Investigation on Variables Contributing to the Synthesis of C-S-H/PCE Nanocomposites by Co-Precipitation Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Orthogonal Experimental Design
2.3. Synthesis of C-S-H/PCE Nanocomposites
2.4. Characterization
3. Results
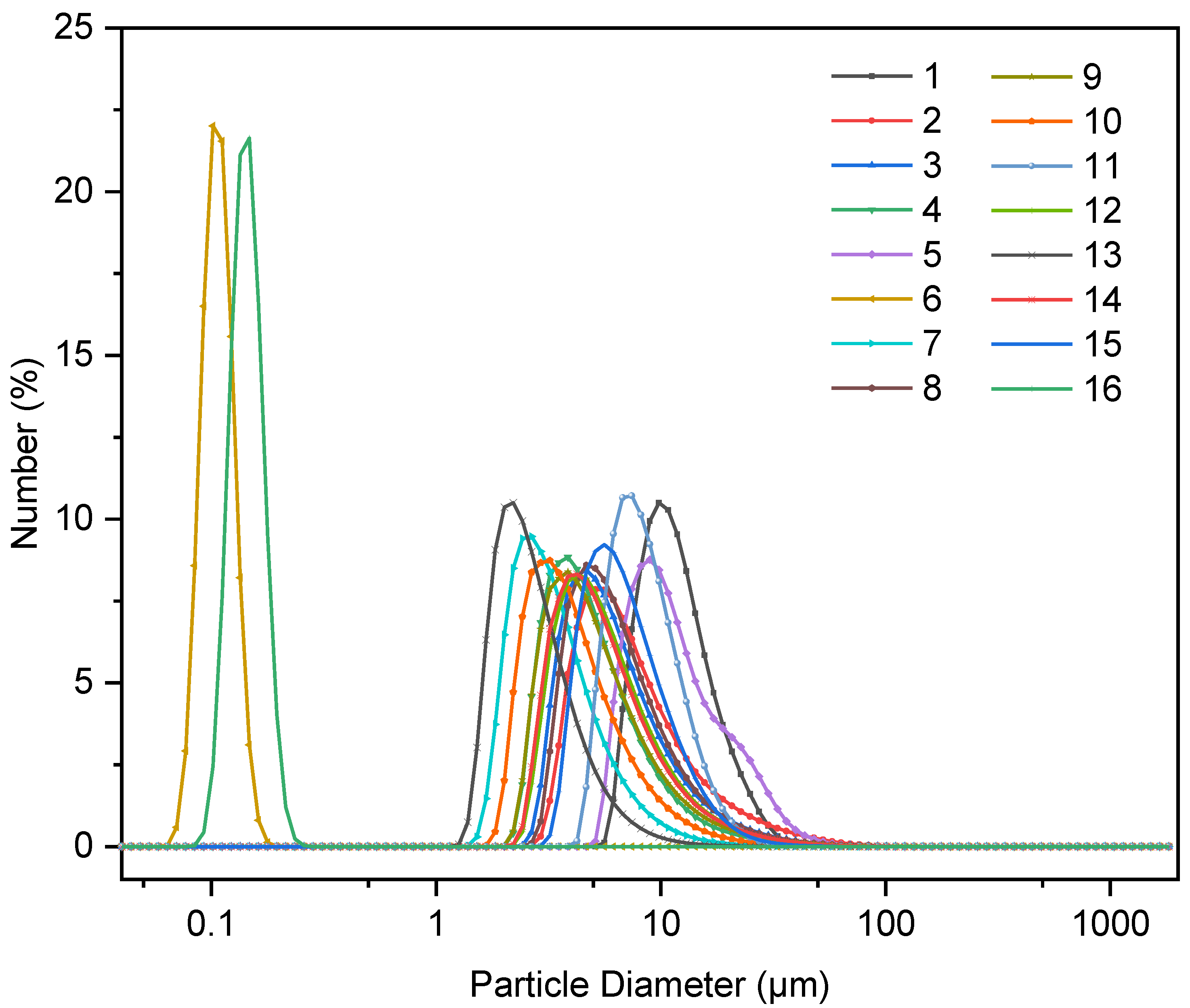
3.1. Particle Size
3.1.1. Effects of Synthetic Variables on the PSD of C-S-H/PCE Nanocomposites
3.1.2. Effects of Ultrasonic Treatment on the PSD of C-S-H/PCE Nanocomposites
3.1.3. Analysis of PSD Based on the Orthogonal Experiment
3.2. Composition, Microstructure, and Morphology
3.2.1. XRD
3.2.2. SEM/TEM
3.2.3. Raman Spectrum
4. Conclusions
- The concentration of reactants had a significant effect on the particle size of the synthesized C-S-H/PCE, followed by the dosage of dispersant, while the feeding sequence and flow rate of reactants had little impact on the particle size. Low concentration of reactants and sufficient dispersant content are conducive to the synthesis of C-S-H/PCE with nano median size;
- Ultrasonic treatment for 5 min could effectively break the unstable structure of nano C-S-H/PCE aggregates. However, it had a negligible effect on the stable nano C-S-H/PCE aggregates, even if the treatment time was extended to 30 min;
- The change in variables had little influence on the composition of the synthesized C-S-H/PCE nanocomposites but had a significant influence on their crystallinity and morphology. Low concentrations of reactants tended to form products with high crystallinity. The concentration of reactants affected the morphology of the nanocomposites so that low concentrations of reactants tended to form incompact floccules, while high concentrations of reactants tended to form relatively dense flakes or blocks.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sanchez, F.; Sobolev, K. Nanotechnology in concrete—A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 24, 2060–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Qi, T.; Zhou, W.; Hui, D.; Xiao, C.; Qi, J.; Zheng, Z.; Zhao, Z. A review on the properties, reinforcing effects, and commercialization of nanomaterials for cement-based materials. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2020, 9, 303–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norhasri, M.S.M.; Hamidah, M.S.; Fadzil, A.M. Applications of using nano material in concrete: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 133, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Xu, J. Application of microbial precipitation in self-healing concrete: A review on the protection strategies for bacteria. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 306, 124950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Tang, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Yao, W. Application of ureolysis-based microbial CaCO3 precipitation in self-healing of concrete and inhibition of reinforcement corrosion. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 265, 120364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, P.; Xu, J.; Wang, J.; Jiang, C. Multi-scale study on synergistic effect of cement replacement by metakaolin and typical supplementary cementitious materials on properties of ultra-high performance concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 307, 125082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, E.; Matschei, T.; Stephan, D. Nucleation seeding with calcium silicate hydrate—A review. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 113, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, P.J.M.; Geng, G.; Marchon, D.; Li, J.; Alapati, P.; Kurtis, K.E.; Qomi, M.J.A. Advances in characterizing and understanding the microstructure of cementitious materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 124, 105806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Land, G.; Stephan, D. Controlling cement hydration with nanoparticles. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2015, 57, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Yao, W.; Stephan, D. Preparation of calcium silicate hydrate seeds by means of mechanochemical method and its effect on the early hydration of cement. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2019, 11, 168781401984058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Land, G.; Stephan, D. The effect of synthesis conditions on the efficiency of C-S-H seeds to accelerate cement hydration. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2018, 87, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, E.; Epping, J.D.; Stephan, D. The influence of the chemical and physical properties of C-S-H seeds on their potential to accelerate cement hydration. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 228, 116723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Peng, X.; Tang, L.; Zeng, L.; Lan, C. Influence of Hydrothermal Synthesis Conditions on the Formation of Calcium Silicate Hydrates: From Amorphous to Crystalline Phases. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit. 2018, 33, 1150–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Jiang, Z.; He, B.; Qian, C. Investigation on the physical stability of calcium-silicate-hydrate with varying CaO/SiO2 ratios under cryogenic attack. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 252, 119103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Peng, X.; Geng, J.; Li, B.; Wang, K. Synthesis of calcium silicate hydrate based on steel slag with various alkalinities. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit. 2014, 29, 789–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogur, E.; Botti, R.; Bortolotti, M.; Colombo, P.; Vakifahmetoglu, C. Synthesis and additive manufacturing of calcium silicate hydrate scaffolds. J. Mater. Res. Technol-JMRT 2021, 11, 1142–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Yang, L.; Wang, S.; Yang, K. Synthesis and Characterization of Different Crystalline Calcium Silicate Hydrate: Application for the Removal of Aflatoxin B1 from Aqueous Solution. J. Nanomater. 2014, 2014, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, S.; Fang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Ma, X. Preparation of nano-calcium silicate hydrate and its application in concrete. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 631, 022052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Kong, X.; Jiang, L.; Wang, D. The acceleration mechanism of nano-C-S-H particles on OPC hydration. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 249, 118734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Wei, Y.; She, A. Synthesis and structure of calcium silicate hydrate (C-S-H) modified by hydroxyl-terminated polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS). Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 267, 120731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanchanason, V.; Plank, J. Role of pH on the structure, composition and morphology of C-S-H–PCE nanocomposites and their effect on early strength development of Portland cement. Cem. Concr. Res. 2017, 102, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Shi, H.; Qian, B.; Xu, Z.; Li, W.; Shen, X. Effects of synthetic C-S-H/PCE nanocomposites on early cement hydration. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 140, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.J.; Jennings, H.M.; Chen, J.J. Influence of Nucleation Seeding on the Hydration Mechanisms of Tricalcium Silicate and Cement. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 4327–4334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicoleau, L. New Calcium Silicate Hydrate Network. Transp. Res. Record 2010, 2142, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plank, J.; Schönlein, M.; Kanchanason, V. Study on the early crystallization of calcium silicate hydrate (C-S-H) in the presence of polycarboxylate superplasticizers. J. Organomet. Chem. 2018, 869, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, F.; Hu, C.; Wang, F.; Ruan, Y.; Hu, S. Enhancement of early-age strength of the high content fly ash blended cement paste by sodium sulfate and C–S–H seeds towards a greener binder. J. Clean Prod. 2020, 244, 118566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Zhu, H.; Lan, X.; Liu, H.; Long, G.; Ma, C. Effects of asphalt emulsion on calcium silicate hydrate gel: Morphology and porosity. Asia-Pac. J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 16, e2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamali, M.; Ghahremaninezhad, A. Effect of Biomolecules on the Nanostructure and Nanomechanical Property of Calcium-Silicate-Hydrate. Sci Rep 2018, 8, 9491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuyama, H.; Young, J.F. Intercalation of Polymers in Calcium Silicate Hydrate: A New Synthetic Approach to Biocomposites? Chem. Mater. 1999, 11, 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuyama, H.; Young, J.F. Synthesis of calcium silicate hydrate/polymer complexes: Part I. Anionic and nonionic polymers. J. Mater. Res. 1999, 14, 3379–3388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Z.; Zhao, Q.L.; Zhou, S.Q.; Wang, S. Effect of C/S Ratio on Microstructure of Calcium Silicate Hydrates Synthesised By Solution Reaction Method. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 472, 012003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.; Ma, H.; Li, Z. Morphology of calcium silicate hydrate (C-S-H) gel: A molecular dynamic study. Adv. Cem. Res. 2015, 27, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaudoin, J.J.; Raki, L.; Alizadeh, R. A 29Si MAS NMR study of modified C–S–H nanostructures. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2009, 31, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallucci, E.; Zhang, X.; Scrivener, K.L. Effect of temperature on the microstructure of calcium silicate hydrate (C-S-H). Cem. Concr. Res. 2013, 53, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sáez del Bosque, I.F.; Martínez-Ramírez, S.; Blanco-Varela, M.T. FTIR study of the effect of temperature and nanosilica on the nano structure of C–S–H gel formed by hydrating tricalcium silicate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 52, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Picker, A.; Nicoleau, L.; Burghard, Z.; Bill, J.; Zlotnikov, I.; Labbez, C.; Nonat, A.; Cölfen, H. Mesocrystalline calcium silicate hydrate: A bioinspired route toward elastic concrete materials. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1701216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, F.; Kong, X.; Wang, D.; Wang, Q. The effects of nano-C-S-H with different polymer stabilizers on early cement hydration. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2019, 102, 5103–5116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelisser, F.; Gleize, P.J.P.; Mikowski, A. Structure and micro-nanomechanical characterization of synthetic calcium–silicate–hydrate with Poly(Vinyl Alcohol). Cem. Concr. Compos. 2014, 48, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanchanason, V.; Plank, J. Effectiveness of a calcium silicate hydrate—Polycarboxylate ether (C-S-H–PCE) nanocomposite on early strength development of fly ash cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 169, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, W.S.; Fratini, E.; Ridi, F.; Lim, S.H.; Yeh, Y.Q.; Baglioni, P.; Choi, S.M.; Jeng, U.S.; Chen, S.H. Microstructural changes of globules in calcium-silicate-hydrate gels with and without additives determined by small-angle neutron and X-ray scattering. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 398, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanchanason, V.; Plank, J. C-S-H-PCE Nanocomposites for Enhancement of Early Strength of Portland Cement. In Proceedings of the 14th International Congress on the Chemistry of Cement, Beijing, China, 13–16 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kirkpatrick, R.J.; Yarger, J.L.; McMillan, P.F.; Yu, P.; Cong, X.D. Raman spectroscopy of C-S-H, tobermorite, and jennite. Adv. Cem. Based Mater. 1997, 5, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Levels | A | B | C | D |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Feeding Sequence of Reactants | Flow Rate of Reactants | Concentration of Reactant Solution | Dosage of PCE | |
| a | Calcium and siliceous were added to the PCE solution | 0.2 mL/min | Ca(NO3)2: 0.1 mol/L Na2SiO3: 0.05 mol/L | 5% |
| b | Calcium was added to a mixture of silica and PCE | 0.5 mL/min | Ca(NO3)2: 1 mol/L Na2SiO3: 0.5 mol/L | 15% |
| c | Silica was added to a mixture of calcium and PCE | 0.8 mL/min | Ca(NO3)2: 3 mol/L Na2SiO3: 1.5 mol/L | 30% |
| d | Calcium, siliceous, and PCE were added simultaneously | 1.1 mL/min | Ca(NO3)2: 7 mol/L Na2SiO3: 3.5 mol/L | 50% |
| Groups | A | B | C | D |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | a | a | a | a |
| 2 | a | b | b | b |
| 3 | a | c | c | c |
| 4 | a | d | d | d |
| 5 | b | a | b | c |
| 6 | b | b | a | d |
| 7 | b | c | d | a |
| 8 | b | d | c | b |
| 9 | c | a | c | d |
| 10 | c | b | d | c |
| 11 | c | c | a | b |
| 12 | c | d | b | a |
| 13 | d | a | d | b |
| 14 | d | b | c | a |
| 15 | d | c | b | d |
| 16 | d | d | a | c |
| Groups | A | B | C | D | Median Particle Size, μm | S, μm−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | a | a | a | a | 11.66 | 0.09 |
| 2 | a | b | b | b | 0.08 | 11.78 |
| 3 | a | c | c | c | 5.91 | 0.17 |
| 4 | a | d | d | d | 4.77 | 0.21 |
| 5 | b | a | b | c | 0.08 | 11.90 |
| 6 | b | b | a | d | 0.11 | 8.99 |
| 7 | b | c | d | a | 3.27 | 0.31 |
| 8 | b | d | c | b | 6.17 | 0.16 |
| 9 | c | a | c | d | 4.87 | 0.21 |
| 10 | c | b | d | c | 3.94 | 0.25 |
| 11 | c | c | a | b | 0.06 | 16.43 |
| 12 | c | d | b | a | 5.48 | 0.18 |
| 13 | d | a | d | b | 2.66 | 0.38 |
| 14 | d | b | c | a | 5.33 | 0.19 |
| 15 | d | c | b | d | 0.09 | 11.55 |
| 16 | d | d | a | c | 0.15 | 6.68 |
| Ka1 | 12.25 | 12.56 | 32.19 | 0.76 | Optimal scheme | |
| Kb1 | 21.35 | 21.21 | 35.41 | 28.75 | ||
| Kc1 | 17.08 | 28.46 | 0.72 | 19.00 | Ab Bc Cb Db | |
| Kd1 | 18.80 | 7.23 | 1.15 | 20.95 | ||
| Source of Variance | Sum of Squares of Deviations | Degree of Freedom | Sum of Squares of Mean Deviations | F | Critical Value | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 11.057 | 3 | 3.686 | 0.20 | ||
| B | 65.899 | 3 | 21.966 | 1.21 | ||
| C | 271.320 | 3 | 90.440 | 4.97 | F0.05(3,15) = 3.29 | * 2 |
| D | 105.219 | 3 | 35.073 | 1.93 | ||
| Test error | 54.616 | 3 | 18.205 | |||
| Sum | 508.111 | 15 |
| Groups | 2 | 5 | 10 | 11 | 15 | 16 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Relative crystallinity/% | 91.14 ± 1.43 | 91.46 ± 1.49 | 85.62 ± 1.36 | 90.62 ± 1.47 | 90.42 ± 1.69 | 94.30 ± 1.52 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
You, Z.; Xu, J. Investigation on Variables Contributing to the Synthesis of C-S-H/PCE Nanocomposites by Co-Precipitation Method. Materials 2021, 14, 7673. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14247673
You Z, Xu J. Investigation on Variables Contributing to the Synthesis of C-S-H/PCE Nanocomposites by Co-Precipitation Method. Materials. 2021; 14(24):7673. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14247673
Chicago/Turabian StyleYou, Ziyang, and Jing Xu. 2021. "Investigation on Variables Contributing to the Synthesis of C-S-H/PCE Nanocomposites by Co-Precipitation Method" Materials 14, no. 24: 7673. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14247673
APA StyleYou, Z., & Xu, J. (2021). Investigation on Variables Contributing to the Synthesis of C-S-H/PCE Nanocomposites by Co-Precipitation Method. Materials, 14(24), 7673. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14247673





