Superhydrophobic and Corrosion Behaviour of PVDF-CeO2 Composite Coatings
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Work
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of the Coatings
2.3. Characterization Methods
3. Results
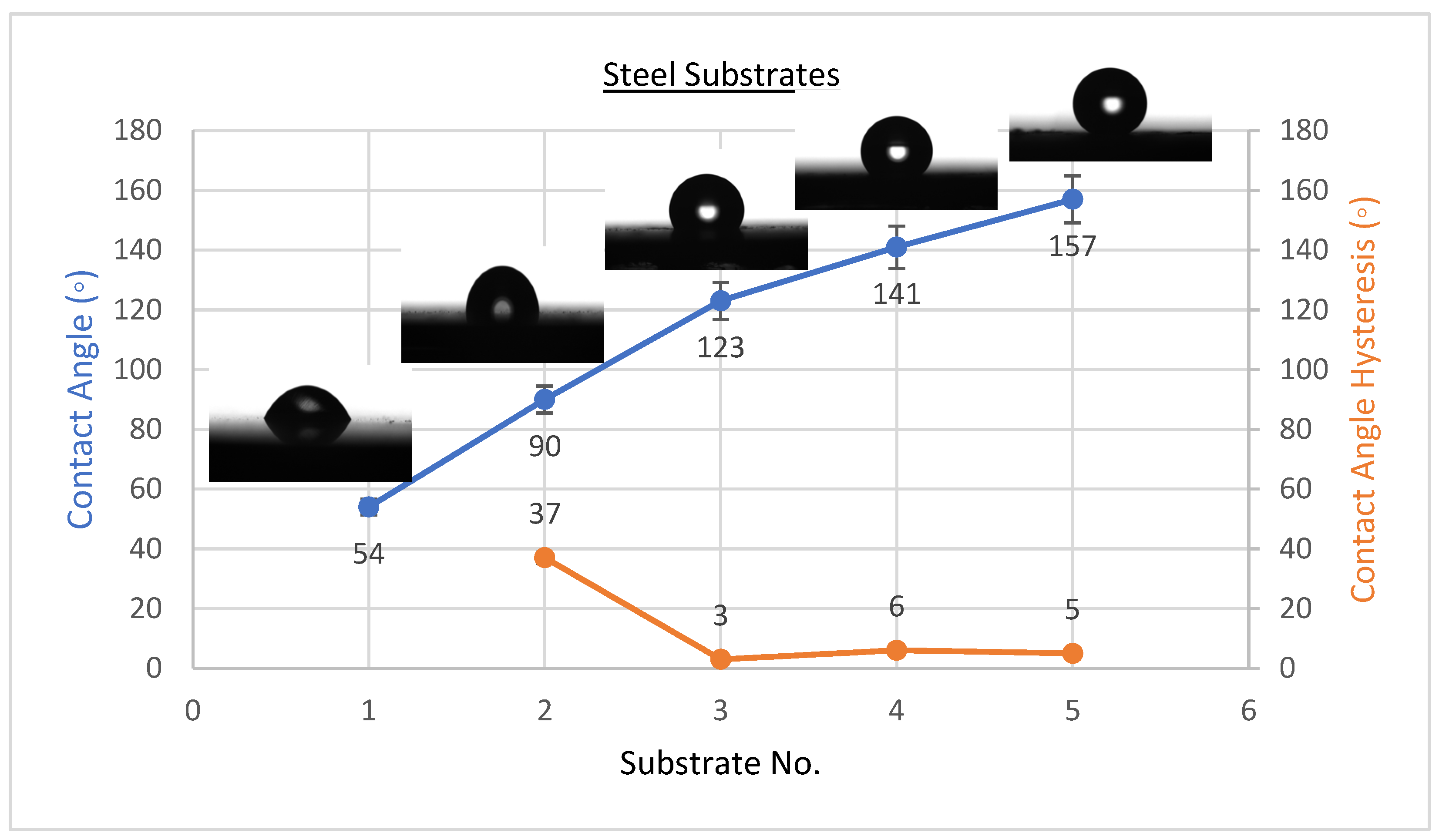
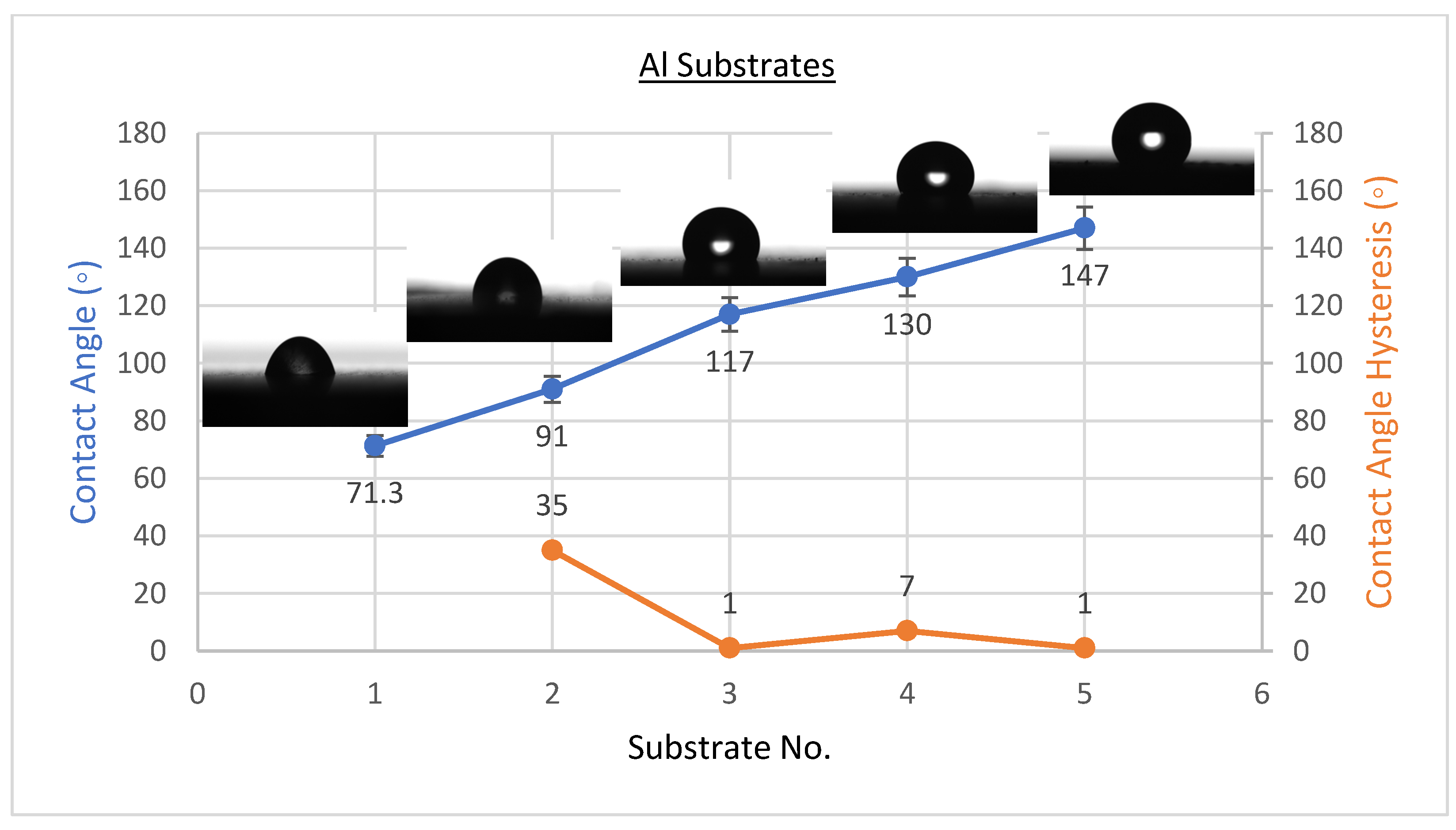
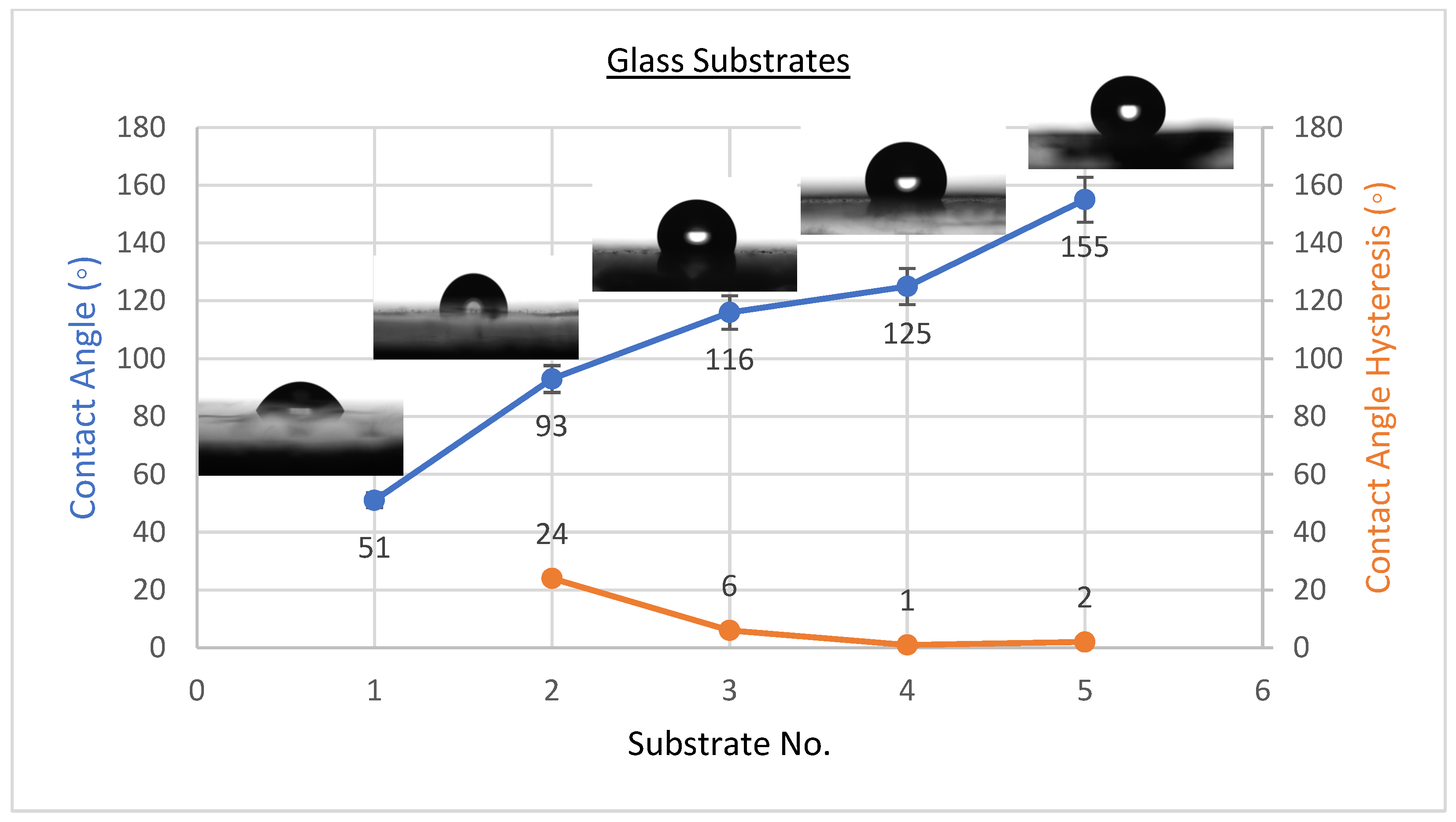
3.1. Wettability Results
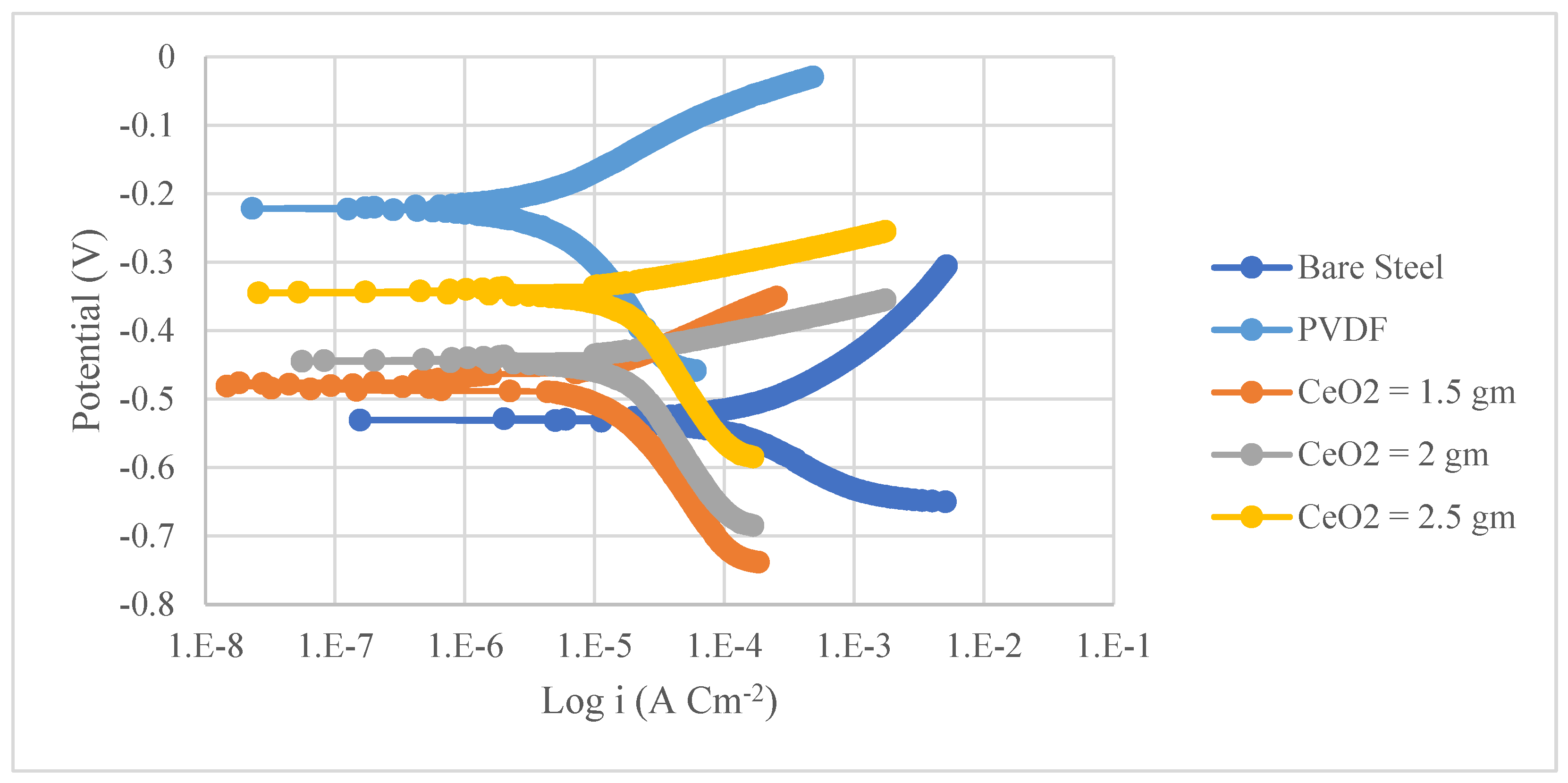
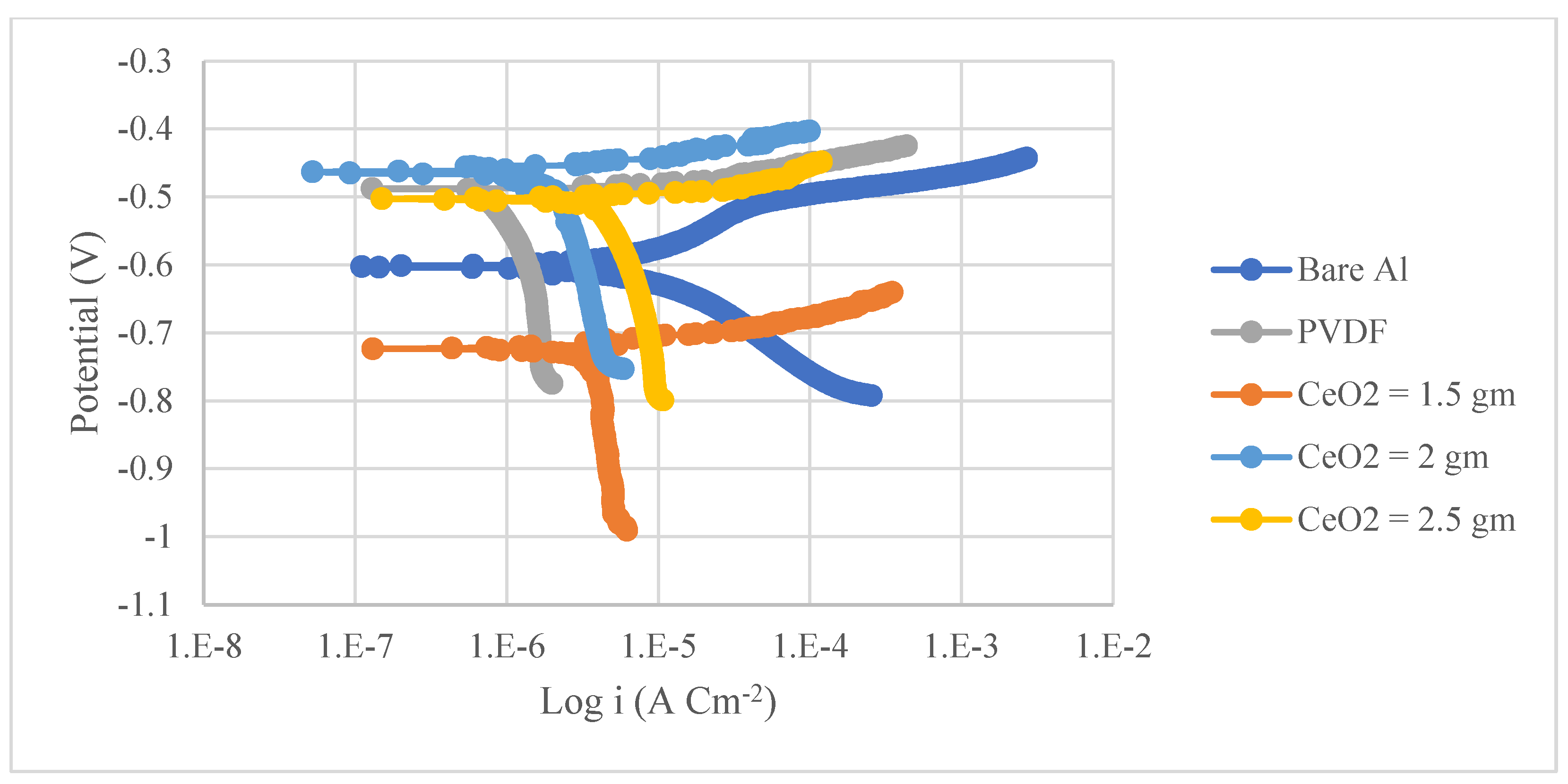
3.2. Corrosion Analysis
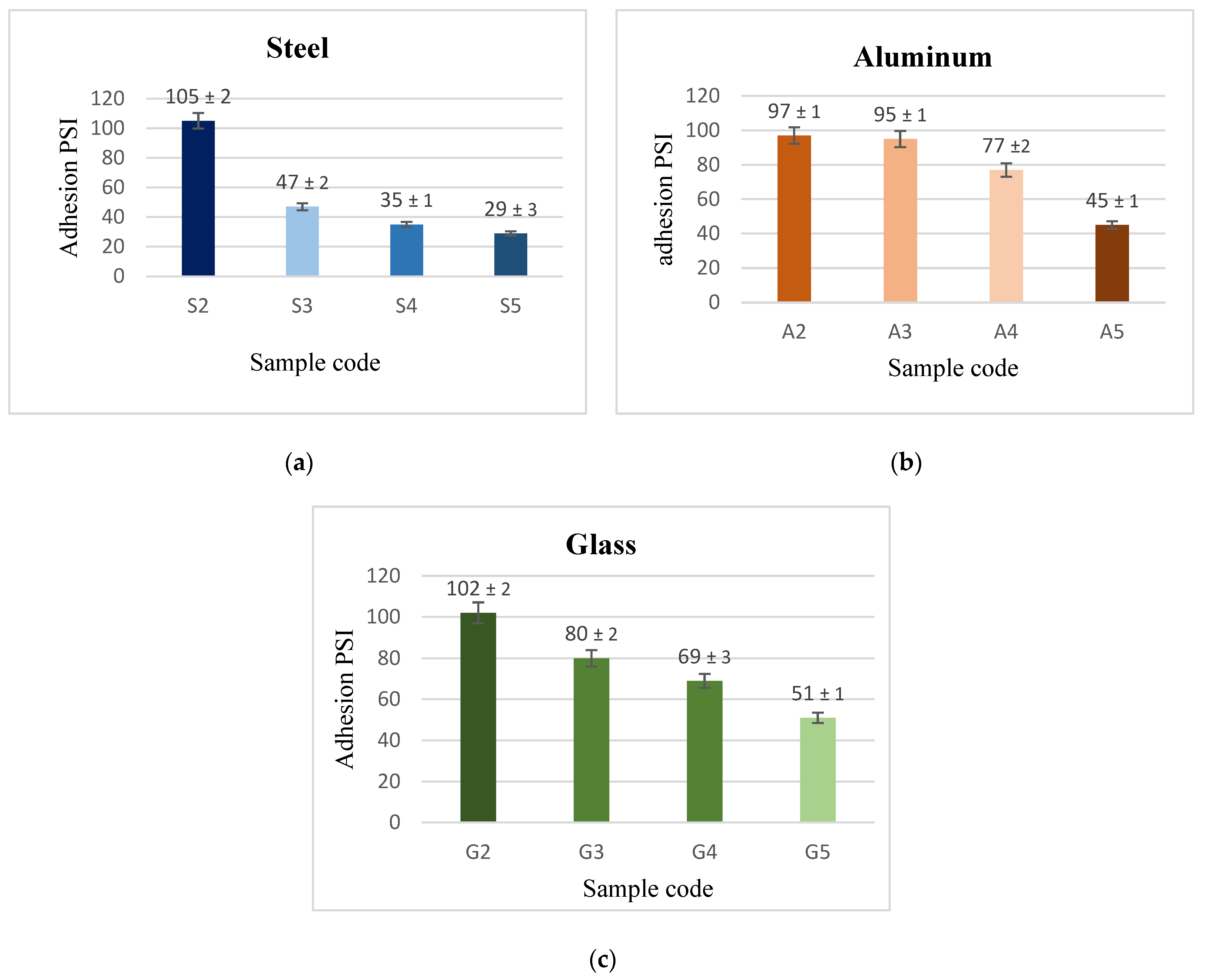
3.3. Adhesion Results
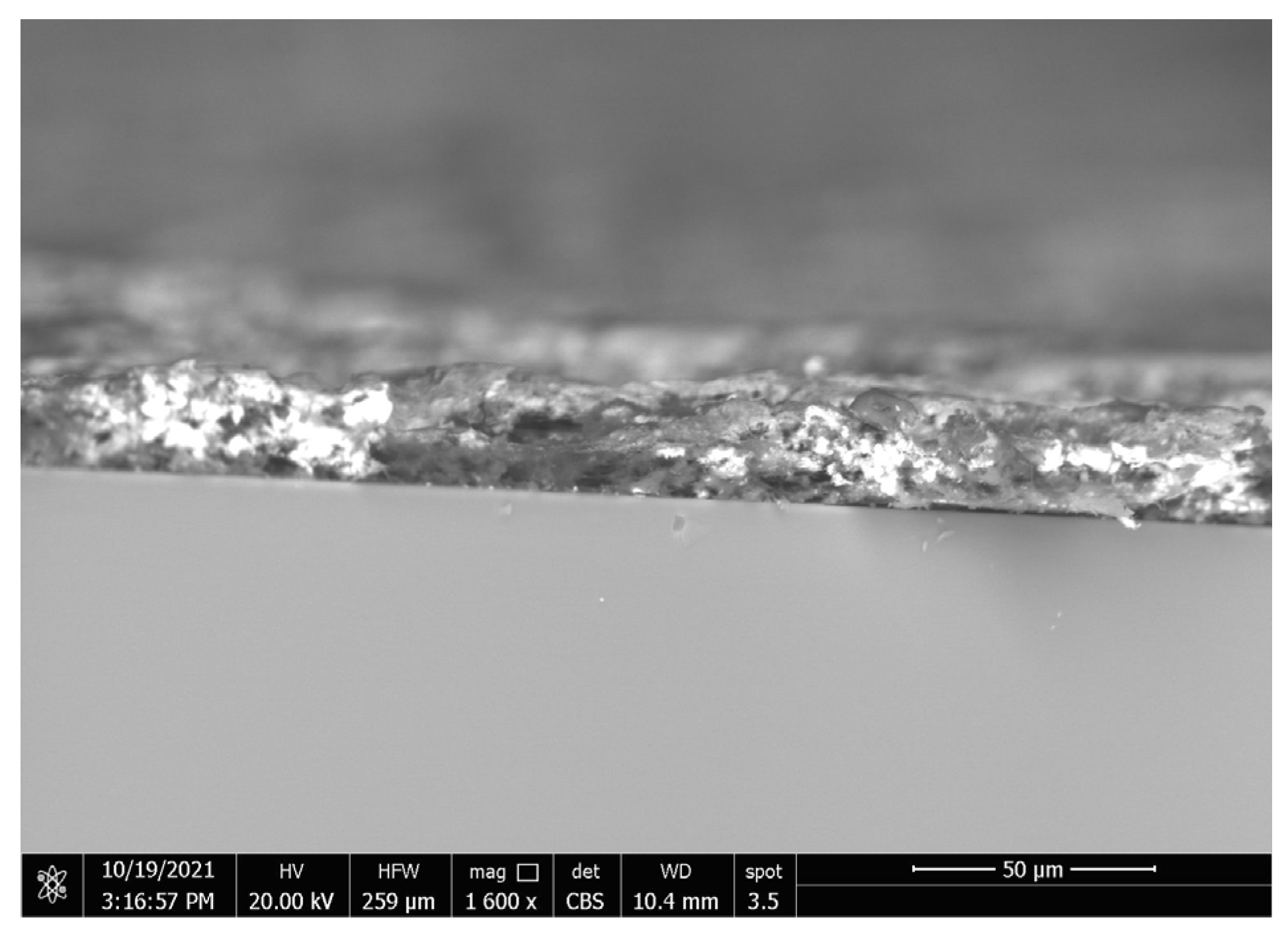
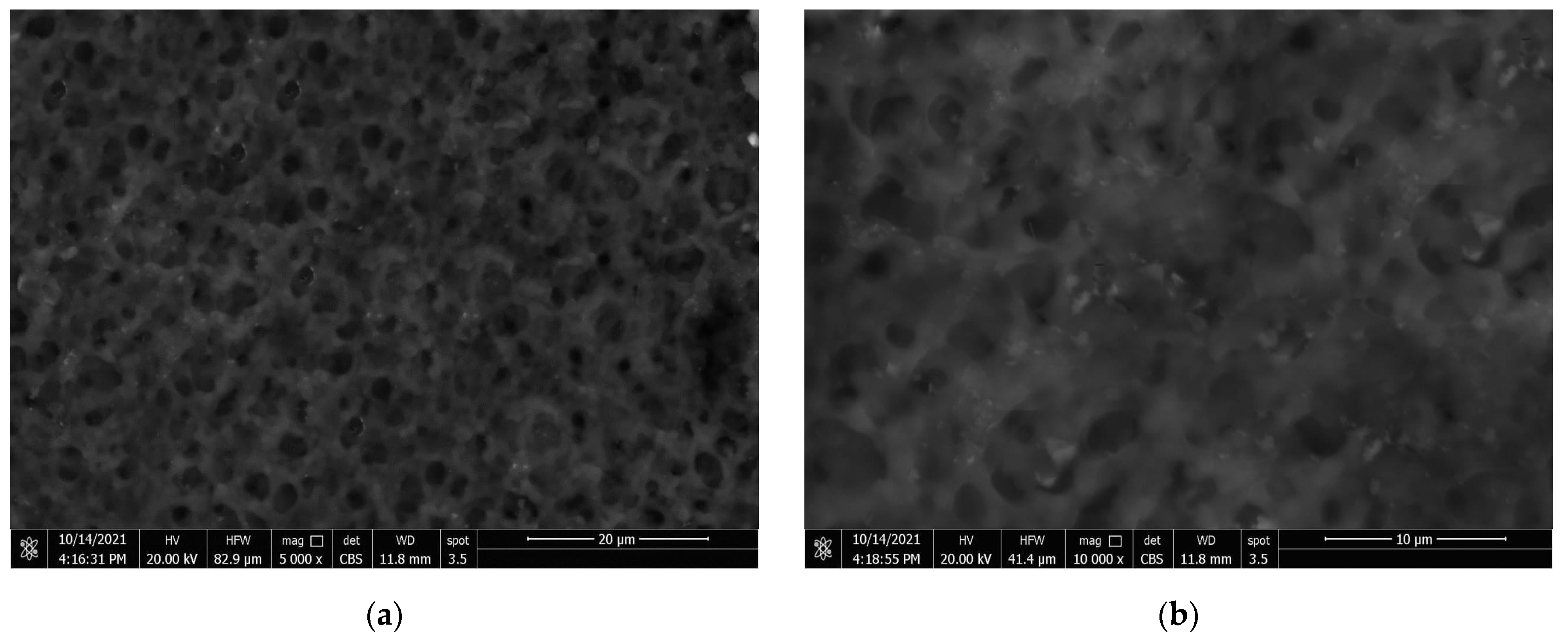
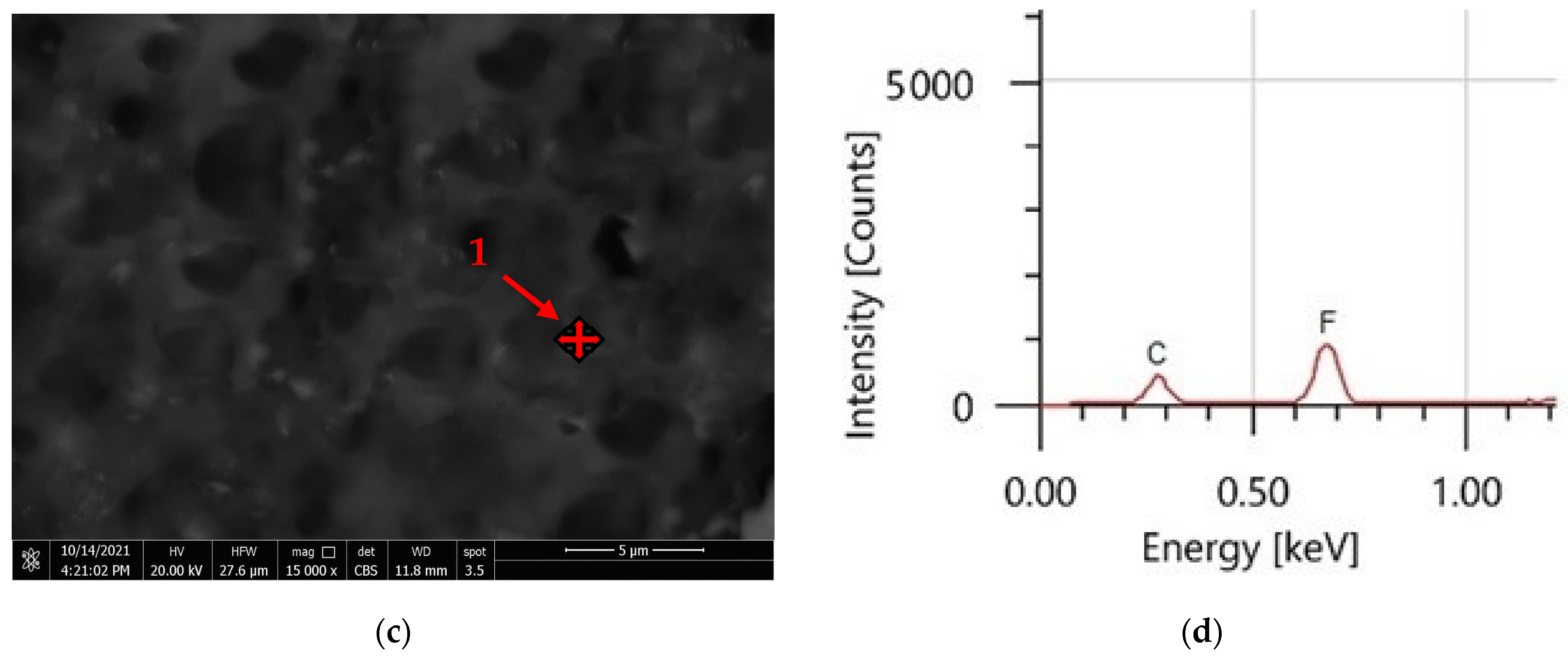
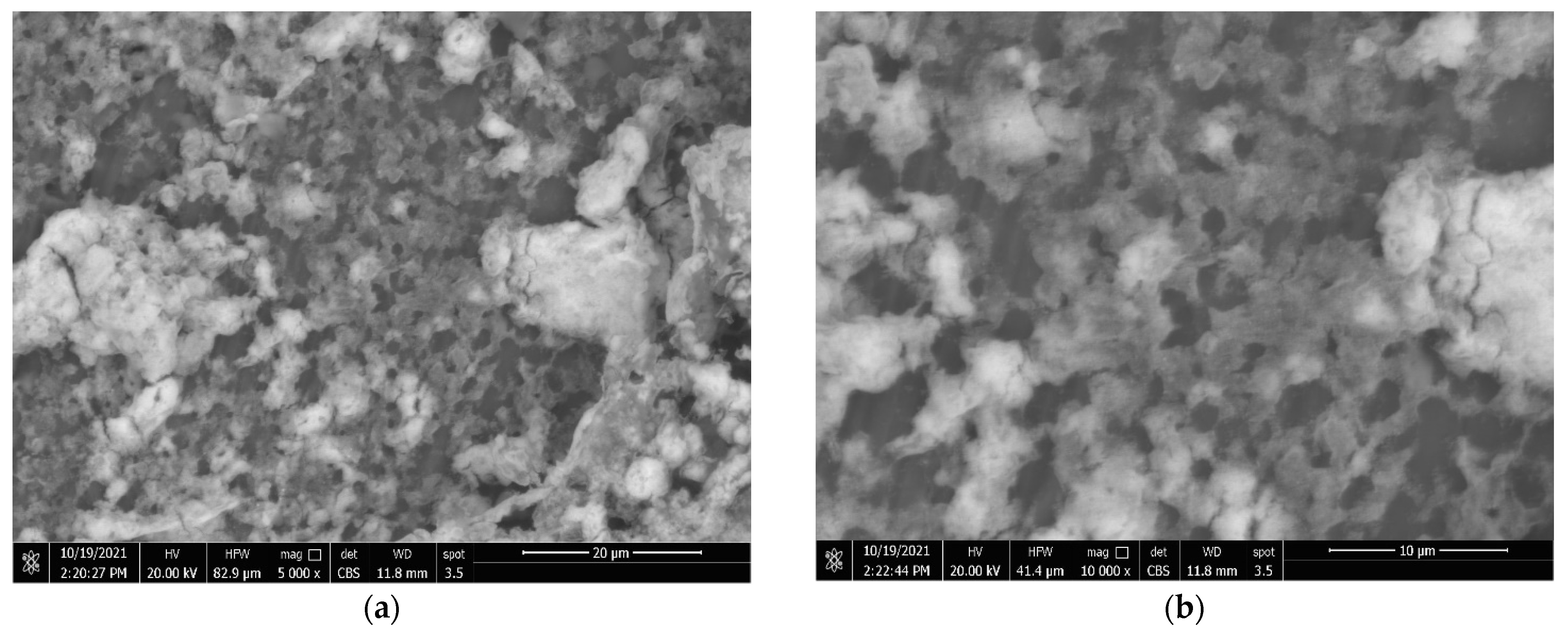
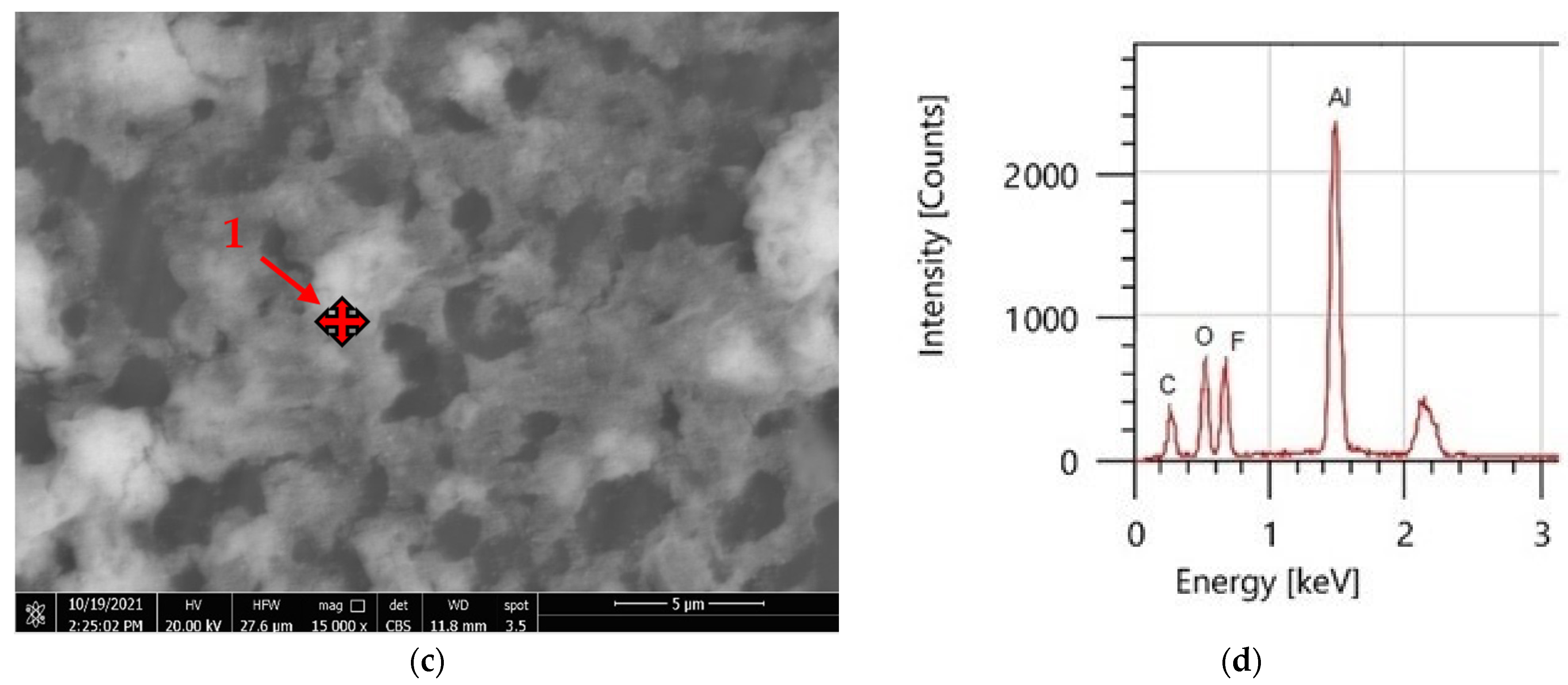
3.4. Coatings’ Surface Morphology
4. Conclusions
- PVDF/CeO2 composites were successfully made using spray coating processes. This technology has the potential to be employed in wide-scale procedures and to be a cheap solution for industrial applications.
- The superhydrophobicity of PVDF/CeO2 composite coatings is due to the PVDF’s low surface energy and the mixing of hierarchical micro and nanostructures of CeO2 incorporated in the polymer.
- If we raise the concentration of CeO2 nanoparticles to 2.5 g/100 mL, the complex solution on the steel surface in the PVDF matrix obtained a considerable increase of WCA from 90 ± 2° to 157 ± 2°, with a fall in WCAH to 5 ± 1°. Both Al and glass substrates produced similar results.
- By minimizing the size of pores in the composite coating and raising air trapping within the surface’s gaps, CeO2 nanoparticles improve the hydrophobicity of PVDF coatings.
- A significant enhancement in the corrosion resistance of the superhydrophobic PVDF/CeO2 composite coatings was observed as 77 times less than the uncoated steel and 177 times lower than the Al substrate. The corrosion rates of the prepared PVDF coating without CeO2 nanoparticles were 71 times less than on steel and 44 times lower than on the Al substrates.
- Although PVDF alone has a stronger adhesive force than (PVDF + 2.5 g CeO2) composite coatings, the composite’s adherence is acceptable.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mohamed, A.M.A.; Jafari, R.; Farzaneh, M. An optimization of superhydrophobic polyvinylidene fluoride/zinc oxide materials using Taguchi method. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 288, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radwan, A.B.; Mohamed, A.M.A.; Abdullah, A.M.; Al-Maadeed, M.A. Corrosion protection of electrospun PVDF-ZnO superhydrophobic coating. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2016, 289, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, B.; Shen, Z. Fabrication of superhydrophobic surfaces by dislocation-selective chemical etching on aluminum, copper, and zinc substrates. Langmuir 2005, 21, 9007–9009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkarter, E.; Saul, C.K.; Thomazi, F.; Cruz, N.C.; Zanata, S.M.; Roman, L.S.; Schreiner, W.H. Electrosprayed superhydrophobic PTFE: A non-contaminating surface. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2007, 40, 7778–7781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.Y.; Park, S.J. Effect of fluorination of carbon nanotubes on superhydrophobic properties of fluoro-based films. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 342, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Lau, S.P.; Yang, H.Y.; Leong, E.S.P.; Yu, S.F.; Prawer, S. Stable superhydrophobic surface via carbon nanotubes coated with a ZnO thin film. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 7746–7748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, W.Y.; Lam, S.W.; Chiang, K.; Amal, R.; Zhao, H.; Brungs, M.P. Novel TiO2 thin film with non-UV activated superwetting and antifogging behaviours. J. Mater. Chem. 2007, 17, 952–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolas, M.; Guittard, F.; Géribaldi, S. Stable superhydrophobic and lipophobic conjugated polymers films. Langmuir 2006, 22, 3081–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taurino, R.; Fabbri, E.; Messori, M.; Pilati, F.; Pospiech, D.; Synytska, A. Facile preparation of superhydrophobic coatings by sol-gel processes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 325, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amigoni, S.; De, E.T.G.; Dufay, M.; Guittard, F. Covalent layer-by-layer assembled superhydrophobic organic-inorganic hybrid films. Langmuir 2009, 25, 11073–11077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Fadeev, A.Y.; Hsieh, M.C.; Öner, D.; Youngblood, J.; McCarthy, T.J. Ultrahydrophobic and ultralyophobic surfaces: Some comments and examples. Langmuir 1999, 15, 3395–3399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, C.; Liu, F.; Yuan, R.; Wang, H. Durable superhydrophobic PVDF/FEVE/GO@TiO2 composite coating with excellent anti-scaling and UV resistance properties. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 411, 128632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roach, P.; Shirtcliffe, N.J.; Newton, M.I. Progess in superhydrophobic surface development. Soft Matter 2008, 4, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Zhai, J.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, L. Fabrication of Superhydrophobic Surfaces by Self-Assembly and Their Water-Adhesion Properties. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 4048–4052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, C.-H.; Jia, S.-T.; Zhang, J.; Ma, J.-Z. Large-area fabrication of superhydrophobic surfaces for practical applications: An overview. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2010, 11, 033002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Men, X.; Xu, X.; Zhu, X. A simple approach to fabricate regenerable superhydrophobic coatings. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2010, 367, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, F.; Liu, X.; Jin, J.; Jiang, L. Superhydrophobic and superoleophilic PVDF membranes for effective separation of water-in-oil emulsions with high flux. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 2071–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Xing, S.; Yuan, Z.; Xiao, J.; Wang, C.; Zeng, J. Preparation and anti-icing of superhydrophobic PVDF coating on a wind turbine blade. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 259, 764–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, Z.; Wang, E.; Yuan, R.; Gao, D.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, Y. A robust superhydrophobic PVDF composite coating with wear/corrosion-resistance properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 332, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, X.; Hu, X.; Wang, C.; Yang, Y. Preparation and characterization of PSF-TiO2 hybrid hollow fiber UF membrane by sol-gel method. J. Polym. Res. 2020, 27, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, H.M.; Wang, Y.; Takahashi, K.; Cao, G.Z.; Li, D.; Xia, Y.N. Nanostructured superhydrophobic surfaces. J. Mater. Sci. 2005, 40, 3587–3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Huang, Z.; Jiang, L.; Xiao, T.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, H.; Li, S.; Chen, X. A simple fabrication of superhydrophobic PVDF/SiO2 coatings and their ant-icing properties. J. Mater. Res. 2021, 210, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Lv, C.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, C. Durable and self-healing superhydrophobic polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) composite coating with in-situ gas compensation function. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 327, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, Y.; Yang, C.; Yu, N.; Shang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, C. Superhydrophobic TiO2/polyvinylidene fluoride composite surface with reversible wettability switching and corrosion resistance. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 290, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazali, N.; Basirun, W.J.; Nor, A.M.; Johan, M.R. Super-amphiphobic coating system incorporating functionalized nano-Al2O3 in polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) with enhanced corrosion resistance. Coatings 2020, 10, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, E.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, R.; Zhu, Y. Superhydrophobic poly(vinylidene fluoride) membranes with controllable structure and tunable wettability prepared by one-step electrospinning. Polymer 2016, 82, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; He, Y. Effects of nano sized zinc oxide on the performance of PVDF microfiltration membranes. Desalination 2012, 302, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.L.; Li, N.; Yi, W.J.; Li, L.J.; Chao, Z.S. High performance super-hydrophobic ZrO2-SiO2 porous ceramics coating with flower-like CeO2 micro/nano-structure. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 325, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Luo, D.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, G. Patterning ZrO2 films surface: Superhydrophilic and superhydrophobic properties. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 5089–5094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latthe, S.S.; Gurav, A.B.; Maruti, C.S.; Vhatkar, R.S. Recent Progress in Preparation of Superhydrophobic Surfaces: A Review. J. Surf. Eng. Mater. Adv. Technol. 2012, 2, 76–94. [Google Scholar]
- Lakshmi, R.V.; Bharathidasan, T.; Bera, P.; Basu, B.J. Fabrication of superhydrophobic and oleophobic sol-gel nanocomposite coating. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2012, 206, 3888–3894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, D.; Liu, G.; Duncan, E.J.S. Robust amphiphobic coatings from bi-functional silica particles on flat substrates. Polymer 2013, 54, 3008–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.T.; Wu, F.L.; Chen, W.Y. Superhydrophobicity and superoleophobicity from hierarchical silica sphere stacking layers. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2010, 121, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, B.J.; Kumar, V.D.; Anandan, C. Surface studies on superhydrophobic and oleophobic polydimethylsiloxane- silica nanocomposite coating system. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 261, 807–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Li, B.; Jing, L.; Tian, N.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, J. Efficient protection of Mg alloy enabled by combination of a conventional ant-corrosion coating and a superamphiphobic coating. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 390, 124562–124575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Xiong, D. Applied Surface Science Superhydrophobic membranes on metal substrate and their corrosion protection in different corrosive media. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 305, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhoke, S.K.; Khanna, A.S. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) study of nano-alumina modified alkyd based waterborne coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2012, 74, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Jung, R.; Kim, H.S.; Jin, H.J. Preparation of superhydrophobic polystyrene membranes by electrospinning. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2008, 313–314, 411–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.M.A.; Abdullah, A.M.; Younan, N.A. Corrosion behavior of superhydrophobic surfaces: A review. Arab. J. Chem. 2015, 8, 749–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakajima, A.; Hashimoto, K.; Watanabe, T. Recent Studies on Super-Hydrophobic Films. In Molecular Materials and Functional Polymers; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 2001; Volume 41, pp. 31–41. [Google Scholar]
- el Haleem, S.M.A.; el Wanees, S.A.; Bahgat, A. Environmental factors affecting the corrosion behaviour of reinforcing steel. VI. Benzotriazole and its derivatives as corrosion inhibitors of steel. Corros. Sci. 2014, 87, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Substrate | Coating | Wt/100 mL of Composite Solution | Substrate Code |
|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Uncoated | - | S1 |
| PVDF | 5.0 g | S2 | |
| CeO2 | 1.5 g | S3 | |
| 2.0 g | S4 | ||
| 2.5 g | S5 | ||
| Aluminium | Uncoated | - | A1 |
| PVDF | 5.0 g | A2 | |
| CeO2 | 1.5 g | A3 | |
| 2.0 g | A4 | ||
| 2.5 g | A5 | ||
| Glass | Uncoated | - | G1 |
| PVDF | 5.0 g | G2 | |
| CeO2 | 1.5 g | G3 | |
| 2.0 g | G4 | ||
| 2.5 g | G5 |
| Steel Substrates | βa (mV) | βc (mV) | Rp (K Ω cm2) | CR Rate (mpy) | η (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Uncoated Steel | 117 | 139 | 0.7 | 17 | 37.75 | - |
| PVDF | 73 | 198 | 6.9 | 0.24 | 3.34 | 91 |
| PVDF + 2.5 g CeO2 | 538 | 689 | 42.6 | 0.22 | 3.08 | 92 |
| Aluminium Substrates | βa (mV) | βc (mV) | Rp (K Ω cm2) | CR Rate (mpy) | (µA/cm2) | η(%) |
| Uncoated Aluminium | 54 | 122 | 1.9 | 3.54 | 8.26 | - |
| PVDF | 93 | 865 | 28 | 0.08 | 1.3 | 84 |
| PVDF + 2.5 g CeO2 | 383 | 658 | 525 | 0.02 | 0.2 | 97 |
| Element | PVDF Only | PVDF + 2.5 g CeO2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mass % | Atom % | Mass % | Atom % | |
| C | 55.80 | 59.35 | 33.18 | 53.52 |
| F | 44.20 | 40.65 | 24.90 | 25.40 |
| O | - | - | 14.25 | 17.25 |
| Ce | - | - | 27.67 | 3.83 |
| Total | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saleh, S.M.; Alminderej, F.M.; Mohamed, A.M.A. Superhydrophobic and Corrosion Behaviour of PVDF-CeO2 Composite Coatings. Materials 2022, 15, 8674. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15238674
Saleh SM, Alminderej FM, Mohamed AMA. Superhydrophobic and Corrosion Behaviour of PVDF-CeO2 Composite Coatings. Materials. 2022; 15(23):8674. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15238674
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaleh, Sayed M., Fahad M. Alminderej, and Adel M. A. Mohamed. 2022. "Superhydrophobic and Corrosion Behaviour of PVDF-CeO2 Composite Coatings" Materials 15, no. 23: 8674. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15238674
APA StyleSaleh, S. M., Alminderej, F. M., & Mohamed, A. M. A. (2022). Superhydrophobic and Corrosion Behaviour of PVDF-CeO2 Composite Coatings. Materials, 15(23), 8674. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15238674







