Design Optimization of Reconfigurable Liquid Crystal Patch Antenna
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
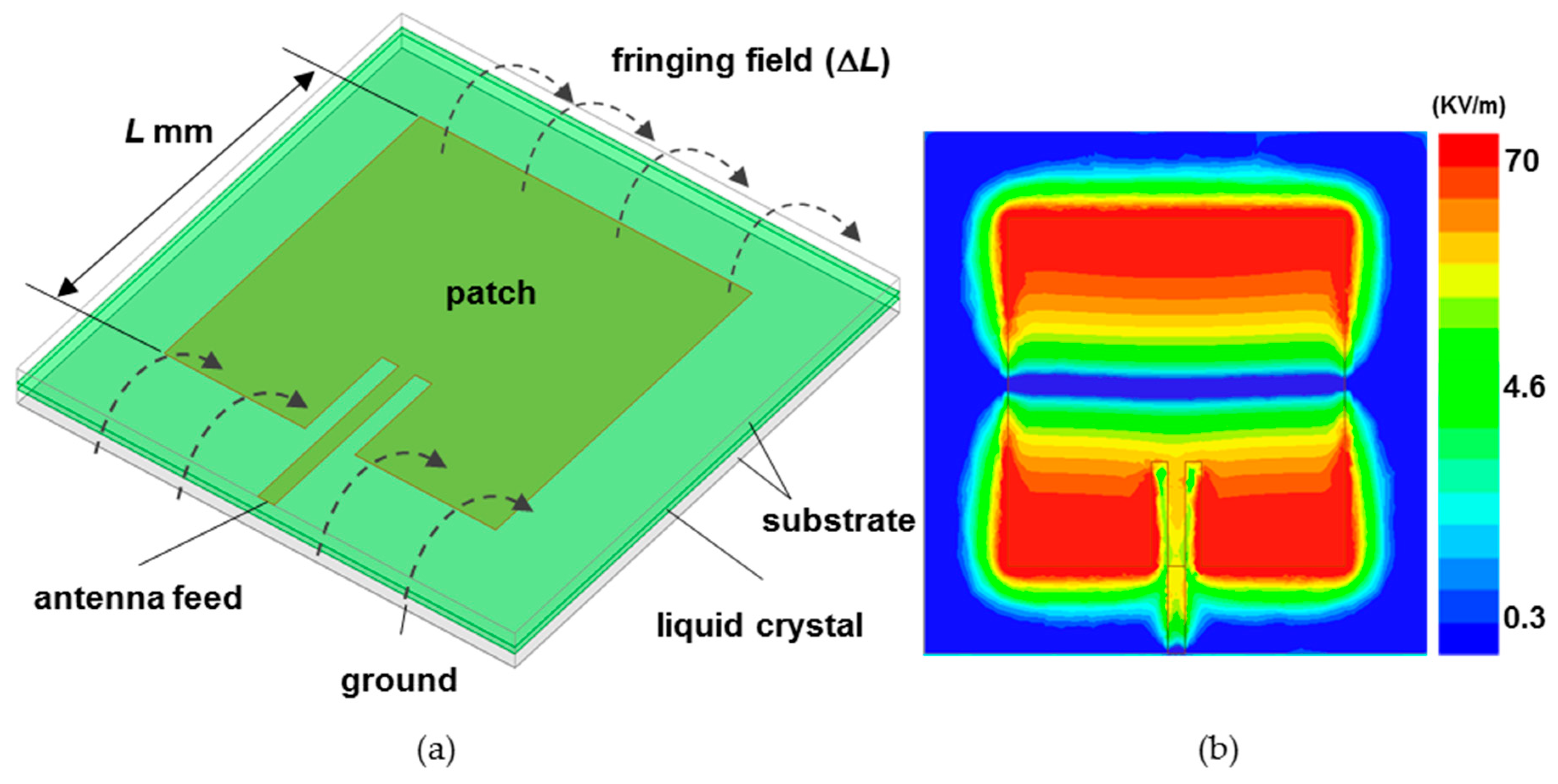
2.1. Modeling of Numerical Calculation
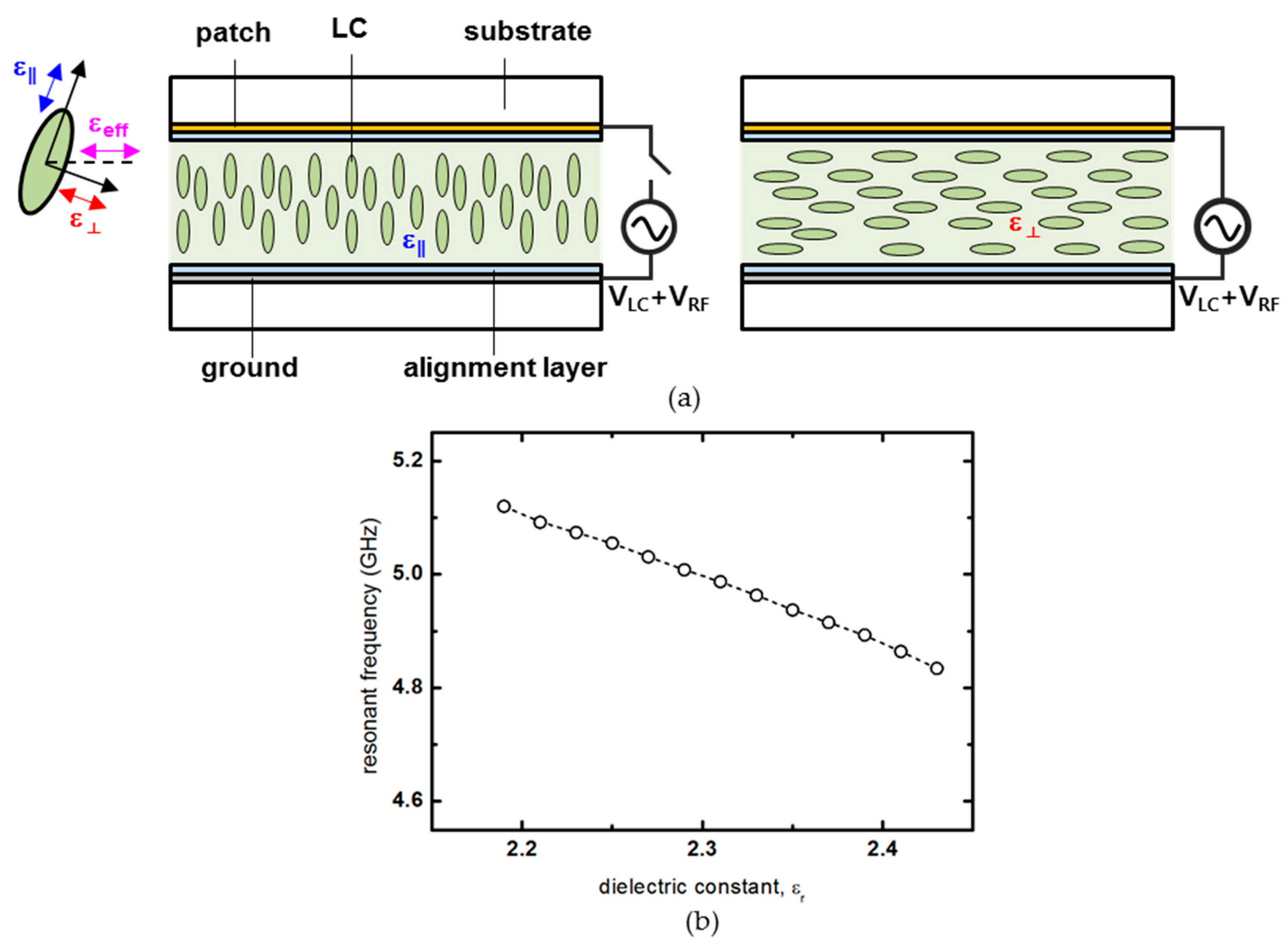
2.2. Liquid Crystal
3. Results and Discussion
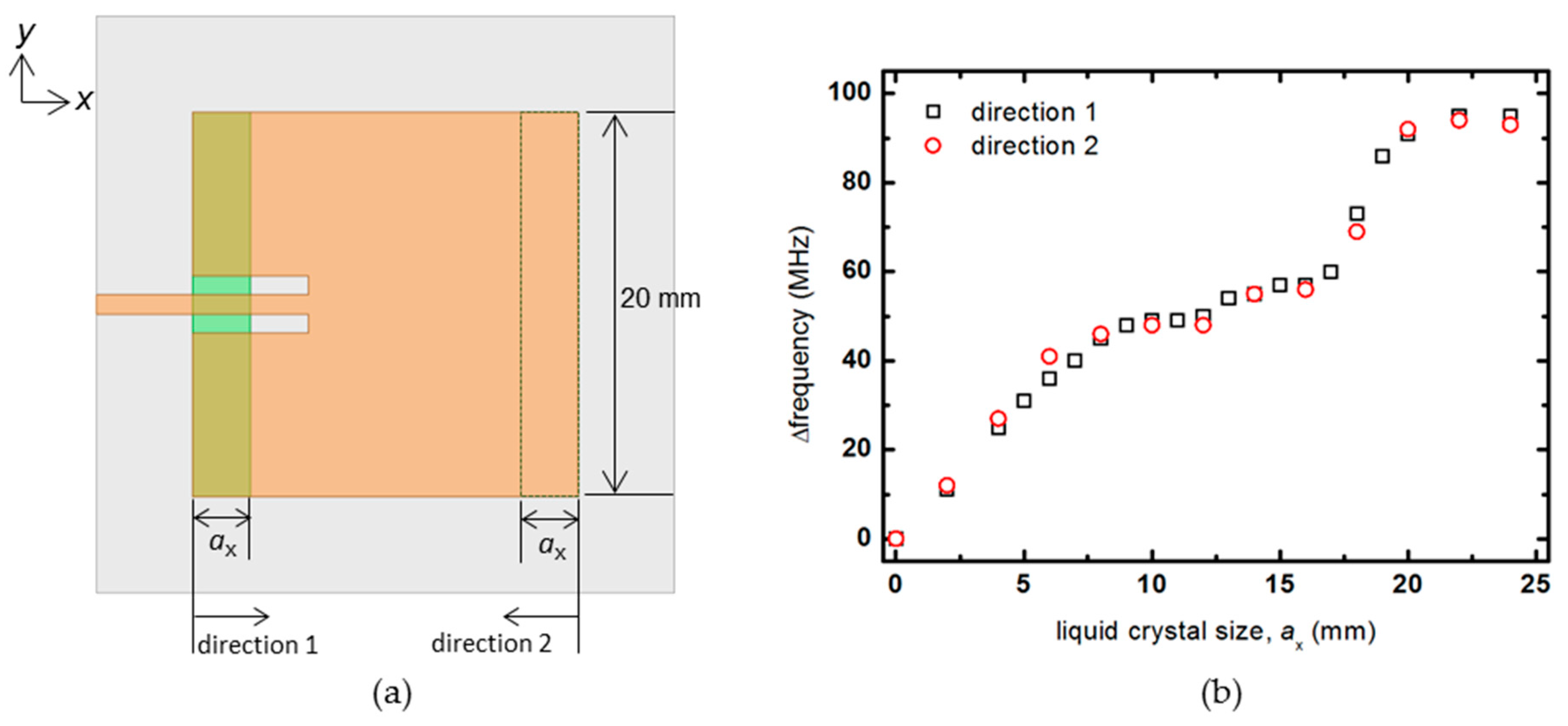
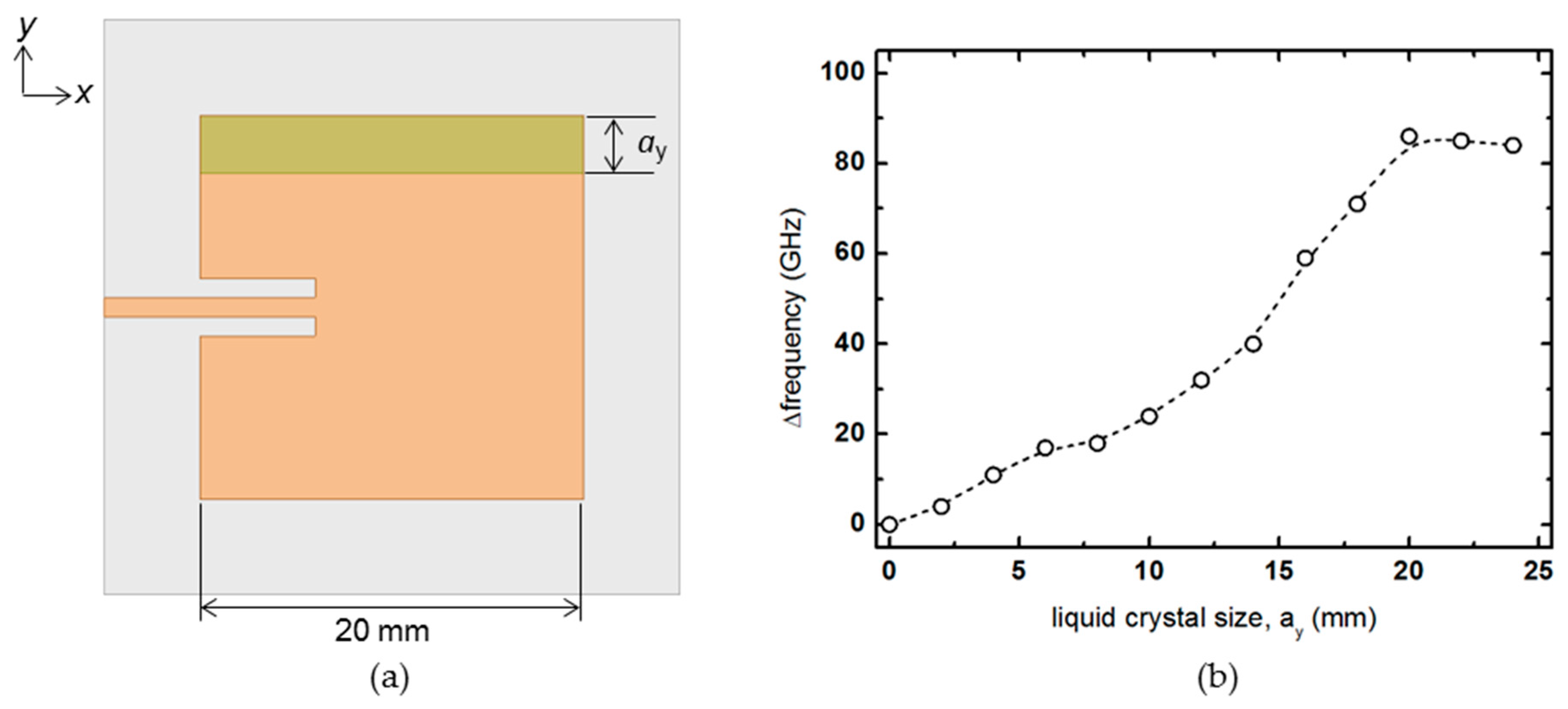
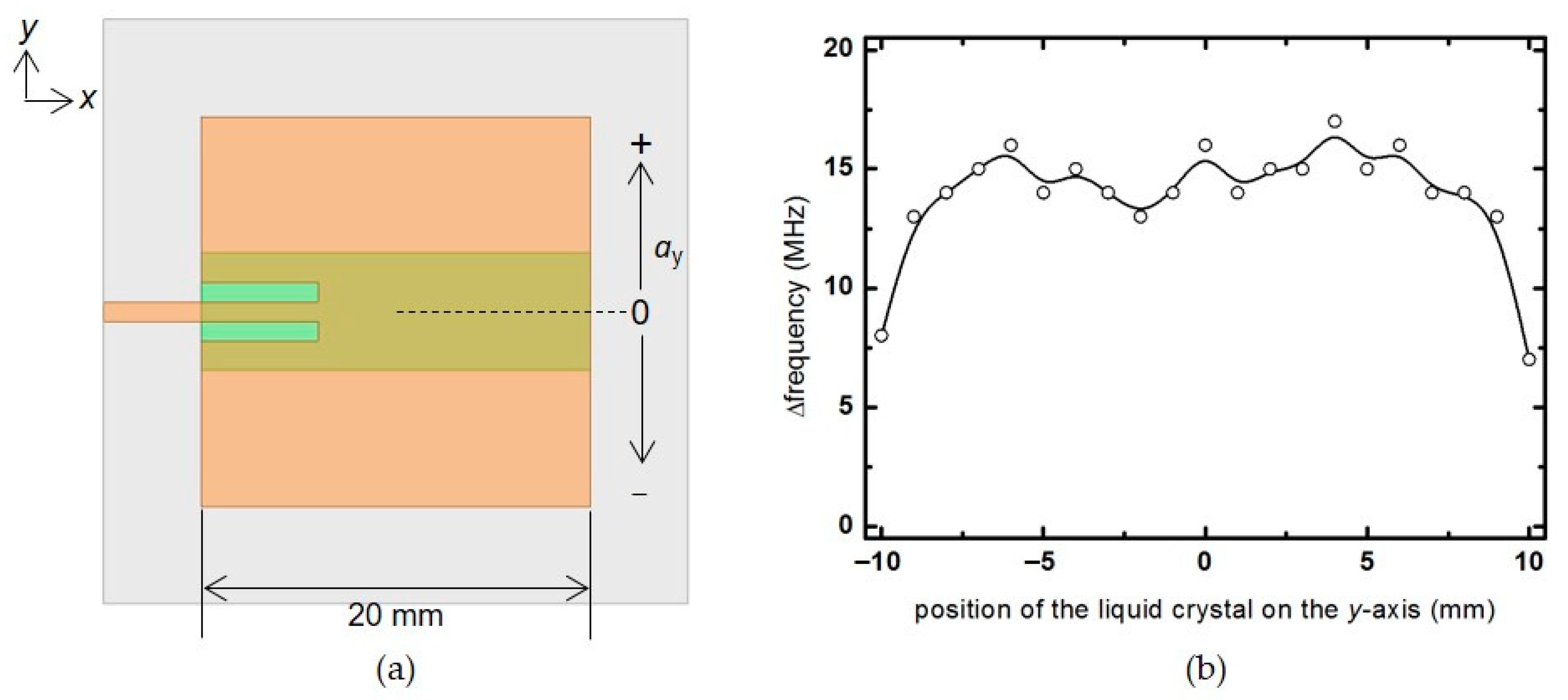
3.1. Analysis of Optimal Liquid crystal Position on the Patch Surface
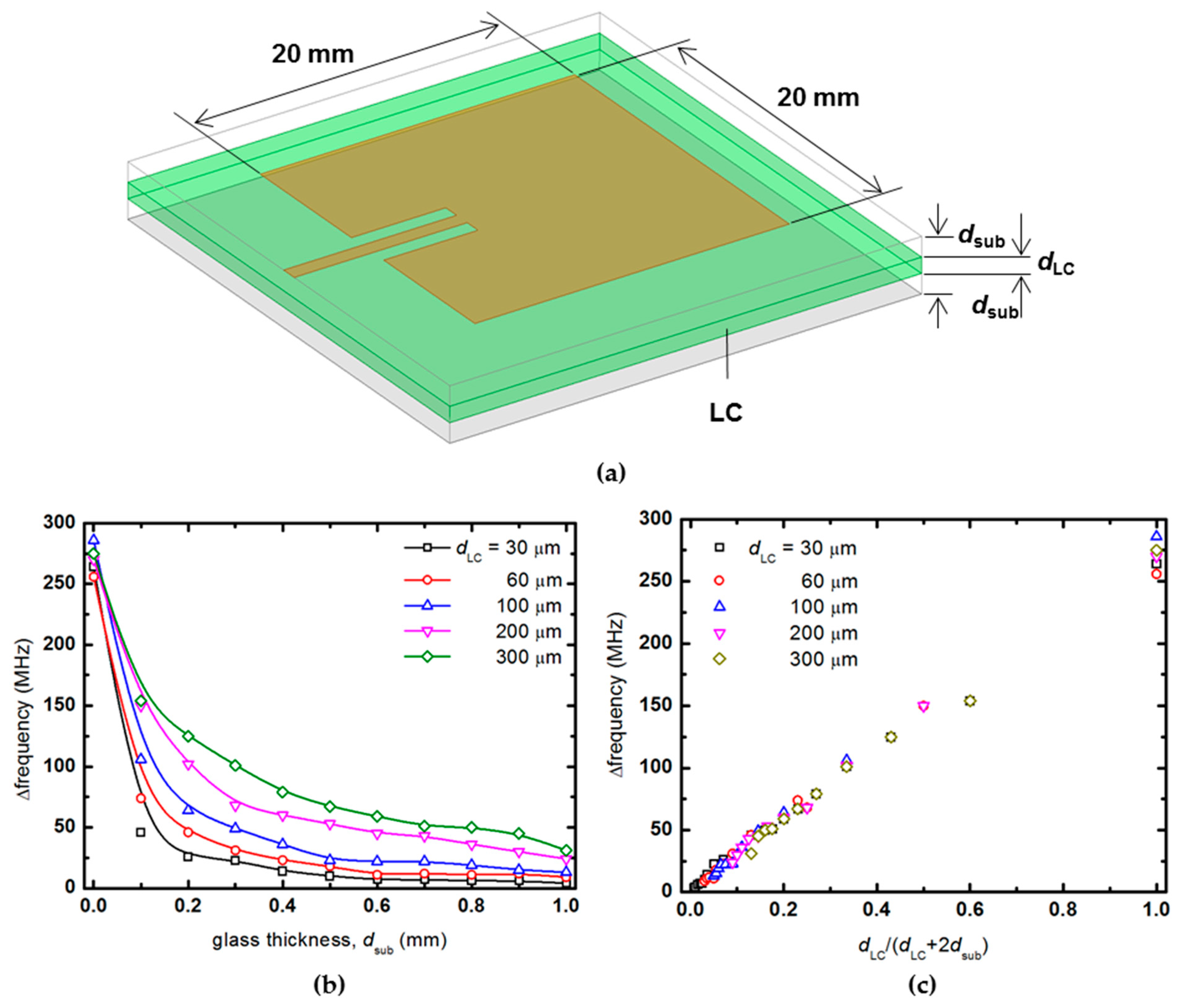
3.2. Analysis of Optimal Liquid Crystal Thickness in Patch Antenna Substrate
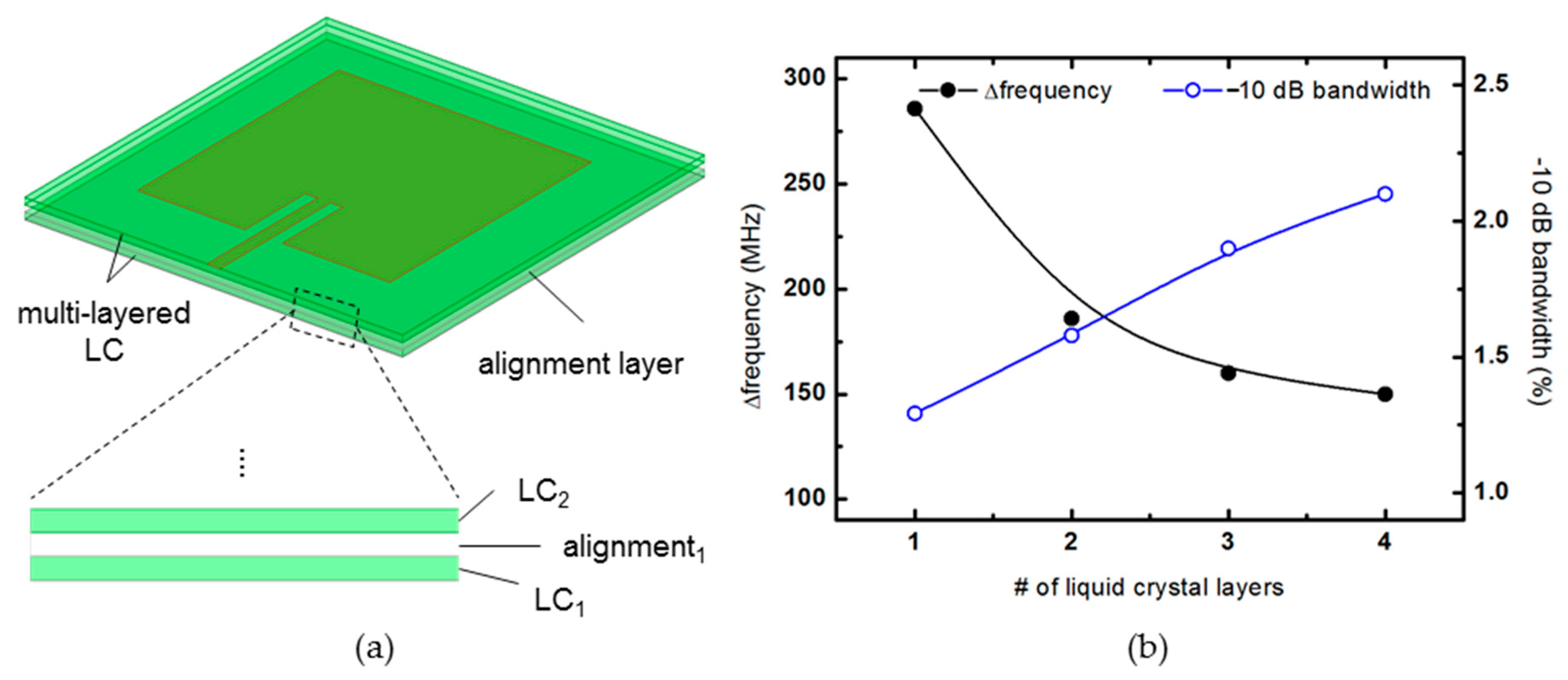
3.3. Liquid Crystal Patch Antenna Performance Enhancement Technique
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mousavi, P.; Fakharzadeh, M.; Jamali, S.H.; Narimani, K.; Hossu, M.; Bolandhemmat, H.; Rafi, G.; Safavi-Naeini, S. A low-cost ultra low profile phased array system for mobile satellite reception using zero-knowledge beamforming algorithm. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2008, 56, 3667–3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.; Jiang, Z.H.; Yu, C.; Zhou, J.; Chen, P.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Yang, B.; Pang, X.; Jiang, M.; et al. Multibeam antenna technologies for 5G wireless communications. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2017, 65, 6231–6249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, Y.L.; Li, C.; Sim, C.Y.D.; Wu, G.; Wong, K.L. 4G/5G multiple antennas for future multi-mode smartphone applications. IEEE Access 2016, 4, 2981–2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.; Lim, S.; Ko, S.; Kim, Y.G. Optically invisible antenna integrated within an OLED touch display panel for IoT applications. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2017, 65, 3750–3755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marnat, L.; Shamim, A. Liquid Crystal Polymer (LCP) based antenna for flexible system on package (SoP) applications. In Proceedings of the 15th International Symposium on Antenna Technology and Applied Electromagnetics, Toulouse, France, 25–28 June 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, A.; Upadhyaya, T.; Patel, R. Compact wideband transparent antenna for 5G communication systems. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2019, 61, 781–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polo-Lopez, L.; Masa-Campos, J.L.; Muriel-Barrado, A.T.; Sanchez-Olivares, P.; Garcia-Marin, E.; Corcoles, J.; Ruiz-Cruz, J.A. Mechanically reconfigurable linear phased array antenna based on single-block waveguide reflective phase shifters with tuning screws. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 113487–113497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, J.; Liu, X.; Georgakopoulos, S.V.; Ware, T.; Wie, J.J.; White, T.J. Novel reconfigurable antennas using Liquid Crystals Elastomers. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation & USNC/URSI National Radio Science Meeting, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 19–25 July 2015; pp. 2297–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, G.J.; Liu, Y.; Genzer, J.; Lazzi, G.; Dickey, M.D. Self-folding origami microstrip antennas. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2014, 62, 5416–5419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, A.; Guldiken, R.; Mumcu, G. Microfluidically reconfigured wideband frequency-tunable liquid-metal monopole antenna. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2016, 64, 2572–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayraktar, O.; Civi, O.A.; Member, S.; Akin, T. Beam switching re fl ectarray monolithically integrated with RF MEMS switches. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2012, 60, 854–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, I.; Rana, I.E.; Mir, N.A.; Afreen, K. Design and analysis of a frequency reconfigurable microstrip patch antenna switching between four frequency bands. Prog. Electromagn. Res. C 2016, 68, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karnati, K.K.; Trampler, M.E.; Gong, X. A Monolithically BST-integrated K-{a} -band beamsteerable reflectarray antenna. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2017, 65, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.V.; Benzerga, R.; Borderon, C.; Delaveaud, C.; Sharaiha, A.; Renoud, R.; Le Paven, C.; Pavy, S.; Nadaud, K.; Gundel, H.W. Miniaturized and reconfigurable notch antenna based on a BST ferroelectric thin film. Mater. Res. Bull. 2015, 67, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.-P.; Lu, W.-B.; Liu, Z.-G.; Zhang, A.-Q.; Wu, B.; Chen, H. Dynamically tunable integrated device for attenuation, amplification and transmission of SSPP using graphene. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2020, 68, 3953–3962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christou, M.A.; Papanicolaou, N.C.; Polycarpou, A.C. A nematic liquid crystal tunable patch antenna. In Proceedings of the 8th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP 2014), Hague, The Netherlands, 6–11 April 2014; pp. 1875–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Missaoui, S.; Missaoui, S.; Kaddour, M. Tunable microstrip patch antenna based on liquid crystals. In Proceedings of the 2016 XXIst International Seminar/Workshop on Direct and Inverse Problems of Electromagnetic and Acoustic Wave Theory (DIPED), Tbilisi, Georgia, 26–29 September 2016; pp. 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polat, E.; Reese, R.; Tesmer, H.; Nickel, M.; Jakoby, R.; Maune, H. Fully dielectric phased array for beamsteering using liquid crystal technology at W-Band. In Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP), Copenhagen, Denmark, 15–20 March 2020; pp. 4–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, M.; Inam, M. Design of liquid crystal based tunable reflectarray antenna using slot embedded patch element configurations. Waset.Org 2014, 8, 1420–1425. [Google Scholar]
- Chandra, S.; Dwivedi, S. Comparative analysis of reconfigurable patch antenna array for different liquid crystal substrates. In Proceedings of the 2019 URSI Asia-Pacific Radio Science Conference (AP-RASC), New Delhi, India, 9–15 March 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Huang, C.; Qing, A.Y.; Luo, X. A Frequency and pattern reconfigurable antenna array based on liquid crystal technology. IEEE Photonics J. 2017, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuscaldo, W.; Tofani, S.; Zografopoulos, D.C.; Baccarelli, P.; Burghignoli, P.; Beccherelli, R.; Galli, A. A reconfigurable multilayered THz leaky-wave antenna employing liquid crystals. In Proceedings of the 11th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EUCAP), Paris, France, 19–24 March 2017; pp. 849–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, J.U.N.; Member, G.S.; Zhang, Y. A novel beam steerable antenna employing tunable high impedance surface with liquid crystal. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 118687–118695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maune, H.; Jost, M.; Reese, R.; Polat, E.; Nickel, M.; Jakoby, R. Microwave liquid crystal technology. Crystals 2018, 8, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reese, R.; Jost, M.; Polat, E.; Tesmer, H.; Strobl, J.; Schuster, C.; Nickel, M.; Jakoby, R.; Maune, H. A millimeter-wave beam-steering lens antenna with reconfigurable aperture using liquid crystal. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2019, 67, 5313–5324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaebler, A.; Moessinger, A.; Goelden, F.; Manabe, A.; Goebel, M.; Follmann, R.; Koether, D.; Modes, C.; Kipka, A.; Deckelmann, M.; et al. Liquid crystal-reconfigurable antenna concepts for space applications at microwave and millimeter waves. Int. J. Antennas Propag. 2009, 2009, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirshnan, D.; Nasimuddin; Alphones, A.; Sun, M. Enhanced frequency tuning based on optimized liquid crystal cavity based patch antenna. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Asia-Pacific Microwave Conference (APMC), Singapore, 10–13 December 2019; pp. 1545–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stutzman, W.L.; Davis, W.A. Antenna theory. Wiley Encycl. Electr. Electron. Eng. 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulja, S.; Mirshekar-Syahkal, D.; James, R.; Day, S.E.; Fernández, F.A. Measurement of dielectric properties of nematic liquid crystals at millimeter wavelength. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2010, 58, 3493–3501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittek, M.; Fritzsch, C.; Canisius, J. 55.1 invited paper: Liquid crystals for smart antennas and other microwave applications. SID Symp. Dig. Tech. Pap. 2015, 46, 824–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, D.C.; Tantot, O.; Jallageas, H.; Ponchak, G.E.; Tentzeris, M.M.; Papapolymerou, J. Characterization of liquid crystal polymer (LCP) material and transmission lines on LCP substrates from 30 to 110 GHz. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2004, 52, 1343–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, D.; Kim, K.; Kim, H.; Choi, M.; Na, J.-H. Design Optimization of Reconfigurable Liquid Crystal Patch Antenna. Materials 2021, 14, 932. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14040932
Kim D, Kim K, Kim H, Choi M, Na J-H. Design Optimization of Reconfigurable Liquid Crystal Patch Antenna. Materials. 2021; 14(4):932. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14040932
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Dowon, Kitae Kim, Hogyeong Kim, Moonyoung Choi, and Jun-Hee Na. 2021. "Design Optimization of Reconfigurable Liquid Crystal Patch Antenna" Materials 14, no. 4: 932. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14040932
APA StyleKim, D., Kim, K., Kim, H., Choi, M., & Na, J.-H. (2021). Design Optimization of Reconfigurable Liquid Crystal Patch Antenna. Materials, 14(4), 932. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14040932






