Novel Design and Finite Element Analysis of Diamond-like Porous Implants with Low Stiffness
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
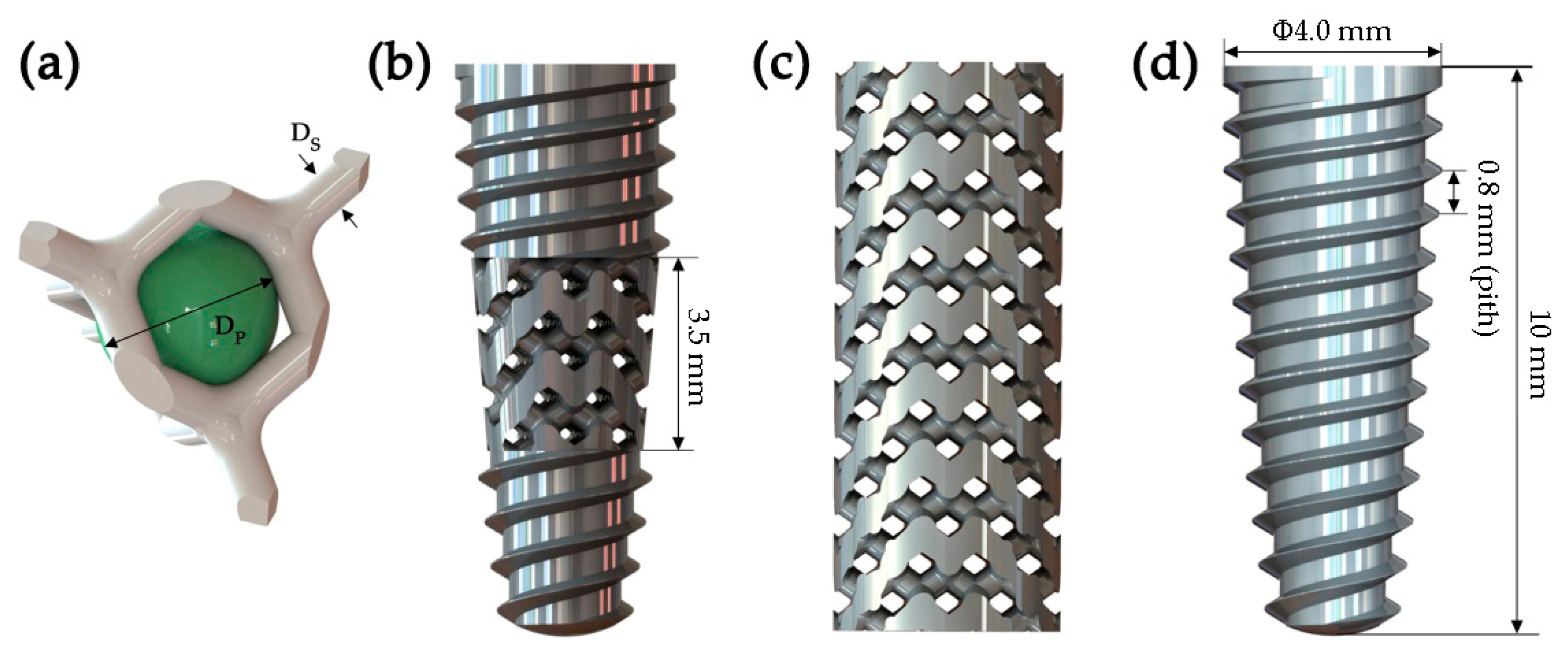
2.1. Modeling of New-Type Porous Implants
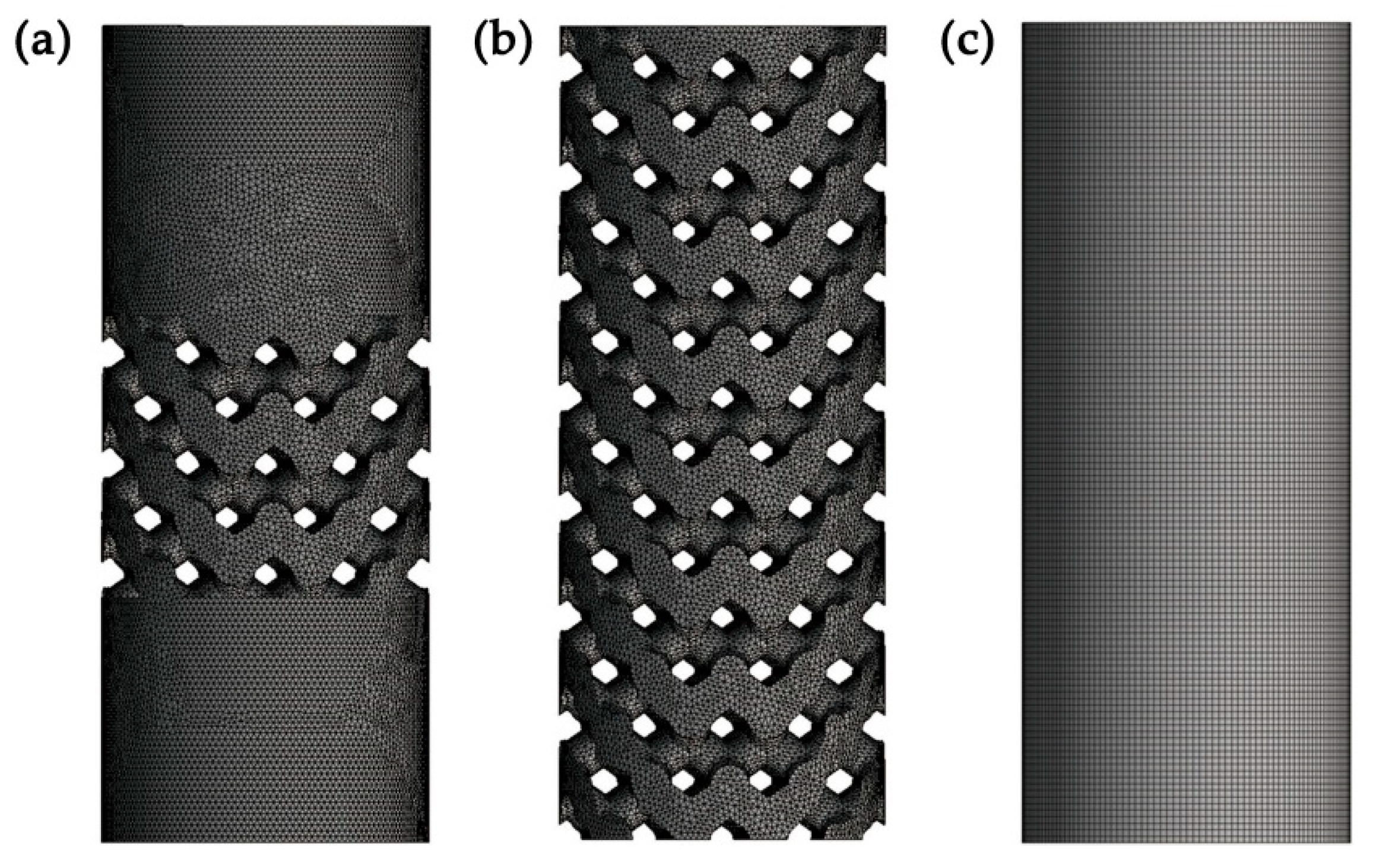
2.2. Three-Dimensional Finite Element Analysis
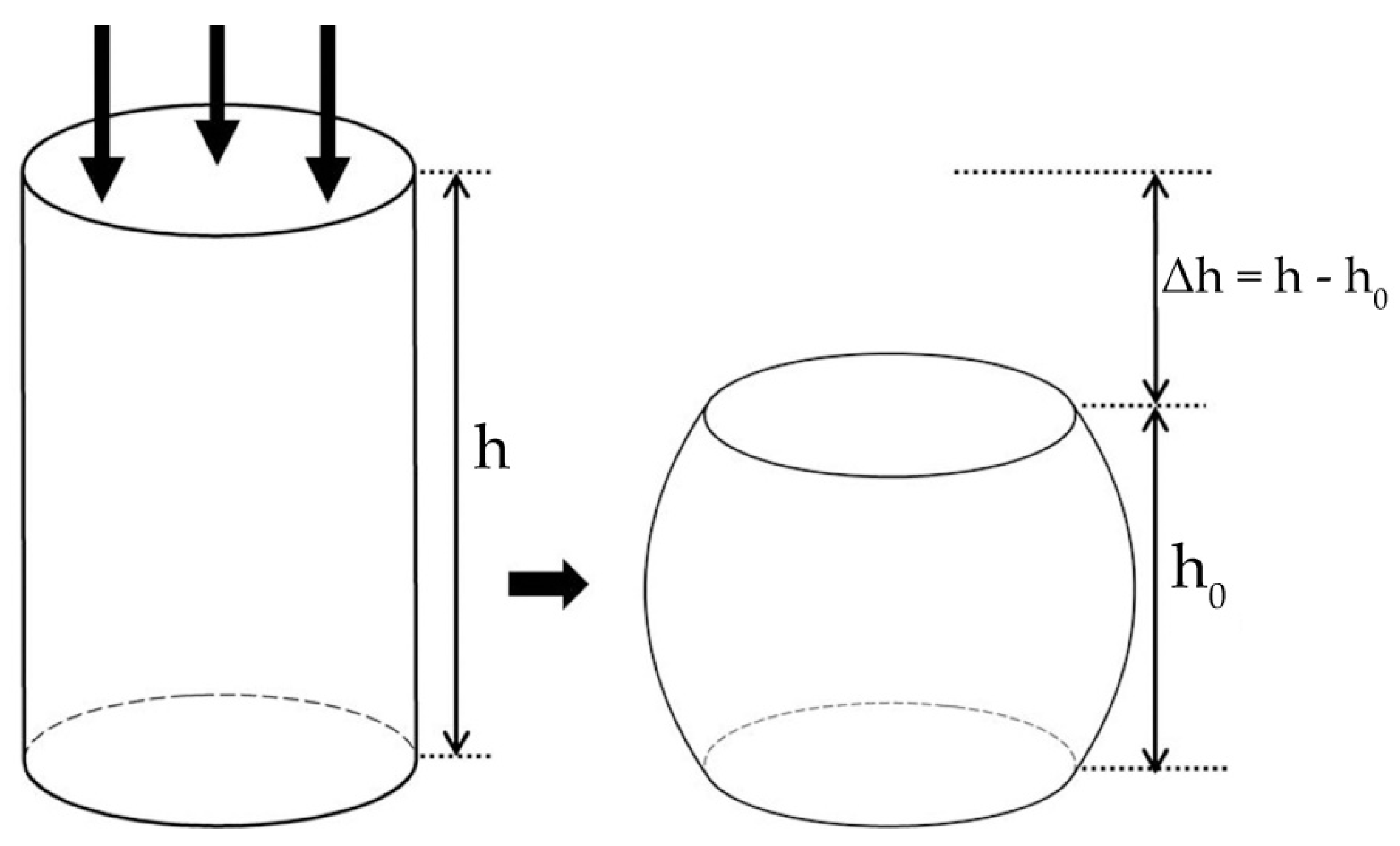
2.3. Compression Test Simulation
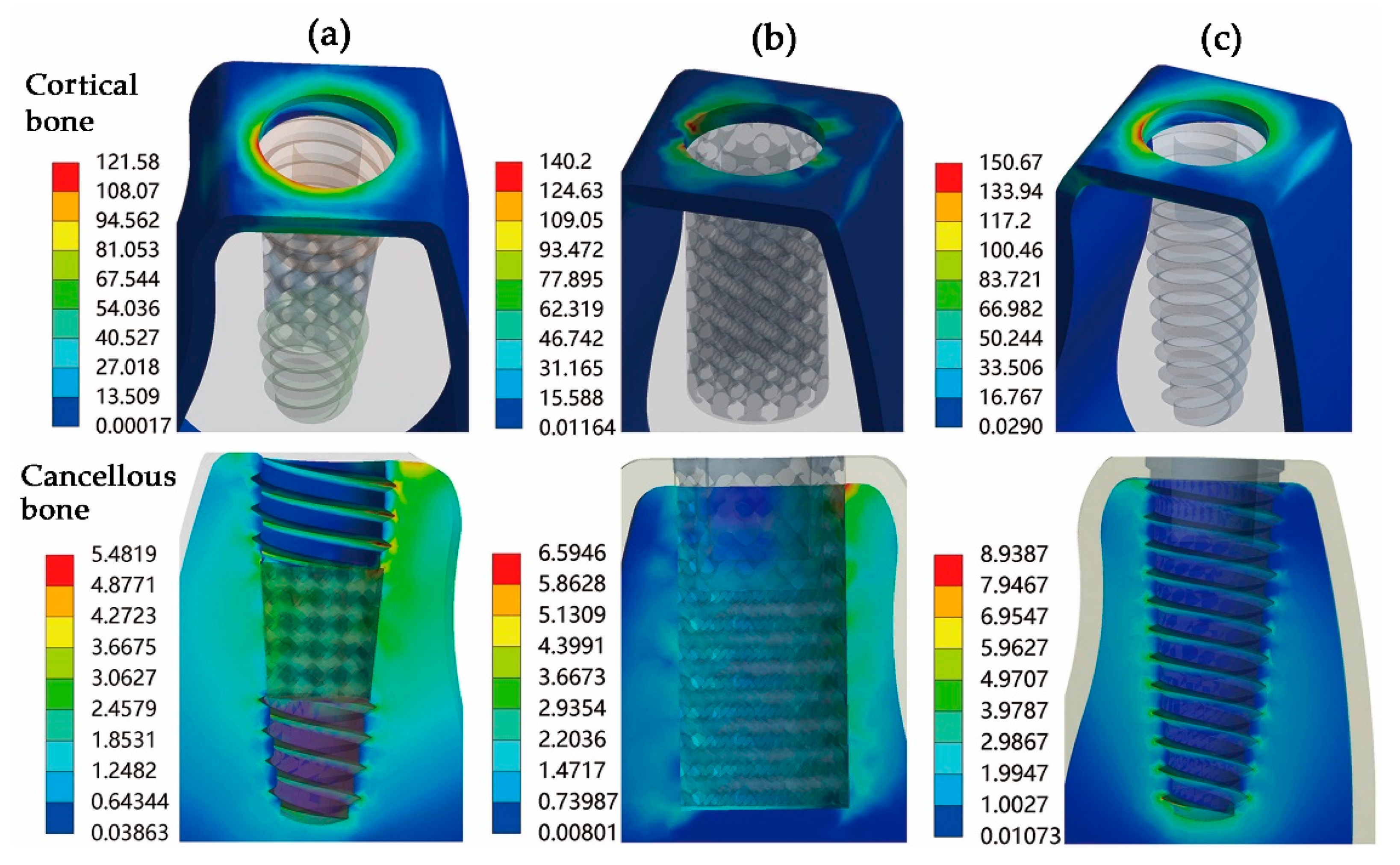
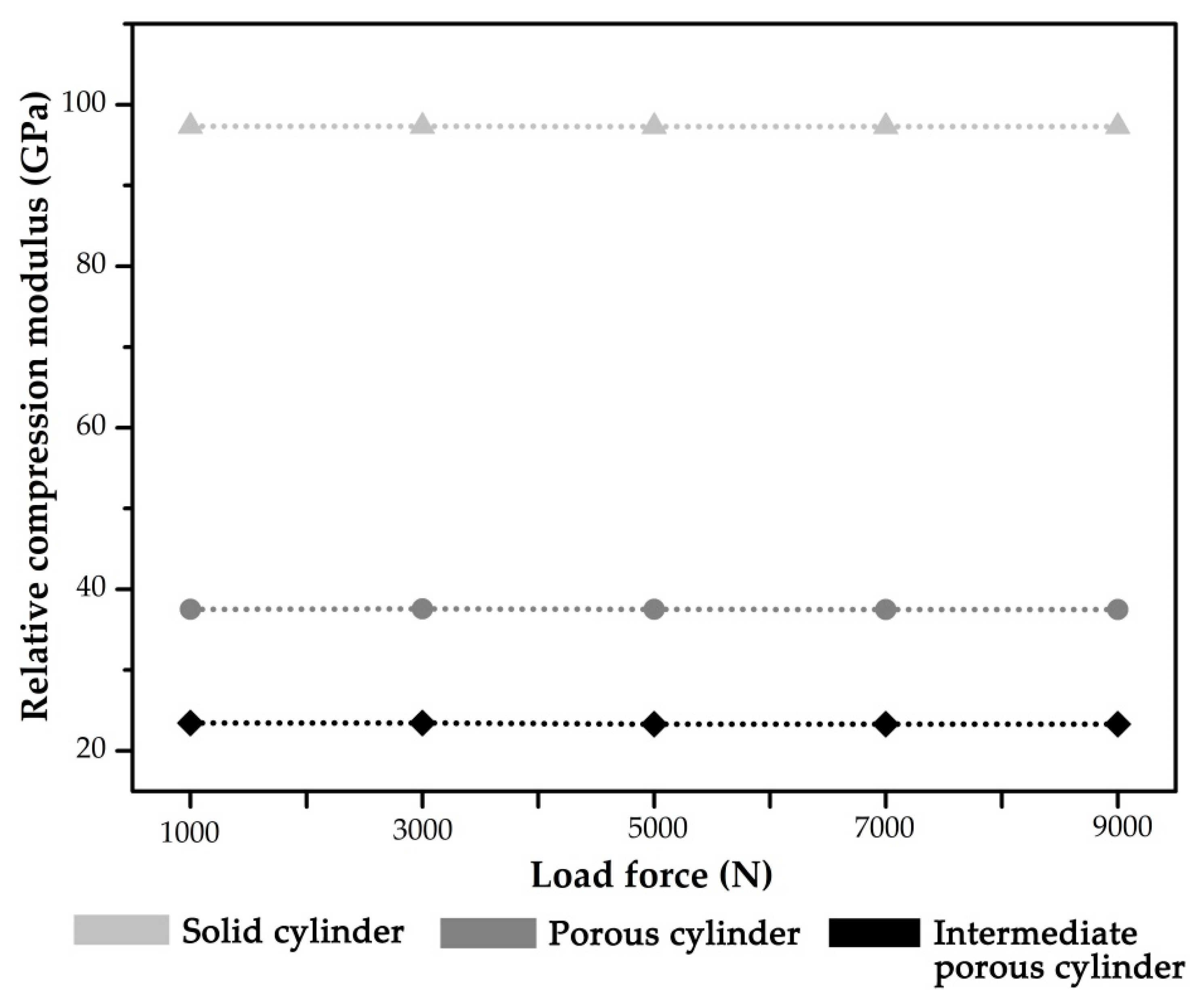
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Diamond-Like Porous Implant Design
4.2. Static Mechanical Performance
4.3. Compression Performance
4.4. Limitations and Future Developments
5. Conclusions
- A novel design method of a porous dental implant (Type I porous implant) was proposed by combining the diamond-like pore structure with traditional tapered thread characteristics.
- Compared with the solid implant, the stiffness of the diamond-like porous implant was significantly reduced. Furthermore, the Type I porous implant exhibited better biomechanical behavior and stress distribution than the completely porous structure design. In summary, the Type I implant is superior to the other two implant designs.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Degerliyurt, K.; Simsek, B.; Erkmen, E.; Eser, A. Effects of different fixture geometries on the stress distribution in mandibular peri-implant structures: A 3-dimensional finite element analysis. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endodontology 2010, 110, e1–e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.G.; Jeong, Y.H.; Chien, H.H. Immediate mechanical stability of threaded and porous implant systems. Clin. Biomech. 2017, 48, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.C.; Lin, S.C.; Kang, M.J. Effects of implant threads on the contact area and stress distribution of marginal bone. J. Dent. Sci. 2010, 5, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steigenga, J.T.; Al-Shammari, K.F.; Nociti, F.; Misch, C.E.; Wang, H.-L. Dental Implant Design and Its Relationship to Long-Term Implant Success. Implant. Dent. 2003, 12, 306–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres-Sanchez, C.; Al Mushref, F.; Norrito, M.; Yendall, K.; Liu, Y.; Conway, P. The effect of pore size and porosity on mechanical properties and biological response of porous titanium scaffolds. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 77, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teixeira, L.; Crippa, G.; Lefebvre, L.-P.; De Oliveira, P.; Rosa, A.; Beloti, M. The influence of pore size on osteoblast phenotype expression in cultures grown on porous titanium. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2012, 41, 1097–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.C.; Klemm, D.; Eckert, J.; Hao, Y.L.; Sercombe, T.B. Manufacture by selective laser melting and mechanical behavior of a biomedical Ti-24Nb-4Zr-8Sn alloy. Scripta Mate 2011, 65, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, B.V.; Bose, S.; Bandyopadhyay, A. Low stiffness porous Ti structures for load-bearing implants. Acta Biomater. 2007, 3, 997–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geetha, M.; Singh, A.K.; Asokamani, R.; Gogia, A.K. Ti based biomaterials, the ultimate choice for orthopaedic implants—A review. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2009, 54, 397–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, B. Biomaterials for Musculoskeletal Regeneration: Concepts, 1st ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2017; pp. 1–147. [Google Scholar]
- Barui, S.; Panda, A.K.; Naskar, S.; Kuppuraj, R.; Basu, S.; Basu, B. 3D inkjet printing of biomaterials with strength reliability and cytocompatibility: Quantitative process strategy for Ti-6Al-4V. Biomaterials 2019, 213, 119212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paka, K.; Pokrowiecki, R. Porous Titanium Implants: A Review. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2018, 20, 1700648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wei, Q.; Fan, D.; Liu, X.; Li, W.; Song, C.; Tian, Y.; Cai, H.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, Z. Improved osseointegration with rhBMP-2 intraoperatively loaded in a specifically designed 3D-printed porous Ti6Al4V vertebral implant. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 1279–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, D.; Nakashima, Y.; Sato, T.; Hirata, M.; Kanazawa, M.; Kohno, Y.; Yoshimoto, K.; Yoshihara, Y.; Nakamura, A.; Nakao, Y.; et al. Bone bonding strength of diamond-structured porous titanium-alloy implants manufactured using the electron beam-melting technique. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 59, 1047–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edelmann, A.R.; Patel, D.; Allen, R.K. Retrospective analysis of porous tantalum trabecular metal-enhanced titanium dental implants. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2019, 121, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bencharit, S.; Byrd, W.C.; Altarawneh, S.; Hosseini, B.; Leong, A.; Reside, G.; Morelli, T.; Dds, S.O. Development and Applications of Porous Tantalum Trabecular Metal-Enhanced Titanium Dental Implants. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2014, 16, 817–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sato, Y.; Wadamoto, M.; Tsuga, K.; Teixeira, E.R. The effectiveness of elemant downsizlng on a three-dimensional finite element model of bone trabeculae in implant biomechanies. J. Oral Rehabil. 1999, 26, 288–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velazquez, F.A.; Castillo-Oyagüe, R.; Oliveros-López, L.-G.; Torres-Lagares, D.; Martínez-González, J.; Pérez-Velasco, A.; Lynch, C.D.; Gutiérrez-Pérez, J.-L.; Serrera-Figallo, M.-Á. Influence of bone quality on the mechanical interaction between implant and bone: A finite element analysis. J. Dent. 2019, 88, 103161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, A.H.; Conway, C. Finite-element modeling and analysis in nanomedicine and dentistry. Nanomedicine 2014, 9, 1681–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, S.R.; Desai, M.S.; Katti, G.; Karthikeyan, I. Evaluation of design parameters of eight dental implant designs: A two-dimensional finite element analysis. Niger. J. Clin. Pract. 2012, 15, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, H.-Y.; Müftü, S. Simulation of peri-implant bone healing due to immediate loading in dental implant treatments. J. Biomech. 2013, 46, 871–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanishi, Y.; Yamaguchi, S.; Imazato, S.; Nakano, T.; Yatani, H. Influences of implant neck design and implant–abutment joint type on peri-implant bone stress and abutment micromovement: Three-dimensional finite element analysis. Dent. Mater. 2012, 28, 1126–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, C.C.; Li, M.J.; Tsai, P.I. Novel design of additive manufactured hollow porous implants. Dent. Mater. 2020, 36, 1437–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, C.; Li, C.; Qin, Y.; Zhong, L.; Chen, B.; Li, Z.; Liu, H.; Chang, F.; Wang, J. Analysis of factors influencing bone ingrowth into three-dimensional printed porous metal scaffolds: A review. J. Alloy. Compd. 2017, 717, 271–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bra-Nemark, P.-I.; Zarb, G.A.; Albrektsson, T.; Rosen, H.M. Tissue-Integrated Prostheses. Osseointegration in Clinical Dentistry. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1986, 77, 496–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, G.; Xu, Z. Design and manufacture of customized dental implants by using reverse engineering and selective laser melting technology. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2014, 112, 1088–1095.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tribst, J.P.M.; Piva, A.D.; Giudice, R.L.; Borges, A.; Ausiello, P. The Influence of Custom-Milled Framework Design for an Implant-Supported Full-Arch Fixed Dental Prosthesis: 3D-FEA Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calì, M.; Zanetti, E.M.; Oliveri, S.M.; Asero, R.; Ciaramella, S.; Martorelli, M.; Bignardi, C. Influence of thread shape and inclination on the biomechanical behaviour of plateau implant systems. Dent. Mater. 2018, 34, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, A.; Datta, P.; Majumder, S.; Mondal, S.C.; Roychowdhury, A. Finite element and experimental analysis to select patient’s bone condition specific porous dental implant, fabricated using additive manufacturing. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 124, 103902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Sarkar, S.; Kalidindi, S.R.; Basu, B. Periprosthetic biomechanical response towards dental implants, with functional gradation, for single/multiple dental loss. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2019, 94, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolomeu, F.; Fonseca, J.; Peixinho, N.; Alves, N.; Gasik, M.; Silva, F.; Miranda, G. Predicting the output dimensions, porosity and elastic modulus of additive manufactured biomaterial structures targeting orthopedic implants. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2019, 99, 104–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Su, K.; Su, L.; Liang, P.; Ji, P.; Wang, C. The effect of 3D-printed Ti6Al4V scaffolds with various macropore structures on osteointegration and osteogenesis: A biomechanical evaluation. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2018, 88, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, P.; Dong, H.; He, X.; Cai, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Li, H.; Jin, Z. Hydromechanical mechanism behind the effect of pore size of porous titanium scaffolds on osteoblast response and bone ingrowth. Mater. Des. 2019, 183, 108151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, Z.; Shi, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, R.; Tu, J.; Jin, G. In vitro and in vivo comparisons of the porous Ti6Al4V alloys fabricated by the selective laser melting technique and a new sintering technique. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2018, 91, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sola, A.; Bellucci, D.; Cannillo, V. Functionally graded materials for orthopedic applications—An update on design and manufacturing. Biotechnol. Adv. 2016, 34, 504–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karl, M.; Dickinson, A.; Holst, S.; Holst, A. Biomechanical methods applied in dentistry: A comparative overview of photoelastic examinations, strain gauge measurements, finite element analysis and three-dimensional deformation analysis. Eur. J. Prosthodont. Restor. Dent. 2009, 17, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bordin, D.; Bergamo, E.T.P.; Fardin, V.P. Fracture strength and probability of survival of narrow and extra-narrow dental implants after fatigue testing: In vitro and in silico analysis. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2017, 71, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kw, A.; Jg, B.; Dj, C.; Wei, X.D. Comparison of the fracture resistance of dental implants with different abutment taper angles. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 2016, 63, 164–171. [Google Scholar]
- Dallago, M.; Fontanari, V.; Torresani, E.; Leoni, M.; Pederzolli, C.; Potrich, C.; Benedetti, M. Fatigue and biological properties of Ti-6Al-4V ELI cellular structures with variously arranged cubic cells made by selective laser melting. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2018, 78, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Thouas, G.A. Metallic implant biomaterials. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2015, 87, 1–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Hao, L.; Hussein, A.; Young, P. Ti–6Al–4V triply periodic minimal surface structures for bone implants fabricated via selective laser melting. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2015, 51, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tetè, G.; D’Orto, B.; Nagni, M.; Agostinacchio, M.; Agliardi, E. Role of induced pluripotent stem cells (IPSCS) in bone tissue regeneration in dentistry: A narrative review. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2020, 34, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Capparé, P.; Vinci, R.; Stefano, D.; Traini, T.; Pantaleo, G.; Gherlone, E.F.; Gastaldi, G. Correlation between Initial BIC and the Insertion Torque/Depth Integral Recorded with an Instantaneous Torque-Measuring Implant Motor: An in vivo Study. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2015, 17, e613–e620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tetè, G.; Sacchi, L.; Camerano, C.; Nagni, M.; Polizzi, E. Management of the delicate phase of the temporary crown: An in vitro study. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2020, 34, 67–78. [Google Scholar]



| Model | Diameter (mm) | Length (mm) | Pore Size (mm) | Strut Diameter (mm) | Specific Surface Area (mm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type Ⅰ | 4.0 | 10 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 186.65 |
| Type Ⅱ | 4.0 | 10 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 429.18 |
| Control group | 4.0 | 10 | - | - | 142.07 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Feng, W.; Chen, X. Novel Design and Finite Element Analysis of Diamond-like Porous Implants with Low Stiffness. Materials 2021, 14, 6918. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14226918
Zhang J, Zhang X, Chen Y, Feng W, Chen X. Novel Design and Finite Element Analysis of Diamond-like Porous Implants with Low Stiffness. Materials. 2021; 14(22):6918. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14226918
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jinyang, Xiao Zhang, Yang Chen, Wei Feng, and Xianshuai Chen. 2021. "Novel Design and Finite Element Analysis of Diamond-like Porous Implants with Low Stiffness" Materials 14, no. 22: 6918. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14226918
APA StyleZhang, J., Zhang, X., Chen, Y., Feng, W., & Chen, X. (2021). Novel Design and Finite Element Analysis of Diamond-like Porous Implants with Low Stiffness. Materials, 14(22), 6918. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14226918





