Effect of Annealing on the Structural, Magnetic and Surface Energy of CoFeBY Films on Si (100) Substrate
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
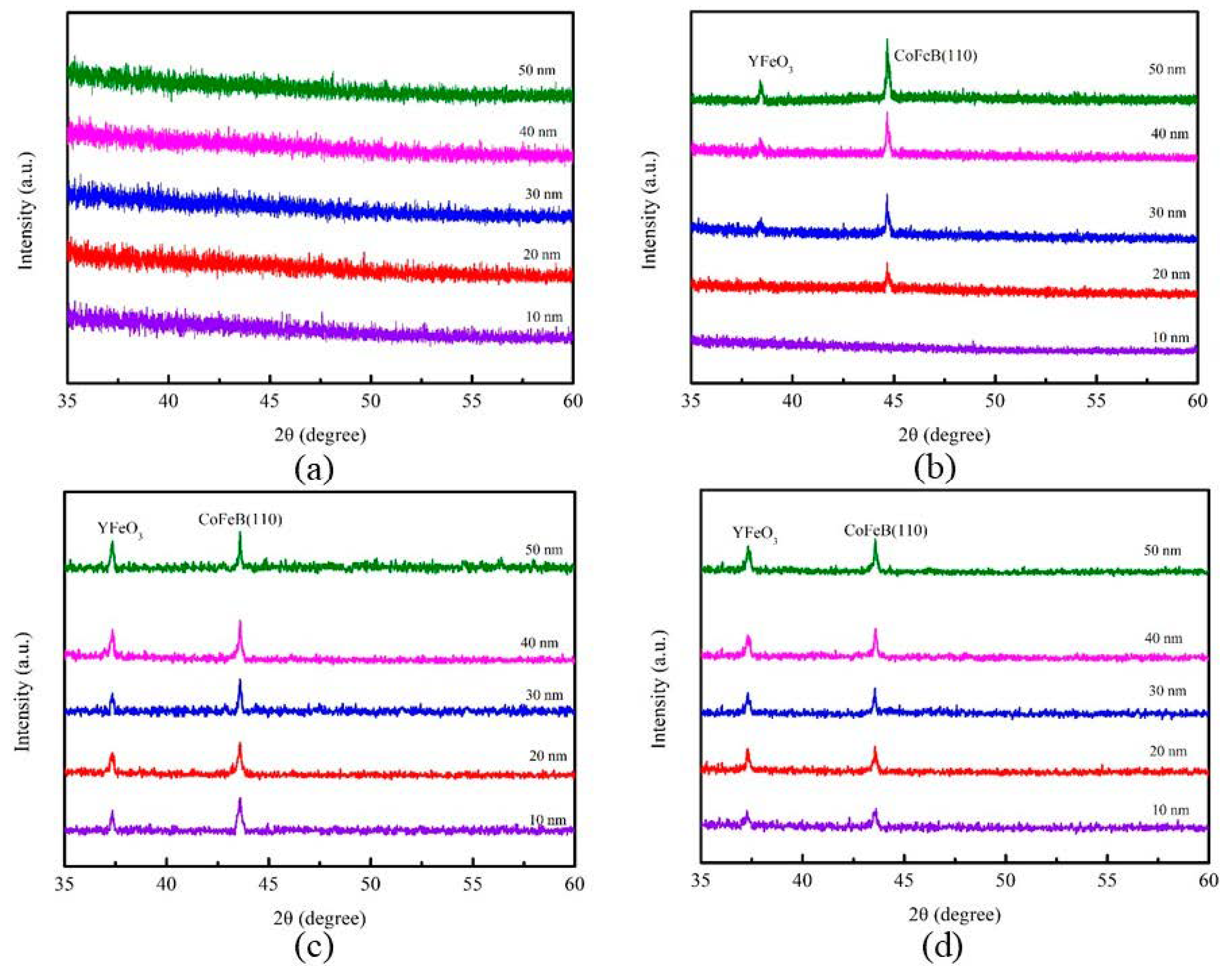
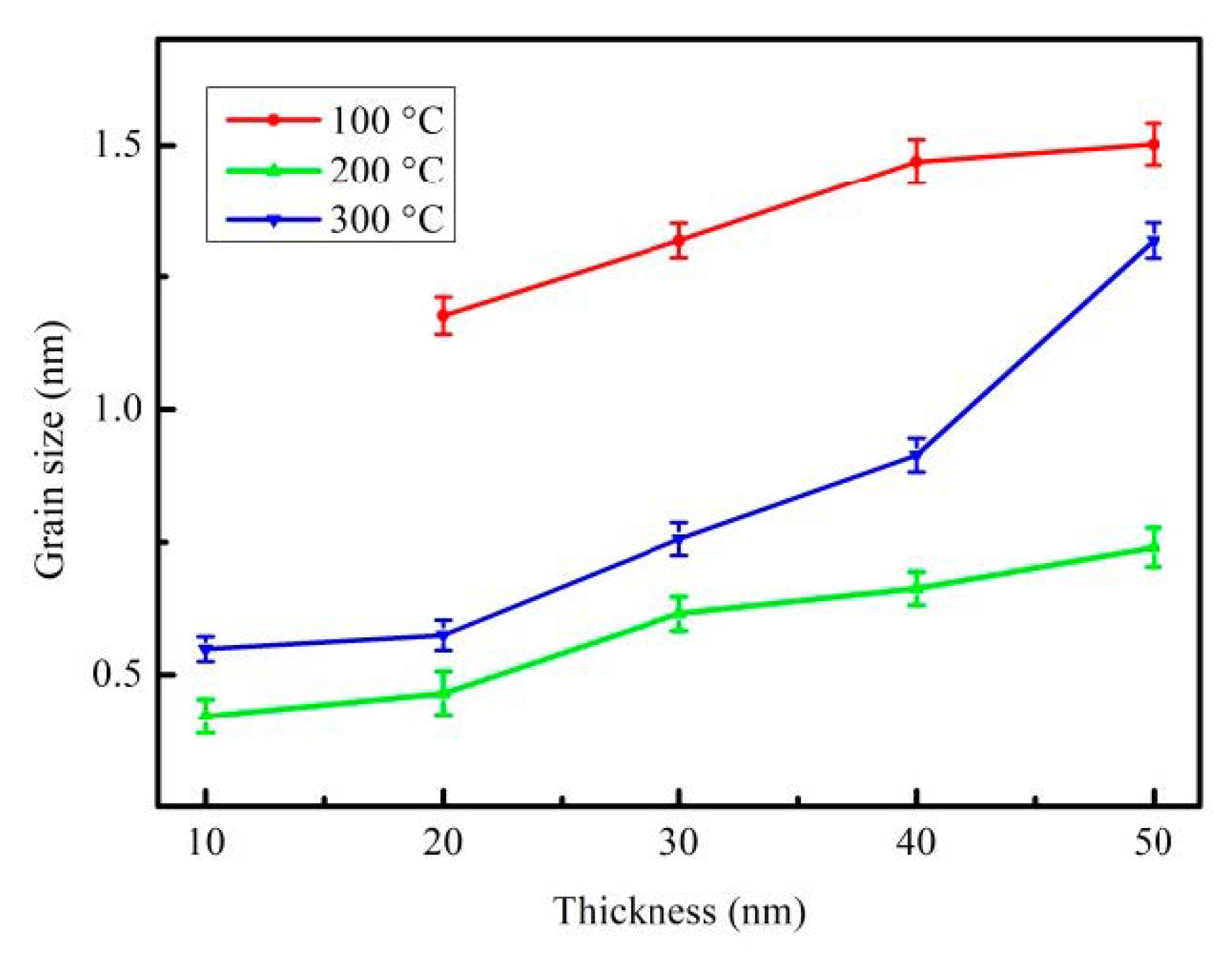
3.1. Structure Property and Grain Size Distribution
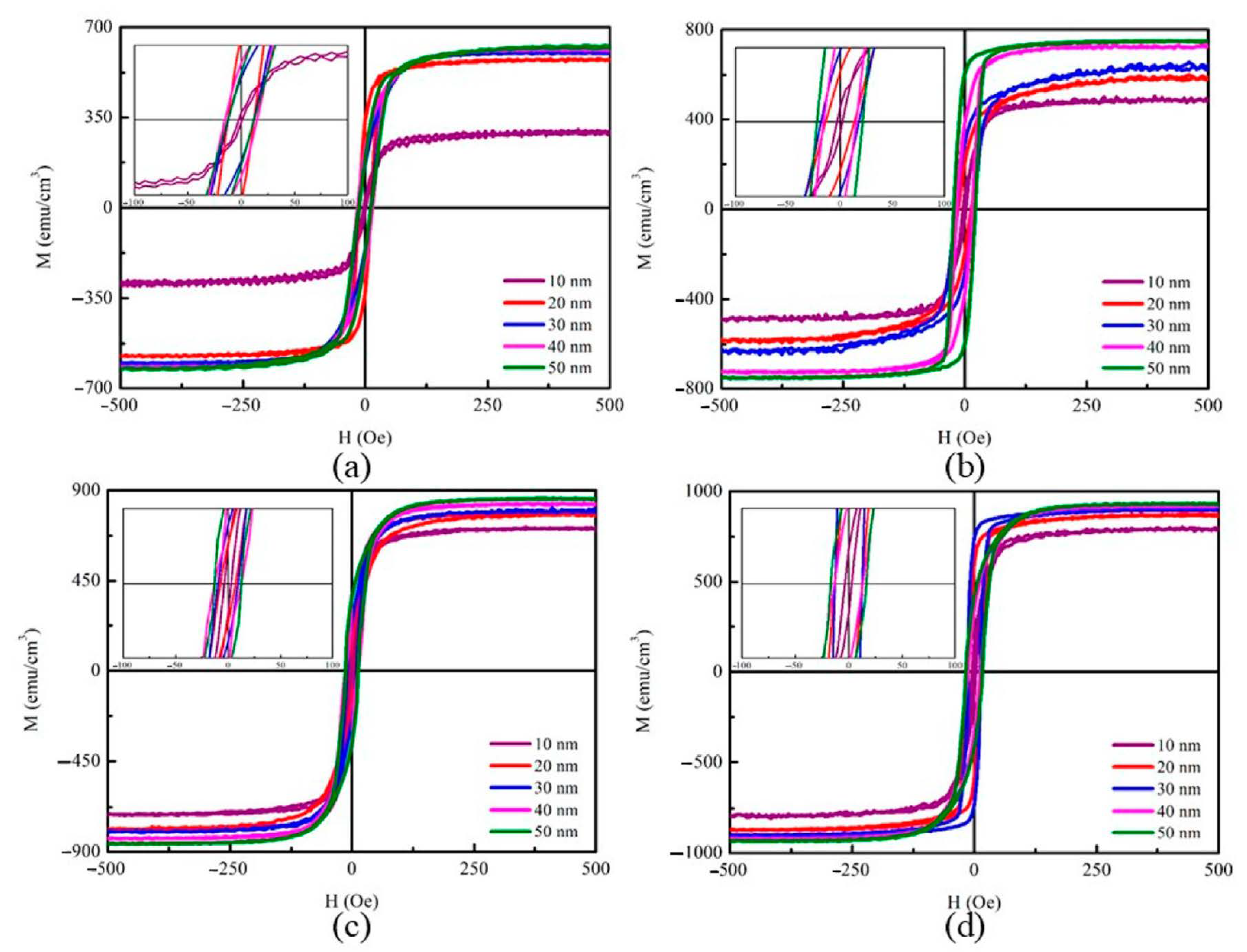
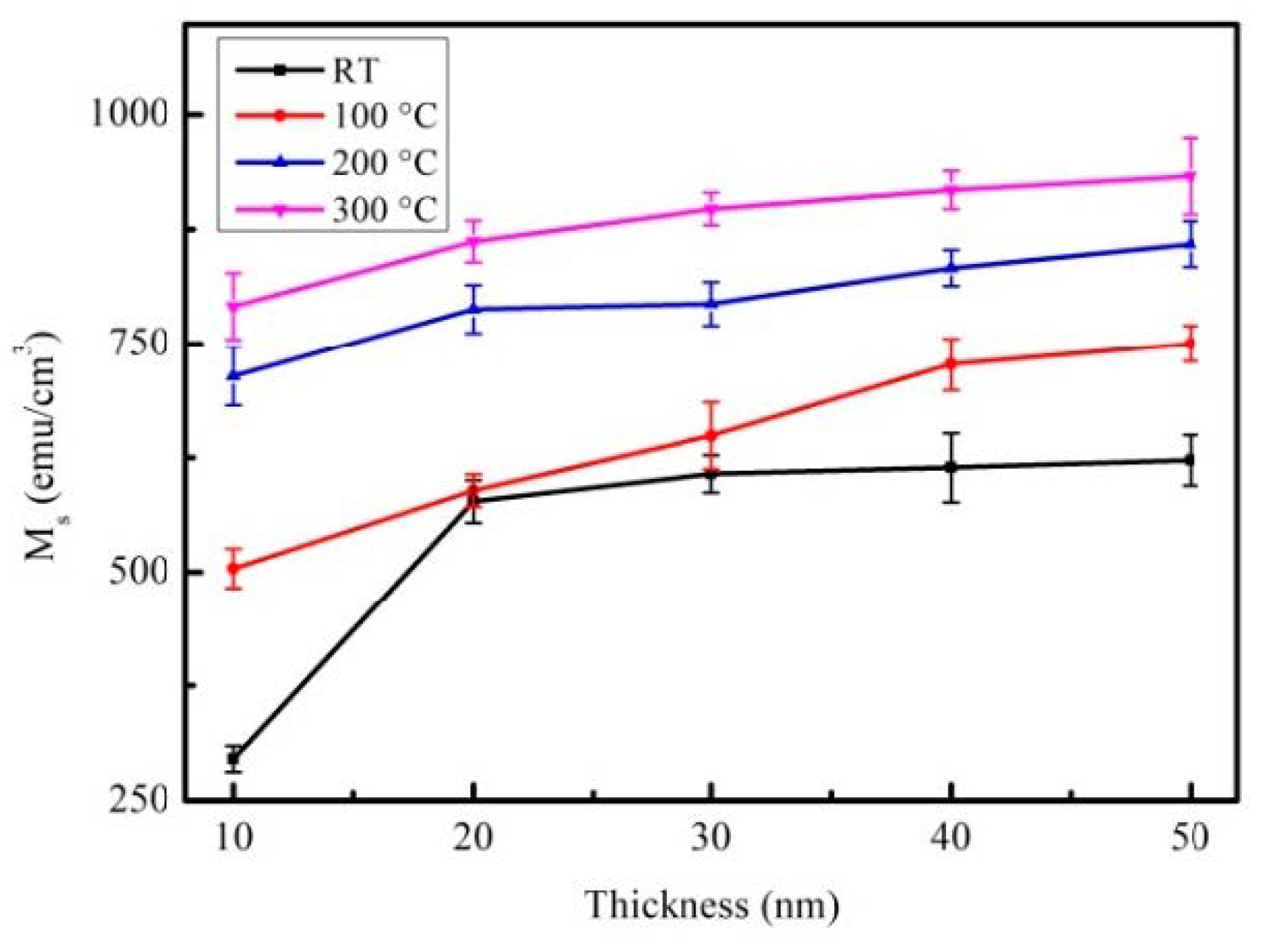
3.2. Magnetic Properties
3.3. Analysis of Surface Energy and Adhesion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hayakawa, J.; Ikeda, S.; Lee, Y.; Sasaki, R.; Matsukura, F.; Meguro, T.; Takahashi, H.; Ohno, H. Current-Driven Magnetization Switching in CoFeB/MgO/CoFeB Magnetic Tunnel Junctions. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 44, 1267–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-T.; Chang, Z. Low-Frequency Alternative-Current Magnetic Susceptibility of Amorphous and Nanocrystalline Co60Fe20B20 films. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2012, 324, 2224–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, C.Y.; Ohkubo, T.; Takahashi, Y.K.; Hono, K. Boron Segregation in Crystallized MgO/Amorphous-Co40Fe40B20 Thin Films. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 104, 033517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, T.; Ando, Y.; Watanabe, D.; Oogane, M.; Miyazaki, T. Spin Transfer Switching in the Nanosecond Regime for CoFeB/MgO/CoFeB Ferromagnetic Tunnel Junctions. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 103, 103911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifert, T.; Jaiswal, S.; Martens, U.; Hannegan, J.; Braun, L.; Maldonado, P.; Freimuth, F.; Kronenberg, A.; Henrizi, J.; Radu, I.; et al. Efficient Metallic Spintronic Emitters of Ultrabroadband Terahertz Radiation. Nat. Photonics 2016, 10, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, D.; Muñoz, J.; Kurlyandskaya, G.; Vázquez, M.; Ali, M.; Gibbs, M. Induced Anisotropy, Magnetic Domain Structure and Magnetoimpedance Effect in CoFeB Amorphous Thin Films. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1999, 191, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, M.S.; Mori, T.J.A.; Schelp, L.F.; Chesman, C.; Bohn, F.; Correa, M.A. High Frequency Magnetic Behavior Through the Magnetoimpedance Effect in CoFeB/(Ta, Ag, Cu) Multilayered Ferromagnetic Thin Films. Thin Solid Films 2012, 520, 2173–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ikeda, S.; Miura, K.; Yamamoto, H.; Mizunuma, K.; Gan, H.D.; Endo, M.; Kanai, S.; Hayakawa, J.; Matsukura, F.; Ohno, H. A Perpendicular-Anisotropy CoFeB-MgO Magnetic Tunnel Junction. Nat. Mate. 2010, 9, 721–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, C.Y.; Goripati, H.S.; Furubayashi, T.; Takahashi, Y.K.; Hono, K. Exchange Bias of Spin Valve Structure with a Top-Pinned Co40Fe40B20/IrMn. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 93, 012501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.X.; Yang, Y.; Naganuma, H.; Ando, Y.; Yu, R.C.; Han, X.F. The Perpendicular Anisotropy of Co40Fe40B20 Sand-Wiched Between Ta and MgO Layers and its Application in CoFeB/MgO/CoFeB tunnel junction. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 99, 012502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, W.X.; Yao, Y.; Liu, H.F.; Naganuma, H.; Sakul, T.S.; Han, X.F.; Yu, R.C. Chemical Diffusion: Another Factor Affecting the Magnetoresistance Ratio in Ta/CoFeB/MgO/CoFeB/Ta Magnetic Tunnel Junction. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 101, 012406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.Y.; Lim, W.C.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, T.D.; Kim, K.W.; Kim, T.W. Compositional Change of MgO Barrier and Interface in CoFeB∕MgO∕CoFeB Tunnel Junction After Annealing. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 99, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, G.I.R.; Wei, H.-X.; Porter, N.A.; Harnchana, V.; Brown, A.P.; Brydson, R.M.D.; Arena, D.A.; Dvořák, J.; Han, X.-F.; Marrows, C. Changes in the Layer Roughness and Crystallography During the Annealing of CoFeB/MgO/CoFeB Magnetic Tunnel Junctions. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 105, 063904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawaa, J.; Ikeda, S.; Lee, Y.M.; Matsukura, F.; Ohno, H. Effect of High Annealing Temperature on Giant Tunnel Mag-Netoresistance Ratio of CoFeB/MgO/CoFeB Magnetic Tunnel Junctions. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 232510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wu, Q.; Yan, H.; Zhong, S.; Huang, Z. Effect of Trace Yttrium Addition and Heat Treatmenton the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of As-Cast ADC12 Aluminum Alloy. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baulin, O.; Bugnet, M.; Fabrègue, D.; Lenain, A.; Gravier, S.; Cazottes, S.; Kapelski, G.; Ovanessian, B.T.; Balvay, S.; Hartmann, D.J.; et al. Improvement of Mechanical, Thermal, and Corrosion Properties of Ni- and Al-free Cu–Zr–Ti Metallic Glass with Yttrium Addition. Materialia 2018, 1, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Qian, D.; Zhao, L.; Zheng, Z.; Gao, X.; Ramanujan, R. Enhancing the Coercivity, Thermal Stability and Exchange Coupling of Nano-Composite (Nd,Dy,Y)–Fe–B alloys with reduced Dy content by Zr addition. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 606, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Ma, D.; Xu, C.; Liu, T.; Cheng, L.; Du, Y.; Zhang, W. Crystal Structure and Phase Relations of the R2Fe14B–Y2Fe14B (R = Nd and Pr) Systems. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 2017, 31, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, Z.; Yan, M.; Liu, Z.W.; Tao, S.; Ma, T. High coercivity (Nd8Y3)–(Fe62Nb3Cr)–B23 Magnets Produced by Injection Casting. J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 48, 1779–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshizawa, Y.; Oguma, S.; Yamauchi, K. New Fe-Based Soft Magnetic Alloys Composed of Ultrafine Grain Structure. J. Appl. Phys. 1988, 64, 6044–6046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzer, G. Soft Magnetic Nanocrystalline Materials. Scr. Met. Mater. 1995, 33, 1741–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makino, A.; Hatanai, T.; Naitoh, Y.; Bitoh, T.; Inoue, A.; Masumoto, T. ChemInform Abstract: Applications of Nanocrystalline Soft Magnetic Fe-M-B (M: Zr, Nb) Alloys “NANOPER”. Chemistry 2010, 29, 3793–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.-J.; Ou, S.-L.; Chang, Y.-H.; Chen, Y.-T.; Wang, Y.-T.; Liang, Y.-C.; Tseng, J.-Y.; Chi, P.-W. Magnetic Susceptibility, Optical, and Adhesive Properties of Co40Fe40V10B10 films. Surf. Eng. 2020, 36, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, S.-L.; Liu, W.-J.; Chang, Y.-H.; Chen, Y.-T.; Wang, Y.-T.; Li, W.-H.; Tseng, J.-Y.; Wu, T.-H.; Chi, P.-W.; Chu, C.-L. Structure, Magnetic Property, Surface Morphology, and Surface Energy of Co40Fe40V10B10 Films on Si(100) Substrate. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.; Chung, T.S.; Good, R.J. Surface Energy of Thermotropic Liquid Crystalline Polyesters and Polyesteramide. J. Polym. Sci. 1998, 36, 2327–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, D.K.; Wendt, R.C. Estimation of the Surface Free Energy of Polymers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1969, 13, 1741–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaelble, D.H.; Uy, K.C. A Reinterpretation of Organic Liquid-Polytetrafluoroethylene Surface Interactions. J. Adhes. 1970, 2, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullity, B.D.; Weymouth, J.W. Elements of X-Ray Diffraction. Am. J. Phys. 1957, 25, 394–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.H.; Luo, Y.; Yu, D.B.; Quan, N.T.; Wu, G.Y.; Dou, Y.K.; Hu, Z.; Wang, Z.L. Permanent Magnetic Properties of Nd–Fe–B Melt-Spun Ribbons with Y Substitution. Rare Metals 2020, 39, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svalov, A.; Bespalko, O. Rotational Magnetic Anisotropy in Amorphous Gd-Co films. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1995, 148, 134–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-T.; Xie, S.M. Magnetic and Electric Properties of Amorphous Co40Fe40B20Thin Films. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.P.; Liu, C.T.; Porter, W.D. Role of Yttrium in Glass Formation of Fe-Based Bulk Metallic Glasses. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 83, 2581–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Shen, J.; Zhang, T.; Zou, J. Enhanced Glass-Forming Ability of a Zr-Based Bulk Metallic Glass with Yttrium Doping. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2006, 352, 3109–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Pan, M.X.; Zhao, D.Q.; Wang, R.J.; Wang, W.H. Formation of Zr-Based Bulk Metallic Glasses from Low Purity of Materials by Yttrium Addition. Mater. Trans. JIM 2000, 41, 1410–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckert, J.; Mattern, N.; Zinkevitch, M.; Seidel, M. Crystallization Behavior and Phase Formation in Zr–Al–Cu–Ni Metallic Glass Containing Oxygen. Mater. Trans. JIM 1998, 39, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.T.; Xie, S.M.; Jheng, H.Y. The Low-Frequency Alternative-Current Magnetic Susceptibility and Electrical Properties of Si(100)/Fe40Pd40B20(X Å)/ZnO(500 Å) and Si(100)/ZnO(500 Å)/Fe40Pd40B20 (Y Å) systems. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 113, 17B303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, S.H.; Okamoto, T.; Nakagawa, S. [Ni-Fe/Si] Double Seedlayer with Low Surface Energy for Fe-Co-B Soft Magnetic Underlayer with high Hk for Perpendicular Magnetic Recording Media. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2004, 40, 2389–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
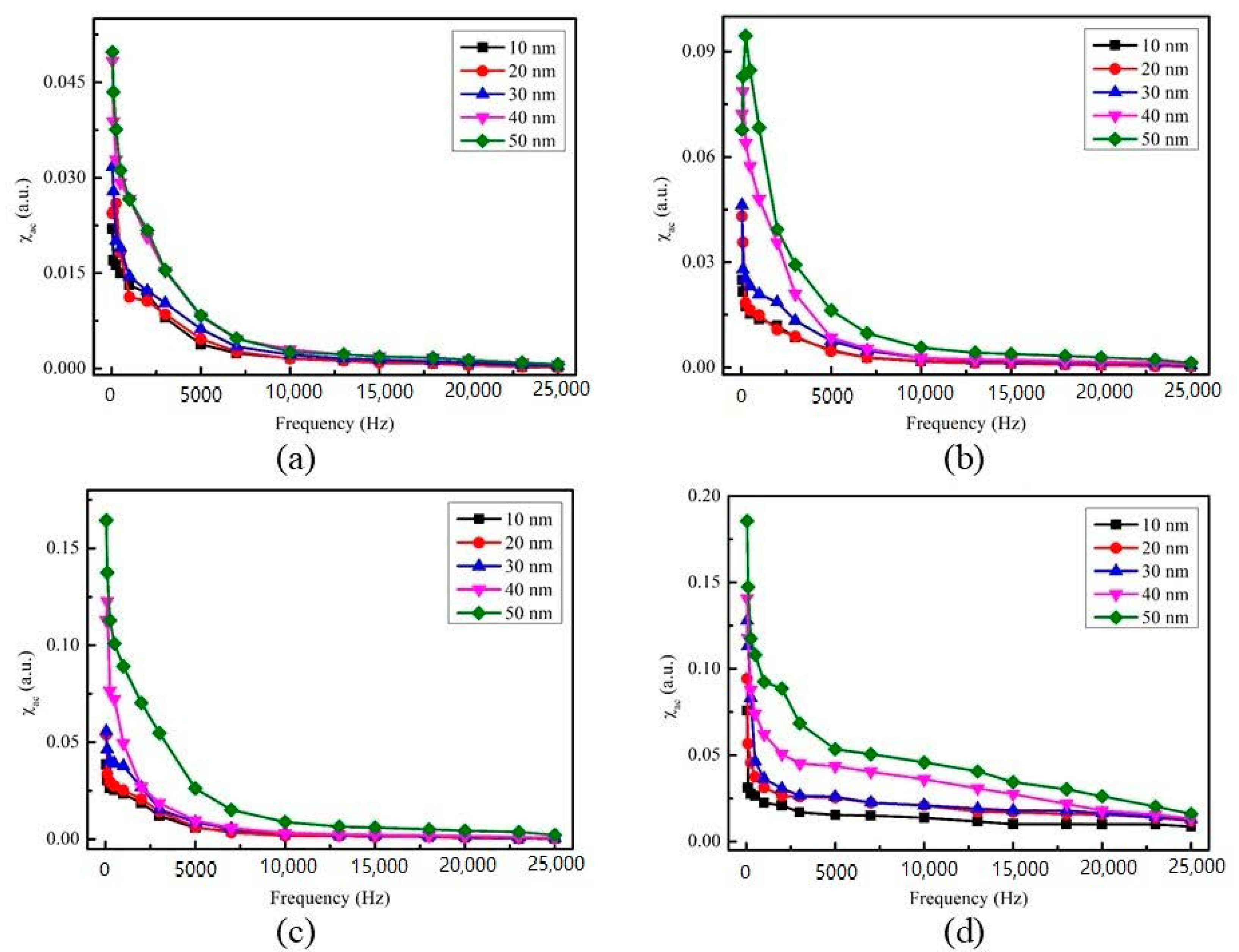
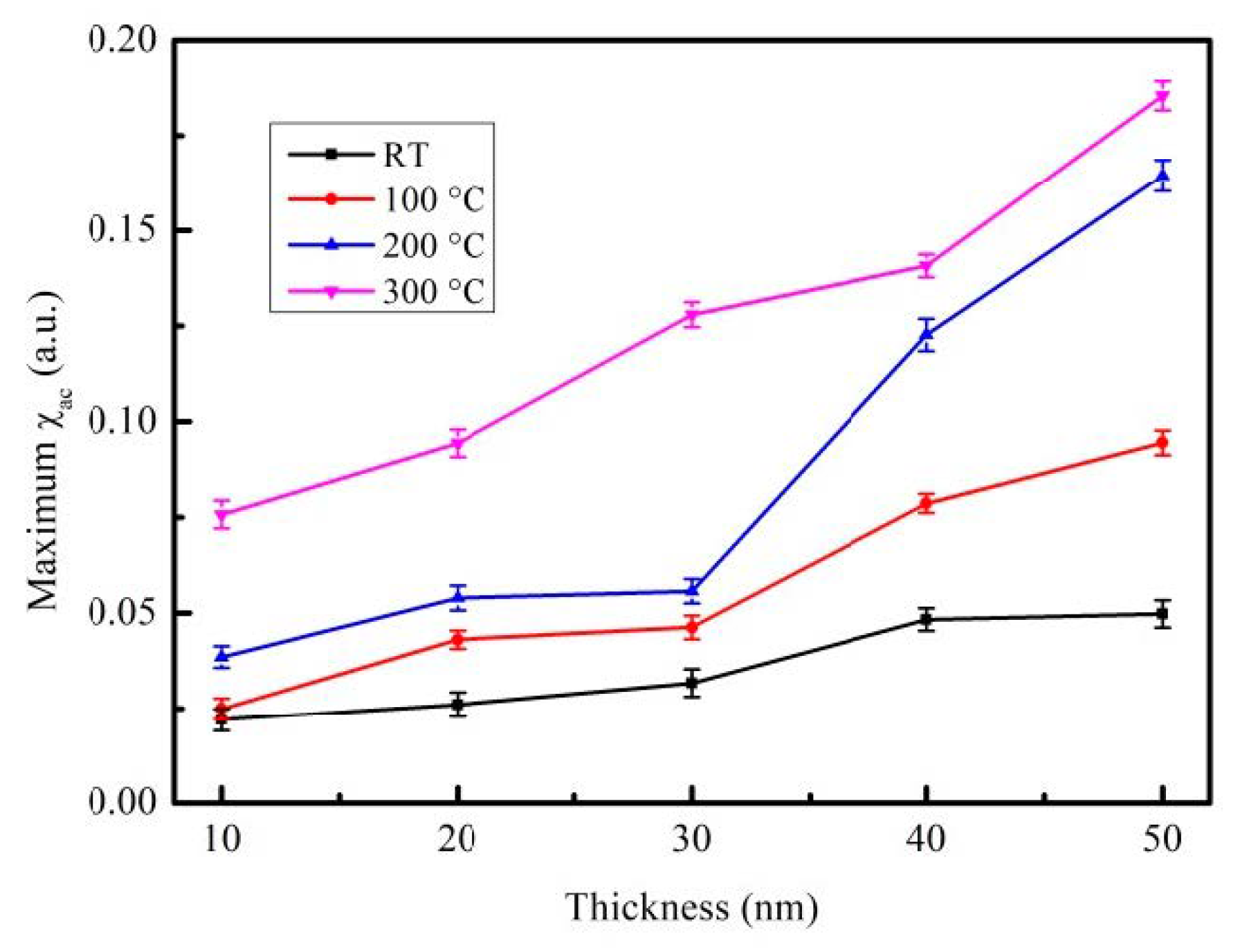

| Material | Thickness (nm) | Maximum χac (a.u.) | Optimal Resonance Frequency, fres (Hz) | Surface Energy (mJ/mm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glass/Co40Fe40V10B10 [23] | 10–40 at RT | 0.068–0.098 | 50–1000 | 65.5–38 |
| Si (100)/Co40Fe40V10B10 [24] | 10–40 at RT | 0.013–0.019 | 50–200 | 34.2–51.5 |
| Si (100)/Co40Fe40B10Y10 | 10–50 at RT and annealed conditions | 0.022–0.185 | 50–250 | 24.6–31.9 |
| Thickness | RT | After Annealing at 100 °C | After Annealing at 200 °C | After Annealing at 300 °C |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 nm | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| 20 nm | 250 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| 30 nm | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| 40 nm | 50 | 100 | 100 | 50 |
| 50 nm | 50 | 250 | 50 | 50 |
| Co40Fe40B10Y10 (10–50 nm) | Contact Angle(θ) with DI Water as Test Liquid | Contact Angle(θ) with Glycerol as Test Liquid |
|---|---|---|
| 10 nm | 80.8° | 79.6° |
| 20 nm | 80.7° | 78.0° |
| 30 nm | 80.1° | 77.7° |
| 40 nm | 80.2° | 77.4° |
| 50 nm | 80.5° | 79.3° |
| Co40Fe40B10Y10 (10–50 nm) | Contact Angle(θ) with DI Water as Test Liquid | Contact Angle(θ) with Glycerol as Test Liquid |
|---|---|---|
| 10 nm | 79.9° | 78.1° |
| 20 nm | 79.9° | 78.1° |
| 30 nm | 80.5° | 79.7° |
| 40 nm | 80.3° | 79.3° |
| 50 nm | 81.0° | 75.1° |
| Co40Fe40B10Y10 (10–50 nm) | Contact Angle(θ) with DI Water as Test Liquid | Contact Angle(θ) with Glycerol as Test Liquid |
|---|---|---|
| 10 nm | 78.8° | 74.4° |
| 20 nm | 79.3° | 73.2° |
| 30 nm | 78.4° | 76.0° |
| 40 nm | 78.6° | 77.6° |
| 50 nm | 78.4° | 73.8° |
| Co40Fe40B10Y10 (10–50 nm) | Contact Angle(θ) with DI Water as Test Liquid | Contact Angle(θ) with Glycerol as Test Liquid |
|---|---|---|
| 10 nm | 76.6° | 75.8° |
| 20 nm | 74.0° | 72.7° |
| 30 nm | 73.4° | 73.0° |
| 40 nm | 72.0° | 71.9° |
| 50 nm | 71.7° | 71.2° |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, W.-J.; Chang, Y.-H.; Chen, Y.-T.; Chiang, Y.-C.; Liu, Y.-C.; Wu, T.-H.; Chi, P.-W. Effect of Annealing on the Structural, Magnetic and Surface Energy of CoFeBY Films on Si (100) Substrate. Materials 2021, 14, 987. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14040987
Liu W-J, Chang Y-H, Chen Y-T, Chiang Y-C, Liu Y-C, Wu T-H, Chi P-W. Effect of Annealing on the Structural, Magnetic and Surface Energy of CoFeBY Films on Si (100) Substrate. Materials. 2021; 14(4):987. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14040987
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Wen-Jen, Yung-Huang Chang, Yuan-Tsung Chen, Yi-Chen Chiang, Yu-Chi Liu, Te-Ho Wu, and Po-Wei Chi. 2021. "Effect of Annealing on the Structural, Magnetic and Surface Energy of CoFeBY Films on Si (100) Substrate" Materials 14, no. 4: 987. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14040987
APA StyleLiu, W.-J., Chang, Y.-H., Chen, Y.-T., Chiang, Y.-C., Liu, Y.-C., Wu, T.-H., & Chi, P.-W. (2021). Effect of Annealing on the Structural, Magnetic and Surface Energy of CoFeBY Films on Si (100) Substrate. Materials, 14(4), 987. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14040987







