Entalpy of Mixing, Microstructure, Structural, Thermomagnetic and Mechanical Properties of Binary Gd-Pb Alloys
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Sample Preparation and Experimental Details
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Warburg, E. Magnetische untersuchungen. Ann. Phys. 1881, 249, 141–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tishin, A.M.; Spichkin, Y.I. The Magnetocaloric Effect and Its Application; Institute of Physics Series in Condensed Matter Physics; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Gschneidner, K.A., Jr.; Pecharsky, V.K. Magnetic refrigeration in Rare Earths. In Science Technology and Applications, 3rd ed.; Bautista, R.G., Bounds, C.O., Ellis, T.W., Killbourn, B.T., Eds.; The Minerals, Metals and Material Society: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1997; p. 209. [Google Scholar]
- Pecharsky, V.K.; Gschneidner, K.A., Jr. Tunable magnetic regenerator alloys with a giant magnetocaloric effect for magnetic refrigeration from ~20 to ~290 K. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1997, 70, 3299–3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.B.; Altounian, Z. Effect of Co content on magnetic entropy change and structure of La(Fe1−xCox)11.4Si1.6. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2003, 264, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gębara, P.; Pawlik, P. Broadening of temperature working range in magnetocaloric La(Fe,Co,Si)13-based multicomposite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 442, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Cong, D.Y.; Huang, L.; Nie, Z.H.; Sun, X.M.; Zhang, Q.Z.; Wang, Y.D. Large elastocaloric effect in a Ni-Co-Mn-Sn magnetic shape memory alloy. Mater. Des. 2016, 92, 932–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.W.; Zhang, H.; Tao, K.; Wang, Y.X.; Wu, M.L.; Long, Y. Giant magnetocaloric effect induced by reemergence of magnetostructural coupling in Si-doped Mn0.95CoGe compounds. Mater. Des. 2017, 114, 410–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegus, O.; Brück, E.; Buschow, K.H.J.; de Boer, F.R. Transition-metal-based magnetic refrigerants for room-temperature applications. Nature 2002, 415, 150–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, J.Y.; Moreno-Ramirez, L.M.; Blazquez, J.S.; Franco, V.; Conde, A. Gd + GdZn biphasic magnetic composites synthesized in a single preparation step: Increasing refrigerant capacity without decresing magnetic entropy change. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 675, 244–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, H.Y.; Zhong, X.C.; Jiao, D.L.; Liu, Z.W.; Zhang, H.; Qiu, W.Q.; Ramanujan, R.V. Table-like magnetocaloric effect and enhanced refrigerant capacity in crystalline Gd55Co35Mn10 alloy melt spun ribbons. Phys. Lett. A 2018, 382, 1679–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaraman, T.V.; Boone, L.; Shield, J.E. Magnetocaloric effect and refrigerant capacity in melt-spun Gd–Mn alloys. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2013, 345, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, J.J.; Du, Y.S.; Cheng, G.; Wu, X.F.; Ma, L.; Wang, J.; Xia, Z.; Rao, G. Magnetic properties and large magnetocaloric effects of GdPd intermetallic compound. J. Rare Earths 2018, 36, 1044–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gębara, P.; Diaz-Garcia, A.; Law, J.Y.; Franco, V. Magnetocaloric response of binary Gd-Pd and ternary Gd-(Mn, Pd) alloys. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 500, 166175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Garcia, A.; Law, J.Y.; Gębara, P.; Franco, V. Phase deconvolution of multiphasic materials by the universal scaling of the magnetocaloric effect. JOM 2020, 72, 2845–2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Hu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, H.; Li, L. Electronic structure, magnetic properties and magnetocaloric performance in rare earths (RE) based RE2BaZnO5 (RE = Gd, Dy, Ho, and Er) compounds. Acta Mater. 2022, 236, 118114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palenzona, A.; Cirafici, S. The gd-pb (gadolinium-lead) system. J. Phase Equilibria 1991, 12, 686–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, W.; Nolze, G. PowderCell 2.0 for Windows. Powder. Diffr. 1998, 13, 256–259. [Google Scholar]
- de Boer, F.R.; Boom, R.; Mattens, W.C.M.; Miedema, A.R.; Niessen, A.K. Cohesion in Metals. In Cohesion and Structure; de Boer, F.R., Pettifor, D.G., Eds.; North Holland Physics: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1988; Volume 1, pp. 1–758. [Google Scholar]
- Bakker, H. Enthalpies in Alloys: Miedema’s Semi-Empirical Model; Materials Science Foundations 1; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Wollerau, Switzerland, 1998; pp. 1–78. [Google Scholar]
- Basu, J.; Murty, B.S.; Ranganathan, S. Glass forming ability: Miedema approach to (Zr, Ti, Hf)–(Cu, Ni) binary and ternary alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2008, 465, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.P.; Yi, D.Q.; Liu, H.Q.; Zang, B.; Jiang, Y. Calculation of glass forming ranges in Al–Ni–RE (Ce, La, Y) ternary alloys and their sub-binaries based on Miedema’s model. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 506, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.H.; Li, J.Q.; Huang, W.D.; Sun, W.A.; Ao, W.Q. Giant magnetocaloric effect enhanced by Pb-doping in Gd5Si2Ge2 compound. J. Alloys Compd. 2006, 421, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demel, J.T.; Gschneidner, K.A., Jr. The gadolinium—lead system. J. Nucl. Mater. 1969, 29, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan’kov, S.Y.; Tishin, A.M.; Pecharsky, V.K.; Gschneidner, K.A., Jr. Magnetic phase transitions and the magnetothermal properties of gadolinium. Phys. Rev. B 1998, 57, 3478–3940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcinkova, A.; de la Cruz, C.; Yip, J.; Zhao, L.L.; Wang, J.K.; Svanidze, E.; Morosan, E. Strong magnetic coupling in the hexagonal R5Pb3 compounds (R=Gd–Tm). J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 384, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pecharsky, V.K.; Gschneidner, K.A., Jr. Magnetocaloric effect and magnetic refrigeration. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1999, 200, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, M.E.; Potter, W.H. General analysis of magnetic refrigeration and its optimization using a new concept: Maximization of refrigerant capacity. Cryogenics 1985, 25, 667–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- la Roca, P.; Lopez-Garcia, J.; Sanchez-Alacros, V.; Recarte, V.; Rodriguez-Velamazan, J.A.; Perez-Landazabal, J.I. Room temperature huge magnetocaloric properties in low hysteresis ordered Cu-doped Ni-Mn-In-Co alloys. J. All. Compd. 2022, 922, 166143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekgül, A.; Acet, M.; Scheibel, F.; Farle, M.; Unal, N. The reversibility of the inverse magnetocaloric effect in Mn2−xCrxSb0.95Ga0.05. Acta Mater. 2017, 124, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, V.; Blazquez, J.S.; Conde, A. The influence of Co addition on the magnetocaloric effect of Nanoperm-type amorphous alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 100, 064307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, V.; Conde, C.F.; Blázquez, J.S.; Conde, A.; Švec, P.; Janičkovič, D.; Kiss, L.F. A constant magnetocaloric response in Fe Mo Cu B amorphous alloys with different Fe/B ratios. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 101, 093903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Świerczek, J. Superparamagnetic behavior and magnetic entropy change in partially crystallized Fe–Mo–Cu–B alloy. Phys. Status Solidi A 2014, 211, 1567–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, W.C.; Pharr, G.M. An improved technique for determining hardness and elastic modulus using load and displacement sensing indentation experiments. J. Mater. Res. 1992, 7, 1564–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, W.C.; Pharr, G.M. Measurement of hardness and elastic modulus by instrumented indentation: Advances in understanding and refinements to methodology. J. Mater. Res. 2004, 19, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
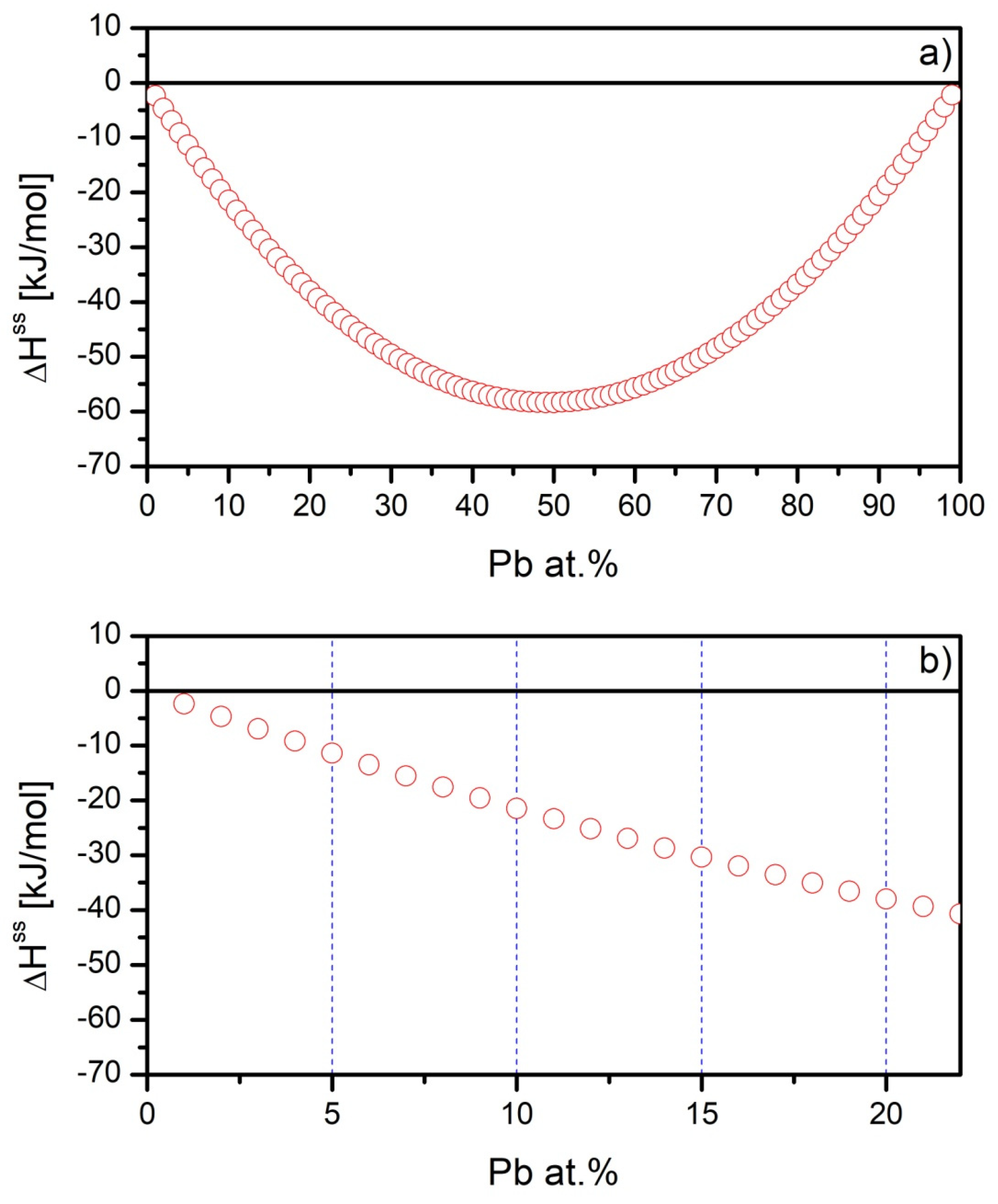

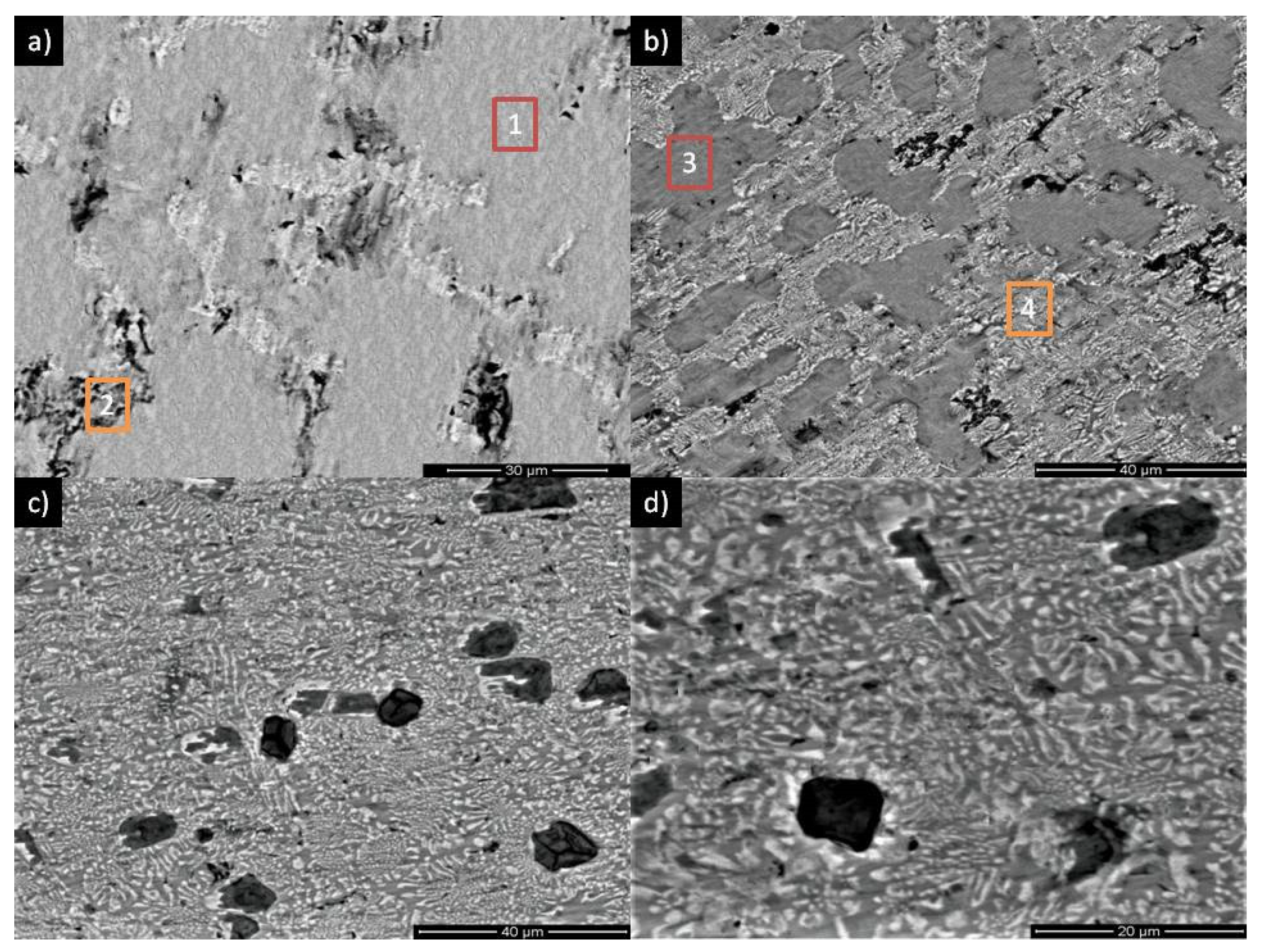
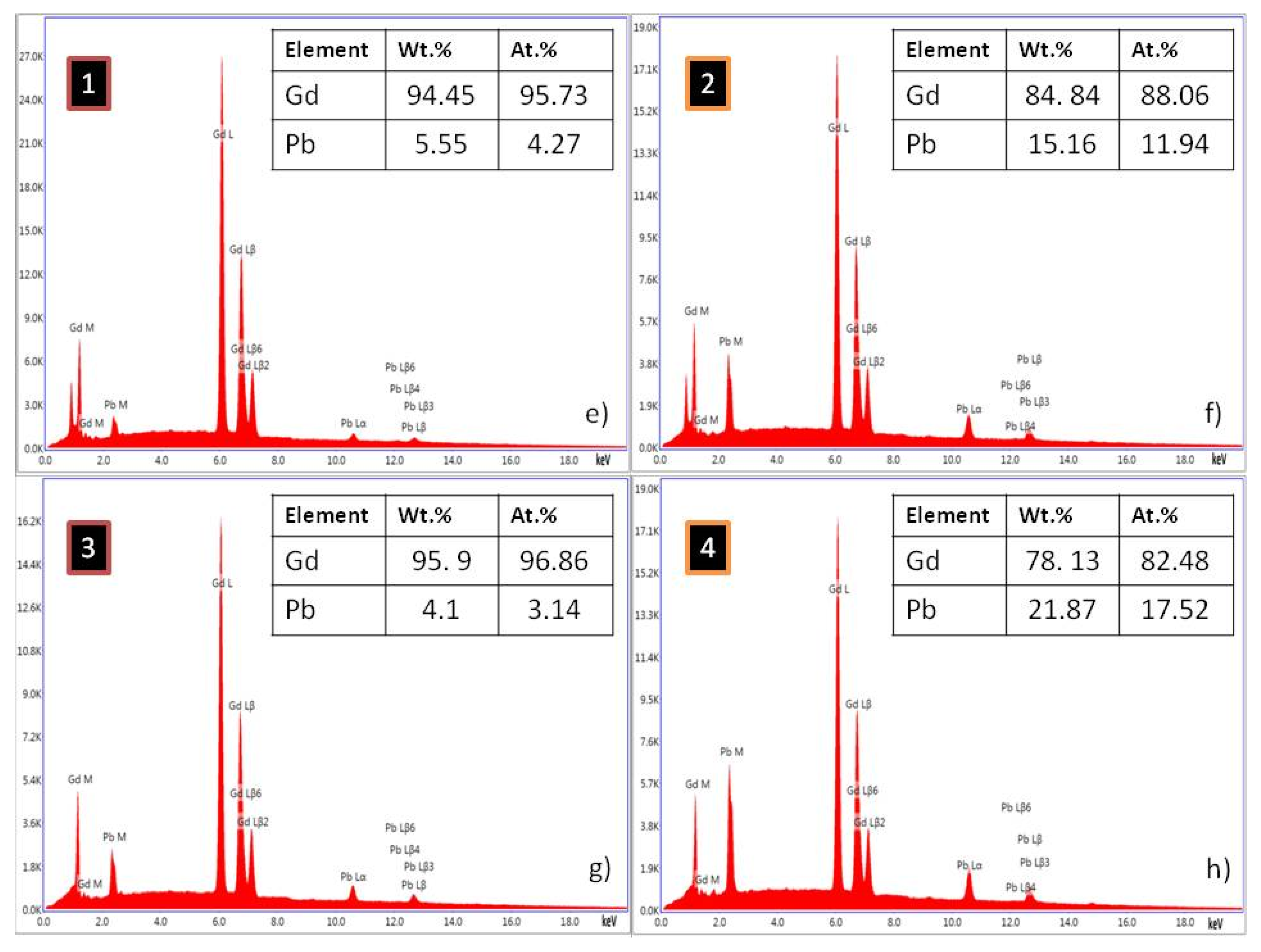
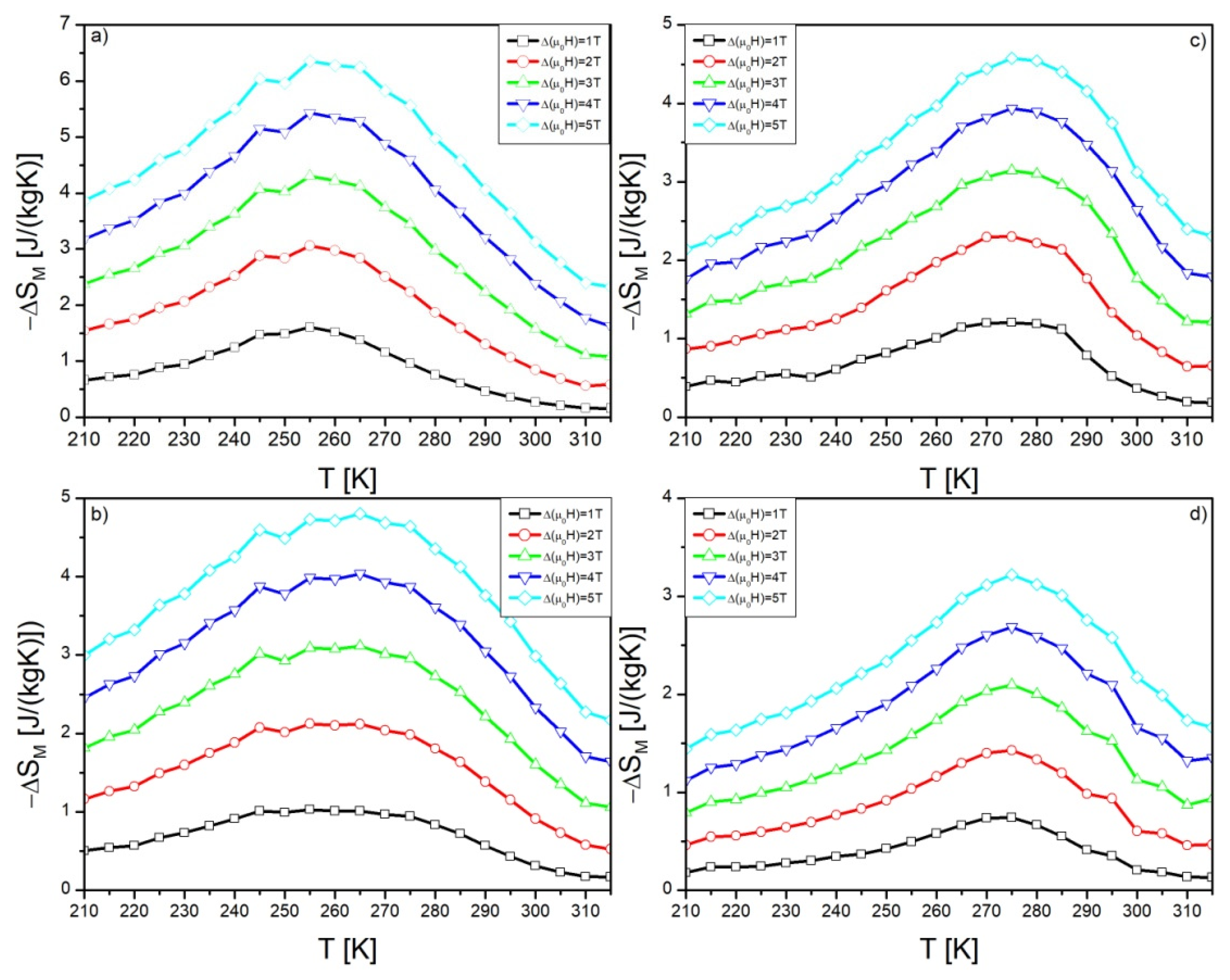

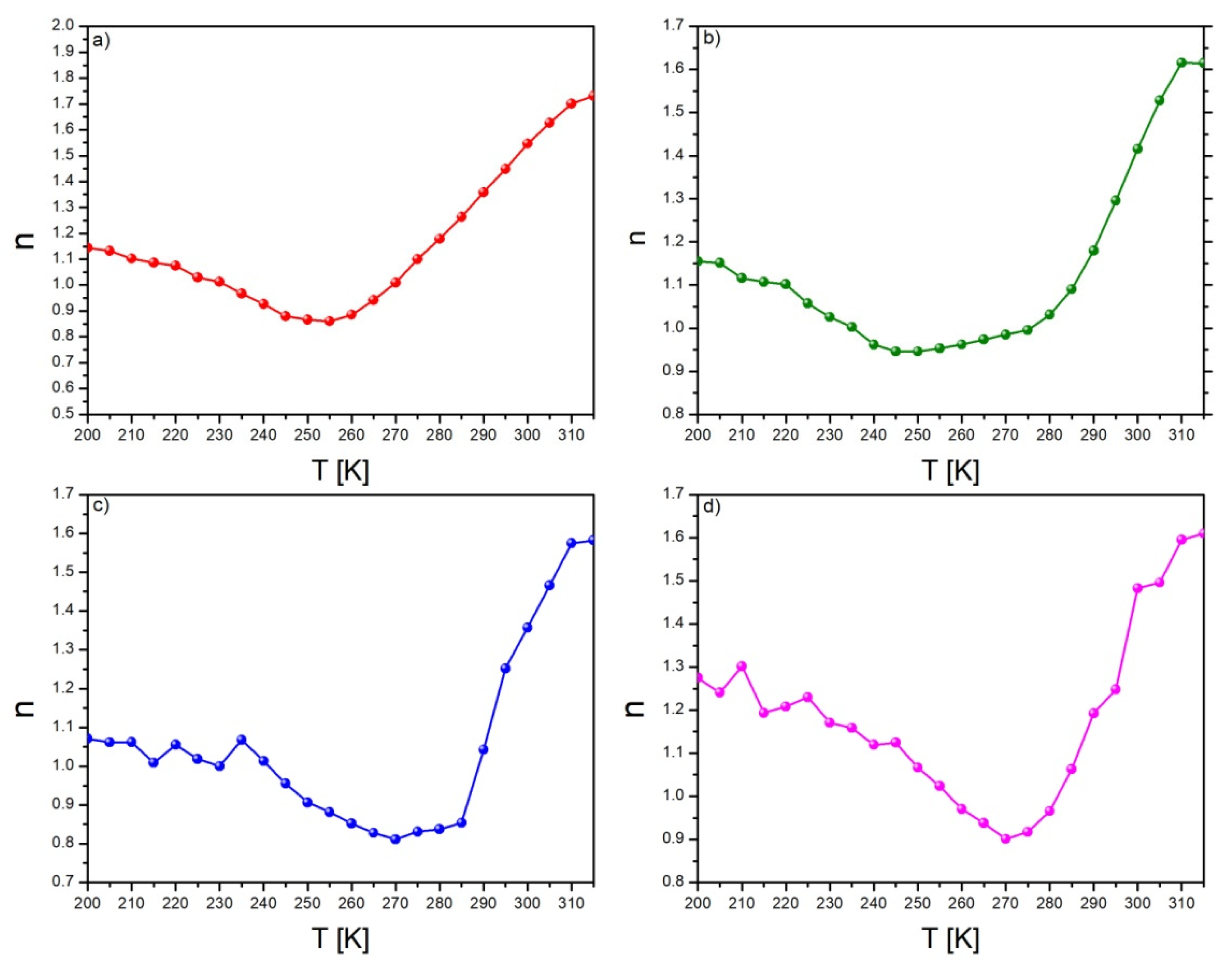
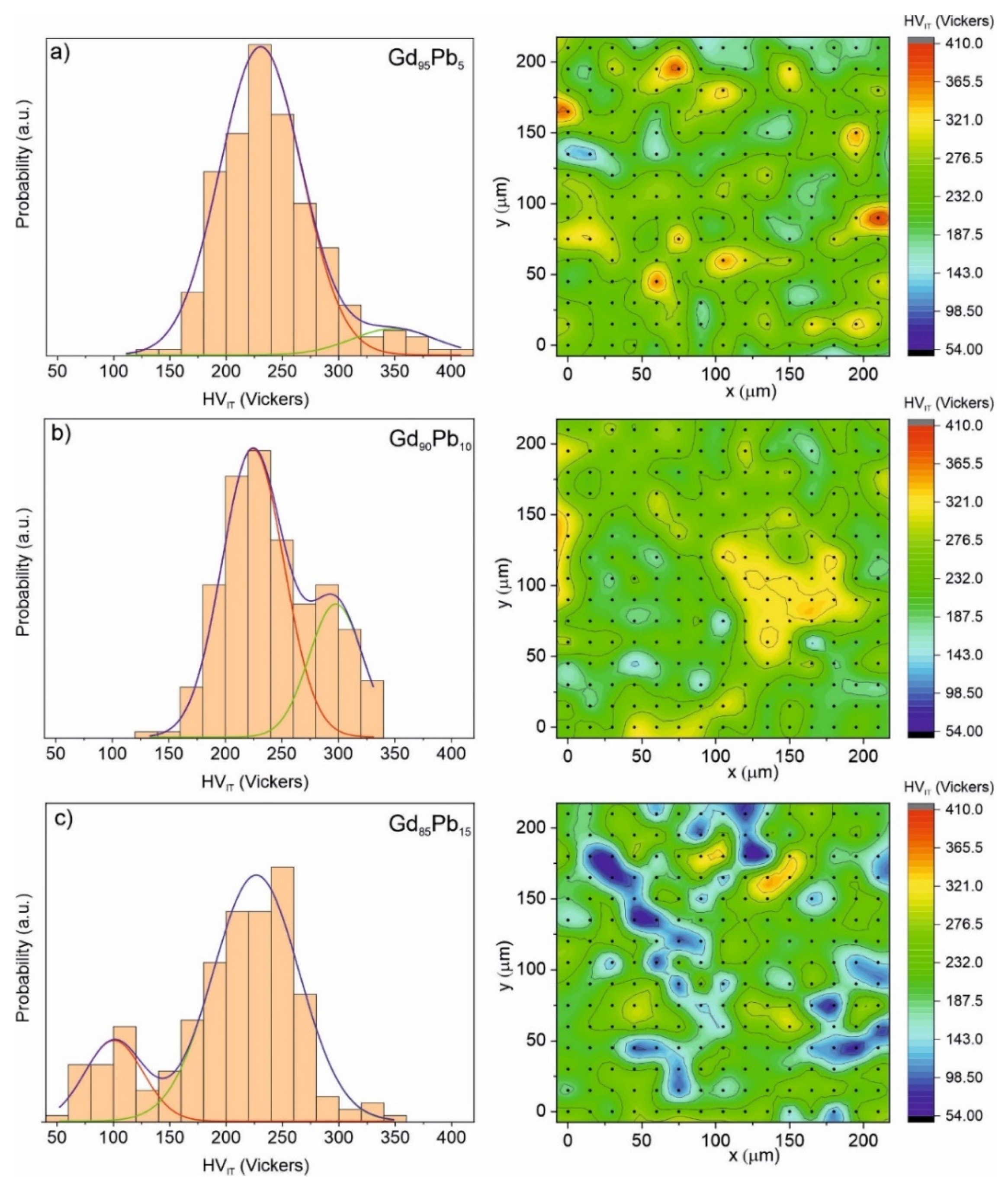

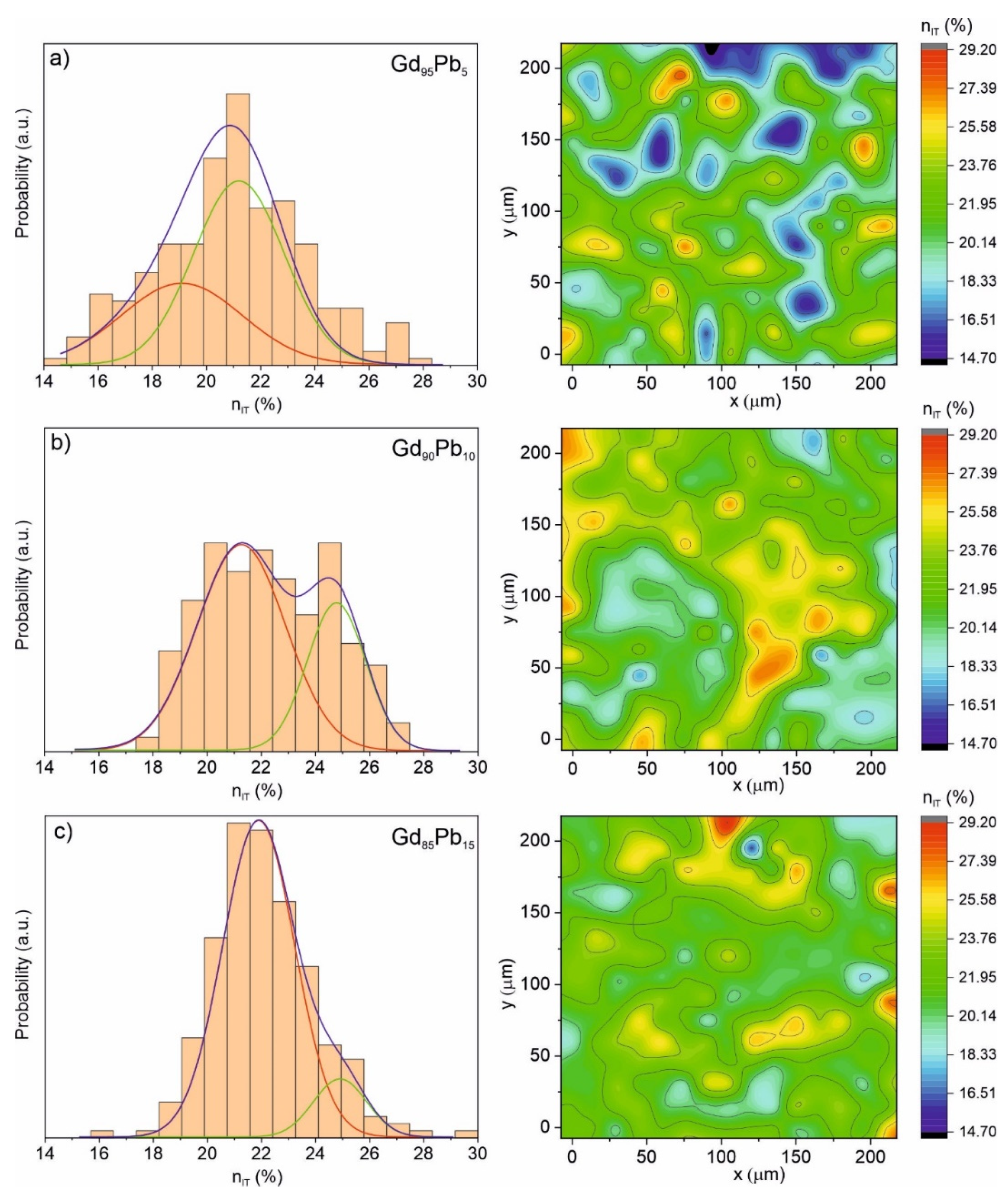
| Alloy | Recognized Phases | Content [vol.%] | Lattice Parameters [Å] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gd95Pb5 | Gd(Pb) | 67 | a = 3.599 c = 5.742 |
| Gd5Pb3 | 27 | a = 9.129 c = 6.675 | |
| GdO1.5 | 6 | a = 5.307 | |
| Gd90Pb10 | Gd(Pb) | 58 | a = 3.614 c = 5.758 |
| Gd5Pb3 | 33 | a = 9.122 c = 6.665 | |
| GdO1.5 | 7 | a = 5.304 | |
| Gd85Pb15 | Gd(Pb) | 45 | a = 3.623 c = 5.769 |
| Gd5Pb3 | 47 | a = 9.119 c = 6.661 | |
| GdO1.5 | 8 | a = 5.309 | |
| Gd80Pb20 | Gd(Pb) | 34 | a = 3.629 c = 5.784 |
| Gd5Pb3 | 58 | a = 9.113 c = 6.657 | |
| GdO1.5 | 8 | a = 5.308 |
| Alloy | Phases | Weight Fraction [wt.%] | Atomic Fraction [at.%] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gd95Pb5 | Gd(Pb) | Gd—94.45 Pb—5.55 | Gd—95.73 Pb—4.27 |
| Gd5Pb3 | Gd—84.84 Pb—15.16 | Gd—88.06 Pb—11.94 | |
| Gd90Pb10 | Gd(Pb) | Gd—95.59 Pb—4.41 | Gd—96.71 Pb—3.29 |
| Gd5Pb3 | Gd—78.13 Pb—21.87 | Gd—82.48 Pb—17.52 | |
| Gd85Pb15 | Gd(Pb) | Gd—95.9 Pb—4.1 | Gd—96.86 Pb—3.14 |
| Gd5Pb3 | Gd—64.33 Pb—35.67 | Gd—70.38 Pb—29.62 | |
| Gd80Pb20 | Gd(Pb) | Gd—96.32 Pb—3.68 | Gd—97.18 Pb—2.82 |
| Gd5Pb3 | Gd—60.83 Pb—39.17 | Gd—67.17 Pb—32.83 |
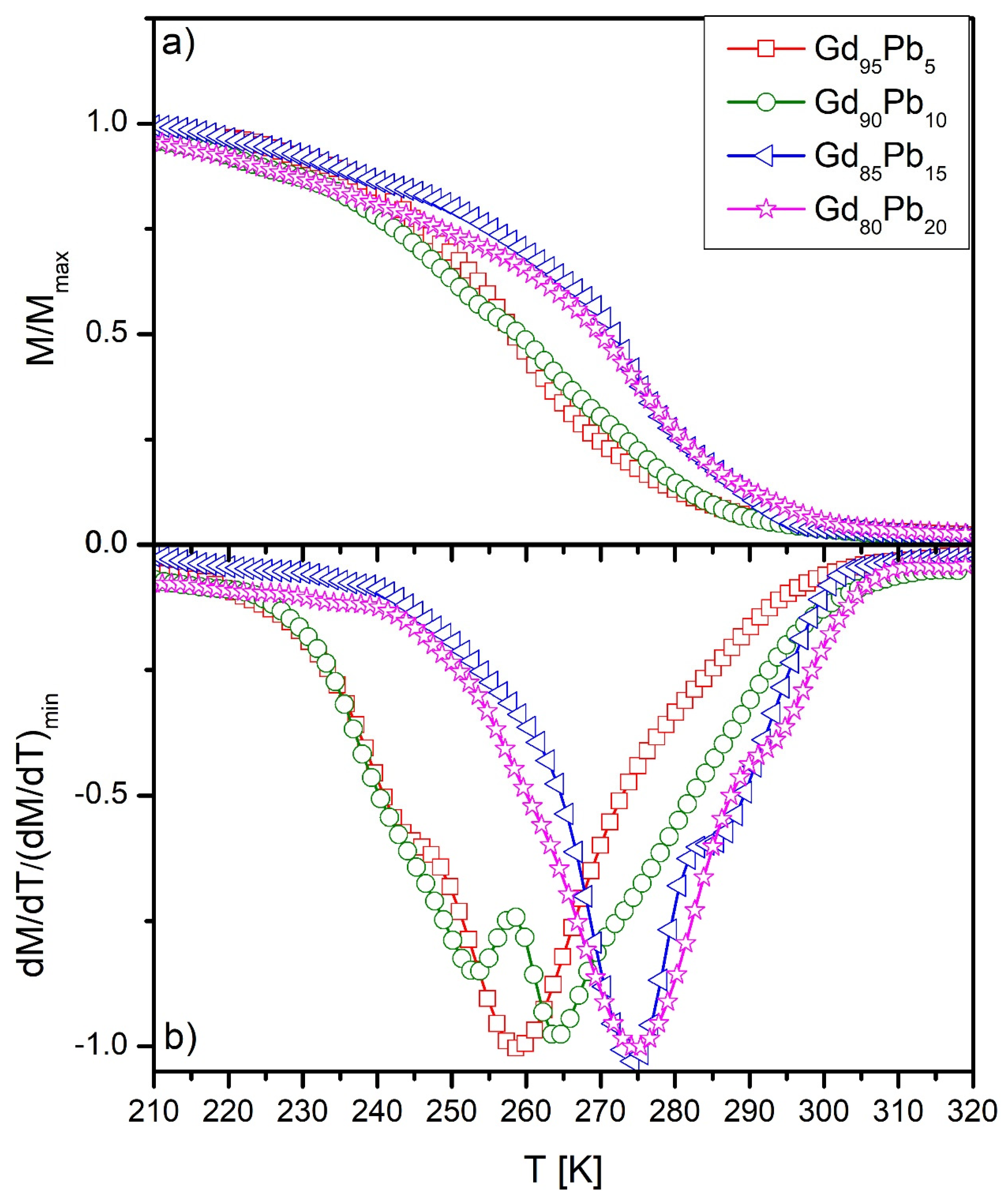
| Alloy | Phases | TC [K] |
|---|---|---|
| Gd95Pb5 | Gd(Pb) | 258 |
| Gd5Pb3 | 243 | |
| Gd90Pb10 | Gd(Pb) | 263 |
| Gd5Pb3 | 252 | |
| Gd85Pb15 | Gd(Pb) | 285 |
| Gd5Pb3 | 274 | |
| Gd80Pb20 | Gd(Pb) | 293 |
| Gd5Pb3 | 275 |
| Alloy | Δ(μ0H) [T] | ΔSM [J (kg K)−1] | RC [J kg−1] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gd95Pb5 | 1 | 1.61 | 59 |
| 2 | 3.04 | 130 | |
| 3 | 4.32 | 189 | |
| 4 | 5.41 | 315 | |
| 5 | 6.36 | 372 | |
| Gd90Pb10 | 1 | 1.03 | 54 |
| 2 | 2.12 | 115 | |
| 3 | 3.11 | 192 | |
| 4 | 4.04 | 252 | |
| 5 | 4.81 | 336 | |
| Gd85Pb15 | 1 | 1.21 | 46 |
| 2 | 2.29 | 90 | |
| 3 | 3.14 | 149 | |
| 4 | 3.93 | 190 | |
| 5 | 4.58 | 239 | |
| Gd80Pb20 | 1 | 0.74 | 26 |
| 2 | 1.45 | 54 | |
| 3 | 2.12 | 88 | |
| 4 | 2.69 | 116 | |
| 5 | 3.25 | 164 |
| Material | ΔSM [J/(kg K)] | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| Gd95Pb5 | 3.04 | This work |
| Gd90Pb10 | 2.12 | This work |
| Gd85Pb15 | 2.29 | This work |
| Gd80Pb20 | 1.45 | This work |
| Gd95Pd5 | 5.25 | [14] |
| Gd90Pd10 | 4.51 | [14] |
| Gd85Pd15 | 4.23 | [14] |
| Gd80Pd20 | 3.15 | [14] |
| Pure Gd | 4.98 | [10] |
| Gd75Zn25 | 3.29 | [10] |
| Gd65Zn35 | 3.11 | [10] |
| Gd55Zn45 | 3.42 | [10] |
| Gd50Zn50 | 3.25 | [10] |
| Ni44.5Mn35.5In13.5Co4Cu2.5 | 11.22 | [29] |
| Mn1.87Cr0.13Sb0.95Ga0.05 | 2.98 | [30] |
| Gd95Pb5 | Gd90Pb10 | Gd85Pb15 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
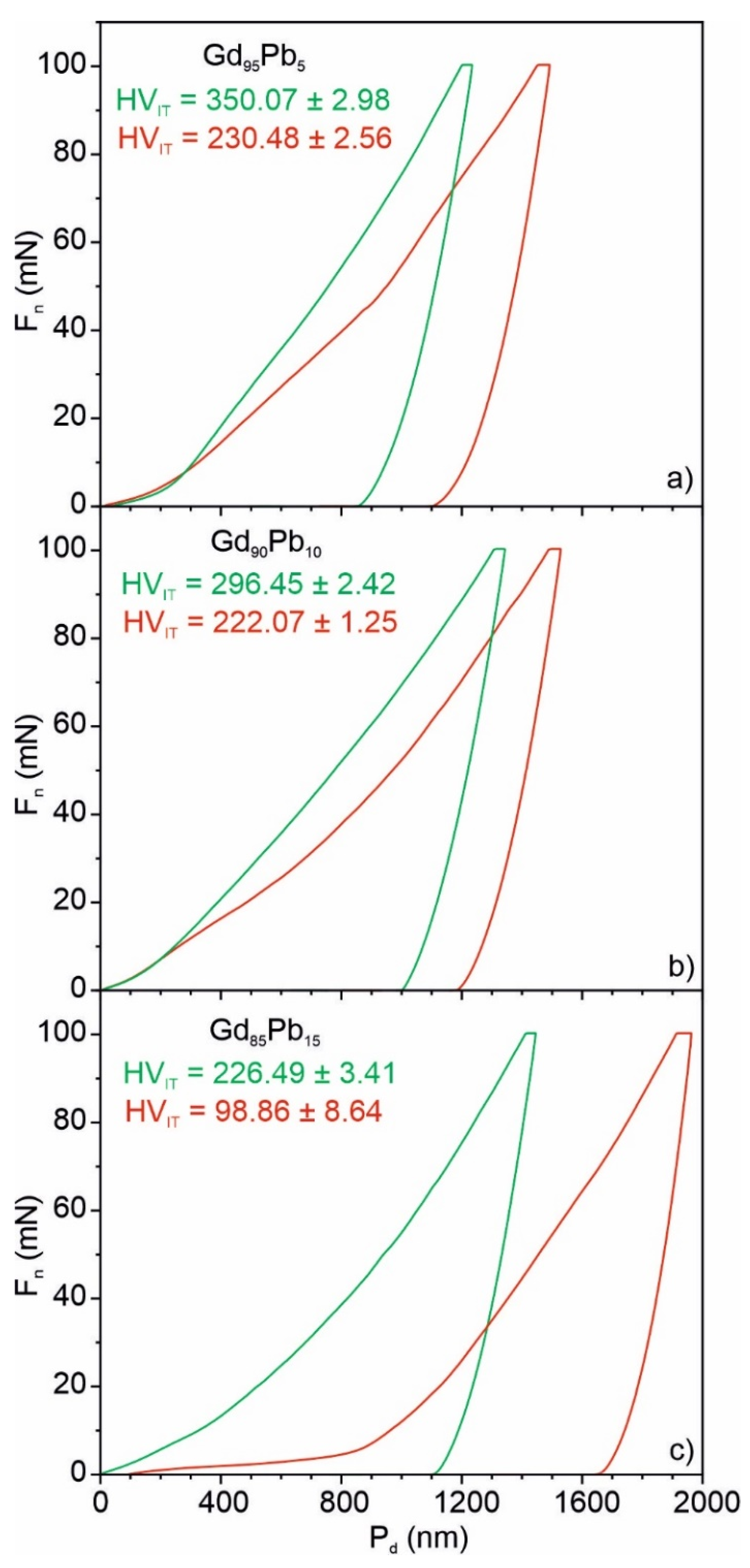
| HVIT (Vickers) | 1st component (red) (Phase) | 230.48 ± 2.56 (Gd95.73Pb4.27) | 222.07 ± 1.25 (Gd96.71Pb3.29) | 98.86 ± 8.64 (Gd70.38Pb29.62) |
| 2nd component (green) (Phase) | 350.07 ± 2.98 (Gd88.06Pb11.94) | 296.45 ± 2.42 (Gd82.48Pb17.52) | 226.49 ± 3.41 (Gd96.86Pb3.14) | |
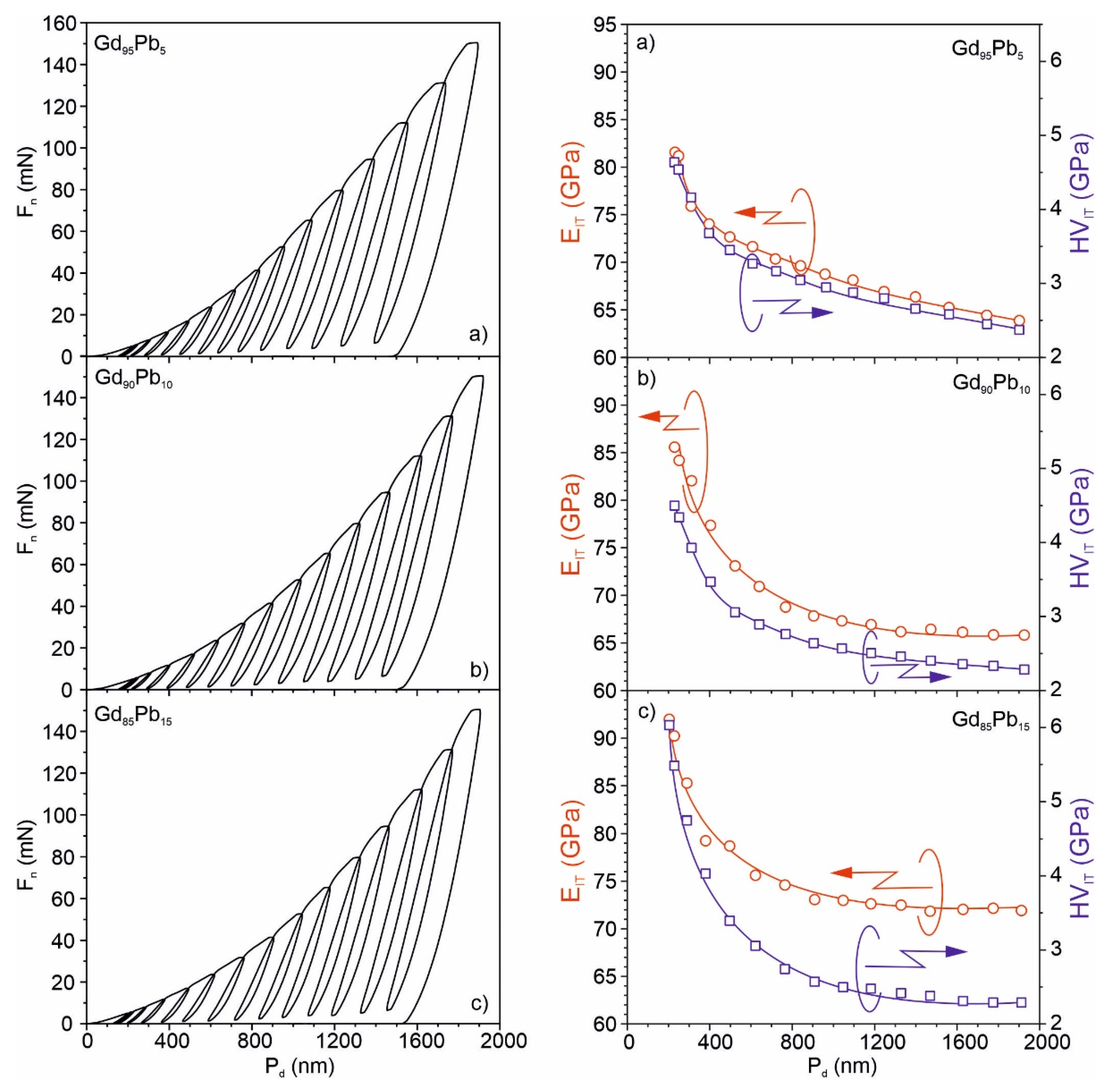
| EIT (GPa) | 1st component (red) (Phase) | 65.27 ± 0.15 (Gd95.73Pb4.27) | 61.15 ± 0.11 (Gd82.48Pb17.52) | 58.93 ± 7.61 (Gd70.38Pb29.62) |
| 2nd component (green) (Phase) | 77.67 ± 0.08 (Gd88.06Pb11.94) | 66.33 ± 0.21 (Gd96.71Pb3.29) | 69.52 ± 0.51 (Gd96.86Pb3.14) | |
| nIT (%) | 1st component (red) (Phase) | 19.22 ± 0.18 (Gd88.06Pb11.94) | 20.98 ± 0.29 (Gd96.71Pb3.29) | 21.69 ± 0.04 (Gd96.86Pb3.14) |
| 2nd component (green) (Phase) | 21.51 ± 0.24 (Gd95.73Pb4.27) | 24.73 ± 0.28 (Gd82.48Pb17.52) | 25.12 ± 0.17 (Gd70.38Pb29.62) | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gębara, P.; Hasiak, M.; Kovac, J.; Rajnak, M. Entalpy of Mixing, Microstructure, Structural, Thermomagnetic and Mechanical Properties of Binary Gd-Pb Alloys. Materials 2022, 15, 7213. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15207213
Gębara P, Hasiak M, Kovac J, Rajnak M. Entalpy of Mixing, Microstructure, Structural, Thermomagnetic and Mechanical Properties of Binary Gd-Pb Alloys. Materials. 2022; 15(20):7213. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15207213
Chicago/Turabian StyleGębara, Piotr, Mariusz Hasiak, Jozef Kovac, and Michal Rajnak. 2022. "Entalpy of Mixing, Microstructure, Structural, Thermomagnetic and Mechanical Properties of Binary Gd-Pb Alloys" Materials 15, no. 20: 7213. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15207213
APA StyleGębara, P., Hasiak, M., Kovac, J., & Rajnak, M. (2022). Entalpy of Mixing, Microstructure, Structural, Thermomagnetic and Mechanical Properties of Binary Gd-Pb Alloys. Materials, 15(20), 7213. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15207213






