Use of Cement Suspension as an Alternative Matrix Material for Textile-Reinforced Concrete
Abstract
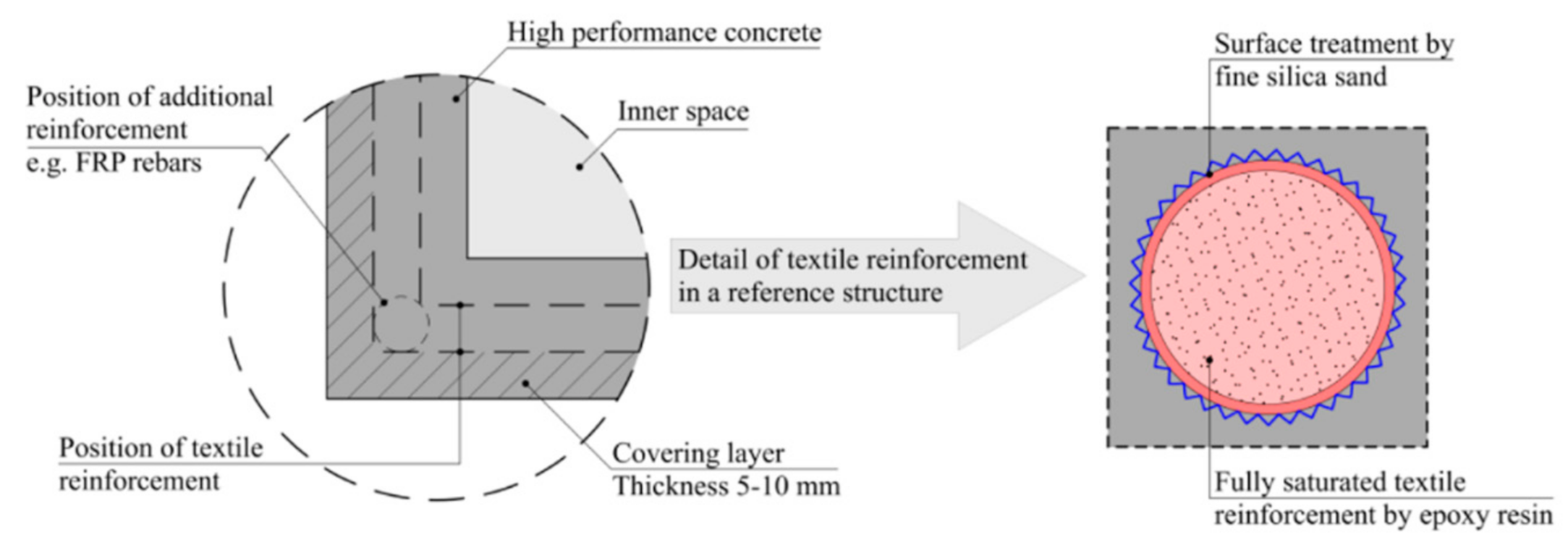
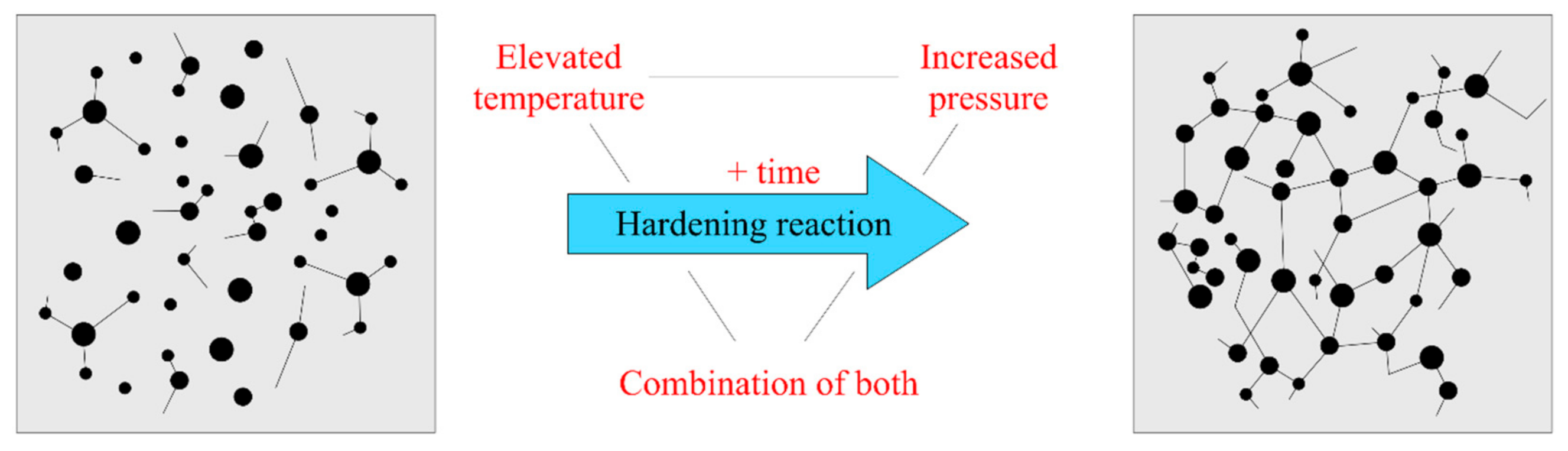
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. High-Performance Concrete Mixture
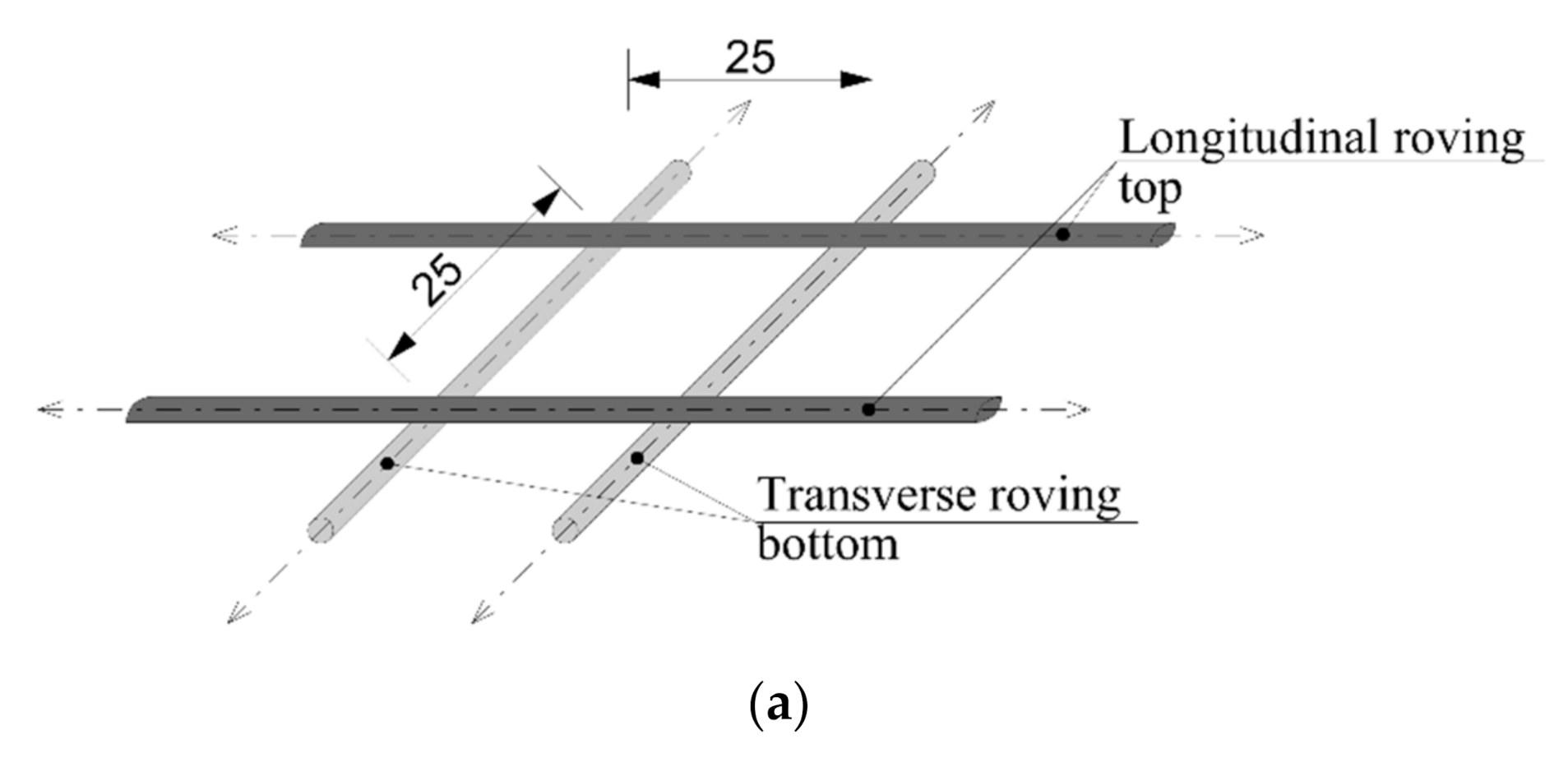
2.2. Textile Tensile Reinforcement
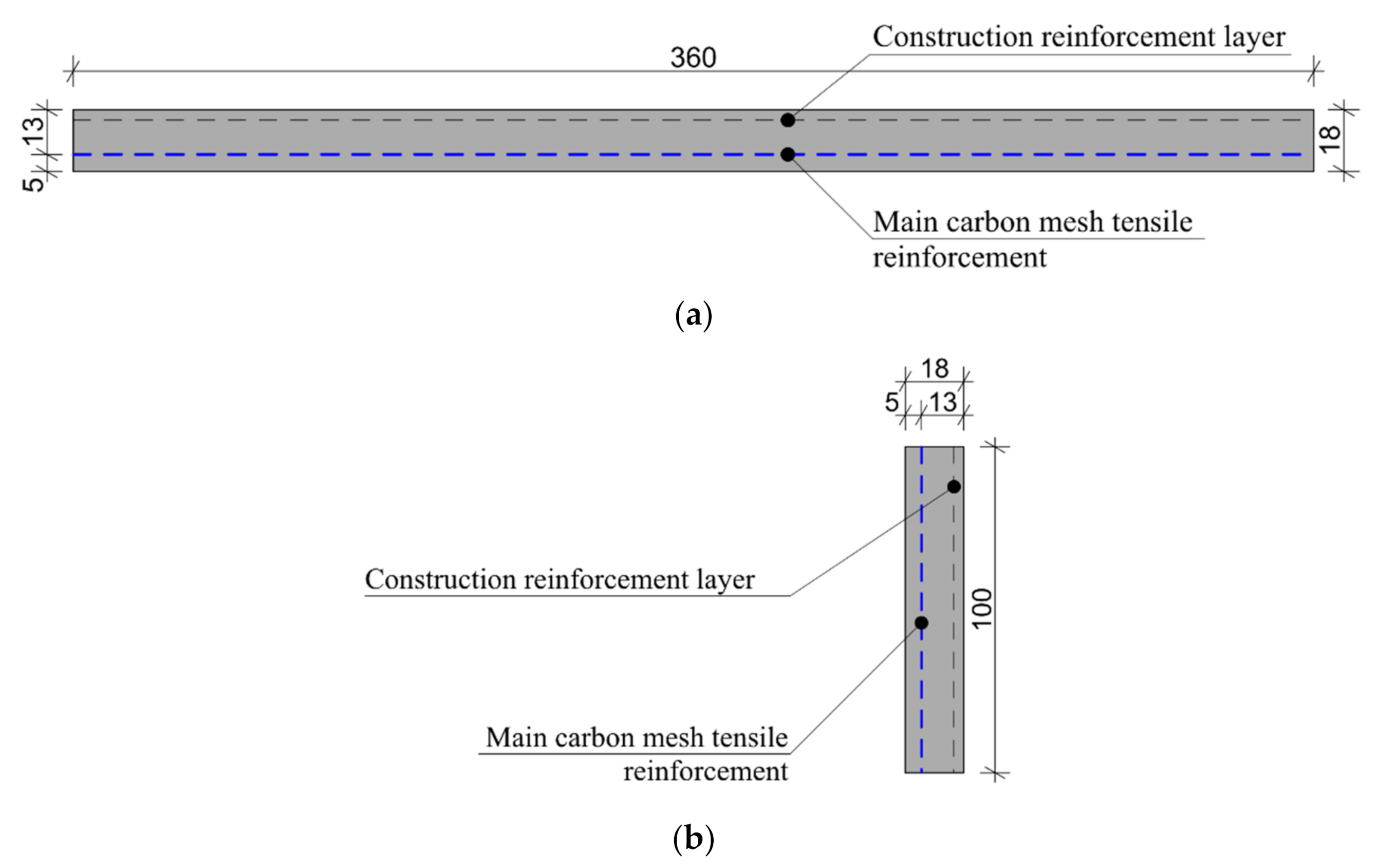
2.3. Geometry of Experimental Samples
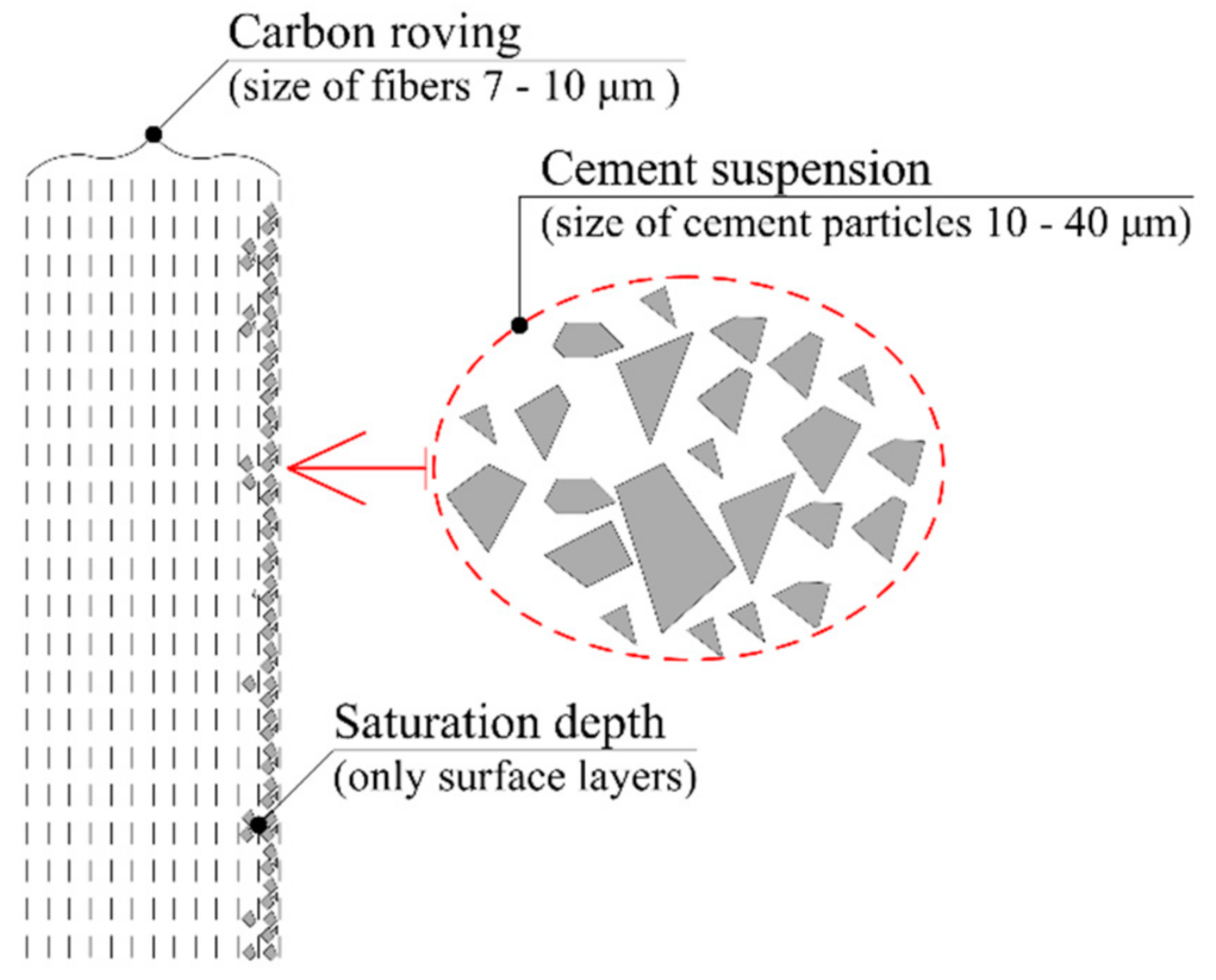
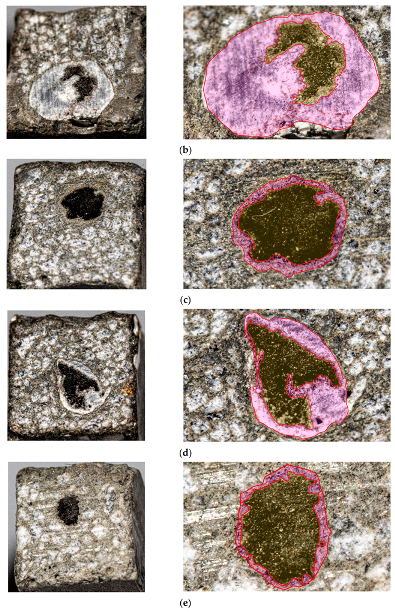
2.4. Microscopy
2.5. Preparations of Experimental Samples
2.6. Statistical Data Analysis
3. Results
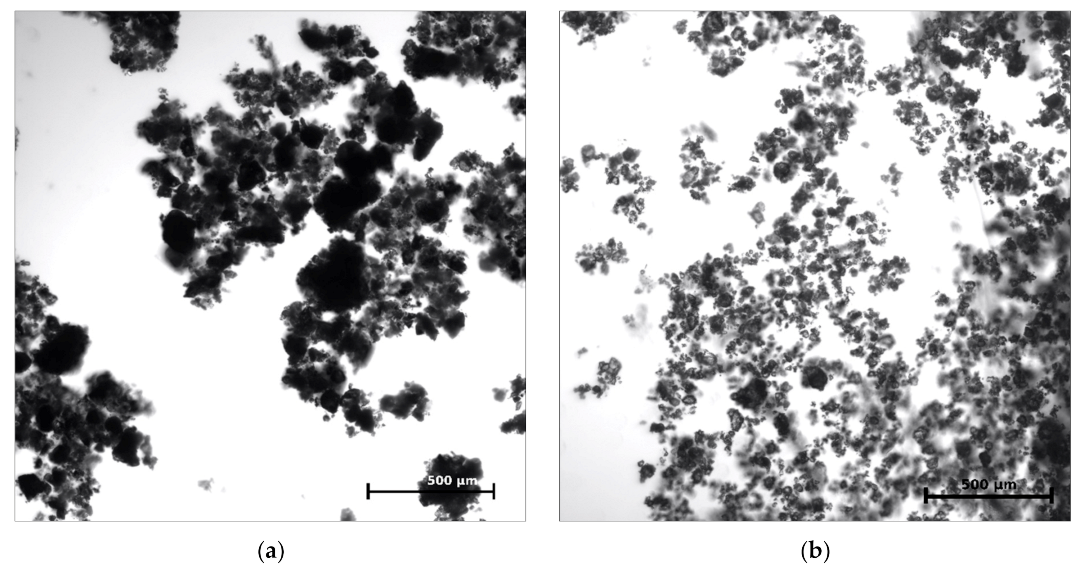
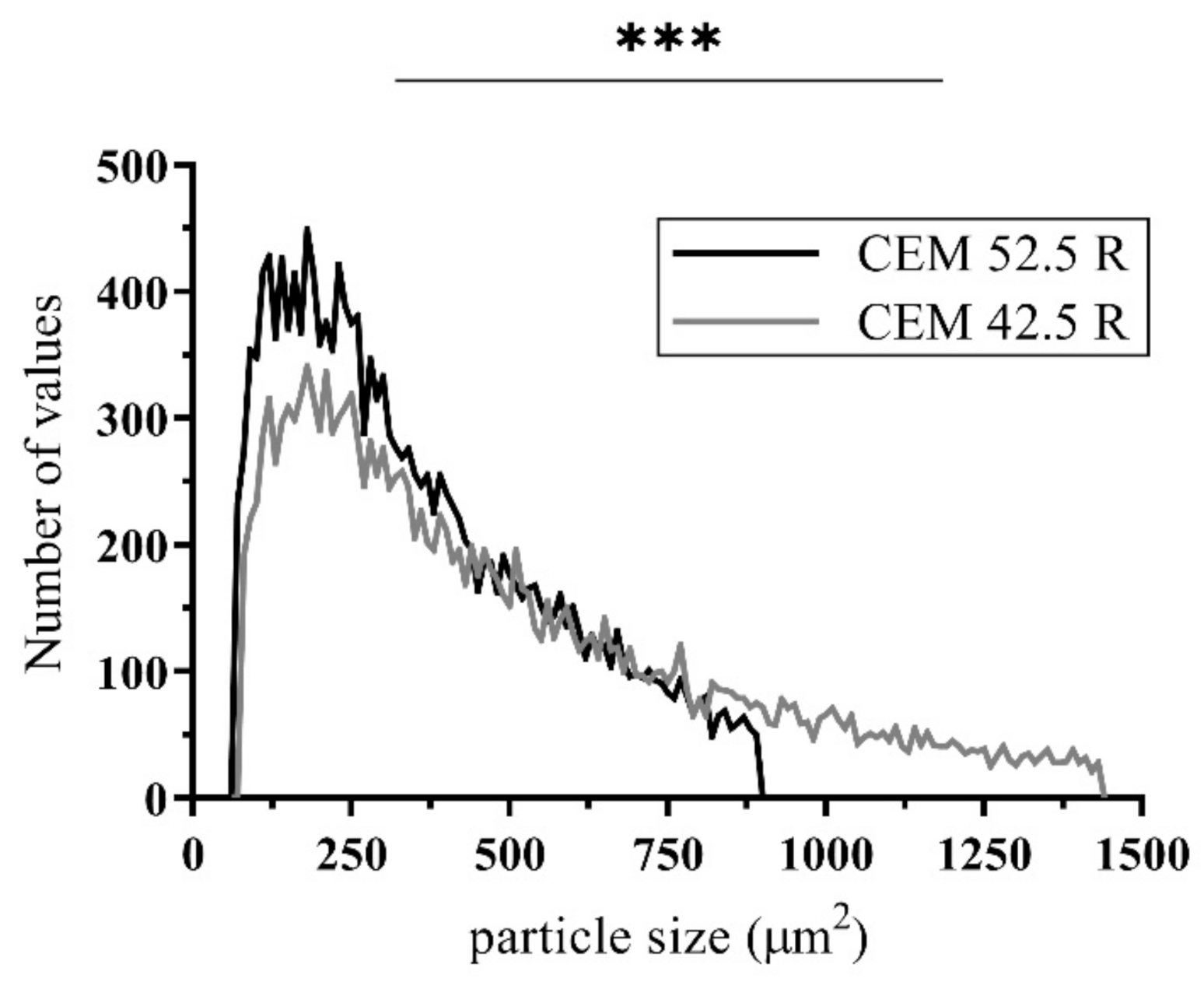
3.1. Particle Size Distribution in Cement Suspension
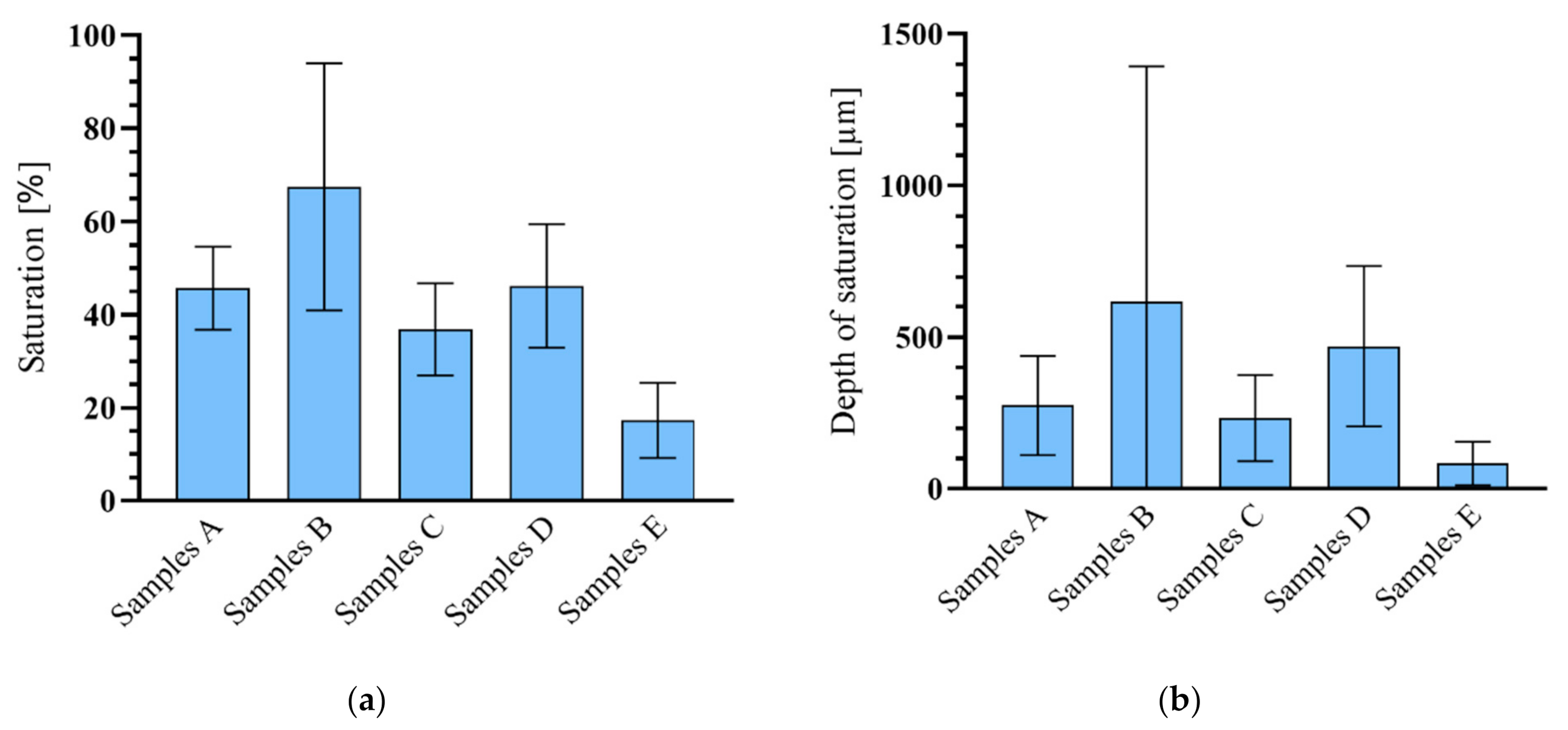
3.2. Saturation Depth of Beam Samples
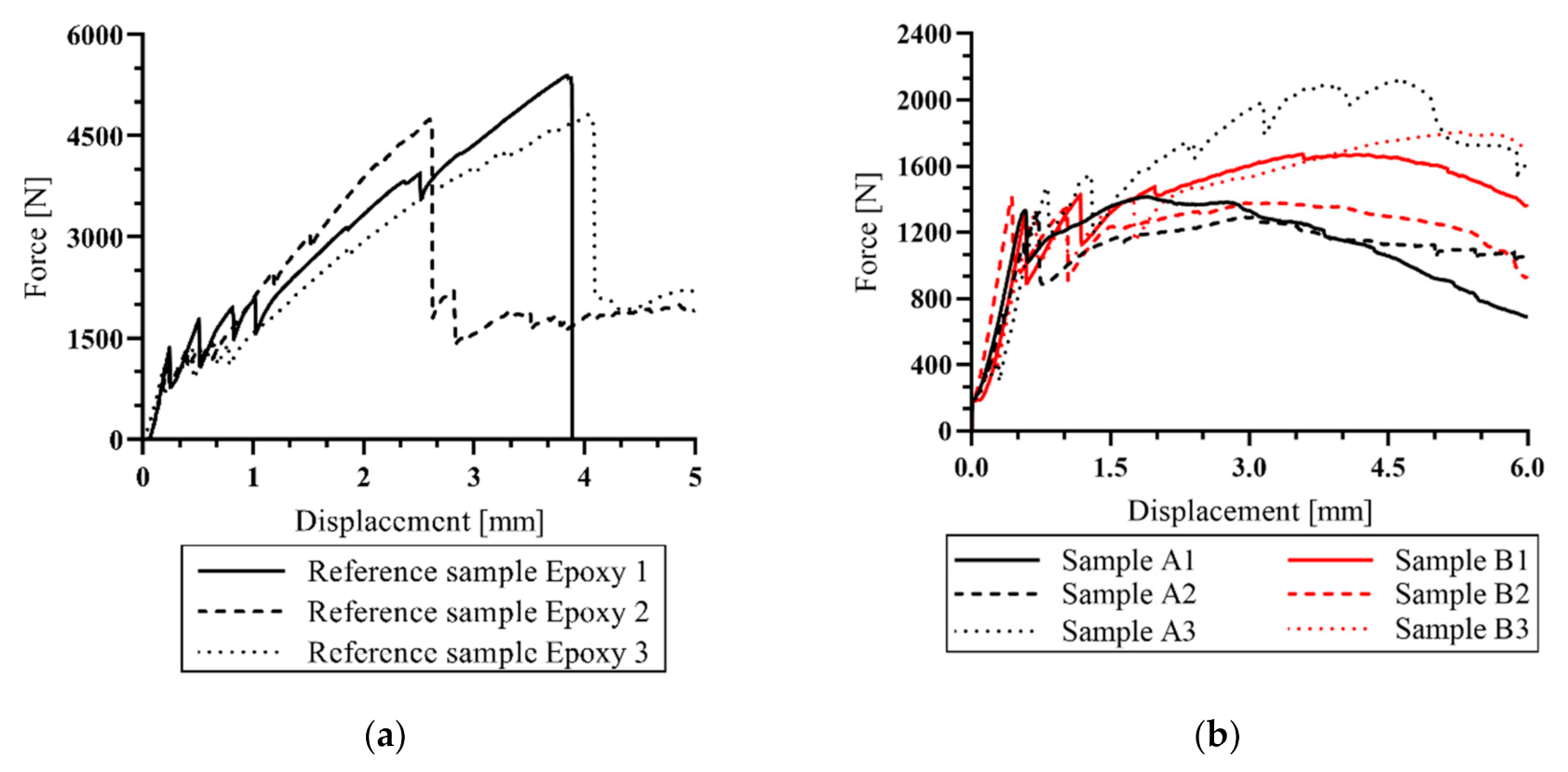
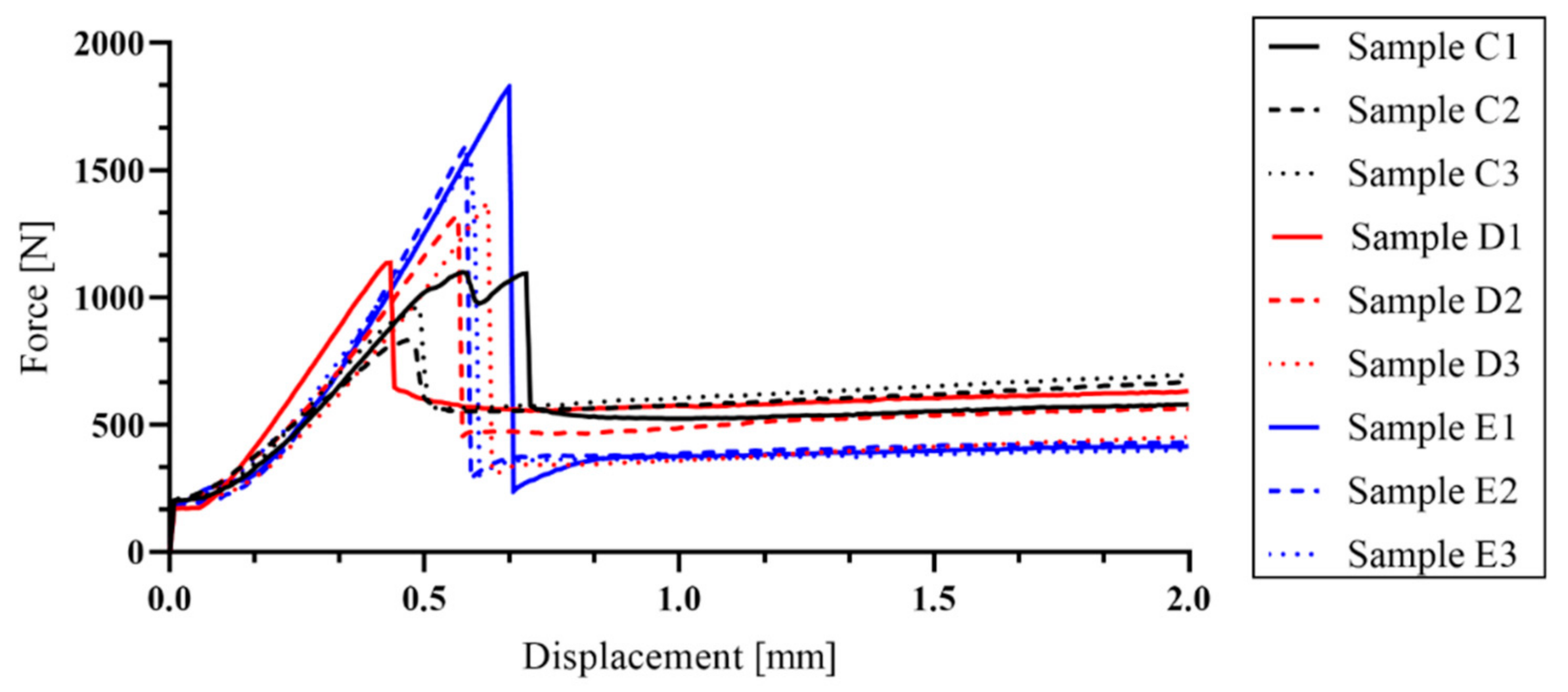
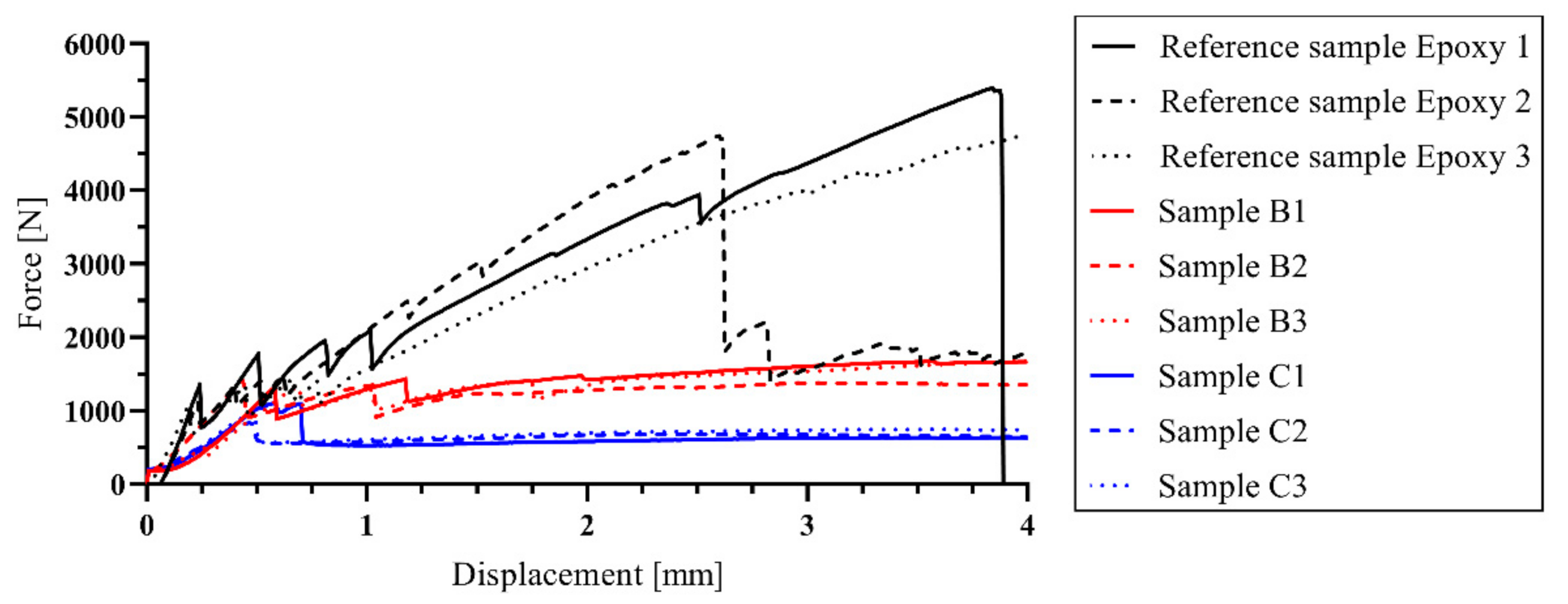
3.3. Four-Point Bending Tests
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tailor Made Concrete Structures: New Solutions for Our Society. In Proceedings of the International FIB Symposium, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 19–21 May 2008.
- Hegger, J.; Schneider, H.; Sherif, A.; Molter, M.; Voss, N. Exterior Cladding Panels as An Application of Textile Reinforced Concrete. ACI Symp. Publ. 2004, 224, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chira, A.; Kumar, A.; Vlach, T.; Laiblová, L.; Hájek, P. Textile-reinforced concrete facade panels with rigid foam core prisms. J. Sandw. Struct. Mater. 2016, 18, 200–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laiblová, L.; Pešta, P.; Kumar, A.; Hájek, P.; Fiala, C.; Vlach, T.; Kočí, V. Environmental Impact of Textile Reinforced Concrete Facades Compared to Conventional Solutions—LCA Case Study. Materials 2019, 12, 3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Řepka, J.; Vlach, T.; Laiblová, L.; Hájek, P.; Ženíšek, M.; Kokeš, P. Thin Lightweight Panels Made of Textile Reinforced Concrete. Solid State Phenom. 2017, 259, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peled, A.; Bentur, A.; Mobasher, B. Textile Reinforced Concrete; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019; ISBN 978-1-351-64546-1. [Google Scholar]
- Hegger, J.; Will, N.; Bruckermann, O.; Voss, S. Load-bearing behaviour and simulation of textile reinforced concrete. Mater. Struct. 2006, 39, 765–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fürst, R.; Pokorný, M.; Vlach, T.; Mózer, V. Study of behavior of textile-reinforced concrete with epoxy resin matrix in fire. Fire Technol. in press.
- Kapsalis, P.; El Kadi, M.; Vervloet, J.; De Munck, M.; Wastiels, J.; Triantafillou, T.; Tysmans, T. Thermomechanical Behavior of Textile Reinforced Cementitious Composites Subjected to Fire. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ducháček, V. Polymery: Výroba, Vlastnosti, Zpracování, Použití, 2nd ed.; VŠCHT: Praha, Czech Republic, 2006; ISBN 80-7080-617-6. [Google Scholar]
- Fidelus, J.D.; Wiesel, E.; Gojny, F.H.; Schulte, K.; Wagner, H.D. Thermo-mechanical properties of randomly oriented carbon/epoxy nanocomposites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2005, 36, 1555–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Andrade Silva, F.; Butler, M.; Hempel, S.; Toledo Filho, R.D.; Mechtcherine, V. Effects of elevated temperatures on the interface properties of carbon textile-reinforced concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2014, 48, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foreman, J.P.; Porter, D.; Behzadi, S.; Curtis, P.T.; Jones, F.R. Predicting the thermomechanical properties of an epoxy resin blend as a function of temperature and strain rate. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2010, 41, 1072–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brameshuber, W. Textile reinforced concrete-state-of-the-art report of RILEM TC 201-TRC. In Reunion Internationale des Laboratoires et Experts des Materiaux, Systemes de Construction et Ouvrages (RILEM); RILEM Publications SARL: Paris, France, 2006; ISBN 2-912143-99-3. [Google Scholar]
- Moravec, R. Technical Sheet: Epoxy Resin Resistant up to 160 °C LH 300. Havel Composites CZ s.r.o. Available online: https://www.havel-composites.com/uploads/files/products/659/8526af61ad9b157d63f68fcf16cebd65058e3b88.pdf (accessed on 22 November 2020).
- Nguyen, J.; Migonney, V.; Ruse, N.D.; Sadoun, M. Resin composite blocks via high-pressure high-temperature polymerization. Dent. Mater. 2012, 28, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GRENA, A.S. Technical Sheet: Požární Ochrana Uhlíkovo-Vláknitých CFRP Lamel Deskami Grenamat® AL. Available online: https://www.grena.cz/res/dwe-files/1404056575.pdf (accessed on 26 October 2020).
- Soupionis, G.; Georgiou, P.; Zoumpoulakis, L. Polymer Composite Materials Fiber-Reinforced for the Reinforcement/Repair of Concrete Structures. Polymers 2020, 12, 2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huseien, G.F.; Sam, A.R.M.; Faridmehr, I.; Baghban, M.H. Performance of Epoxy Resin Polymer as Self-Healing Cementitious Materials Agent in Mortar. Materials 2021, 14, 1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anagnostopoulos, C.A.; Dimitriadi, M. Study on High Performance Polymer-Modified Cement Grouts. Civil. Eng. 2021, 2, 134–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapsalis, P.; Tysmans, T.; Verbruggen, S.; Triantafillou, T. Preliminary High-Temperature Tests of Textile Reinforced Concrete (TRC). Proceedings 2018, 2, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Micelli, F.; Aiello, M.A. Residual tensile strength of dry and impregnated reinforcement fibres after exposure to alkaline environments. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouritz, A.P.; Mathys, Z.; Gibson, A.G. Heat release of polymer composites in fire. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2006, 37, 1040–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Signorini, C.; Nobili, A.; Cedillo González, E.I.; Siligardi, C. Silica coating for interphase bond enhancement of carbon and AR-glass Textile Reinforced Mortar (TRM). Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 141, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bompadre, F.; Donnini, J. Surface Modification of Glass Textile for the Reinforcement of a Cement-Based Composite: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Xiao, H.; Liu, M.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Sun, L. Improved interfacial strength of SiO2 coated carbon fiber in cement matrix. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2018, 91, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadiv, R.; Peled, A.; Mechtcherine, V.; Hempel, S.; Schroefl, C. Micro- and nanoparticle mineral coating for enhanced properties of carbon multifilament yarn cement-based composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2017, 111, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Maida, P.; Radi, E.; Sciancalepore, C.; Bondioli, F. Pullout behavior of polypropylene macro-synthetic fibers treated with nano-silica. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 82, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schneider, K.; Michel, A.; Liebscher, M.; Terreri, L.; Hempel, S.; Mechtcherine, V. Mineral-impregnated carbon fibre reinforcement for high temperature resistance of thin-walled concrete structures. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2019, 97, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, Z.; Peled, A. Effect of nanofillers and production methods to control the interfacial characteristics of glass bundles in textile fabric cement-based composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2012, 43, 962–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teijin®. Technical Sheet: Carbon Roving Tenax STS40 F13 24K 1600tex. Available online: https://shop1.r-g.de/en/art/205105STS (accessed on 8 November 2020).
- Lu, Z.C.; Haist, M.; Ivanov, D.; Jakob, C.; Jansen, D.; Leinitz, S.; Link, J.; Mechtcherine, V.; Neubauer, J.; Plank, J. Characterization Data of Reference Cement CEM I 42.5 R Used for Priority Program DFG SPP 2005 “Opus Fluidum Futurum—Rheology of Reactive, Multiscale, Multiphase Construction Materials”. Data Brief 2019, 27, 104699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentz, D.P.; Garboczi, E.J.; Haecker, C.J.; Jensen, O.M. Effects of cement particle size distribution on performance properties of Portland cement-based materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 1999, 29, 1663–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambo, D.A.S.; Silva, F.A.; Filho, R.D.T.; Gomes, O.F.M. Effect of Elevated Temperatures on the Mechanical Behavior of Basalt Textile Reinforced Refractory Concrete. Mater. Des. 2015, 65, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.H.; Vu, X.H.; Si Larbi, A.; Ferrier, E. Experimental Study of the Effect of Simultaneous Mechanical and High-Temperature Loadings on the Behaviour of Textile-Reinforced Concrete (TRC). Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 125, 253–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ČSN EN 12390-3, Testing Hardened Concrete-Part 3: Compressive Strength of Test Specimens; Czech Office for Standards, Metrology and Testing: Prague, Czech Republic, 2020.
- ČSN EN 12390-5, Testing Hardened Concrete-Part 5: Flexural Strength of Test Specimens; Czech Office for Standards, Metrology and Testing: Prague, Czech Republic, 2020.
- ČSN EN 12390-1, Testing Hardened Concrete-Part 1: Shape, Dimensions and Other Requirements for Specimens and Moulds; Czech Office for Standards, Metrology and Testing: Prague, Czech Republic, 2013.
- Vlach, T.; Laiblová, L.; Ženíšek, M.; Chira, A.; Kumar, A.; Hájek, P. The effect of surface treatments of textile reinforcement on mechanical parameters of HPC facade elements. Key Engineering Materials 2016, 677, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlach, T.; Laiblová, L.; Ženíšek, M.; Řepka, J.; Hájek, P. Soft insert for support modeling of slightly textile reinforced concrete. Key Eng. Mater. 2018, 760, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soranakom, C.; Mobasher, B. Geometrical and Mechanical Aspects of Fabric Bonding and Pullout in Cement Composites. Mater. Struct. 2006, 42, 765–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lura, P. Autogenous Deformation and Internal Curing of Concrete; Delft University Press: Delft, The Netherlands, 2003; ISBN 978-90-407-2404-6. [Google Scholar]
- Kuzielová, E.; Pach, L.; Palou, M. Evolution of lightweight foam concretes by water procedure. Ceram. Silikáty 2015, 59, 10–16. [Google Scholar]
- Vlach, T.; Řepka, J.; Hájek, J.; Fürst, R.; Jirkalová, Z.; Hajek, P. Cohesion test of a single impregnated ar-glass roving in high-performance concrete. Stavební Obz. Civ. Eng. J. 2020, 29, 358–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidi, M.; Gabor, A. Experimental analysis and analytical modelling of the textile/matrix interface shear stress in textile reinforced cementitious matrix composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2020, 135, 105961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegger, J.; Voss, S. Investigations on the bearing behaviour and application potential of textile reinforced concrete. Eng. Struct. 2008, 30, 2050–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Mixture Components | Quantity |
|---|---|
| kg∙m−3 | |
| CEM I 42.5 R | 680 |
| Silica sand | 960 |
| Silica flour (ground quartz) | 325 |
| Silica fume (microsilica) | 175 |
| Superplasticizer | 29 |
| Water | 171 |
| Total | 2420 |
| Material Properties | Value | Units |
|---|---|---|
| Sizing properties | F13 | - |
| Number of filaments | 24 000 | - |
| Nominal linear density | 1600 | tex |
| Filament diameter | 7.0 | µm |
| Density | 1.77 | g·cm−3 |
| Tensile properties | ||
| Tensile strength | 4000.0 | MPa |
| Modulus of elasticity | 240.0 | GPa |
| Description of Samples | Type of Saturation |
|---|---|
| A | Experimental samples saturated with CEM 42.5 R–pressure saturation. |
| B | Experimental samples saturated with CEM 52.5 R–pressure saturation. |
| C | Experimental samples saturated with CEM 42.5 R–surface saturation by a roller. |
| D | Experimental samples saturated with CEM 52.5 R–surface saturation by a roller. |
| E | Experimental samples without any saturation. |
| - | Reference samples with epoxy resin matrix–surface saturation by a roller. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fürst, R.; Fürst, E.; Vlach, T.; Řepka, J.; Pokorný, M.; Mózer, V. Use of Cement Suspension as an Alternative Matrix Material for Textile-Reinforced Concrete. Materials 2021, 14, 2127. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14092127
Fürst R, Fürst E, Vlach T, Řepka J, Pokorný M, Mózer V. Use of Cement Suspension as an Alternative Matrix Material for Textile-Reinforced Concrete. Materials. 2021; 14(9):2127. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14092127
Chicago/Turabian StyleFürst, Richard, Eliška Fürst, Tomáš Vlach, Jakub Řepka, Marek Pokorný, and Vladimír Mózer. 2021. "Use of Cement Suspension as an Alternative Matrix Material for Textile-Reinforced Concrete" Materials 14, no. 9: 2127. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14092127
APA StyleFürst, R., Fürst, E., Vlach, T., Řepka, J., Pokorný, M., & Mózer, V. (2021). Use of Cement Suspension as an Alternative Matrix Material for Textile-Reinforced Concrete. Materials, 14(9), 2127. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14092127






