Mechanical Properties of Orthodontic Cements and Their Behavior in Acidic Environments
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials Description
2.2. Mechanical Properties
2.2.1. Compressive Strength
2.2.2. Diametral Tensile Strength
2.2.3. Flexural Strength
2.2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.3. Liquid Absorbtion and Samples Solubility
2.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy SEM
2.5. Atomic Force Microscopy AFM
3. Results
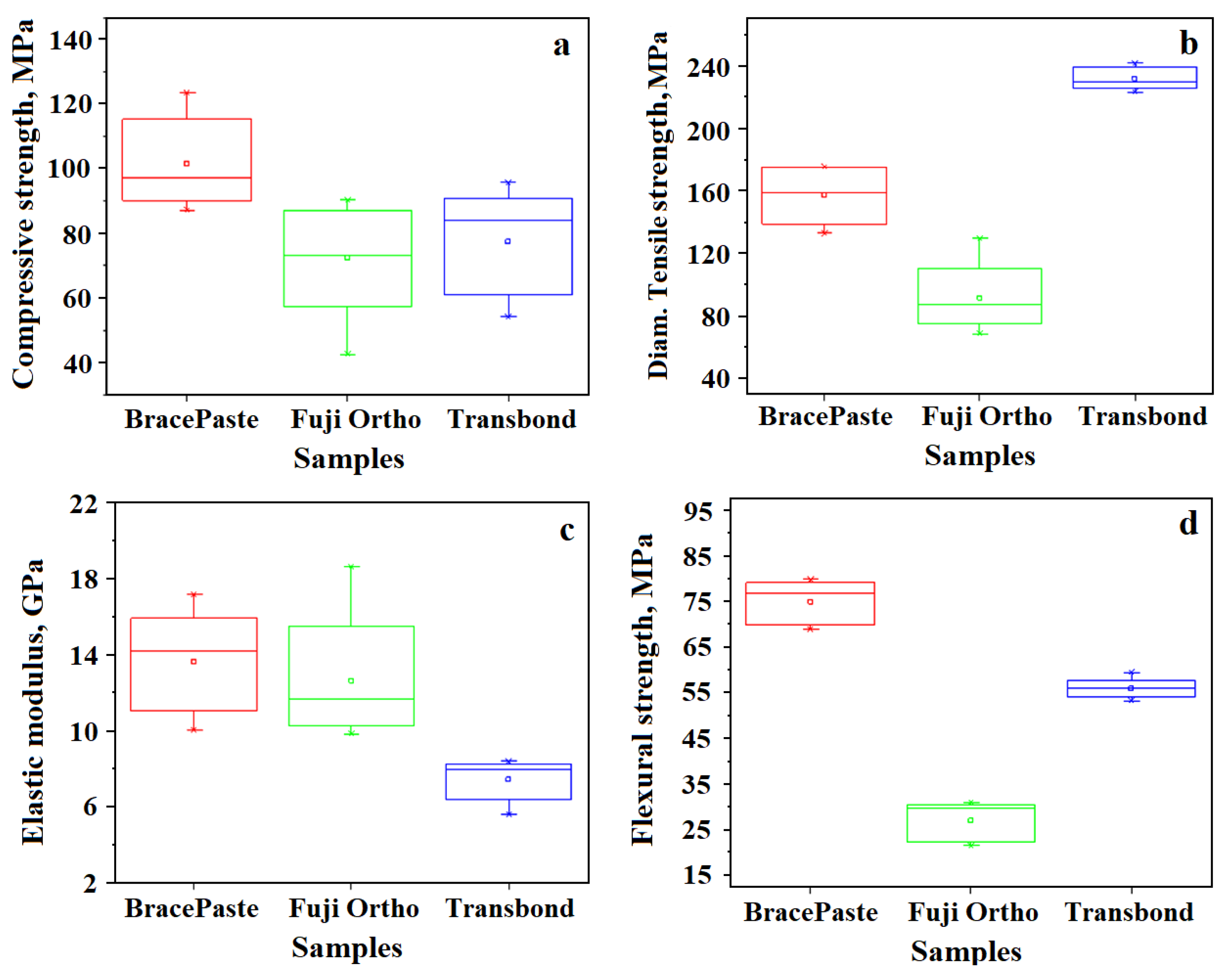
3.1. Mechanical Properties
3.2. Liquid Absorbtion
3.3. Solubility in Liquid Environment
3.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy SEM
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- BracePaste presents the best combination of mechanical properties and erosion resistance in various acidic environments, with it being recommended for long-term orthodontic treatment especially when the patient regularly consumes acidic drinks such as Coca-Cola and Red Bull. Prolonged exposure to acid overtime will make the debonding procedure at the end of the orthodontic treatment easy.
- Fuji Ortho RMGIC features the best handling associated with easy bracket procedures and presents low erosive resistance overtime. Therefore, it is easy to be applied at the beginning of treatment and it is easy to use in debonding at the end of the orthodontic treatment with minimal discomfort for the patient. Beside these important aspects, it is recommended only for short-term orthodontic treatment and is suitable for patients who regularly consume acidic beverages such as Coca-Cola and Red Bull.
- Transbond presents the highest diametral tensile strength but its compressive and flexural strength are inferior to BracePaste, and it also presents poor erosive resistance in acidic environments. This adhesive may ensure good adhesion of the brackets for orthodontic treatment over an average period of time for patients who do not regularly consume acidic beverages.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chee, S.; Mangum, J.; Teeramongkolgul, T.; Tan, S.; Schneider, P. Clinician preferences for orthodontic bracket bonding materials: A quantitative analysis. Australas. Orthod. J. 2022, 38, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vartolomei, A.-C.; Serbanoiu, D.-C.; Ghiga, D.-V.; Moldovan, M.; Cuc, S.; Pollmann, M.C.F.; Pacurar, M. Comparative Evaluation of Two Bracket Systems’ Kinetic Friction: Conventional and Self-Ligating. Materials 2022, 15, 4304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urichianu, M.; Makowka, S.; Covell, D., Jr.; Warunek, S.; Al-Jewair, T. Shear Bond Strength and Bracket Base Morphology of New and Rebonded Orthodontic Ceramic Brackets. Materials 2022, 15, 1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfondrini, M.F.; Pascadopoli, M.; Gallo, S.; Ricaldone, F.; Kramp, D.D.; Valla, M.; Gandini, P.; Scribante, A. Effect of Enamel Pretreatment with Pastes Presenting Different Relative Dentin Abrasivity (RDA) Values on Orthodontic Bracket Bonding Efficacy of Microfilled Composite Resin: In Vitro Investigation and Randomized Clinical Trial. Materials 2022, 15, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fricker, J.P. Therapeutic properties of glass-ionomer cements: Their application to orthodontic treatment. Aust. Dent. J. 2021, 67, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naranjo, A.A.; Triviño, M.L.; Jaramillo, A.; Betancourth, M.; Botero, J.E. Changes in the subgingival microbiota and periodontal parameters before and 3 months after bracket placement. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2006, 130, 275.e17–275.e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mickenautsch, S.; Yengopal, V.; Banerjee, A. Retention of orthodontic brackets bonded with resin-modified GIC versus composite resin adhesives—A quantitative systematic review of clinical trials. Clin. Oral. Investig. 2012, 16, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgrami, A.; Maqsood, A.; Alam, M.K.; Ahmed, N.; Mustafa, M.; Alqahtani, A.R.; Alshehri, A.; Alqahtani, A.A.; Alghannam, S. Evaluation of Shear Bond Strength between Resin Composites and Conventional Glass Ionomer Cement in Class II Restorative Technique—An In Vitro Study. Materials 2022, 15, 4293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, A.; Ikeda, M.; Takagaki, T.; Nikaido, T.; Sadr, A.; Shimada, Y.; Tagami, J. Effects of Immediate and Delayed Cementations for CAD/CAM Resin Block after Alumina Air Abrasion on Adhesion to Newly Developed Resin Cement. Materials 2021, 14, 7058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nica, I.; Stoleriu, S.; Iovan, A.; Tărăboanță, I.; Pancu, G.; Tofan, N.; Brânzan, R.; Andrian, S. Conventional and Resin-Modified Glass Ionomer Cement Surface Characteristics after Acidic Challenges. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaga, N.; Nagano-Takebe, F.; Nezu, T.; Matsuura, T.; Endo, K.; Kaga, M. Protective Effects of GIC and S-PRG Filler Restoratives on Demineralization of Bovine Enamel in Lactic Acid Solution. Materials 2020, 13, 2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgrami, A.; Alam, M.K.; Qazi, F.u.R.; Maqsood, A.; Basha, S.; Ahmed, N.; Syed, K.A.; Mustafa, M.; Shrivastava, D.; Nagarajappa, A.K.; et al. An In-Vitro Evaluation of Microleakage in Resin-Based Restorative Materials at Different Time Intervals. Polymers 2022, 14, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, A.; Rodríguez-Lozano, F.J.; Martínez-Beneyto, Y.; Jaimez, M.; Guerrero-Gironés, J.; Ortiz-Ruiz, A.J. Biophysical and Fluoride Release Properties of a Resin Modified Glass Ionomer Cement Enriched with Bioactive Glasses. Symmetry 2021, 13, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thepveera, W.; Potiprapanpong, W.; Toneluck, A.; Channasanon, S.; Khamsuk, C.; Monmaturapoj, N.; Tanodekaew, S.; Panpisut, P. Rheological Properties, Surface Microhardness, and Dentin Shear Bond Strength of Resin-Modified Glass Ionomer Cements Containing Methacrylate-Functionalized Polyacids and Spherical Pre-Reacted Glass Fillers. J. Funct. Biomater. 2021, 12, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolowski, K.; Szczesio-Wlodarczyk, A.; Bociong, K.; Krasowski, M.; Fronczek-Wojciechowska, M.; Domarecka, M.; Sokolowski, J.; Lukomska-Szymanska, M. Contraction and Hydroscopic Expansion Stress of Dental Ion-Releasing Polymeric Materials. Polymers 2018, 10, 1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gorseta, K.; Borzabadi-Farahani, A.; Vrazic, T.; Glavina, D. An In-Vitro Analysis of Microleakage of Self-Adhesive Fissure Sealant vs. Conventional and GIC Fissure Sealants. Dent. J. 2019, 7, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sajadi, S.S.; EslamiAmirabadi, G.; Sajadi, S. Effects of two soft drinks on shear bond strength and adhesive remnant index of orthodontic metal brackets. J. Dent. 2014, 11, 389–397. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, C.N.; Souza Matos, F.; Mello Rode, S.; Cesar, P.F.; Nahsan, F.P.S.; Paranhos, L.R. Effect of two erosive protocols using acidic beverages on the shear bond strength of orthodontic brackets to bovine enamel. Dental Press J. Orthod. 2018, 23, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panpan, L.; Chungik, O.; Hongjun, K.; Chen-Glasser, M.; Park, G.; Jetybayeva, A.; Yeom, J.; Kim, H.; Ryu, J.; Hong, S. Nanoscale effects of beverages on enamel surface of human teeth: An atomic force microscopy study. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2020, 110, 103930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Gallegos, I.; Zavala-Alonso, V.; Patino-Marin, N.; Martinez-Castanon, G.A.; Anusavice, K.; Loyola-Rodriguez, J.P. Enamel roughness and depth profile after phosphoric acid etching of healthy and fluorotic enamel. Aust. Dent. J. 2012, 57, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulgaonkar, R.; Chitra, P. Stereomicroscopic analysis of microleakage, evaluation of shear bond strengths and adhesive remnants beneath orthodontic brackets under cyclic exposure to commonly consumed commercial “soft” drinks”. Indian J. Dent. Res. 2021, 32, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanachai, S.; Chaichana, W.; Insee, K.; Benjakul, S.; Aupaphong, V.; Panpisut, P. Physical/Mechanical and Antibacterial Properties of Orthodontic Adhesives Containing Calcium Phosphate and Nisin. J. Funct. Biomater. 2021, 12, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, L.A. Evaluation the properties of orthodontic adhesive incorporated with nano-hydroxyapatite particles. Saudi Dent. J. 2021, 33, 1190–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voina, C.; Delean, A.; Muresan, A.; Valeanu, M.; Mazilu Moldovan, A.; Popescu, V.; Petean, I.; Ene, R.; Moldovan, M.; Pandrea, S. Antimicrobial activity and the effect of green tea experimental gels on teeth surfaces. Coatings 2020, 10, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esberg, A.; Johansson, L.; Berglin, E.; Mohammad, A.J.; Jonsson, A.P.; Dahlqvist, J.; Stegmayr, B.; Johansson, I.; Rantapää-Dahlqvist, S. Oral Microbiota Profile in Patients with Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody–Associated Vasculitis. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunrath, M.F.; Dahlin, C. The Impact of Early Saliva Interaction on Dental Implants and Biomaterials for Oral Regeneration: An Overview. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniele, V.; Macera, L.; Taglieri, G.; Di Giambattista, A.; Spagnoli, G.; Massaria, A.; Messori, M.; Quagliarini, E.; Chiappini, G.; Campanella, V.; et al. Thermoplastic Disks Used for Commercial Orthodontic Aligners: Complete Physicochemical and Mechanical Characterization. Materials 2020, 13, 2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarosi, C.; Moldovan, M.; Soanca, A.; Roman, A.; Gherman, T.; Trifoi, A.; Chisnoiu, A.M.; Cuc, S.; Filip, M.; Gheorghe, G.F.; et al. Effects of Monomer Composition of Urethane Methacrylate Based Resins on the C=C Degree of Conversion, Residual Monomer Content and Mechanical Properties. Polymers 2021, 13, 4415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastrav, M.; Chisnoiu, A.M.; Pastrav, O.; Sarosi, C.; Pordan, D.; Petean, I.; Muntean, A.; Moldovan, M.; Chisnoiu, R.M. Surface Characteristics, Fluoride Release and Bond Strength Evaluation of Four Orthodontic Adhesives. Materials 2021, 14, 3578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishnaevvsky, J.L. Nanostructured interfaces for enhancing mechanical properties of composites: Computational micromechanical studies. Compos. Part B Eng. 2015, 68, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghoubril, V.; Ghoubril, J.; Khoury, E. A comparison between RMGIC and composite with acid-etch preparation or hypochlorite on the adhesion of a premolar metal bracket by testing SBS and ARI: In vitro study. Int. Orthod. 2020, 18, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- .Najeeb, S.; Khurshid, Z.; Zafar, M.S.; Khan, A.S.; Zohaib, S.; Martí, J.M.N.; Sauro, S.; Matinlinna, J.P.; Rehman, I.U. Modifications in Glass Ionomer Cements: Nano-Sized Fillers and Bioactive Nanoceramics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, B.-W.; Cao, S.; Ali-Somairi, M.A.; He, J.; Liu, Y. Effect of enamel-surface modifications on shear bond strength using different adhesive materials. BMC Oral Health 2022, 22, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberhoffer, F.S.; Li, P.; Jakob, A.; Dalla-Pozza, R.; Haas, N.A.; Mandilaras, G. Energy Drinks Decrease Left Ventricular Efficiency in Healthy Children and Teenagers: A Randomized Trial. Sensors 2022, 22, 7209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caixeta, R.V.; Berger, S.B.; Lopes, M.B.; Paloco, E.A.C.; Faria-Junior, E.M.; Contreras, E.F.R.; Gonini-Junior, A.; Guiraldo, R.D. Evaluation of enamel roughness after the removal of brackets bonded with different materials: In vivo study. Braz. Dent. J. 2021, 32, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, P.; Turp, J.P. Influence of Coca-Cola on orthodontic material. Swiss Dent. J. SSO 2020, 130, 777–780. [Google Scholar]
- Oncag, G.; Tuncer, A.V.; Tosun, Y.S. Acidic Soft Drinks Effects on the Shear Bond Strength of Orthodontic Brackets and a Scanning Electron Microscopy Evaluation of the Enamel. Angle Orthod. 2005, 75, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisler, C.E.; Moldovan, M.; Petean, I.; Buduru, S.D.; Prodan, D.; Sarosi, C.; Leucuţa, D.-C.; Chifor, R.; Badea, M.E.; Ene, R. Human Enamel Fluorination Enhancement by Photodynamic Laser Treatment. Polymers 2022, 14, 2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimunović, L.; Blagec, T.; Vrankić, A.; Meštrović, S. Color Stability of Orthodontic Ceramic Brackets and Adhesives in Potentially Staining Beverages—In Vitro Study. Dent. J. 2022, 10, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goracci, C.; Di Bello, G.; Franchi, L.; Louca, C.; Juloski, J.; Juloski, J.; Vichi, A. Bracket Bonding to All-Ceramic Materials with Universal Adhesives. Materials 2022, 15, 1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Product Name | Producer | Composition |
|---|---|---|
| BracePaste | American Orthodontics, Sheboygan, WI, USA | Methacrylic acid ester, activator, Ethoxylated Bisphenol A, Dimethacrylate, Tetramethylene Dimethacrylate, Diphenyl (2,4,6-trimethylbenzoyl) phosphine oxide. |
| Fuji Ortho LC | GC Company, Tokio, Japan | 20% Polyacrilic acid Fluoro-aluminium-silicate glass Polyacrilic acid, HEMA, UDMA, silicon dioxide, distilled water, initiators, pigment. |
| Transbond Colour Change | 3M Unitek, St.Paul, MN, USA | 35%Phosphoric acid Primer- bis-GMA, TEGMA Adhesive paste- bis-GMA, TEGMA, Silane, treated quartz, amorphous silica, camphor quinone. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iosif, C.; Cuc, S.; Prodan, D.; Moldovan, M.; Petean, I.; Labunet, A.; Barbu Tudoran, L.; Badea, I.C.; Man, S.C.; Badea, M.E.; et al. Mechanical Properties of Orthodontic Cements and Their Behavior in Acidic Environments. Materials 2022, 15, 7904. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15227904
Iosif C, Cuc S, Prodan D, Moldovan M, Petean I, Labunet A, Barbu Tudoran L, Badea IC, Man SC, Badea ME, et al. Mechanical Properties of Orthodontic Cements and Their Behavior in Acidic Environments. Materials. 2022; 15(22):7904. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15227904
Chicago/Turabian StyleIosif, Cristina, Stanca Cuc, Doina Prodan, Marioara Moldovan, Ioan Petean, Anca Labunet, Lucian Barbu Tudoran, Iulia Clara Badea, Sorin Claudiu Man, Mîndra Eugenia Badea, and et al. 2022. "Mechanical Properties of Orthodontic Cements and Their Behavior in Acidic Environments" Materials 15, no. 22: 7904. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15227904
APA StyleIosif, C., Cuc, S., Prodan, D., Moldovan, M., Petean, I., Labunet, A., Barbu Tudoran, L., Badea, I. C., Man, S. C., Badea, M. E., & Chifor, R. (2022). Mechanical Properties of Orthodontic Cements and Their Behavior in Acidic Environments. Materials, 15(22), 7904. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15227904










