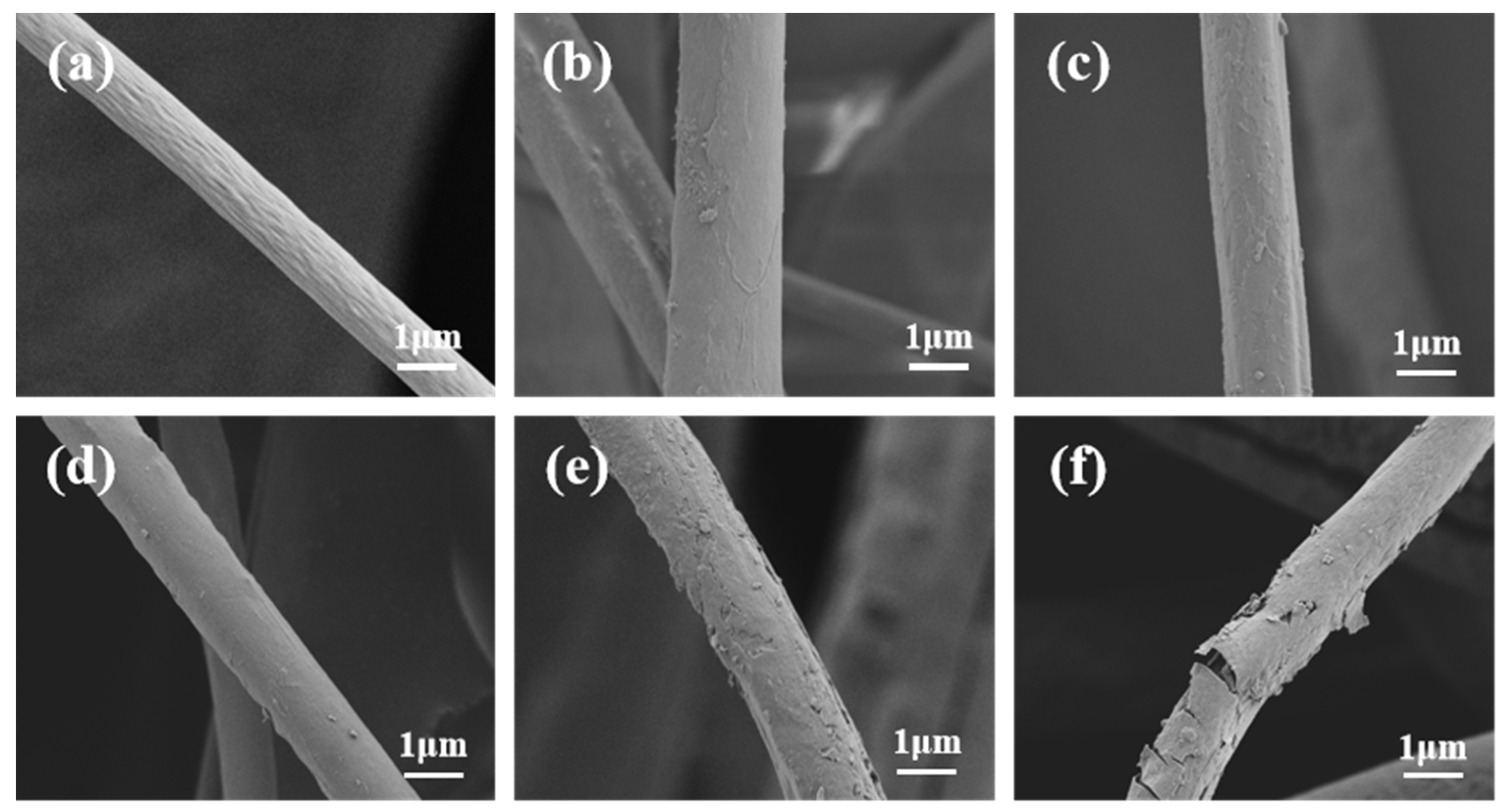
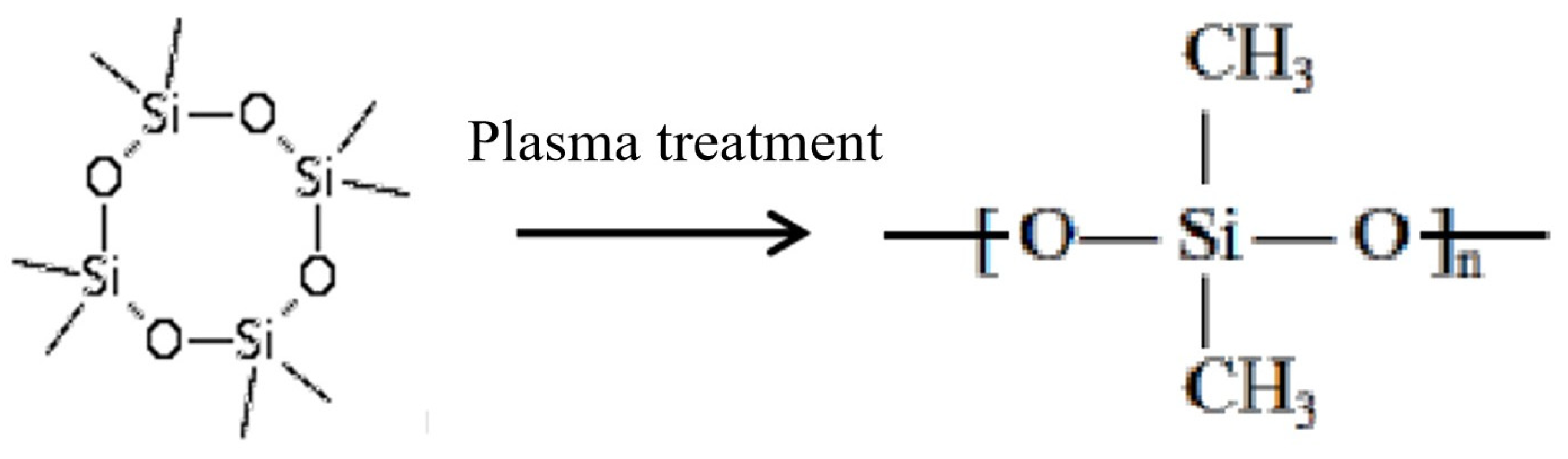
3.2. The Effect of Plasma Grafting D4 on Fiber Morphology and Wetting Properties
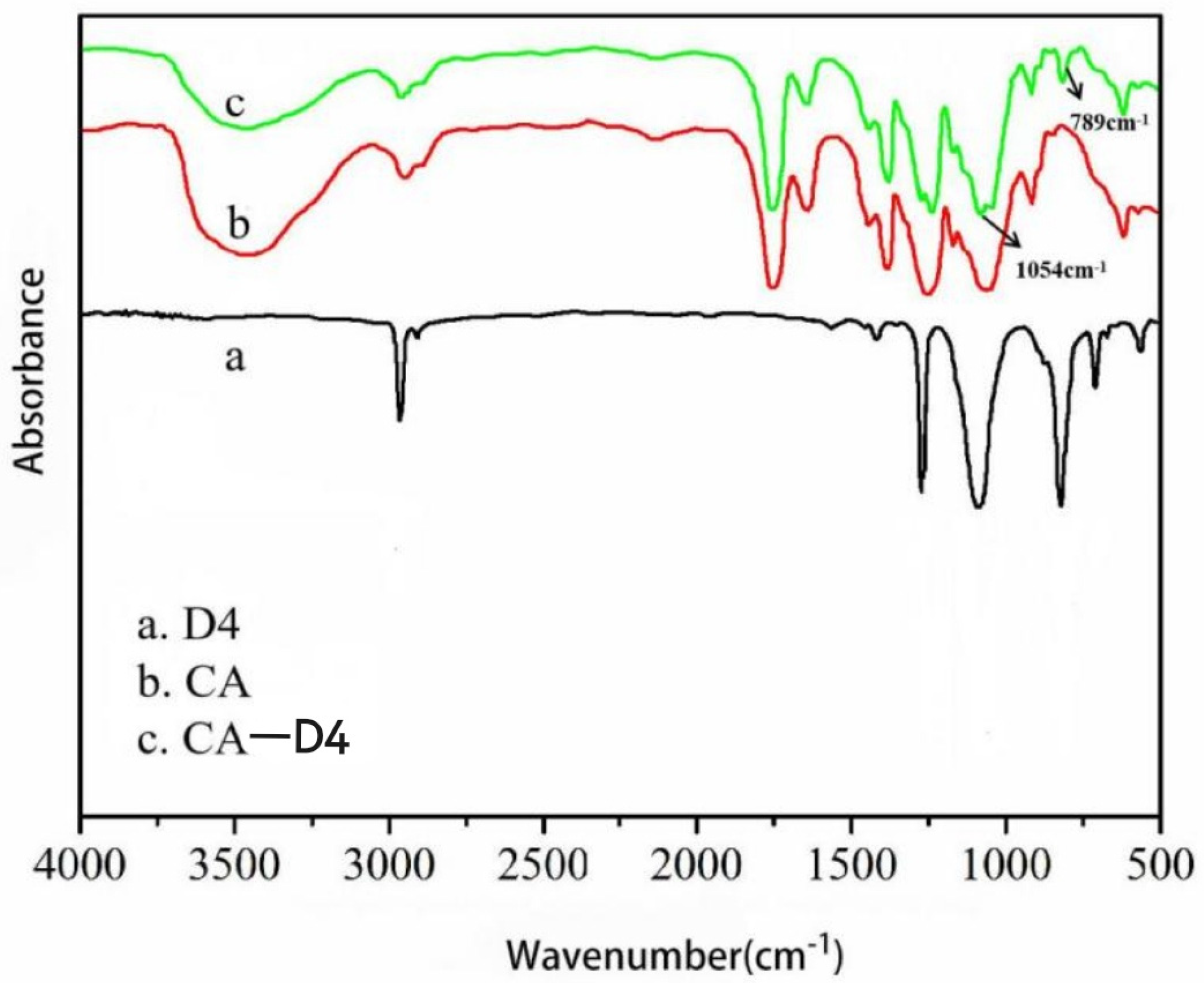
3.3. Surface Chemical Structure Analysis
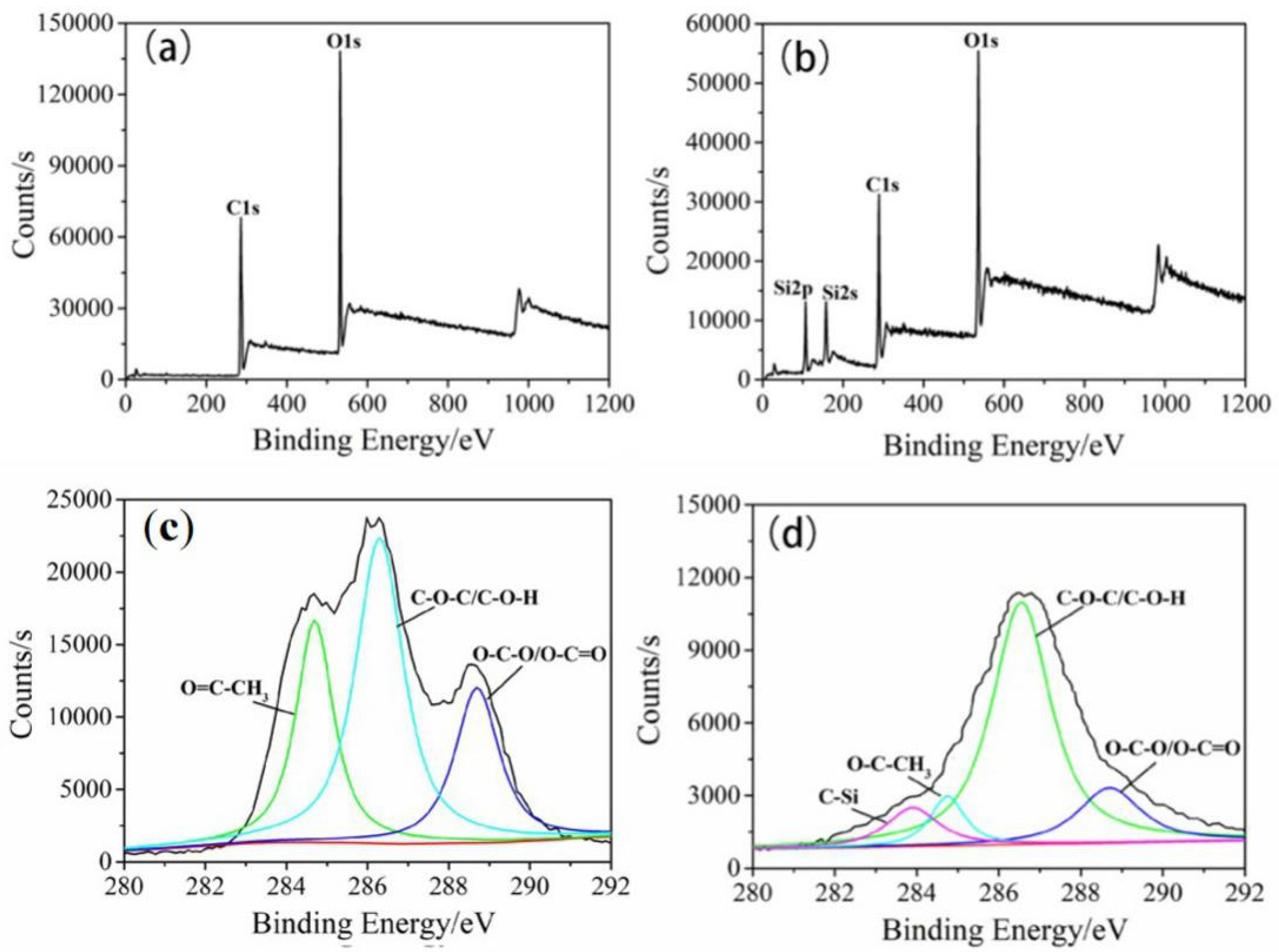
3.4. Janus–CA Fiber Surface EDS Analysis
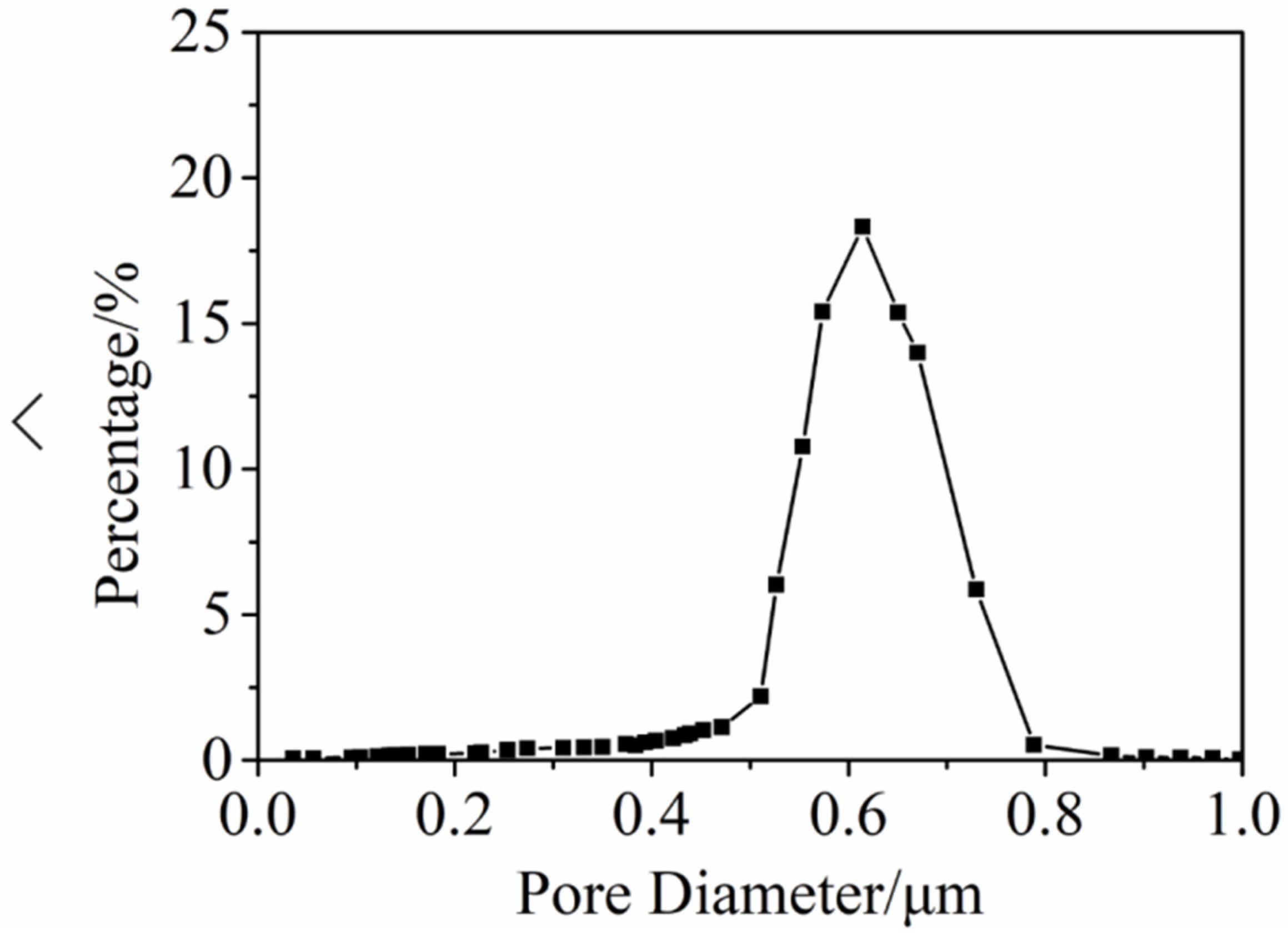
3.5. Janus–CA Fiber Membrane Pore Size Test
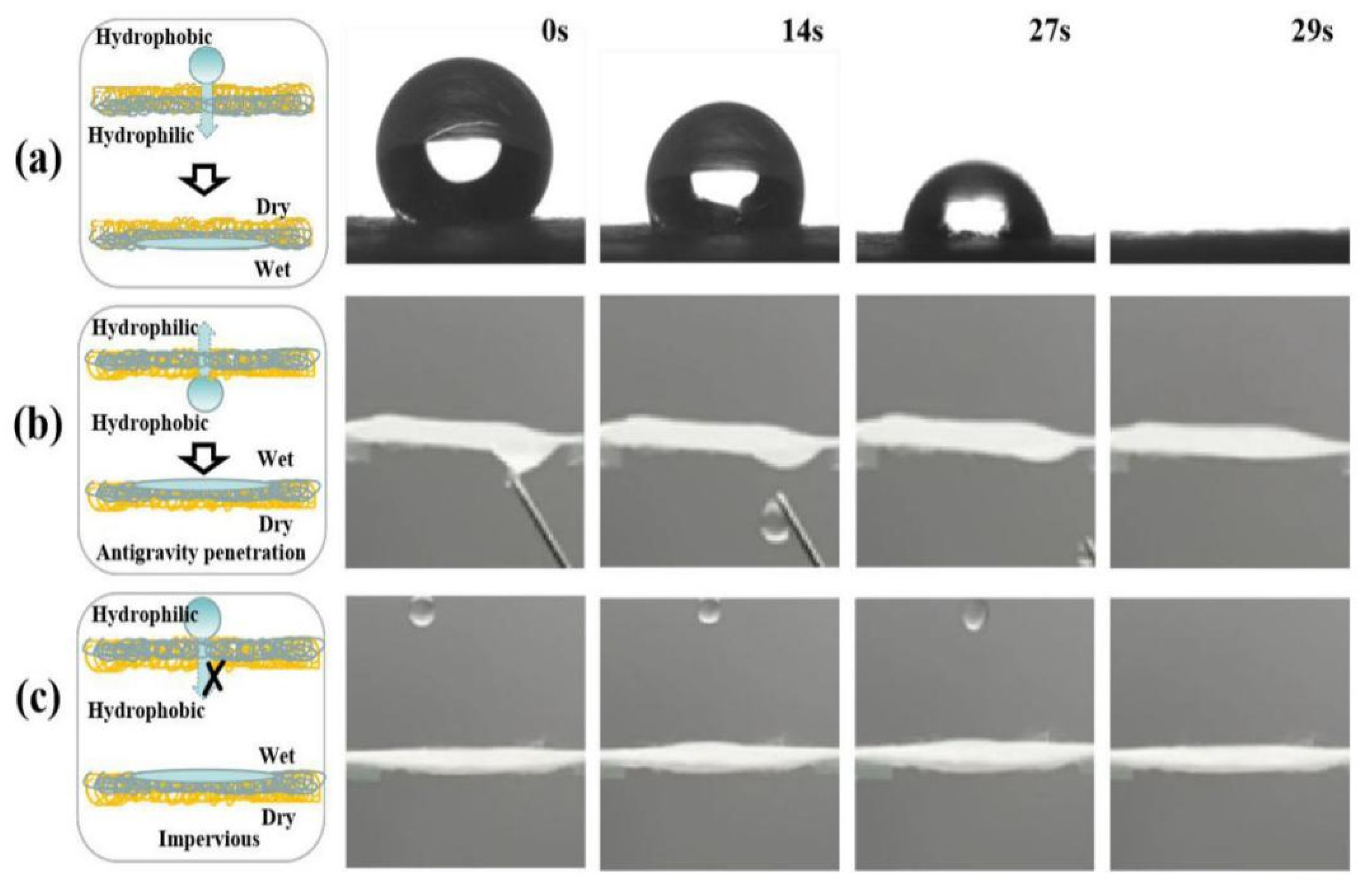
3.6. Janus–CA Fiber Membrane Oil–Water Separation Performance Test
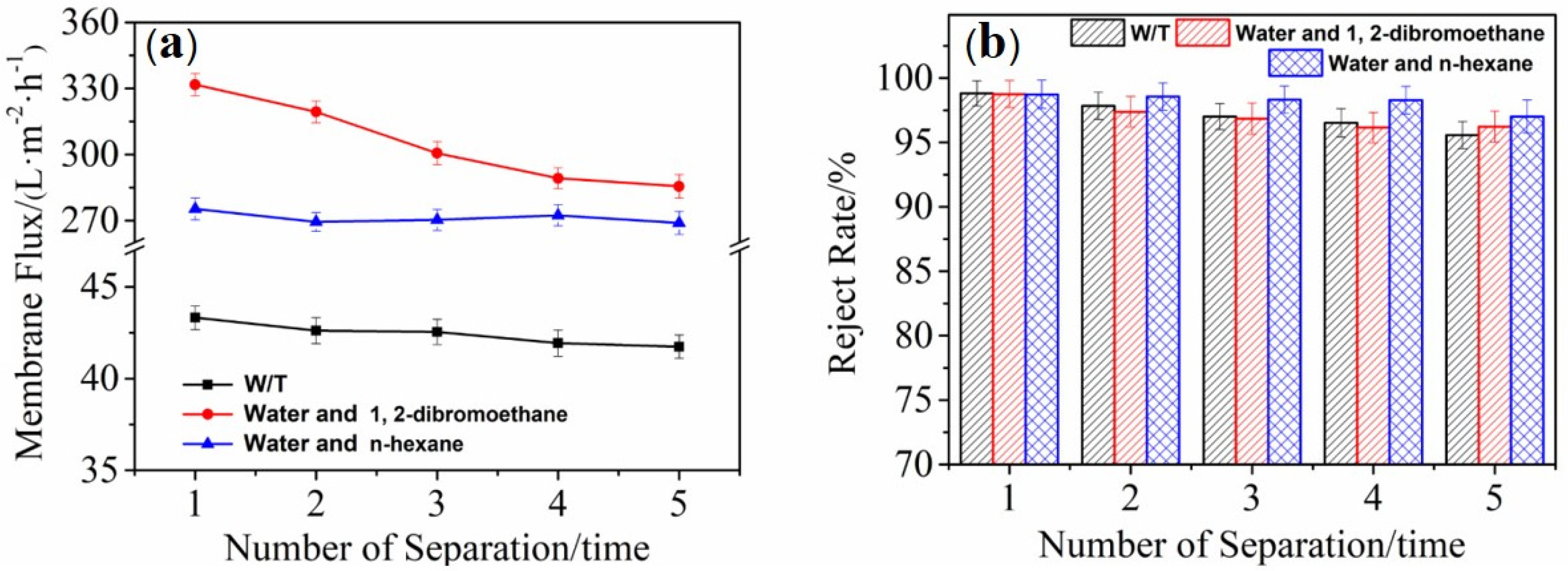
3.7. Membrane Flux Test
3.8. Rejection Rate Test
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ren, C.; Ng, G.H.B.; Wu, H.; Chan, K.-H.; Shen, J.; Teh, C.; Ying, J.Y.; Zeng, H. Instant Room-Temperature Gelation of Crude Oil by Chiral Organogelators. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 4001–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, M.; Ma, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, X.; He, J. Multifunctional Superwettable Material with Smart pH Responsiveness for Efficient and Controllable Oil/Water Separation and Emulsified Wastewater Purification. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 24668–24682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhao, X.; Wu, P.; Zhang, S.; Geng, B. Facile preparation of superhydrophobic and superoleophilic porous polymer membranes for oil/water separation from a polyarylester polydimethylsiloxane block copolymer. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 51, 3211–3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Zong, D.; Jin, Q.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Biomimetic and Superwettable Nanofibrous Skins for Highly Efficient Separation of Oil-in-Water Emulsions. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venault, A.; Chang, C.-Y.; Tsai, T.-C.; Chang, H.-Y.; Bouyer, D.; Lee, K.-R.; Chang, Y. Surface zwitterionization of PVDF VIPS membranes for oil and water separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 563, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, F.; Li, G.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Fan, H.; Zhou, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Mu, K.; et al. A single-layer Janus membrane with dual gradient conical micropore arrays for self-driving fog collection. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 18403–18408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Liu, J.; Ye, Q.; Wang, D.; Lianga, Y.; Zhou, F. A general approach for construction of asymmetric modification membranes for gated flow nanochannels. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 8804–8814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Chen, D.; Li, N.; Xu, Q.; Li, H.; He, J.; Lu, J. A facile method to fabricate a double-layer stainless steel mesh for effective separation of water-in-oil emulsions with high flux. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 18815–18821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Jin, H.; Sainio, J.; Ras, R.H.A.; Ikkala, O. Droplet and Fluid Gating by Biomimetic Janus Membranes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 6023–6028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.-B.; Yang, H.-C.; Wang, J.-J.; Wu, G.-P.; Xu, Z.-K. Janus Membranes with Opposing Surface Wettability Enabling Oil-to-Water and Water-to-Oil Emulsification. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 5062–5066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Hou, J.; Xu, J.; Shan, B. Switchable oil/water separation with efficient and robust Janus nanofiber membranes. Carbon 2017, 115, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xiao, T.; Bao, C.; Fu, Y.; Yang, X. Fabrication of novel Janus membrane by nonsolvent thermally induced phase separation (NTIPS) for enhanced performance in membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 563, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zhong, L.; Song, C.; Shi, W.; Cui, F.; Wang, W. Breathable and asymmetrically superwettable Janus membrane with robust oil-fouling resistance for durable membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 563, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Wang, N.; Man, X.; Cui, Z.; Wu, J.; Liu, J.; Li, S.; Gao, Y.; Li, D.; Jiang, L.; et al. Interpenetrating Janus Membrane for High Rectification Ratio Liquid Unidirectional Penetration. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 4124–4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.C.; Xie, Y.; Hou, J.; Cheetham, A.K.; Chen, V.; Darling, S.B. Janus Membranes: Creating Asymmetry for Energy Efficiency. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, e1801495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Liu, Y.; Guo, D.; Cao, M.; Jiang, L. Under-water unidirectional air penetration via a Janus mesh. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 11872–11875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Ding, J.; Dai, L.; Wang, X.; Lin, T. Directional water-transfer through fabrics induced by asymmetric wettability. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 7938–7940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, G. Rapid and Efficient Separation of Oil from Oil-in-Water Emulsions Using a Janus Cotton Fabric. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2016, 55, 1291–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, C.; Yang, F. Improvement of antifouling performances for modified PVDF ultrafiltration membrane with hydrophilic cellulose nanocrystal. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 440, 1091–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-Y.; Aitomaki, Y.; Berglund, L.A.; Oksman, K.; Bismarck, A. On the use of nanocellulose as reinforcement in polymer matrix composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2014, 105, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thakur, V.K.; Thakur, M.K. Processing and characterization of natural cellulose fibers/thermoset polymer composites. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 109, 102–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dufresne, A. Cellulose nanomaterial reinforced polymer nanocomposites. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 29, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer, A.; Pal, L.; Hubbe, M. Nanocellulose in packaging: Advances in barrier layer technologies. Ind. Crops. Prod. 2017, 95, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; Ma, M.-G.; Li, Z.; Mu, T. Advances in the conversion of glucose and cellulose to 5-hydroxymethylfurfural over heterogeneous catalysts. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 98874–98892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaki, N.; Aljawish, A.; Humeau, C.; Muniglia, L.; Jasniewski, J. Enzymatic modification of polysaccharides: Mechanisins, properties, and potential applications: A review. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2016, 90, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, O.; Aytac, Z.; Uyar, T. Superhydrophobic, Hybrid, Electrospun Cellulose Acetate Nanofibrous Mats for Oil/Water Separation by Tailored Surface Modification. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 19747–19754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Ma, J.; Ling, J.; Li, N.; Wang, D.; Yue, F.; Xu, S. Cellulose acetate-based SiO2/TiO2 hybrid microsphere composite aerogel films for water-in-oil emulsion separation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 435, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Livazovic, S.; Falca, G.; Nunes, S.P. Oil-Water Separation using Membranes Manufactured from Cellulose/Ionic Liquid Solutions. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 5649–5659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, M.; Liao, Y.; Wang, R. Engineering a superwetting thin film nanofibrous composite membrane with excellent antifouling and self-cleaning properties to separate surfactant-stabilized oil-in-water emulsions. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.J.; Dreyer, D.R.; Bielawski, C.W.; Paul, D.R.; Freeman, B.D. Surface Modification of Water Purification Membranes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2017, 56, 4662–4711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zanjanijam, A.R.; Hajian, M.; Koohmareh, G.A. Improving the Thermal and Mechanical Properties of Poly(vinyl butyral) Through the Incorporation of Acid- Treated Single- Walled Carbon Nanotubes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoba, B.; Jeyanthi, J.; Vairam, S. Synthesis, characterization of cellulose acetate membrane and application for the treatment of oily wastewater. Environ. Technol. 2020, 41, 1590–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zargham, S.; Bazgir, S.; Tavakoli, A.; Rashidi, A.S.; Damerchely, R. The Effect of Flow Rate on Morphology and Deposition Area of Electrospun Nylon 6 Nanofiber. J. Eng. Fiber. Fabr. 2012, 7, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bakar, S.S.S.; Fong, K.C.; Eleyas, A.; Nazeri, M.F.M. Effect of Voltage and Flow Rate Electrospinning Parameters on Polyacrylonitrile Electrospun Fibers. In Proceedings of the Malaysian Technical Universities Conference on Engineering and Technology 2017 (MUCET 2017), Penang, Malaysia, 6–7 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sanito, R.C.; You, S.J.; Wang, Y.F. Application of plasma technology for treating e-waste: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 288, 112380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Al-Yaari, M. Development of Polymeric Membranes for Oil/Water Separation. Membranes 2021, 11, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; Xue, L.; Liu, F.; Jiang, L. An intelligent superwetting PVDF membrane showing switchable transport performance for oil/water separation. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 2943–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Su, X.; Lai, X.; Chen, W.; Li, H.; Zeng, X. Conductive superhydrophobic cotton fabrics via layer-by-layer assembly of carbon nanotubes for oil-water separation and human motion detection. Mater. Lett. 2019, 253, 230–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Shao, L. A novel mussel-inspired strategy toward superhydrophobic surfaces for self-driven crude oil spill cleanup. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 12171–12178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Su, Y.; Zheng, L.; Wang, L.; Jiang, Z. The improved oil/water separation performance of cellulose acetate-graft-polyacrylonitrile membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 337, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czapka, T.; Winkler, A.; Maliszewska, I.; Kacprzyk, R. Fabrication of Photoactive Electrospun Cellulose Acetate Nanofibers for Antibacterial Applications. Energies 2021, 14, 2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Shao, J.; Zou, C. Fabrication of superhydrophobic fluorine-free films on cotton fabrics through plasma-induced grafting polymerization of 1,3,5,7-tetravinyl-1,3,5,7-tetramethylcyclotetrasiloxane. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 276, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

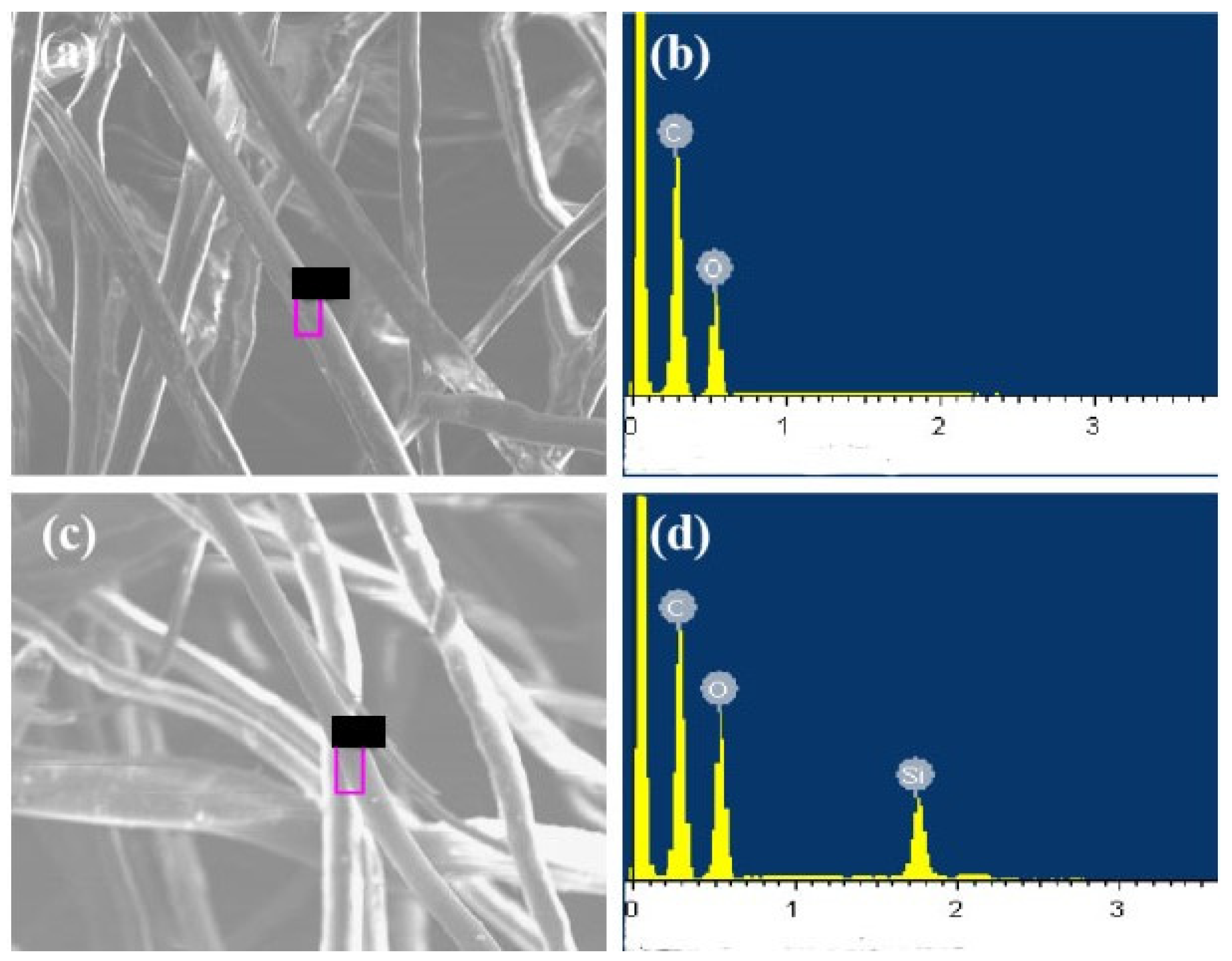

| Element Content Ratio | C/% | O/% | Si/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| CA | 56.66 | 43.34 | / |
| Janus–CA hydrophobic surface | 50.27 | 38.13 | 11.60 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, X.; Zhang, X.; Xing, Y.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, W.; Zhou, K.; Li, Y. Development of Janus Cellulose Acetate Fiber (CA) Membranes for Highly Efficient Oil–Water Separation. Materials 2021, 14, 5916. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14205916
Yu X, Zhang X, Xing Y, Zhang H, Jiang W, Zhou K, Li Y. Development of Janus Cellulose Acetate Fiber (CA) Membranes for Highly Efficient Oil–Water Separation. Materials. 2021; 14(20):5916. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14205916
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Xiaotian, Xian Zhang, Yajie Xing, Hongjing Zhang, Wuwei Jiang, Ke Zhou, and Yongqiang Li. 2021. "Development of Janus Cellulose Acetate Fiber (CA) Membranes for Highly Efficient Oil–Water Separation" Materials 14, no. 20: 5916. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14205916
APA StyleYu, X., Zhang, X., Xing, Y., Zhang, H., Jiang, W., Zhou, K., & Li, Y. (2021). Development of Janus Cellulose Acetate Fiber (CA) Membranes for Highly Efficient Oil–Water Separation. Materials, 14(20), 5916. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14205916






