Effect of Sc on the Hot Cracking Properties of 7xxx Aluminum Alloy and the Microstructure of Squeeze Castings
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Alloy Preparation
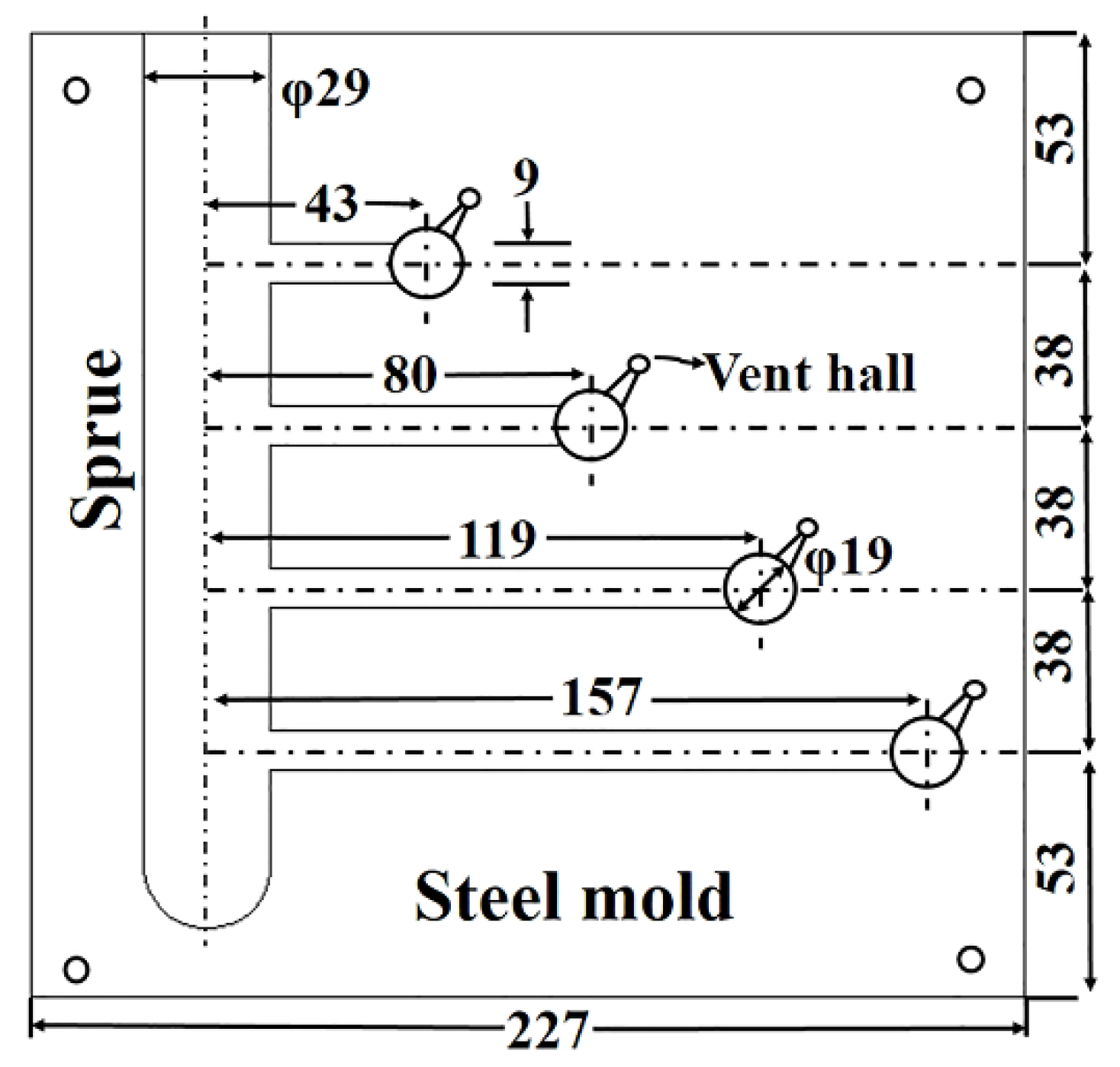
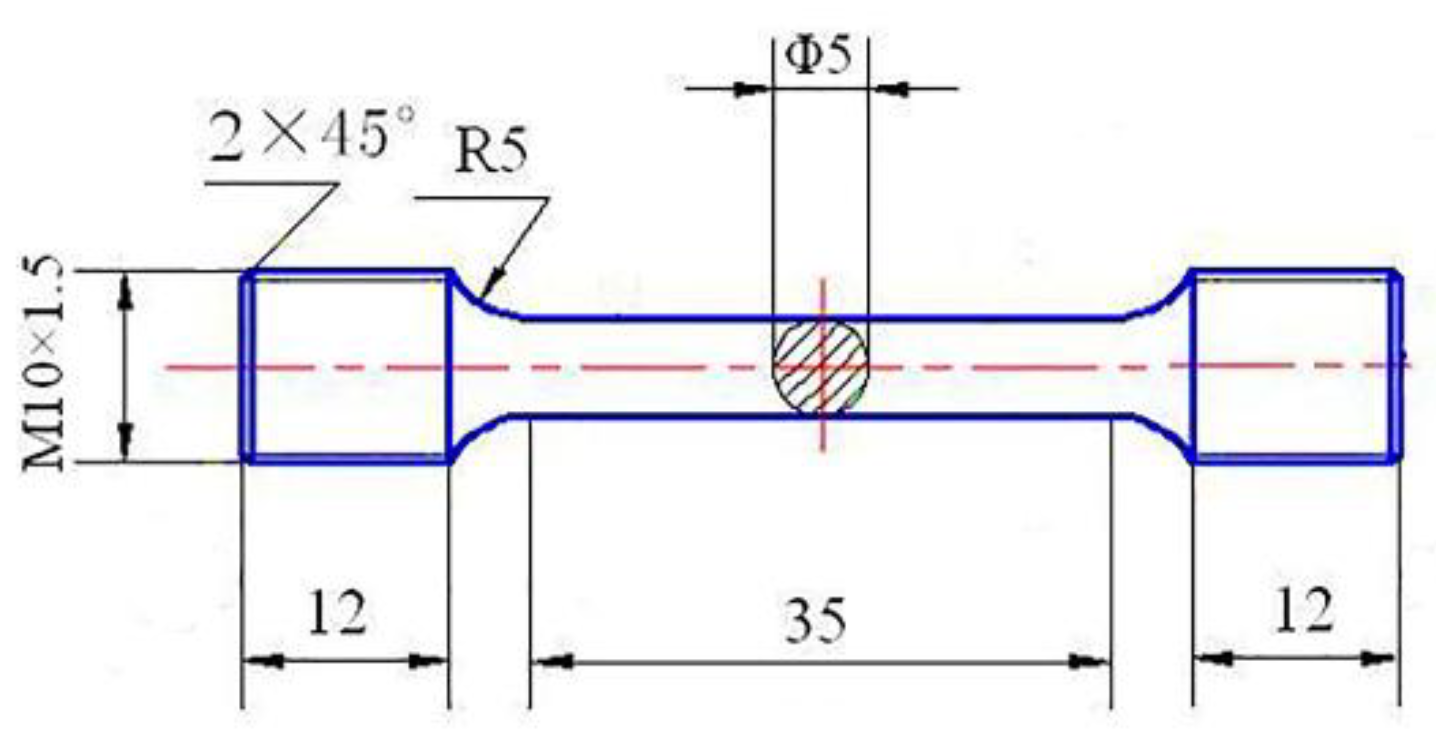
2.2. Experimental Device for a Thermal Cracking Performance
2.3. Organization and Performance Analysis
3. Results
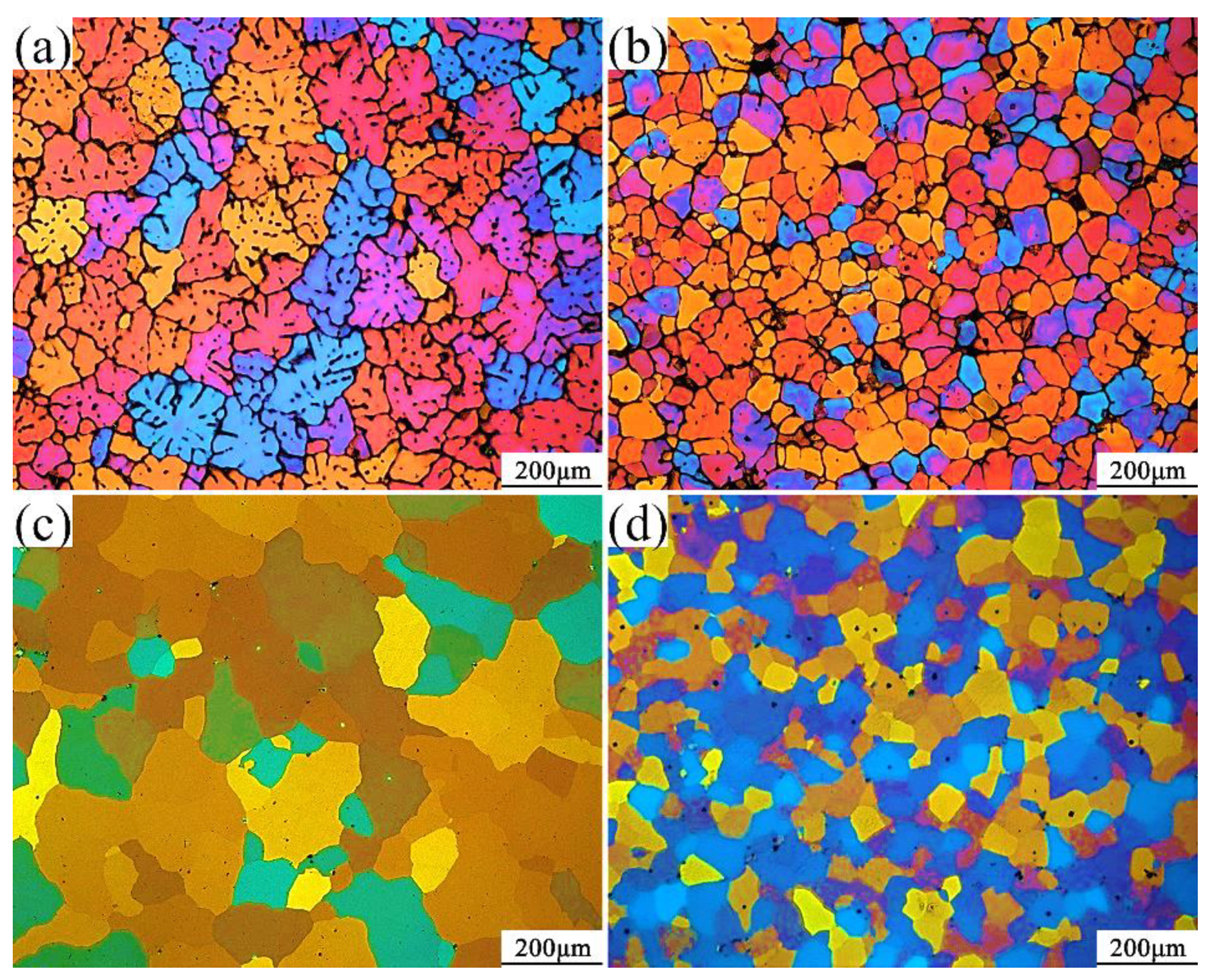
3.1. Results of Alloy Microstructure
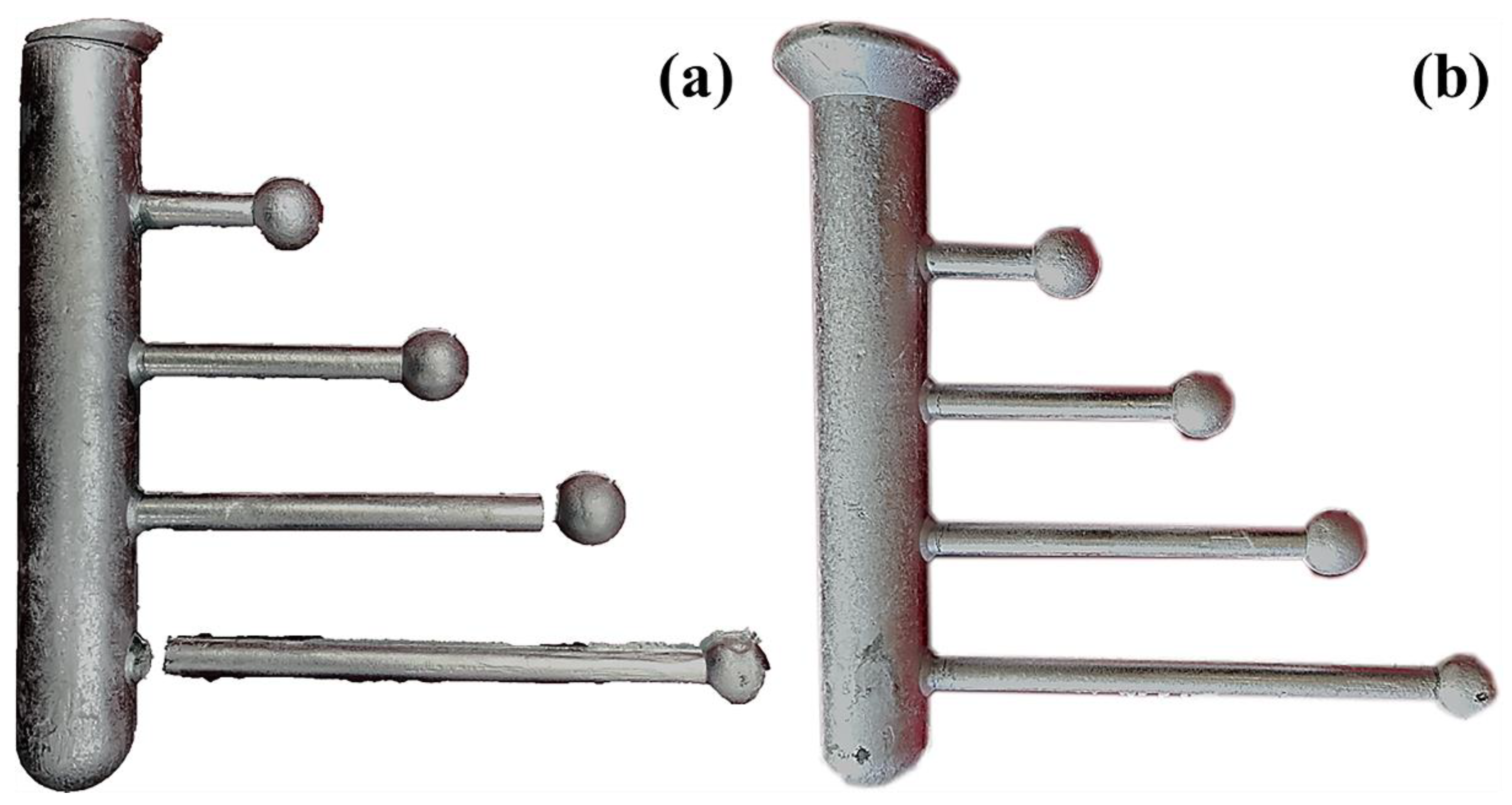
3.2. Thermal Cracking Performance Results of the Alloy
3.3. Results of Alloy Mechanical Properties
4. Analysis and Discussion
4.1. Analysis of Alloy Microstructure
4.2. Analysis of Alloy Thermal Cracking Performance
4.3. Analysis of Alloy Mechanical Properties
5. Conclusions
- When the alloy is not added with the Sc element, the grain structure of the squeeze casting is coarse dendrites, with an average grain size of about 86 μm. After adding 0.15% of the Sc element, the grain size of the casting is significantly refined, and the average grain size is about 53 μm. The morphology of the crystal grains changed from coarse dendritic crystals to equiaxed crystals.
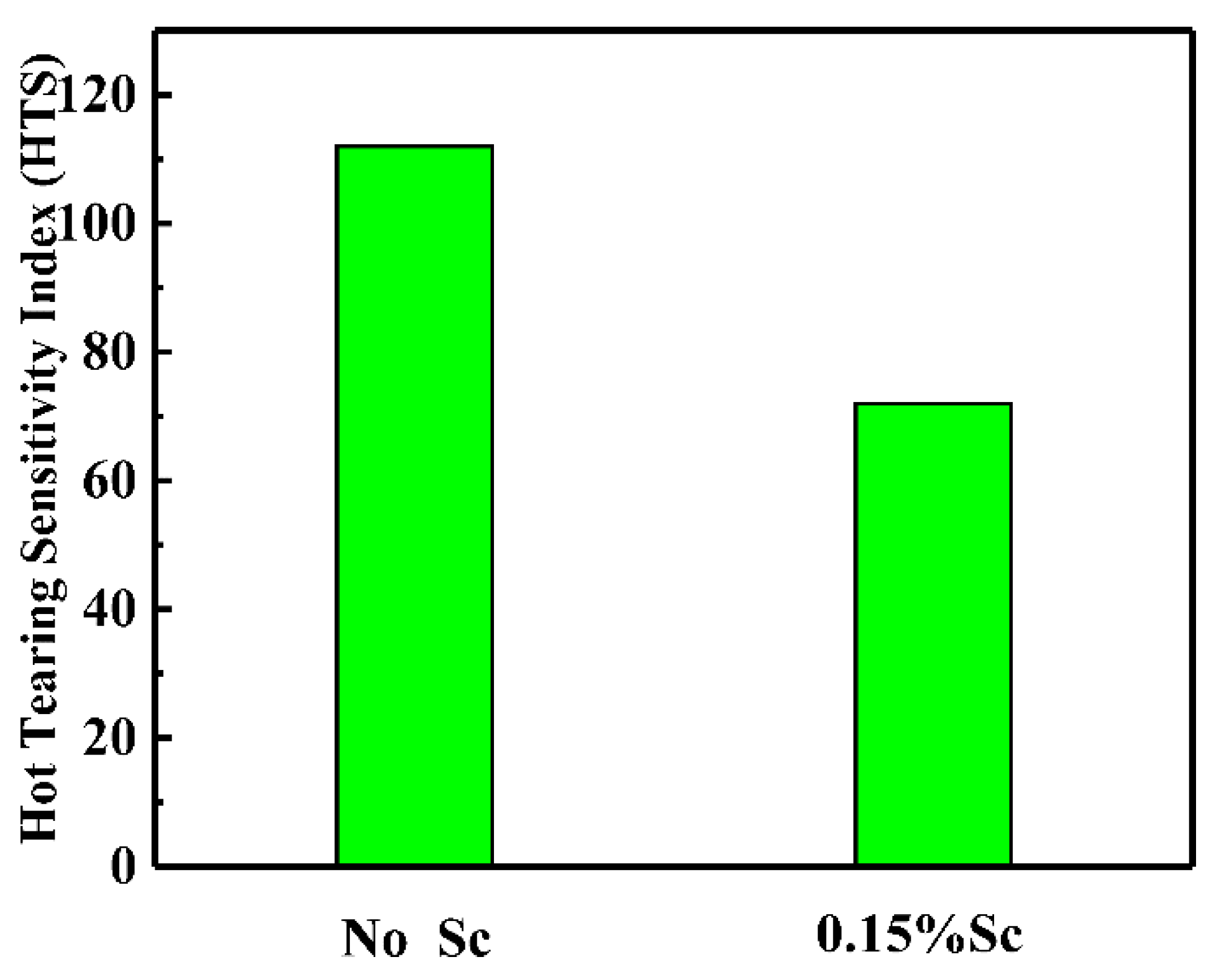
- When the Sc element is not added, the alloy is prone to hot cracking. After adding 0.15% of the Sc element, the fluidity of the alloy is improved, the hot tearing sensitivity is significantly reduced, and the hot tearing sensitivity index drops from 120 to about 80.
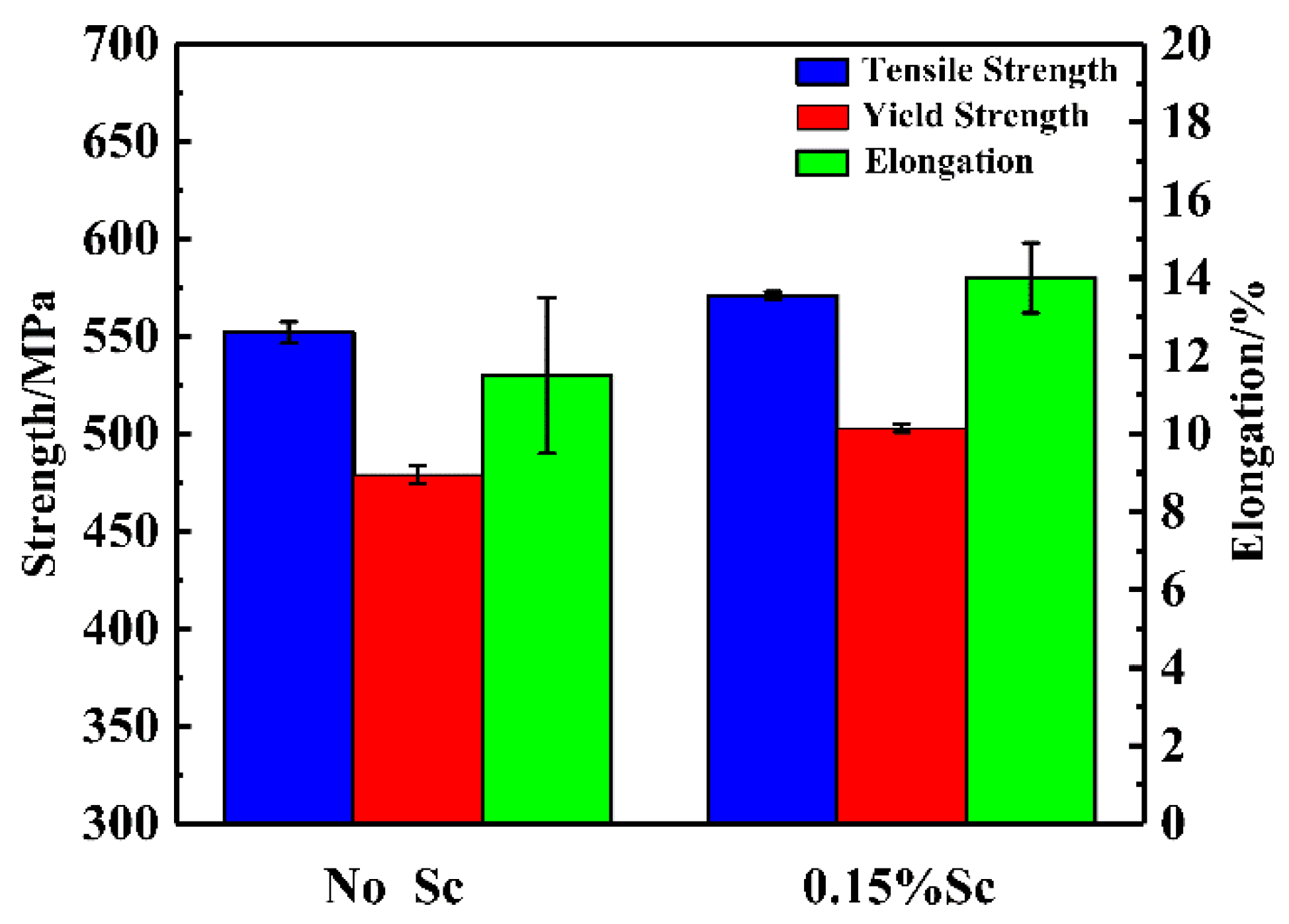
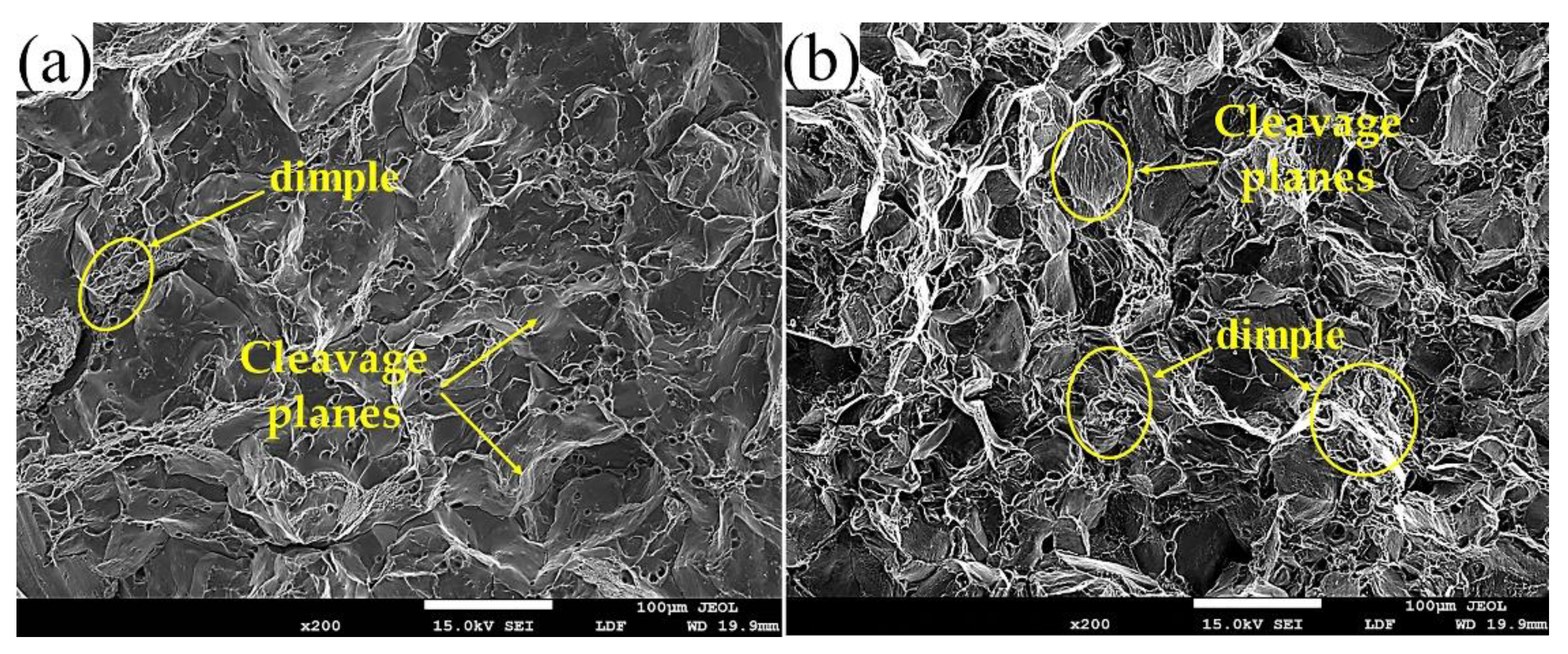
- When the Sc element is not added, the mechanical properties of the squeeze castings are poor. The tensile strength is 552 MPa, and the elongation is about 11%. After adding 0.15% of the Sc element, the tensile strength of the alloy is increased to 571 Mpa, and the elongation is increased to 14%. The alloy fracture mode changed from mixed fracture without adding the Sc element to fracture dominated by ductile fracture after adding the Sc element.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Booth-Morrison, C.; Dunand, D.; Seidman, D.N. Coarsening resistance at 400 °C of precipitation-strengthened Al–Zr–Sc–Er alloys. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 7029–7042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Pan, L.; Wang, R.; Liu, G.; Cheng, P.; Xiao, L.; Sun, J. Effect of solution treatment on precipitation behaviors and age hardening response of Al–Cu alloys with Sc addition. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 530, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Yin, Z.; Duan, J.; Zhao, K.; Tang, B.; He, Z. Evolution of microstructure and properties in a new type 2mm Al–Zn–Mg–Sc–Zr alloy sheet. J. Alloys Compd. 2012, 517, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bommareddy, A.; Quadir, M.; Ferry, M. Time and temperature regime of continuous grain coarsening in an ECAP-processed Al(0.1 wt % Sc) alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2012, 527, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, Y. Development of high strength aluminum alloys and processing techniques for the materials. Jinshu Xuebao/Acta Metall. Sin. 2015, 51, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furong, C.; Guowei, L. Research Status of 7075 Aluminum. Alloys 2019, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Shuming, X.; Nan, L.I.; Wenlong, G.U.O. Advance in the Rheological processing for clean and perfect castings. Spec. Cast. Nonferrous Alloys 2008, 1, 22–25. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Ma, Z.; Gao, Z. Effects of severe cold rolling on tensile properties and stress corrosion cracking of 7050 aluminum alloy. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2009, 117, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-H.; Xue, J.; Jiang, Y.-B.; Jin, F. Effect of pre-annealing treatment on the microstructure and mechanical properties of extruded Al–Zn–Mg–Cu alloy bars. Int. J. Miner. Met. Mater. 2017, 24, 1284–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, C.-B.; Yan, B.-H.; Zhang, K.; Yi, G. Electrochemical investigation on the hydrogen permeation behavior of 7075-T6 Al alloy and its influence on stress corrosion cracking. Int. J. Miner. Met. Mater. 2015, 22, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Lei, Q.; Xie, L.; Wang, M.; Li, Z. Microstructure and mechanical properties of high product of strength and elongation Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr alloys fabricated by spray deposition. Mater. Des. 2016, 96, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitterlin, M.; Loucif, A.; Charbonnier, N.; Jahazi, M.; Lapierre-Boire, L.-P.; Morin, J.-B. Cracking mechanisms in large size ingots of high nickel content low alloyed steel. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2016, 68, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vepřek, S. The search for novel, superhard materials. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 1999, 17, 2401–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, T.; He, C.; Ding, J.; Liu, E.; Shi, C.; Li, J.; Zhao, N. Evolution of microstructure and properties of Al–Zn–Mg–Cu–Sc–Zr alloy during aging treatment. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 658, 946–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Pan, Q.; Huang, X.; Yin, Z. Microstructures and properties of Al–Zn–Mg–Mn alloy with trace amounts of Sc and Zr. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 616, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Pan, Q.; Li, B.; Liu, Z.; Huang, Z.; Yin, Z. Microstructure, mechanical properties and stress corrosion cracking of Al–Zn–Mg–Zr alloy sheet with trace amount of Sc. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 650, 805–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhao, N.; Liu, T.; Li, J.; He, C.; Shi, C.; Liu, E.; Sha, J. Effect of Sc/Zr ratio on the microstructure and mechanical properties of new type of Al–Zn–Mg–Sc–Zr alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 617, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Peng, B.; Xu, G.; Pan, Q.; Yin, Z.; Ye, R.; Wang, Y.; Lu, L. Effects of Sc and Zr on mechanical property and microstructure of tungsten inert gas and friction stir welded aerospace high strength Al–Zn–Mg alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 639, 500–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buranova, Y.; Kulitskiy, V.; Peterlechner, M.; Mogucheva, A.; Kaibyshev, R.; Divinski, S.; Wilde, G. Al3(Sc,Zr)-based precipitates in Al–Mg alloy: Effect of severe deformation. Acta Mater. 2017, 124, 210–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; He, C.-N.; Li, G.; Meng, X.; Shi, C.-S.; Zhao, N.-Q. Microstructural evolution in Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Sc-Zr alloys during short-time homogenization. Int. J. Miner. Met. Mater. 2015, 22, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wiessner, M.; Albu, M.; Wurster, S.; Sartory, B.; Hofer, F.; Schumacher, P. Correlative characterization of primary Al3(Sc,Zr) phase in an Al–Zn–Mg based alloy. Mater. Charact. 2015, 102, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G.; Kou, S. Hot cracking of binary Mg–Al alloy castings. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 417, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, K.; Samal, S. Solidification of Peritectic Alloys. Solidif. Contain. Undercooled Melts 2012, 41, 509–541. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, X.; Yang, S.; Fang, C.; Hao, H.; Dai, S. Microstructure and mechanical properties of forged Al-7.1Zn-1.1Mg-1.6Cu-0.14Zr alloy after two-step ageing treatment at 120 and 170 °C. Rare Met. 2010, 29, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shercliff, H.; Ashby, M. A process model for age hardening of aluminium alloys—I. The model. Acta Met. Mater. 1990, 38, 1789–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyot, P.; Cottignies, L. Precipitation kinetics, mechanical strength and electrical conductivity of AlZnMgCu alloys. Acta Mater. 1996, 44, 4161–4167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M. Modeling the hardness and yield strength evolutions of aluminum alloy with rod/needle-shaped precipitates. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 443, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Q.L.; Li, Y.; Li, H.X.; Du, Q.; Zhang, J.S.; Zhuang, L.Z. Roles of Alloy Composition and Grain Refinement on Hot Tearing Susceptibility of 7××× Aluminum Alloys. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2016, 47, 4080–4091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Zn | Mg | Cu | Zr | Sc | Fe | Si | Others | Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7.15 | 1.79 | 1.28 | 0.14 | - | 0.002 | 0.002 | ≤0.01 | Bal. |
| 7.08 | 1.76 | 1.3 | 0.14 | 0.15 | 0.002 | 0.002 | ≤0.01 | Bal. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, Z.; Bai, Y.; Zhao, P.; Mao, W. Effect of Sc on the Hot Cracking Properties of 7xxx Aluminum Alloy and the Microstructure of Squeeze Castings. Materials 2021, 14, 6881. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14226881
Xu Y, Zhang Z, Gao Z, Bai Y, Zhao P, Mao W. Effect of Sc on the Hot Cracking Properties of 7xxx Aluminum Alloy and the Microstructure of Squeeze Castings. Materials. 2021; 14(22):6881. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14226881
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Yongtao, Zhifeng Zhang, Zhihua Gao, Yuelong Bai, Purui Zhao, and Weimin Mao. 2021. "Effect of Sc on the Hot Cracking Properties of 7xxx Aluminum Alloy and the Microstructure of Squeeze Castings" Materials 14, no. 22: 6881. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14226881
APA StyleXu, Y., Zhang, Z., Gao, Z., Bai, Y., Zhao, P., & Mao, W. (2021). Effect of Sc on the Hot Cracking Properties of 7xxx Aluminum Alloy and the Microstructure of Squeeze Castings. Materials, 14(22), 6881. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14226881







