The Advances and Challenges of Liposome-Assisted Drug Release in the Presence of Serum Albumin Molecules: The Influence of Surrounding pH
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
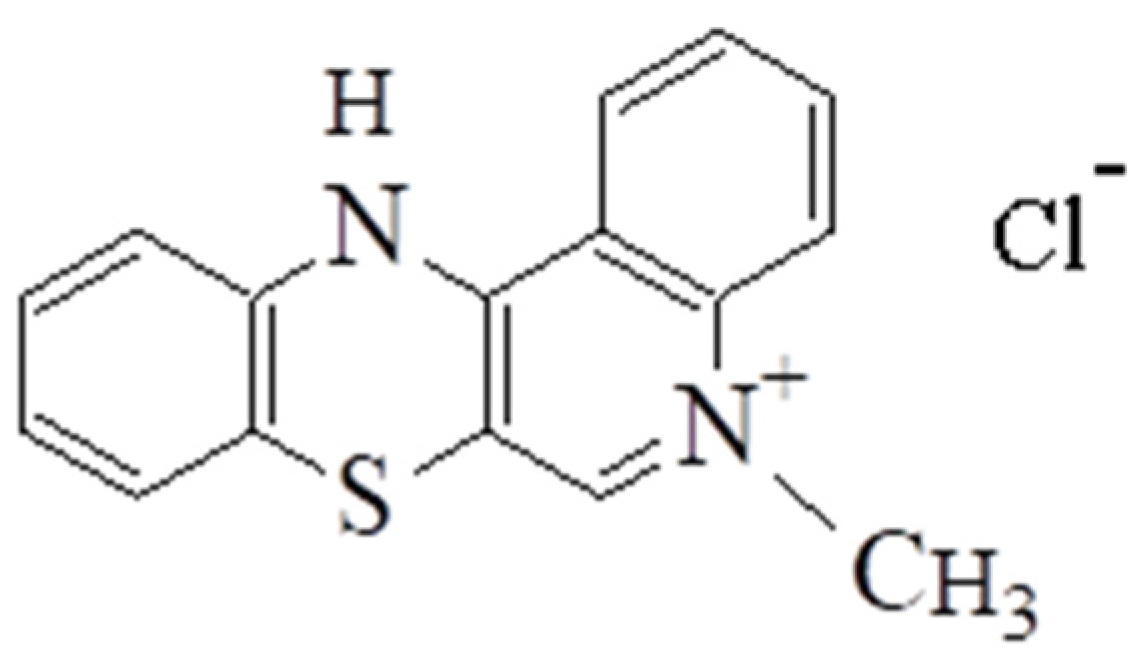
2.2.1. The Synthesis of 5-Methyl-12(H)-quino[3,4-b] [1,4] Benzothiazine Chloride
2.2.2. Liposome Preparation
2.2.3. Solutions and Sample Preparation
2.2.4. UV/Vis Measurements
Encapsulation Efficiency and Drug Loading
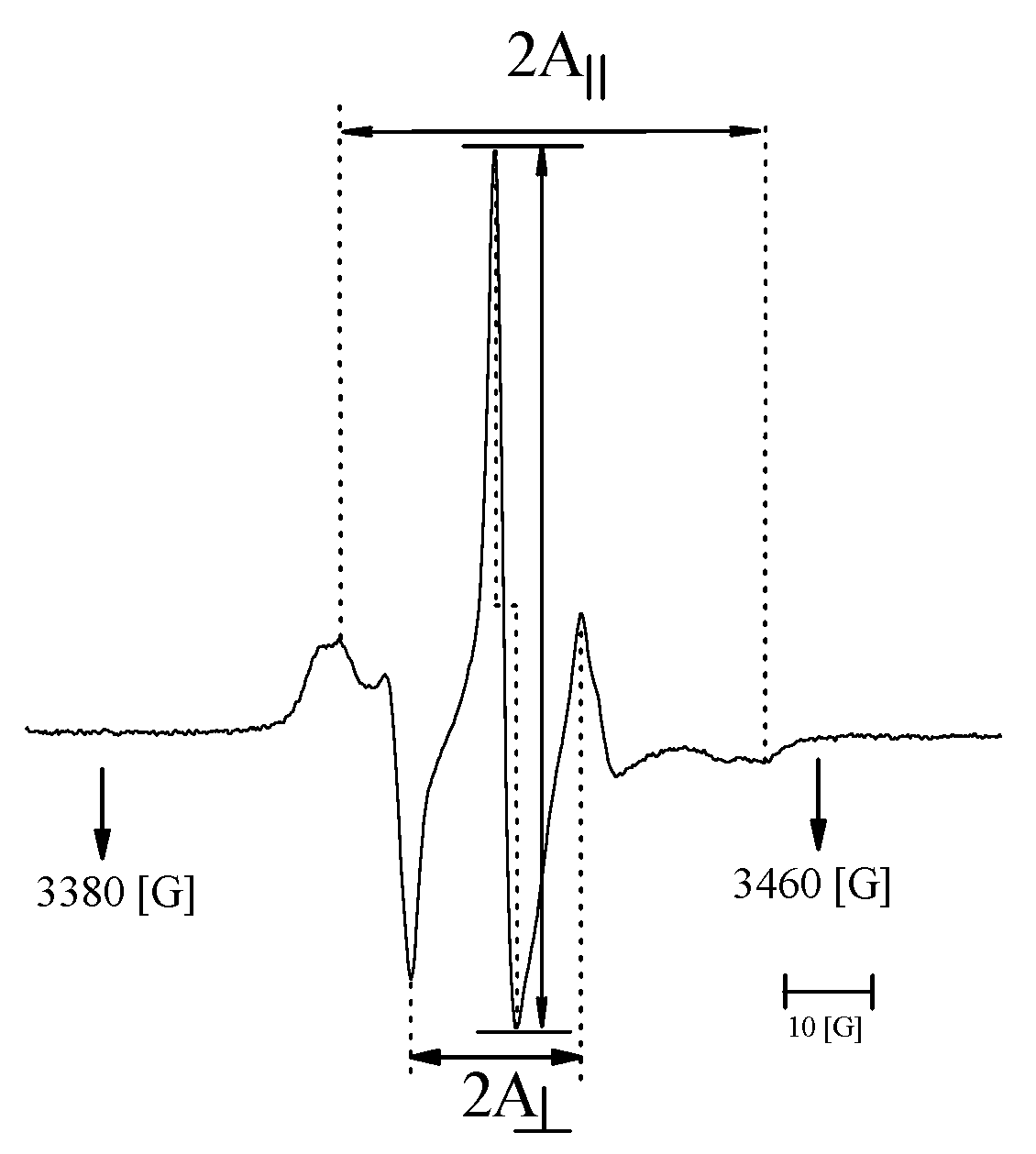
2.2.5. Electron Paramagnetic Resonance
2.2.6. Drug Release and the Mathematic Modeling Study
2.2.7. Differential Scanning Calorimetry
2.2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Encapsulation Degree Analysis
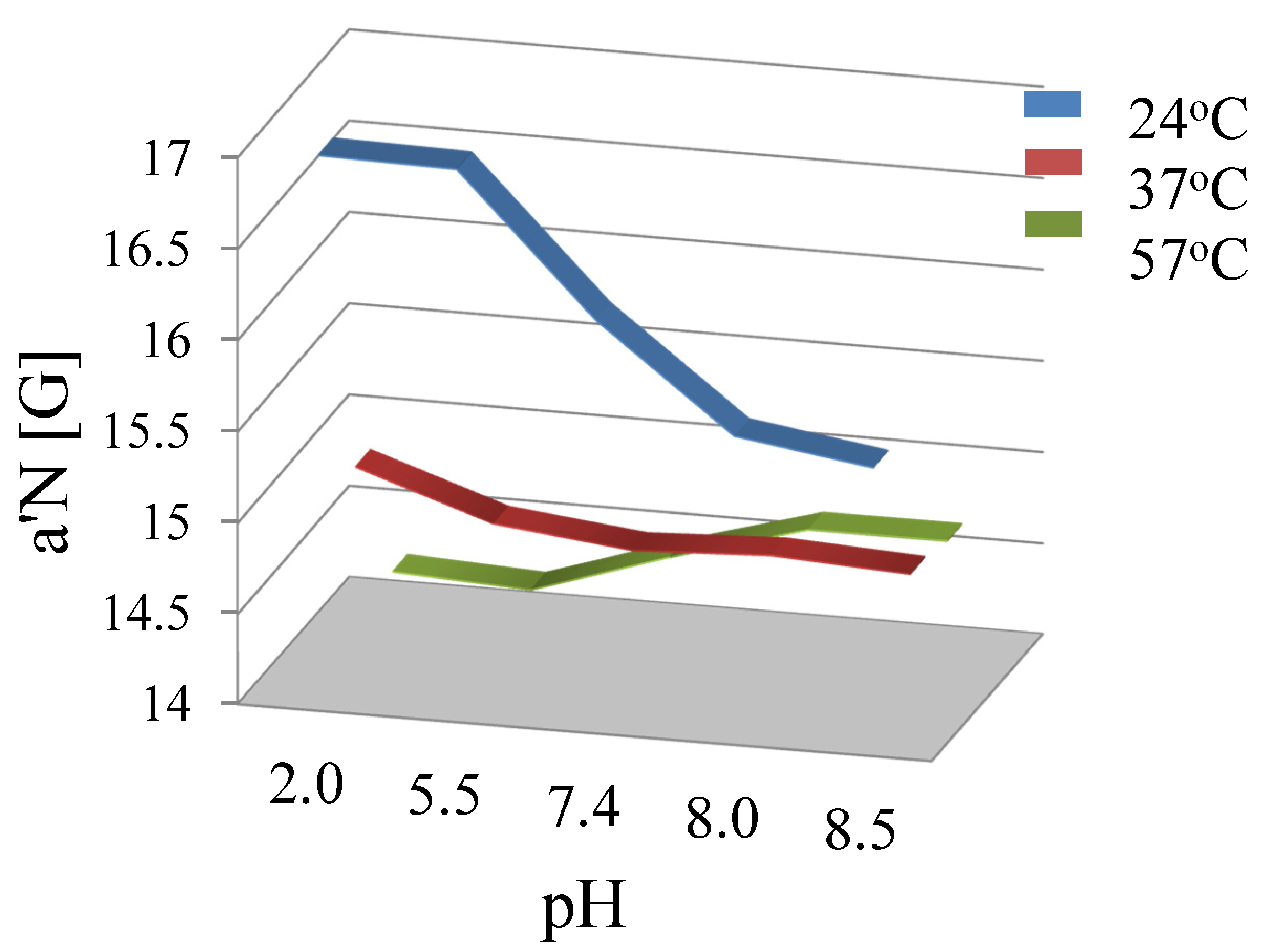
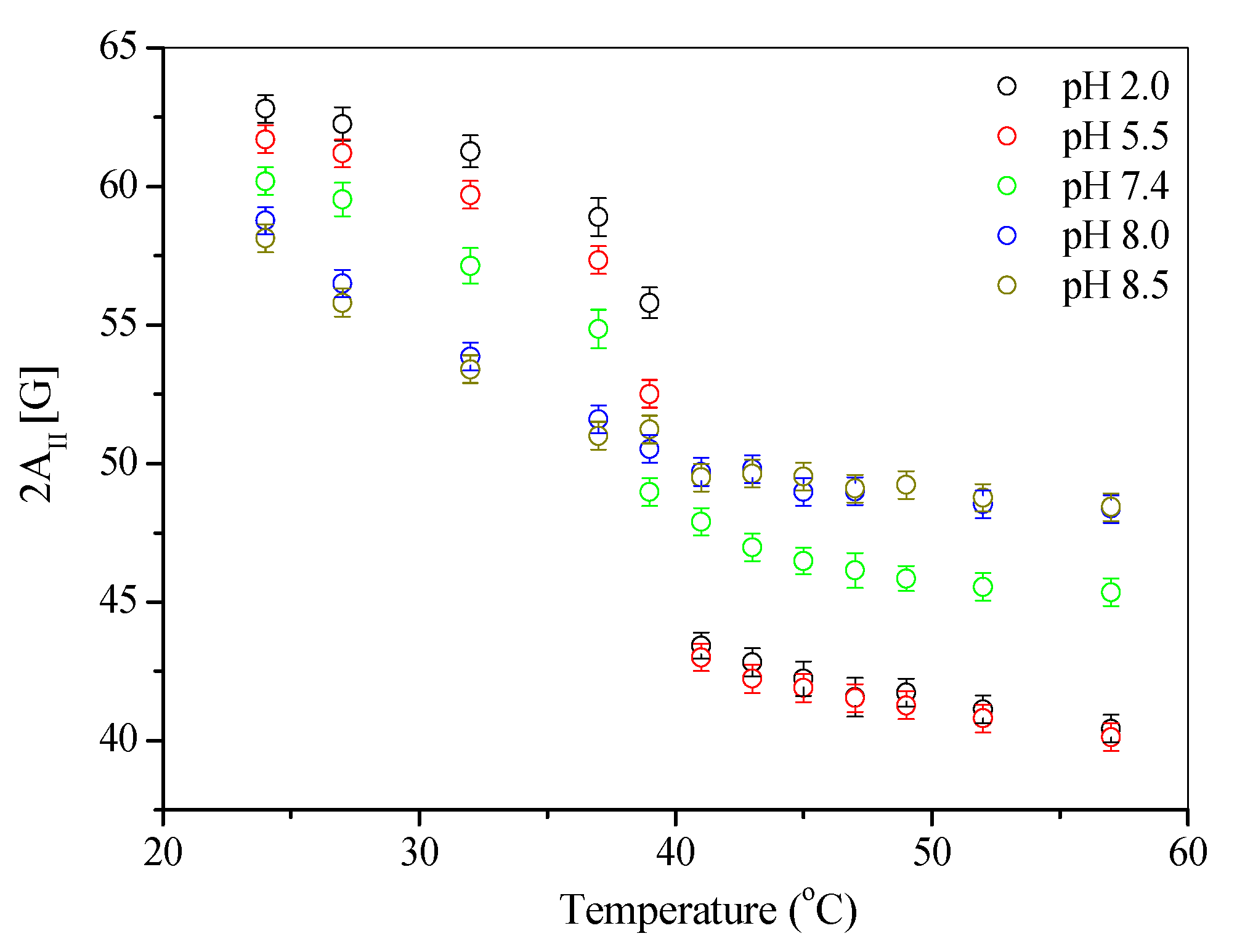
3.2. Stability of Liposomal Preparations
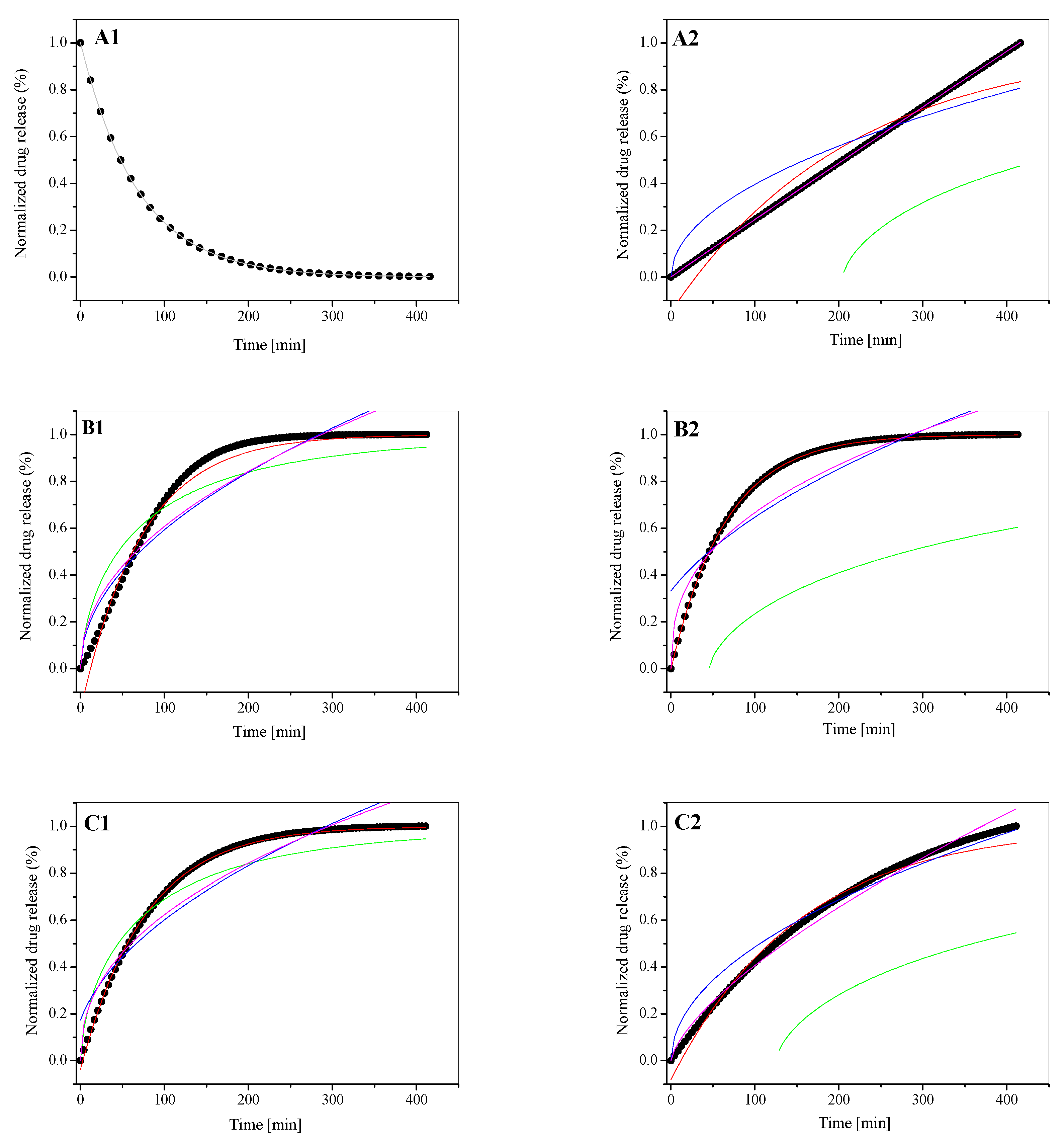
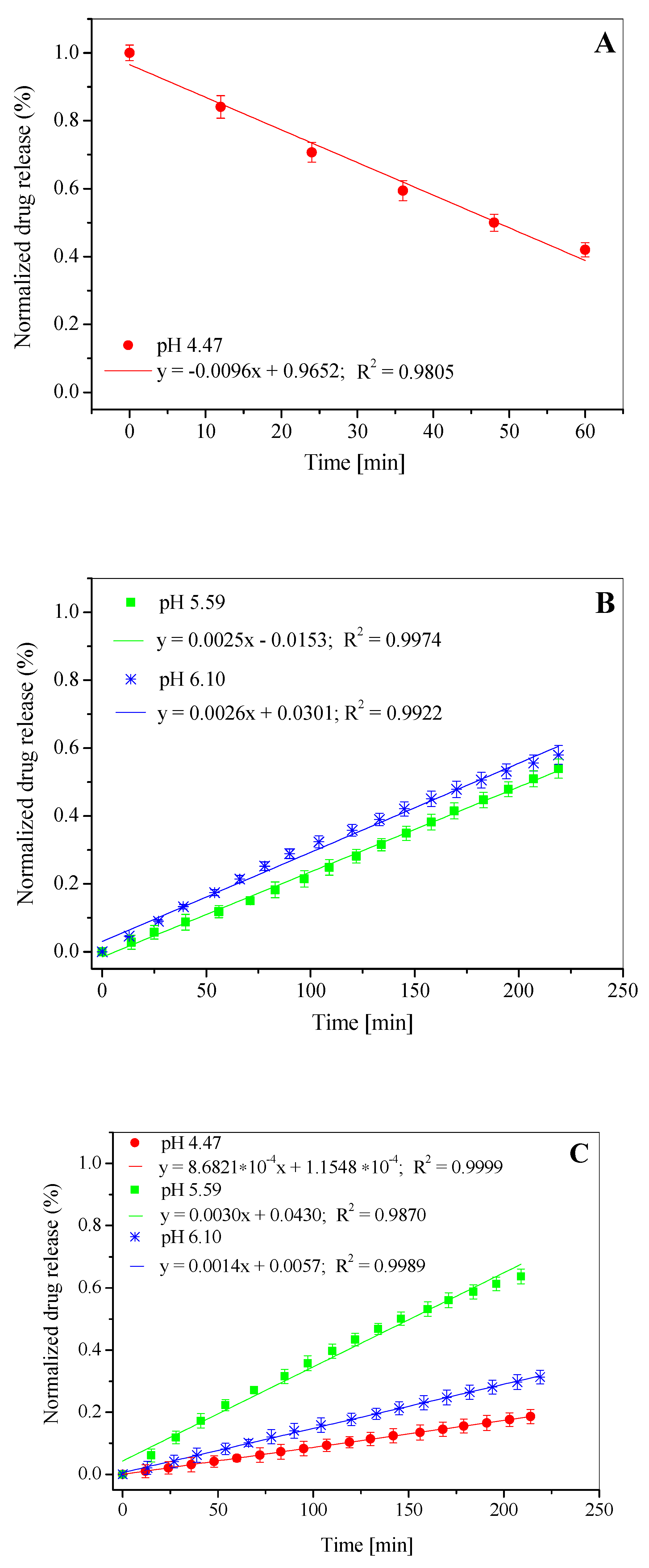
3.3. In Vitro Drug Release Study
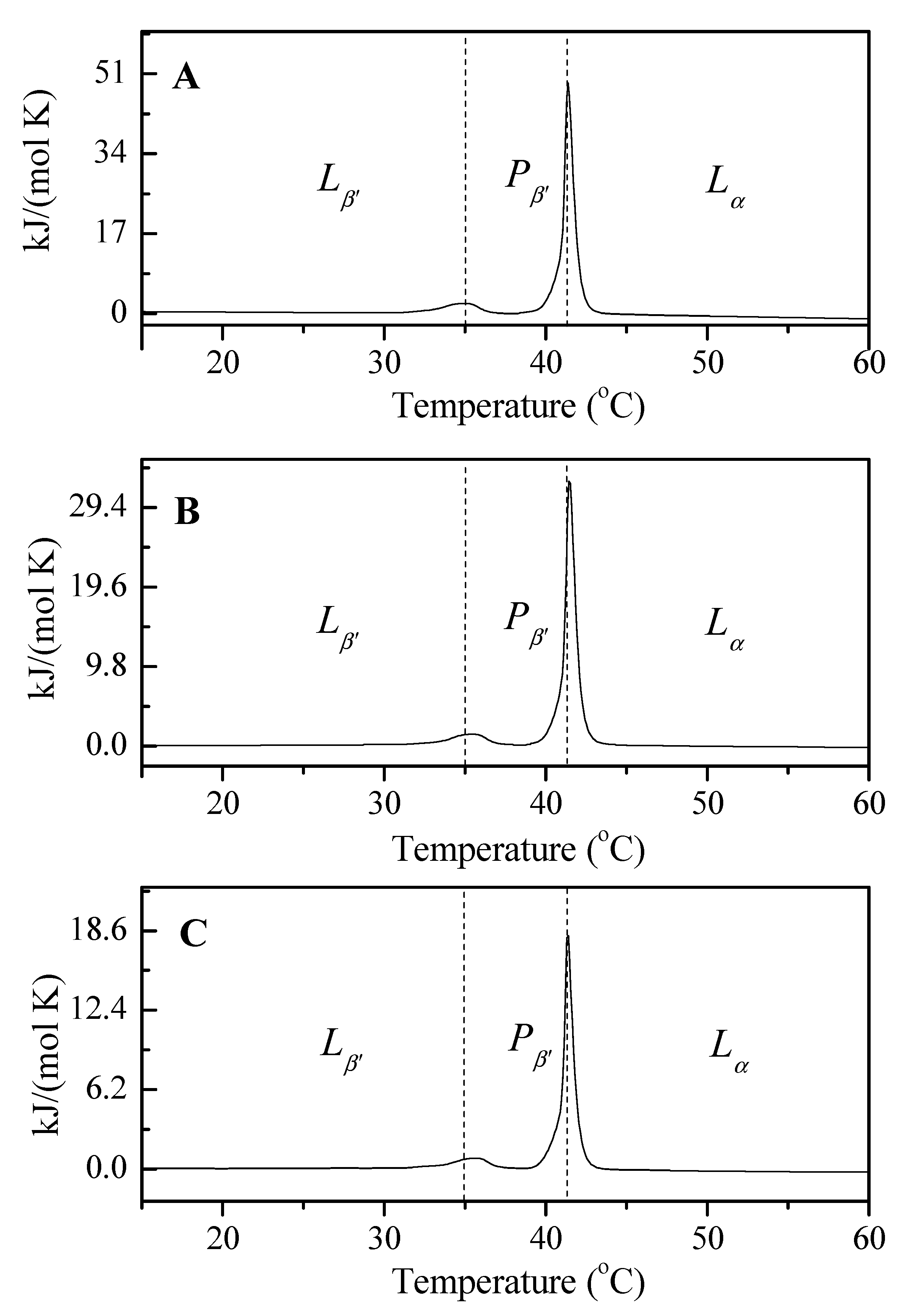
3.4. Analysis of the Thermotropic Changes in the Phospholipid Bilayers: A DSC Study
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Daniel, M.C.; Astruc, D. Gold nanoparticles: Assembly, supramolecular chemistry, quantum-size-related properties, and applications toward biology, catalysis, and nanotechnology. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 293–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peer, D.; Karp, J.M.; Hong, S.; Farokhzad, O.C.; Margalit, R.; Langer, R. Nanocarriers as an emerging platform for cancer therapy. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veiseh, O.; Tang, B.C.; Whitehead, K.A.; Anderson, D.G.; Langer, R. Managing diabetes with nanomedicine: Challenges and opportunities. Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov. 2015, 14, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- des Rieux, A.; Fievez, V.; Garinot, M.; Schneider, Y.J.; Préat, V. Nanoparticles as potential oral delivery systems of proteins and vaccines: A mechanistic approach. J. Control. Release 2006, 116, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulaklak, K.; Gresbach, C.A. The once and future gene therapy. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.D.; Huang, L. Pharmacokinetics and biodistribution of nanoparticles. Mol. Pharm. 2008, 5, 496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, T.M.; Cullis, P.R. Liposomal drug delivery systems: From concept to clinical applications. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pentak, D.; Sułkowski, W.W.; Sułkowska, A. Influence of some physical properties of 5-fluorouracil on encapsulation efficiency in liposomes. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2012, 108, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Langer, R. Drug delivery and targeting. Nature 1998, 392, 5–10. [Google Scholar]
- Szoka, F., Jr.; Papahadjopoulos, D. Procedure for preparation of liposomes with large internal aqueous space and high capture by reverse-phase evaporation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1978, 75, 4194–4198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malam, Y.; Loizidou, M.; Seifalian, A.M. Liposomes and nanoparticles: Nanosized vehicles for drug delivery in cancer. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2009, 30, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Li, S. Calorimetric and molecular mechanics studies of the thermotropic phase behavior of membrane phospholipids. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1999, 1422, 273–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.J.; Wang, S.; Turk, M.J.; Low, P.S. The effects of pH and intraliposomal buffer strength on the rate of liposome content release and intracellular drug delivery. Biosci. Rep. 1998, 18, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dewhirst, M.W.; Secomb, T.W. Transport of drugs from blood vessels to tumour tissue. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 738–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Wen, G.; Yang, L.; Tang, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, L.; Ma, F.; Xiao, L.; et al. Dual-targeted and pHsensitive doxorubicin prodrug-microbubble complex with ultrasound for tumor treatment. Theranostics 2017, 7, 452–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, K. Intracellular targeting delivery of liposomal drugs to solid tumors based on EPR effects. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jong, W.H.; Borm, P.J. Drug delivery and nanoparticles:applications and hazards. Int. J. Nanomed. 2008, 3, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zięba, A.; Sochanik, A.; Szurko, A.; Rams, M.; Mrozek, A.; Cmoch, P. Synthesis and in vitro antiproliferative activity of 5-alkyl-12(H)-quino[3,4-b] [1,4]benzothiazinium salts. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 4733–4739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szoka, F., Jr.; Papahadjopoulos, D. Comparative properties and methods of preparation of lipid vesicles (liposomes). Annu. Rev. Biophys. Bioeng. 1980, 9, 467–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pentak, D.; Maciążek-Jurczyk, M.; Zawada, Z.H. The role of nanoparticles in the albumin-cytarabine and albumin-methotrexate interactions. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2017, 73, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, N.; Kimpfler, A.; Massing, U.; Burger, A.M.; Fiebig, H.H.; Brandl, M.; Schubert, R. 5-Fluorouracil in vesicular phospholipid gels for anticancer treatment: Entrapment and release properties. Int. J. Pharm. 2003, 256, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harisa, G.I.; Badran, M.M. Simvastatin nanolipid carriers decreased hypercholesterolemia induced cholesterol inclusion and phosphatidylserine exposure on human erythrocytes. J. Mol. Liq. 2015, 208, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, D. Polarity and permeation profiles in lipid membranes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 7777–7782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coderch, L.; Fonollosa, J.; De Pera, M.; Estelrich, J.; De La Maza, A.; Parra, J.L. Influence of cholesterol on liposome fluidity by EPR. Relationship with percutaneous absorption. J. Control. Release 2000, 68, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagimo, A.; Sato, Y.; Suzuki, Y. Electron spin resonance studies of phosphatidylcholine interacted with cholesterol and with a hopanoid in liposomal membrane. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1991, 39, 3071–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jin, Y.; Li, M.; Hou, X. Pyrocatechol violet as a marker to characterize liposomal membrane permeability using the chelation and the first-order derivative spectrophotometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2005, 37, 379–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siepmann, J.; Siepmann, F. Modeling of diffusion controlled drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2012, 161, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritger, P.L.; Peppas, N.A. A simple equation for description of solute release I. Fickian and non-fickian release from non-swellable devices in the form of slabs, spheres, cylinders or discs. J. Control. Release 1987, 5, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buczek, A.; Kupka, T.; Broda, M.A.; Maślanka, S.; Pentak, D. Liposomes as nonspecific nanocarriers for 5-Fluorouracil in the presence of cyclodextrins. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 343, 117623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pentak, D.; Maciążek-Jurczyk, M. Self-assembled nanostructures formed by phospholipids and anticancer drugs. Serum albumin—Nanoparticle interactions. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 224, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.L.; Tian, D.Y.; Li, S.P.; Li, X.D.; Lu, T.H. MTX/LDHs hybrids synthesized from reverse microemulsions: Particle control and bioassay study. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 473, 414–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Jin, L.; Han, J.; Wei, M.; Li, C. Synthesis and Controlled Release Properties of Prednisone Intercalated Mg-Al Layered Double Hydroxide Composite. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 5590–5597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Guan, Y.X.; Yao, S.J.; Zhu, Z.Q. Preparation of ibuprofen-loaded chitosan films for oral mucosal drug delivery using supercritical solution impregnation. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 473, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salome, A.C.; Godswill, O.C.; Ikechukwu, I.O. Kinetics and mechanisms of drug release from swellable and non swellable matrices: A Review. Res. J. Pharm. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2013, 4, 97–103. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y.; Kao, W.J. Drug release kinetics and transport mechanisms of non-degradable and degradable polymeric delivery systems. Expert Opin. Drug. Deliv. 2010, 7, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, S.; Yoo, C.Y.; Park, S.N. Improved stability and skin permeability of sodium hyaluronate-chitosan multilayered liposomes by Layer-by-Layer electrostatic deposition for quercetin delivery. Colloid Surf. B-Biointerfaces 2015, 129, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrache, H.I.; Dodd, S.W.; Brown, M.F. Area per lipid and acyl length distributions in fluid phosphatidylcholines determined by 2H NMR spectroscopy. Biophys. J. 2000, 79, 3172–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, M.F.; Seelig, J. Influence of Cholesterol on the Polar Region of Phosphatidylcholine and Phosphatidylethanolamine Bilayers. Biochemistry 1978, 17, 381–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boggara, M.B.; Faraone, A.; Krishnamoorti, R. Effect of pH and Ibuprofen on the Phospholipid Bilayer Bending Modulus. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 8061–8066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sułkowski, W.W.; Pentak, D.; Nowak, K.; Sułkowska, A. The influence of temperature, cholesterol content and pH on liposome stability. J. Mol. Struct. 2005, 744–747, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torchilin, V.P. Recent advances with liposomes as pharmaceutical carriers. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2005, 4, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bibi, S.; Lattmann, E.; Mohammed, A.R.; Perrie, Y. Trigger release liposome systems: Local and remote controlled delivery? J. Microencapsul. 2012, 29, 262–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derycke, A.S.; de Witte, P.A. Liposomes for photodynamic therapy. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 2004, 56, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pentak, D.; Maciążek-Jurczyk, M. Nonspecific nanocarriers for doxorubicin and cytarabine in the presence of fatted and defatted human albumin. Part I. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 278, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pentak, D. Evaluation of the physicochemical properties of liposomes as potential carriers of anticancer drugs: Spectroscopic study. J. Nanopart. Res. 2016, 18, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Liposome | Encapsulation Efficiency (EE%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| pH 4.47 | pH 5.59 | pH 6.10 | |
| LDPPC/5-MBT | 75.76 | 83.08 | 70.37 |
| LDPPC/5-MBT | Parameter | Korsmeyer–Peppas Eq | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.47 | SUM | 1.321 × 10−6 | |||
| k | 1.001 | ||||
| t | 0.985 | ||||
| n | 0.45 < n < 0.89 | ||||
| R2adj | 0.999 | ||||
| LDPPC/5-MBT | Parameter | First-Order Eq | Bhaskas Eq | Higuchi Eq | Ritger–Peppas Eq |
| 5.59 | SUM | 0.001 | 0.011 | 0.013 | 0.012 |
| α | 11.871 | −1.253 × 10−24 | −1.727 × 10−7 | −2.915 × 10−44 | |
| k | 0.013 | 0.012 | 0.059 | 0.069 | |
| n | - | - | - | 0.472 | |
| R2adj | 0.989 | 0.859 | 0.829 | 0.844 | |
| 6.10 | SUM | 6.537 × 10−5 | 0.006 | 0.010 | 0.007 |
| α | 2.741 | −1.158 × 10−25 | −9.175 | −3.173 × 10−42 | |
| k | 0.013 | 0.012 | 0.057 | 0.084 | |
| n | - | - | - | 0.435 | |
| R2adj | 0.999 | 0.910 | 0.847 | 0.890 | |
| [LDPPC/5-MBT]:HSA | Parameter | First-Order Eq | Bhaskas Eq | Higuchi Eq | Ritger–Peppas Eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.47 | SUM | 0.004 | 0.202 | 0.013 | 8.522 × 10−7 |
| α | 29.651 | 204.913 | −6.737 × 10−61 | −3.539 × 10−9 | |
| k | 0.004 | 0.002 | 0.039 | 0.002 | |
| n | - | - | - | 0.985 | |
| R2adj | 0.952 | −0.673 | 0.846 | 0.999 | |
| 5.59 | SUM | 1.776 × 10−6 | 0.257 | 0.01377 | 0.008 |
| α | 0.195 | 45.700 | −35.702 | −1.513 × 10−46 | |
| k | 0.015 | 0.002 | 0.055 | 0.112 | |
| n | - | - | - | 0.386 | |
| R2adj | 0.999 | −3.079 | 0.764 | 0.860 | |
| 6.10 | SUM | 0.001 | 0.193 | 0.003 | 0.001 |
| α | 11.907 | 125.132 | −1.052 × 10−32 | −2.574 × 10−17 | |
| k | 0.006 | 0.002 | 0.048 | 0.017 | |
| n | - | - | - | 0.686 | |
| R2adj | 0.987 | −0.977 | 0.961 | 0.987 |
| LDPPC/5-MBT | pH 4.47 | pH 5.59 | pH 6.10 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lβ’–Pβ’ | Tp (°C) | 34.84 | 35.35 | 35.56 |
| ΔS (kJ/mol∙K) | 0.0233 | 0.0171 | 0.0097 | |
| ΔH (kJ/mol) | 7.1704 | 5.2780 | 3.0086 | |
| Pβ’–Lα | Tc (°C) | 41.37 | 41.43 | 41.39 |
| ΔS (kJ/mol∙K) | 0.1441 | 0.0992 | 0.0539 | |
| ΔH (kJ/mol) | 45.335 | 31.211 | 16.939 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pentak, D.; Ploch-Jankowska, A.; Zięba, A.; Kozik, V. The Advances and Challenges of Liposome-Assisted Drug Release in the Presence of Serum Albumin Molecules: The Influence of Surrounding pH. Materials 2022, 15, 1586. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15041586
Pentak D, Ploch-Jankowska A, Zięba A, Kozik V. The Advances and Challenges of Liposome-Assisted Drug Release in the Presence of Serum Albumin Molecules: The Influence of Surrounding pH. Materials. 2022; 15(4):1586. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15041586
Chicago/Turabian StylePentak, Danuta, Anna Ploch-Jankowska, Andrzej Zięba, and Violetta Kozik. 2022. "The Advances and Challenges of Liposome-Assisted Drug Release in the Presence of Serum Albumin Molecules: The Influence of Surrounding pH" Materials 15, no. 4: 1586. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15041586
APA StylePentak, D., Ploch-Jankowska, A., Zięba, A., & Kozik, V. (2022). The Advances and Challenges of Liposome-Assisted Drug Release in the Presence of Serum Albumin Molecules: The Influence of Surrounding pH. Materials, 15(4), 1586. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15041586






