A Greener Stability-Indicating High-Performance Thin-Layer Chromatography Approach for the Estimation of Topiramate
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Chromatography and Analysis
2.3. Derivatization and Scanning
2.4. Preparation of TPM Standard Solutions for Calibration and Quality Control (QC)
2.5. Validation Studies
2.6. Selectivity and Degradation Evaluations
2.7. Analysis of TPM in Marketed Tablets
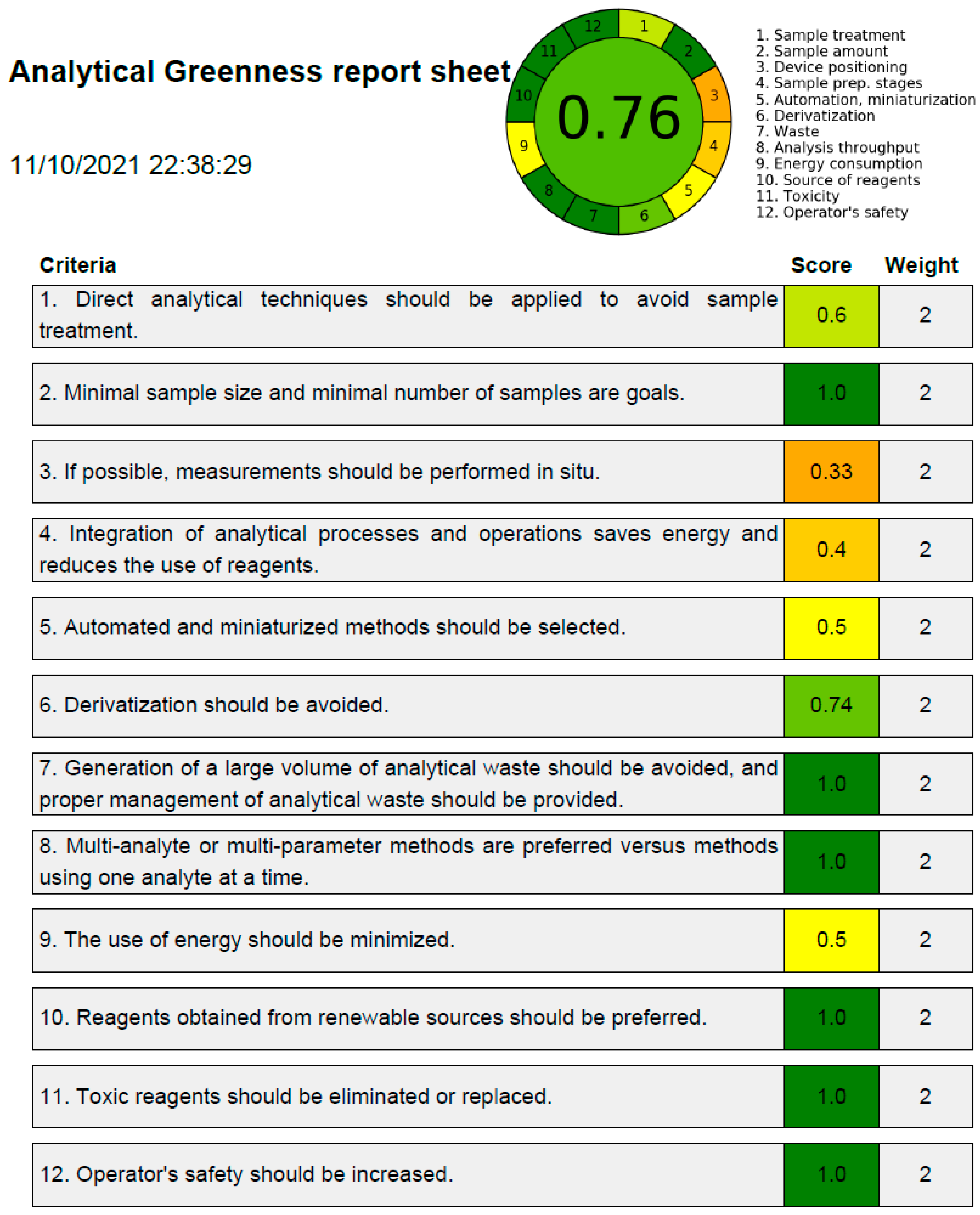
2.8. Greenness Evaluation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Method Development
3.2. Validation Studies
3.3. Selectivity and Degradation Studies
3.4. Determination of TPM in Commercial Tablet Dosage Forms
3.5. Greenness Evaluation
3.6. Comparison with Reported Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guerrini, R.; Parmeggiani, L. Topiramate and its clinical applications in epilepsy. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2006, 7, 811–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shank, R.P.; Gardocki, J.F.; Streeter, A.J.; Maryanoff, B.E. An Overview of the Preclinical Aspects of Topiramate: Pharmacology, Pharmacokinetics, and Mechanism of Action. Epilepsia 2000, 41, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johannessen, S.I. Pharmacokinetics and Interaction Profile of Topiramate: Review and Comparison with Other Newer Antiepileptic Drugs. Epilepsia 1997, 38, S18–S23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majnooni, M.B.; Jalili, R.; Mohammadi, B.; Miraghaee, S.S.; Bahrami, M.T.; Fakhri, S.; Bahrami, G. Development and validation of a new method for determination of topiramate in bulk and pharmaceutical formulation using high performance liquid chromatography-UV detection after pre-column derivatization. J. Rep. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 3, 179–183. [Google Scholar]
- El-Yazbi, A.F.; Wagih, M.M.; Ibrahim, F.; Barary, M.A. Spectrofluorimetric determination of topiramate and levetiracetam as single components in tablet formulations and in human plasma and simultaneous fourth derivative synchronous fluorescence determination of their co-administered mixture in human plasma. J. Fluoresc. 2016, 26, 1225–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunitha, P.G.; Deattu, N.; Dhanalakshmi, R.; Gangatharan, A.; Kavi, B.A.; Shankar, G.M.; Sathya, M. Colorimetric methods for the estimation of topiramate in tablets. J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 2016, 6, 11–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Styslo-Zalasik, M.; Li, W. Determination of topiramate and its degradation product in liquid oral solutions by high performance liquid chromatography with a chemiluminescent nitrogen detector. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2005, 37, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, A.; Rezanour, N.; Ansari, M.; Walker, R.B. Development of a stability-indicating high performance liquid chromatographic method for the analysis of topiramate and dissolution rate testing in topiramate tablets. Asian J. Chem. 2010, 22, 3856–3866. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Wu, S.; Ql, Y.; Hao, L.-H.; Deng, J. HPLC-RID determination of topiramate and its main related substance. Chin. J. Pharm. Anal. 2011, 31, 266–269. [Google Scholar]
- Kshirsagar, M.B.; Mahajan, M.P.; Sawant, S.D. Method development and validation by RP-HPLC method for estimation of topiramate in bulk and pharmaceutical dosage form. Int. J. ChemTech. Res. 2017, 10, 843–849. [Google Scholar]
- Narayana, P.S.; Nisa, S.; Jawahar, K.R. A New Analytical Rp-Hplc Method for the Estimation of Topiramate In Bulk Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms. Ann. Trop. Med. Public Health 2020, 23, 231921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, V.; Parikh, R.H.; Patel, R.J. HPTLC Method for Estimation of Topiramate in Solubility Studies, Diffusion Studies, Plasma, Brain Homogenate and Pharmaceutical Formulation. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2016, 54, 1105–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Salama, N.N.E.A.; Mohamed, A.O.; Taha, E.A. Development and validation of spectrofluorometric, spectrophotometric and thin layer chromatography stability indicating methods for analysis of topiramate. Int. J. Pharm. Technol. 2010, 2, 1299–1314. [Google Scholar]
- Koba, M.; Marszall, M.; Sroka, W.; Tarczykowska, M.; Buciński, A. Application of HPTLC and LC-MS Methods for Determination of Topiramate in Pharmaceutical Formulations. Curr. Pharm. Anal. 2012, 8, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munshi, R.; Gawde, N.; Dalal, S.; Ganachari, D. Development and validation of a high-performance thin-layer chromatographic method for the quantitative assessment of topiramate from human serum: Application in therapeutic drug monitoring. J. Planar Chromatogr. 2018, 31, 112–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cifuentes, C.; Mennickent, S.; De Diego, M. Quantitative Determination of Topiramate in Human Breast Milk. J. Anal. Bioanal. Tech. 2016, 7, 1000334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangamithra, R.; Narenderan, S.T.; Meyyanathan, S.N.; Sharma, P.; Sanjay, M.S.; Babu, B.; Kalaivani, M. A sensitive analytical liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for the estimation of Topiramate in bulk and pharmaceutical formulation. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 10, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, K.; Sai, T.V.; Ghosh, B.; Uppalapati, Y. To develop a new UPLC method for estimation of topiramate in pharmaceutical dosage forms. J. Drug Dev. Deliv. 2018, 1, 21–27. [Google Scholar]
- Hadad, G.M.; Abdel-Salam, R.A.; Emara, S. Optimized and validated flow-injection spectrophotometric analysis of topiramate, piracetam and levetiracetam in pharmaceutical formulations. Acta Pharm. 2011, 61, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Wang, X.; Lu, D. Quantitative determination and validation of topiramate and its tablet formulation by 1H-NMR spectroscopy. Anal. Methods 2019, 11, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Almeida, J.M.F.; Silva, E.M.F.; Verissimo, F.; Fernandes, N.S. Salting-out assisted liquid-liquid extraction method combined with GC-MS for the determination of topiramate in aqueous solutions: Development and applications of the methodology. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 2303–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrami, G.; Mirzaeei, S.; Mohammadi, B.; Kiani, A. High performance liquid chromatographic determination of topiramate in human serum using UV detection. J. Chromatogr. B 2005, 822, 322–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, R.; Imai, K.; Yoshida, T.; Tanaka, M.; Hamano, S.-I.; Arai, Y. Determination of Topiramate in Infant Plasma by High-performance Liquid Chromatography Using Fluorescence Derivatizing Agent. Iryo Yakugaku 2010, 36, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britzi, M.; Soback, S.; Isoherranen, N.; Levy, R.H.; Perucca, E.; Doose, D.R.; Maryanoff, B.E.; Bialer, M. Analysis of Topiramate and Its Metabolites in Plasma and Urine of Healthy Subjects and Patients with Epilepsy by Use of a Novel Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry Assay. Ther. Drug Monit. 2003, 25, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.-H.; Park, Y.-S.; Lee, M.-H.; Rhim, S.-Y.; Song, J.-C.; Lee, S.-J.; Kim, J.-M.; Shaw, L.M.; Kang, J.-S. Determination of plasma topiramate concentration using LC-MS/MS for pharmacokinetic and bioequivalence studies in healthy Korean volunteers. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2008, 22, 822–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popov, T.V.; Maricic, L.C.; Prosen, H.; Voncina, D.B. Determination of topiramate in human plasma using liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Acta Chim. Slov. 2013, 60, 144–150. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, D.G. Estimation of topiramate in human plasma using LC-MS/MS method. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2013, 6, 217–220. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Kim, J.; Yum, H.; Jang, M.; Rhee, J.; Lee, S.; Han, S.B. Simultaneous determination of barbiturates, phenytoin and topiramate in hair by LC-MS/MS and application to real samples. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2020, 106, 106931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cifuentes, C.; Mennickent, S.; De Diego, M. Quantitative Determination of Topiramate in Human Serum and Umbilical Cord Blood. Curr. Pharm. Anal. 2019, 15, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malakova, J.; Brozmanova, H.; Vorisek, V.; Prochazkova, V.; Palicka, V. A capillary GC method using nitrogen phosphorous detection for determination of topiramate in patients with epilepsy. Chromatographia 2007, 66, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, J.M.; Birnbaum, A.K.; Marino, S.E.; Cloyd, J.C.; Remmel, R.P. A sensitive capillary GC-MS method for analysis of topiramate from plasma obtained from single-dose studies. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2012, 26, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, R.Z.; Antunes, M.V.; Arnhold, P.C.; Andriguetti, N.B.; Verza, S.G.; Linden, R. Determination of topiramate in dried blood spots using single-quadrupole gas chromatography–mass spectrometry after flash methylation with trimethylanilinium hydroxide. J. Chromatogr. B 2017, 1046, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishikawa, A.K.; da Silva, R.M.; Santos, M.S.F.; da Costa, E.T.; Sakamoto, A.C.; Carrilho, E.; de Gaitani, C.M.; Garcia, C.D. Determination of topiramate by capillary electrophoresis with capacitively-coupled contactless conductivity detection: A powerful tool for therapeutic monitoring in epileptic patients. Electrophoresis 2018, 39, 2598–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, F.A.; El-Yazbi, A.F.; Wagih, M.M.; Barary, M.A. Chromatographic determination of zonisamide, topiramate and sulpiride in plasma by a fluorescent ‘turn-on’ chemosensor. Bioanalysis 2017, 9, 1049–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, P.; Ezzeldin, E.; Iqbal, M.; Anwer, K.; Mostafa, G.A.E.; Alqarni, M.H.; Foudah, A.I.; Shakeel, F. Ecofriendly densitometric RP-HPTLC method for determination of rivaroxaban in nanoparticle formulations using green solvents. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 2133–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, P.; Iqbal, M.; Ezzeldin, E.; Khalil, N.Y.; Foudah, A.I.; Alqarni, M.H.; Shakeel, F. Simple and accurate HPTLC-densitometry method for quantification of delafloxacin (a novel fluoroquinolone antibiotic) in plasma samples: Application to pharmacokinetic study in rats. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, F.A.; Elmansi, H.; Fathy, M.E. Green RP-HPLC method for simultaneous determination of moxifloxacin combinations: Investigation of the greenness for the proposed method. Microchem. J. 2019, 148, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Taleb, N.H.; El-Enany, N.M.; El-Sherbiny, D.T.; El-Subbagh, H.I. Digitally enhanced thin layer chromatography for simultaneous determination of norfloxacin and tinidazole with the aid of Taguchi orthogonal array and desirability function approach: Greenness assessment by analytical Eco-Scale. J. Sep. Sci. 2019, 43, 1195–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahman, M.M.; Abdelwahab, N.S.; Hegazy, M.A.; Fares, M.Y.; El-Sayed, G.M. Determination of the abused intravenously self-administered madness drops (Tropicamide) by liquid chromatography in rat plasma; an application to pharmacokinetic study and greenness profile assessment. Microchem. J. 2020, 159, 105582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Liu, X.; Dong, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J.; He, S.; Yang, F.; Wang, Z.; Dong, Y. A Green HPLC Method for Determination of Nine Sulfonamides in Milk and Beef, and Its Greenness Assessment with Analytical Eco-Scale and Greenness Profile. J. AOAC Int. 2020, 103, 1181–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena-Pereira, F.; Wojnowski, W.; Tobiszewski, M. AGREE—Analytical GREEnness Metric Approach and Software. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 10076–10082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowak, P.M.; Koscielniak, P. What Color Is Your Method? Adaptation of the RGB Additive Color Model to Analytical Method Evaluation. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 10343–10352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karmaker, R.; Sinha, D.; Sinha, U.B. Rationalizing between the efficiency and greenness of solvents—A computational study of their influence on TBATB. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2021, 20, 100387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Nunes, S.P. Green solvents for membrane manufacture: Recent trends and perspectives. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2021, 28, 100427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, F.P.; Jin, S.; Paggiola, G.; Petchey, T.H.M.; Clark, J.H.; Farmer, T.J.; Hunt, A.J.; McElroy, C.R.; Sherwood, J. Tools and techniques for solvent selection: Green solvent selection guides. Sustain. Chem. Process. 2016, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foudah, A.I.; Shakeel, F.; Alqarni, M.H.; Ali, A.; Alshehri, S.; Ghoneim, M.M.; Alam, P. Determination of Thymol in Commercial Formulation, Essential Oils, Traditional, and Ultrasound-Based Extracts of Thymus vulgaris and Origanum vulgare Using a Greener HPTLC Approach. Molecule 2022, 27, 1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Conference on Harmonization (ICH). Validation of Analytical Procedures–Text and Methodology; Q2 (R1): Geneva, Switzerland, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Foudah, A.I.; Shakeel, F.; Alqarni, M.H.; Alam, P. A rapid and sensitive stability-indicating green RP-HPTLC method for the quantitation of flibanserin compared to green NP-HPTLC method: Validation studies and greenness assessment. Microchem. J. 2021, 164, 105960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, P.; Shakeel, F.; Alqarni, M.H.; Foudah, A.I.; Faiyazuddin, M.; Alshehri, S. Rapid, Sensitive, and Sustainable Reversed-Phase HPTLC Method in Comparison to the Normal-Phase HPTLC for the Determination of Pterostilbene in Capsule Dosage Form. Processes 2021, 9, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
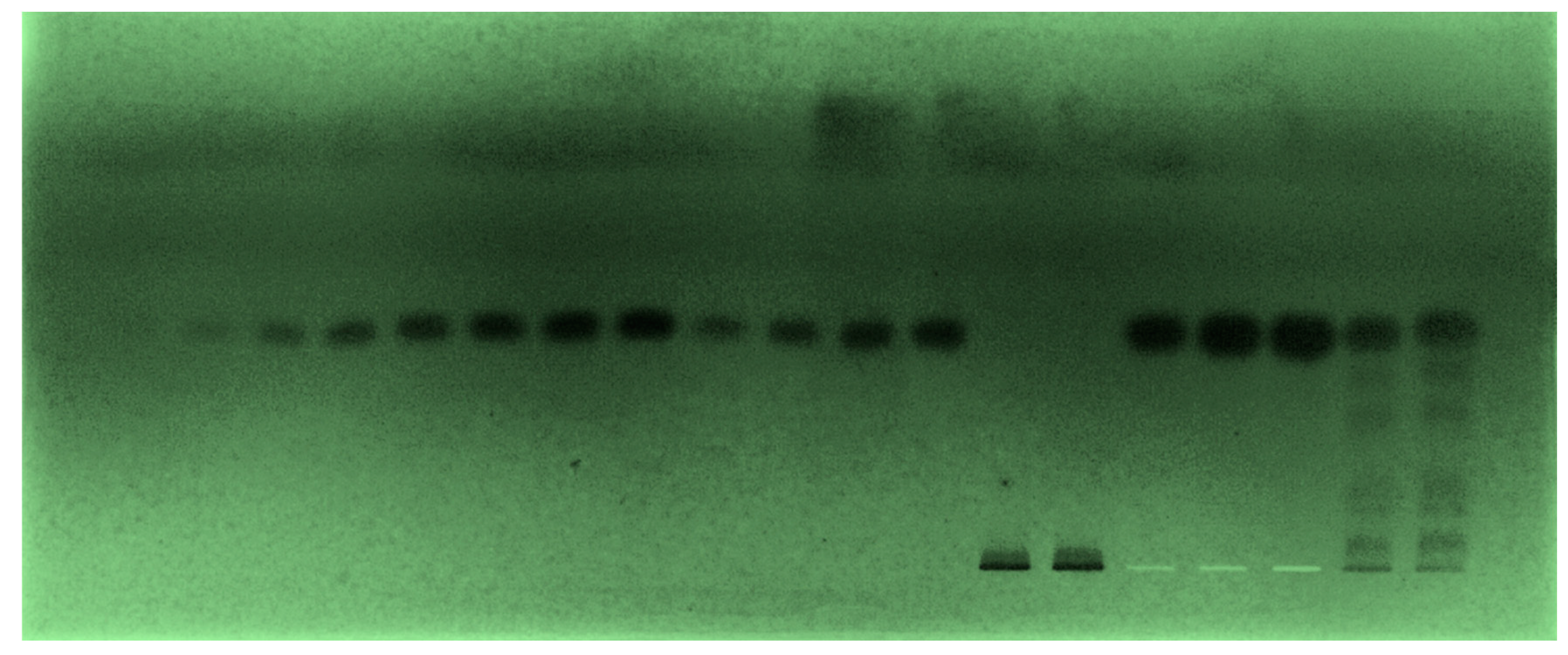




| Parameters | Values a |
|---|---|
| Linearity range (ng band−1) | 30–1200 |
| Regression equation | y = 7.5498x + 524.24 |
| R2 | 0.9945 |
| R | 0.9973 |
| Slope ± SD | 7.5498 ± 0.32000 |
| Intercept ± SD | 524.24 ± 7.2800 |
| Standard error of slope | 0.130 |
| Standard error of intercept | 2.97 |
| 95% confidence interval of slope | 6.9875–8.1120 |
| 95% confidence interval of intercept | 511.44–537.03 |
| LOD ± SD (ng band−1) | 10.16 ± 0.21 |
| LOQ ± SD (ng band−1) | 30.48 ± 0.63 |
| Conc. (ng band−1) | Parameters | Value a |
|---|---|---|
| Rf | 0.45 ± 0.01 | |
| 400 | As | 1.02 ± 0.02 |
| N m−1 | 4780 ± 3.11 |
| Conc. (ng band−1) | Conc. Found (ng band−1) ± SD | Recovery (%) | CV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 101.08 ± 1.41 | 101.08 | 1.39 |
| 400 | 395.68 ± 2.41 | 98.92 | 0.60 |
| 1200 | 1181.24 ± 5.31 | 98.43 | 0.44 |
| Conc. (ng band−1) | Intra-Day Precision | Inter-Day Precision | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conc. (ng band−1) ± SD | Standard Error | CV (%) | Conc. (ng band−1) ± SD | Standard Error | CV (%) | |
| 100 | 99.11 ± 0.92 | 0.37 | 0.92 | 100.25 ± 0.98 | 0.40 | 0.97 |
| 400 | 403.54 ± 2.52 | 1.02 | 0.62 | 396.21 ± 2.71 | 1.10 | 0.68 |
| 1200 | 1187.23 ± 5.61 | 2.29 | 0.47 | 1210.32 ± 5.84 | 2.38 | 0.48 |
| Conc. (ng band−1) | Mobile Phase Composition (CyHex-EtAc) | Results | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original | Used | Level | Conc. (ng Band−1) ± SD | % CV | Rf | |
| 42:58 | +2.0 | 393.65 ± 2.89 | 0.73 | 0.44 | ||
| 400 | 40:60 | 40:60 | 0.0 | 404.23 ± 3.02 | 0.74 | 0.45 |
| 38:62 | −2.0 | 408.21 ± 3.15 | 0.77 | 0.46 | ||
| Stress Condition | Number of Degradation Products (Rf) | TPM Rf | TPM Remaining (ng band−1) | TPM Recovered (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 M HCl | 5 (0.16, 0.33, 0.59, 0.66, 0.70) | 0.44 | 114.24 | 28.56 ± 1.41 |
| 1 M NaOH | 3 (0.32, 0.66, 0.75) | 0.44 | 287.96 | 71.99 ± 1.78 |
| 30% H2O2 | 5 (0.11, 0.14, 0.28, 0.35, 0.61) | 0.44 | 258.12 | 64.53 ± 1.57 |
| Photolytic | 0 | 0.45 | 400.00 | 100 ± 0.00 |
| Thermal | 0 | 0.45 | 400.00 | 100 ± 0.00 |
| Analytical Method | Linearity Range | Accuracy (% Recovery) | Precision (% CV) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Colorimetry | 100–1200 (µg mL−1) | 99.97–100.02 | 0.54–0.58 | [6] |
| Flow injection spectrometry | 5–35 (µg mL−1) | 99.70–101.30 | 1.30–2.00 | [19] |
| HPLC | 1–300 (µg mL−1) | - | 1.35–1.45 | [4] |
| HPLC | 1–100 (µg mL−1) | 99.93 | 0.35–3.23 | [8] |
| HPLC | 5000–15,000 (µg mL−1) | - | 0.30–1.00 | [9] |
| HPLC | 10–50 (µg mL−1) | 100.02–100.57 | 0.08–0.19 | [10] |
| HPLC | 50–3000 (µg mL−1) | 99.60 | 0.17–0.65 | [11] |
| LC-MS | 1–1000 (ng mL−1) | 93.30–99.70 | 0.10–1.85 | [17] |
| UPLC | 50–150 (µg mL−1) | 99.00–99.70 | 0.05–0.10 | [18] |
| NMR | 50–850 (µg mL−1) | 98.86–99.70 | <2.00 | [20] |
| HPTLC | 1000–5000 (ng band−1) | 89.11–102.24 | 3.10–5.16 | [12] |
| HPTLC | 250–4000 (ng band−1) | 104.47 | 4.16 | [14] |
| HPTLC | 30–1200 (ng band−1) | 98.43–101.08 | 0.47–0.97 | Present work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alqarni, M.H.; Shakeel, F.; Mahdi, W.A.; Foudah, A.I.; Aljarba, T.M.; Alshehri, S.; Ghoneim, M.M.; Alam, P. A Greener Stability-Indicating High-Performance Thin-Layer Chromatography Approach for the Estimation of Topiramate. Materials 2022, 15, 1731. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15051731
Alqarni MH, Shakeel F, Mahdi WA, Foudah AI, Aljarba TM, Alshehri S, Ghoneim MM, Alam P. A Greener Stability-Indicating High-Performance Thin-Layer Chromatography Approach for the Estimation of Topiramate. Materials. 2022; 15(5):1731. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15051731
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlqarni, Mohammed H., Faiyaz Shakeel, Wael A. Mahdi, Ahmed I. Foudah, Tariq M. Aljarba, Sultan Alshehri, Mohammed M. Ghoneim, and Prawez Alam. 2022. "A Greener Stability-Indicating High-Performance Thin-Layer Chromatography Approach for the Estimation of Topiramate" Materials 15, no. 5: 1731. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15051731
APA StyleAlqarni, M. H., Shakeel, F., Mahdi, W. A., Foudah, A. I., Aljarba, T. M., Alshehri, S., Ghoneim, M. M., & Alam, P. (2022). A Greener Stability-Indicating High-Performance Thin-Layer Chromatography Approach for the Estimation of Topiramate. Materials, 15(5), 1731. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15051731








