Solvent-Impregnated Sorbents for Tantalum from Niobium Separation Using a Fixed-Bed Column
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Apparatus
2.3. Feed Solution Preparation
2.4. Solvent-Impregnated Coals Preparation and Characterization
2.5. Preliminary Sorption Studies (Batch Mode)
2.6. Separation of Tantalum from Niobium Using Fixed-Bed Column
2.7. Stripping Tantalum from Solvent-Impregnated Active Coal (Batch Mode)
3. Results
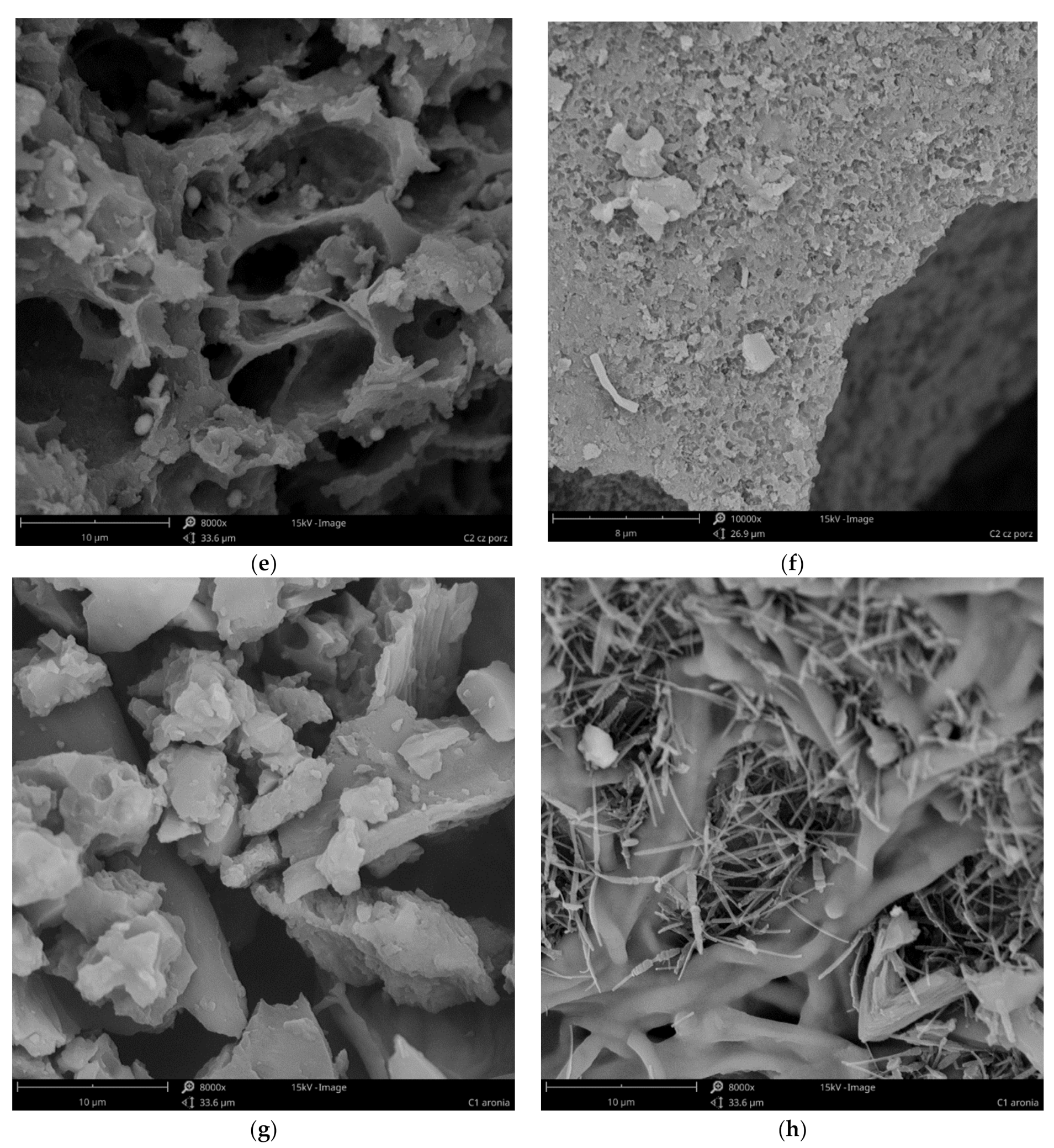
3.1. Carbons Characterization
3.2. Preliminary Sorption Studies
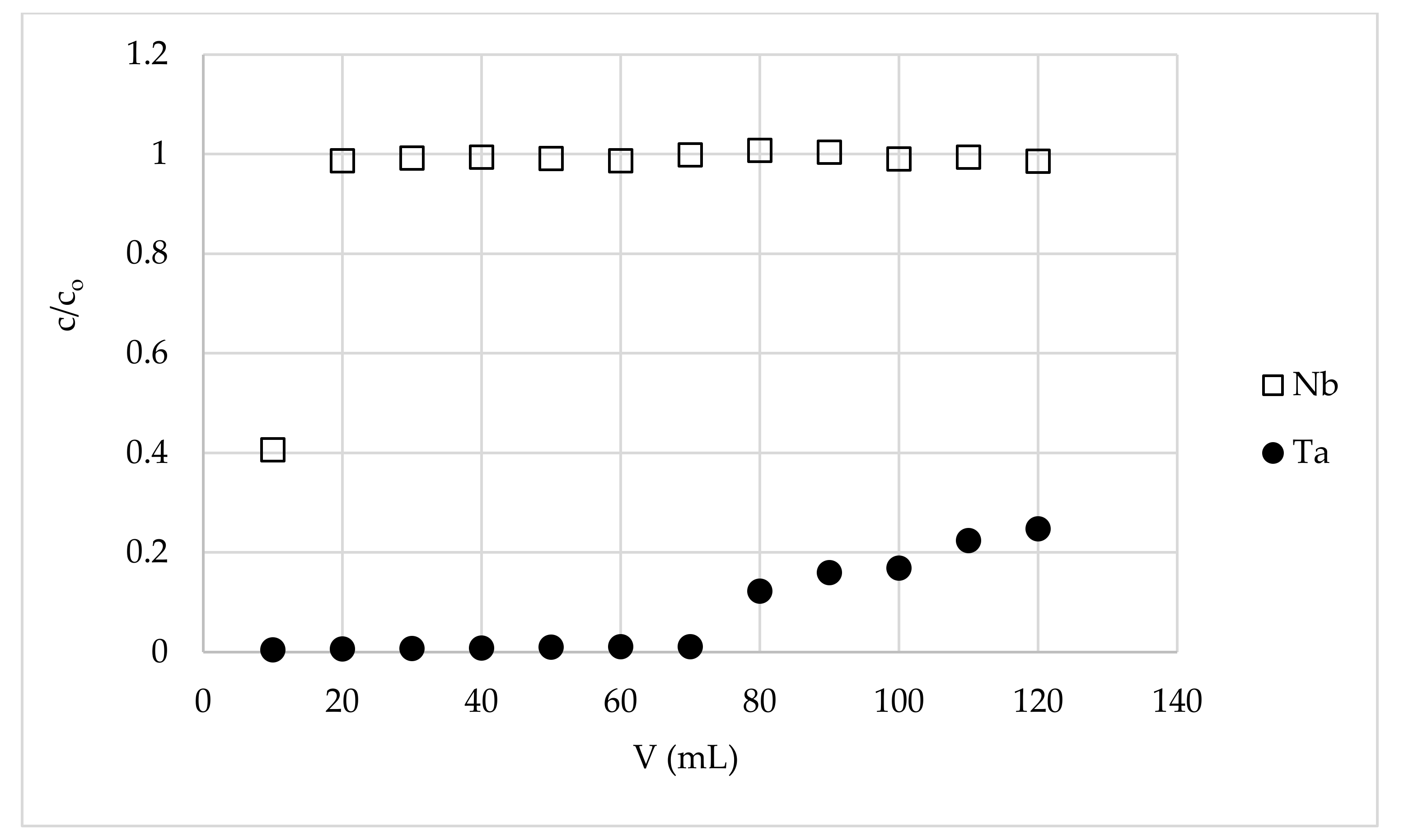
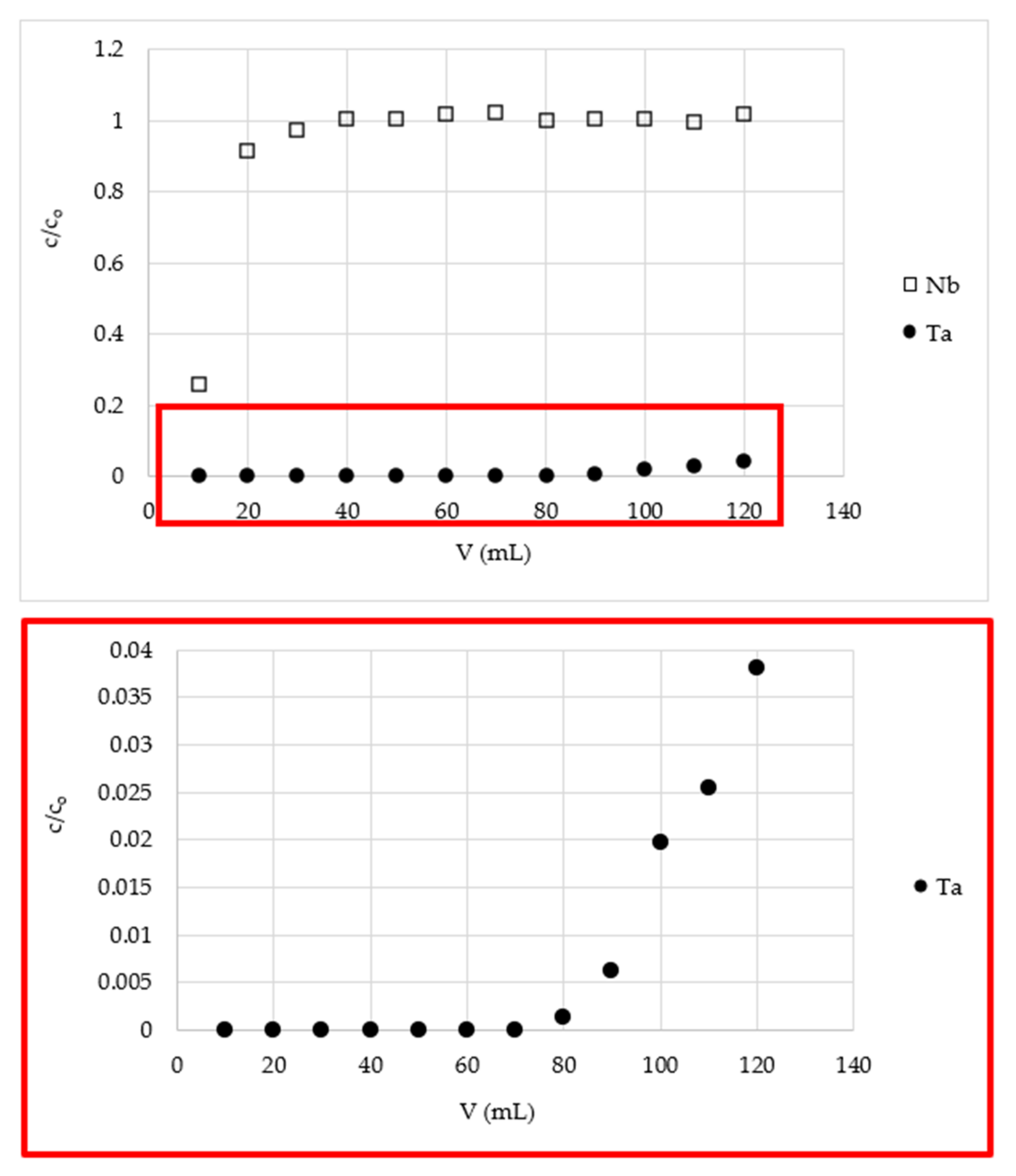
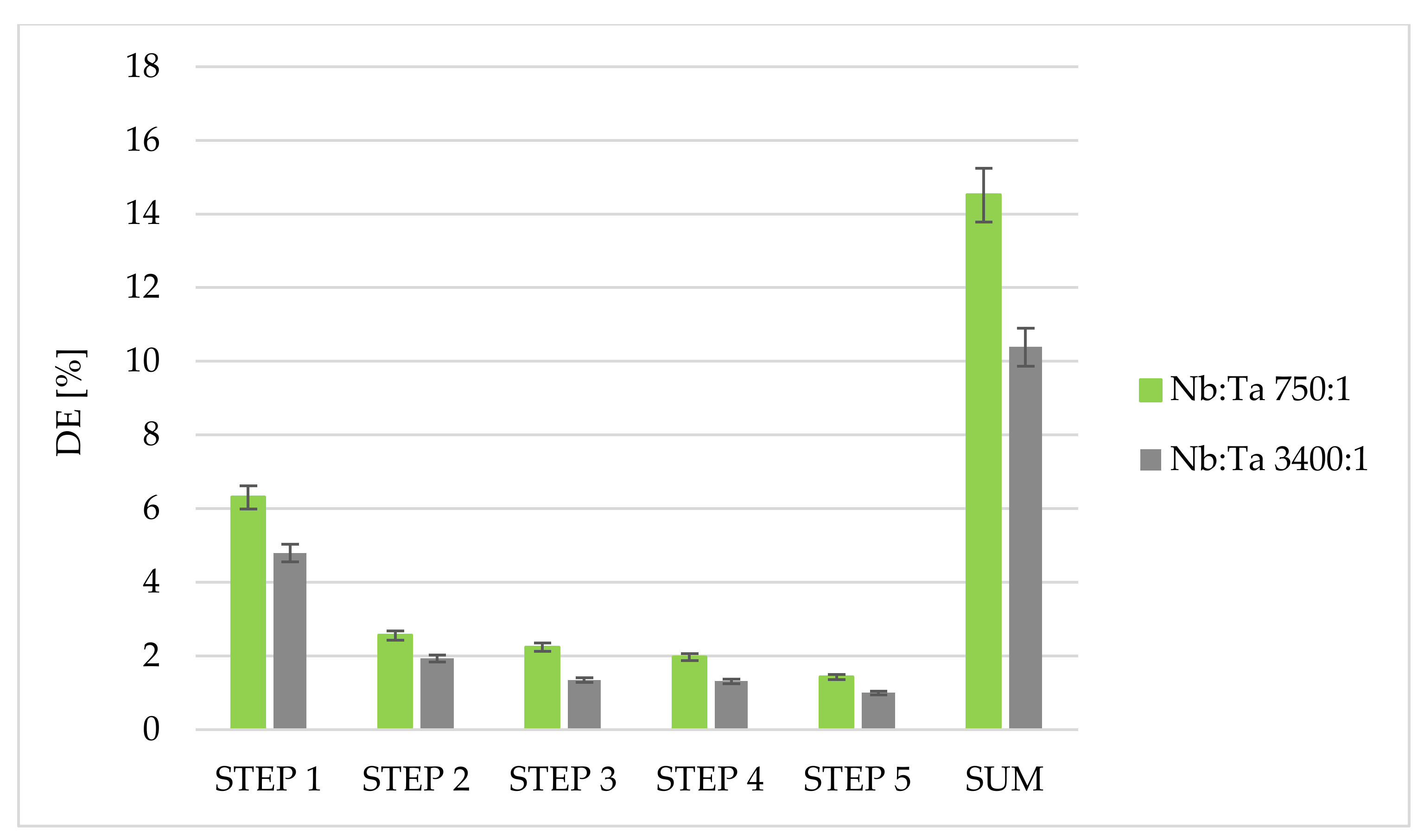
3.3. Separation of Tantalum from Niobium Using Fixed-Bed Column
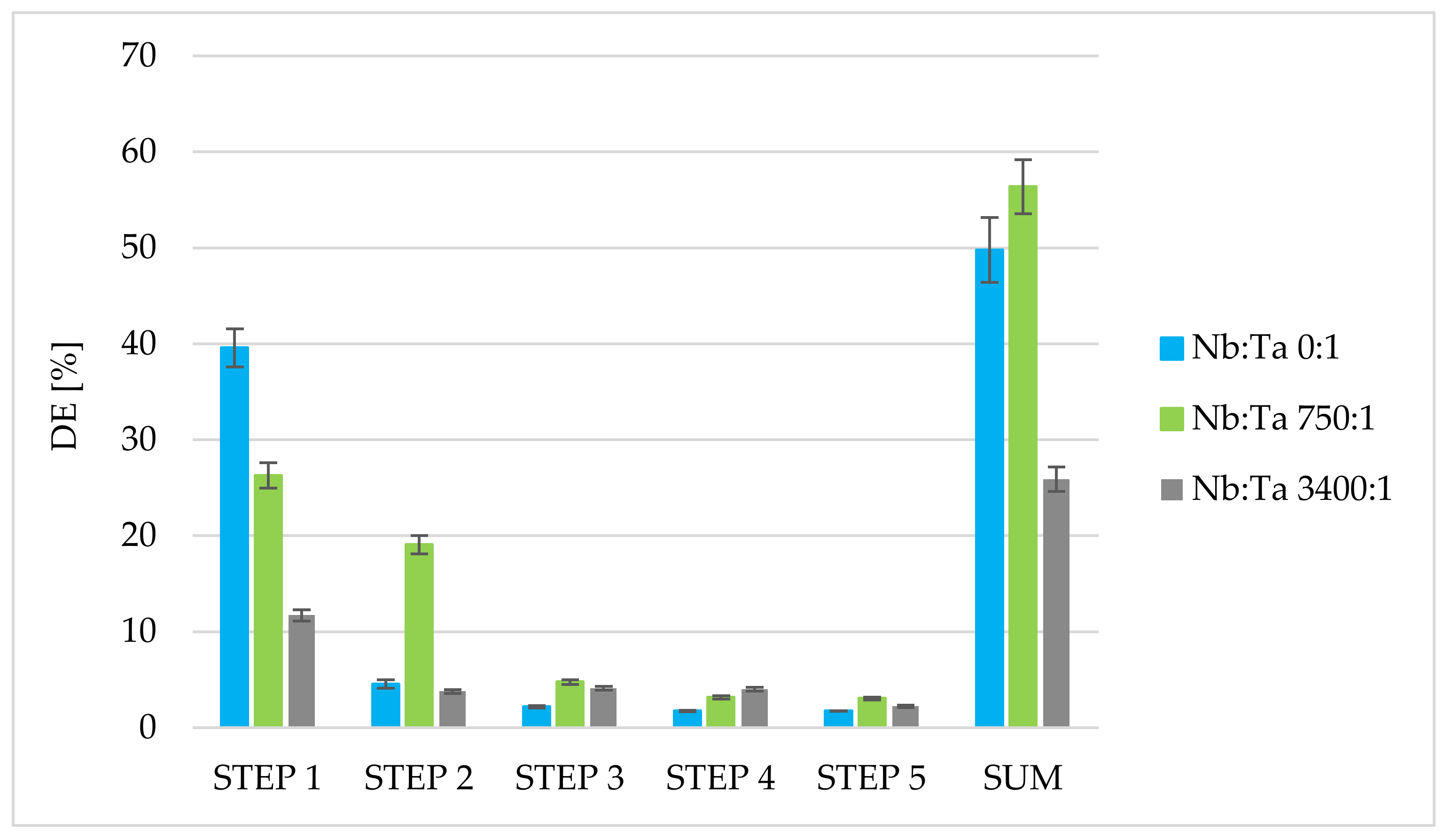
3.4. Stripping of Tantalum from Solvent-Impregnated Active Coal
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eckert, J.; Hermann, C. Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Niobium and Niobium Compounds, A17; VCH Verlagsgesellschaft: Weinheim, Germany, 1996; pp. 251–264. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz, M.D.C.; Rodriguez, M.H.; Perino, E.; Olsina, R.A. Determination of Nb, Ta, Fe and Mn by X-Ray Fluorescence. Miner. Eng. 2002, 15, 373–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuno, H.; Yokoyama, A.; Watari, F.; Uo, M.; Kawasaki, T. Biocompatibility and osteogenesis of refractory metal implants, titanium, hafnium, niobium, tantalum and rhenium. Biomaterials 2001, 22, 1253–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Report on Critical Raw Materials and the Circular Economy. Available online: https://weee4future.eitrawmaterials.eu/wp-content/uploads/2020/09/09_report-of-CRM-and-CE.pdf (accessed on 5 November 2018).
- Roskill Information Services Ltd. The Economics of Niobium; Roskill Information Services: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Nikishina, E.E.; Drobot, D.V.; Lebedeva, E.N. Niobium and tantalum: State of the world market, field of application, and raw sources. Part I. Russ. J. Non-Ferr. Met. 2013, 54, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikishina, E.E.; Drobot, D.V.; Lebedeva, E.N. Niobium and tantalum: State of the world market, field of application, and raw sources. Part II. Russ. J. Non-Ferr. Met. 2014, 55, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izlar, K. Future LHC Super-Magnets Pass Muster. Available online: https://www.symmetrymagazine.org/article/july-2013/future-lhc-super-magnets-pass-muster (accessed on 31 October 2018).
- LHC Machine Outreach Super Conducting Cable. Available online: https://lhc-machine-outreach.web.cern.ch/components/cable.htm (accessed on 31 October 2018).
- Whitfield, T.E.; Wise, G.J.; Stone, H.J.; Jones, N.G. The influence of the Nb:Ta ratio on the microstructural evolution in refractory metal superalloy systems. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2021, 119, 211901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, K.J.; Piatak, N.M.; Papp, J.F. Niobium and tantalum. Critical mineral resources of the United States—Economic and environmental geology and prospects for future supply. U.S. Geol. Surv. Prof. Pap. 2017, 1802, M1–M34. [Google Scholar]
- Ungerer, M.J.; Van Der Westhuizen, D.J.; Lachmann, G.; Krieg, H.M. Comparison of extractants for the separation of TaF5 and NbF5 in different acidic media. Hydrometallurgy 2014, 144–145, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairbrother, F. The Chemistry of Niobium and Tantalum; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Nete, M.; Purcell, W.; Nel, J.T. Separation and isolation of tantalum and niobium from tantalite using solvent extraction and ion exchange. Hydrometallurgy 2014, 149, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grebneva, O.N.; Kubrakova, I.V.; Kudinova, T.F.; Kuz’min, N.M. Direct determination of trace elements in niobium, tantalum and their oxides by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry after microwave dissolution. Spectrochem. Acta Part B 1997, 52, 1151–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikika, A.; Sethurajan, M.; Muvundj, F.; Mugumaoderha, M.C.; Gaydardzhiev, S. A review on extractive metallurgy of tantalum and niobium. Hydrometallurgy 2020, 198, 105496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albercht, S.; Cymorek, C.; Eckert, J. Niobium and Niobium Compounds. In Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry; Wiley Online Library: Berlin, Germany, 2011; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Purcell, W.; Potgieter, H.; Nete, M.; Mnculwane, H. Possible methodology for niobium, tantalum and scandium separation in ferrocolumbite. Miner. Eng. 2018, 119, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabangu, M.J.; Crouse, P.L. Separation of niobium and tantalum from Mozambican tantalite by ammonium bifluoride. Hydrometallurgy 2012, 129–130, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nete, M.; Purcell, W.; Nel, J.T. Comparative study of tantalite dissolution using different fluoride salts as fluxes. J. Fluor. Chem. 2014, 165, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agulyansky, A. The Chemistry of Tantalum and Niobium Fluoride Compounds; Elsevier, B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004; p. 263. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.H.; Lee, M.-S. A Review on the Separation of Niobium and Tantalum by Solvent Extraction. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. 2019, 40, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Cheng, C.Y. Solvent extraction technology for the separation and purification of niobium and tantalum: A review. Hydrometallurgy 2011, 107, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathsarma, K.C.; Nayak, B.B.; Brahmbhatt, P.; Pradhan, S. Purification of niobium oxide by dissolution and solvent extraction. Miner. Metall. Process. 2012, 28, 204–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, Y. Leaching of a low-grade niobium–tantalum ore by highly concentrated caustic potash solution. Hydrometallurgy 2005, 80, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turgis, R.; Arrachart, G.; Michel, S.; Legeai, S.; Lejeune, M.; Draye, M.; Pellet-Rostaing, S. Ketone functionalized task specific ionic liquids for selective tantalum extraction. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 196, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaev, A.I.; Maiorov, V.G.; Baklanova, I.V. Decrease of HF Concentration in Process Solutions before Extractive Separation of Tantalum(V) from Niobium(V). Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2002, 75, 1748–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hussaini, O.M.; El-Hakammahdy, M. Extraction of niobium and tantalum from nitrate and sulfate media by using MIBK. Min. Pro Ext. Met. Rev. 2001, 22, 633–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nete, M.; Purcell, W.; Nel, J.T. Hydrometallurgical Separation of Niobium and Tantalum: A Fundamental Approach. JOM 2016, 68, 556–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, X.; Wei, C.; Zheng, S.; Sun, Q.; Wang, D. Extraction kinetics of tantalum by MIBK from pulp using Lewis cell. Hydrometallurgy 2013, 131–132, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.G.; Wu, Y.K.; Zhang, J.D.; Zang, L.; Wang, L.J. Equilibrium and kinetic data of adsorption and separation for zirconium and hafnium onto MIBK extraction resin. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2010, 20, 1527–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caletka, R.; Krivan, V. Separation of niobium and tantalum on polyurethane foam pretreated with diantipyrylmethane, TBP or MIBK. Fresenius J. Anal. Chem. 1985, 321, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doustkhah, E.; Tahawy, R.; Simon, U.; Tsunoji, N.; Ide, Y.; Hanaor, D.A.H.; Assadi, H.M.N. Bispropylurea bridged polysilsesquioxane: A microporous MOF-like material for molecular recognition. Chemosphere 2021, 276, 130181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakui, Y.; Matsunga, H.; Itabashi, O. Chromatographic separation of niobium and tantalum in a hydrofluoric acid-hydrochloric acid system with macroporous polyacrylate resin beads. Anal. Sci. 1995, 11, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsumiya, H.; Yasuno, S.; Iki, N.; Miyano, S. Sulfinylcalix[4]arene-impregnated amberlite XAD-7 resin for the separation of niobium (V) from tantalum (V). J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1090, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilk, P.A.; Landrum, J.H.; Shaughnessy, D.A. Separation of group five elements by reversed-phase chromatography. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2008, 275, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, J.S.; Dahmer, L.H. Column chromatographic separation of niobium, tantalum, molybdenum and tungsten. Anal. Chem. 1968, 40, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vin, Y.Y.; Khopkar, S.M. Separation of niobium and tantalum by extraction chromatography with bis(2-ethylhexyl)phosphoric acid. Talanta 1991, 38, 971–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, E.S.; Mutelet, F.; Abdel-Khalek, N.; Abdallah, M.; Elmenshawy, A.; Youssef, M. Beneficiation and separation of Egyptian tantalite ore. Key Eng. Mater. 2020, 835, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Gaddam, S.; Shenoy, K.T.; Mirji, K.V. Process development for the separation of niobium and tantalum from fluoride medium using trioctyl amine and application of Taguchi’s method to optimize solvent extraction parameters. Hydrometallurgy 2021, 199, 105522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolik, M.; Turkowska, M. Method of low tantalum amounts determination in niobium and its compounds by ICP-OES technique. Talanta 2013, 115, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turkowska, M.; Smolik, M. Pre-concentration of Ta(V) by solvent extraction before determination of trace amounts of Ta in Nb and Nb compounds. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 5304–5310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deblonde, G.J.P.; Bengio, D.; Beltrami, D.; Bélair, S.; Cote, G.; Chagnes, A. Niobium and tantalum processing in oxalic-nitric media: Nb2O5·nH2O and Ta2O5·nH2O precipitation with oxalates and nitrates recycling. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 226, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayot, D.; Devillers, M. Peroxo complexes of niobium (V) and tantalum (V). Coord. Chem. Rev. 2006, 250, 2610–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.; Patel, P.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Gaddam, S.; Shenoy, K.T. Separation of niobium and tantalum using continuous multistage counter-current solvent extraction with trioctyl amine. Hydrometallurgy 2022, 207, 105773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deblonde, G.J.P.; Bengio, D.; Beltrami, D.; Bélair, S.; Cote, G.; Chagnes, A. A fluoride-free liquid-liquid extraction process for the recovery and separation of niobium and tantalum from alkaline leach solutions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 215, 634–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghambi, S.; Sanchez-Segado, S.; Chipakwe, V.; Jha, A. An investigation on hydrofluoric (HF) acid-free extraction for niobium oxide (Nb2O5) and tantalum oxide (Ta2O5) from columbite/tantalite concentrates using alkali reductive roasting. Miner. Eng. 2021, 173, 107183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nete, M.; Purcell, W.; Nel, J.T. Non-fluoride dissolution of tantalum and niobium oxides and their separation using ion exchange. Hydrometallurgy 2017, 173, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furigay, M.H.; Chaudhuri, S.; Deresh, S.M.; Weberg, A.B.; Pandey, P.; Carroll, P.J.; Schatz, G.C.; Schelter, E.J. Selective reduction of niobium (V) species to promote molecular niobium/tantalum separation. Inorg. Chem. 2022, 61, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Material Modified with MIBK | Removal Efficiency of Ta ETa (%) | Removal Efficiency of Nb ENb (%) | Separation Factor SF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | active carbon | >97 | <1.5 * | >2123 |
| C2 | pulverized activated carbon | >97 | <1.5 * | >2123 |
| C3 | carbonized blackcurrant pomace | 81 | <1.5 * | >280 |
| C4 | carbonized chokeberry pomace | 85 | <1.5 * | >372 |
| S1 | strong base anion exchange resin | 96 | 41 | 35 |
| S2 | strong acid cation exchange resin | 3.4 | 9.6 | 0.3 |
| S3 | bentonite | 82 | 74 | 1.6 |
| S4 | cellulose ion exchanger | 45 | 14 | 5.0 |
| S5 | polyurethane foam in lumps | 95 | <1.5 * | >1248 |
| Approx. Ta:Nb Ratio in Feed Solution (Accurate ppm of Ta in Relation to Nb) | Volume of Collected Effluent, mL | Nb Yield, % | The Content of Ta in Relation to Nb in Collected Effluent, ppm | Purge Factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1:1 (994,490) | 10 | 48.1 | 3156 | 315 |
| 20 | 73.3 | 320,477 | 3.1 | |
| 30 | 81.9 | 585,130 | 1.7 | |
| 1:100 (10,373) | 70 | 90.9 | 106.0 | 97.9 |
| 120 | 94.6 | 906.7 | 11.4 | |
| 1:1000 (946) | 70 | 88.4 | 0.027 | 35,037 |
| 120 | 93.3 | 7.69 | 123 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Turkowska, M.; Karoń, K.; Milewski, A.; Jakóbik-Kolon, A. Solvent-Impregnated Sorbents for Tantalum from Niobium Separation Using a Fixed-Bed Column. Materials 2022, 15, 1513. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15041513
Turkowska M, Karoń K, Milewski A, Jakóbik-Kolon A. Solvent-Impregnated Sorbents for Tantalum from Niobium Separation Using a Fixed-Bed Column. Materials. 2022; 15(4):1513. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15041513
Chicago/Turabian StyleTurkowska, Magdalena, Krzysztof Karoń, Andrzej Milewski, and Agata Jakóbik-Kolon. 2022. "Solvent-Impregnated Sorbents for Tantalum from Niobium Separation Using a Fixed-Bed Column" Materials 15, no. 4: 1513. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15041513
APA StyleTurkowska, M., Karoń, K., Milewski, A., & Jakóbik-Kolon, A. (2022). Solvent-Impregnated Sorbents for Tantalum from Niobium Separation Using a Fixed-Bed Column. Materials, 15(4), 1513. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15041513







