Hydrotalcite-Modified Clinoptilolite as the Catalyst for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NO with Ammonia (NH3-SCR)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of the Catalysts
2.2. Characterization of the Catalysts
2.3. Catalytic Tests
3. Results
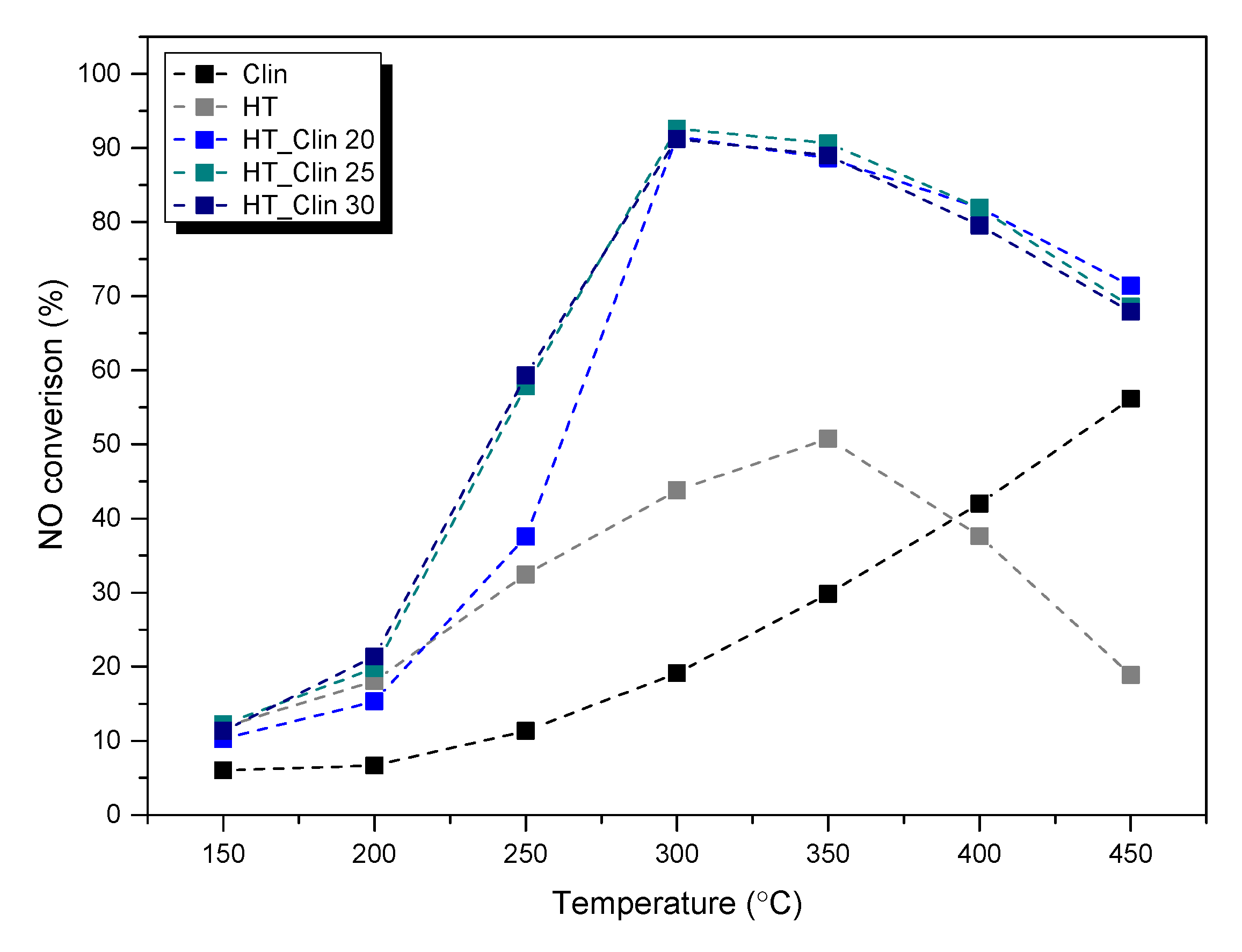
3.1. Catalytic Tests
Catalytic Performance of Fresh HT-Clinoptilolite
3.2. Characterization of the Catalysts
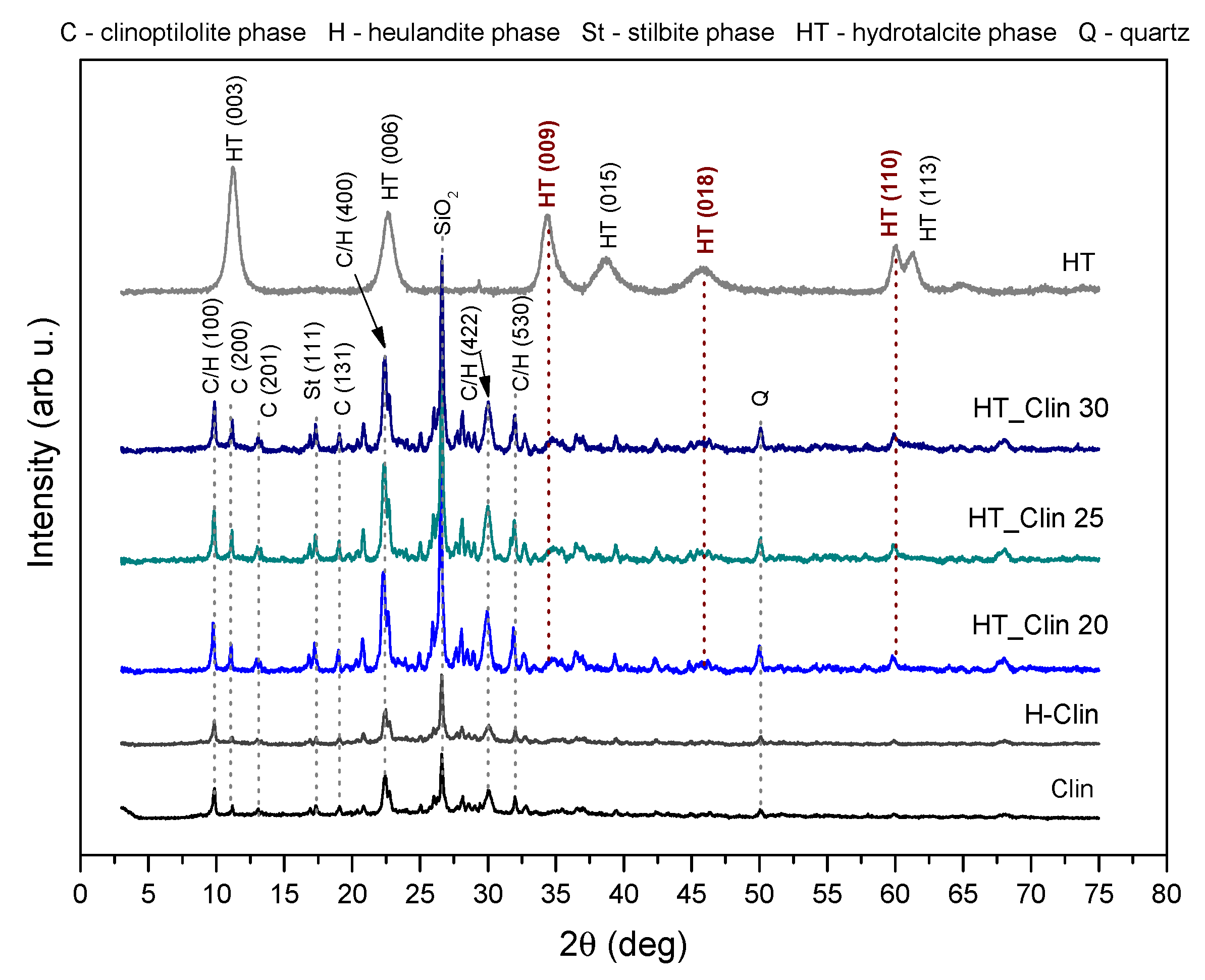
3.2.1. Chemical Composition and Crystallinity of the Samples
3.2.2. Textural and Surface Properties of the Samples
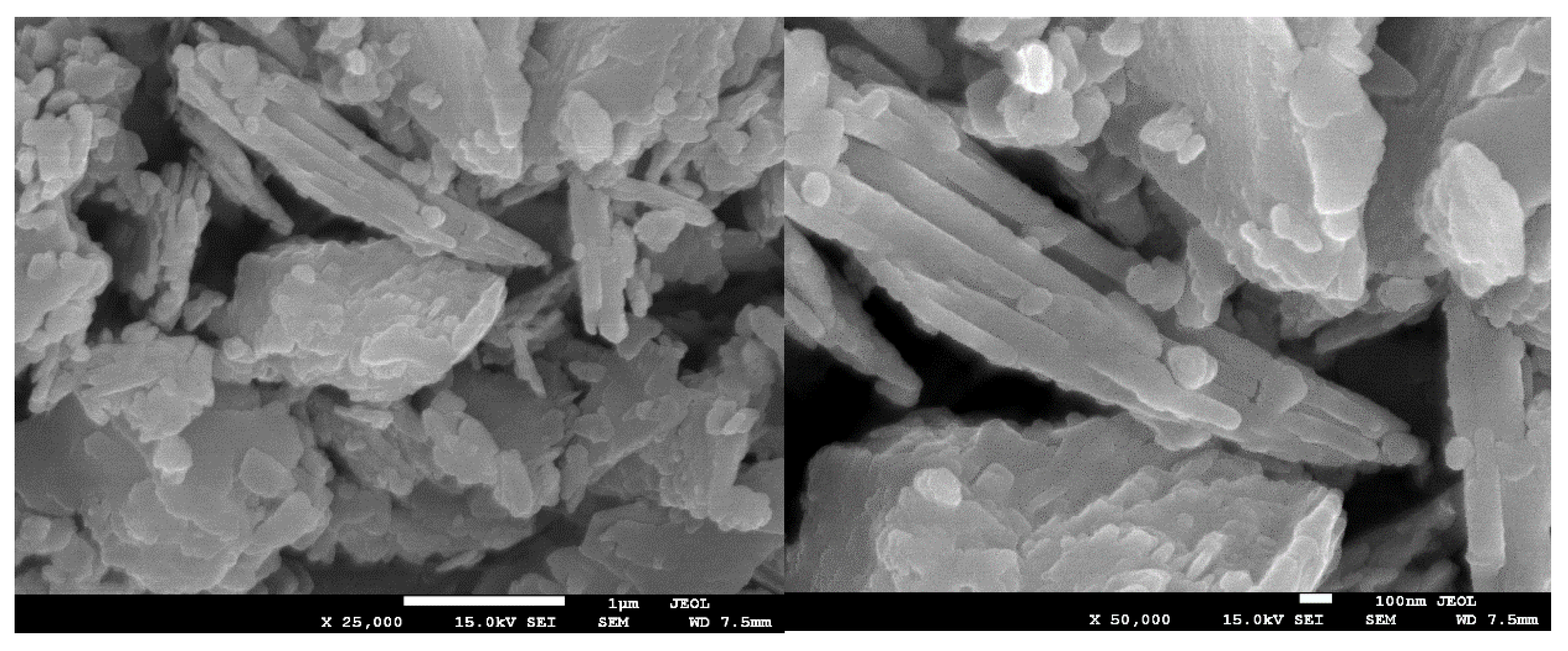
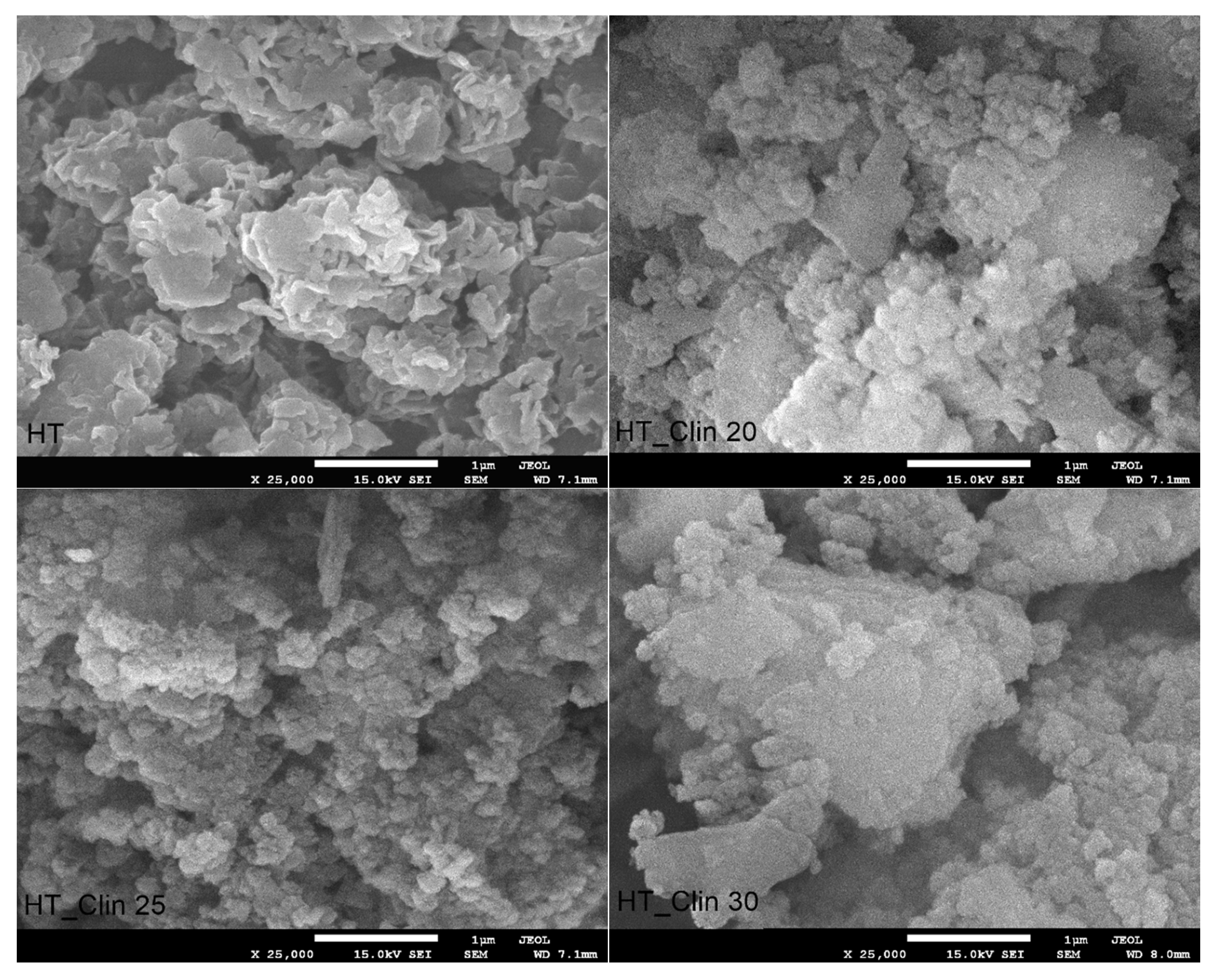
3.2.3. Morphology of the Samples
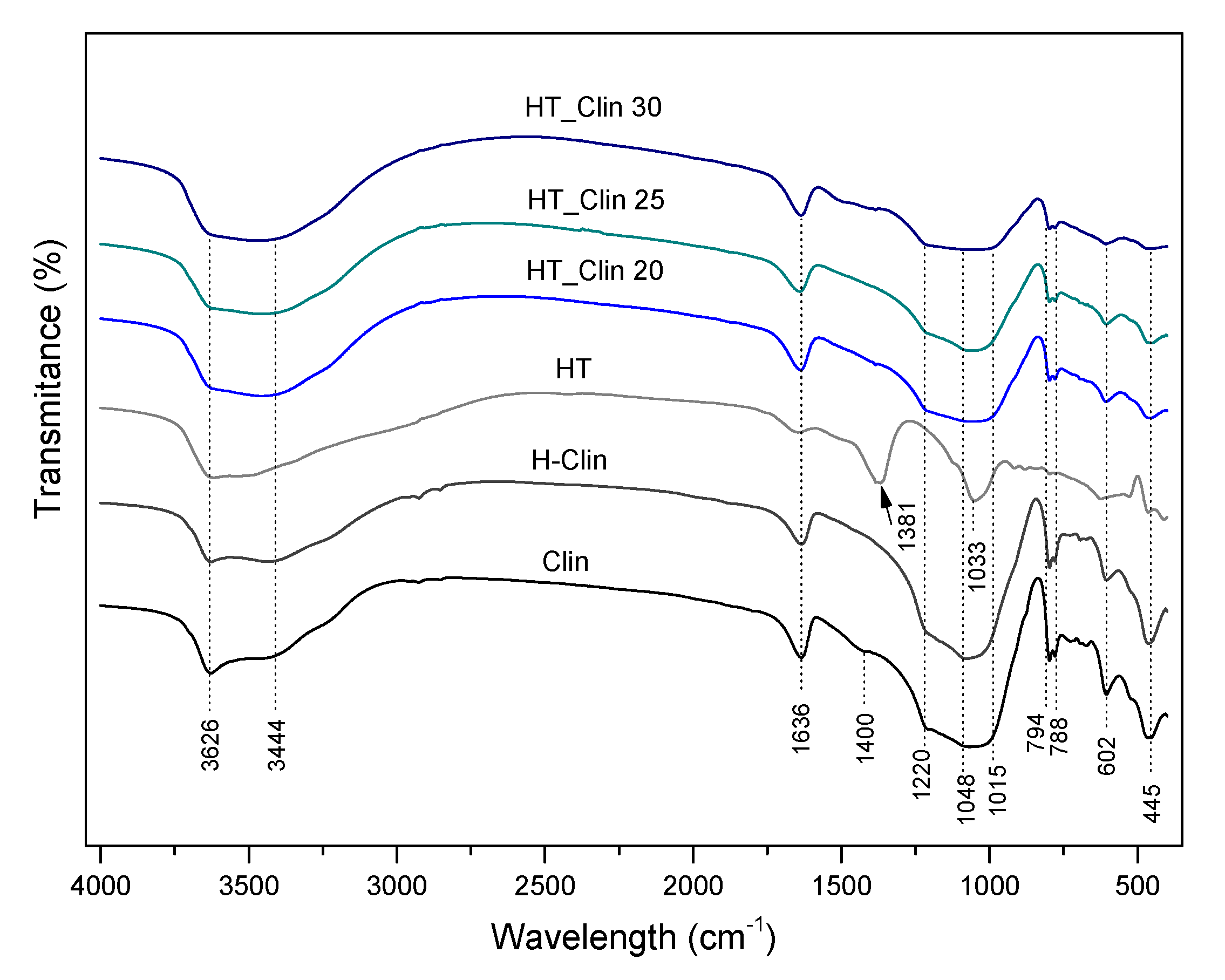
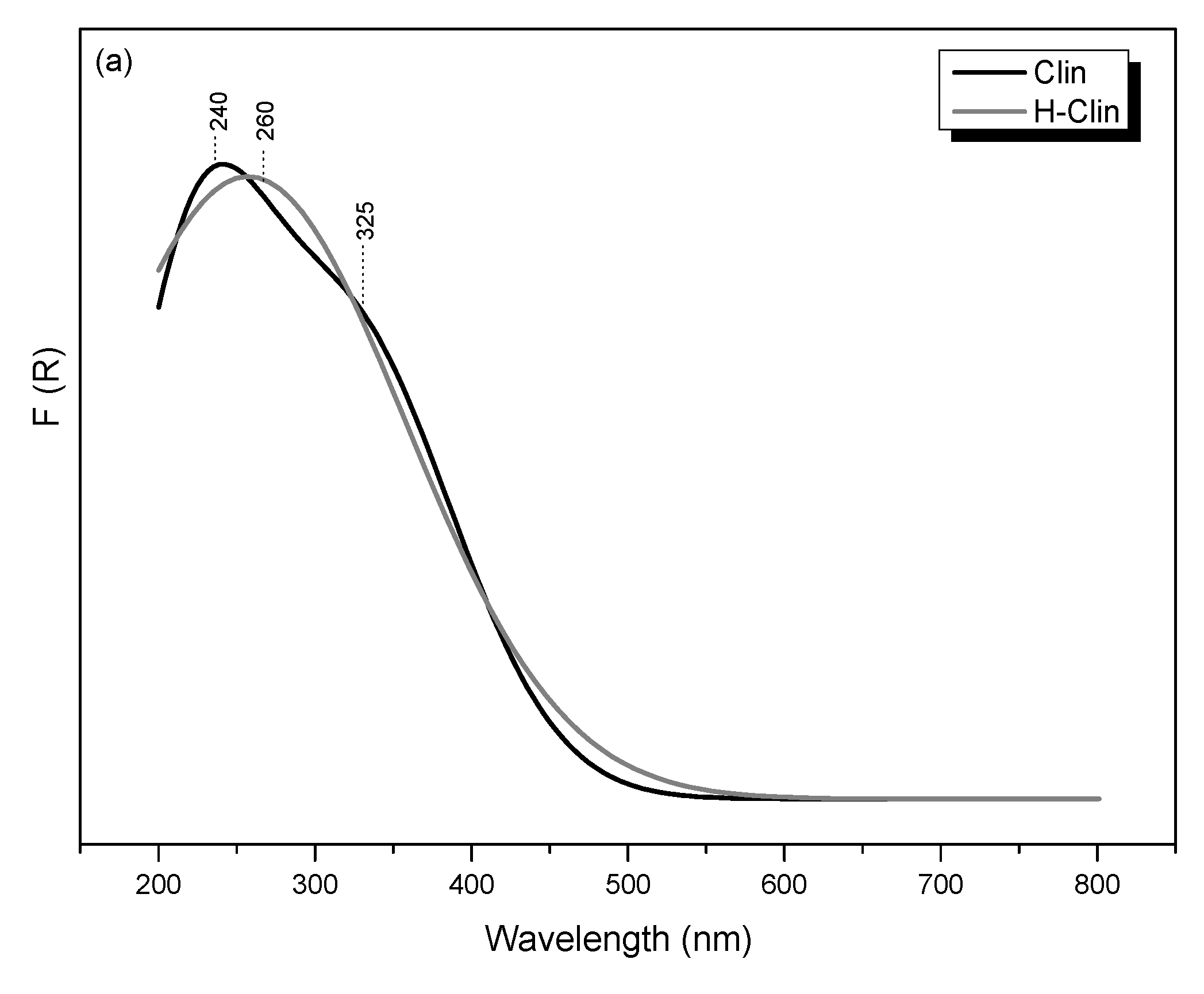
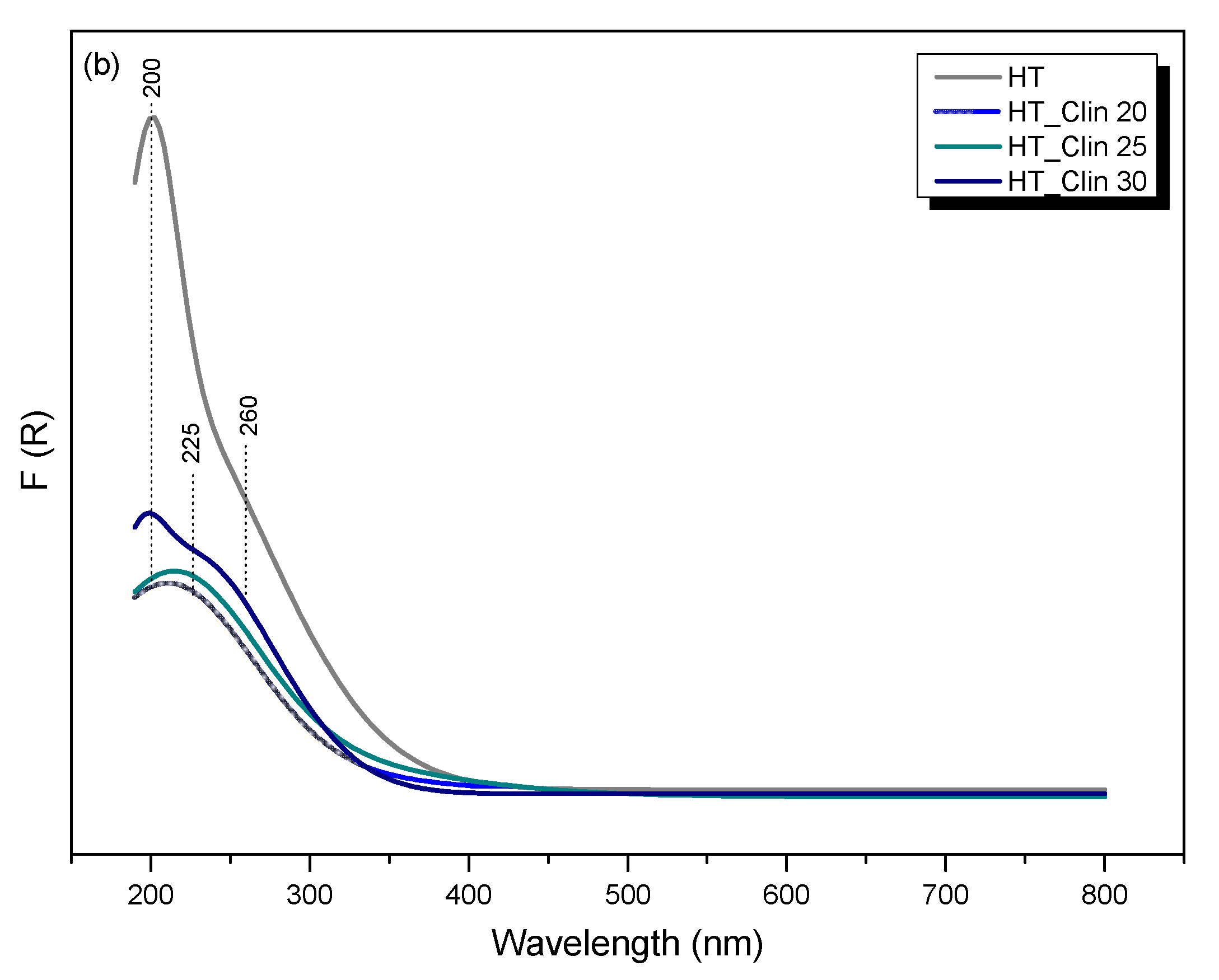
3.2.4. Characteristic Chemical Groups in the Samples
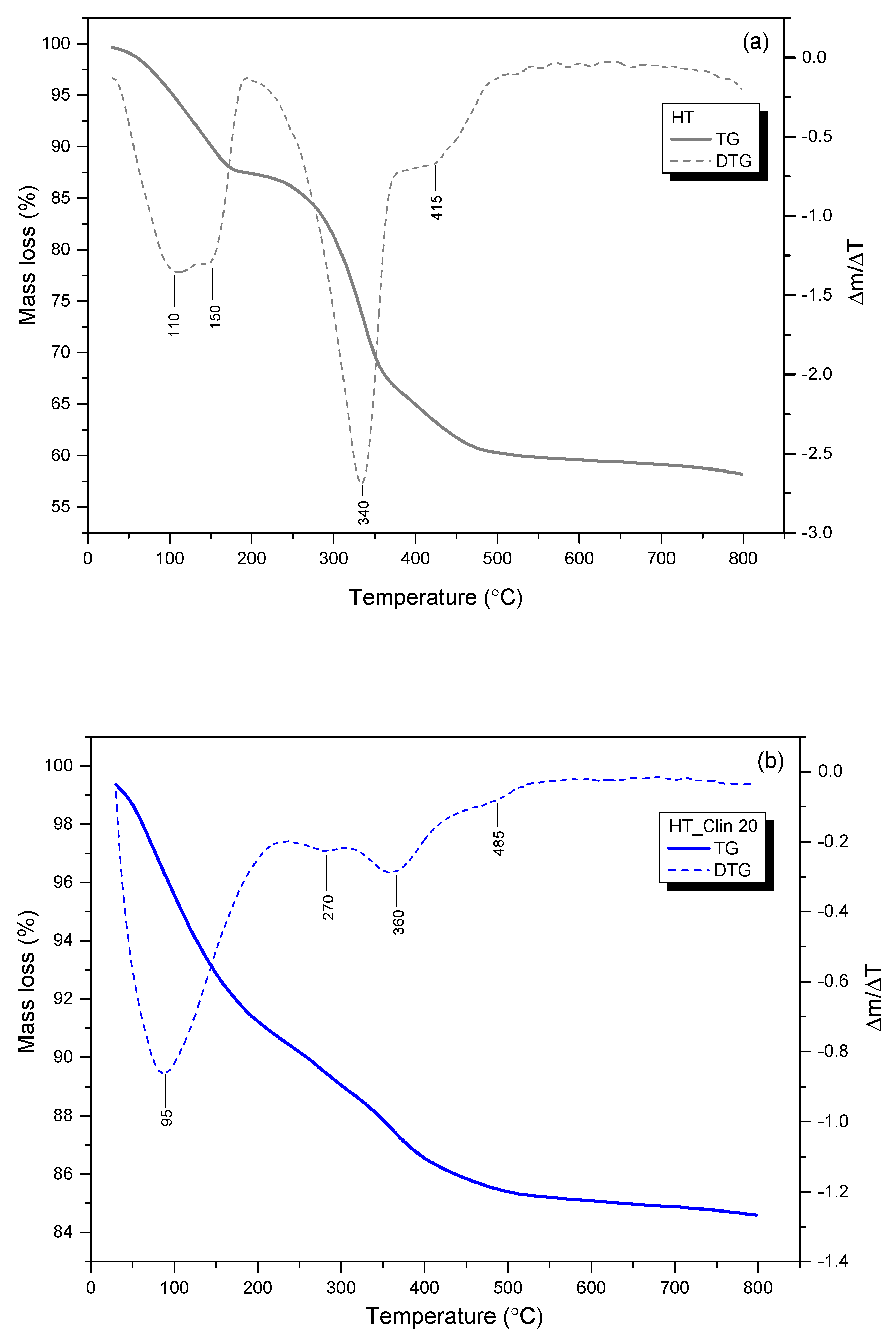
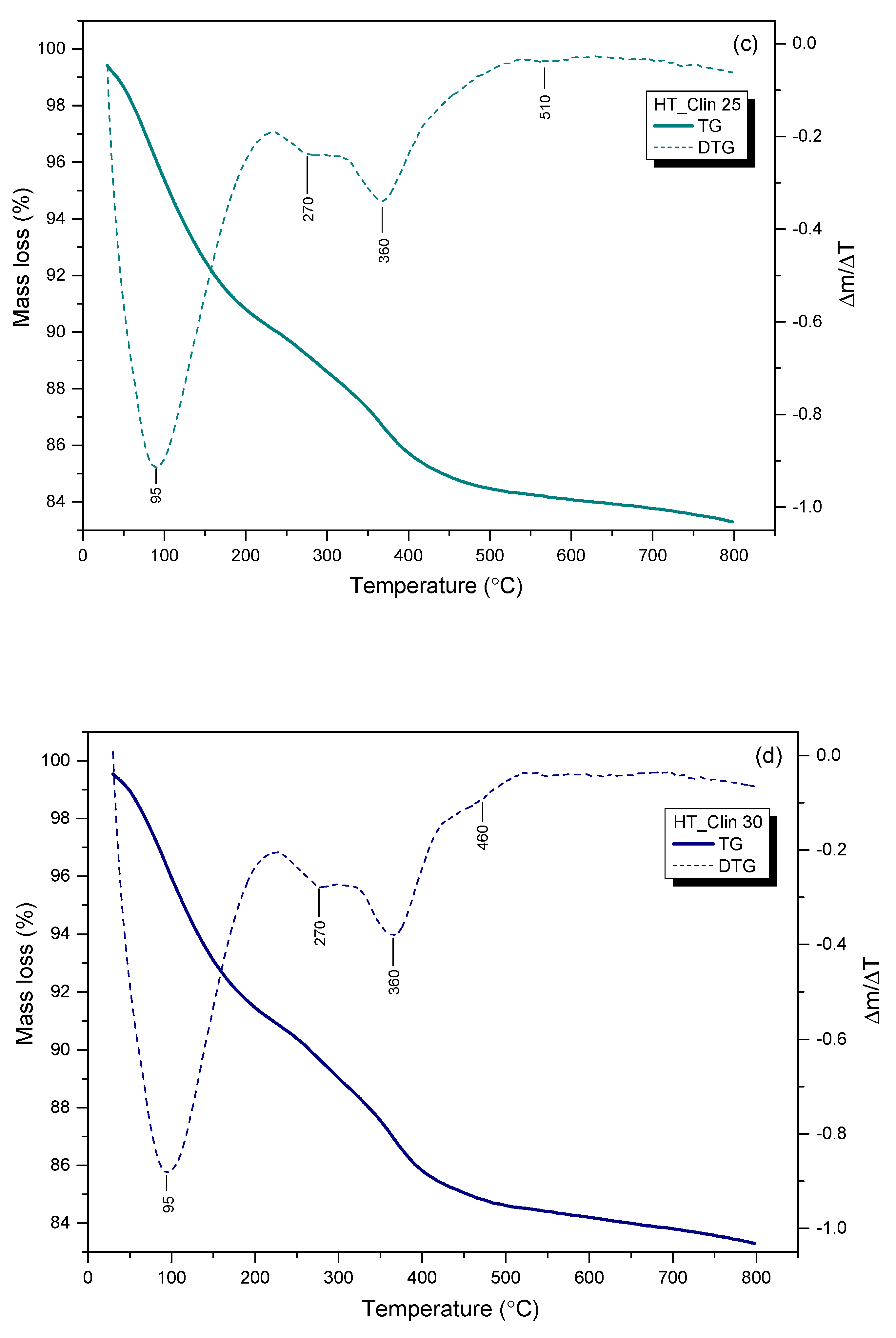
3.2.5. Thermal Stability of the Samples
3.2.6. Speciation of Metals in the Samples
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cavani, F.; Trifirò, F.; Vaccari, A. Hydrotalcite-type anionic clays: Preparation, properties and applications. Catal. Today 1991, 11, 173–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forano, C.; Costantino, U.; Prévot, V.; Gueho, C.T. Layered double hydroxides (LDH). In Handbook of Clay Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 5, ISBN 9780080982588. [Google Scholar]
- Summa, P.; Świrk, K.; Wierzbicki, D.; Motak, M.; Alxneit, I.; Rønning, M.; Da Costa, P. Co-precipitated ni-mg-al hydrotalcite-derived catalyst promoted with vanadium for CO2 methanation. Molecules 2021, 26, 6506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, T.; Bosch, P.; Ramos, E.; Gomez, R.; Novaro, O.; Acosta, D.; Figueras, F. Synthesis and characterization of sol-gel hydrotalcites. Structure and texture. Langmuir 1996, 12, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooli, F.; Rives, V.; Ulibarri, M.A. Preparation and Study of Decavanadate-Pillared Hydrotalcite-like Anionic Clays Containing Transition Metal Cations in the Layers. 1. Samples Containing Nickel-Aluminum Prepared by Anionic Exchange and Reconstruction. Inorg. Chem. 1995, 34, 5114–5121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutmann, N.; Müller, B. Insertion of the dinuclear dihydroxo-bridged Cr(III) aquo complex into the layered double hydroxides of hydrotalcite-type. J. Solid State Chem. 1996, 122, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabłońska, M.; Arán, M.A.; Beale, A.M.; Delahay, G.; Petitto, C.; Nocuń, M.; Palkovits, R. Understanding the origins of N2O decomposition activity in Mn(Fe)CoAlOx hydrotalcite derived mixed metal oxides. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2019, 243, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabłońska, M.; Nothdurft, K.; Nocuń, M.; Girman, V.; Palkovits, R. Redox-performance correlations in Ag–Cu–Mg–Al, Ce–Cu–Mg–Al, and Ga–Cu–Mg–Al hydrotalcite derived mixed metal oxides. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 207, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Zou, R.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ran, M.; Xin, Q.; Yang, Y.; Song, H.; Wu, W.; Liu, S.; et al. Mechanism and Enhancement of the Low-Temperature Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx with NH3 by Bifunctional Catalytic Mixtures. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 6446–6454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymaszek, A.; Samojeden, B.; Motak, M. The Deactivation of Industrial SCR Catalysts—A Short Review. Energies 2020, 13, 3870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Wang, C.; Wang, H.; Zhang, M. Synthesis of highly efficient MnOx catalyst for low-temperature NH3-SCR prepared from Mn-MOF-74 template. Mater. Lett. 2016, 168, 17–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chang, H.; Ma, L.; Hao, J.; Yang, R.T. Low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 over metal oxide and zeolite catalysts—A review. Catal. Today 2011, 175, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.X.; Xiong, Z.; Du, Y.P.; Ning, X.; Li, Z.Z.; He, J.F.; Qu, X.K.; Lu, W.; Wu, S.M.; Tan, L.Z. Promotional effect of tungsten modification on magnetic iron oxide catalyst for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. J. Energy Inst. 2020, 93, 1809–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chmielarz, L.; Ku, P.; Majda, D.; Dziembaj, R. Catalytic activity of Co-Mg-Al, Cu-Mg-Al and Cu-Co-Mg-Al mixed oxides derived from hydrotalcites in SCR ofNO with ammonia. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2002, 35, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierzbicki, D.; Dębek, R.; Szczurowski, J.; Basąg, S.; Włodarczyk, M.; Motak, M.; Baran, R. Copper, cobalt and manganese: Modified hydrotalcite materials as catalysts for the selective catalytic reduction of NO with ammonia. the influence of manganese concentration. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2015, 18, 1074–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Bian, C.; Ming, S.; Guo, L.; Zhang, S.; Pang, L.; Liu, P.; Chen, Z.; Li, T. The opportunities and challenges of iron-zeolite as NH3-SCR catalyst in purification of vehicle exhaust. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2020, 607, 117865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wu, X.; Zou, C.; Li, X.; Du, Y. Nox removal by selective catalytic reduction with ammonia over a hydrotalcite-derived NiFe mixed oxide. Catalysts 2018, 8, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jabłońska, M.; Palkovits, R. Nitrogen oxide removal over hydrotalcite-derived mixed metal oxides. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 49–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Basąg, S.; Kocoł, K.; Piwowarska, Z.; Rutkowska, M.; Baran, R.; Chmielarz, L. Activating effect of cerium in hydrotalcite derived Cu–Mg–Al catalysts for selective ammonia oxidation and the selective reduction of NO with ammonia. React. Kinet. Mech. Catal. 2017, 121, 225–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Basąg, S.; Piwowarska, Z.; Kowalczyk, A.; Węgrzyn, A.; Baran, R.; Gil, B.; Michalik, M.; Chmielarz, L. Cu-Mg-Al hydrotalcite-like materials as precursors of effective catalysts for selective oxidation of ammonia to dinitrogen—The influence of Mg/Al ratio and calcination temperature. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 129, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chmielarz, L.; Jabłońska, M.; Strumiński, A.; Piwowarska, Z.; Wegrzyn, A.; Witkowski, S.; Michalik, M. Selective catalytic oxidation of ammonia to nitrogen over Mg-Al, Cu-Mg-Al and Fe-Mg-Al mixed metal oxides doped with noble metals. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2013, 130–131, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrozova, P.; Kynicky, J.; Urubek, T.; Nguyen, V.D. Synthesis and Modification of Clinoptilolite. Molecules 2017, 22, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gelves, J.F.; Dorkis, L.; Márquez, M.A.; Álvarez, A.C.; González, L.M.; Villa, A.L. Activity of an iron Colombian natural zeolite as potential geo-catalyst for NH3-SCR of NOx. Catal. Today 2019, 320, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doula, M.K. Synthesis of a clinoptilolite-Fe system with high Cu sorption capacity. Chemosphere 2007, 67, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doula, M.; Ioannou, A.; Dimirkou, A. Copper adsorption and Si, Al, Ca, Mg, and Na release from clinoptilolite. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 245, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doula, M.K. Removal of Mn2+ ions from drinking water by using Clinoptilolite and a Clinoptilolite-Fe oxide system. Water Res. 2006, 40, 3167–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saramok, M.; Szymaszek, A.; Inger, M.; Antoniak-Jurak, K.; Samojeden, B.; Motak, M. Modified Zeolite Catalyst for a NOx Selective Catalytic Reduction Process in Nitric Acid Plants. Catalysts 2021, 11, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saramok, M.; Inger, M.; Antoniak-Jurak, K.; Szymaszek-Wawryca, A.; Samojeden, B.; Motak, M. Physicochemical Features and NH3-SCR Catalytic Performance of Natural Zeolite Modified with Iron—The Effect of Fe Loading. Catalysts 2022, 12, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishkin, A.; Shwan, S.; Pingel, T.N.; Olsson, E.; Clemens, A.; Carlsson, P.A.; Härelind, H.; Skoglundh, M. Functionalization of SSZ-13 and Fe-beta with copper by NH3 and NO facilitated solid-state ion-exchange. Catalysts 2017, 7, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boroń, P.; Chmielarz, L.; Gurgul, J.; Łątka, K.; Gil, B.; Marszałek, B.; Dzwigaj, S. Influence of iron state and acidity of zeolites on the catalytic activity of FeHBEA, FeHZSM-5 and FeHMOR in SCR of NO with NH3 and N2O decomposition. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2015, 203, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Chen, B.; Bai, Z.; Yu, L.; Crocker, M.; Shi, C. Hybrid catalysts with enhanced C3H6 resistance for NH3-SCR of NOx. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2019, 242, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymaszek-Wawryca, A.; Díaz, U.; Samojeden, B.; Motak, M. Catalytic Performance of One-Pot Synthesized Fe-MWW Layered Zeolites (MCM-22, MCM-36, and ITQ-2) in Selective Catalytic Reduction of Nitrogen Oxides with Ammonia. Molecules 2022, 27, 2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szymaszek-Wawryca, A.; Diaz, U.; Duraczyńska, D.; Świerczek, K.; Samojeden, B.; Motak, M. Catalytic Performance and Sulfur Dioxide Resistance of One-Pot Synthesized Fe-MCM-22 in Selective Catalytic Reduction of Nitrogen Oxides with Ammonia (NH3-SCR)—The Effect of Iron Content. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Wang, R.; Du, Y.; Li, X.; Meng, H.; Xie, X. NOx removal by selective catalytic reduction with ammonia over hydrotalcite-derived NiTi mixed oxide. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 2640–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.; Li, X.; Zhao, Q.; Zhao, J.; Tadé, M.; Liu, S. A novel CuTi-containing catalyst derived from hydrotalcite-like compounds for selective catalytic reduction of NO with C3H6 under lean-burn conditions. J. Catal. 2014, 309, 268–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakya, B.M.; Harold, M.P.; Balakotaiah, V. Simulations and optimization of combined Fe- and Cu-zeolite SCR monolith catalysts. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 278, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, L.; Zhong, Z.; Yang, H.; Wang, C. Comparison study of Cu-Fe-Ti and Co-Fe-Ti oxide catalysts for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 at low temperature. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 478, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basąg, S.; Kovanda, F.; Piwowarska, Z.; Kowalczyk, A.; Pamin, K.; Chmielarz, L. Hydrotalcite-derived Co-containing mixed metal oxide catalysts for methanol incineration: Role of cobalt content, Mg/Al ratio and calcination temperature. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2017, 129, 1301–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rives, V.; Ulibarri, M.A. Layered double hydroxides (LDH) intercalated with metal coordination compounds and oxometalates. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1999, 181, 61–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouquerol, J.; Llewellyn, P.; Rouquerol, F. Is the BET equation applicable to microporous adsorbents? Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 2007, 160, 49–56. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.; Janssens, T.V.W.; Vennestrøm, P.N.R.; Jansson, J.; Skoglundh, M.; Grönbeck, H. The Role of H+- And Cu+-Sites for N2O Formation during NH3-SCR over Cu-CHA. J. Phys. Chem. C 2021, 125, 4595–4601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Cai, S.; Gao, M.; Hasegawa, J.; Wang, P.; Zhang, J.; Shi, L.; Zhang, D. Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx with NH3 by Using Novel Catalysts: State of the Art and Future Prospects. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 10916–10976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucjan Chmielarz; Wojciechowska, M.; Rutkowska, M.; Adamski, A.; Węgrzyn, A.; Kowalczyk, A.; Dudek, B.; Boroń, P.; Michalik, M.; Matusiewicz, A. Acid-activated vermiculites as catalysts of DeNOx process. Catal. Today 2012, 191, 25–31. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Yang, R.T. N2O Formation Pathways over Zeolite-Supported Cu and Fe Catalysts in NH3-SCR. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 2170–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Du, X.; Xue, J.; Yang, G.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L. New insights into the N2O formation mechanism during selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 over V-based catalyst. Catal. Today 2020, 355, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobzaru, C.; Marinoiu, A.; Cernatescu, C. Sorption of vitamin C on acid modified clinoptilolite. Rev. Roum. Chim. 2015, 60, 241–247. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Basabe, Y.; Rodriguez-Iznaga, I.; De Menorval, L.C.; Llewellyn, P.; Maurin, G.; Lewis, D.W.; Binions, R.; Autie, M.; Ruiz-Salvador, A.R. Step-wise dealumination of natural clinoptilolite: Structural and physicochemical characterization. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2010, 135, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemian, N.; Falamaki, C.; Kalbasi, M.; Khosravi, M. Enhancement of the catalytic performance of H-clinoptilolite in propane-SCR-NOx process through controlled dealumination. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 252, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroutan, R.; Peighambardoust, S.J.; Hemmati, S.; Khatooni, H.; Ramavandi, B. Preparation of clinoptilolite/starch/CoFe2O4 magnetic nanocomposite powder and its elimination properties for cationic dyes from water and wastewater. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 189, 432–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noori, M.; Tahmasebpoor, M.; Foroutan, R. Enhanced adsorption capacity of low-cost magnetic clinoptilolite powders/beads for the effective removal of methylene blue: Adsorption and desorption studies. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 278, 125655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymaszek, A.; Samojeden, B.; Motak, M. Selective catalytic reduction of NOx with ammonia (NH3-SCR) over transition metal-based catalysts—Influence of the catalysts support. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 2019, 55, 1429–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summa, P.; Świrk, K.; Wang, Y.; Samojeden, B.; Rønning, M.; Hu, C.; Motak, M.; Da Costa, P. Effect of cobalt promotion on hydrotalcite-derived nickel catalyst for CO2 methanation. Appl. Mater. Today 2021, 25, 101211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rives, V. Characterisation of layered double hydroxides and their decomposition products. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2002, 75, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summa, P.; Samojeden, B.; Motak, M.; Wierzbicki, D.; Alxneit, I.; Świerczek, K.; Da Costa, P. Investigation of Cu promotion effect on hydrotalcite-based nickel catalyst for CO2 methanation. Catal. Today 2022, 384–386, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S.W. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Foroutan, R.; Jamaleddin, S.; Latifi, P.; Ahmadi, A. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering Carbon nanotubes/β-cyclodextrin/MnFe2O4 as a magnetic nanocomposite powder for tetracycline antibiotic decontamination from different aqueous environments. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassileva, P.; Voikova, D. Investigation on natural and pretreated Bulgarian clinoptilolite for ammonium ions removal from aqueous solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 170, 948–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortazavi, N.; Bahadori, M.; Marandi, A.; Tangestaninejad, S.; Moghadam, M.; Mirkhani, V.; Mohammadpoor-Baltork, I. Enhancement of CO2 adsorption on natural zeolite, modified clinoptilolite with cations, amines and ionic liquids. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2021, 22, 100495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprynskyy, M.; Golembiewski, R.; Trykowski, G.; Buszewski, B. Heterogeneity and hierarchy of clinoptilolite porosity. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2010, 71, 1269–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, E.M.; Da Costa Faro, A.; De Freitas Silva, T.; Assaf, J.M.; Rangel, M.D.C. A comparison between copper and nickel-based catalysts obtained from hydrotalcite-like precursors for WGSR. Catal. Today 2011, 171, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, N.; Rikhtegar, N.; Panahi, H.A.; Atami, F.; Shahraki, B.K. Porosity, characterization and structural properties of natural zeolity—Clinoptilolite—As a sorbent. Environ. Prot. Eng. 2013, 39, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugrina, M.; Gaberšek, M.; Daković, A.; Nuić, I. Preparation and Characterization of the Sulfur-Impregnated Natural Zeolite Clinoptilolite for Hg (II) Removal from Aqueous Solutions. Processes 2021, 9, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulkifli, M.; Pungot, N.H.; Tajuddin, N.A.; Aluwi, M.F.F.M.; Jumali, N.S.; Shaameri, Z. A short review on the influence of the preparation method on the physicochemical properties of Mg/Al hydrotalcite for glucose isomerization. Malaysian J. Anal. Sci. 2022, 26, 191–201. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Shu, P.; Zhai, F.; Chen, S.; Wang, K.; Deng, J.; Kang, F.; Li, L. Preparation and properties of hydrotalcite microcapsules for coal spontaneous combustion prevention. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 152, 536–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parashar, P.; Sharma, V.; Agarwal, D.D.; Richhariya, N. Rapid synthesis of hydrotalcite with high antacid activity. Mater. Lett. 2012, 74, 93–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oelkers, E.H.; Schott, J. Experimental study of anorthite dissolution and the relative mechanism of feldspar hydrolysis. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1995, 59, 5039–5053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippidis, A.; Godelitsas, A.; Charistos, D.; Misaelides, P.; Kassoli-Fournaraki, A. The chemical behavior of natural zeolites in aqueous environments: Interactions between low-silica zeolites and 1 M NaCl solutions of different initial pH-values. Appl. Clay Sci. 1996, 11, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiyantoko, B.; Kurniawati, P.; Purbaningtias, T.E.; Fatimah, I. Synthesis and Characterization of Hydrotalcite at Different Mg/Al Molar Ratios. Procedia Chem. 2015, 17, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nezamzadeh-Ejhieh, A.; Kabiri-Samani, M. Effective removal of Ni(II) from aqueous solutions by modification of nano particles of clinoptilolite with dimethylglyoxime. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 260, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rives, V.; Kannan, S. Layered double hydroxides with the hydrotalcite-type structure containing Cu2+, Ni2+ and Al3+. J. Mater. Chem. 2000, 10, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, P.; Eniyarppu, S.; Ahmed, M.; Sharma, D.; Sakthivel, A. Cerium ion-exchanged layered MCM-22: Preparation, characterization and its application for esterification of fatty acids. J. Porous Mater. 2018, 25, 999–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, W.J.; Gil, B.; Makowski, W.; Sławek, A.; Korzeniowska, A.; Grzybek, J.; Siwek, M.; Michorczyk, P. Framework-substituted cerium MCM-22 zeolite and its interlayer expanded derivative MWW-IEZ. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 2742–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vágvölgyi, V.; Palmer, S.J.; Kristóf, J.; Frost, R.L.; Horváth, E. Mechanism for hydrotalcite decomposition: A controlled rate thermal analysis study. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 318, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, K.; Xia, H.; Hensen, E.; van Santen, R.; Li, C. Chemistry of N2O decomposition on active sites with different nature: Effect of high-temperature treatment of Fe/ZSM-5. J. Catal. 2006, 238, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, T.; Kang, Y.; Nam, I.S.; Hong, S.B. Iron-exchanged high-silica LTA zeolites as hydrothermally stable NH3-SCR catalysts. React. Chem. Eng. 2019, 4, 1050–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkowska, M.; Díaz, U.; Palomares, A.E.; Chmielarz, L. Cu and Fe modified derivatives of 2D MWW-type zeolites (MCM-22, ITQ-2 and MCM-36) as new catalysts for DeNOx process. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 168–169, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Zheng, Y.; Kukkadapu, R.K.; Wang, Y.; Walter, E.D.; Schwenzer, B.; Szanyi, J.; Peden, C.H.F. Iron Loading Effects in Fe/SSZ-13 NH3-SCR Catalysts: Nature of the Fe Ions and Structure-Function Relationships. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 2939–2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, S.; Chen, Z.; Fan, C.; Pang, L.; Guo, W.; Albert, K.B.; Liu, P.; Li, T. The effect of copper loading and silicon content on catalytic activity and hydrothermal stability of Cu-SAPO-18 catalyst for NH3-SCR. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2018, 559, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Kamasamudram, K.; Epling, W.S. NH3-SCR over Cu/SAPO-34—Zeolite acidity and Cu structure changes as a function of Cu loading. Catal. Today 2014, 231, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grajciar, L.; Areán, C.O.; Pulido, A.; Nachtigall, P. Periodic DFT investigation of the effect of aluminium content on the properties of the acid zeolite H-FER. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 1497–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Ren, S.; Liu, L.; Su, B.; Yang, J.; Chen, Z.; Wang, M.; Liu, Q. Catalytic performance over Mn-Ce catalysts for NH3-SCR of NO at low temperature: Different zeolite supports. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Wang, H.F.; Hu, P. Theoretical investigation of NH3-SCR processes over zeolites: A review. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 2015, 115, 618–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Zhang, S.; Gu, M.; Hu, J.; Long, H.; Chen, Y.; Shao, N.; Zhao, R.; Jiang, J. DFT and experimental study on denitration mechanism over VPO/TiO2 catalyst. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2019, 45, 2695–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Wang, Y.; Kollár, M.; Washton, N.M.; Szanyi, J.; Peden, C.H.F. A comparative kinetics study between Cu/SSZ-13 and Fe/SSZ-13 SCR catalysts. Catal. Today 2015, 258, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pereda-Ayo, B.; De La Torre, U.; Illán-Gómez, M.J.; Bueno-López, A.; González-Velasco, J.R. Role of the different copper species on the activity of Cu/zeolite catalysts for SCR of NOx with NH3. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2014, 147, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandenberger, S.; Kröcher, O.; Tissler, A.; Althoff, R. The state of the art in selective catalytic reduction of NOx by ammonia using metal-exchanged zeolite catalysts. Catal. Rev. 2008, 50, 492–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, M.; Nova, I.; Tronconi, E. A comparative study of the NH 3 -SCR reactions over a Cu-zeolite and a Fe-zeolite catalyst. Catal. Today 2010, 151, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metkar, P.S.; Harold, M.P.; Balakotaiah, V. Selective catalytic reduction of NOx on combined Fe- and Cu-zeolite monolithic catalysts: Sequential and dual layer configurations. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2012, 111–112, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metkar, P.S.; Harold, M.P.; Balakotaiah, V. Experimental and kinetic modeling study of NH3-SCR of NOx on Fe-ZSM-5, Cu-chabazite and combined Fe- and Cu-zeolite monolithic catalysts. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2013, 87, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandenberger, S.; Kröcher, O.; Tissler, A.; Althoff, R. The determination of the activities of different iron species in Fe-ZSM-5 for SCR of NO by NH3. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2010, 95, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, P.; Dash, B.N. X-ray Diffraction and UV-Visible Characterizations of α-Fe2O3 Nanoparticles Annealed at Different Temperature. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2013, 3, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunalan, S.; Sivaraj, R.; Venckatesh, R. Aloe barbadensis Miller mediated green synthesis of mono-disperse copper oxide nanoparticles: Optical properties. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2012, 97, 1140–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papp, T.G.J.P.H. Supported manganese catalysts for the selective catalytic reduction of nitrogen oxides with ammonia: Part II. Catalytic experiments. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 1999, 1, 341–348. [Google Scholar]
- Rutkowska, M.; Jankowska, A.; Różycka-Dudek, E.; Dubiel, W.; Kowalczyk, A.; Piwowarska, Z.; Llopis, S.; Díaz, U.; Chmielarz, L. Modification of mcm-22 zeolite and its derivatives with iron for the application in n2o decomposition. Catalysts 2020, 10, 1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sklenak, S.; Andrikopoulos, P.C.; Boekfa, B.; Jansang, B.; Nováková, J.; Benco, L.; Bucko, T.; Hafner, J.; Ddeek, J.; Sobalík, Z. N2O decomposition over Fe-zeolites: Structure of the active sites and the origin of the distinct reactivity of Fe-ferrierite, Fe-ZSM-5, and Fe-beta. A combined periodic DFT and multispectral study. J. Catal. 2010, 272, 262–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Ramírez, J.; Kapteijn, F.; Groen, J.C.; Doménech, A.; Mul, G.; Moulijn, J.A. Steam-activated FeMFI zeolites. Evolution of iron species and activity in direct N2O decomposition. J. Catal. 2003, 214, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sample Code | Si (wt%) | Al (wt%) | Mg (wt%) | Fe (wt%) | Cu (wt%) | Si/Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HT | 0.16 | 6.20 | 21.42 | 5.24 | 4.47 | - |
| Clin | 32.11 | 6.89 | 0.38 | 1.10 | - | 4.4 |
| H-Clin | 32.71 | 5.89 | 0.24 | 0.99 | - | 5.3 |
| HT_Clin 20 | 27.52 | 5.62 | 4.19 | 1.78 | 0.81 | 4.7 |
| HT_Clin 25 | 26.25 | 5.70 | 4.99 | 1.94 | 0.97 | 4.5 |
| HT_Clin 30 | 25.95 | 5.86 | 5.67 | 2.09 | 1.02 | 4.2 |
| Sample Code | SBET a (m2·g−1) | Micropore Volume b (m3·g−1) | Mesopore Volume c (m3·g−1) | Mean Pore Diameter d (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HT | 256 | 0.027 | 1.35 | 21 |
| Clin | 13 | 0.003 | 0.059 | 18 |
| H-Clin | 47 | 0.016 | 0.120 | 7 |
| HT_Clin 20 | 88 | 0.002 | 0.393 | 14 |
| HT_Clin 25 | 103 | 0.002 | 0.495 | 18 |
| HT_Clin 30 | 102 | 0.002 | 0.523 | 17 |
| Sample Code | Weight Loss in the Temperature Range (wt%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30–200 °C | 200–375 °C | 375–800 °C | Total | |
| HT | 12.0 | 22.5 | 7.0 | 41.5 |
| HT_Clin 20 | 8.5 | 3.5 | 0.5 | 12.5 |
| HT_Clin 25 | 9.0 | 4.5 | 3.0 | 16.5 |
| HT_Clin 30 | 8.0 | 5.5 | 3.0 | 16.5 |
| Sample Code | NO Conversion (%) a | N2O Concentration (ppm) a | Composition of the Gas Mixture | GHSV (ml·h−1·g−1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HT | 32|51 | 34|79 | 800 ppm NH3 800 ppm NO 3.5 vol% O2 He as an inert | 30,000 | This work |
| HT_Clin 20 | 37|88 | 69|101 | This work | ||
| HT_Clin 25 | 57|89 | 118|97 | This work | ||
| HT_Clin 30 | 58|91 | 84|50 | This work | ||
| Fe-MCM-22 b | 100|87 | <10 | [33] | ||
| Fe-MCM-36 b | 100|90 | <10 | [32] | ||
| Fe-ITQ-2 b | 95|78 | <10 | [32] | ||
| Co0.08Cu0.16 c | 80|60 | <10|70 | [15] | ||
| Fe-Clin d | 64|100 | 65|75 | [27] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szymaszek-Wawryca, A.; Summa, P.; Duraczyńska, D.; Díaz, U.; Motak, M. Hydrotalcite-Modified Clinoptilolite as the Catalyst for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NO with Ammonia (NH3-SCR). Materials 2022, 15, 7884. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15227884
Szymaszek-Wawryca A, Summa P, Duraczyńska D, Díaz U, Motak M. Hydrotalcite-Modified Clinoptilolite as the Catalyst for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NO with Ammonia (NH3-SCR). Materials. 2022; 15(22):7884. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15227884
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzymaszek-Wawryca, Agnieszka, Paulina Summa, Dorota Duraczyńska, Urbano Díaz, and Monika Motak. 2022. "Hydrotalcite-Modified Clinoptilolite as the Catalyst for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NO with Ammonia (NH3-SCR)" Materials 15, no. 22: 7884. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15227884
APA StyleSzymaszek-Wawryca, A., Summa, P., Duraczyńska, D., Díaz, U., & Motak, M. (2022). Hydrotalcite-Modified Clinoptilolite as the Catalyst for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NO with Ammonia (NH3-SCR). Materials, 15(22), 7884. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15227884








