Immediate and Long-Term Radiopacity and Surface Morphology of Hydraulic Calcium Silicate-Based Materials
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Assessment of Radiopacity
2.2. Characterization of Surface Morphology
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Radiopacity
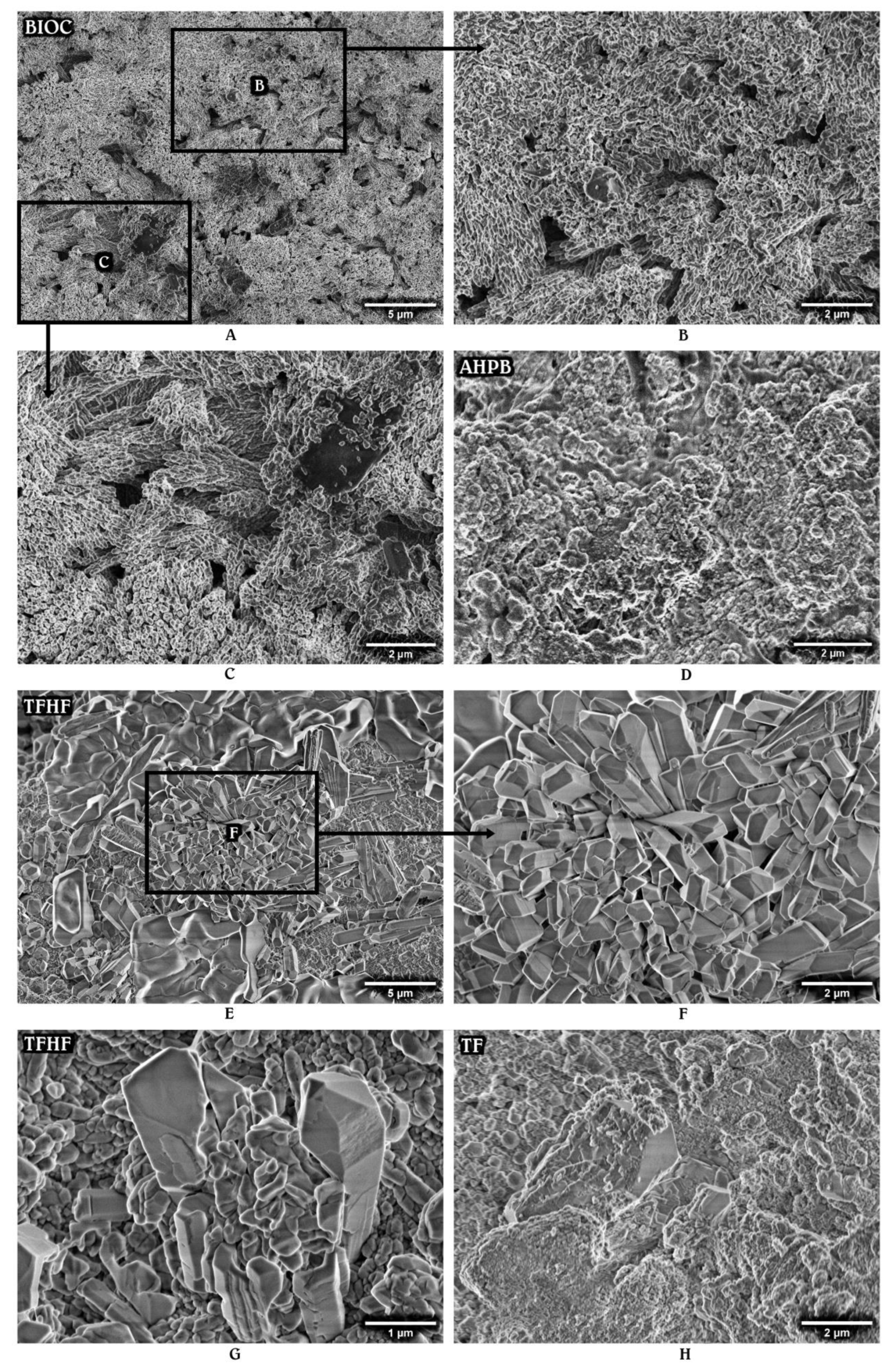
3.2. Surface Morphology
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Camilleri, J. Characterization and Properties of Bioceramic Materials for Endodontics. In Bioceramic Materials in Clinical Endodontics, 1st ed.; Drukteinis, S., Camilleri, J., Eds.; Spinger: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 7–18. [Google Scholar]
- Candeiro, G.T.; Correia, F.C.; Duarte, M.A.; Ribeiro-Siqueira, D.C.; Gavini, G. Evaluation of radiopacity, pH, release of calcium ions, and flow of a bioceramic root canal sealer. J. Endod. 2012, 38, 842–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zordan-Bronzel, C.L.; Esteves Torres, F.F.; Tanomaru-Filho, M.; Chávez-Andrade, G.M.; Bosso-Martelo, R.; Guerreiro-Tanomaru, J.M. Evaluation of Physicochemical Properties of a New Calcium Silicate-based Sealer, Bio-C Sealer. J. Endod. 2019, 45, 1248–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antunes, T.B.M.; Janini, A.C.P.; Pelepenko, L.E.; Abuna, G.F.; Paiva, E.M.; Sinhoreti, M.A.C.; Raimundo, I.M.; Gomes, B.P.F.A.; de-Jesus-Soares, A.; Marciano, M.A. Heating stability, physical and chemical analysis of calcium silicate-based endodontic sealers. Int. Endod. J. 2021, 54, 1175–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malka, V.B.; Hochscheidt, G.L.; Larentis, N.L.; Grecca, F.S.; Fontanella, V.R.; Kopper, P.M. A new in vitro method to evaluate radio-opacity of endodontic sealers. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2015, 44, 20140422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, A.T.; Silva, P.B.D.; Só, B.B.; Hashizume, L.N.; Vivan, R.R.; Rosa, R.A.D.; Duarte, M.A.H.; Só, M.V.R. Evaluation of Physicochemical Properties of New Calcium Silicate-Based Sealer. Braz. Dent. J. 2018, 29, 536–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, W.; Zheng, Q.; Duan, X.; Zhou, X.; Huang, D. Comparing cone-beam computed tomography with periapical radiography for assessing root canal obturation in vivo using microsurgical findings as validation. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2017, 46, 20160463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 6876:2012; Dentistry-Root canal sealing materials. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012.
- Saghiri, M.A.; Gutmann, J.L.; Orangi, J.; Asatourian, A.; Sheibani, N. Radiopacifier particle size impacts the physical properties of tricalcium silicate-based cements. J. Endod. 2015, 41, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camilleri, J. Will bioceramics be the future root canal filling materials? Curr. Oral Health Rep. 2017, 4, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camilleri, J.; Borg, J.; Damidot, D.; Salvadori, E.; Pilecki, P.; Zaslansky, P.; Darvell, B.W. Colour and chemical stability of bismuth oxide in dental materials with solutions used in routine clinical practice. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0240634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuereb, M.; Sorrentino, F.; Damidot, D.; Camilleri, J. Development of novel tricalcium silicate-based endodontic cements with sintered radiopacifier phase. Clin. Oral Investig. 2016, 20, 967–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelepenko, L.E.; Saavedra, F.; Bombarda, G.F.; Gomes, B.P.F.A.; DE-Jesus-Soares, A.; Zaia, A.A.; Duarte, M.A.H.; Tanomaru-Filho, M.; Marciano, M.A. Dental discoloration caused by Grey-MTAFlow cement: Analysis of its physicochemical, biological and antimicrobial properties. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2020, 28, e20200269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyashita, H.; Asaumi, R.; Sakamoto, A.; Kawai, T.; Igarashi, M. Root canal sealers affect artifacts on cone-beam computed tomography images. Odontology 2021, 109, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firoozmand, L.M.; Cordeiro, M.G.; Da Silva, M.A.; De Jesus Tavarez, R.R.; Matos, M.F.E. Radiopacity of Methacrylate and Silorane Composite Resins Using a Digital Radiographic System. Sci. World J. 2016, 2016, 6389347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochoa-RodrÍguez, V.M.; Wilches-Visbal, J.H.; Roma, B.; Coaguila-Llerena, H.; Tanomaru-Filho, M.; GonÇalves, A.; Spin-Neto, R.; Faria, G. Radiopacity of endodontic materials using two models for conversion to millimeters of aluminum. Braz. Oral Res. 2020, 34, e080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chawla, N.; Williams, J.J. Fatigue and fracture of powder metallurgy steels. In Advances in Powder Metallurgy: Properties, Processing and Applications, 1st ed.; Chang, I., Zhao, Y., Eds.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 455–490. [Google Scholar]
- Milanovic, I.; Milovanovic, P.; Antonijevic, D.; Dzeletovic, B.; Djuric, M.; Miletic, V. Immediate and long-term porosity of calcium silicate-based sealers. J. Endod. 2020, 46, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, D.; Bergold, S.T.; Goetz-Neunhoeffer, F.; Neubauer, J. The hydration of alite: A time-resolved quantitative X-ray diffraction approach using the G-factor method compared with heat release. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2011, 44, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camerini, R.; Poggi, G.; Ridi, F.; Baglioni, P. The kinetic of calcium silicate hydrate formation from silica and calcium hydroxide nanoparticles. J. Colloid. Iterface Sci. 2022, 605, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuolo, M.; Silva, E.J.N.L.; Souza, E.; De Deus, G.; Versiani, M.A. Shaping for Cleaning in Retreatment Cases. In Shaping for Cleaning the Root Canals, 1st ed.; De Deus, G., Silva, E.J.N.L., Souza, E., Versiani, M.A., Zuolo, M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 249–294. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, A.; Zeng, Y.; Kirkpatrick, T.; van der Hoeven, R.; Silva, R.; Letra, A.; Chaves de Souza, L. Evaluation of the Physicochemical and Biological Properties of EndoSequence BC Sealer HiFlow. J. Endod. 2022, 48, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, D.T. Radiopaque Masses. In Emergency Radiology: Case Studies, 1st ed.; Schwartz, D.T., Ed.; McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2008; Chapter II-8. [Google Scholar]
- Pelepenko, L.E.; Saavedra, F.; Antunes, T.B.M.; Bombarda, G.F.; Gomes, B.P.F.A.; Zaia, A.A.; Camilleri, J.; Marciano, M.A. Physicochemical, antimicrobial, and biological properties of White-MTAFlow. Clin. Oral Investig. 2021, 25, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prati, C.; Gandolfi, M.G. Calcium silicate bioactive cements: Biological perspectives and clinical applications. Dent. Mater. 2015, 31, 351–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belal, R.S.; Edanami, N.; Yoshiba, K.; Yoshiba, N.; Ohkura, N.; Takenaka, S.; Noiri, Y. Comparison of calcium and hydroxyl ion release ability and in vivo apatite-forming ability of three bioceramic-containing root canal sealers. Clin. Oral Investig. 2022, 26, 1443–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, S.; Han, L.; Noiri, Y.; Okiji, T. Evaluation of the Ca ion release, pH and surface apatite formation of a prototype tricalcium silicate cement. Int. Endod. J. 2017, 50, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camilleri, J.; Cutajar, A.; Mallia, B. Hydration characteristics of zirconium oxide replaced Portland cement for use as a root-end filling material. Dent. Mater. 2011, 27, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camilleri, J.; Portoles, C.A. Clinical perspective on hydraulic materials developed for root-end surgery. ENDO EPT 2020, 14, 205–216. [Google Scholar]
- He, W.; Fu, Y.; Andersson, M. Morphological control of calcium phosphate nanostructures using lyotropic liquid crystals. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 3214–3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camilleri, J.; Atmeh, A.; Li, X.; Meschi, N. Present status and future directions: Hydraulic materials for endodontic use. Int. Endod. J. 2022, 55, 710–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutajar, A.; Mallia, B.; Abela, S.; Camilleri, J. Replacement of radiopacifier in mineral trioxide aggregate; characterization and determination of physical properties. Dent. Mater. 2011, 27, 879–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, H.; Wang, Z.; Haapasalo, M.; Jiang, Q.; Shen, Y. Long-term porosity and retreatability of oval-shaped canals obturated using two different methods with a novel tricalcium silicate sealer. Clin. Oral Investig. 2022, 26, 1045–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashofteh, Y.K.; Ghabraei, S.; Bolhari, B.; Kafili, M.; Meraji, N.; Nekoofar, M.H.; Dummer, P.M.H. Microstructure and chemical analysis of four calcium silicate-based cements in different environmental conditions. Clin. Oral Investig. 2019, 23, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meschi, N.; Li, X.; Van Gorp, G.; Camilleri, J.; Van Meerbeek, B.; Lambrechts, P. Bioactivity potential of Portland cement in regenerative endodontic procedures: From clinic to lab. Dent. Mater. 2019, 35, 1342–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, L.V.; de Souza, G.L.; da Silva, G.R.; Magalhães, T.E.A.; Freitas, G.A.N.; Turrioni, A.P.; de Rezende Barbosa, G.L.; Moura, C.C.G. Biological parameters, discolouration and radiopacity of calcium silicate-based materials in a simulated model of partial pulpotomy. Int. Endod. J. 2021, 54, 2133–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, C.T.; Jacobs, R.; Vasconcelos, K.F.; Lambrechts, P.; Rubira-Bullen, I.R.F.; Gaêta-Araujo, H.; Oliveira-Santos, C.; Duarte, M.A.H. Influence of CBCT-based volumetric distortion and beam hardening artefacts on the assessment of root canal filling quality in isthmus-containing molars. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2021, 50, 20200503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Material | Composition Declared by Manufacturers | Preparation |
|---|---|---|
| AH Plus Bioceramic Sealer (AHPB) | Tricalcium silicate, lithium carbonate, zirconium oxide, dimethyl sulfoxide, thickening agents | Paste ready to use |
| Bio-C Sealer (BIOC) | Tricalcium silicate, dicalcium silicate, tricalcium aluminate, calcium oxide, zirconium oxide, silicon oxide, iron oxide, polyethylene glycol | Paste ready to use |
| Biodentine (BD) | Powder: tricalcium silicate, dicalcium silicate, calcium carbonate, calcium oxide, iron oxide, zirconium oxide Liquid: water, calcium chloride, polycarboxylate | 1 capsule of BD to 5 drops of liquid mixed for 30 s in the amalgamator |
| BioRoot RCS (BR) | Powder: tricalcium silicate, zirconium oxide, povidone Liquid: water, calcium chloride, polycarboxylate | 1 spoon of powder to 5 drops of liquid mixed for 60 s until a smooth paste |
| Grey-MTAFlow (GMF) | Powder: tricalcium silicate, dicalcium silicate, calcium sulfate, silica, bismuth oxide Liquid: water, water-soluble silicone-based gel | 1 big-end plus 1 small-end spoon of powder (0.19 g) to 3 drops of liquid mixed until a thin consistency |
| White-MTAFlow (WMF) | Powder: tricalcium silicate, dicalcium silicate, calcium sulfate, tantalum oxide Liquid: water, water-soluble silicone-based gel | 1 big-end plus 1 small-end spoon of powder (0.19 g) to 3 drops of liquid mixed until a thin consistency |
| TotalFill BC Sealer (TF) | Tricalcium silicate, dicalcium silicate, calcium phosphate monobasic, zirconium oxide, tantalum oxide, calcium hydroxide, filler and thickening agents | Paste ready to use |
| TotalFill BC Sealer HiFlow (TFHF) | Tricalcium silicate, dicalcium silicate, calcium hydroxide, zirconium oxide, filler and thickening agents | Paste ready to use |
| Material | Radiopacity (mm Al) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 min | 24 h | 28 days | Total Increase | |
| AHPB | 10.82 ± 0.69 | 11.07 ± 0.94 | 11.26 ± 0.65 | 0.44 |
| BIOC | 8.15 ± 0.44 | 8.17 ± 0.41 | 8.85 ± 0.44 | 0.70 |
| BD | 3.34 ± 0.43 | 3.35 ± 0.40 | 3.75 ± 0.36 | 0.41 |
| BR | 7.19 ± 0.32 A | 7.47 ± 0.35 B | 8.08 ± 0.40 A,B | 0.89 |
| GMF | 6.27 ± 0.41 | 6.62 ± 0.37 | 6.98 ± 0.32 | 0.71 |
| WMF | 5.76 ± 0.20 | 5.80 ± 0.48 | 6.20 ± 0.46 | 0.44 |
| TF | 8.56 ± 0.47 C | 9.03 ± 0.25 | 9.66 ± 0.73 C | 1.10 |
| TFHF | 8.81 ± 0.30 D | 9.19 ± 0.31 E | 9.79 ± 0.43 D,E | 0.98 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bilvinaite, G.; Drukteinis, S.; Brukiene, V.; Rajasekharan, S. Immediate and Long-Term Radiopacity and Surface Morphology of Hydraulic Calcium Silicate-Based Materials. Materials 2022, 15, 6635. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15196635
Bilvinaite G, Drukteinis S, Brukiene V, Rajasekharan S. Immediate and Long-Term Radiopacity and Surface Morphology of Hydraulic Calcium Silicate-Based Materials. Materials. 2022; 15(19):6635. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15196635
Chicago/Turabian StyleBilvinaite, Goda, Saulius Drukteinis, Vilma Brukiene, and Sivaprakash Rajasekharan. 2022. "Immediate and Long-Term Radiopacity and Surface Morphology of Hydraulic Calcium Silicate-Based Materials" Materials 15, no. 19: 6635. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15196635
APA StyleBilvinaite, G., Drukteinis, S., Brukiene, V., & Rajasekharan, S. (2022). Immediate and Long-Term Radiopacity and Surface Morphology of Hydraulic Calcium Silicate-Based Materials. Materials, 15(19), 6635. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15196635







