Gelatin- and Papaya-Based Biodegradable and Edible Packaging Films to Counter Plastic Waste Generation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Film
2.3. Film Characterization
2.3.1. FT-IR Analysis
2.3.2. UV-VIS
2.3.3. Contact Angle
2.3.4. Tensile Test
2.3.5. Bending and Hardness
2.3.6. WVTR
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. FT-IR
3.2. Light Transmission Rate and Transparency
3.3. Contact Angle
3.4. Tensile Test
3.5. Bendability
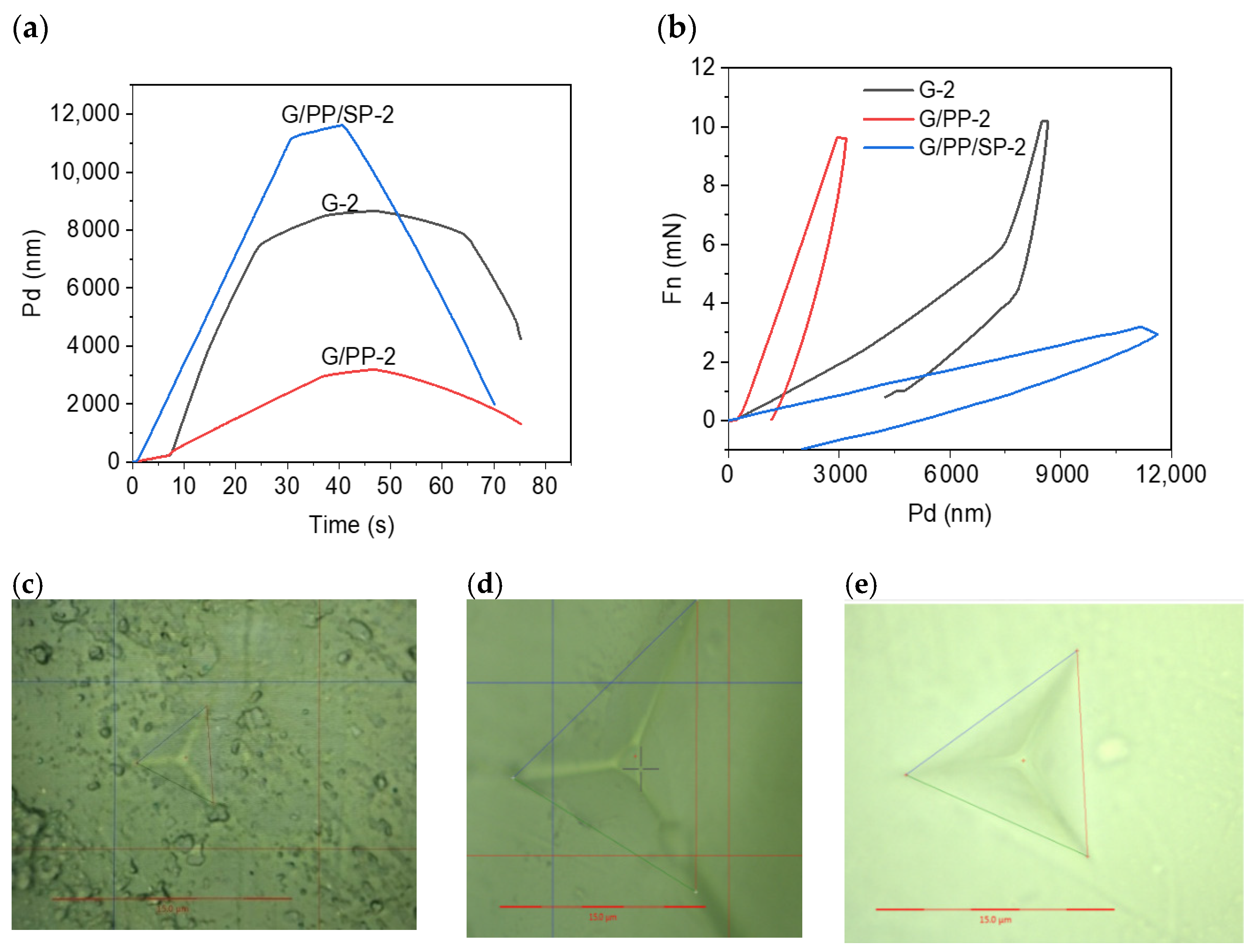
3.6. Hardness
3.7. Water Vapor Transmission Rate
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Verghese, K.; Lewis, H.; Lockrey, S.; Williams, H. The role of packaging in minimising food waste in the supply chain of the future. TAF Prev. Med. Bull. 2013, 15, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abro, S.H.; Chandio, A.; Alaboodi, A.S.; Channad, I.A. Role of Automotive Industry in Global Warming. Pak. J. Sci. Ind. Res. Ser. A Phys. Sci. 2019, 62, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Channa, I.A.; Chandio, A.; Rizwan, M.; Shah, A.; Bhatti, J.; Shah, A.; Hussain, F.; Shar, M.; AlHazaa, A. Solution Processed PVB /Mica Flake Coatings for the Encapsulation of Organic Solar Cells. Materials 2021, 14, 2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Channa, I.A.; Distler, A.; Egelhaaf, H.; Brabec, C.J. Solution Coated Barriers for Flexible Electronics. In Organic Flexible Electronics, Fundamentals, Devices, and Applications; Cosseddu, P., Caironi, M., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Southston, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal, M.; Ahmed, I.; Iqbal, M.; Khan, M.S.; Salman, S.M.; Noor, S. Preparation and Characterization of Co-Polymer (Acrylic Acid and Acrylamide) as Super Absorbent Composites Grafted with Thar Clay. Sci. Int. Lahore 2020, 32, 451–458. [Google Scholar]
- Chandio, A.D.; Channa, I.; Rizwan, M.; Akram, S.; Javed, M.; Siyal, S.; Saleem, M.; Makhdoom, M.; Ashfaq, T.; Khan, S.; et al. Polyvinyl alcohol and nano-clay based solution processed packaging coatings. Coatings 2021, 11, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, K.; Bugusu, B. Food packaging—Roles, materials, and environmental issues: Scientific status summary. J. Food Sci. 2007, 72, R39–R55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ASTM-E460. Standard Practice for Determining Effect of Packaging on Food and Beverage Products During Storage. 2021. Available online: https://www.astm.org/e0460-21.html (accessed on 1 December 2021).
- Channa, I.A.; Distler, A.; Scharfe, B.; Feroze, S.; Forberich, K.; Lipovšek, B.; Brabec, C.J.; Egelhaaf, H.-J. Solution processed oxygen and moisture barrier based on glass flakes for encapsulation of organic (opto-) electronic devices. Flex. Print. Electron. 2021, 6, 25006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerqueira, M.A.P.R.; Pereira, R.N.C.; Ramos, O.L.d.; Teixeira, J.A.C.; Vicente, A.A. Edible Food Packaging: Materials and Processing Technologies; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- de Oliveira, L.B.; de Azevedo, A.R.G.; Marvila, M.T.; Pereira, E.C.; Fediuk, R.; Vieira, C.M.F. Durability of geopolymers with industrial waste. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 16, e00839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ncube, L.K.; Ude, A.U.; Ogunmuyiwa, E.N.; Zulkifli, R.; Beas, I.N. Environmental impact of food packaging materials: A review of contemporary development from conventional plastics to polylactic acid based materials. Materials 2020, 13, 4994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ncube, L.K.; Ude, A.U.; Ogunmuyiwa, E.N.; Zulkifli, R.; Beas, I.N. An overview of plasticwaste generation and management in food packaging industries. Recycling 2021, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrose, D.C.P. Biodegradable Packaging—An Eco-Friendly Approach. Curr. Agric. Res. J. 2020, 8, 4–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delepierre, G.; Vanderfleet, O.M.; Niinivaara, E.; Zakani, B.; Cranston, E.D. Benchmarking Cellulose Nanocrystals Part II: New Industrially Produced Materials. Langmuir 2021, 37, 8393–8409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eric Stefan Kandelin Koons. What Is Biodegradable Packaging. Biodegradable. 2019. Available online: https://www.desjardin.fr/en/blog/what-is-biodegradable-packaging (accessed on 1 December 2021).
- Hann, S.; Fletcher, E.; Sherrington, C.; Molteno, S.; Elliott, L. Conventional and Biodegradable Plastics in Agriculture Presenters. 2021. Available online: https://www.eunomia.co.uk/reports-tools/conventional-and-biodegradable-plastics-in-agriculture/ (accessed on 1 December 2021).
- de Azevedo, A.R.G.; Amin, M.; Hadzima-Nyarko, M.; Agwa, I.S.; Zeyad, A.M.; Tayeh, B.A.; Adesina, A. Possibilities for the application of agro-industrial wastes in cementitious materials: A brief review of the Brazilian perspective. Clean. Mater. 2022, 3, 100040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, R.; Gajjela, S.; Thirumdasu, R.K. Recycling of Organic Wastes for Sustainable Soil Health and Crop Growth. Int. J. Waste Resour. 2017, 7, 296-2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Closas, L.; Costa, J.; Pelacho, A.M. Soil Degradable Bioplastics for a Sustainable Modern Agriculture; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Shit, S.C.; Shah, P.M. Edible Polymers: Challenges and Opportunities. J. Polym. 2014, 2014, 427259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohamed, S.A.A.; El-Sakhawy, M.; El-Sakhawy, M.A.-M. Polysaccharides, Protein and Lipid -Based Natural Edible Films in Food Packaging: A Review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 238, 116178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourtoom, T. Edible films and coatings: Characteristics and properties. Int. Food Res. J. 2008, 15, 237–248. [Google Scholar]
- Jeevahan, J.; Studies, A.; Govindaraj, M. A Brief Review on Edible Food Packaging Materials Article. J. Glob. Eng. Probl. Solut. 2017, 1, 9–19. [Google Scholar]
- Tulamandi, S.; Rangaraju, V.; Rizvi, S.; Singhal, R.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Saha, N. A biodegradable and edible packaging film based on papaya puree, gelatin, and defatted soy protein. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2016, 10, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Gago, M.B.; Rhim, J.-W. Chapter 13—Edible Coating and Film Materials: Lipid Bilayers and Lipid Emulsions. In Food Science and Technology, 2nd ed.; Han, J.H., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2014; pp. 325–350. [Google Scholar]
- Suput, D.; Lazic, V.; Popović, S.; Hromis, N. Edible films and coatings: Sources, properties and application. Food Feed Res. 2015, 42, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhouri, F.M.; Martelli, S.M.; Caon, T.; Velasco, J.I.; Mei, L.H.I. Edible films and coatings based on starch/gelatin: Film properties and effect of coatings on quality of refrigerated Red Crimson grapes. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2015, 109, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhim, J.W.; Shellhammer, T.H. 21—Lipid-based edible films and coatings. In Food Science and Technology; Han, F.P., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2005; pp. 362–383. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez, G.M.; Sibaja, J.C.; Espitia, P.J.P.; Otoni, C.G. Antioxidant active packaging based on papaya edible films incorporated with Moringa oleifera and ascorbic acid for food preservation. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 103, 105630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afifah, N.; Ratnawati, L.; Darmajana, D.A. Evaluation of Plasticizer Addition in Composite Edible Coating on Quality of Fresh-Cut Mangoes during Storage. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 251, 012029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Guo, C.; Yang, Q.; Li, C.; Zhao, P.; Xia, Q.; Kaplan, D.L. Protein composites from silkworm cocoons as versatile biomaterials. Acta Biomater. 2020, 121, 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Channa, I.A. Development of Solution Processed Thin Film Barriers for Encapsulating Thin Film Electronics Entwicklung von Lösungsprozessierten Dünnschichtbarrieren für Die Verpackung von Dünnschichtelektronik. 2019. Available online: https://opus4.kobv.de/opus4-fau/frontdoor/index/index/year/2019/docId/12583 (accessed on 1 December 2021).
- Simona, J.; Dani, D.; Petr, S.; Marcela, N.; Jakub, T.; Bohuslava, T. Edible films from carrageenan/orange essential oil/trehalose—structure, optical properties, and antimicrobial activity. Polymers 2021, 13, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, R.M.S.; Ferreira, M.S.L.; Gonçalves, É.C.B.A. Development and Characterization of Edible Films Based on Fruit and Vegetable Residues. J. Food Sci. 2016, 81, E412–E418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putri, D.A.; Setiawan, A.; Anggraini, P.D. Physical properties of edible sorgum starch film added with carboxymethyl cellulose. J. Phys. Sci. 2018, 29, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, K.; Wang, W.; Ye, R.; Xiao, J.; Liu, Y.; Ding, J.; Zhang, S.; Liu, A. Mechanical and barrier properties of maize starch–gelatin composite films: Effects of amylose content. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 3613–3622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Ma, M.; Ma, S.; Zheng, Y. Characterization of Chitosan Films Incorporated with Different Substances of Konjac Glucomannan, Cassava Starch, Maltodextrin and Gelatin, and Application in Mongolian Cheese Packaging. Coatings 2021, 11, 84. [Google Scholar]
- Khoirunnisa, A.R.; Joni, I.M.; Panatarani, C.; Rochima, E.; Praseptiangga, D. UV-screening, transparency and water barrier properties of semi refined iota carrageenan packaging film incorporated with ZnO nanoparticles. AIP Conf. Proc. 2018, 1927, 030041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellá, M.C.G.; Silva, O.A.; Pellá, M.G.; Beneton, A.G.; Caetano, J.; Simões, M.R.; Dragunski, D.C. Effect of gelatin and casein additions on starch edible biodegradable films for fruit surface coating. Food Chem. 2020, 309, 125764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Huang, J.; Zheng, X.; Liu, S.; Lu, K.; Tang, K.; Liu, J. Heat sealable soluble soybean polysaccharide/gelatin blend edible films for food packaging applications. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2020, 24, 100485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval, D.C.G.; Sosa, B.L.; Martínez-Ávila, G.C.G.; Fuentes, H.R.; Abarca, V.H.A.; Rojas, R. Formulation and characterization of edible films based on organic mucilage from Mexican Opuntia ficus-indica. Coatings 2019, 9, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lalnunthari, C.; Devi, L.M.; Amami, E.; Badwaik, L.S. Valorisation of pumpkin seeds and peels into biodegradable packaging films. Food Bioprod. Process. 2019, 118, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirado-Gallegos, J.M.; Zamudio-Flores, P.B.; Ornelas-Paz, J.D.J.; Rios-Velasco, C.; Orozco, G.I.O.; Espino-Díaz, M.; Baeza-Jiménez, R.; Buenrostro-Figueroa, J.J.; Aguilar-González, M.A.; Lardizábal-Gutiérrez, D.; et al. Elaboration and Characterization of Active Apple Starch Films Incorporated with Ellagic Acid. Coatings 2018, 8, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chakravartula, S.S.N.; Soccio, M.; Lotti, N.; Balestra, F.; Rosa, M.D.; Siracusa, V. Characterization of Composite Edible Films Based on Pectin/Alginate/Whey Protein Concentrate. Materials 2019, 12, 2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Slavutsky, A.M.; Gamboni, J.E.; Bertuzzi, M.A. Formulation and characterization of bilayer films based on Brea gum and Pectin. Brazilian J. Food Technol. 2018, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.-F.; Huang, Z.; Zhao, Y.-H.; Yuan, X.-Y.; Wang, X.-Y.; Li, M. Moisture sorption and water vapor permeability of soy protein isolate/poly(vinyl alcohol)/glycerol blend films. Ind. Crops Prod. 2010, 31, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.-F.; Huang, Z.; Yuan, X.-Y.; Wang, X.-Y.; Li, M. Structure and properties of carboxymethyl cellulose/soy protein isolate blend edible films crosslinked by Maillard reactions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 79, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-S.; Lee, E.; Han, J. Enhancement of the water-resistance properties of an edible film prepared from mung bean starch via the incorporation of sunflower seed oil. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pająk, P.; Przetaczek-Rożnowska, I.; Juszczak, L. Development and physicochemical, thermal and mechanical properties of edible films based on pumpkin, lentil and quinoa starches. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 138, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadhim, M.M.; Shakheer, A.I.; Fahim, A.H.; Kadhim, M.M.H.A. Effect of type and concentration of plasticizer on mechanical properties of protein edible films. Int. J. Mech. Eng. Technol. 2018, 9, 1493–1503. [Google Scholar]
- Jordan, J.L.; Casem, D.T.; Bradley, J.M.; Dwivedi, A.K.; Brown, E.N.; Jordan, C.W. Mechanical Properties of Low Density Polyethylene. J. Dyn. Behav. Mater. 2016, 2, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, L.; Shi, H.; Cao, A.; Jia, J. Characterization of gelatin/chitosan ploymer films integrated with docosahexaenoic acids fabricated by different methods. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Li, J.; Xing, Y.; Nie, X.; Lang, F.; Yang, S.; Hou, X.; Zhao, C. Experimental study on the thickness-dependent hardness of SiO2 thin films using nanoindentation. Coatings 2020, 11, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siskawardani, D.D.; Warkoyo; Hidayat, R.; Sukardi. Physic-mechanical properties of edible film based on taro starch (Colocasia esculenta L. Schoott) with glycerol addition. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 458, 012039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, T.M.P.; Nguyen, T.H.; Dang, T.M.Q.; Tran, T.X.; Rachtanapun, P. Characteristics and Antimicrobial Properties of Active Edible Films Based on Pectin and Nanochitosan. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pizarro, R.D.A.; Skurtys, O.; Osorio-Lira, F. Effect of cellulose nanofibers concentration on mechanical, optical, and barrier properties of gelatin-based edible films. Dyna 2015, 82, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, M.I.; Erwanto, Y.; Abustam, E. Properties of Edible Film Produced using Combination of Collagen Extracts of Bligon Goatskin with Glycerol. Am. J. Anim. Vet. Sci. 2016, 11, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pokatong, W.D.R.; Decyree, J. Characterization and Development of Edible Film/Coating from Lesser Yam Starch-Plasticizer Added with Potassium Sorbate or Cinnamon Oil in Affecting Characteristics and Shelf Life of Stored, Coated Strawberry. Reaktor 2019, 18, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Sample | Composition |
|---|---|
| G-1 | Gelatin (6 wt.%) + Corn Starch (2 wt.%) + Glycerin (3 wt.%) |
| G-2 | Gelatin (9 wt.%) + Corn Starch (2 wt.%) + Glycerin (3 wt.%) |
| G/PP-1 | Gelatin (9 wt.%) + Papaya (8 wt.%) + Corn Starch (2 wt.%) + Glycerin (3 wt.%) |
| G/PP-2 | Gelatin (9 wt.%) + Papaya (10 wt.%) + Corn Starch (2 wt.%) + Glycerin (3 wt.%) |
| G/PP/SP-1 | Gelatin (9 wt.%) + Papaya (10 wt.%) + Soy Protein (2 wt.%) + Corn Starch (2 wt.%) + Glycerin (3 wt.%) |
| G/PP/SP-2 | Gelatin (9 wt.%) + Papaya (10 wt.%) + Soy Protein (4 wt.%) + Corn Starch (2 wt.%) + glycerin (3 wt.%) |
| Sample | T (%) | CA (°) |
|---|---|---|
| G-2 | 15.20 | 65.13 ± 5.13 |
| G/PP-2 | 25.9 | 47.97 ± 4.28 |
| G/PP/SP-2 | 6.08 | 41.91 ± 5.23 |
| Sample | Young’s Modulus (MPa) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation at Break (%) | Indentation Hardness (MPa) | Vickers Hardness (MPa) | Bending Cycle |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G-2 | 45.9 | 2.33 | 48.1 | 6.5875 | 610.07 | 2000 |
| G/PP-2 | 48.9 | 2.44 | 50.5 | 67.287 | 6231.5 | 2000 |
| G/PP/SP-2 | 39.8 | 1.71 | 6.2 | 1.7431 | 161.43 | <560 |
| Sample | Thickness (µm) | WVTR (g·m−2·Day−1) | Weight Loss (gm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| G-1 | 102.85 ± 4.87 | 82.01 ± 0.856 | 5.75 |
| G-2 | 97.142 ± 3.06 | 80.05 ± 1.003 | 5.65 |
| PP-1 | 118.57 ± 6.26 | 54.19 ± 1.553 | 3.8 |
| PP-2 | 107.14 ± 4.87 | 51.34 ± 0.788 | 3.6 |
| SP-1 | 131.42 ± 2.08 | 70.60 ± 1.321 | 4.95 |
| SP-2 | 175.71 ± 5.34 | 69.03 ± 2.411 | 4.84 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ashfaq, J.; Channa, I.A.; Shaikh, A.A.; Chandio, A.D.; Shah, A.A.; Bughio, B.; Birmahani, A.; Alshehri, S.; Ghoneim, M.M. Gelatin- and Papaya-Based Biodegradable and Edible Packaging Films to Counter Plastic Waste Generation. Materials 2022, 15, 1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15031046
Ashfaq J, Channa IA, Shaikh AA, Chandio AD, Shah AA, Bughio B, Birmahani A, Alshehri S, Ghoneim MM. Gelatin- and Papaya-Based Biodegradable and Edible Packaging Films to Counter Plastic Waste Generation. Materials. 2022; 15(3):1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15031046
Chicago/Turabian StyleAshfaq, Jaweria, Iftikhar Ahmed Channa, Asif Ahmed Shaikh, Ali Dad Chandio, Aqeel Ahmed Shah, Bushra Bughio, Ashfaque Birmahani, Sultan Alshehri, and Mohammed M. Ghoneim. 2022. "Gelatin- and Papaya-Based Biodegradable and Edible Packaging Films to Counter Plastic Waste Generation" Materials 15, no. 3: 1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15031046
APA StyleAshfaq, J., Channa, I. A., Shaikh, A. A., Chandio, A. D., Shah, A. A., Bughio, B., Birmahani, A., Alshehri, S., & Ghoneim, M. M. (2022). Gelatin- and Papaya-Based Biodegradable and Edible Packaging Films to Counter Plastic Waste Generation. Materials, 15(3), 1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15031046








