Collagen-Carboxymethylcellulose Biocomposite Wound-Dressings with Antimicrobial Activity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. AgNPs Synthesis
2.3. Biocomposite Materials Synthesis
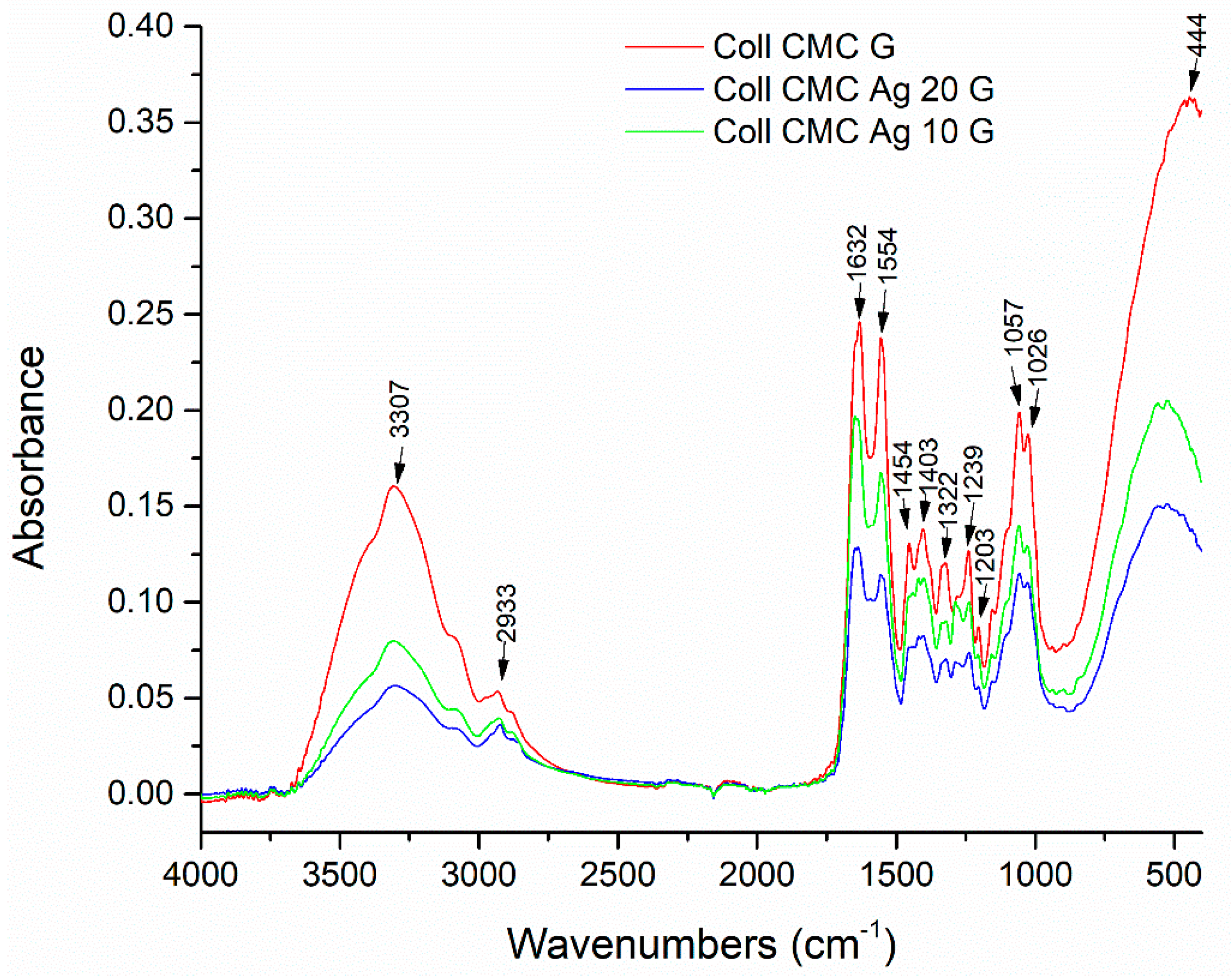
2.4. Structural and Morphological Analyses
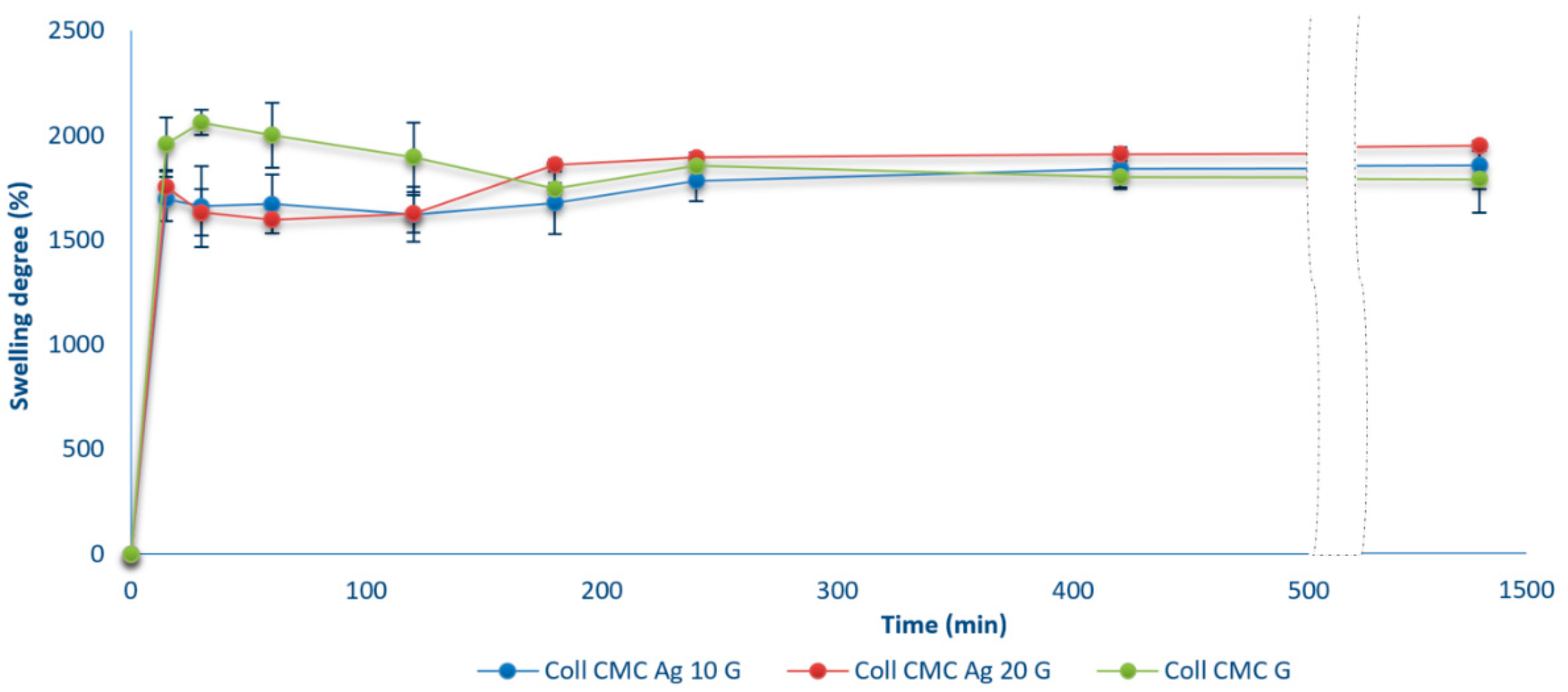
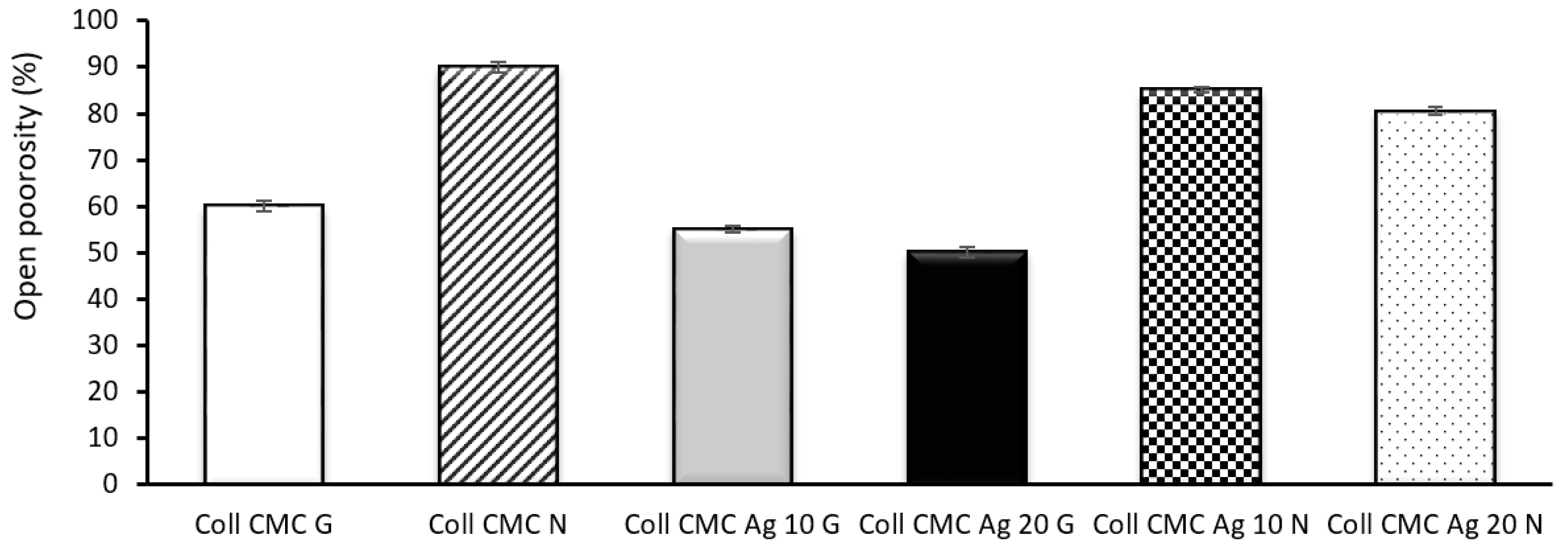
2.5. Swelling Ratio and Open Porosity
2.6. Enzymatic Degradation in Collagenase Solution
2.7. Antimicrobial Assay
2.7.1. Inhibition Zone Diameter Assay
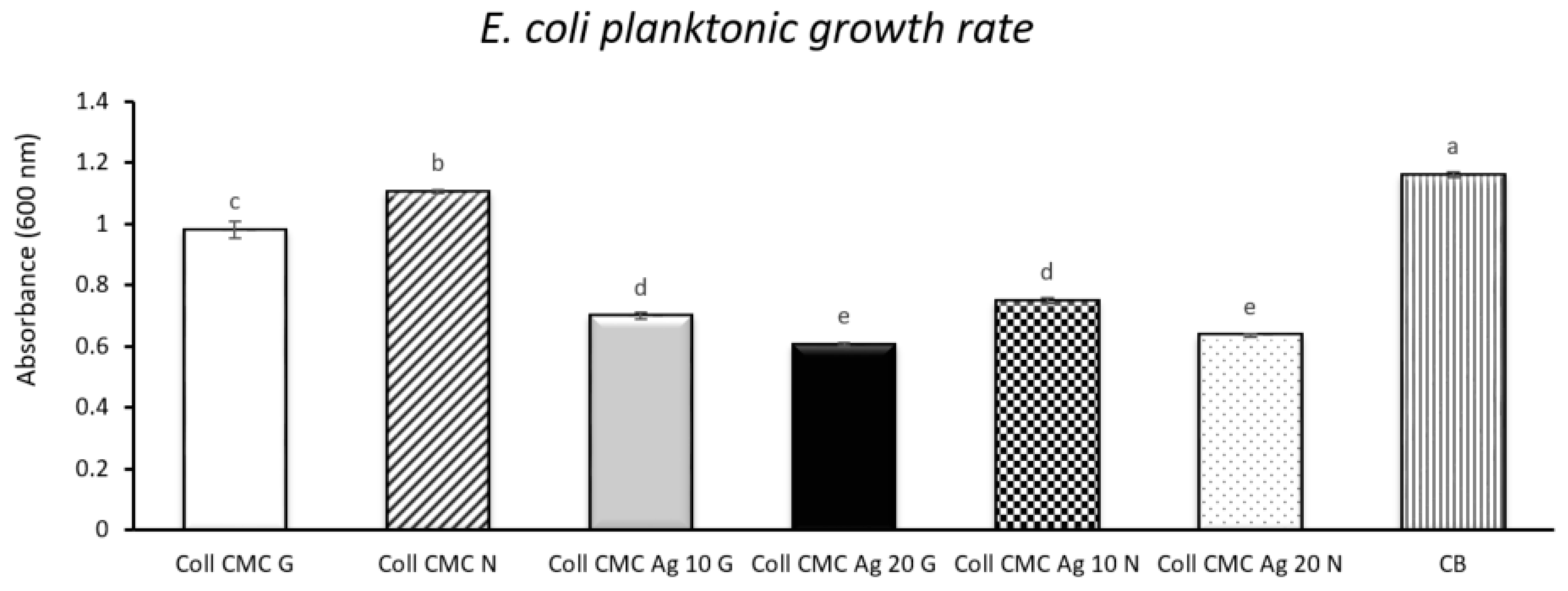
2.7.2. Planktonic Growth Rate
2.8. Cell Toxicity Studies
2.8.1. Cell Viability Assessment
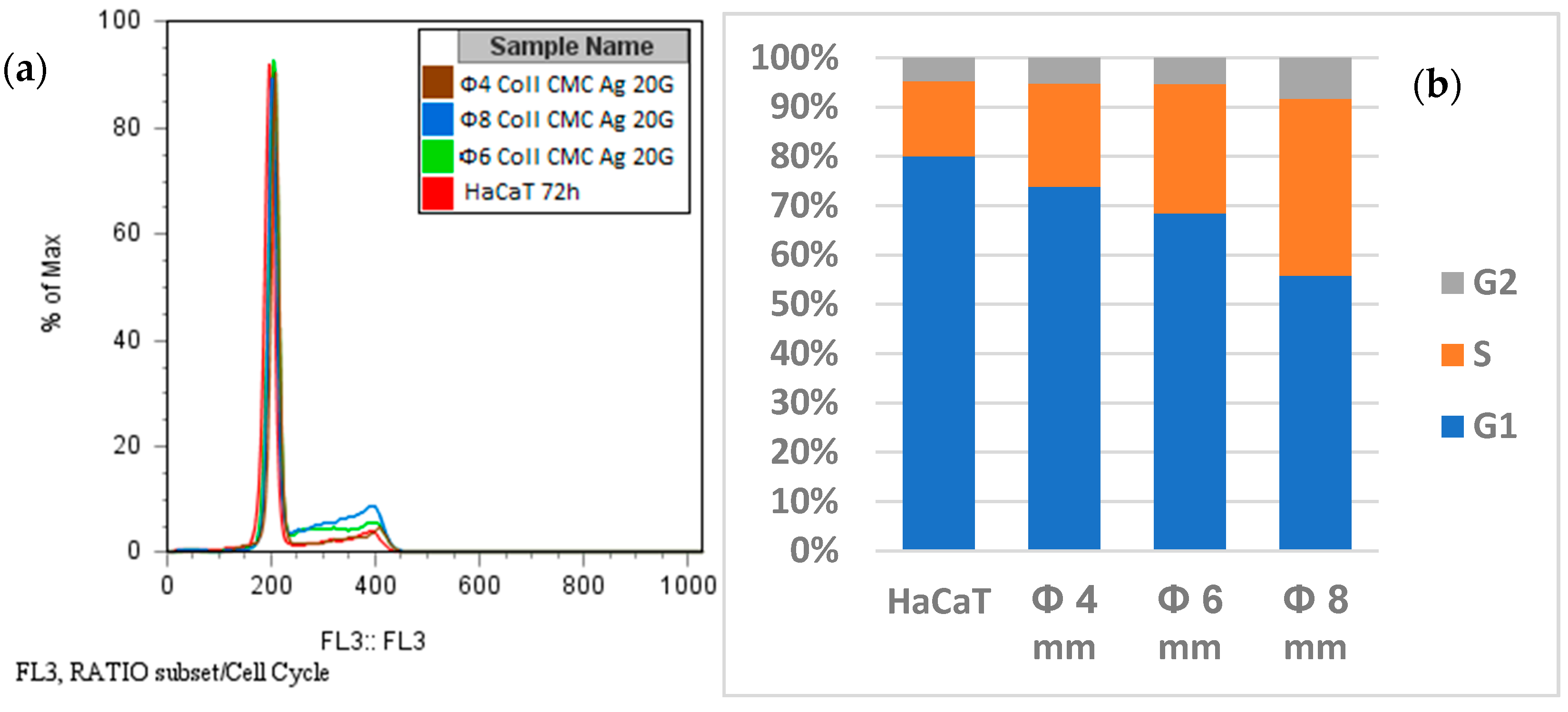
2.8.2. Propidium Iodide (PI) Staining and Cell Cycle Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Benítez, J.M.; Montáns, F.J. The mechanical behavior of skin: Structures and models for the finite element analysis. Comput. Struct. 2017, 190, 75–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai-Cheong, J.E.; McGrath, J.A. Structure and function of skin, hair and nails. Medicine 2017, 46, 347–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminsky, D. The Netter Collection of Medical Illustrations: Respiratory System; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 4, pp. 109–276. [Google Scholar]
- Negut, I.; Grumezescu, V.; Grumezescu, A.M. Treatment Strategies for Infected Wounds. Molecules 2018, 23, 2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayramov, D.F.; Neff, J.A. Beyond conventional antibiotics—New directions for combination products to combat biofilm. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2017, 112, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, C.; Sarkar, P.; Issa, R.; Haldar, J. Alternatives to Conventional Antibiotics in the Era of Antimicrobial Resistance. Trends Microbiol. 2019, 27, 323–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.; Russo, J.; Fiegel, J.; Brogden, N. Antibiotic Delivery Strategies to Treat Skin Infections When Innate Antimicrobial Defense Fails. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amanzadi, B.; Mirzaei, E.; Hassanzadeh, G.; Mahdaviani, P.; Boroumand, S.; Abdollahi, M.; Hosseinabdolghaffari, A.; Majidi, R.F. Chitosan-based layered nanofibers loaded with herbal extract as wound-dressing materials on wound model studies. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2019, 9, 3979–3986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saghazadeh, S.; Rinoldi, C.; Schot, M.; Kashaf, S.S.; Sharifi, F.; Jalilian, E.; Nuutila, K.; Giatsidis, G.; Mostafalu, P.; Derakhshandeh, H.; et al. Drug delivery systems and materials for wound healing applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 127, 138–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelghany, A.M.; Meikhail, M.S.; El-Bana, A.A. Microbial Activity and Swelling Behavior of Chitosan/Polyvinyl Alcohol/Sodium Alginate Semi-Natural Terpolymer Interface Containing Amoxicillin for Wound Dressing Applications. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2019, 9, 4368–4373. [Google Scholar]
- Gokarneshan, N. Application of natural polymers and herbal extracts in wound management. In Advanced Textiles for Wound Care, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 541–561. [Google Scholar]
- Nuutila, K.; Eriksson, E. Moist Wound Healing with Commonly Available Dressings. In Advances in Wound Care; Mary Ann Liebert, Inc.: Larchmont, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel, U.J.S.; Oda, H.; Akerman, J.; Wang, Z.; Chang, J.; Fox, P.M. Topical Antibiotic Elution in a Collagen Rich Hydrogel for Healing of Infected Wounds. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2020, 8, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanikireddy, V.; Varaprasad, K.; Jayaramudu, T.; Karthikeyan, C.; Sadiku, R. Carboxymethyl cellulose-based materials for infection control and wound healing: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 963–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koneru, A.; Dharmalingam, K.; Anandalakshmi, R. Cellulose based nanocomposite hydrogel films consisting of sodium carboxymethylcellulose–grapefruit seed extract nanoparticles for potential wound healing applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 148, 833–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simões, D.; Miguel, S.P.; Ribeiro, M.P.; Coutinho, P.; Mendonça, A.G.; Correia, I.J. Recent advances on antimicrobial wound dressing: A review. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 127, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehler, J.; Brandl, F.P.; Goepferich, A.M. Hydrogel wound dressings for bioactive treatment of acute and chronic wounds. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 100, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, D.I.; Balaban, N.Q.; Baquero, F.; Courvalin, P.; Glaser, P.; Gophna, U.; Kishony, R.; Molin, S.; Tønjum, T. Antibiotic resistance: Turning evolutionary principles into clinical reality. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 44, 171–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, V.W.; Chan, J.M.; Sardon, H.; Ono, R.J.; García, J.M.; Yang, Y.Y.; Hedrick, J.L. Antimicrobial hydrogels: A new weapon in the arsenal against multidrug-resistant infections. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2014, 78, 46–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neacsu, I.-A.; Melente, A.E.; Holban, A.-M.; Ficai, A.; Ditu, L.-M.; Kamerzan, C.-M.; Tihăuan, B.M.; Nicoara, A.I.; Bezirtzoglou, E.; Chifiriuc, M.-C.; et al. Novel hydrogels based on collagen and ZnO nanoparticles with antibacterial activity for improved wound dressings. Rom. Biotechnol. Lett. 2019, 24, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paduraru, A.; Ghitulica, C.; Trusca, R.; Surdu, V.A.; Neacsu, I.A.; Holban, A.M.; Birca, A.C.; Iordache, F.; Vasile, B.S. Antimicrobial Wound Dressings as Potential Materials for Skin Tissue Regeneration. Materials 2019, 12, 1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahid, F.; Zhong, C.; Wang, H.-S.; Hu, X.-H.; Chu, L.-Q. Recent Advances in Antimicrobial Hydrogels Containing Metal Ions and Metals/Metal Oxide Nanoparticles. Polymers 2017, 9, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshmukh, S.; Patil, S.; Mullani, S.; Delekar, S. Silver nanoparticles as an effective disinfectant: A review. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 97, 954–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, G.W.; Abd El-Moez, S.H.; Abdel-Fattah, W.A. Synthesis and characterization of nontoxic silver nano-particles with preferential bactericidal activity. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2019, 9, 4617–4623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoica, A.E.; Chircov, C.; Grumezescu, A.M. Hydrogel Dressings for the Treatment of Burn Wounds: An Up-To-Date Overview. Materials 2020, 13, 2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielińska, A.; Skwarek, E.; Zaleska, A.; Gazda, M.; Hupka, J. Preparation of silver nanoparticles with controlled particle size. Procedia Chem. 2009, 1, 1560–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demchenko, V.; Riabov, S.; Kobylinskyi, S.; Goncharenko, L.; Rybalchenko, N.; Kruk, A.; Moskalenko, O.; Shut, M. Effect of the type of reducing agents of silver ions in interpolyelectrolyte-metal complexes on the structure, morphology and properties of silver-containing nanocomposites. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djokić, S. Synthesis and Antimicrobial Activity of Silver Citrate Complexes. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2008, 2008, 436458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Qiao, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, X.; Ding, S. Mechanisms of PVP in the preparation of silver nanoparticles. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2005, 94, 449–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, N.; Karimi, L.; Mirjalili, M.; Derakhshan, S.J. Effect of Silver Particle size on color and Antibacterial properties of silk and cotton Fabrics. Fibers Polym. 2016, 17, 888–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albu, M.G. Collagen Gels and Matrices for Biomedical Applications; Lambert Academic Publishing: Saarbrücken, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Tsakovska, I.; Pajeva, I.; Al Sharif, M.; Alov, P.; Fioravanzo, E.; Kovarich, S.; Worth, A.P.; Richarz, A.-N.; Yang, C.; Mostrag-Szlichtyng, A.; et al. Quantitative structure-skin permeability relationships. Toxicology 2017, 387, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokubo, T.; Kushitani, H.; Sakka, S.; Kitsugi, T.; Yamamuro, T. Solutions able to reproduce in vivo surface-structure changes in bioactive glass-ceramic A-W3. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1990, 24, 721–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neacsu, I.A.; Serban, A.P.; Nicoara, A.I.; Trusca, R.; Ene, V.L.; Iordache, F. Biomimetic Composite Scaffold Based on Naturally Derived Biomaterials. Polymers 2020, 12, 1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghica, M.V.; Albu, M.G.; Popa, L.; Moisescu, S. Response surface methodology and Taguchi approach to assess the combined effect of formulation factors on minocycline delivery from collagen sponges. Die Pharm. 2013, 68, 340–348. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, C.; Dinda, A.K.; Potdar, P.D.; Chou, C.-F.; Mishra, N.C. Fabrication and characterization of novel nano-biocomposite scaffold of chitosan–gelatin–alginate–hydroxyapatite for bone tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 64, 416–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Datta, S.; Roche, E.; Chaffee, S.; Jose, E.; Shi, L.; Grover, K.; Khanna, S.; Sen, C.K.; Roy, S. Novel mechanisms of Collagenase Santyl Ointment (CSO) in wound macrophage polarization and resolution of wound inflammation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, Ș.; Albu Kaya, M.G.; Ghica, M.V.; Dinu-Pîrvu, C.; Popa, L.; Udeanu, D.I.; Mihai, G.; Enachescu, M. Collagen-Polyvinyl Alcohol-Indomethacin Biohybrid Matrices as Wound Dressings. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, B.; Garmaroudi, F.S.; Hashemi, M.; Nezhad, H.; Nasrollahi, A.; Ardalan, S.; Ardalan, S. Comparison of the anti-bacterial activity on the nanosilver shapes: Nanoparticles, nanorods and nanoplates. Adv. Powder Technol. 2012, 23, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasile, O.R.; Andronescu, E.; Truşcă, R.; Vasile, E.; Holban, A.M.; Chifiriuc, M.C.; Iordache, F.; Maniu, H.; Bleotu, C.; Neacşu, I.A.; et al. Structure-grain size-synthesis route of silver nanoparticles: A correlation with the cytotoxic effect. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2019, 60, 617–628. [Google Scholar]
- Khodashenas, B.; Ghorbani, H.R. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles with different shapes. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 1823–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tak, Y.K.; Pal, S.; Naoghare, P.K.; Rangasamy, S.; Song, J.M. Shape-Dependent Skin Penetration of Silver Nanoparticles: Does It Really Matter? Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amri, M.; Firdaus, M.; Fauzi, M.; Chowdhury, S.; Fadilah, N.; Hamirul, W.W.; Reusmaazran, M.; Aminuddin, B.; Ruszymah, B. Cytotoxic evaluation of biomechanically improved crosslinked ovine collagen on human dermal fibroblasts. Bio-Med. Mater. Eng. 2014, 24, 1715–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhshabi, S.; Biazar, E.; Singh, V.; Keshel, S.H.; Nagaraja, G. The effect of glutaraldehyde cross-linker on structural and biocompatibility properties of collagen-chondroitin sulfate electrospun mat. Mater. Technol. 2018, 33, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drobotă, M.; Grierosu, I.; Radu, I.; Vasilescu, D.S. The Effect of Silver Nanoparticles on the Collagen Secondary Structure. Key Eng. Mater. 2015, 638, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, M.; Donia, D.T.; Sabbatella, G.; Antiochia, R. Silver nanoparticles in polymeric matrices for fresh food packaging. J. King Saud Univ.-Sci. 2016, 28, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negut, I.; Dorcioman, G.; Grumezescu, V. Scaffolds for Wound Healing Applications. Polymers 2020, 12, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Fleury, C.; Jalalvand, F.; Riesbeck, K. Human pathogens utilize host extracellular matrix proteins laminin and collagen for adhesion and invasion of the host. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 36, 1122–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrington, D.J. Bacterial collagenases and collagen-degrading enzymes and their potential role in human disease. Infect. Immun. 1996, 64, 1885–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sood, A.; Granick, M.S.; Tomaselli, N.L. Wound Dressings and Comparative Effectiveness Data. Adv. Wound Care 2014, 3, 511–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keshvadi, M.; Karimi, F.; Valizadeh, S.; Valizadeh, A. Comparative study of antibacterial inhibitory effect of silver nanoparticles and garlic oil nanoemulsion with their combination. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2019, 9, 4560–4566. [Google Scholar]
- Garibo, D.; Borbón-Nuñez, H.A.; De León, J.N.D.; Mendoza, E.G.; Estrada, I.; Toledano-Magaña, Y.; Tiznado, H.; Ovalle-Marroquin, M.; Soto-Ramos, A.G.; Blanco, A.; et al. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Lysiloma acapulcensis exhibit high-antimicrobial activity. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadlilah, D.R.; Endarko, E.; Ratnasari, A.; Hozairi, H.; Yusop, Z.; Syafiuddin, A. Enhancement of antibacterial properties of various polymers functionalized with silver nanoparticles. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2019, 10, 5592–5598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, P.; Ghosh, S. Green Approach to the Synthesis of Poly(Vinyl Alcohol)-Silver Nanoparticles Hybrid Using Rice Husk Extract and Study of its Antibacterial Activity. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2020, 10, 6474–6480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunell, M.; Haapanen, J.; Brobbey, K.J.; Saarinen, J.J.; Toivakka, M.; Mäkelä, J.M.; Huovinen, P.; Eerola, E. Antimicrobial characterization of silver nanoparticle-coated surfaces by “touch test” method. Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 2017, 10, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, I.X.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, I.S.; Mei, M.L.; Li, Q.; Chu, C.H. The Antibacterial Mechanism of Silver Nanoparticles and Its Application in Dentistry. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 2555–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elgorban, A.M.; El-Samawaty, A.E.-R.M.; Yassin, M.A.; Sayed, S.R.; Adil, S.F.; Elhindi, K.M.; Bakri, M.; Khan, M. Antifungal silver nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization and biological evaluation. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2016, 30, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussin, J.E.; Roldán, M.V.; Rojas, F.; Sosa, M.D.L. Ángeles; Pellegri, N.; Giusiano, G. Antifungal activity of silver nanoparticles in combination with ketoconazole against Malassezia furfur. AMB Express 2019, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.S.; Kim, D.W.; Oh, J.H.; Yoon, S.; Choi, M.S.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, J.W.; Lee, K.; Song, C.-W. Silver nanoparticles induce apoptosis and G2/M arrest via PKCζ-dependent signaling in A549 lung cells. Arch. Toxicol. 2011, 85, 1529–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asharani, P.V.; Mun, G.L.K.; Hande, M.P.; Valiyaveettil, S. Cytotoxicity and Genotoxicity of Silver Nanoparticles in Human Cells. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

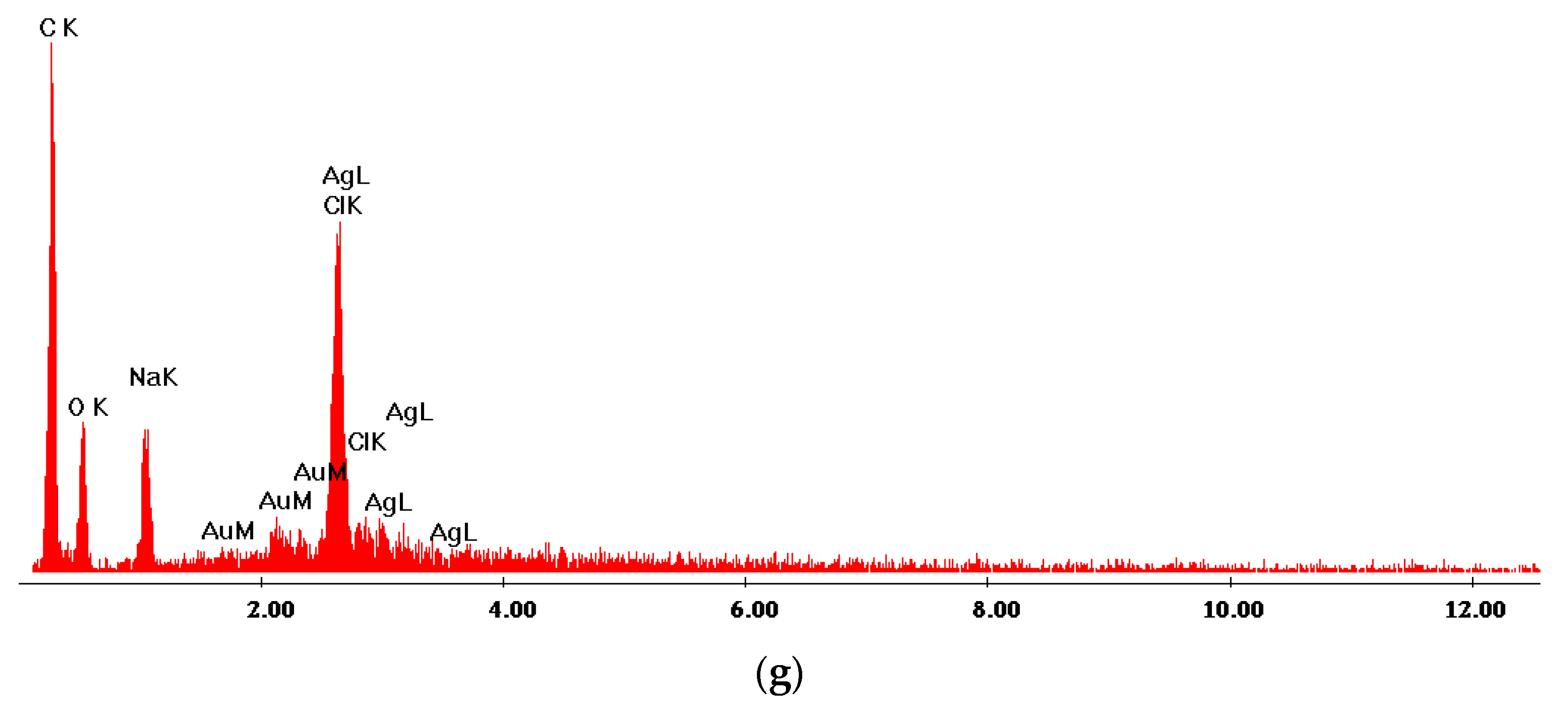
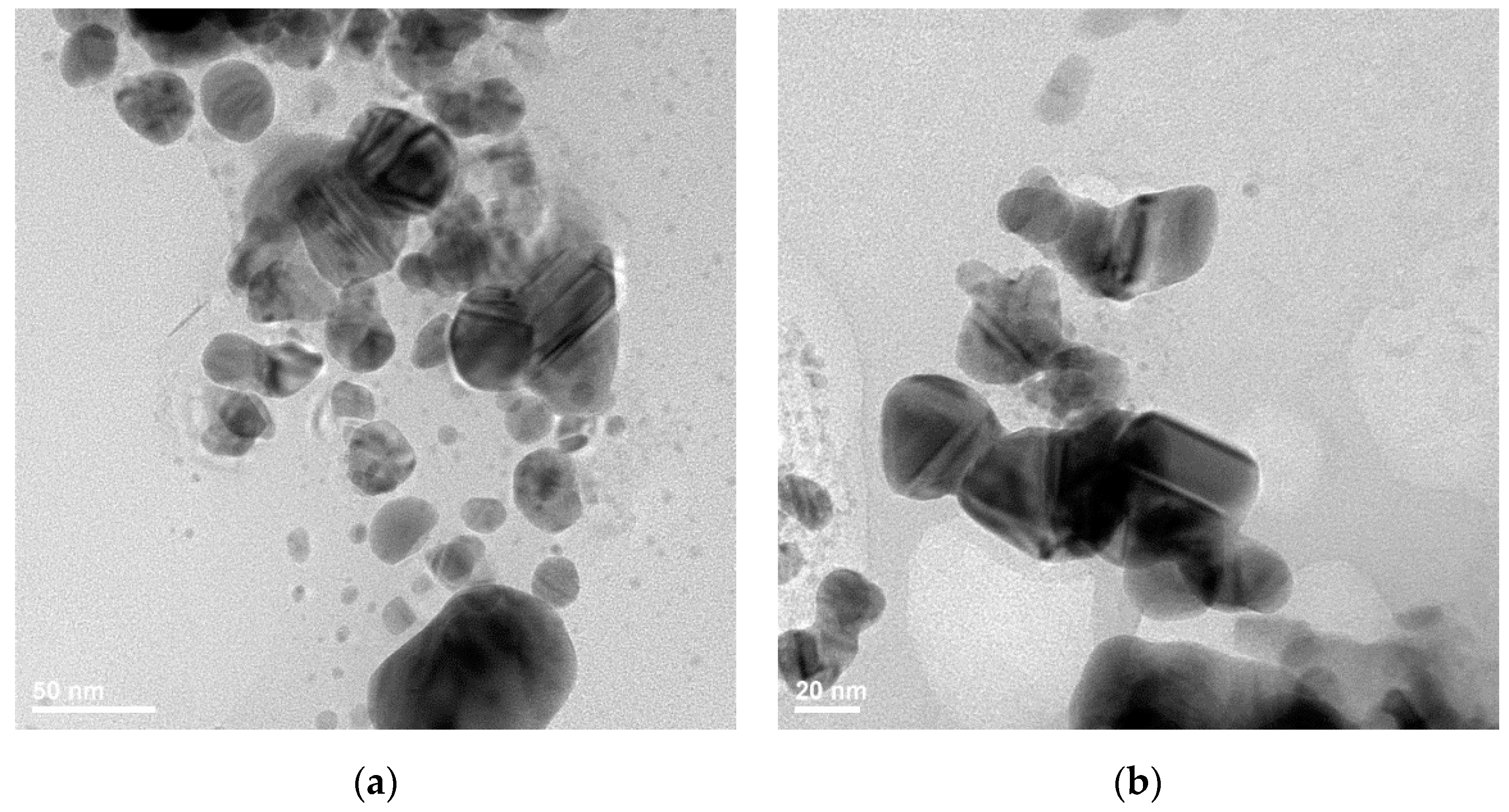
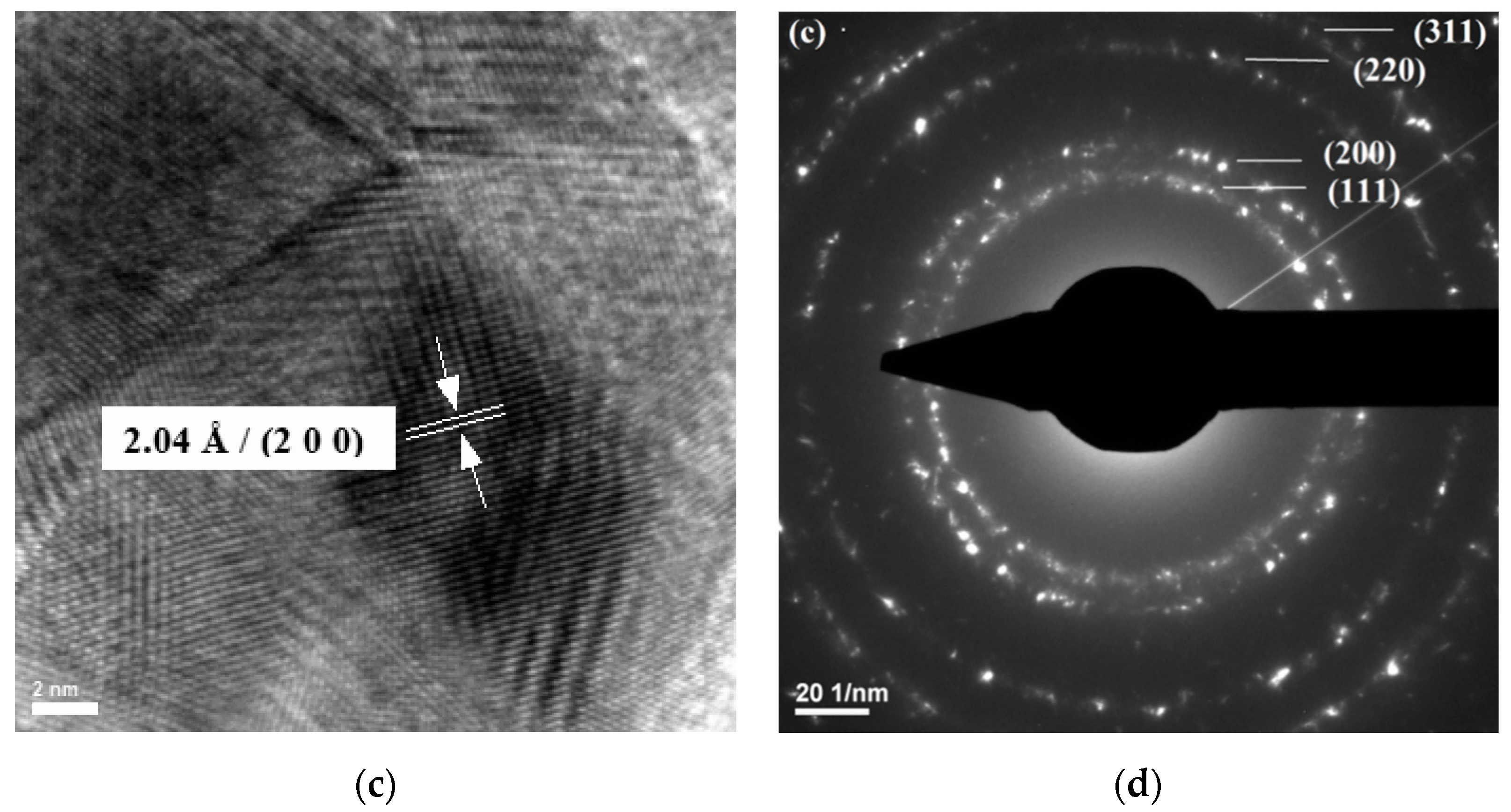
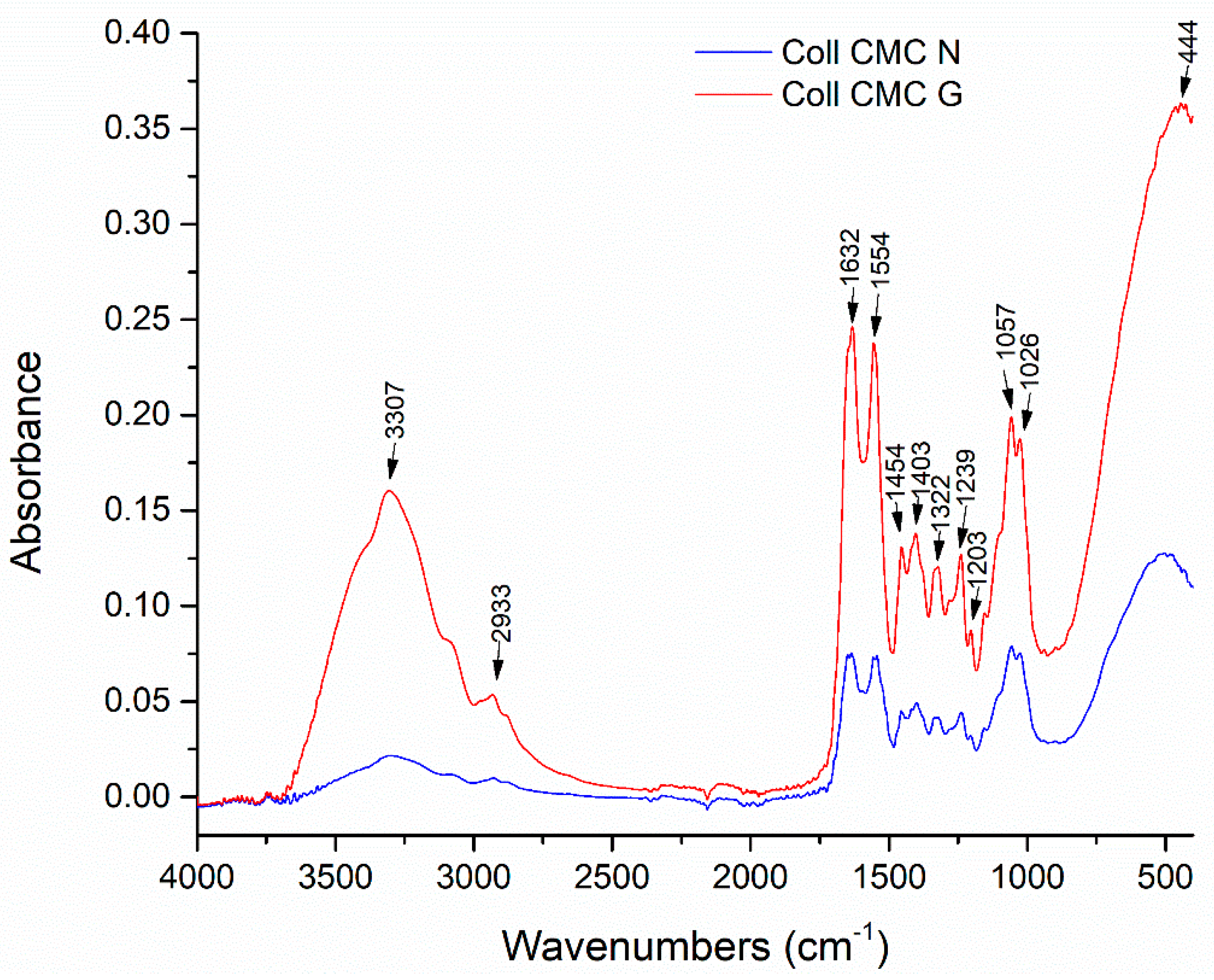




| Sample Name | 100 ppm Colloidal AgNPs Solution (mL) | Calculated AgNPs Concentration in the Dried Sample (w/w %) | Glutaraldehyde 0.025% (mL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coll CMC Ag 20 G | 20 | 0.02 | 5 |
| Coll CMC Ag 10 G | 10 | 0.01 | 5 |
| Coll CMC G | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| Coll CMC Ag 20 N | 20 | 0.02 | 0 |
| Coll CMC Ag 10 N | 10 | 0.01 | 0 |
| Coll CMC N | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Ionic Species Concentrations (mmol/L) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBF Solution | Na+ | K+ | Mg2+ | Ca2+ | Cl− | HCO3− | HPO42− | SO42− | Buffer Solution | pH |
| 142.0 | 5.0 | 1.5 | 2.5 | 147.8 | 4.2 | 1.0 | 0.5 | 7.25 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Neacsu, I.A.; Leau, S.-A.; Marin, S.; Holban, A.M.; Vasile, B.-S.; Nicoara, A.-I.; Ene, V.L.; Bleotu, C.; Albu Kaya, M.G.; Ficai, A. Collagen-Carboxymethylcellulose Biocomposite Wound-Dressings with Antimicrobial Activity. Materials 2021, 14, 1153. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14051153
Neacsu IA, Leau S-A, Marin S, Holban AM, Vasile B-S, Nicoara A-I, Ene VL, Bleotu C, Albu Kaya MG, Ficai A. Collagen-Carboxymethylcellulose Biocomposite Wound-Dressings with Antimicrobial Activity. Materials. 2021; 14(5):1153. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14051153
Chicago/Turabian StyleNeacsu, Ionela Andreea, Sorina-Alexandra Leau, Stefania Marin, Alina Maria Holban, Bogdan-Stefan Vasile, Adrian-Ionut Nicoara, Vladimir Lucian Ene, Coralia Bleotu, Mădălina Georgiana Albu Kaya, and Anton Ficai. 2021. "Collagen-Carboxymethylcellulose Biocomposite Wound-Dressings with Antimicrobial Activity" Materials 14, no. 5: 1153. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14051153
APA StyleNeacsu, I. A., Leau, S.-A., Marin, S., Holban, A. M., Vasile, B.-S., Nicoara, A.-I., Ene, V. L., Bleotu, C., Albu Kaya, M. G., & Ficai, A. (2021). Collagen-Carboxymethylcellulose Biocomposite Wound-Dressings with Antimicrobial Activity. Materials, 14(5), 1153. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14051153













