Self-Pierce Riveting of Three Thin Sheets of Aluminum Alloy A5052 and 980 MPa Steel
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Three Sheets of Self-Pierce Riveting
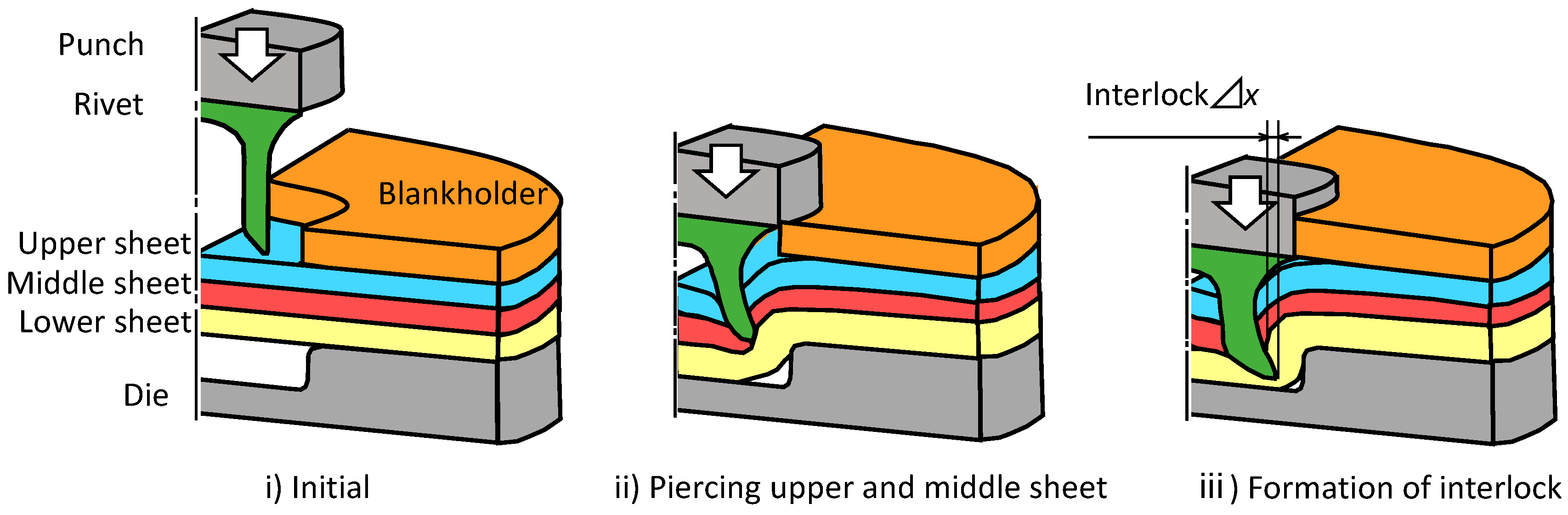
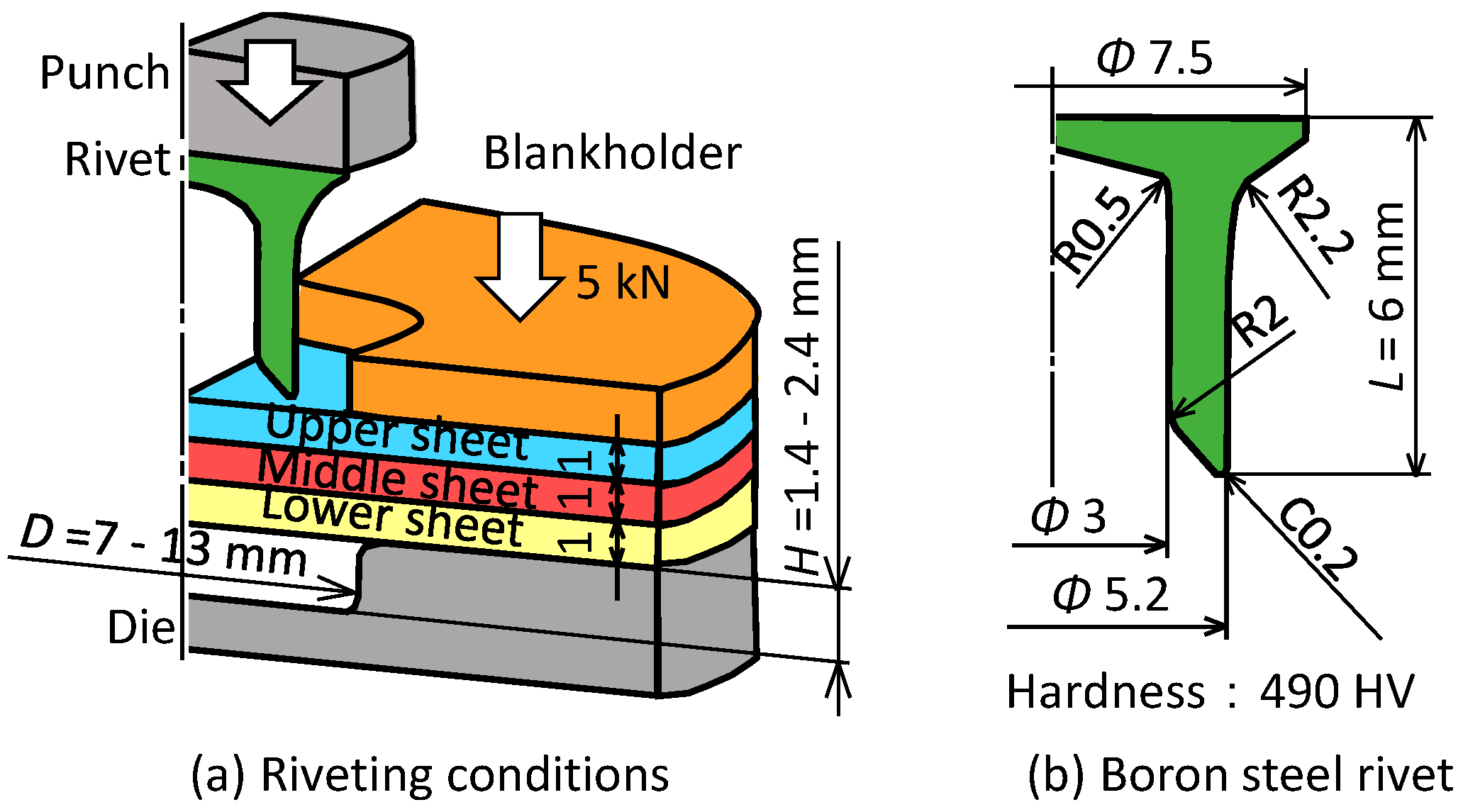
2.1. Process and Conditions for Self-Pierce Riveting of Three Sheets
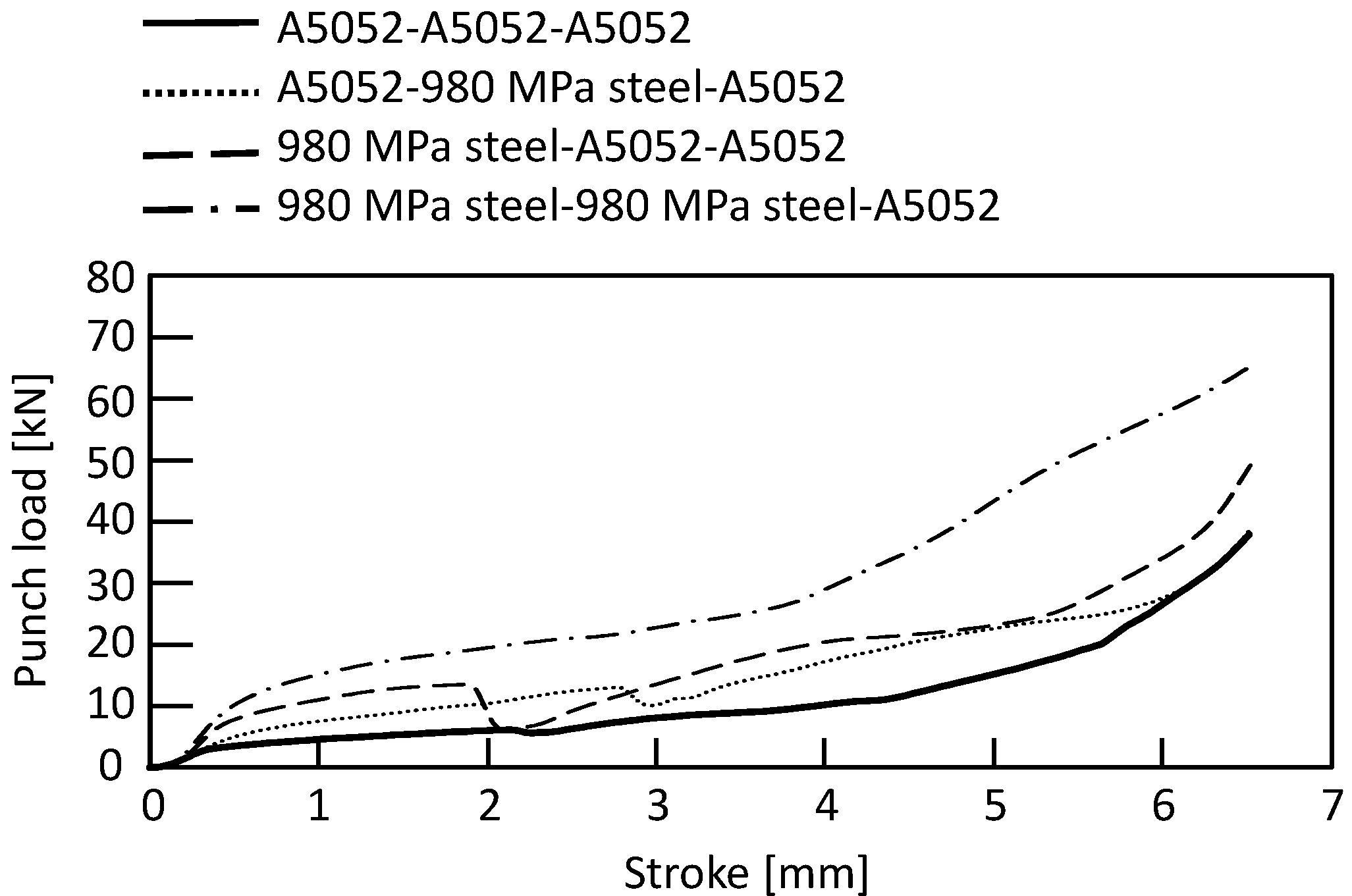
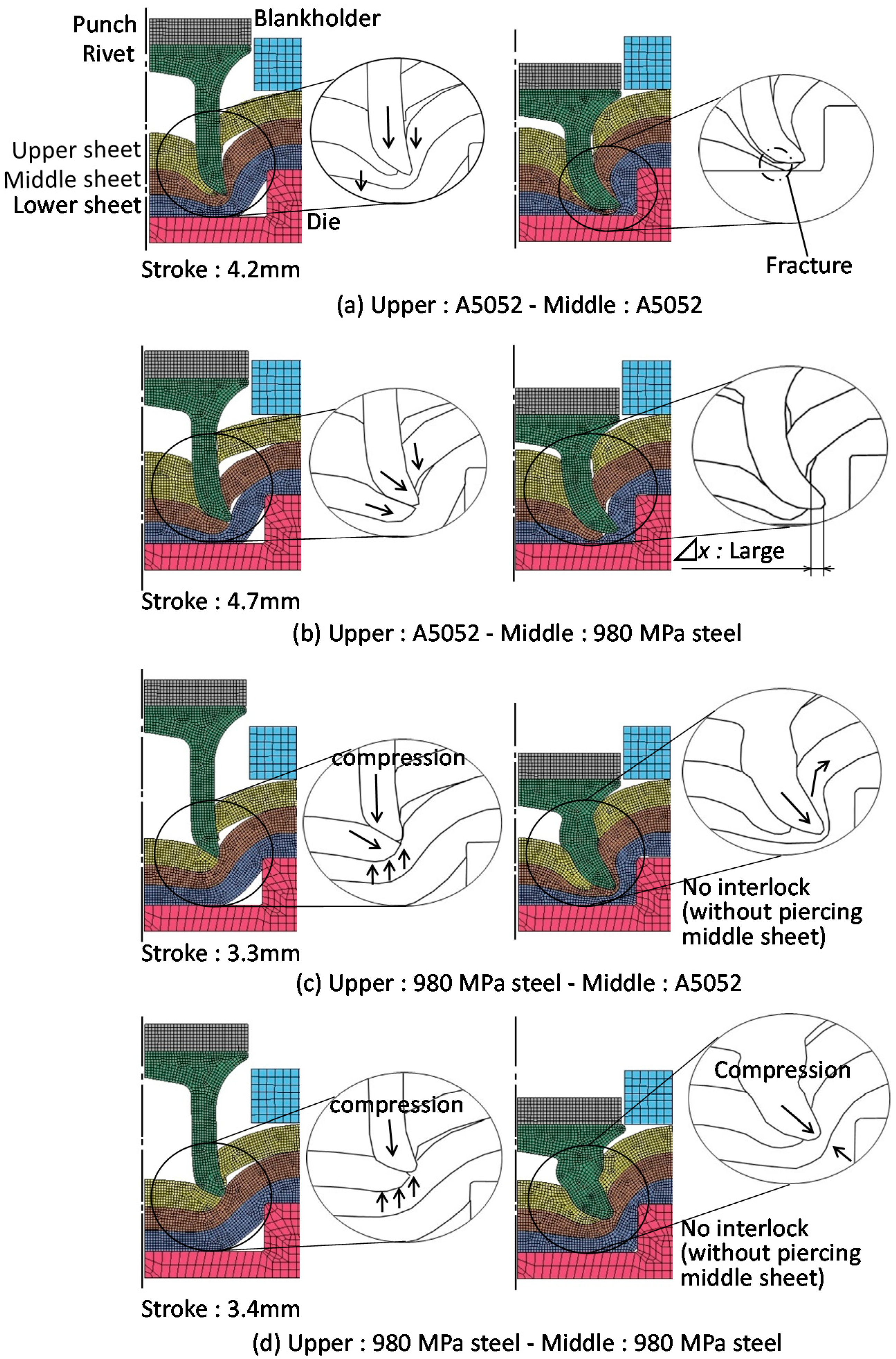
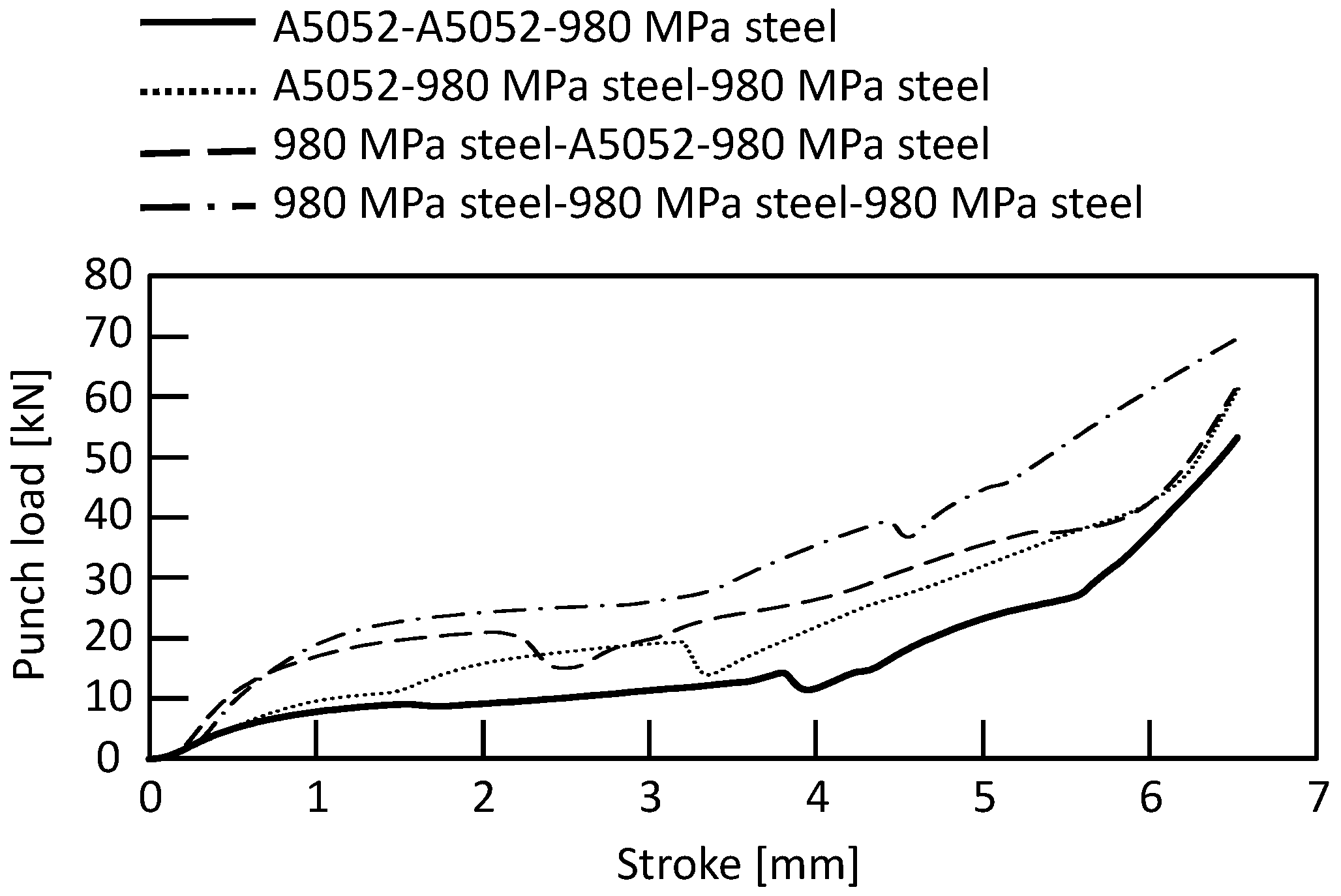
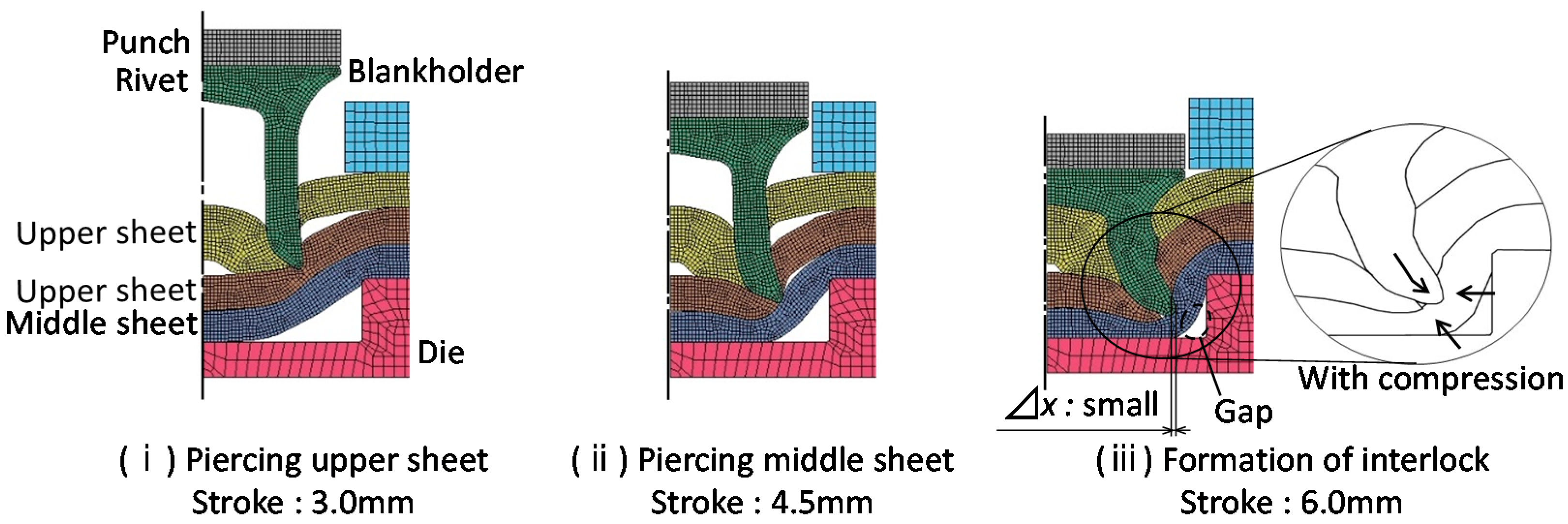
2.2. Simulation Conditions and Results
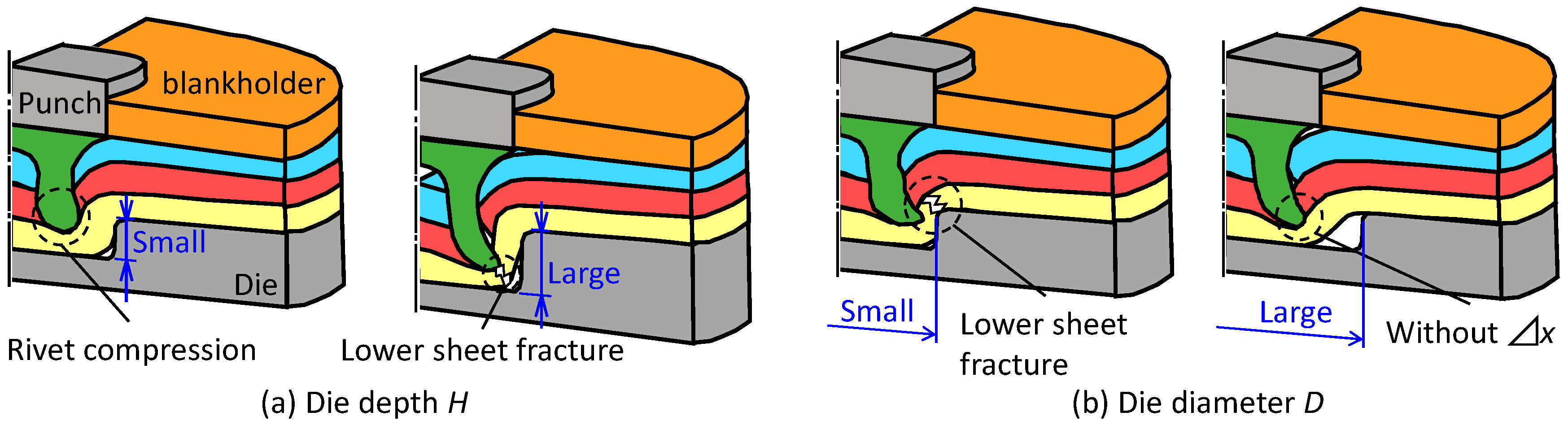
2.3. Joining Requirements
3. Three Sheets Joining of 980 MPa Steel and Aluminum Alloy
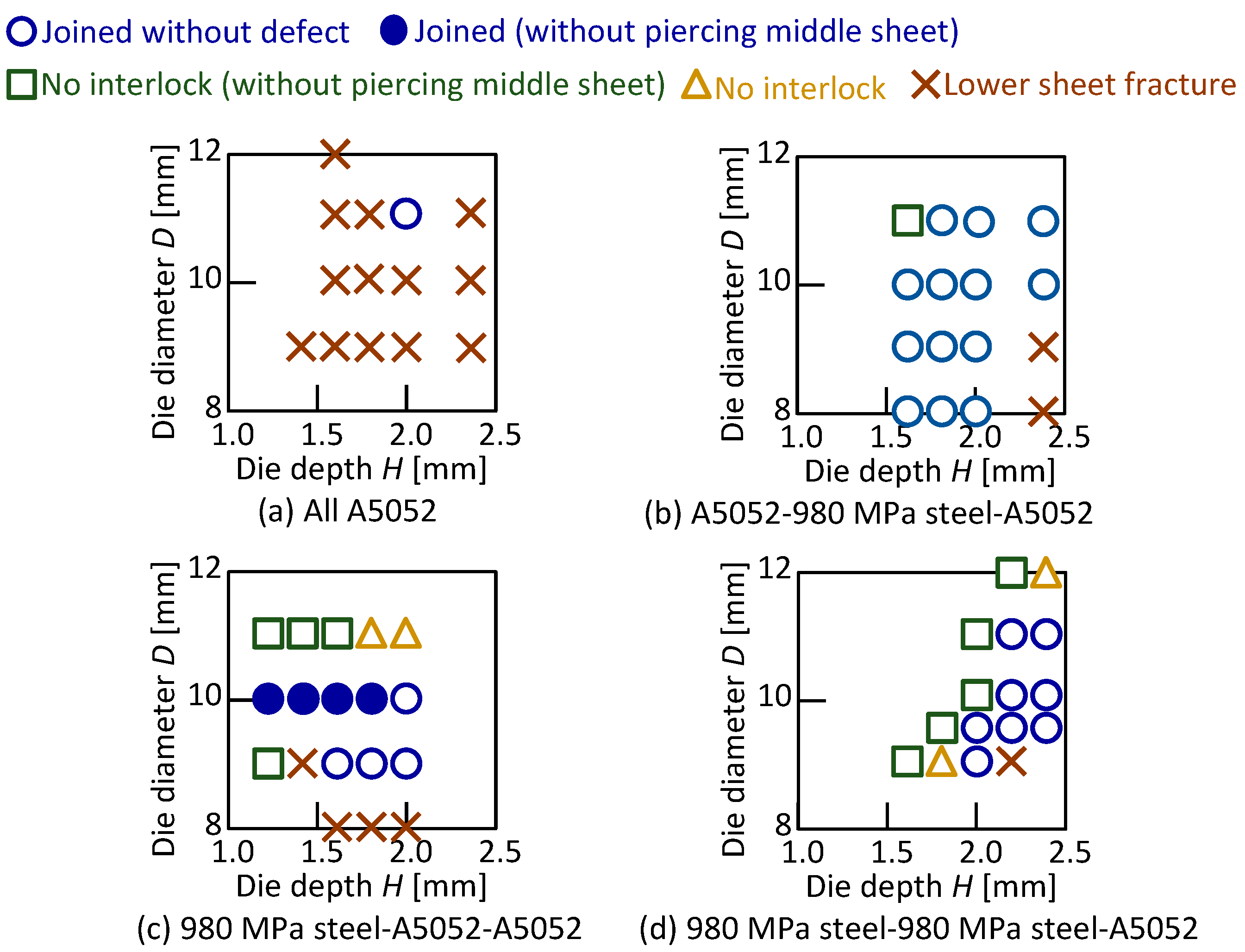
3.1. Three Sheets Joining in Lower Aluminum Alloy
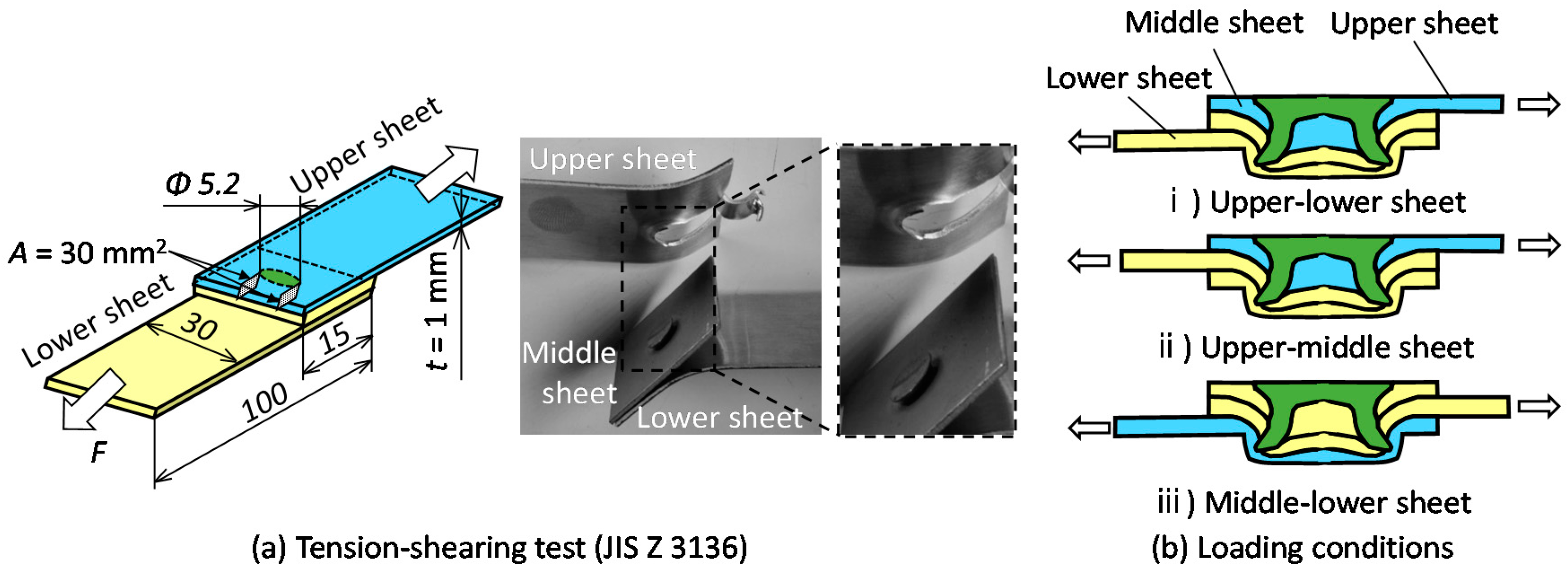
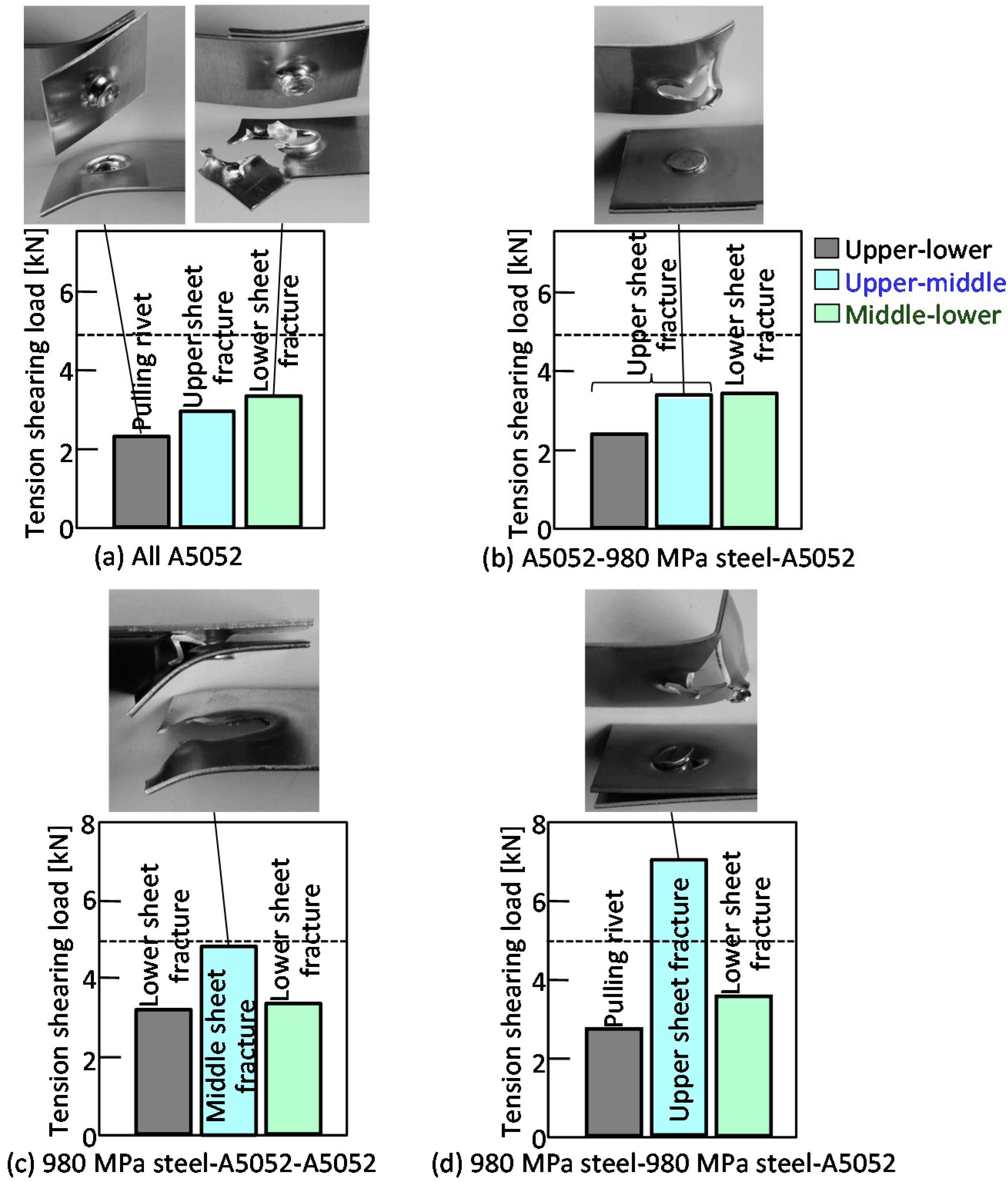
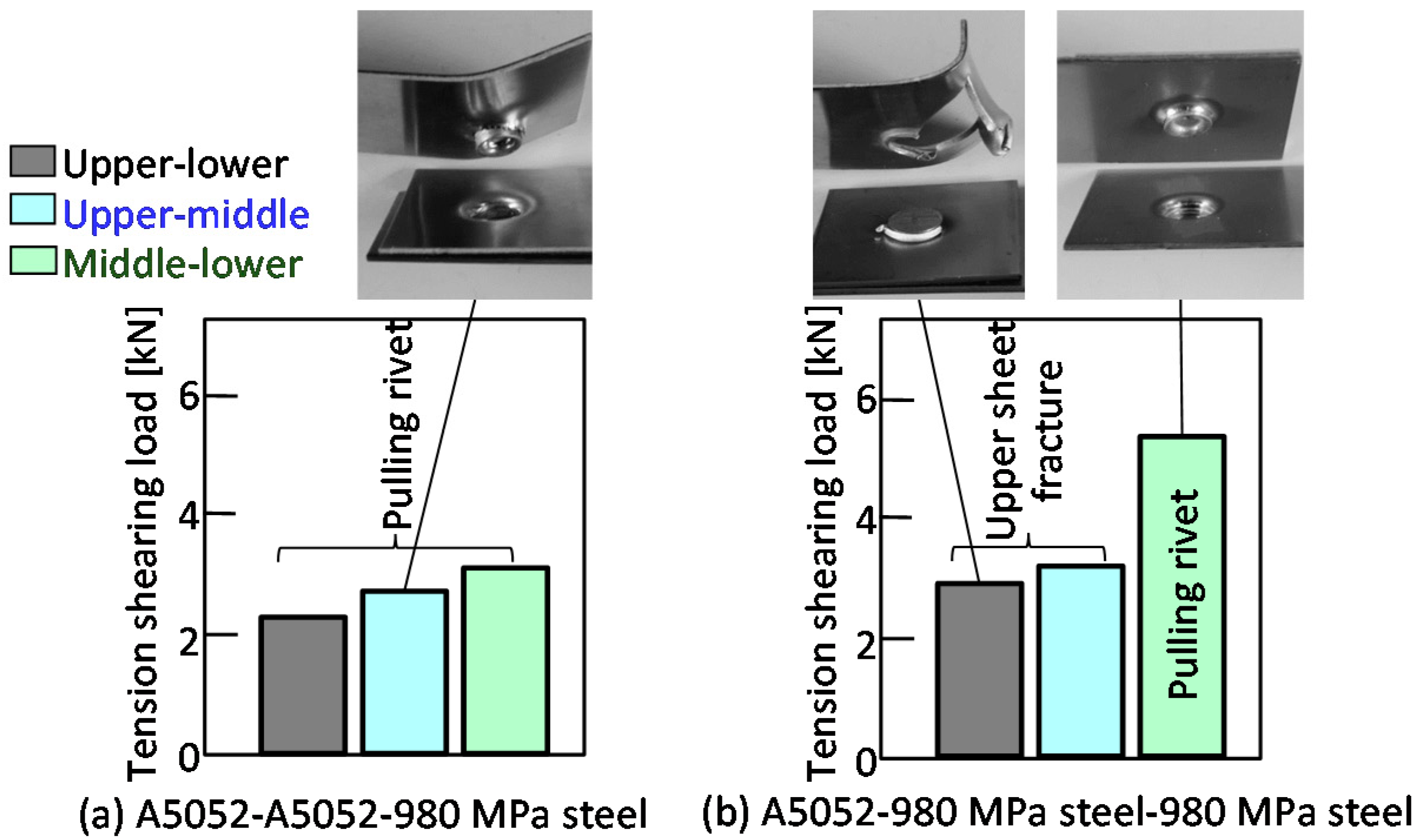
3.2. The Tension-Shearing Test in Lower Aluminum Alloy
3.3. Three Sheets Joining in Lower 980 MPa Steel
3.4. The Tension-Shearing Test in Lower 980 MPa Steel
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- When the lower sheet was the aluminum alloy, the joint range was relatively wide, and the interlock tended to be large;
- (2)
- In the lower 980 MPa steel sheet, A5052-A5052-980 MPa steel and A5052-980 MPa steel-980 MPa steel were joined by selecting an appropriate die shape. Due to the low ductility and high flow stress of the lower sheet, fracture tended to occur, resulting in a narrower joining range where the interlock was not large;
- (3)
- Among the eight types of sheet configurations, A5052-980 MPa steel-A5052 was the best configuration to join because it provided the widest joining range by moderately spreading the rivet leg so that a large interlock was obtained;
- (4)
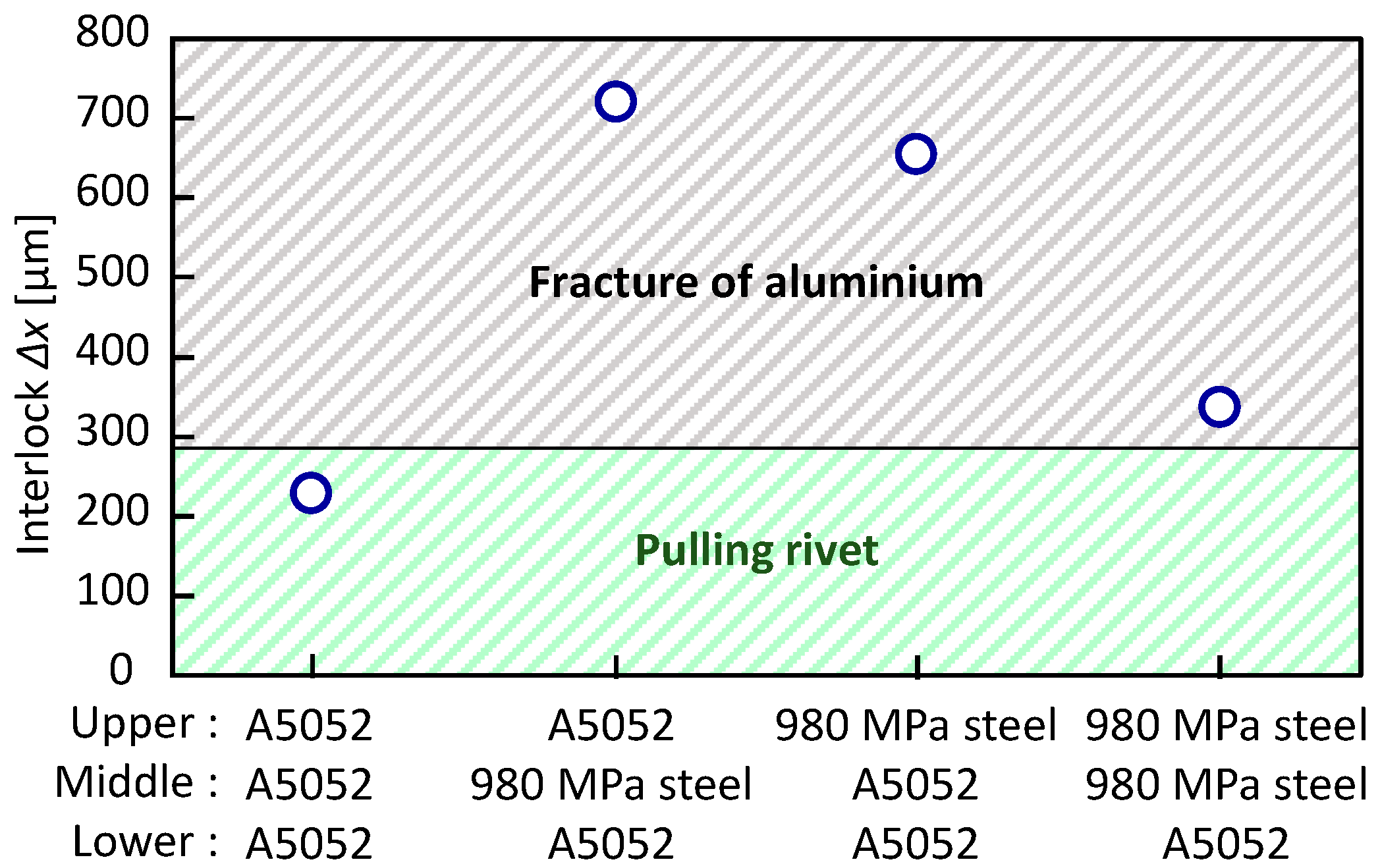
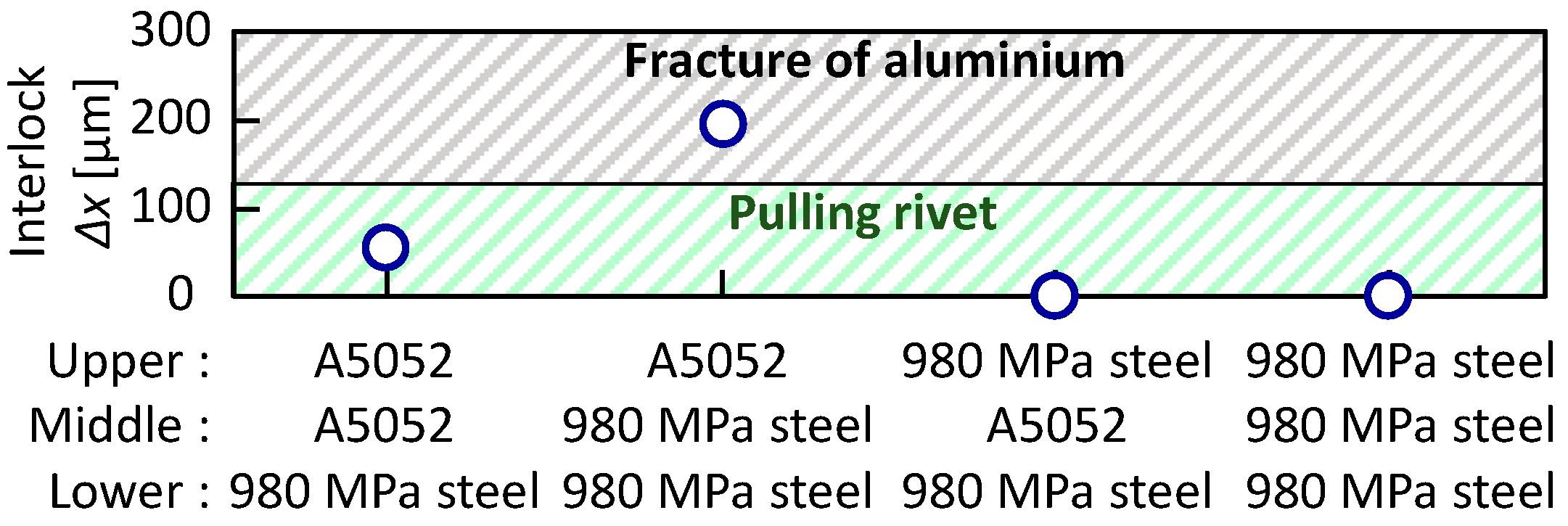
- In the tension-shearing test, fracture occurred in the lower-strength aluminum alloy sheet if interlocks of about 300 μm and 150 μm could be formed in the lower aluminum alloy sheet and 980 MPa steel sheet, respectively.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lai, M.; Brun, R. Latest developments in sheet metal forming technology and materials for automotive application: The use of ultra high strength steels at Fiat to reach weight reduction at sustainable costs. Key Eng. Mater. 2007, 344, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Haque, R.; Beynon, J.H.; Durandet, Y.; Kirstein, O.; Blacket, S. Feasibility of measuring residual stress profile in different self-pierce riveted joints. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2013, 17, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Kang, H.; Liu, Y. Finite Element Analysis for Transient Thermal Characteristics of Resistance Spot Welding Process with Three Sheets Assemblies. Procedia Eng. 2011, 16, 622–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, N.; Murakawa, H. Numerical and experimental study on nugget formation in resistance spot welding for three pieces of high strength steel sheets. J. Mater. Proc. Technol. 2010, 210, 2045–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakiyama, T.; Naito, Y.; Miyazaki, Y.; Nose, T.; Murayama, G.; Saita, K.; Oikawa, H. Dissimilar Metal Joining Technologies for Steel Sheet and Aluminium Alloy Sheet in Auto Body. Nippon Steel Tech. Rep. 2013, 103, 91–98. Available online: https://www.nipponsteel.com/en/tech/report/nsc/pdf/103-14.pdf (accessed on 1 September 2021).
- Meschut, G.; Janzen, V.; Olfermann, T. Innovative and Highly Productive Joining Technologies for Multi-Material Lightweight Car Body Structures. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2014, 23, 1515–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fereiduni, E.; Movahedi, M.; Kokabi, A.H. Aluminium/steel joints made by an alternative friction stir spot welding process. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2015, 224, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Tada, M.; Shiota, A.; Kokawa, H.; Nakagawa, S.; Miyamoto, K. Effect of Zn coating on tensile shear strength in dissimilar friction stir spot welds of Al alloy and Zn-coated steel. Prepr. Natl. Meet. JWS 2009, 84, 46–47. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, K.; Watanabe, M.; Kumai, S. Microstructure and Joint Strength of Friction Stir Spot Welded 6022 Aluminium Alloy Sheets and Plated Steel Sheets. Mater. Trans. 2011, 52, 48–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamamoto, M.; Ogura, T.; Ohashi, R.; Fujimoto, M.; Hirose, A. Effects of interfacial microstructures on joint strength in friction stir spot welded 6061 aluminium alloy/zinc coated steel joints. J. Light Met. Weld. 2013, 51, 223–232. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Chen, C.; Zhang, H.; Ran, X. Recent Development of Improved Clinching Process. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 110, 3169–3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Liu, F.; Xing, B.; Yang, H.; Wang, Y.; Gu, F.; Ball, A. Numerical and experimental investigations of extensible die clinching. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2014, 74, 1229–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhao, S.; Cui, M.; Han, X.; Fan, S. Mechanical properties of the two-steps clinched joint with a clinch-rivet. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2016, 237, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hörhold, R.; Müller, M.; Merklein, M.; Meschut, G. Mechanical properties of an innovative shear-clinching technology for ultra-high-strength steel and aluminium in lightweight car body structures. Weld. World 2016, 60, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.J.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, J.M.; Kim, B.H.; Kim, B.M.; Ko, D.C. Design of Hole-Clinching Process for Joining CFRP and Aluminium Alloy Sheet. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2014, 15, 1151–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, Y.; Mori, K.; Kato, T. Joining of high strength steel and aluminium alloy sheets by mechanical clinching with dies for control of metal flow. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2012, 212, 884–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaðèák, L.; Spiðák, E.; Kubík, R.; Mucha, J. Finite Element Calculation of Clinching with Rigid Die of Three Steel Sheets. Strength Mater. 2017, 49, 488–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, T.A.; Pashby, I.R. Joining Techniques for Aluminium Spaceframes Used in Automobiles: Part II-Adhesive Bonding and Mechanical Fasteners. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2000, 99, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, K.; Bay, N.; Fratini, L.; Micari, F.; Tekkaya, A.E. Joining by plastic deformation. CIRP Ann.–Manuf. Technol. 2013, 62, 673–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, K.; Abe, Y.; Kato, T. Mechanism of Superiority of Fatigue Strength for Aluminium Alloy Sheets Joined by Mechanical Clinching and Self-Pierce Riveting. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2012, 212, 1900–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, Y.; Kato, T.; Mori, K. Joinability of Aluminium Alloy and Mild Steel Sheets by Self Piercing Rivet. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2006, 177, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzeni, E.; lppolito, R.; Settineril, L. FEM Modeling of Self Piercing Riveted Joint. Key Eng. Mater. 2007, 344, 655–662. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, P.K.C.; Schley, C.A.; Williams, M.A.; Rusinek, A. Model to Describe the High Rate Performance of Self-Piercing Riveted Joints in Sheet Aluminium. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 2246–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H. Influence of riveting sequence/direction on distortion of steel and aluminum sheets. J. Manuf. Processes. 2020, 53, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, T.-E.; Kam, D.-H.; Kim, C. Parametric investigation of effect of abnormal process conditions on self-piercing riveting. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Porcaro, R.; Hanssen, A.G.; Langseth, M.; Aalberg, A. The behaviour of a self-piercing riveted connection under quasi-static loading conditions. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2016, 43, 5110–5131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, Y.M.; Lou, M.; Li, Y.B.; Lin, Z.Q. Effect of Rivet and Die on Self-Piercing Rivetability of AA6061-T6 and Mild Steel CR4 of Different Gauges. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2018, 251, 282–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y. Effects of factors on physical attributes of self-piercing riveted joints. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2006, 11, 666–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, J.; Jordon, J.; Su, X.; Brewer, L.; Fay, B.; Bunn, J.; Sochalski-Kolbus, L.; Barkey, M. Residual stresses and plastic deformation in self-pierce riveting of dissimilar aluminum-to-magnesium alloys. SAE Int. J. Mater. Manf. 2018, 11, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, Y.; Kato, T.; Mori, K. Self-piercing riveting of high tensile strength steel and aluminium alloy sheets using conventional rivet and die. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2009, 209, 3914–3922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, K.; Kato, T.; Abe, Y.; Ravshanbek, Y. Plastic joining of ultra high strength steel and aluminium alloy sheets by self piercing rivet. Ann. CIRP 2006, 55, 283–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Chrysanthou, A.; Young, K.W. Mechanical Behaviour of Self-Piercing Riveted Multi-Layer Joints under Different Specimen Configurations. Mater. Des. 2007, 28, 2024–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, Y.; Kato, T.; Mori, K. Self-Pierce Riveting of Three High Strength Steel and Aluminium Alloy Sheets. Int. J. Mater. Form. 2008, 1, 1271–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, K.; Abe, Y.; Kato, T. Self-pierce riveting of multiple steel and aluminium alloy sheets. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2014, 214, 2002–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, K.; Abe, Y.; Kato, T.; Sakai, S. Self-Pierce Riveting of Three Aluminium Alloy and Mild Steel Sheets. AIP Conf. Proc. 2010, 1252, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, Y.; Maeda, T.; Yoshioka, D.; Mori, K. Mechanical clinching and self-pierce riveting of thin three sheets of 5000 series aluminium alloy and 980 MPa grade cold rolled ultra-high strength steel. Materials 2020, 13, 4741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Japanese Industrial Standards. Specimen Dimensions and Procedure for Shear Testing Resistance Spot and Embossed Projection Welds; JIS Z3136; Japanese Industrial Standards (JIS): Tokyo, Japan, 1999. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]






| Sheet | Sheet Thickness [mm] | Tensile Strength [MPa] | Elongation [%] | Reduction in Area [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A5052 | 1.05 | 275 | 25 | 65 |
| 980 MPa steel | 1.05 | 1002 | 14 | 35 |
| Sheet | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upper | A5052 | A5052 | 980 MPa steel | 980 MPa steel | A5052 | A5052 | 980 MPa steel | 980 MPa steel |
| Middle | A5052 | 980 MPa steel | A5052 | 980 MPa steel | A5052 | 980 MPa steel | A5052 | 980 MPa steel |
| Lower | A5052 | A5052 | A5052 | A5052 | 980 MPa steel | 980 MPa steel | 980 MPa steel | 980 MPa steel |
| Solver | LS-DYNA |
|---|---|
| Simulation method | Dynamic explicit |
| Model | Axial symmetry |
| Plastic deformation | Isotropy |
| Yield criterion | Von Mises |
| Hardening equation | |
| Coefficient of friction | 0.2 |
| Sheet | Young’s Modulus [GPa] | K-Value ※ [MPa] | n-Value ※ [-] |
|---|---|---|---|
| A5052 | 70.3 | 550 | 0.32 |
| 980 MPa steel | 210 | 1406 | 0.13 |
| Upper Sheet | Middle Sheet | Die Depth H [mm] | Die Diameter D [mm] | Joining Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A5052 | A5052 | 1.4 | 9.0 | × |
| A5052 | A5052 | 1.6 | 9.0 | × |
| A5052 | A5052 | 1.6 | 10.0 | × |
| A5052 | A5052 | 1.6 | 11.0 | × |
| A5052 | A5052 | 1.6 | 12.0 | × |
| A5052 | A5052 | 1.8 | 9.0 | × |
| A5052 | A5052 | 1.8 | 10.0 | × |
| A5052 | A5052 | 1.8 | 11.0 | × |
| A5052 | A5052 | 2.0 | 9.0 | × |
| A5052 | A5052 | 2.0 | 10.0 | × |
| A5052 | A5052 | 2.0 | 11.0 | ○ |
| A5052 | A5052 | 2.4 | 9.0 | × |
| A5052 | A5052 | 2.4 | 10.0 | × |
| A5052 | A5052 | 2.4 | 11.0 | × |
| A5052 | 980 MPa Steel | 1.6 | 8.0 | ○ |
| A5052 | 980 MPa Steel | 1.6 | 9.0 | ○ |
| A5052 | 980 MPa Steel | 1.6 | 10.0 | ○ |
| A5052 | 980 MPa Steel | 1.6 | 11.0 | □ |
| A5052 | 980 MPa Steel | 1.8 | 8.0 | ○ |
| A5052 | 980 MPa Steel | 1.8 | 9.0 | ○ |
| A5052 | 980 MPa Steel | 1.8 | 10.0 | ○ |
| A5052 | 980 MPa Steel | 1.8 | 11.0 | ○ |
| A5052 | 980 MPa Steel | 2.0 | 8.0 | ○ |
| A5052 | 980 MPa Steel | 2.0 | 9.0 | ○ |
| A5052 | 980 MPa Steel | 2.0 | 10.0 | ○ |
| A5052 | 980 MPa Steel | 2.0 | 11.0 | ○ |
| A5052 | 980 MPa Steel | 2.4 | 8.0 | × |
| A5052 | 980 MPa Steel | 2.4 | 9.0 | × |
| A5052 | 980 MPa Steel | 2.4 | 10.0 | ○ |
| A5052 | 980 MPa Steel | 2.4 | 11.0 | ○ |
| 980 MPa Steel | A5052 | 1.2 | 9.0 | □ |
| 980 MPa Steel | A5052 | 1.2 | 10.0 | ● |
| 980 MPa Steel | A5052 | 1.2 | 11.0 | □ |
| 980 MPa Steel | A5052 | 1.4 | 9.0 | × |
| 980 MPa Steel | A5052 | 1.4 | 10.0 | ● |
| 980 MPa Steel | A5052 | 1.4 | 11.0 | □ |
| 980 MPa Steel | A5052 | 1.6 | 8.0 | × |
| 980 MPa Steel | A5052 | 1.6 | 9.0 | ○ |
| 980 MPa Steel | A5052 | 1.6 | 10.0 | ● |
| 980 MPa Steel | A5052 | 1.6 | 11.0 | □ |
| 980 MPa Steel | A5052 | 1.8 | 8.0 | × |
| 980 MPa Steel | A5052 | 1.8 | 9.0 | ○ |
| 980 MPa Steel | A5052 | 1.8 | 10.0 | ● |
| 980 MPa Steel | A5052 | 1.8 | 11.0 | △ |
| 980 MPa Steel | A5052 | 2.0 | 8.0 | × |
| 980 MPa Steel | A5052 | 2.0 | 9.0 | ○ |
| 980 MPa Steel | A5052 | 2.0 | 10.0 | ○ |
| 980 MPa Steel | A5052 | 2.0 | 11.0 | △ |
| 980 MPa Steel | 980 MPa Steel | 1.6 | 9.0 | □ |
| 980 MPa Steel | 980 MPa Steel | 1.8 | 9.0 | △ |
| 980 MPa Steel | 980 MPa Steel | 1.8 | 9.5 | □ |
| 980 MPa Steel | 980 MPa Steel | 2.0 | 9.0 | ○ |
| 980 MPa Steel | 980 MPa Steel | 2.0 | 9.5 | ○ |
| 980 MPa Steel | 980 MPa Steel | 2.0 | 10.0 | □ |
| 980 MPa Steel | 980 MPa Steel | 2.0 | 11.0 | □ |
| 980 MPa Steel | 980 MPa Steel | 2.2 | 9.0 | × |
| 980 MPa Steel | 980 MPa Steel | 2.2 | 9.5 | ○ |
| 980 MPa Steel | 980 MPa Steel | 2.2 | 10.0 | ○ |
| 980 MPa Steel | 980 MPa Steel | 2.2 | 11.0 | ○ |
| 980 MPa Steel | 980 MPa Steel | 2.2 | 12.0 | □ |
| 980 MPa Steel | 980 MPa Steel | 2.4 | 9.5 | ○ |
| 980 MPa Steel | 980 MPa Steel | 2.4 | 10.0 | ○ |
| 980 MPa Steel | 980 MPa Steel | 2.4 | 11.0 | ○ |
| 980 MPa Steel | 980 MPa Steel | 2.4 | 12.0 | △ |
| Upper Sheet | Middle Sheet | Die Depth H [mm] | Die Diameter D [mm] | Joining Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A5052 | A5052 | 1.4 | 11.0 | △ |
| A5052 | A5052 | 1.6 | 9.0 | × |
| A5052 | A5052 | 1.6 | 10.0 | △ |
| A5052 | A5052 | 1.6 | 11.0 | △ |
| A5052 | A5052 | 1.8 | 9.0 | × |
| A5052 | A5052 | 1.8 | 10.0 | × |
| A5052 | A5052 | 1.8 | 11.0 | ○ |
| A5052 | A5052 | 1.8 | 12.0 | △ |
| A5052 | A5052 | 2.0 | 9.0 | × |
| A5052 | A5052 | 2.0 | 10.0 | × |
| A5052 | A5052 | 2.0 | 11.0 | × |
| A5052 | A5052 | 2.4 | 9.0 | × |
| A5052 | A5052 | 2.4 | 10.0 | × |
| A5052 | 980 MPa Steel | 1.6 | 8.0 | ○ |
| A5052 | 980 MPa Steel | 1.6 | 9.0 | ○ |
| A5052 | 980 MPa Steel | 1.6 | 10.0 | △ |
| A5052 | 980 MPa Steel | 1.8 | 8.0 | ○ |
| A5052 | 980 MPa Steel | 1.8 | 9.0 | ○ |
| A5052 | 980 MPa Steel | 1.8 | 10.0 | △ |
| A5052 | 980 MPa Steel | 2.0 | 8.0 | × |
| A5052 | 980 MPa Steel | 2.0 | 9.0 | × |
| A5052 | 980 MPa Steel | 2.0 | 10.0 | × |
| A5052 | 980 MPa Steel | 2.4 | 10.0 | × |
| 980 MPa Steel | A5052 | 1.6 | 8.0 | × |
| 980 MPa Steel | A5052 | 1.6 | 9.0 | × |
| 980 MPa Steel | A5052 | 1.6 | 10.0 | □ |
| 980 MPa Steel | A5052 | 1.8 | 8.0 | × |
| 980 MPa Steel | A5052 | 1.8 | 9.0 | □ |
| 980 MPa Steel | A5052 | 1.8 | 10.0 | □ |
| 980 MPa Steel | A5052 | 2.0 | 8.0 | × |
| 980 MPa Steel | A5052 | 2.0 | 9.0 | × |
| 980 MPa Steel | A5052 | 2.0 | 10.0 | □ |
| 980 MPa Steel | A5052 | 2.4 | 8.0 | × |
| 980 MPa Steel | A5052 | 2.4 | 9.0 | × |
| 980 MPa Steel | A5052 | 2.4 | 10.0 | □ |
| 980 MPa Steel | 980 MPa Steel | 1.6 | 9.0 | × |
| 980 MPa Steel | 980 MPa Steel | 1.6 | 10.0 | × |
| 980 MPa Steel | 980 MPa Steel | 1.6 | 11.0 | × |
| 980 MPa Steel | 980 MPa Steel | 2.4 | 9.0 | × |
| 980 MPa Steel | 980 MPa Steel | 2.4 | 10.0 | × |
| 980 MPa Steel | 980 MPa Steel | 2.4 | 11.0 | × |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Achira, S.; Abe, Y.; Mori, K.-i. Self-Pierce Riveting of Three Thin Sheets of Aluminum Alloy A5052 and 980 MPa Steel. Materials 2022, 15, 1010. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15031010
Achira S, Abe Y, Mori K-i. Self-Pierce Riveting of Three Thin Sheets of Aluminum Alloy A5052 and 980 MPa Steel. Materials. 2022; 15(3):1010. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15031010
Chicago/Turabian StyleAchira, Satoshi, Yohei Abe, and Ken-ichiro Mori. 2022. "Self-Pierce Riveting of Three Thin Sheets of Aluminum Alloy A5052 and 980 MPa Steel" Materials 15, no. 3: 1010. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15031010
APA StyleAchira, S., Abe, Y., & Mori, K.-i. (2022). Self-Pierce Riveting of Three Thin Sheets of Aluminum Alloy A5052 and 980 MPa Steel. Materials, 15(3), 1010. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15031010







