Glass-Forming Ability and Corrosion Behavior of Ti-Based Amorphous Alloy Ti-Zr-Si-Fe
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedures
3. Results and Discussion
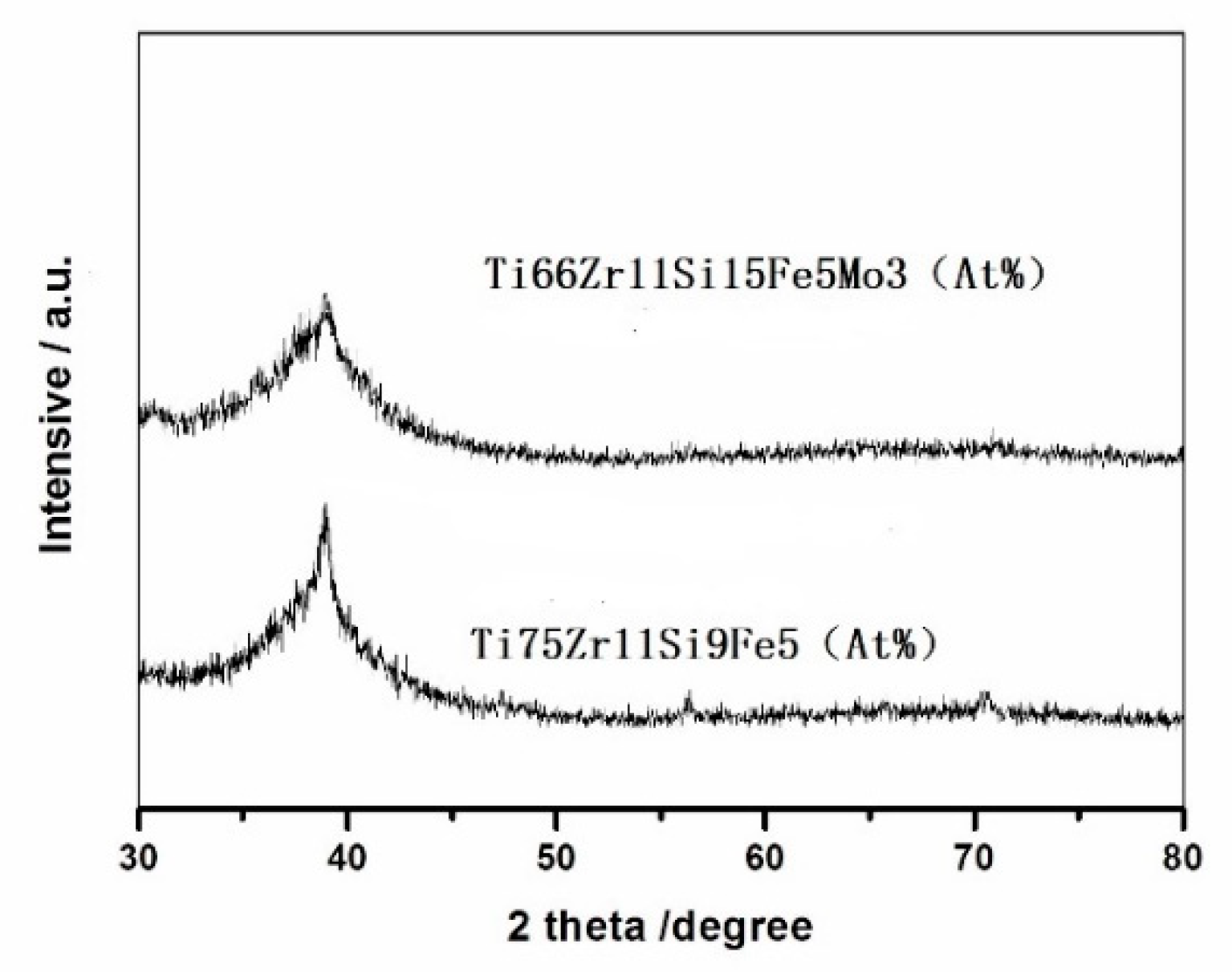
3.1. Amorphous Structure of the Melt-Spun
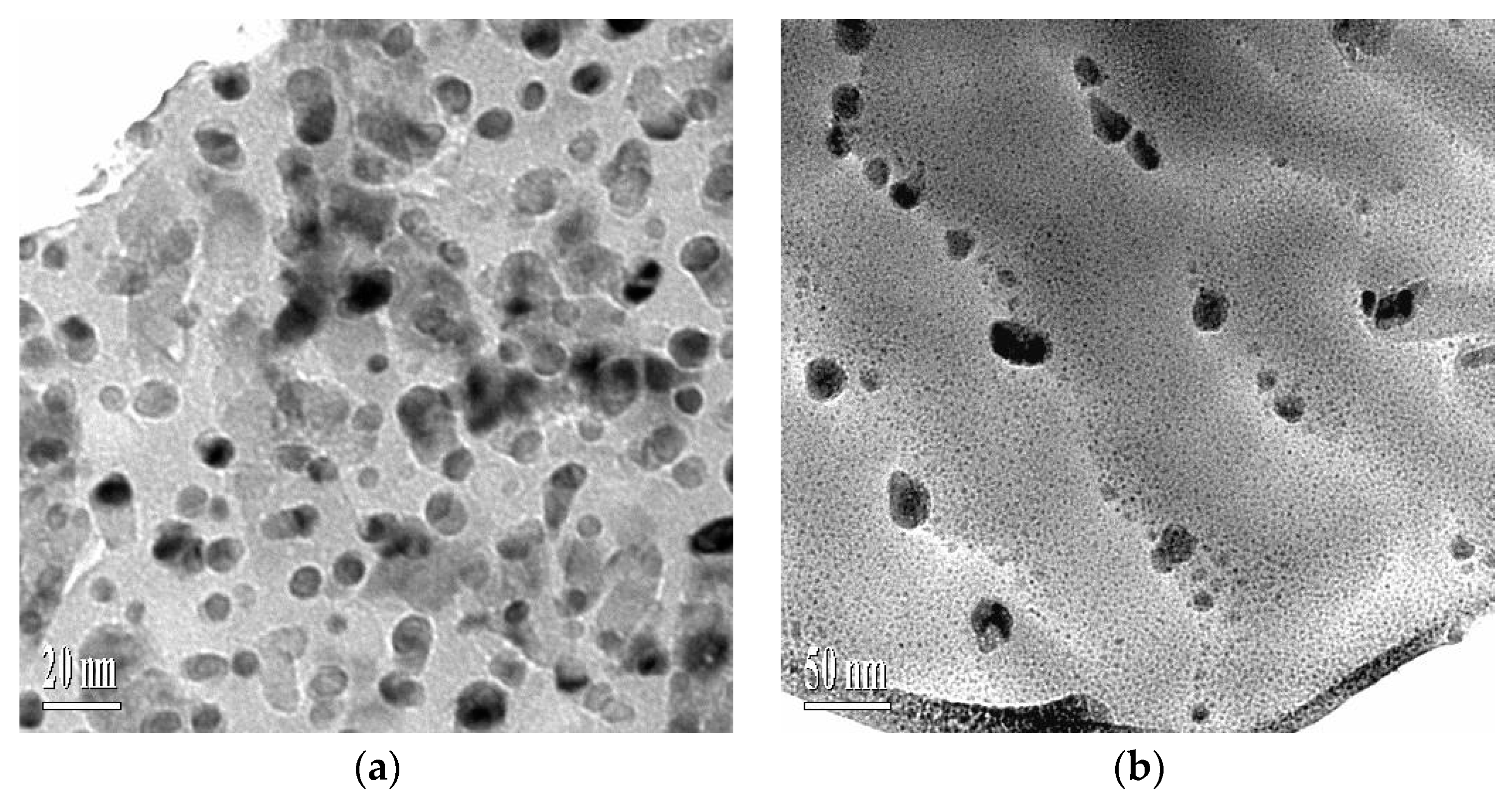
3.2. Microstructure Morphologies
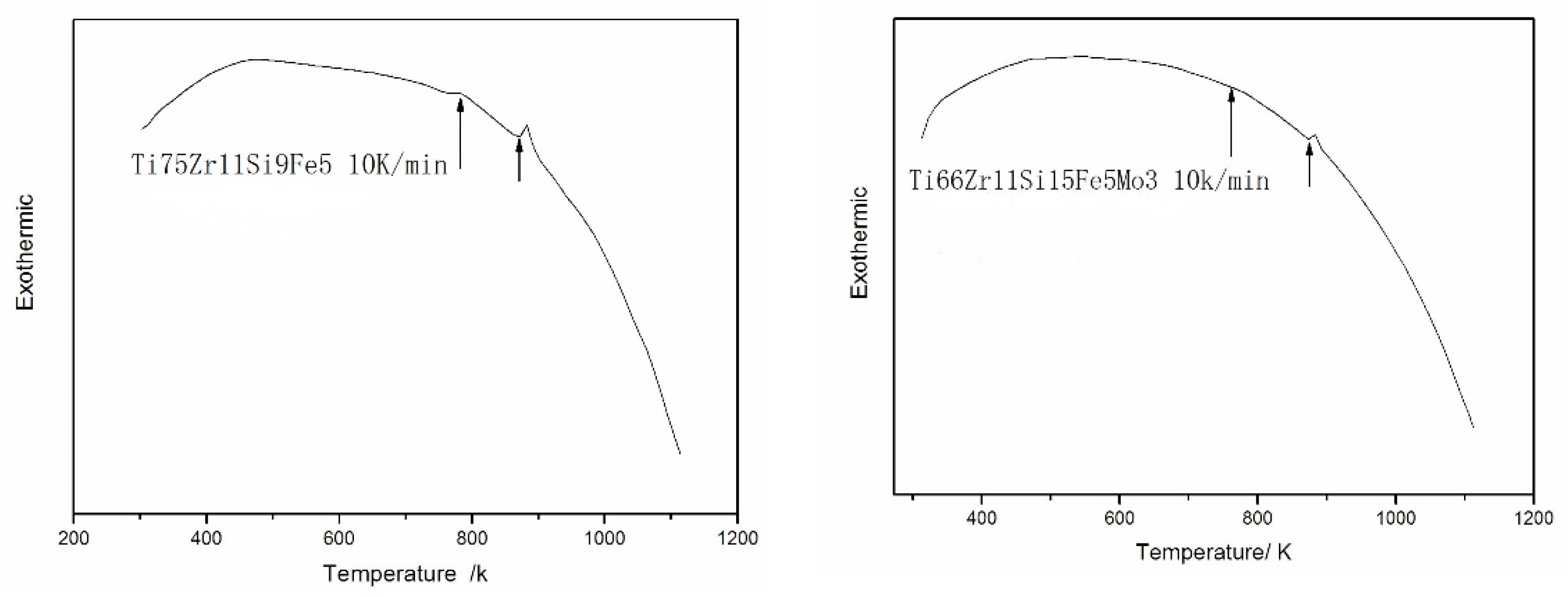
3.3. Analysis of DSC
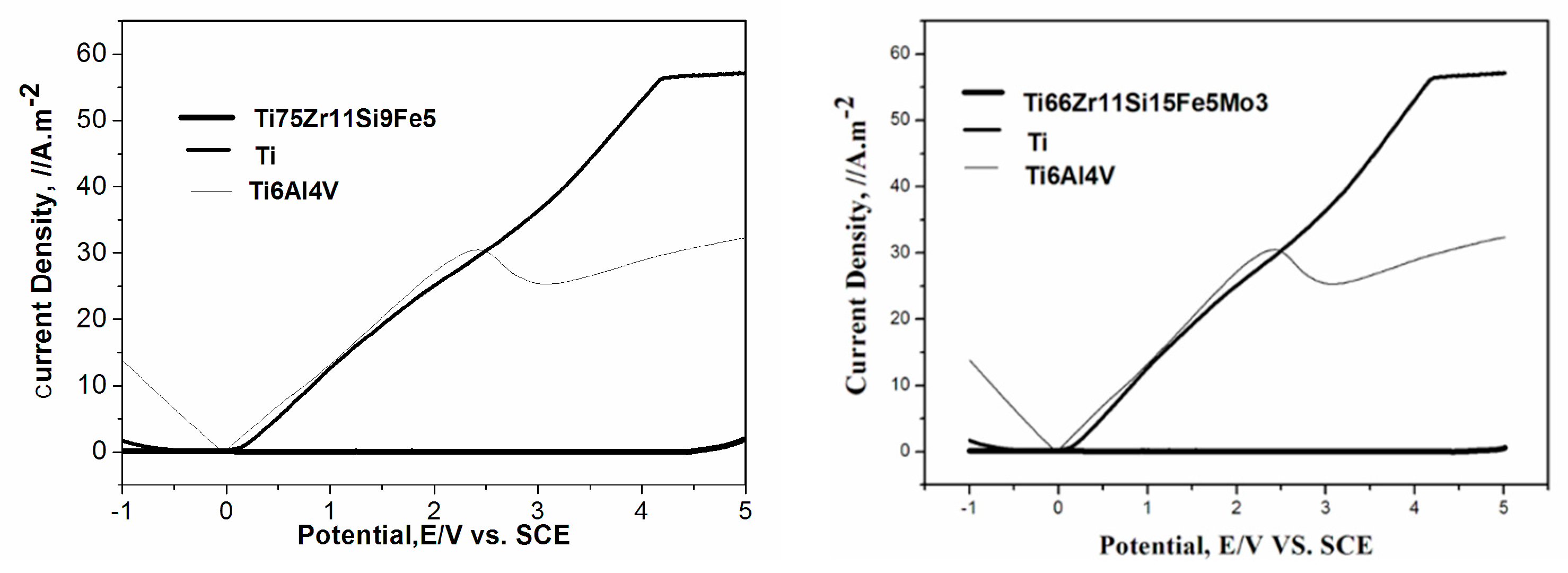
3.4. The Potentiodynamic Polarization Curve
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Ti−based alloys with nominal compositions of Ti75Zr11Si9Fe5 (At %) and Ti66Zr11Si15Fe5Mo3 (At %) have excellent amorphous-forming ability, which both satisfies the three empirical rules.
- (2)
- Both 75Zr11Si9Fe5 (At %) and Ti66Zr11Si15Fe5Mo3 (At %) amorphous alloys have a large, supercooled liquid region before crystallization, which is important to the amorphous-forming ability of the alloys.
- (3)
- The addition of Si and Mo improve the amorphous-forming ability of Ti66Zr11Si15Fe5Mo3 (At %) alloy.
- (4)
- Both 75Zr11Si9Fe5 (At %) and Ti66Zr11Si15Fe5Mo3 (At %) possess relatively excellent corrosion resistance, compared with pure Ti and Ti6Al4V alloys.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Straumal, B.B.; Gornakova, A.S.; Kilmametov, A.R.; Rabkin, E.; Anisimova, N.Y.; Kiselevskiy, M.V. β-Ti-Based Alloys for Medical Applications. Russ. J. Non-Ferr. Met. 2021, 62, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.D. Titanium and Its alloys for biomedical applications. Metals 2021, 11, 1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarka, M.; Dikici, B.; Niinomi, M.; Ezirmik, K.V.; Nakai, M.; Yilmazer, H. A systematic study of β-type Ti-based PVD coatings on magnesium for biomedical application. Vacuum 2021, 183, 109850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Shang, T.; Xian, H.; Sun, B.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, Q.; Bai, H.; Gu, L.; Wang, W. Structures and Functional Properties of Amorphous Alloys. Small Struct. 2020, 2, 2000057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cai, W.; Li, D.-S.; Xu, J.; Tao, H.; Liu, B. Amorphous alloys for electrocatalysis: The significant role of the amorphous alloy structure. Nano Res. 2021, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, T. Application of 3D Balanced Growth Theory to the Formation of Bulk Amorphous Alloys. Front. Mater. 2021, 8, 694920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Shi, T.; Yu, W.; Shao, J.; Zhou, X.; He, Y.; Zhang, B. Preparation and electrochemical characterization of Ti-based amorphous metallic glass with high strength. Mater. Corros. 2020, 72, 951–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Wei, D.; Li, C.; Liu, L.; Zhou, Q.; Wu, F. Influence of laser pulse on solidification of molten pool during laser welding of dissimilar Ti-based amorphous alloys. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2021, 26, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Jiao, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z. Strain-rate effect on yielding behavior of an in-situ Ti-based metallic glass matrix composite upon dynamic compression. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 815, 141267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Q.; Zhou, Q.; Ren, Y.; Du, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wang, X.-Z.; Wang, H.; Beake, B.D.; Zhou, F. Tribological characteristics of Ti-based bulk metallic glass via deep cryogenic-cycling treatment. Mater. Charact. 2021, 179, 111356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yin, D.; Lv, J.; Zhang, S.; Ma, M.; Zhang, X.; Liu, R. Effect on microstructure and plastic deformation behavior of a Zr-based amorphous alloy by cooling rate control. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 82, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Bai, L.; Liu, S.; Qi, Y.; Zhao, L. Ti 5 Si 3/β-Ti nano-core–shell structure toughened glassy Ti alloy matrix biocomposites. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 8355–8361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.S.; Yang, Y.J.; Zhang, Z.P.; Ma, X.Z.; Lv, J.W.; Wang, F.L.; Ma, M.Z.; Zhang, X.Y.; Liu, R.P. Effect of Hf substitution Cu on glass-forming ability, mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of Ni-free Zr–Ti–Cu–Al bulk metallic glasses. J. Alloy. Compd. 2019, 806, 668–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, F.; Sun, T.; Song, W.; Peng, C.; Sun, H.; Gong, J.; Song, K. A bridge from metallic glasses to medium-entropy alloys in Ti-Cu-Zr-Pd-Co system: Design, microstructure, and deformation-induced-martensitic transformation. J. Non-Crystalline Solids 2022, 587, 121608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Lee, H.J.; Baek, J.H.; Park, S.S.; Lee, J.G. Microstructural and Corrosion Properties of Ti-to-Zr Dissimilar Alloy Joints Brazed with a Zr-Ti-Cu-Ni Amorphous Filler Alloy. Metals 2021, 11, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.; Hu, R.; Qi, J.; He, Y.; Meng, Q.; Wei, F.; Ren, Y.; Sui, Y. Fabrication and Degradation Properties of Nanoporous Copper with Tunable Pores by Dealloying Amorphous Ti-Cu Alloys with Minor Co Addition. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2021, 30, 1759–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.C.; Dai, F.P.; Yang, X.Y.; Ruan, Y.; Wei, B.B. Effect of Sn and Al additions on the microstructure and mechanical properties of amorphous Ti–Cu–Zr–Ni alloys. Chin. Phys. B 2020, 29, 066401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Feng, K.; Zhang, W.; Mao, Y. Microstructural and mechanical properties of CFC composite/Ti6Al4V joints brazed with Ag–Cu–Ti and refractory metal foils. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2021, 21, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, Y.; Vincent, S.; Bhatt, J. Thermodynamic modelling to optimize glass forming composition in multicomponent Zr-Cu-Co-Al system. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 28, 1239–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louzguine-Luzgin, D.V. High-strength Ti-based alloys containing Fe as one of the main alloying elements. Mater. Trans. 2018, M2018114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.J.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, T.K.; Hong, S.H.; Wang, W.M.; Choi, T.J.; Kim, K.B. Formation of photo-reactive heterostructure from a multicomponent amorphous alloy with atomically random distribution. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 109, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, A.; Inoue, A. Classificaion of Bulk Metallic Glasses by Atomic Size Difference, Heat of Mixing and Period of Constituent Elements and Its Application to Characterization of the Main Alloying Element. Mater. Trans. 2005, 46, 2817–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, W.C.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Hyun, J.I.; Hong, S.H.; Kim, W.T.; Kim, D.H. Enhancement of superelastic property in Ti–Zr–Ni–Cu alloy by using glass alloy precursor with high glass forming ability. Acta Mater. 2019, 173, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiorova, A.V.; Kulikova, T.V.; Bykov, A.S. New criteria for predicting compositions with high glass-forming ability in Zr–Co–Al alloys. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2022, 594, 121812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, J.S.; Miska, J.P.; Lei, F.; AuYeung, N.; Xu, D. Hafnium based metallic glasses with high density and high glass-forming ability. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 882, 160896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, E. Unusual dislocation behavior in high-entropy alloys. Scr. Mater. 2020, 181, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boer, F.R.; Perrifor, D.G. Cohesion in Metals; Elsevier Science Publishers B. V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, X.; Liu, Z.; Wu, G.; Tong, X.; Xiong, Y.; Cheng, X.; Wang, X.; Yamaguchi, T. Microstructure and high-temperature properties of laser cladded AlCoCrFeNiTi0.5 high-entropy coating on Ti 6Al-4V alloy. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 418, 127243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaRosa, C.R.; Shih, M.; Varvenne, C.; Ghazisaeidi, M. Solid solution strengthening theories of high-entropy alloys. Mater. Charact. 2019, 151, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luan, H.; Zhang, X.; Ding, H.; Zhang, F.; Luan, J.H.; Jiao, Z.B.; Yang, Y.-C.; Bu, H.; Wang, R.; Gu, J.; et al. High-entropy induced a glass-to-glass transition in a metallic glass. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocchetta, P.; Chen, L.Y.; Tardelli, J.D.C.; Reis, A.C.D.; Almeraya-Calderón, F.; Leo, P. Passive Layers and Corrosion Resistance of Biomedical Ti-6Al-4V and β-Ti Alloys. Coatings 2021, 11, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Element | Ti | Zr | Fe | Si | Mo |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atomic radii | 0.417 | 0.162 | 0.124 | 0.117 | 0.136 |
| Ti | Zr | Fe | Si | Mo | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti | 0 | 0 | −17 | −66 | −4 |
| Zr | 0 | 0 | −25 | −84 | −6 |
| Fe | −17 | −25 | 0 | −35 | −2 |
| Si | −66 | −84 | −35 | 0 | −35 |
| Mo | −4 | −6 | −2 | −35 | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bai, L.; Ding, Z.; Zhang, H.; Cui, C. Glass-Forming Ability and Corrosion Behavior of Ti-Based Amorphous Alloy Ti-Zr-Si-Fe. Materials 2022, 15, 7229. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15207229
Bai L, Ding Z, Zhang H, Cui C. Glass-Forming Ability and Corrosion Behavior of Ti-Based Amorphous Alloy Ti-Zr-Si-Fe. Materials. 2022; 15(20):7229. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15207229
Chicago/Turabian StyleBai, Ling, Ziyang Ding, Haiying Zhang, and Chunxiang Cui. 2022. "Glass-Forming Ability and Corrosion Behavior of Ti-Based Amorphous Alloy Ti-Zr-Si-Fe" Materials 15, no. 20: 7229. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15207229
APA StyleBai, L., Ding, Z., Zhang, H., & Cui, C. (2022). Glass-Forming Ability and Corrosion Behavior of Ti-Based Amorphous Alloy Ti-Zr-Si-Fe. Materials, 15(20), 7229. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15207229





