Effect of 3-Mercaptopropyltriethoxysilane Modified Illite on the Reinforcement of SBR
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Modification of Illite
2.3. Preparation of Illite-SBR and K-Illite-SBR Masterbatches
2.4. Preparation of SBR Composites
2.5. Characterization
2.5.1. Particle Size Distribution and Specific Surface Area
2.5.2. FTIR
2.5.3. Mechanical Properties
2.5.4. Crosslinking Density
2.5.5. DSC
2.5.6. Payne Effect
2.5.7. Vulcanization Characteristics
2.5.8. Morphology Observation and Elemental Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Illite Particle Size and Specific Surface Area
3.2. Reinforcement of SBR by Illite or K-Illite with Different Particle Sizes
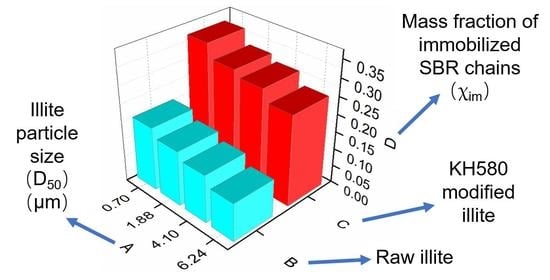
3.3. Dynamics of the Rubber Chain Segments during the Glass Transition
3.4. Payne Effect
3.5. Morphology of Illite/SBR and K-Illite/SBR Vulcanizates
3.6. Dynamic Rheological Properties during Curing Process
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aboubakr, S.H.; Kandil, U.F.; Taha, M.R. Creep of epoxy–clay nanocomposite adhesive at the FRP interface: A multi-scale investigation. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2014, 54, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhao, Y.; Bai, H.; Ai, Z.; Chen, P.; Hu, Y.; Song, S.; Komarneni, S. Role of montmorillonite, kaolinite, or illite in pyrite flotation: Differences in clay behavior based on their structures. Langmuir 2020, 36, 10860–10867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalifa, A.Z.; Cizer, Ö.; Pontikes, Y.; Heath, A.; Patureau, P.; Bernal, S.A.; Marsh, A.T.M. Advances in alkali-activation of clay minerals. Cem. Concr. Res. 2020, 132, 106050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Wang, S.; Sun, W.; Sun, Z.; Zheng, S. Oxygen functionalized carbon nanocomposite derived from natural illite as adsorbent for removal of cationic and anionic dyes. Adv. Powder Technol. 2017, 28, 1943–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Fukumori, T.; Guo, B.; Osseo-Asare, K.; Hirajima, T.; Sasaki, K. Effects of grinding montmorillonite and illite on their modification by dioctadecyl dimethyl ammonium chloride and adsorption of perchlorate. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 146, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, P.-H.; Li, Z.; Jean, J.-S.; Jiang, W.-T.; Wang, C.-J.; Lin, K.-H. Adsorption of tetracycline on 2:1 layered non-swelling clay mineral illite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2012, 67–68, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozola, R.; Krauklis, A.; Burlakovs, J.; Vincevica-Gaile, Z.; Rudovica, V.; Boginska, A.T.; Borovikova, D.; Bhatnagar, A.; Vircava, I.; Klavins, M. Illite clay modified with hydroxyapatite—Innovative perspectives for soil remediation from lead(II). Int. J. Agric. Environ. Res. 2017, 3, 177–189. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, S.; Kim, Y.; Roh, Y. Cesium removal using acid- and base-activated biotite and illite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 401, 123319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Wang, S.; Sun, W.; Sun, Z.; Zheng, S. Synthesis of a novel illite@carbon nanocomposite adsorbent for removal of Cr (VI) from wastewater. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 57, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudette, H.E.; Eades, J.L.; Grim, R.E. The nature of illite. Clay Clay Miner. 1964, 13, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uno, H.; Tamura, K.; Yamada, H.; Umeyama, K.; Hatta, T.; Moriyoshi, Y. Preparation and mechanical properties of exfoliated mica–polyamide 6 nanocomposites using sericite mica. Appl. Clay Sci. 2009, 46, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Yokoyama, S.; Pascua, C.S.; Yamada, H. New age of polymer nanocomposites containing dispersed high-aspect-ratio silicate nanolayers. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 2242–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raji, M.; Essabir, H.; Essassi, E.M.; Rodrigoe, D.; Bouhfid, R.; Qaiss, A.E.K. Morphological, thermal, mechanical, and rheological properties of high density polyethylene reinforced with illite clay. Polym. Compos. 2018, 39, 1522–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nekhlaoui, S.; Abdelaoui, H.; Raji, M.; Essabir, H.; Rodrigue, D.; Bensalah, M.O.; Bouhfid, R.; Qaiss, A.e.K. Assessment of thermo-mechanical, dye discoloration, and hygroscopic behavior of hybrid composites based on polypropylene/clay (illite)/TiO2. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 113, 2615–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Jeong, E.; Lee, Y.-S. Direct fluorination as a novel organophilic modification method for the preparation of illite/polypropylene nanocomposites. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 1046–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Yu, Z.; Chen, B.; Zheng, J. Preparation and mechanical properties of composites based on rigid polyvinyl chloride filled with organic modified illite powder. J. Macromol. Sci. B 2015, 54, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.; Sun, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Yan, S. The influence of illite on the crystallization and properties of isotactic polypropylene. Polym. Crystal. 2019, 2, e10051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, R.; Chi, Q.; Wang, X.; Yang, K.; Jiang, Y.; Li, F.; Xue, B. Crystallinity, ion conductivity, and thermal and mechanical properties of poly(ethylene oxide)–illite nanocomposites with exfoliated illite as a filler. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133, 44226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dannenberg, E.M. Filler choices in the rubber industry. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1982, 55, 860–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera, C.S.; Cornish, K. Processing and mechanical properties of natural rubber/waste-derived nano filler composites compared to macro and micro filler composites. Ind. Crops Prod. 2017, 107, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, P. Characterization of kaolinite/styrene butadiene rubber composite: Mechanical properties and thermal stability. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 124–125, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, K.; Liu, L.; Ji, L.; Liu, Q. Vulcanization, interfacial interaction, and dynamic mechanical properties of in-situ organic amino modified kaolinite/SBR nanocomposites based on latex compounding method. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 185, 105366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwis, C.M.C.; Kottegoda, N.; Ratnayake, U.K. Facile exfoliation method for improving interfacial compatibility in montmorillonite-natural rubber nanocomposites: A novel charge inversion approach. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 191, 105633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.L.; Zhao, L.F.; Huang, Y.D.; Liu, L. Effect of silane coupling agent on the mechanical properties of nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR)/organophilic montmorillonite (OMMT) nanocomposites. Sci. Eng. Compos. Mater. 2016, 23, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Yun, R.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, H.; Yan, D. Nanohybrids of organo-modified layered double hydroxides and polyurethanes with enhanced mechanical, damping and UV absorption properties. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 34288–34296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Lai, X.; Li, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, T.; Zeng, X. Synergistic enhancement of vinyltriethoxysilane and layered Mg–Al double hydroxide on the tracking and erosion resistance of silicone rubber. Polym. Test. 2020, 84, 106373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szadkowski, B.; Marzec, A.; Rybiński, P.; Zaborski, M. Characterization of ethylene-propylene composites filled with perlite and vermiculite minerals: Mechanical, barrier, and flammability properties. Materials 2020, 13, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Wang, Z.; Liu, R.; Zhang, M. Study on preparation and properties of SBR/EVMT composite. Bull. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2012, 31, 1544–1548. [Google Scholar]
- Credico, B.D.; Cobani, E.; Callone, E.; Conzatti, L.; Cristofori, D.; D’Arienzo, M.; Dirè, S.; Giannini, L.; Hanel, T.; Scotti, R.; et al. Size-controlled self-assembly of anisotropic sepiolite fibers in rubber nanocomposites. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 152, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagliaro, I.; Cobani, E.; Carignani, E.; Conzatti, L.; D’Arienzo, M.; Giannini, L.; Martini, F.; Nardelli, F.; Scotti, R.; Stagnaro, P.; et al. The self-assembly of sepiolite and silica fillers for advanced rubber materials: The role of collaborative filler network. Appl. Clay Sci. 2022, 218, 106383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Dai, J.; Bei, Y.; Lin, Q. Modification of illite fines and its application to rubber. China Min. Mag. 1995, 4, 52–55. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, J.; Bei, Y.; Lin, Q.; Huang, J. Reinforcement of rubber by silane modified clay. J. Huaqiao Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 1995, 16, 159–164. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, A.; Yan, C.; Hu, S.; Jiang, L. Study on application of illite in nature rubber. Non-Met. Mines 2009, 32, 5–6. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Li, Y. Study on surface modification of illite. Ind. Miner. Processing 2004, 2, 8–10. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, J.C.; Huang, J.T. Surface modification of clays and clay–rubber composite. Appl. Clay Sci. 1999, 15, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajtášová, M.; Pecušová, B.; Ďurišová, S.; Ondrušová, D.; Mičicová, Z.; Feriancová, A.; Brigantová, S. The use of illite in function of filler applied in rubber blend. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1199, 012035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Q. Study on application of Pingdingshan illite ores to rubbers. Conserv. Util. Miner. Resour. 1999, 3, 25–27. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, P.; Zhao, L.; Tang, Q. Exploration on the ways of application of chlorite, illite and porous silicalite in Hubei province. Hubei Geol. 1993, 7, 97–108. [Google Scholar]
- Monrad, A.H. Reinforcing Filler for the Rubber Industry. U.S. Patent US33148953A, 26 June 1956. [Google Scholar]
- Mermet-Guyennet, M.R.B.; Gianfelice de Castro, J.; Varol, H.S.; Habibi, M.; Hosseinkhani, B.; Martzel, N.; Sprik, R.; Denn, M.M.; Zaccone, A.; Parekh, S.H.; et al. Size-dependent reinforcement of composite rubbers. Polymer 2015, 73, 170–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fröhlich, J.; Niedermeier, W.; Luginsland, H.-D. The effect of filler–filler and filler–elastomer interaction on rubber reinforcement. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2005, 36, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, D.C. Polymer–filler interactions in rubber reinforcement. J. Mater. Sci. 1990, 25, 4175–4185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Bi, W.; Zhao, S. Influence of crosslink density on mechanical properties of natural rubber vulcanizates. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B Phys. 2011, 50, 1460–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, S.; Yu, X.; Zhang, H.; Yan, S. Study on the use of CTAB-treated illite as an alternative filler for natural rubber. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 19017–19025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Q.; Wang, S.; Yan, S. Effects of interface on the dynamic hysteresis loss and static mechanical properties of illite filled SBR composites. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2022, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, Y.; Zheng, J.; Ye, X.; Han, D.; Xi, M.; Zhang, L. Preparation and performance of silica/SBR masterbatches with high silica loading by latex compounding method. Compos. Part B Eng. 2016, 85, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, H.; Zhang, B. The influences of silane coupling agents on rheological properties of bentonite/nitrile butadiene rubber nanocomposites during curing process. J. Vinyl Addit. Technol. 2019, 25, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Lu, Q.; Han, C.; Zhou, Z.; Liang, Z.; Liu, R.; Nie, Y. Reinforcement and toughening of rubber by bridging graphene and nanosilica. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2019, 30, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.-C.; Ge, X.; Cho, U.R. Mechanical performance, water absorption behavior and biodegradability of poly(methyl methacrylate)-modified starch/SBR biocomposites. Macromol. Res. 2013, 21, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kripotou, S.; Pissis, P.; Savelyev, Y.V.; Robota, L.P.; Travinskaya, T.V. Polymer dynamics in polyurethane/clay nanocomposites studied by dielectric and thermal techniques. J. Macromol. Sci. Phys. 2010, 49, 86–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, B.; Jia, Z.; Luo, Y.; Guo, B.; Jia, D. Preparation of halloysite nanotubes supported 2-mercaptobenzimidazole and its application in natural rubber. Compos. Part A—Appl. Sci. 2015, 73, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Xue, B.; Han, M.; Ren, G.; Liu, Y.; Ling, M.; Li, F. Effects of ball milling and ultrasonic treatment on the UV shielding performance of illite micro flakes. Colloids Surf. A 2018, 556, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriaa, A.; Hamdi, N.; Srasra, E. Proton adsorption and acid base properties of Tunisian illites in aqueous solution. J. Struct. Chem. 2009, 50, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, J.; Freakley, P.K. Effect of humidity and water content on the cure behavior of a natural-rubber accelerated sulfur compound. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1992, 65, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasertsri, S.; Rattanasom, N. Fumed and precipitated silica reinforced natural rubber composites prepared from latex system: Mechanical and dynamic properties. Polym. Test. 2012, 31, 593–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idrus, S.S.; Ismail, H.; Palaniandy, S. The effects of silanized ultrafine silica on the curing characteristics, tensile properties, and morphological study of natural rubber compounds. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2011, 50, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, A.; Kang, L.; Zhang, Y. Mechanical properties and thermal stability of kaolinite/emulsion polymerization styrene butadiene rubber composite prepared by latex blending method. Polym. Sci. Ser. A 2020, 62, 407–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangudom, P.; Thongsang, S.; Sombatsompop, N. Cure and mechanical properties and abrasive wear behavior of natural rubber, styrene–butadiene rubber and their blends reinforced with silica hybrid fillers. Mater. Des. 2014, 53, 856–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komadel, P.; Schmidt, D.; Madejová, J.; Číčel, B. Alteration of smectites by treatments with hydrochloric acid and sodium carbonate solutions. Appl. Clay Sci. 1990, 5, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konan, K.L.; Peyratout, C.; Smith, A.; Bonnet, J.-P.; Magnoux, P.; Ayrault, P. Surface modifications of illite in concentrated lime solutions investigated by pyridine adsorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 382, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Sample | SBR | ZnO | SA | NS | S | Illite | KH580 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| unfilled SBR | 100 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1.75 | 0 | 0 |
| illite-x/SBR | 100 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1.75 | 40 | 0 |
| K-illite-x/SBR | 100 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1.75 | 40 | 4 |
| Sample | D10/μm | D50/μm | D90/μm | SBET/m2·g−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| illite-1 | 1.02 ± 0.00 | 6.24 ± 0.02 | 25.80 ± 0.20 | 13 ± 0.2 |
| illite-2 | 0.94 ± 0.00 | 4.10 ± 0.01 | 12.30 ± 0.00 | 15 ± 0.3 |
| illite-3 | 0.71 ± 0.01 | 1.88 ± 0.01 | 5.14 ± 0.02 | 21 ± 0.1 |
| illite-4 | 0.42 ± 0.00 | 0.70 ± 0.00 | 1.82 ± 0.01 | 50 ± 0.3 |
| Sample | Tensile Strength /MPa | Tear Strength /kN·m−1 | Modulus at 300% /MPa | Elongation at Break /% | XLD 1 /10−5mol/cm3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBR | 1.9 ± 0.2 | 12.8 ± 1.0 | 1.21 ± 0.03 | 661 ± 16 | 6.37 ± 0.12 |
| illite-1/SBR | 3.1 ± 0.3 | 16.5 ± 0.4 | 1.82 ± 0.02 | 630 ± 20 | 2.54 ± 0.11 |
| illite-2/SBR | 4.6 ± 0.4 | 17.6 ± 1.4 | 2.04 ± 0.02 | 755 ± 30 | 2.68 ± 0.15 |
| illite-3/SBR | 10.2 ± 0.5 | 19.1 ± 0.4 | 2.12 ± 0.04 | 708 ± 11 | 4.32 ± 0.13 |
| illite-4/SBR | 11.5 ± 0.3 | 21.7 ± 1.0 | 3.00 ± 0.05 | 673 ± 23 | 4.69 ± 0.09 |
| K-illite-1/SBR | 5.0 ± 0.1 | 25.9 ± 1.4 | 3.73 ± 0.15 | 396 ± 23 | 7.06 ± 0.24 |
| K-illite-2/SBR | 6.5 ± 0.5 | 28.2 ± 1.4 | 4.81 ± 0.19 | 393 ± 13 | 8.41 ± 0.25 |
| K-illite-3/SBR | 12.2 ± 0.6 | 32.7 ± 2.1 | 7.98 ± 0.25 | 390 ± 17 | 10.07 ± 0.38 |
| K-illite-4/SBR | 16.7 ± 0.7 | 35.3 ± 1.7 | 12.97 ± 0.49 | 353 ± 11 | 11.88 ± 0.27 |
| Sample | Tg/°C | ∆Cpn/ J·g−1·K−1 | χim |
|---|---|---|---|
| unfilled SBR | −53 | 0.343 | — |
| illite-1-SBR | −54 | 0.306 | 0.109 |
| illite-2-SBR | −54 | 0.296 | 0.138 |
| illite-3-SBR | −54 | 0.289 | 0.158 |
| illite-4-SBR | −55 | 0.281 | 0.182 |
| K-illite-1-SBR | −53 | 0.255 | 0.258 |
| K-illite-2-SBR | −53 | 0.243 | 0.291 |
| K-illite-3-SBR | −53 | 0.238 | 0.307 |
| K-illite-4-SBR | −54 | 0.224 | 0.346 |
| Sample | MH/dN·m | ML/dN·m | MH-ML /dN·m | t10/min | t90/min |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| unfilled SBR | 7.77 | 0.63 | 7.14 | 10.50 | 23.73 |
| illite-1/SBR | 8.13 | 1.13 | 7.00 | 5.88 | 37.85 |
| illite-2/SBR | 8.43 | 1.27 | 7.16 | 5.98 | 37.95 |
| illite-3/SBR | 8.29 | 0.89 | 7.40 | 6.30 | 27.90 |
| illite-4/SBR | 8.37 | 0.87 | 7.50 | 6.57 | 26.55 |
| K-illite-1/SBR | 10.67 | 1.09 | 9.58 | 5.12 | 31.78 |
| K-illite-2/SBR | 11.17 | 1.16 | 10.01 | 4.75 | 28.88 |
| K-illite-3/SBR | 11.36 | 0.88 | 10.48 | 5.07 | 24.20 |
| K-illite-4/SBR | 11.77 | 0.89 | 10.88 | 5.08 | 23.27 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Q.; Wang, S.; Yan, S. Effect of 3-Mercaptopropyltriethoxysilane Modified Illite on the Reinforcement of SBR. Materials 2022, 15, 3459. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15103459
Wang Z, Zhang H, Liu Q, Wang S, Yan S. Effect of 3-Mercaptopropyltriethoxysilane Modified Illite on the Reinforcement of SBR. Materials. 2022; 15(10):3459. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15103459
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zhepeng, Hao Zhang, Qiang Liu, Shaojuan Wang, and Shouke Yan. 2022. "Effect of 3-Mercaptopropyltriethoxysilane Modified Illite on the Reinforcement of SBR" Materials 15, no. 10: 3459. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15103459
APA StyleWang, Z., Zhang, H., Liu, Q., Wang, S., & Yan, S. (2022). Effect of 3-Mercaptopropyltriethoxysilane Modified Illite on the Reinforcement of SBR. Materials, 15(10), 3459. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15103459