Treasure on the Earth—Gold Nanoparticles and Their Biomedical Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Imaging and Diagnosing
3. Therapy
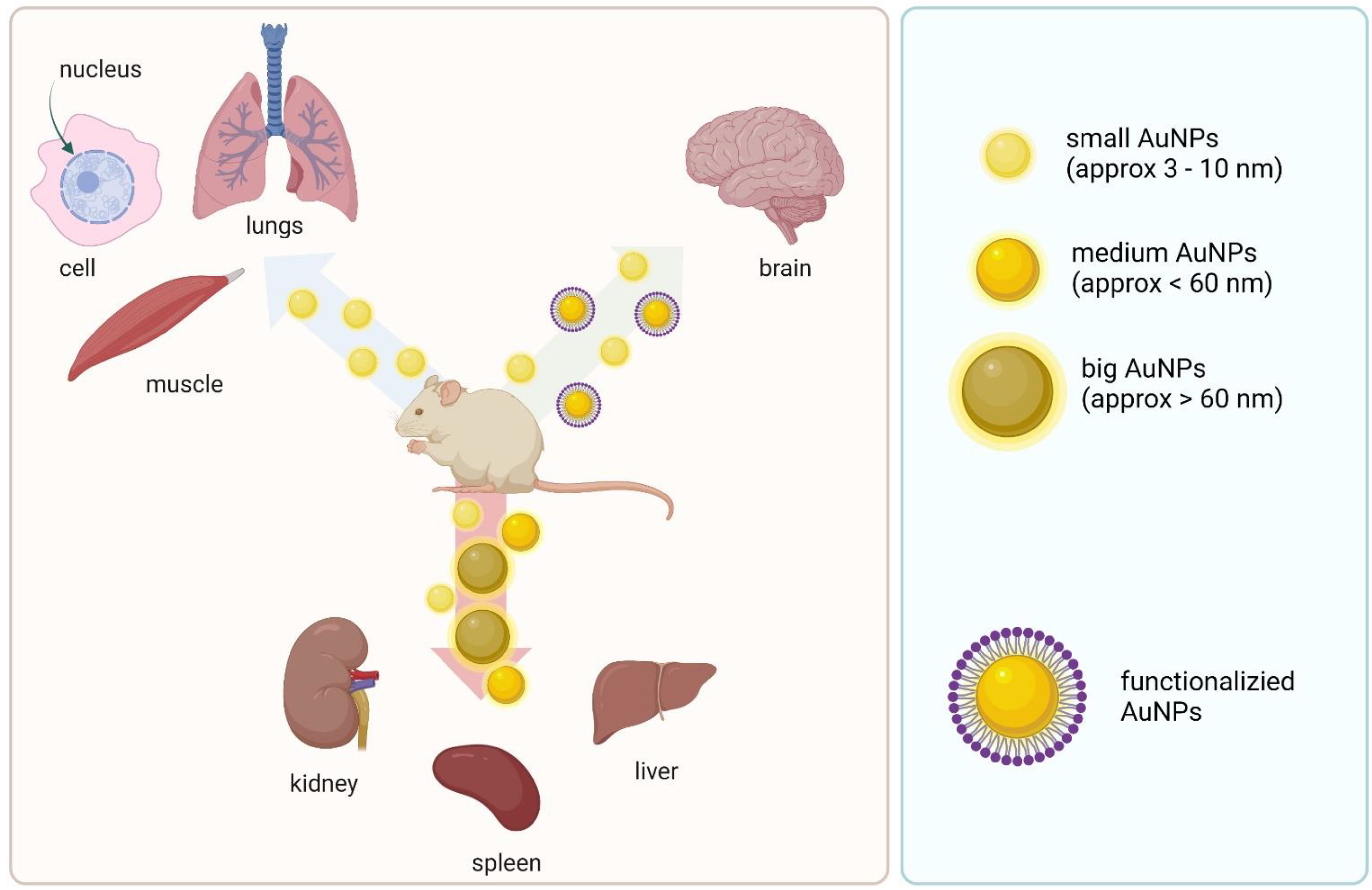
4. Delivery System
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kolahalam, L.A.; Viswanath, I.V.K.; Diwakar, B.S.; Govindh, B.; Reddy, V.; Murthy, Y.L.N. Review on Nanomaterials: Synthesis and Applications. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 18, 2182–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, R.; Mukherjee, P. Biological Properties of “Naked” Metal Nanoparticles. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 1289–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amina, S.J.; Guo, B. A Review on the Synthesis and Functionalization of Gold Nanoparticles as a Drug Delivery Vehicle. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 9823–9857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elahi, N.; Kamali, M.; Baghersad, M.H. Recent Biomedical Applications of Gold Nanoparticles: A Review. Talanta 2018, 184, 537–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chugh, H.; Sood, D.; Chandra, I.; Tomar, V.; Dhawan, G.; Chandra, R. Role of Gold and Silver Nanoparticles in Cancer Nano-Medicine. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 1210–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, P.; Han, G.; De, M.; Kim, C.K.; Rotello, V.M. Gold Nanoparticles in Delivery Applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 1307–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddique, S.; Chow, J.C.L. Gold Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery and Cancer Therapy. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rónavári, A.; Igaz, N.; Adamecz, D.I.; Szerencsés, B.; Molnar, C.; Kónya, Z.; Pfeiffer, I.; Kiricsi, M. Green Silver and Gold Nanoparticles: Biological Synthesis Approaches and Potentials for Biomedical Applications. Molecules 2021, 26, 844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailova, E.O. Gold Nanoparticles: Biosynthesis and Potential of Biomedical Application. J. Funct. Biomater. 2021, 12, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Annu; Ikram, S.; Yudha, S.S. Biosynthesis of Gold Nanoparticles: A Green Approach. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2016, 161, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, J.P.M.; Chen, A.L.; Foster, A.; Drezek, R. In Vivo Biodistribution of Nanoparticles. Nanomedicine 2011, 6, 815–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daraee, H.; Eatemadi, A.; Abbasi, E.; Aval, S.F.; Kouhi, M.; Akbarzadeh, A. Application of Gold Nanoparticles in Biomedical and Drug Delivery. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2016, 44, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connor, D.M.; Broome, A.-M. Gold Nanoparticles for the Delivery of Cancer Therapeutics. Adv. Cancer Res. 2018, 139, 163–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carnovale, C.; Bryant, G.; Shukla, R.; Bansal, V. Identifying Trends in Gold Nanoparticle Toxicity and Uptake: Size, Shape, Capping Ligand, and Biological Corona. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 242–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.-D.; Wu, H.-Y.; Wu, D.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Chang, J.-H.; Zhai, Z.-B.; Meng, A.-M.; Liu, P.-X.; Zhang, L.-A.; Fan, F.-Y. Toxicologic Effects of Gold Nanoparticles in Vivo by Different Administration Routes. Int. J. Nanomed. 2010, 5, 771–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bednarski, M.; Dudek, M.; Knutelska, J.; Nowiński, L.; Sapa, J.; Zygmunt, M.; Nowak, G.; Luty-Błocho, M.; Wojnicki, M.; Fitzner, K.; et al. The Influence of the Route of Administration of Gold Nanoparticles on Their Tissue Distribution and Basic Biochemical Parameters: In Vivo Studies. Pharmacol. Rep. 2015, 67, 405–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khlebtsov, N.; Dykman, L. Biodistribution and Toxicity of Engineered Gold Nanoparticles: A Review of in Vitro and in Vivo Studies. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 1647–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Yang, J.; Li, S.; Li, Q.; Liu, S.; Zheng, W.; Jiang, X. Oral Administration of Starting Materials for In Vivo Synthesis of Antibacterial Gold Nanoparticles for Curing Remote Infections. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 1124–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, Y.; Singh, S.K.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, B.; Kaur, G.; Gulati, M.; Tewari, D.; Gowthamarajan, K.; Karri, V.V.S.N.R.; Ayinkamiye, C.; et al. Modified Apple Polysaccharide Capped Gold Nanoparticles for Oral Delivery of Insulin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 149, 976–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Chaves, C.; Soto-Alvaredo, J.; Montes-Bayon, M.; Bettmer, J.; Llopis, J.; Sanchez-Gonzalez, C. Gold Nanoparticles: Distribution, Bioaccumulation and Toxicity. In Vitro and in Vivo Studies. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2018, 14, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boisselier, E.; Astruc, D. Gold Nanoparticles in Nanomedicine: Preparations, Imaging, Diagnostics, Therapies and Toxicity. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 1759–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Hu, Z.; Ma, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Yuan, Z. The Systematic Evaluation of Size-Dependent Toxicity and Multi-Time Biodistribution of Gold Nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 167, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-S.; Hung, Y.-C.; Liau, I.; Huang, G.S. Assessment of the In Vivo Toxicity of Gold Nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2009, 4, 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Enea, M.; de Almeida, M.P.; Eaton, P.; da Silva, D.D.; Pereira, E.; Soares, M.E.; de Lourdes Bastos, M.; Carmo, H. A Multiparametric Study of Gold Nanoparticles Cytotoxicity, Internalization and Permeability Using an in Vitro Model of Blood–Brain Barrier. Influence of Size, Shape and Capping Agent. Nanotoxicology 2019, 13, 990–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adewale, O.B.; Davids, H.; Cairncross, L.; Roux, S. Toxicological Behavior of Gold Nanoparticles on Various Models: Influence of Physicochemical Properties and Other Factors. Int. J. Toxicol. 2019, 38, 357–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comune, M.; Rai, A.; Palma, P.; TondaTuro, C.; Ferreira, L. Antimicrobial and Pro-Angiogenic Properties of Soluble and Nanoparticle-Immobilized LL37 Peptides. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 8153–8159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, A.; Ferrão, R.; Palma, P.; Patricio, T.; Parreira, P.; Anes, E.; Tonda-Turo, C.; Martins, M.C.L.; Alves, N.; Ferreira, L. Antimicrobial Peptide-Based Materials: Opportunities and Challenges. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 2384–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.R.; Gambhir, S.S. Nanomaterials for in Vivo Imaging. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 901–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.; Yoo, D.; Ling, D.; Cho, M.H.; Hyeon, T.; Cheon, J. Iron Oxide Based Nanoparticles for Multimodal Imaging and Magnetoresponsive Therapy. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 10637–10689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nune, K.C.; Montes, I.; Injeti, V.S.Y.; Somani, M.C.; Misra, R.D.K. The Determining Role of Nanoscale Mechanical Twinning on Cellular Functions of Nanostructured Materials. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2018, 88, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.C.; Mwakwari, S.C.; Oyelere, A.K. Gold Nanoparticles: From Nanomedicine to Nanosensing. Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 2008, 1, 45–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seeram, E. Computed Tomography: A Technical Review. Radiol. Technol. 2018, 89, 279CT–302CT. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Kiessling, F.; Gätjens, J. Advanced Nanomaterials in Multimodal Imaging: Design, Functionalization, and Biomedical Applications. J. Nanomater. 2010, 2010, 894303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haller, C.; Hizoh, I. The Cytotoxicity of Iodinated Radiocontrast Agents on Renal Cells In Vitro. Investig. Radiol. 2004, 39, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Park, S.; Jae, H.L.; Yong, Y.J.; Jon, S. Antibiofouling Polymer-Coated Gold Nanoparticles as a Contrast Agent for in Vivo X-Ray Computed Tomography Imaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 7661–7665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cormode, D.P.; Naha, P.C.; Fayad, Z.A. Nanoparticle Contrast Agents for Computed Tomography: A Focus on Micelles. Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 2014, 9, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Popovtzer, R.; Agrawal, A.; Kotov, N.A.; Popovtzer, A.; Balter, J.; Carey, T.E.; Kopelman, R. Targeted Gold Nanoparticles Enable Molecular CT Imaging of Cancer. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 4593–4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, W.; Chen, X. Nanoplatforms for Targeted Molecular Imaging in Living Subjects. Small 2007, 3, 1840–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meir, R.; Popovtzer, R. Cell Tracking Using Gold Nanoparticles and Computed Tomography Imaging. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 10, e1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galper, M.W.; Saung, M.T.; Fuster, V.; Roessl, E.; Thran, A.; Proksa, R.; Fayad, Z.A.; Cormode, D.P. Effect of Computed Tomography Scanning Parameters on Gold Nanoparticle and Iodine Contrast. Investig. Radiol. 2012, 47, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, A.L.; Dhanantwari, A.; Jurcova, M.; Cheheltani, R.; Naha, P.C.; Ivanc, T.; Shefer, E.; Cormode, D.P. Improved Sensitivity of Computed Tomography towards Iodine and Gold Nanoparticle Contrast Agents via Iterative Reconstruction Methods. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Q.-Y.; Kim, S.H.; Choi, K.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Byun, S.J.; Kim, K.W.; Park, S.H.; Juhng, S.K.; Yoon, K.-H. Colloidal Gold Nanoparticles as a Blood-Pool Contrast Agent for X-ray Computed Tomography in Mice. Investig. Radiol. 2007, 42, 797–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, L.E.; Ross, R.D.; Tilley, J.M.; Vargo-Gogola, T.; Roeder, R.K. Gold Nanoparticles as Contrast Agents in X-Ray Imaging and Computed Tomography. Nanomedicine 2015, 10, 321–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klębowski, B.; Depciuch, J.; Parlińska-Wojtan, M.; Baran, J. Applications of Noble Metal-Based Nanoparticles in Medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hainfeld, J.F.; O’Connor, M.J.; Dilmanian, F.A.; Slatkin, D.N.; Adams, D.J.; Smilowitz, H.M. Micro-CT Enables Microlocalisation and Quantification of Her2-Targeted Gold Nanoparticles within Tumour Regions. Br. J. Radiol. 2011, 84, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shilo, M.; Motiei, M.; Hana, P.; Popovtzer, R. Transport of Nanoparticles through the Blood–Brain Barrier for Imaging and Therapeutic Applications. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 2146–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, H.; Stanciauskas, R.; Stigloher, C.; Dizon, K.K.; Jospin, M.; Bessereau, J.-L.; Pinaud, F. In Vivo Single-Molecule Imaging Identifies Altered Dynamics of Calcium Channels in Dystrophin-Mutant C. Elegans. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, W.C.W.; Maxwell, D.J.; Gao, X.; Bailey, R.E.; Han, M.; Nie, S. Luminescent Quantum Dots for Multiplexed Biological Detection and Imaging. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2002, 13, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yguerabide, J.; Yguerabide, E.E. Resonance Light Scattering Particles as Ultrasensitive Labels for Detection of Analytes in a Wide Range of Applications. J. Cell. Biochem. 2001, 84, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Ali, M.R.K.; Chen, K.; Fang, N.; El-Sayed, M.A. Gold Nanoparticles in Biological Optical Imaging. Nano Today 2019, 24, 120–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühn, S.; Håkanson, U.; Rogobete, L.; Sandoghdar, V. Enhancement of Single-Molecule Fluorescence Using a Gold Nanoparticle as an Optical Nanoantenna. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 017402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masuda, S.; Yanase, Y.; Usukura, E.; Ryuzaki, S.; Wang, P.; Okamoto, K.; Kuboki, T.; Kidoaki, S.; Tamada, K. High-Resolution Imaging of a Cell-Attached Nanointerface Using a Gold-Nanoparticle Two-Dimensional Sheet. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Nicovich, P.R.; Dickson, R.M. Highly Fluorescent Noble-Metal Quantum Dots. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2007, 58, 409–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chandirasekar, S.; Chandrasekaran, C.; Muthukumarasamyvel, T.; Sudhandiran, G.; Rajendiran, N. Biosurfactant Templated Quantum Sized Fluorescent Gold Nanoclusters for in Vivo Bioimaging in Zebrafish Embryos. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 143, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Bao, C.; Liang, S.; Wang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Fu, H.; Wang, K.; et al. Gold Nanoclusters-Based Nanoprobes for Simultaneous Fluorescence Imaging and Targeted Photodynamic Therapy with Superior Penetration and Retention Behavior in Tumors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 1314–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmsen, S.; Huang, R.; Wall, M.A.; Karabeber, H.; Samii, J.M.; Spaliviero, M.; White, J.R.; Monette, S.; O’Connor, R.; Pitter, K.L.; et al. Surface-Enhanced Resonance Raman Scattering Nanostars for High Precision Cancer Imaging. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 271ra7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, D.; Chen, Y.; Hou, S.; Fang, W.; Duan, H. Intracellular and Cellular Detection by SERS-Active Plasmonic Nanostructures. ChemBioChem 2019, 20, 2432–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, J.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, Z.; Tan, H. Optical Diagnostic Based on Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sánchez-Purrà, M.; Carré-Camps, M.; de Puig, H.; Bosch, I.; Gehrke, L.; Hamad-Schifferli, K. Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy-Based Sandwich Immunoassays for Multiplexed Detection of Zika and Dengue Viral Biomarkers. ACS Infect. Dis. 2017, 3, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, V.; Jangra, S.; Yadav, N.R. Nanotechnology Based Approaches for Detection and Delivery of MicroRNA in Healthcare and Crop Protection. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coutinho, C.; Somoza, Á. MicroRNA Sensors Based on Gold Nanoparticles. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 411, 1807–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.D.; Yin, B.C.; Ye, B.C. Ultrasensitive, Colorimetric Detection of MicroRNAs Based on Isothermal Exponential Amplification Reaction-Assisted Gold Nanoparticle Amplification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 86, 1011–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amal, H.; Leja, M.; Funka, K.; Skapars, R.; Sivins, A.; Ancans, G.; Liepniece-Karele, I.; Kikuste, I.; Lasina, I.; Haick, H. Detection of Precancerous Gastric Lesions and Gastric Cancer through Exhaled Breath. Gut 2016, 65, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Runge, V.M. Safety of Approved MR Contrast Media for Intravenous Injection. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2000, 12, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marckmann, P.; Skov, L.; Rossen, K.; Dupont, A.; Damholt, M.B.; Heaf, J.G.; Thomsen, H.S. Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis: Suspected Causative Role of Gadodiamide Used for Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 2359–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanda, T.; Fukusato, T.; Matsuda, M.; Toyoda, K.; Oba, H.; Kotoku, J.; Haruyama, T.; Kitajima, K.; Furui, S. Gadolinium-Based Contrast Agent Accumulates in the Brain Even in Subjects without Severe Renal Dysfunction: Evaluation of Autopsy Brain Specimens with Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectroscopy. Radiology 2015, 276, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iancu, S.D.; Albu, C.; Chiriac, L.; Moldovan, R.; Stefancu, A.; Moisoiu, V.; Coman, V.; Szabo, L.; Leopold, N.; Bálint, Z. Assessment of Gold-Coated Iron Oxide Nanoparticles as Negative T2 Contrast Agent in Small Animal MRI Studies. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 4811–4824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alric, C.; Taleb, J.; Le Duc, G.; Mandon, C.; Billotey, C.; Le Meur-Herland, A.; Brochard, T.; Vocanson, F.; Janier, M.; Perriat, P.; et al. Gadolinium Chelate Coated Gold Nanoparticles as Contrast Agents for Both X-ray Computed Tomography and Magnetic Resonance Imaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 5908–5915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouché, M.; Hsu, J.C.; Dong, Y.C.; Kim, J.; Taing, K.; Cormode, D.P. Recent Advances in Molecular Imaging with Gold Nanoparticles. Bioconjug. Chem. 2020, 31, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Jiang, W.; Luo, K.; Song, H.; Lan, F.; Wu, Y.; Gu, Z. Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles as MRI Contrast Agents for Non-Invasive Stem Cell Labeling and Tracking. Theranostics 2013, 3, 595–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.D.; Paudel, R.; Liu, J.; Ma, C.; Zhang, Z.S.; Zhou, S.K. MRI Contrast Agents: Classification and Application (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 38, 1319–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chauhan, R.; El-Baz, N.; Keynton, R.S.; James, K.T.; Malik, D.A.; Zhu, M.; El-Baz, A.; Ng, C.K.; Bates, P.J.; Malik, M.T.; et al. Targeted Gold Nanoparticle–Oligonucleotide Contrast Agents in Combination with a New Local Voxel-Wise MRI Analysis Algorithm for In Vitro Imaging of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Attia, A.B.E.; Balasundaram, G.; Moothanchery, M.; Dinish, U.S.; Bi, R.; Ntziachristos, V.; Olivo, M. A Review of Clinical Photoacoustic Imaging: Current and Future Trends. Photoacoustics 2019, 16, 100144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahan, M.M.; Doiron, A.L. Gold Nanoparticles as X-Ray, CT, and Multimodal Imaging Contrast Agents: Formulation, Targeting, and Methodology. J. Nanomater. 2018, 2018, 5837276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.V.; Hu, S. Photoacoustic Tomography: In Vivo Imaging from Organelles to Organs. Science 2012, 335, 1458–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jain, K.K. Nanomedicine: Application of Nanobiotechnology in Medical Practice. Med. Princ. Pract. 2008, 17, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copland, J.A.; Eghtedari, M.; Popov, V.L.; Kotov, N.; Mamedova, N.; Motamedi, M.; Oraevsky, A.A. Bioconjugated Gold Nanoparticles as a Molecular Based Contrast Agent: Implications for Imaging of Deep Tumors Using Optoacoustic Tomography. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2004, 6, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Han, Y.; Gao, S.; Yan, H.; Cao, L.; Li, Z.; Liang, X.-J.; Zhang, J. Ultrasmall Gold Nanoparticles in Cancer Diagnosis and Therapy. Theranostics 2020, 10, 4944–4957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.-Y.; Lu, S.-L.; Hu, C.-W.; Yeh, C.-S.; Lee, G.-B.; Lei, H.-Y. Size-Dependent Attenuation of TLR9 Signaling by Gold Nanoparticles in Macrophages. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, C.; Long, M.; Qin, Y.; Sun, X.; Zheng, J. Luminescent Gold Nanoparticles with Efficient Renal Clearance. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 3168–3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, K.; Ma, H.; Liu, J.; Huo, S.; Kumar, A.; Wei, T.; Zhang, X.; Jin, S.; Gan, Y.; Wang, P.C.; et al. Size-Dependent Localization and Penetration of Ultrasmall Gold Nanoparticles in Cancer Cells, Multicellular Spheroids, and Tumors in Vivo. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 4483–4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, F.; Goel, S.; Hernandez, R.; Graves, S.A.; Shi, S.; Nickles, R.J.; Cai, W. Dynamic Positron Emission Tomography Imaging of Renal Clearable Gold Nanoparticles. Small 2016, 12, 2775–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, F.; Si, P.; de la Zerda, A.; Jokerst, J.V.; Myung, D. Gold Nanoparticles to Enhance Ophthalmic Imaging. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 367–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Zerda, A.; Prabhulkar, S.; Perez, V.L.; Ruggeri, M.; Paranjape, A.S.; Habte, F.; Gambhir, S.S.; Awdeh, R.M. Optical Coherence Contrast Imaging Using Gold Nanorods in Living Mice Eyes. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2015, 43, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Masse, F.; Ouellette, M.; Lamoureux, G.; Boisselier, E. Gold Nanoparticles in Ophthalmology. Med. Res. Rev. 2019, 39, 302–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, W.; Lee, J.-C.; Shin, J.-H.; Jin, K.-H.; Park, H.-K.; Choi, S. Instrument-Free Synthesizable Fabrication of Label-Free Optical Biosensing Paper Strips for the Early Detection of Infectious Keratoconjunctivitides. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 5531–5537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, M.S.; Grzelczak, M. Using Gold Nanoparticles to Detect Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms: Toward Liquid Biopsy. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2020, 11, 263–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Lan, L.; Yao, Y.; Ping, J.; Li, Y.; Ying, Y. An Unmodified Gold Nanorods-Based DNA Colorimetric Biosensor with Enzyme-Free Hybridization Chain Reaction Amplification. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 273, 642–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, P.K.; El-Sayed, I.H.; El-Sayed, M.A. Au Nanoparticles Target Cancer. Nano Today 2007, 2, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Jain, P.K.; El-Sayed, I.H.; El-Sayed, M.A. Plasmonic Photothermal Therapy (PPTT) Using Gold Nanoparticles. Lasers Med. Sci. 2008, 23, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, P.C.; Khan, S.A.; Singh, A.K.; Senapati, D.; Fan, Z. Nanomaterials for Targeted Detection and Photothermal Killing of Bacteria. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 3193–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sztandera, K.; Gorzkiewicz, M.; Klajnert-Maculewicz, B. Gold Nanoparticles in Cancer Treatment. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vines, J.B.; Yoon, J.-H.; Ryu, N.-E.; Lim, D.-J.; Park, H. Gold Nanoparticles for Photothermal Cancer Therapy. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, P.; Pandit, S.; Mokkapati, V.R.S.S.; Garg, A.; Ravikumar, V.; Mijakovic, I. Gold Nanoparticles in Diagnostics and Therapeutics for Human Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, H.; Fang, J.; Inutsuka, T.; Kitamoto, Y. Vascular Permeability Enhancement in Solid Tumor: Various Factors, Mechanisms Involved and Its Implications. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2003, 3, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, L.R.; Stafford, R.J.; Bankson, J.A.; Sershen, S.R.; Rivera, B.; Price, R.E.; Hazle, J.D.; Halas, N.J.; West, J.L. Nanoshell-Mediated near-Infrared Thermal Therapy of Tumors under Magnetic Resonance Guidance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 13549–13554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Libutti, S.K.; Paciotti, G.F.; Byrnes, A.A.; Alexander, H.R.; Gannon, W.E.; Walker, M.; Seidel, G.D.; Yuldasheva, N.; Tamarkin, L. Phase I and Pharmacokinetic Studies of CYT-6091, a Novel PEGylated Colloidal Gold-RhTNF Nanomedicine. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 6139–6149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dickerson, E.B.; Dreaden, E.C.; Huang, X.; El-Sayed, I.H.; Chu, H.; Pushpanketh, S.; McDonald, J.F.; El-Sayed, M.A. Gold Nanorod Assisted Near-Infrared Plasmonic Photothermal Therapy (PPTT) of Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Mice. Cancer Lett. 2008, 269, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elsayed, I.; Huang, X.; Elsayed, M. Selective Laser Photo-Thermal Therapy of Epithelial Carcinoma Using Anti-EGFR Antibody Conjugated Gold Nanoparticles. Cancer Lett. 2006, 239, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhan, X.; Xiong, J.; Peng, S.; Huang, W.; Joshi, R.; Cai, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, R.; Yuan, K.; et al. Temperature-Dependent Cell Death Patterns Induced by Functionalized Gold Nanoparticle Photothermal Therapy in Melanoma Cells. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chitgupi, U.; Qin, Y.; Lovell, J.F. Targeted Nanomaterials for Phototherapy. Nanotheranostics 2017, 1, 38–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Shin, K.; Kwon, S.G.; Hyeon, T. Synthesis and Biomedical Applications of Multifunctional Nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1802309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benov, L. Photodynamic Therapy: Current Status and Future Directions. Med. Princ. Pract. 2015, 24, 14–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucharskaya, A.; Maslyakova, G.; Terentyuk, G.; Yakunin, A.; Avetisyan, Y.; Bibikova, O.; Tuchina, E.; Khlebtsov, B.; Khlebtsov, N.; Tuchin, V. Towards Effective Photothermal/Photodynamic Treatment Using Plasmonic Gold Nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calavia, P.G.; Bruce, G.; Pérez-García, L.; Russell, D.A. Photosensitiser-Gold Nanoparticle Conjugates for Photodynamic Therapy of Cancer. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2018, 17, 1534–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, P.; Zhang, K.; Yang, S.; Liu, Q. Ultrasound Enhances the Efficacy of Chlorin E6-Mediated Photodynamic Therapy in MDA-MB-231 Cells. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2013, 39, 1713–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardinal, J.; Klune, J.R.; Chory, E.; Jeyabalan, G.; Kanzius, J.S.; Nalesnik, M.; Geller, D.A. Noninvasive Radiofrequency Ablation of Cancer Targeted by Gold Nanoparticles. Surgery 2008, 144, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zharov, V.P.; Mercer, K.E.; Galitovskaya, E.N.; Smeltzer, M.S. Photothermal Nanotherapeutics and Nanodiagnostics for Selective Killing of Bacteria Targeted with Gold Nanoparticles. Biophys. J. 2006, 90, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Banstola, A.; Jeong, J.H.; Yook, S. Immunoadjuvants for Cancer Immunotherapy: A Review of Recent Developments. Acta Biomater. 2020, 114, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, A.; Khan, T.; Omri, A. Design and Encapsulation of Immunomodulators onto Gold Nanoparticles in Cancer Immunotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savitsky, K.; Yu, X. Combined Strategies for Tumor Immunotherapy with Nanoparticles. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2019, 21, 1441–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surendran, S.P.; Moon, M.J.; Park, R.; Jeong, Y.Y. Bioactive Nanoparticles for Cancer Immunotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, J.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Chu, X.; Lin, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Qiu, S.; Guo, Y.; Ding, H.; Pan, Y.; et al. The Application of and Strategy for Gold Nanoparticles in Cancer Immunotherapy. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 687399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mocan, T.; Matea, C.; Tabaran, F.; Iancu, C.; Orasan, R.; Mocan, L. In Vitro Administration of Gold Nanoparticles Functionalized with MUC-1 Protein Fragment Generates Anticancer Vaccine Response via Macrophage Activation and Polarization Mechanism. J. Cancer 2015, 6, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Cao, W.; Cheng, J.; Fan, S.; Pan, S.; Wang, L.; Niu, J.; Pan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Sun, X.; et al. Human Natural Killer Cells for Targeting Delivery of Gold Nanostars and Bimodal Imaging Directed Photothermal/Photodynamic Therapy and Immunotherapy. Cancer Biol. Med. 2019, 16, 756–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, J.P.M.; Lin, A.Y.; Figueroa, E.R.; Foster, A.E.; Drezek, R.A. In Vivo Gold Nanoparticle Delivery of Peptide Vaccine Induces Anti-Tumor Immune Response in Prophylactic and Therapeutic Tumor Models. Small 2015, 11, 1453–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Chongsathidkiet, P.; Crawford, B.M.; Odion, R.; Dechant, C.A.; Kemeny, H.R.; Cui, X.; Maccarini, P.F.; Lascola, C.D.; Fecci, P.E.; et al. Plasmonic Gold Nanostar-Mediated Photothermal Immunotherapy for Brain Tumor Ablation and Immunologic Memory. Immunotherapy 2019, 11, 1293–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Sun, M.; Lu, Y.; Shi, S.; Yang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Feng, C.; Liu, J.; Dong, C. Cytokine-Induced Killer Cells-Assisted Tumor-Targeting Delivery of Her-2 Monoclonal Antibody-Conjugated Gold Nanostars with NIR Photosensitizer for Enhanced Therapy of Cancer. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 8368–8382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lévy, R.; Shaheen, U.; Cesbron, Y.; Sée, V. Gold Nanoparticles Delivery in Mammalian Live Cells: A Critical Review. Nano Rev. 2010, 1, 4889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, L.A.; Mackey, M.A.; Dreaden, E.C.; El-Sayed, M.A. The Optical, Photothermal, and Facile Surface Chemical Properties of Gold and Silver Nanoparticles in Biodiagnostics, Therapy, and Drug Delivery. Arch. Toxicol. 2014, 88, 1391–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paciotti, G.F.; Myer, L.; Weinreich, D.; Goia, D.; Pavel, N.; McLaughlin, R.E.; Tamarkin, L. Colloidal Gold: A Novel Nanoparticle Vector for Tumor Directed Drug Delivery. Drug Deliv. 2004, 11, 169–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventola, C.L. Progress in Nanomedicine: Approved and Investigational Nanodrugs. Pharm. Ther. 2017, 42, 742–755. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Lu, G. Applications of gold nanoparticles in cancer imaging and treatment. In Noble and Precious Metals—Properties, Nanoscale Effects and Applications; Seehra, M., Bristow, A., Eds.; InTech: London, UK, 2018; Volume 1, Chapter 13; pp. 291–309. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.-H.; Tsai, C.-Y.; Huang, P.-Y.; Chang, M.-Y.; Cheng, P.-C.; Chou, C.-H.; Chen, D.-H.; Wang, C.-R.; Shiau, A.-L.; Wu, C.-L. Methotrexate Conjugated to Gold Nanoparticles Inhibits Tumor Growth in a Syngeneic Lung Tumor Model. Mol. Pharm. 2007, 4, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Wang, Y.-C.; Dou, S.; Xiong, M.-H.; Sun, T.-M.; Wang, J. Doxorubicin-Tethered Responsive Gold Nanoparticles Facilitate Intracellular Drug Delivery for Overcoming Multidrug Resistance in Cancer Cells. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 3679–3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreaden, E.C.; Mwakwari, S.C.; Sodji, Q.H.; Oyelere, A.K.; El-Sayed, M.A. Tamoxifen-Poly(Ethylene Glycol)-Thiol Gold Nanoparticle Conjugates: Enhanced Potency and Selective Delivery for Breast Cancer Treatment. Bioconjug. Chem. 2009, 20, 2247–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cabral, R.M.; Baptista, P. V Anti-Cancer Precision Theranostics: A Focus on Multifunctional Gold Nanoparticles. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2014, 14, 1041–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, M.; Ingle, A.P.; Birla, S.; Yadav, A.; Dos Santos, C.A. Strategic Role of Selected Noble Metal Nanoparticles in Medicine. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 42, 696–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreaden, E.C.; Mwakwari, S.C.; Austin, L.A.; Kieffer, M.J.; Oyelere, A.K.; El-Sayed, M.A. Small Molecule-Gold Nanorod Conjugates Selectively Target and Induce Macrophage Cytotoxicity towards Breast Cancer Cells. Small 2012, 8, 2819–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalimuthu, K.; Lubin, B.-C.; Bazylevich, A.; Gellerman, G.; Shpilberg, O.; Luboshits, G.; Firer, M.A. Gold Nanoparticles Stabilize Peptide-Drug-Conjugates for Sustained Targeted Drug Delivery to Cancer Cells. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oishi, M.; Nakaogami, J.; Ishii, T.; Nagasaki, Y. Smart PEGylated Gold Nanoparticles for the Cytoplasmic Delivery of SiRNA to Induce Enhanced Gene Silencing. Chem. Lett. 2006, 35, 1046–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, S.; Daniel, W.L.; Giljohann, D.A.; Mirkin, C.A.; Lippard, S.J. Polyvalent Oligonucleotide Gold Nanoparticle Conjugates as Delivery Vehicles for Platinum(IV) Warheads. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 14652–14653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, R.; Wu, G.; Li, Z.; Mirkin, C.A.; Schatz, G.C. What Controls the Melting Properties of DNA-Linked Gold Nanoparticle Assemblies? J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 1643–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosi, N.L.; Giljohann, D.A.; Thaxton, C.S.; Lytton-Jean, A.K.R.; Han, M.S.; Mirkin, C.A. Oligonucleotide-Modified Gold Nanoparticles for Intracellular Gene Regulation. Science 2006, 312, 1027–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, J.-M.; Thaxton, C.S.; Mirkin, C.A. Nanoparticle-Based Bio-Bar Codes for the Ultrasensitive Detection of Proteins. Science 2003, 301, 1884–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, I.-H.; Kwon, H.-K.; An, S.; Kim, D.; Kim, S.; Yu, M.K.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, T.-S.; Im, S.-H.; Jon, S. Imageable Antigen-Presenting Gold Nanoparticle Vaccines for Effective Cancer Immunotherapy In Vivo. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 8800–8805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Hallal, R.; Lyu, N.; Wang, Y. Effect of Cetuximab-Conjugated Gold Nanoparticles on the Cytotoxicity and Phenotypic Evolution of Colorectal Cancer Cells. Molecules 2021, 26, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaul, S.; Gulati, N.; Verma, D.; Mukherjee, S.; Nagaich, U. Role of Nanotechnology in Cosmeceuticals: A Review of Recent Advances. J. Pharm. 2018, 2018, 3420204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Starsich, F.H.L.; Herrmann, I.K.; Pratsinis, S.E. Nanoparticles for Biomedicine: Coagulation During Synthesis and Applications. Annu. Rev. Chem. Biomol. Eng. 2019, 10, 155–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao-Milán, R.; Liz-Marzán, L.M. Gold Nanoparticle Conjugates: Recent Advances toward Clinical Applications. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2014, 11, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goddard, Z.R.; Marín, M.J.; Russell, D.A.; Searcey, M. Active Targeting of Gold Nanoparticles as Cancer Therapeutics. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 8774–8789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Materials | Application | Clinical trials.gov Identifier |
|---|---|---|
| Gold nanoparticles | Sensors functionalized with gold nanoparticles. Organic functionalized gold nanoparticles. Detection of gastric lesions. | NCT01420588 |
| Gold nanoparticles | Exhaled breath olfactory signature of pulmonary arterial hypertension. | NCT02782026 |
| Functionalized carbon nanotubes and gold nanoparticle | Exploratory study using nanotechnology to detect biomarkers of Parkinson’s disease from exhaled breath. | NCT01246336 |
| CD24-gold nanocomposite | Diagnostic and prognostic accuracy of gold nanoparticles in salivary gland tumors. | NCT04907422 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Milan, J.; Niemczyk, K.; Kus-Liśkiewicz, M. Treasure on the Earth—Gold Nanoparticles and Their Biomedical Applications. Materials 2022, 15, 3355. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15093355
Milan J, Niemczyk K, Kus-Liśkiewicz M. Treasure on the Earth—Gold Nanoparticles and Their Biomedical Applications. Materials. 2022; 15(9):3355. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15093355
Chicago/Turabian StyleMilan, Justyna, Klaudia Niemczyk, and Małgorzata Kus-Liśkiewicz. 2022. "Treasure on the Earth—Gold Nanoparticles and Their Biomedical Applications" Materials 15, no. 9: 3355. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15093355
APA StyleMilan, J., Niemczyk, K., & Kus-Liśkiewicz, M. (2022). Treasure on the Earth—Gold Nanoparticles and Their Biomedical Applications. Materials, 15(9), 3355. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15093355







